Absorption Variation with Particle Size of Recycled Fine Aggregates Determined by the Electrical Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- C = conductivity
- I = current
- V = potential difference
- Cc = cell constant
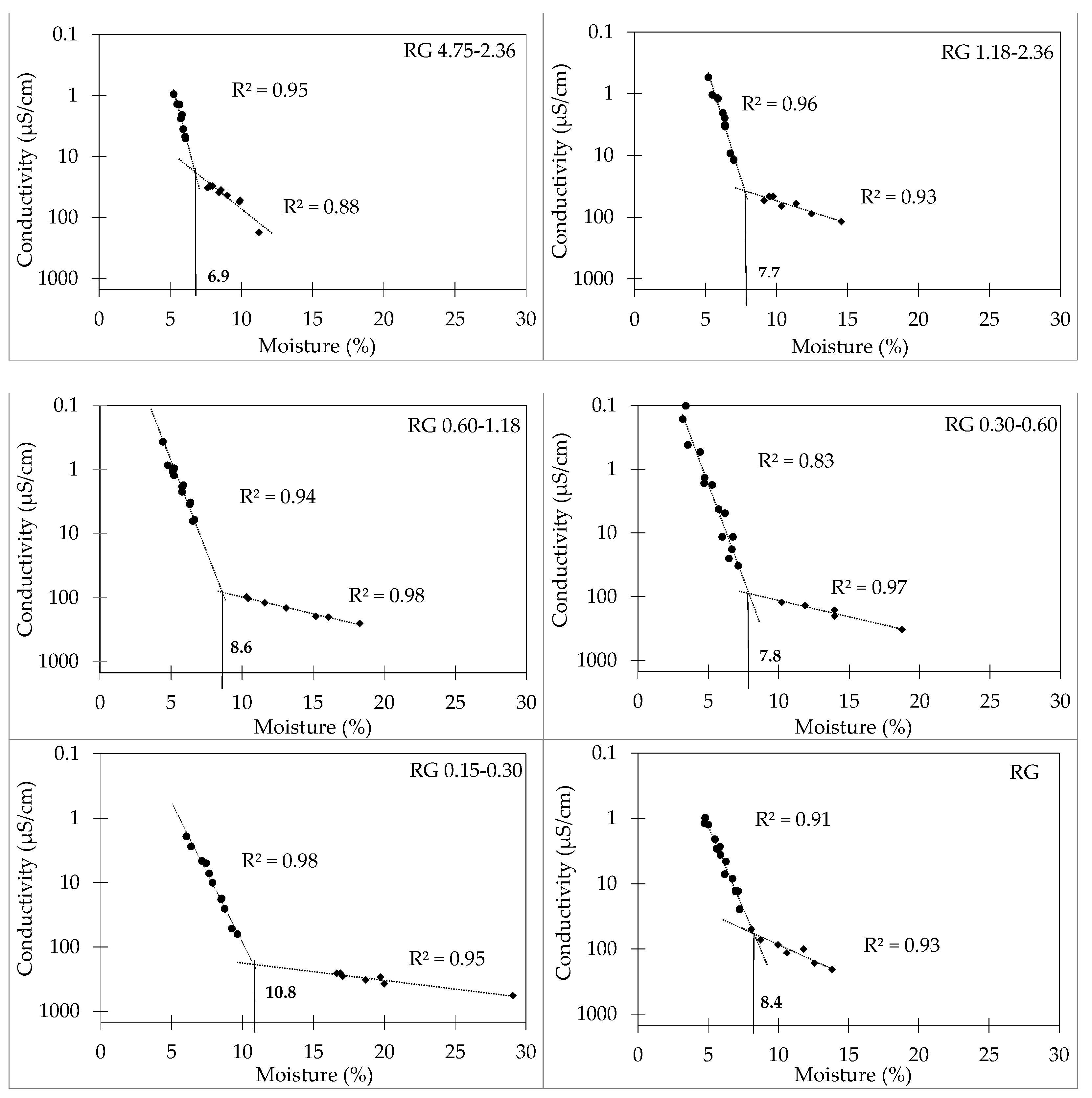
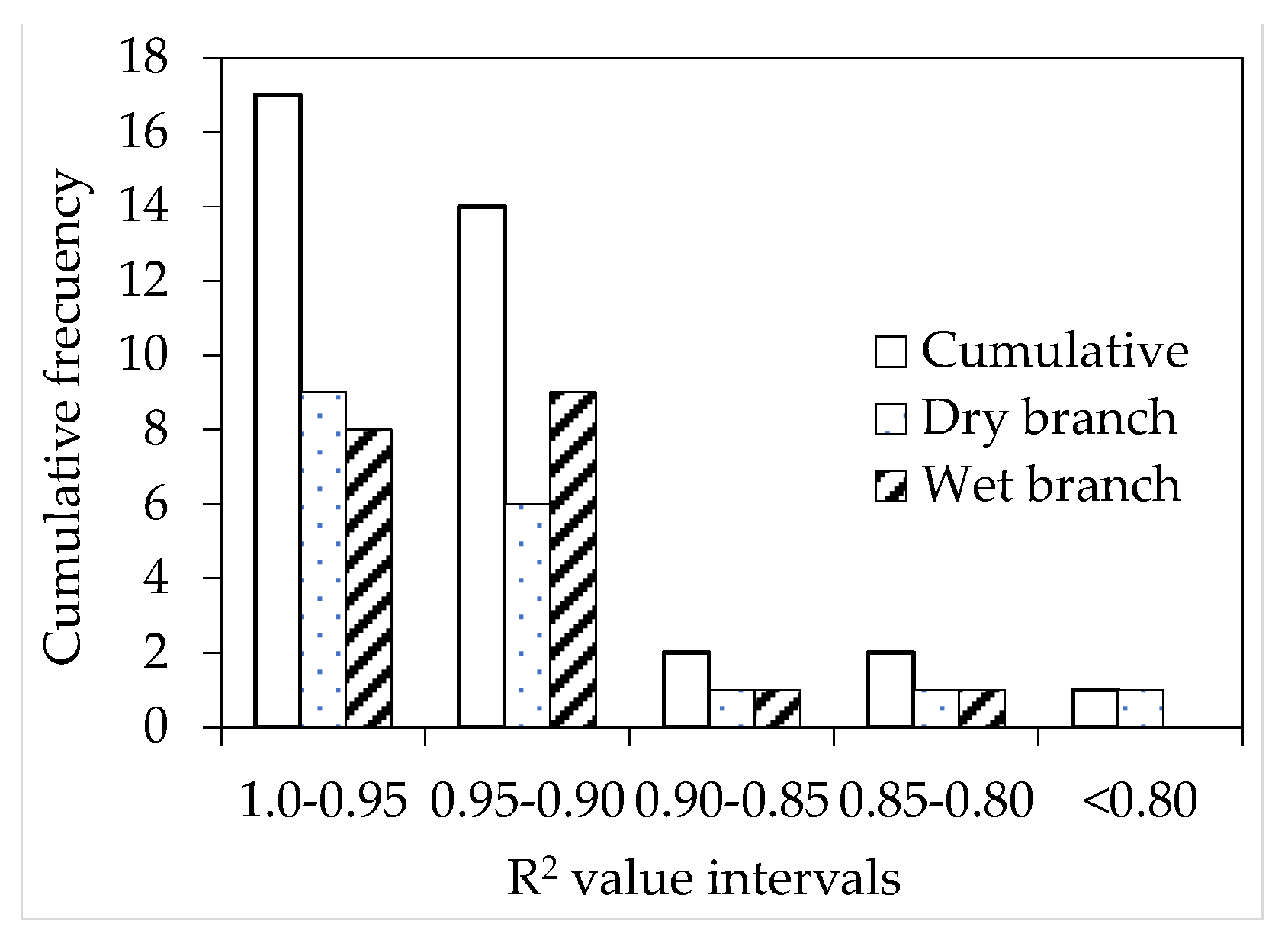
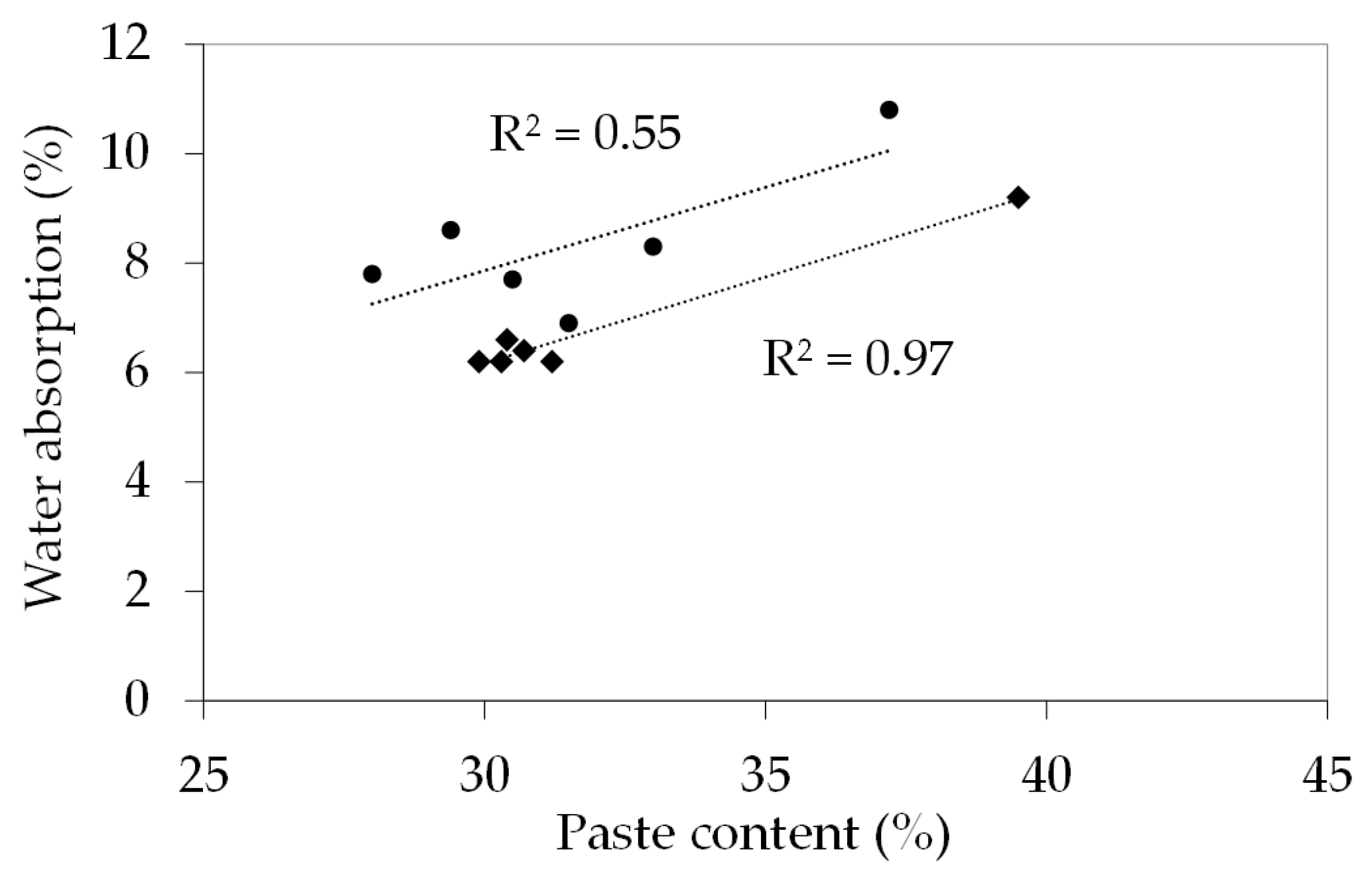
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Global Warming of 1.5 °C; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; 32p. [Google Scholar]
- UNE. Sand and Sustainability: Finding New Solutions for Environmental Governance of Global Sand Resources; UN Environment report; UNE: Gigiri Nairobi, Kenya, 2019; ISBN 978-92-807-3751-6. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, A.; Brandt, J.; Lear, K.; Liu, J. A looming tragedy of the sand commons. Science 2017, 357, 970–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çelik, A.I.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Zeybek, Ö.; Karalar, M.; Qaidi, S.; Ahmad, J.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.D.; Bejinariu, C. Mechanical behaviour of crushed waste glass as replacement of aggregates. Materials 2022, 15, 8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaidi, S.; Najm, H.M.; Abed, S.M.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Al Dughaishi, H.; Alosta, M.; Sabri, M.M.S.; Alkhatib, F.; Milad, A. Concrete containing waste glass as an environmentally friendly aggregate: A review on fresh and mechanical characteristics. Materials 2022, 15, 6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, J. Anthropogenic stresses on the world’s big rivers. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 12, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Khan, R.A. Influence of copper slag and metakaolin on the durability of self-compacting concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1171–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendixen, M.; Hackney, C.; Iversen, L.L. Time is running out for sand. Nature 2019, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisht, A. Conceptualizing sand extractivism: Deconstructing an emerging resource frontier. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2021, 8, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estanqueiro, B.; Silvestre, J.D.; de Brito, J.D.; Pinheiro, M.D. Environmental life cycle assessment of coarse natural and recycled aggregates for concrete. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2016, 22, 429–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRAM 1531-2022; Coarse Aggregate for Concrete. Requeriment and Test Method. Instituto Argentino de Normalización y Certificación: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2022.
- AASHTO MP 16-2013; Standard Specification for Reclaimed Concrete Aggregate (RCA) for Use as Coarse Aggregate in Hydraulic Cement Concrete. American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- ACI 318-2019; Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary. American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2019.
- ASTM C 33:2018; Standard Specification for Concrete Aggregates. ASTM international: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Pacheco, J.; de Brito, J.; Chastre, C.; Evangelista, L. Eurocode Shear Design of Coarse Recycled Aggregate Concrete: Reliability Analysis and Partial Factor Calibration. Materials 2021, 14, 4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ahmad, W.; Ahmad, A.; Aslam, F.; Joyklad, P. A scientometric analysis approach to analyze the present research on recycled aggregate concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 46, 103639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, G.S.; Quattrone, M.; Ambrós, W.M.; Grigore Cazacliu, B.; Hoffmann Sampaio, C. Current Applications of Recycled Aggregates from Construction and Demolition: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvila, M.; de Matos, P.; Rodríguez, E.; Monteiro, S.N.; de Azevedo, A.R.G. Recycled Aggregate: A viable solution for sustainable Concrete Production. Materials 2022, 15, 5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, L.; de Brito, J. Criteria for the use of fine recycled concrete aggregate in concrete production. In Proceedings of the International RILEM Conference: The Use of Recycled Materials in Building and Structures, RILEM, Barcelona, Spain, 8–11 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sosa, M.E.; Zega, C.J.; Di Maio, A.A. Influence of fine recycled aggregates on compressive strength, static modulus of elasticity and drying shrinkage of concrete. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Structural Concrete, RILEM, La Plata, Argentina, 15–18 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista, L.; de Brito, J. Durability performance of concrete made with fine recycled concrete aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zega, C.J.; Di Maio, A.A. Use of recycled fine aggregate in concretes with durable requirements. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2336–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, P.; Evangelista, L.; de Brito, J. The effect of superplasticizers on the workability and compressive strength of concrete with fine recycled concrete aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoshkenari, A.G.; Shafigh, P.; Moghimi, M.; Mahmud, H.B. The role of 0-2 mm fine recycled concrete aggregate on the compressive and splitting tensile strengths of recycled concrete aggregate concrete. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, J.M. Properties of concrete incorporating fine recycled aggregates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Yun, H.D. Evaluation of the bond behavior of steel bars in recycled fine aggregate concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 46, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartuxo, F.; de Brito, J.; Evangelista, L.; Jimenez, J.R.; Ledesma, E.F. Rheological behaviour of concrete made with fine recycled concrete aggregates—influence of the super- plasticizers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 89, 26–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Remond, R.; Daminot, D.; Xu, W. Influence of hardened cement paste content on the water absorption of fine recycled concrete aggregates. J. Sustain. Cem. -Based Mater. 2013, 2, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Huang, R.; Hwang, H.; Chao, S.J. Properties of concrete incorporating fine recycled aggregates from crushed concrete wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez De Juan, M.; Alaejos Gutiérrez, P. Study on the influence of attached mortar content on the properties of recycled concrete aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théréné, F.; Keita, E.; Naël-Redolfi, J.; Boustingorry, P.; Bonafous, L.; Roussel, N. Water absorption of recycled aggregates: Measurements, influence of temperature and practical consequences. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 137, 106196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, M.E.; Villagrán Zaccardi, Y.A.; Zega, C.J. A critical review of the resulting effective water-to-cement ratio of fine recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 313, 125536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, M.B. Avaliaçao de propriedades mecanicas de concretos produzidoscom agregados reciclados de resıduos de construçao e demoliçao. Ph.D. Thesis, Escola de Engenharia, Universidade Federal Rio Grande Do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Gao, X.F.; Tam, C.M.; Chan, C.H. New approach in measuring water absorption of recycled aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damineli, B.L.; Quattrone, M.; Angulo, S.C.; Taqueda, M.E.S.; John, V.M. Rapid method for measuring the water absorption of recycled aggregates. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 4069–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.; Evangelista, L.; de Brito, J. A New Method to Determine the Density and Water Absorption of Fine Recycled Aggregates. Mater. Res. 2013, 16, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IFSTTAR Test Method No. 78:2011. Test on Aggregate for Concrete: Measurement of Total Water Absorption by a Crushed Sand; IFSTTAR: Paris, France, 2011.
- Kim, J.; Zi, G.; Lange, D.A. Measurement of water absorption in very fine particles using electrical resistivity. Mater. J. 2017, 6, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Tian, Q. Method for controlling the absorbed water content of recycled fine aggregate by centrifugation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlawatsch, F.; Aycil, H.; Kropp, J. An automated test method for density in the saturated surface dry state (SSD) of porous granular materials. In Proceedings of the 2nd International RILEM Conference in the Building Environment, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2–4 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gentilini, P.; Yazoghli-Marzouk, O.; Delmotte, V.; Descantes, Y. Determination of the water content of fillerised fine aggregates in the saturated surface dry state. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 98, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, M.E.; Carrizo, L.; Zega, C.J.; Villagrán-Zaccardi, Y.A. Water absorption of fine recycled aggregates: Effective determination by a method based on electrical conductivity. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoornahad, H.; Koenders, E.A.B.; Breguel, K.V. Wettability of particles and its effect on liquid bridges in wet granular materials. J. Silic. Based Compos. Mater. 2015, 67, 142–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JSCE-C506-2003; Test Method for Density and Water Absorption of Slag Fine Aggregate for Concrete by Measurement of Electric Resistance. Japanese Society of Civil Engineers: Tokio, Japan.
- Andrade, C.; D’Andrea, R. La resistividad eléctrica como parámetro de control del hormigón y de su durabilidad. ALCONPAT 2011, 1, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González, J.A.; Andrade, C.; Alonso, C. Aproximación al efecto de la resistividad del hormigón en la corrosión de armaduras embebidas en el hormigón. Mater. De Construcción 1987, 37, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Zhao, W.; Ye, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C. Measurement of water absorption of Recycled Aggregates. Materials 2022, 15, 5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Xiao, J.; Damidot, D.; Rémond, S.; Bulteel, D.; Courard, L. Quantification of the Hardened Cement Paste Content in Fine Recycled Concrete Aggregates by Means of Salicylic Acid Dissolution. Materials 2022, 15, 3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C 1084 - 2010; Standard Test Method for Portland-Cement Content of Hardened Hydraulic-Cement Concrete. ASTM international: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Figuereido, P.; Ulsen, C.; Bergerman, M.; Nery, G. Liberation of cement paste in recycled aggregates by different comminution methods. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference Progress of Recycling in the Built Environment, RILEM, Lisbon, Portugal, 11–12 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
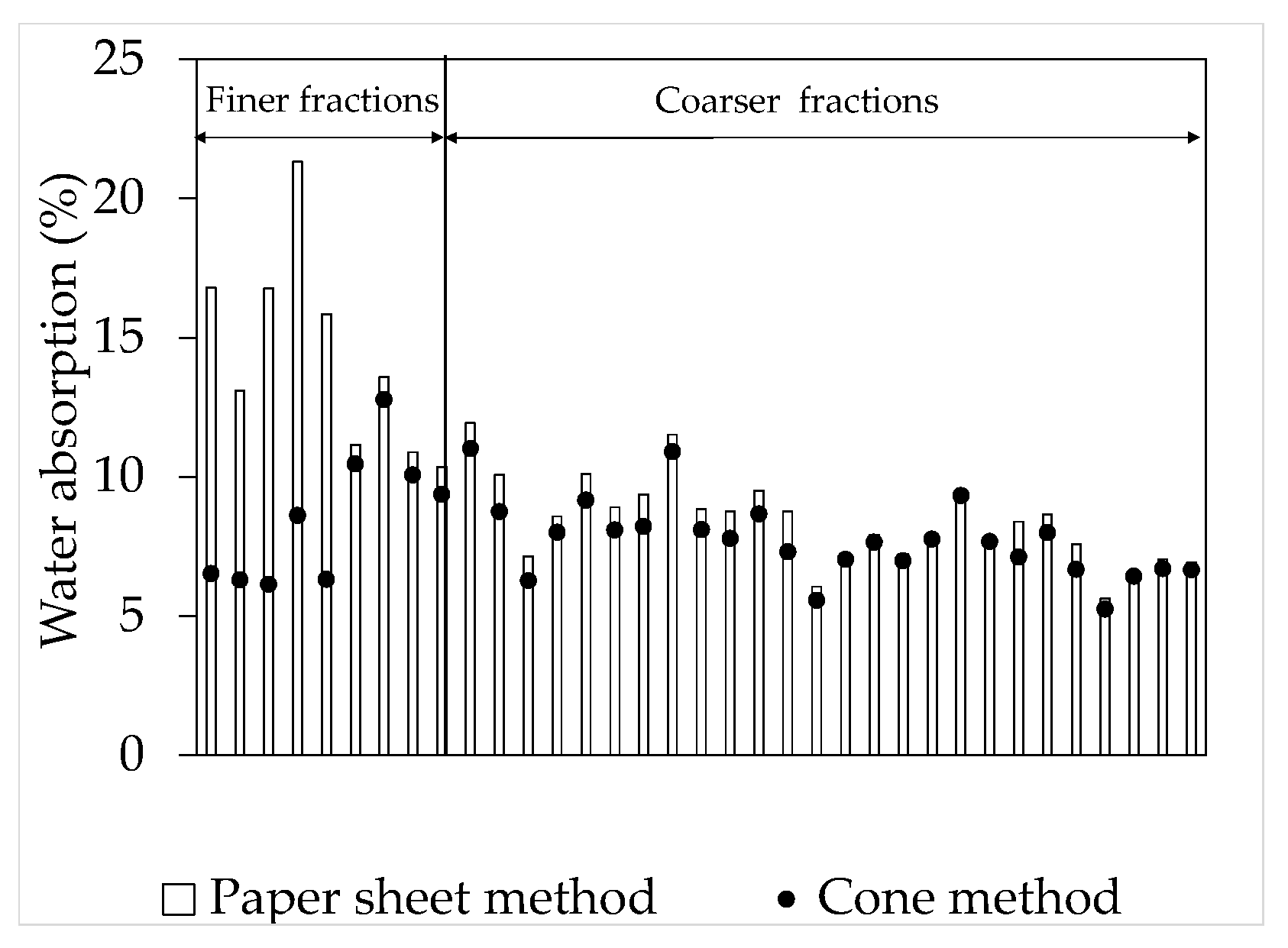
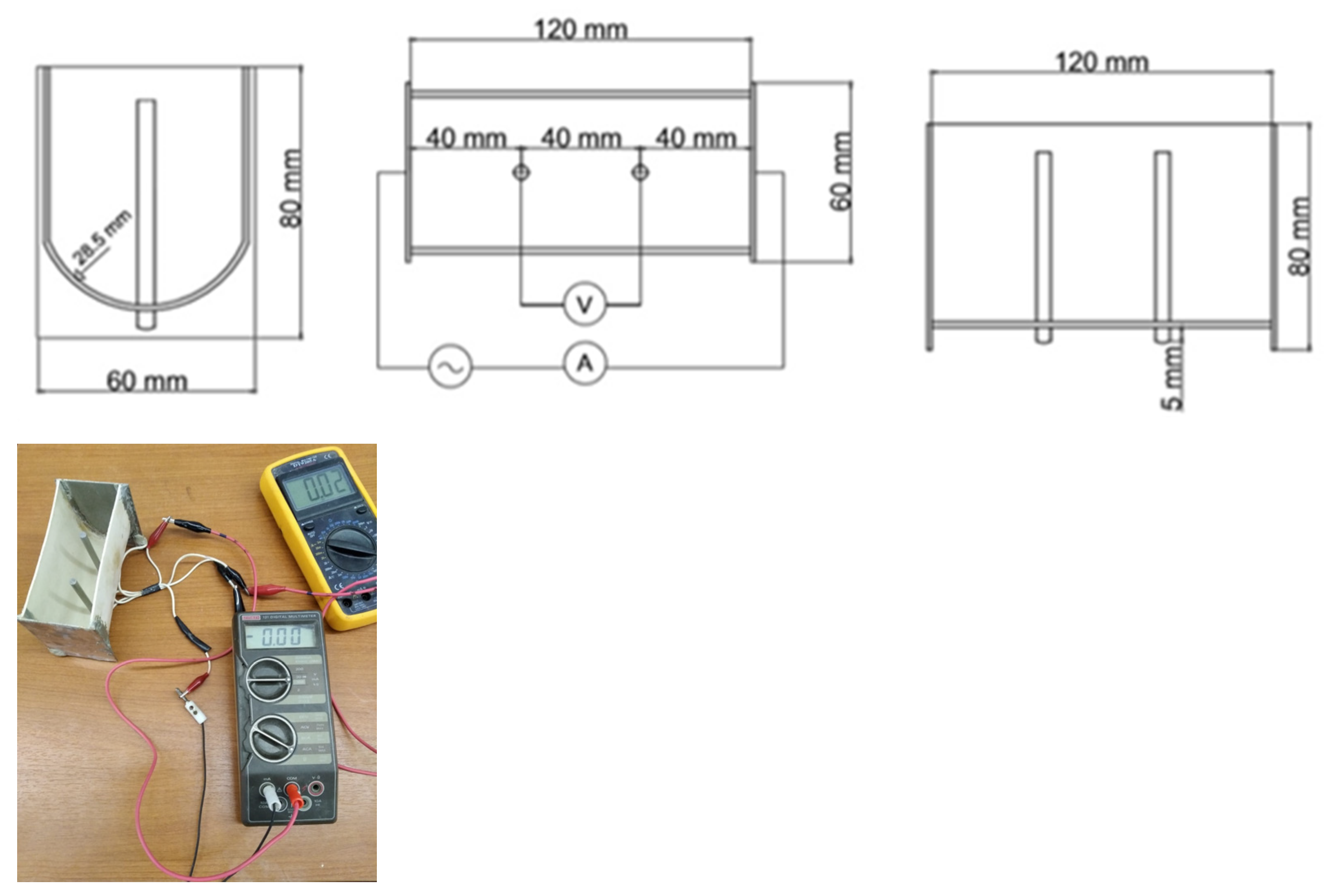
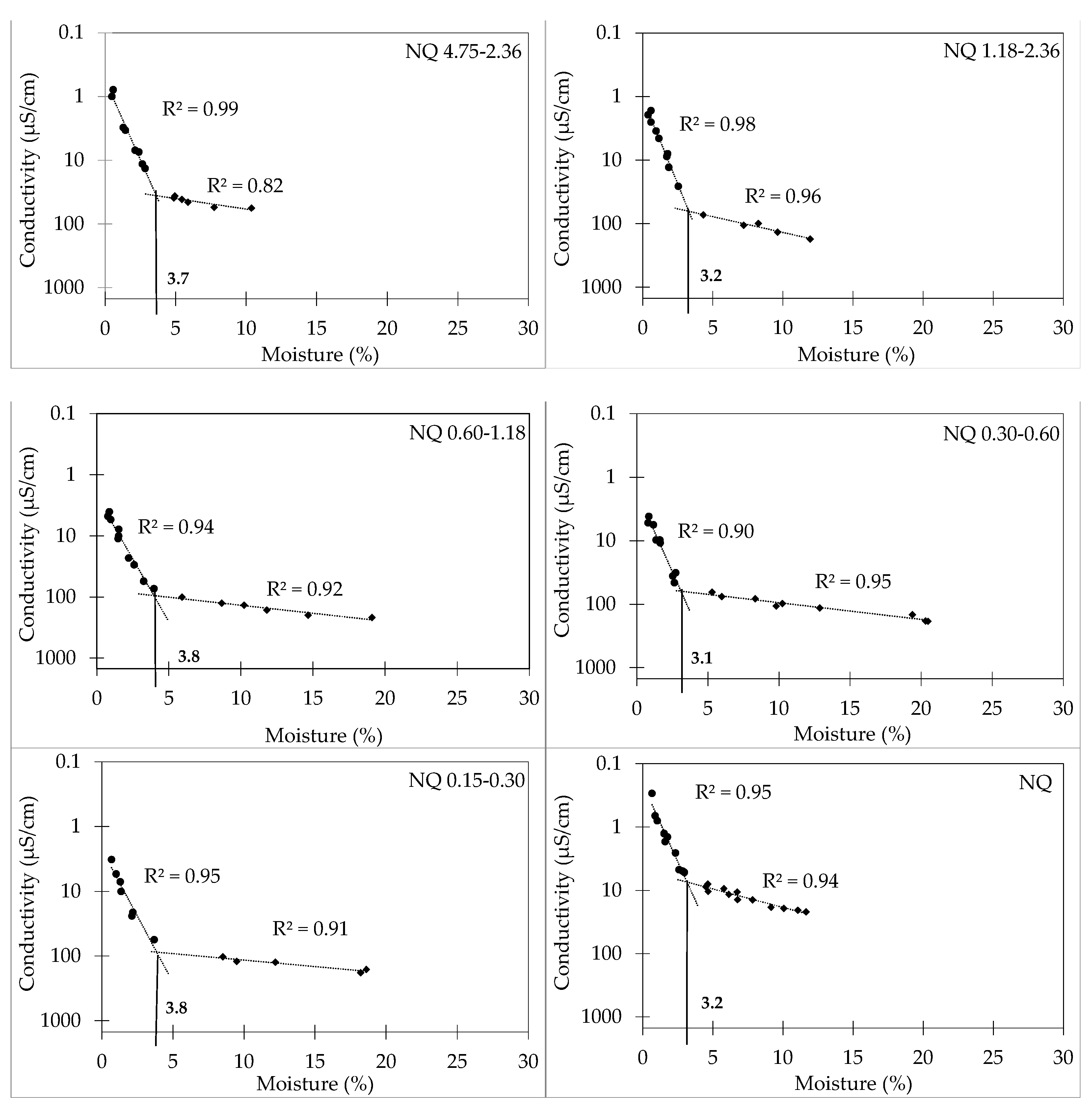
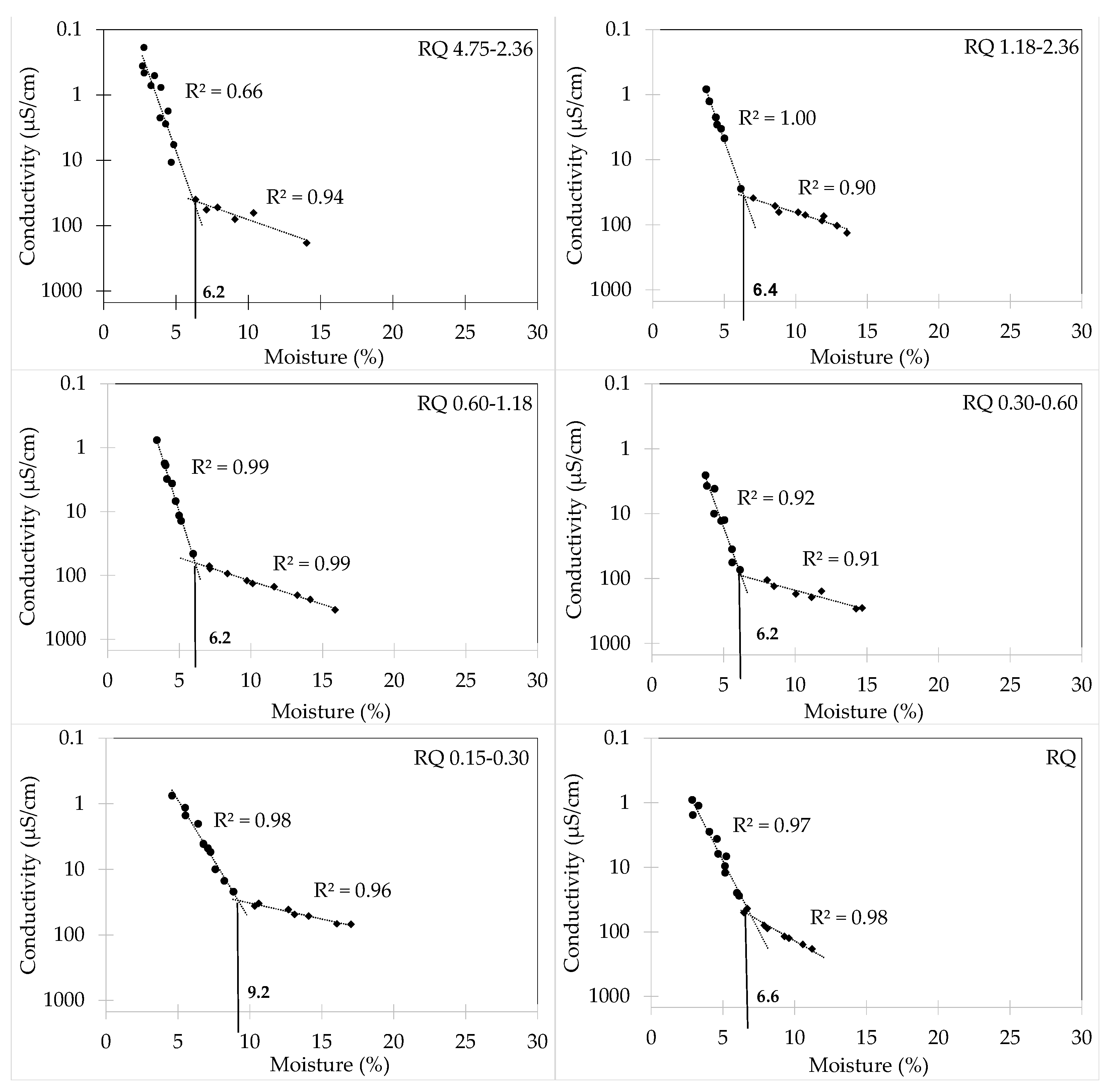
| ID | Fineness Modulus | Density | Paste Content (%) | Particle Size Distribution, Cumulative Retained Mass over Mesh (%) | Material Finer Than 75 µm (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.75 mm | 2.36 mm | 1.18 mm | 600 µm | 300 µm | 150 µm | |||||
| NQ | 3.18 | 2.58 | - | 7 | 27 | 43 | 62 | 83 | 96 | 1.5 |
| RQ | 3.16 | 2.46 | 30.4 | 2 | 27 | 48 | 64 | 83 | 92 | 5.2 |
| RG | 3.45 | 2.49 | 32.1 | 0 | 33 | 57 | 72 | 87 | 95 | 2.7 |
| Size Range (mm) | Water Absorption (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| NQ | RQ | RG | |
| 4.75–2.36 | 3.6 | 6.2 | 6.9 |
| 2.36–1.18 | 3.2 | 6.4 | 7.7 |
| 1.18–0.6 | 3.8 | 6.2 | 8.6 |
| 0.6–0.3 | 3.2 | 6.2 | 7.8 |
| 0.3–0.15 | 3.8 | 9.2 | 10.8 |
| Weighted average | 3.6 | 6.8 | 8.0 |
| 0.0–4.75 | 3.2 | 6.6 | 8.3 |
| Size Fraction (mm) | NQ | NQ | RG | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | |
| 0.0–4.75 | 0.487 | 0.0059 | 0.537 | 0.2108 | 0.507 | 0.097 |
| 4.75–2.36 | 0.543 | 0.050 | 0.614 | 0.070 | 0.744 | 0.073 |
| 2.36–1.18 | 0.504 | 0.026 | 0.718 | 0.073 | 0.570 | 0.052 |
| 1.18–0.6 | 0.411 | 0.026 | 0.609 | 0.060 | 0.596 | 0.051 |
| 0.6–0.3 | 0.411 | 0.020 | 0.365 | 0.064 | 0.434 | 0.027 |
| Standard deviation | 0.501 | 0.033 | 0.628 | 0.078 | 0.899 | 0.111 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sosa, E.; Carrizo, L.; Zega, C.; Zaccardi, Y.V. Absorption Variation with Particle Size of Recycled Fine Aggregates Determined by the Electrical Method. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031578
Sosa E, Carrizo L, Zega C, Zaccardi YV. Absorption Variation with Particle Size of Recycled Fine Aggregates Determined by the Electrical Method. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(3):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031578
Chicago/Turabian StyleSosa, Eva, Leandro Carrizo, Claudio Zega, and Yury Villagrán Zaccardi. 2023. "Absorption Variation with Particle Size of Recycled Fine Aggregates Determined by the Electrical Method" Applied Sciences 13, no. 3: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031578
APA StyleSosa, E., Carrizo, L., Zega, C., & Zaccardi, Y. V. (2023). Absorption Variation with Particle Size of Recycled Fine Aggregates Determined by the Electrical Method. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031578







