An Insight into a Shang Dynasty Bronze Vessel by Nuclear Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
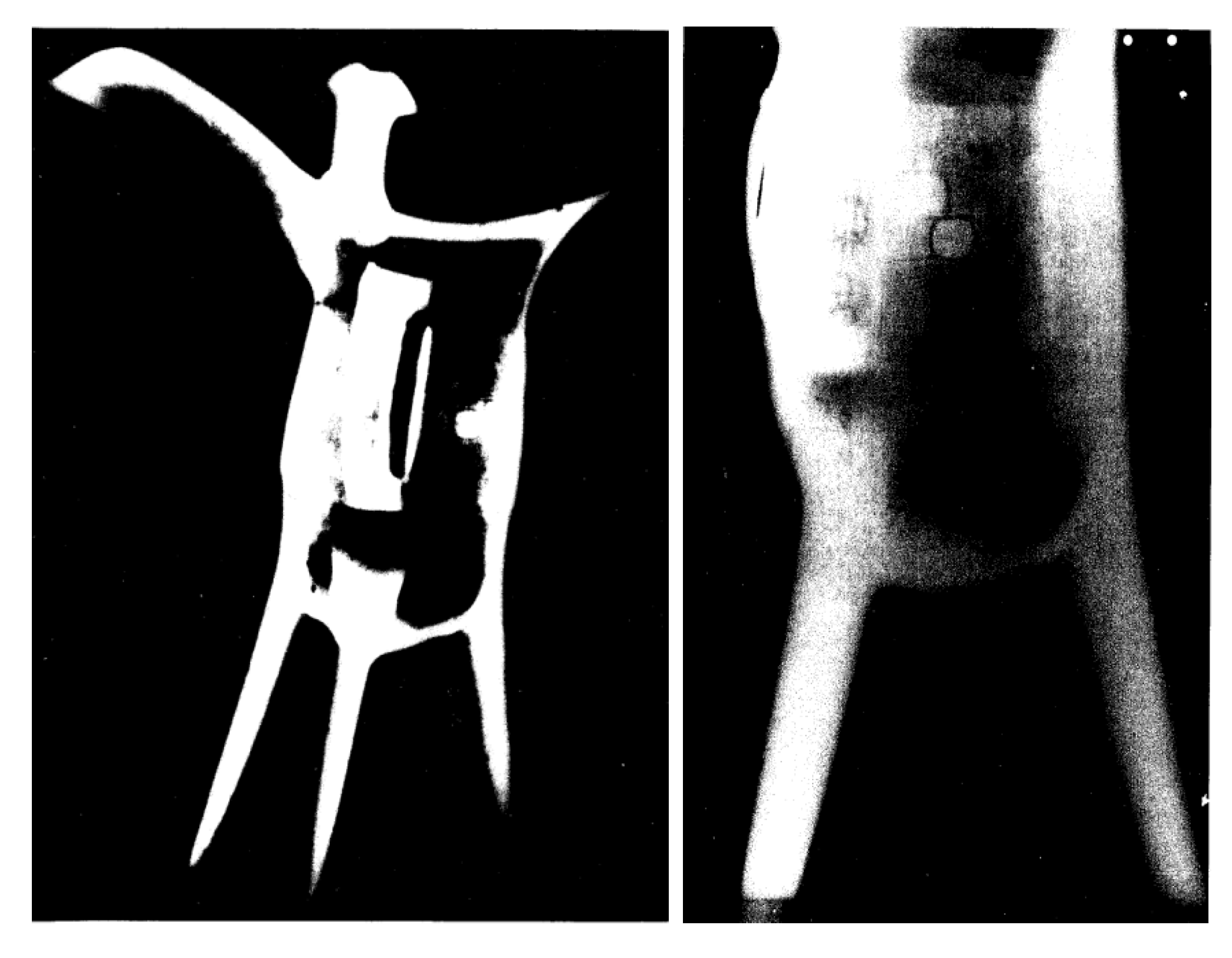
3. Past Scientific Analytical Investigations and Restoration Work
4. Results
4.1. Gamma Spectrometry Assurance
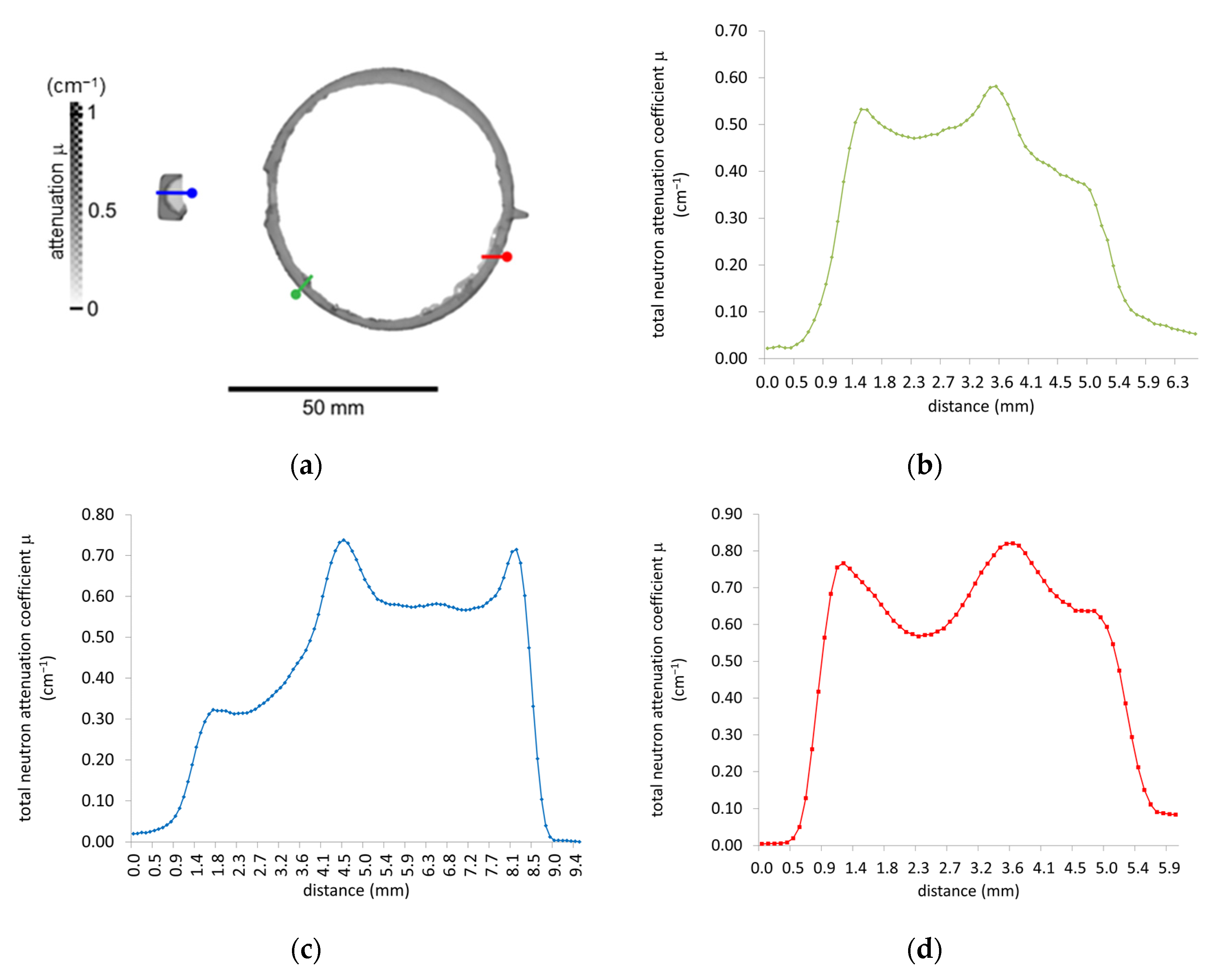
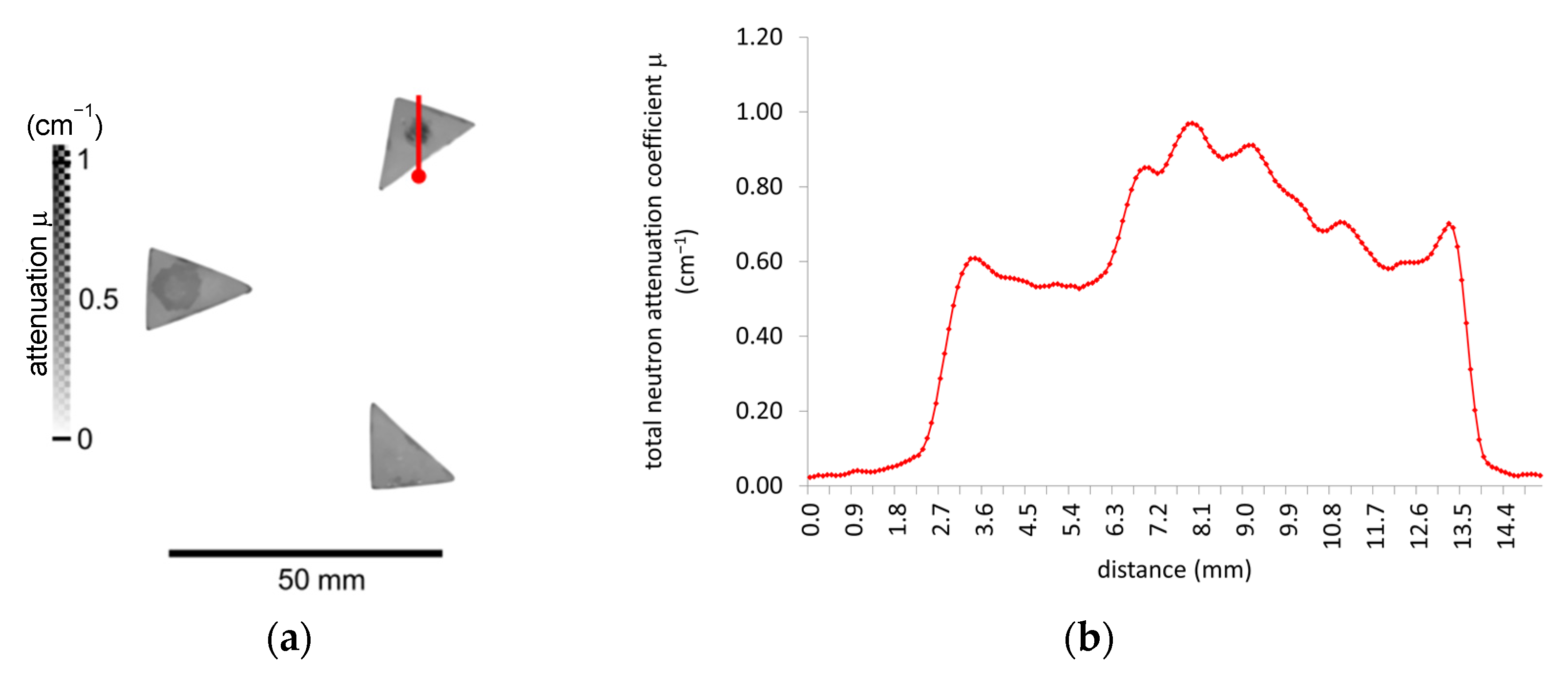
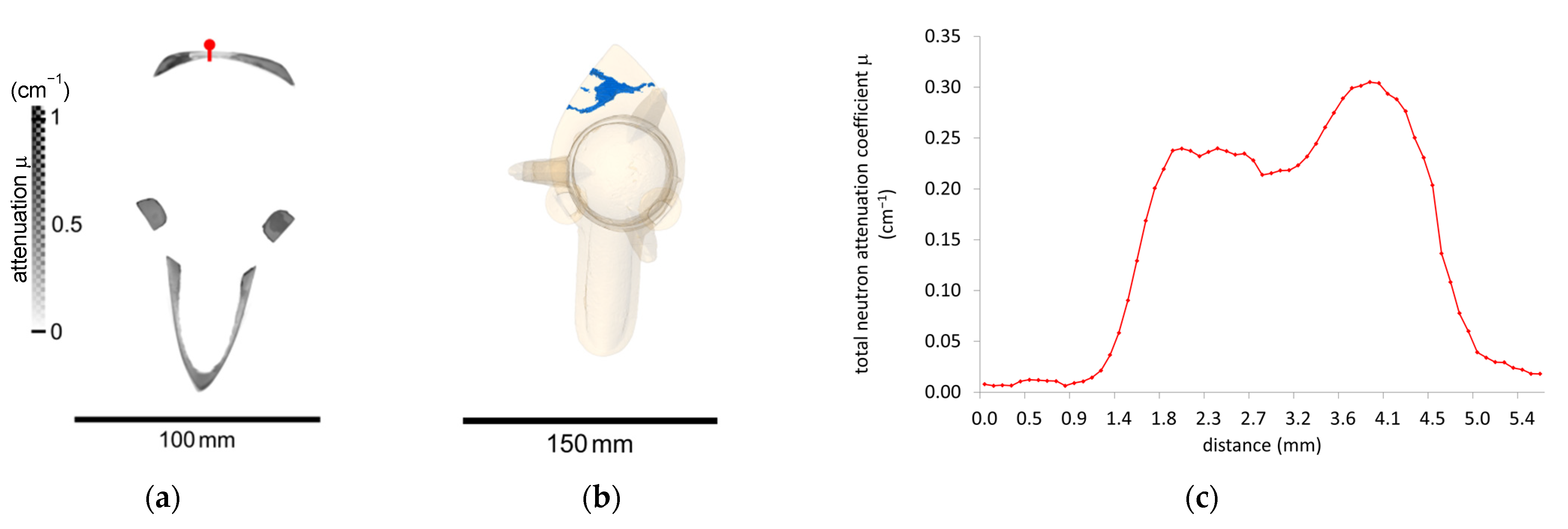
4.2. Neutron Tomography
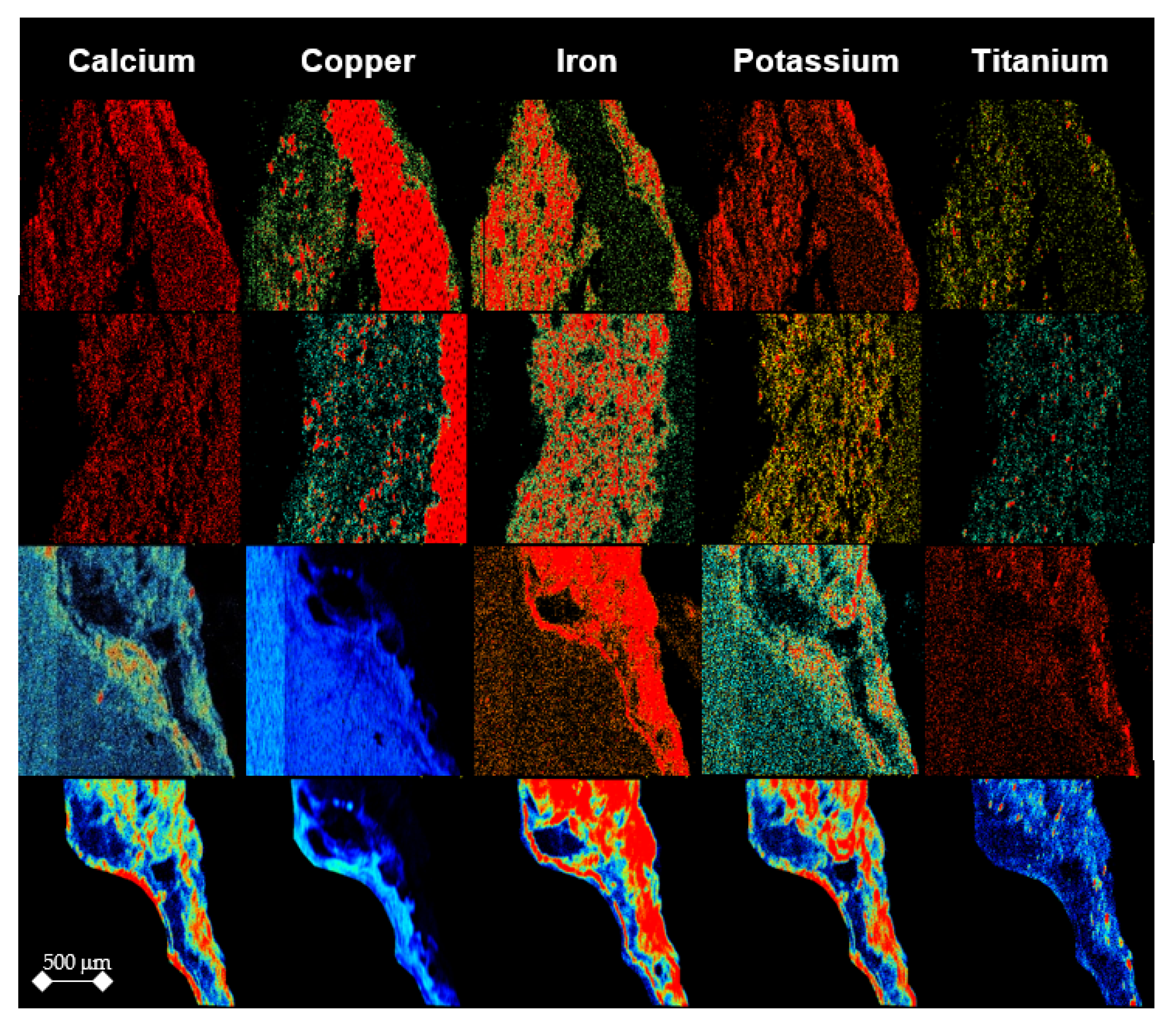
4.3. Particle-Induced X-ray Emission—PIXE Analysis
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hohensee, N. The Metropolitan Museum of Art, Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. Available online: https://www.metmuseum.org/toah/ (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Barnes, G.L. Archaeology of East Asia: The Rise of Civilization in China, Korea and Japan; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Avril, E.; Bonadies, S. Digital radioscopic examination of ancient bronze castings. In Review of Progress in Quantitative Nondestructive Evaluation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; Volume 10B. [Google Scholar]
- Thorp, R.L. China in the Early Bronze Age Shang Civilization; University of Pennsylvania Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Linduff, K.M.; Mei, J. Modeling Early Metallurgy: Old and New World Perspectives, in Metallurgy in Ancient Eastern Asia: How Is It Studied? Where Is the Field Headed? SAA: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Clunas, C. Art in China. Oxford History of Art. China Rev. Int. 1999, 6, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Brill, R.H.; Wampler, J.M. Isotope studies of ancient lead. Am. J. Archaeol. 1967, 71, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B. The mapping of geochemical provinces in China based on Pb isotopes. J. Geochem. Explor. 1995, 55, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.-D.; Zhang, L.-P.; Guo, J.; Li, C.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Zartman, R.E.; Zhang, Z.-F. Origin of the mysterious Yin-Shang bronzes in China indicated by lead isotopes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, H.C.H.; Academia Sinica National Research Institute of History and Philology. Excavation Report of Anyang, IV, Taiwan; Preliminary Report on Chinese Bronzes; Academia Sinica National Research Institute of History and Philology: Beijing, China; Nanjing, China, 1933; pp. 677–680. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D.A.; Podany, J.; Considine, B.B. Ancient & Historic Metals: Conservation and Scientific Research. In Proceedings of a Symposium on Ancient and Historic Metals Organized by the J. Paul Getty Museum and the Getty Conservation Institute, November 1991; Getty Conservation Institute: Marina del Rey, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Bray, P.; Pollard, A.; Hommel, P. Chemical analysis of ancient Chinese copper-based objects: Past, present and future. Archaeol. Res. Asia 2015, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Nan, P. Scientific Analysis of Bronzes in Western Zhou Site of Hengshui Jiangxian; Science Press Kexue Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 2012; ISBN 9787030350039. [Google Scholar]
- Bavarian, B.; Reiner, L.R. Piece Mold Lost Wax & Composite Casting Techniques of the Chinese Bronze Age; California State University: Northridge, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Meyers, P.; Holmes, L. Technical Studies of Ancient Chinese Bronzes: Some Observations. In The Great Bronze Age of China Symposium; Los Angeles County Museum of Art: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Young, M.L.; Casadio, F.; Marvin, J.; Chase, W.T.; Dunand, D.C. An ancient Chinese bronze fragment re-examined after 50 years: Contribution from modern and traditional techniques. Archaeometry 2010, 52, 1015–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, I.; McGreevy, R.L.; Bilheux, H.Z. Neutron Imaging and Applications. A Reference for the Imaging Community; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Salvemini, F.; White, R.; Levchenko, V.A.; Smith, A.M.; Pastuovic, Z.; Stopic, A.; Luzin, V.; Tobin, M.J.; Puskar, L.; Howard, D.; et al. Cultural Heritage Project at Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO). In Handbook of Cultural Heritage Analysis; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 375–441. [Google Scholar]
- Zucchiatti, A. Ion beam analysis for the study of our cultural heritage: A short history and its milestones. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2019, 452, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, T.B.; Akselsson, R.; Johansson, S.A.E. X-ray analysis: Elemental trace analysis at the 10−12 g level. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1970, 84, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, W.G. PIXE: A Novel Technique for Elemental Analysis. S. A. E. Johansson and J. L. Campbell Published by John Wiley & Sons, New York (1988); 347 pages, ISBN 0471920118. X-ray Spectrom. 1989, 18, 248. [Google Scholar]
- Nastasi, M.; Mayer, J.W.; Wang, Y. Ion Beam Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Garbe, U.; Randall, T.; Hughes, C.; Davidson, G.; Pangelis, S.; Kennedy, S.J. A New Neutron Radiography/Tomography/Imaging Station DINGO at OPAL. Phys. Procedia 2015, 69, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierick, M.; Masschaele, B.; Hoorebeke, V. Octopus, a Fast and User-friendly Tomographic Reconstruction Package Developed in LabView®. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/au/en/home/electron-microscopy/products/software-em-3d-vis/avizo-software.html (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Cohen, D.D.; Siegele, R.; Orlic, I.; Stelcer, E. Long-term accuracy and precision of PIXE and PIGE measurements for thin and thick sample analyses. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2002, 189, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastuovic, Z.; Button, D.; Cohen, D.; Fink, D.; Garton, D.; Hotchkis, M.; Ionescu, M.; Long, S.; Levchenko, V.; Mann, M.; et al. SIRIUS—A new 6 MV accelerator system for IBA and AMS at ANSTO. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2016, 371, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastuovic, Z.; Siegele, R.; Cohen, D.; Mann, M.; Ionescu, M.; Button, D.; Long, S. The new confocal heavy ion microprobe beamline at ANSTO: The first microprobe resolution tests and applications for elemental imaging and analysis. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2017, 404, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.A. Metallography and Microstructure of Ancient and Historical Metals; The J. Paul Getty Trust: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Habibullah, P.; Mahmood, M.A.; Anwar, Z. New casting strategy for eliminating both indigenous and exogenous gas porosity within the mould. Codne Jnsmac 2014, 57, 37–57. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J. Complete Casting Handbook: Metal Casting Processes, Metallurgy, Techniques and Design; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay, D. Study of materials using Mössbauer spectroscopy. Int. Mater. Rev. 2006, 51, 171–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, N.J. Mössbauer spectroscopy in archaeology. Nature 1975, 254, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

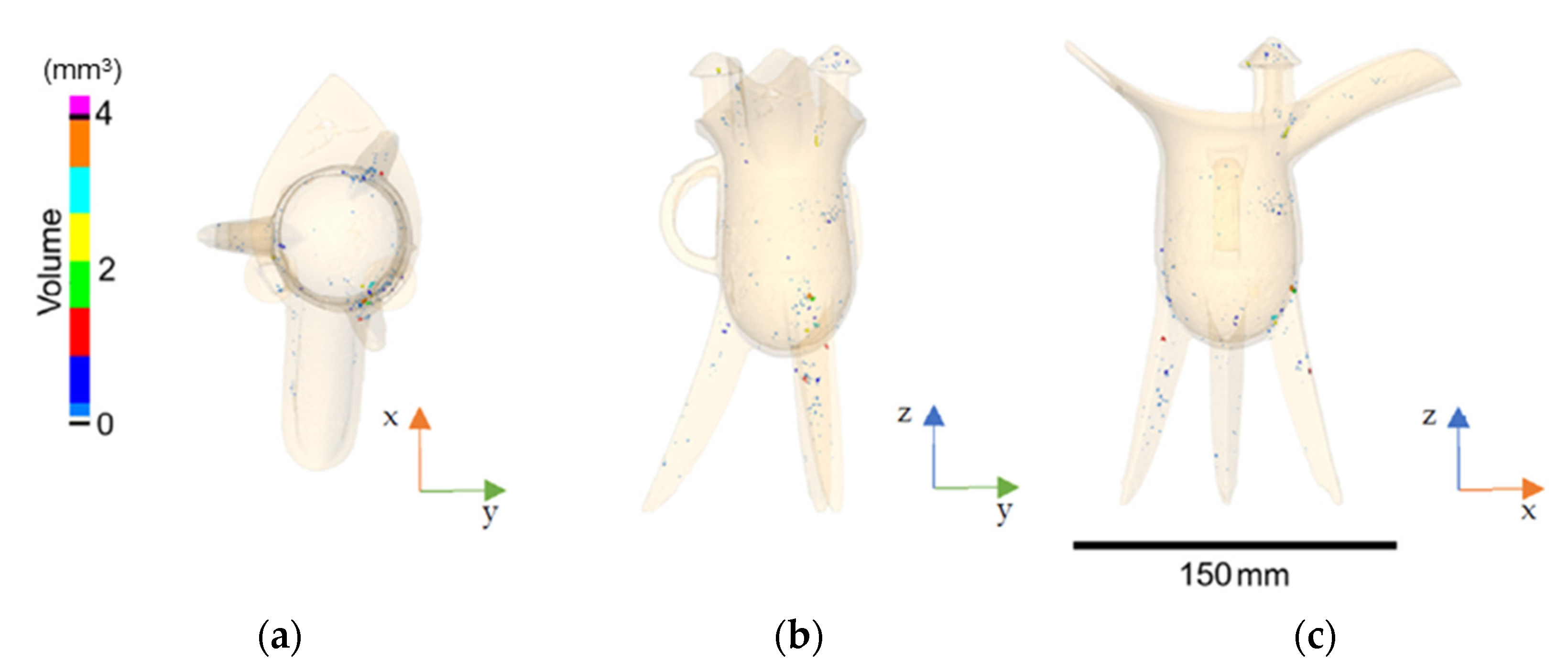

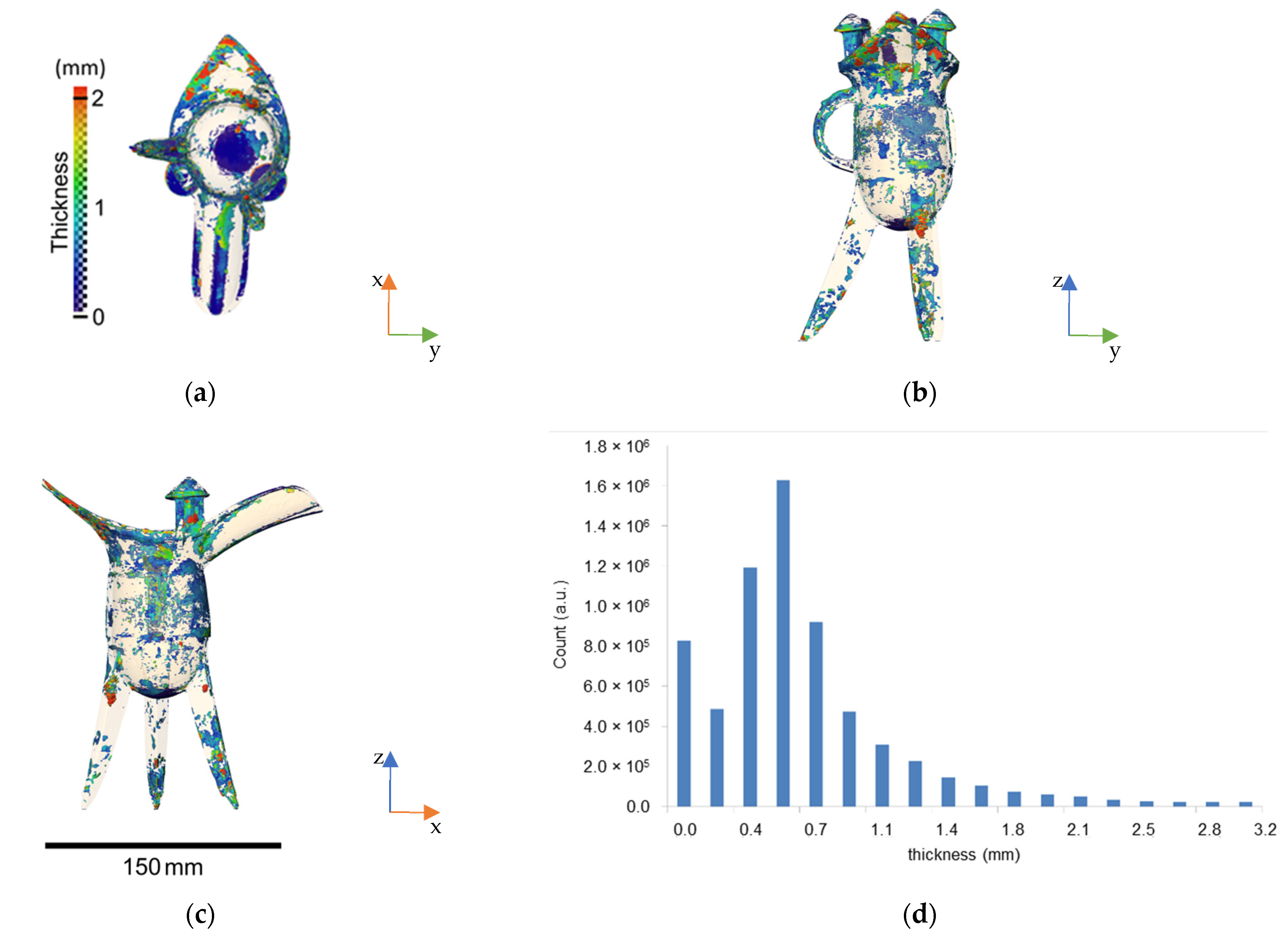
| Volume | Aspect Ratio | 3D Feret Shape | Equivalent Diameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Average | Fraction | Average length | Average width | Min | Max | |
| mm3 | mm3 | % | mm | mm | |||
| 59.257 | 0.225 | 0.05 | 1.091 | 0.626 | 1.642 | 0.335 | 1.994 |
| Component | Volume % |
|---|---|
| Vase | 83.47 |
| Porosities | 0.05 |
| Patina | 16.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salvemini, F.; Pastuovic, Z.; Stopic, A.; Kim, M.-J.; Gatenby, S. An Insight into a Shang Dynasty Bronze Vessel by Nuclear Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031549
Salvemini F, Pastuovic Z, Stopic A, Kim M-J, Gatenby S. An Insight into a Shang Dynasty Bronze Vessel by Nuclear Techniques. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(3):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031549
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalvemini, Filomena, Zeljko Pastuovic, Attila Stopic, Min-Jung Kim, and Sue Gatenby. 2023. "An Insight into a Shang Dynasty Bronze Vessel by Nuclear Techniques" Applied Sciences 13, no. 3: 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031549
APA StyleSalvemini, F., Pastuovic, Z., Stopic, A., Kim, M.-J., & Gatenby, S. (2023). An Insight into a Shang Dynasty Bronze Vessel by Nuclear Techniques. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031549








