Analysis of Dust Detection Algorithms Based on FY-4A Satellite Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Qualitatively evaluated the performance of the four algorithms/products on the dust identification during two typical dust events;
- (2)
- Quantitatively compared the BTD, NDDI, and two FY-4A dust products with the real-time ground-based PM10 (less than 10μm in aerodynamic diameter) concentration data and assess their accuracy in identifying dust in the spring of 2021.
2. Study Area and Data
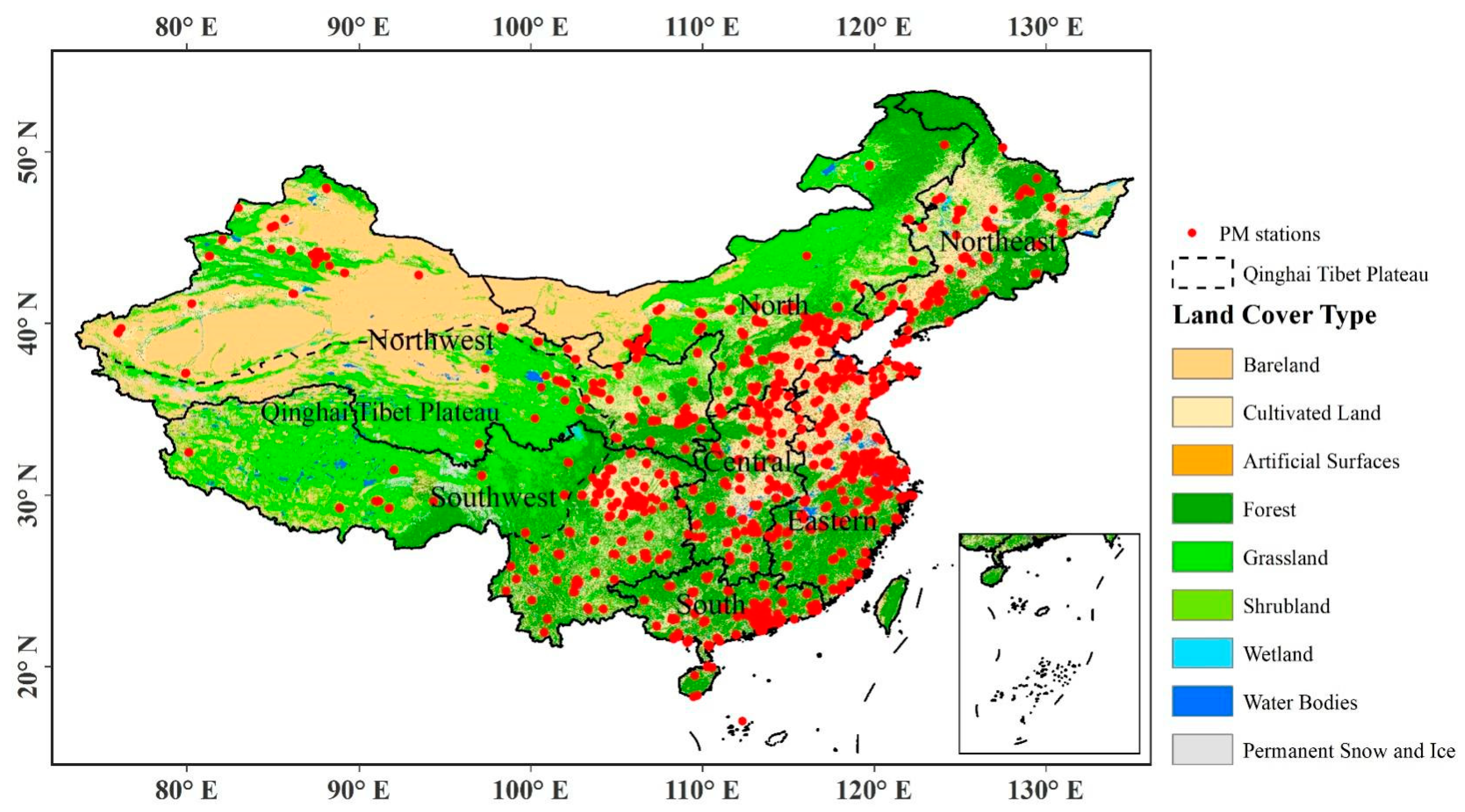
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset
2.2.1. FY-4A Data
2.2.2. FY-4A DSD Data
2.2.3. Particulate Matter (PM) Data
3. Methods
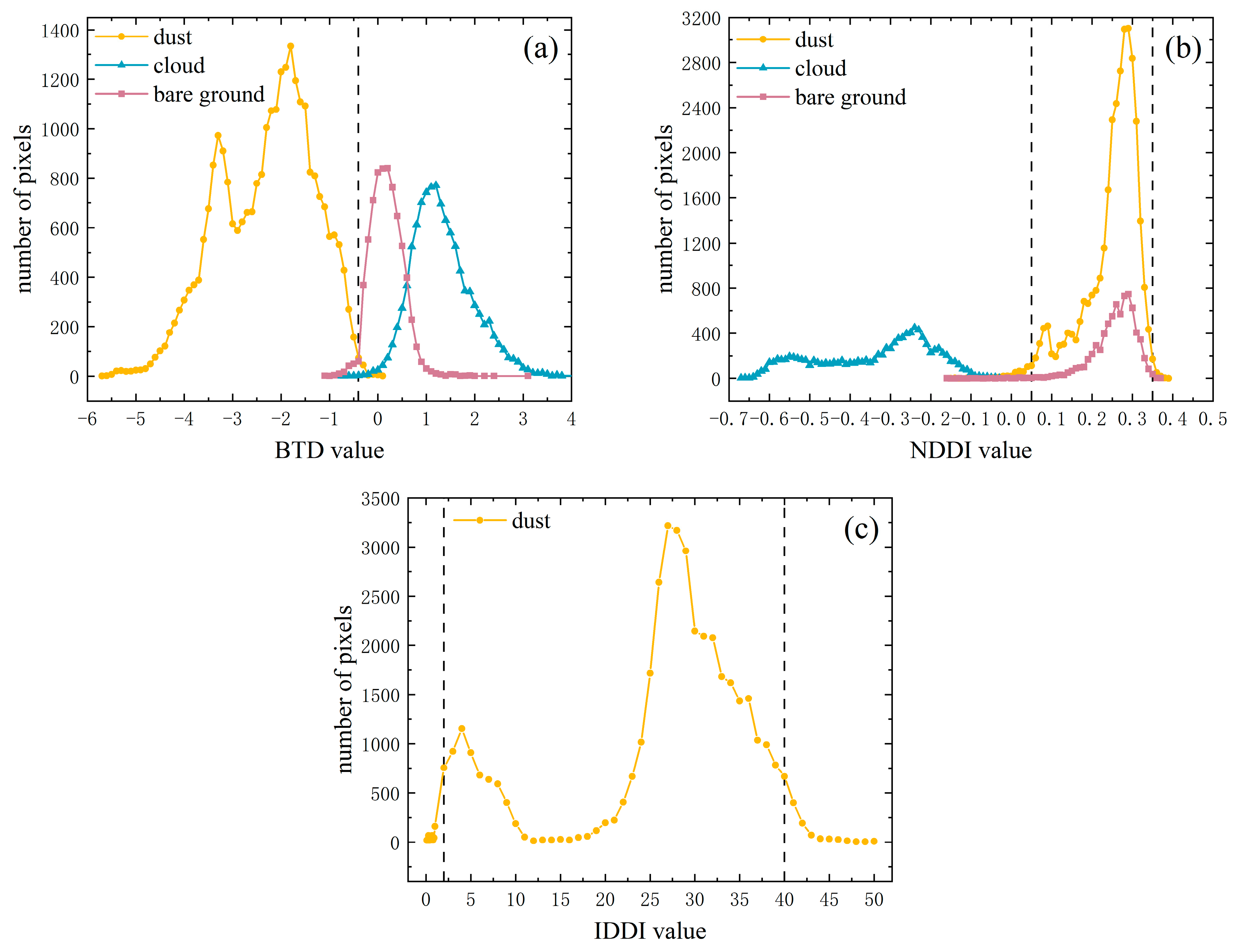
3.1. Brightness Temperature Difference (BTD)
3.2. Normalized Difference Dust Index (NDDI)
3.3. Infrared Difference Dust Index (IDDI)
3.4. Infrared Difference Dust Index (DST)
3.5. Performance Indicators (POCD and POFD)
4. Results and Validation
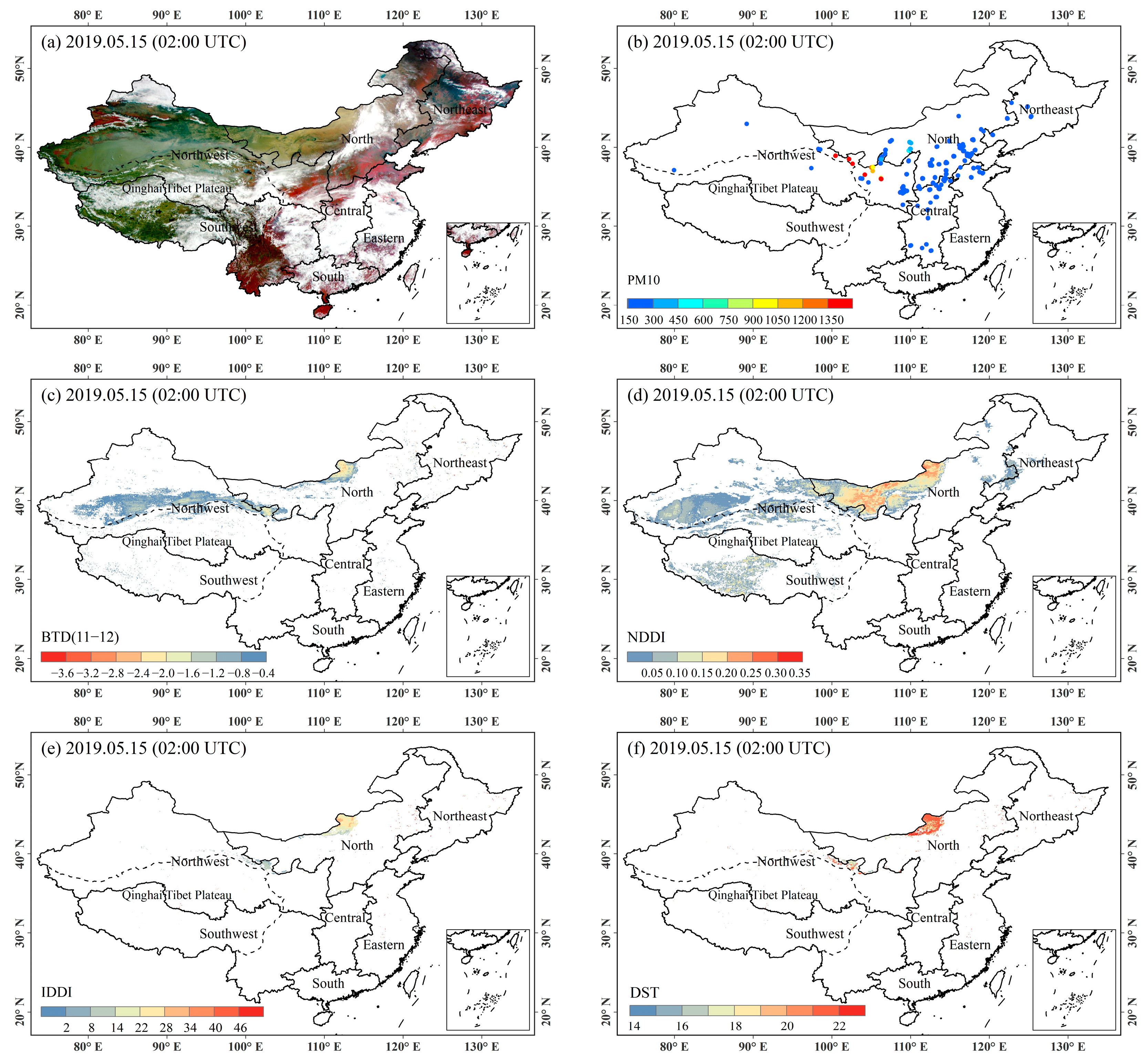
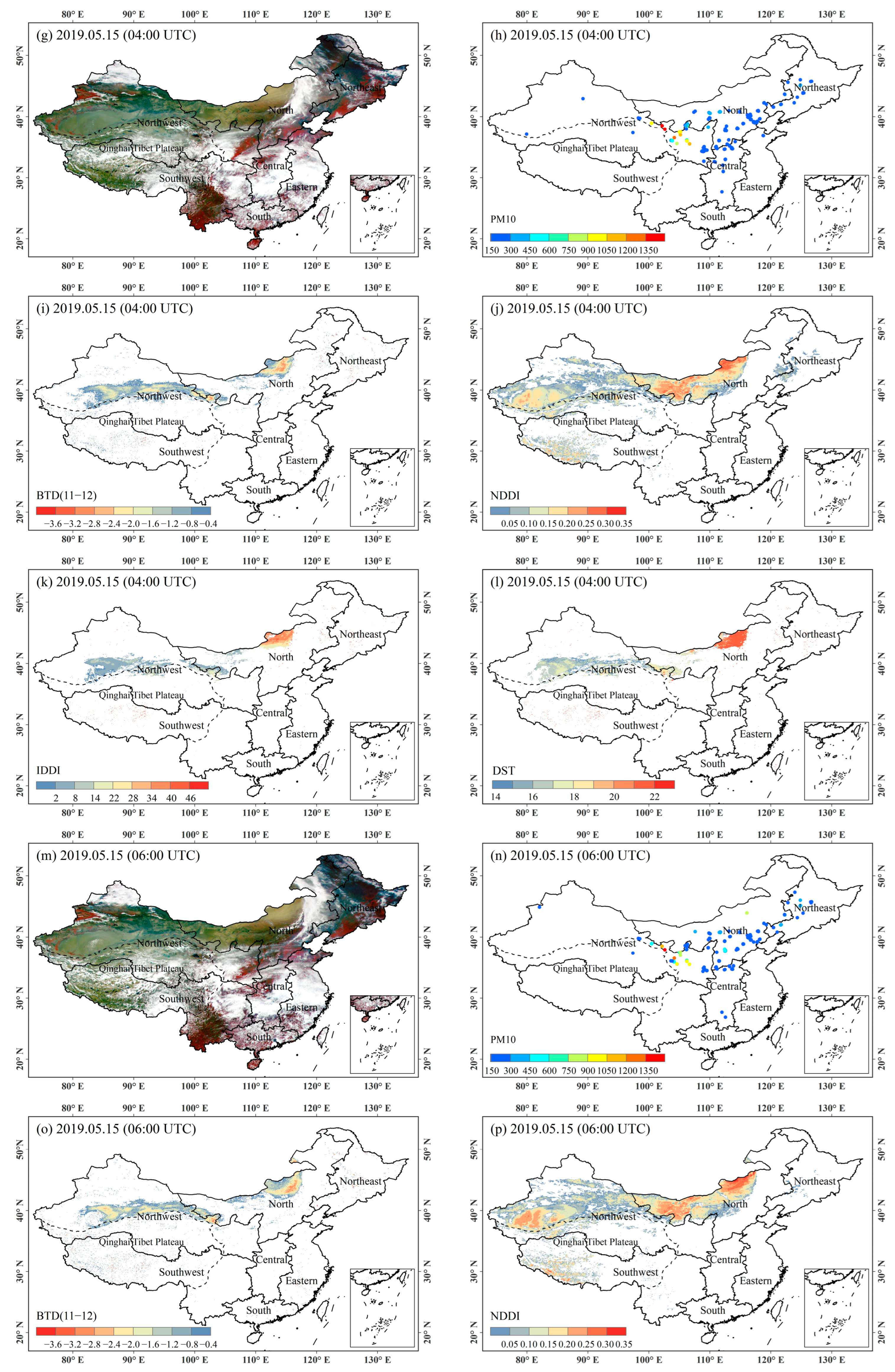
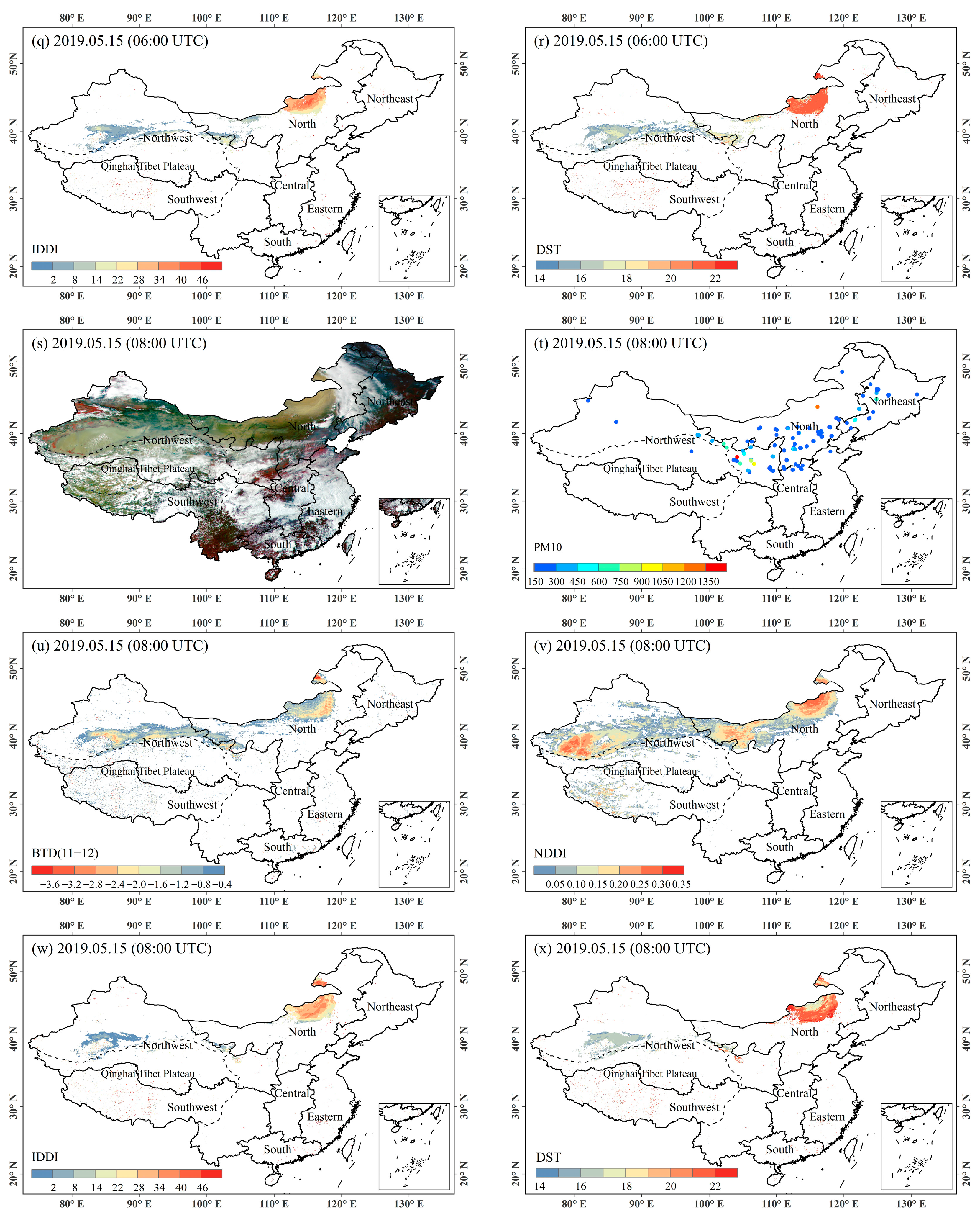
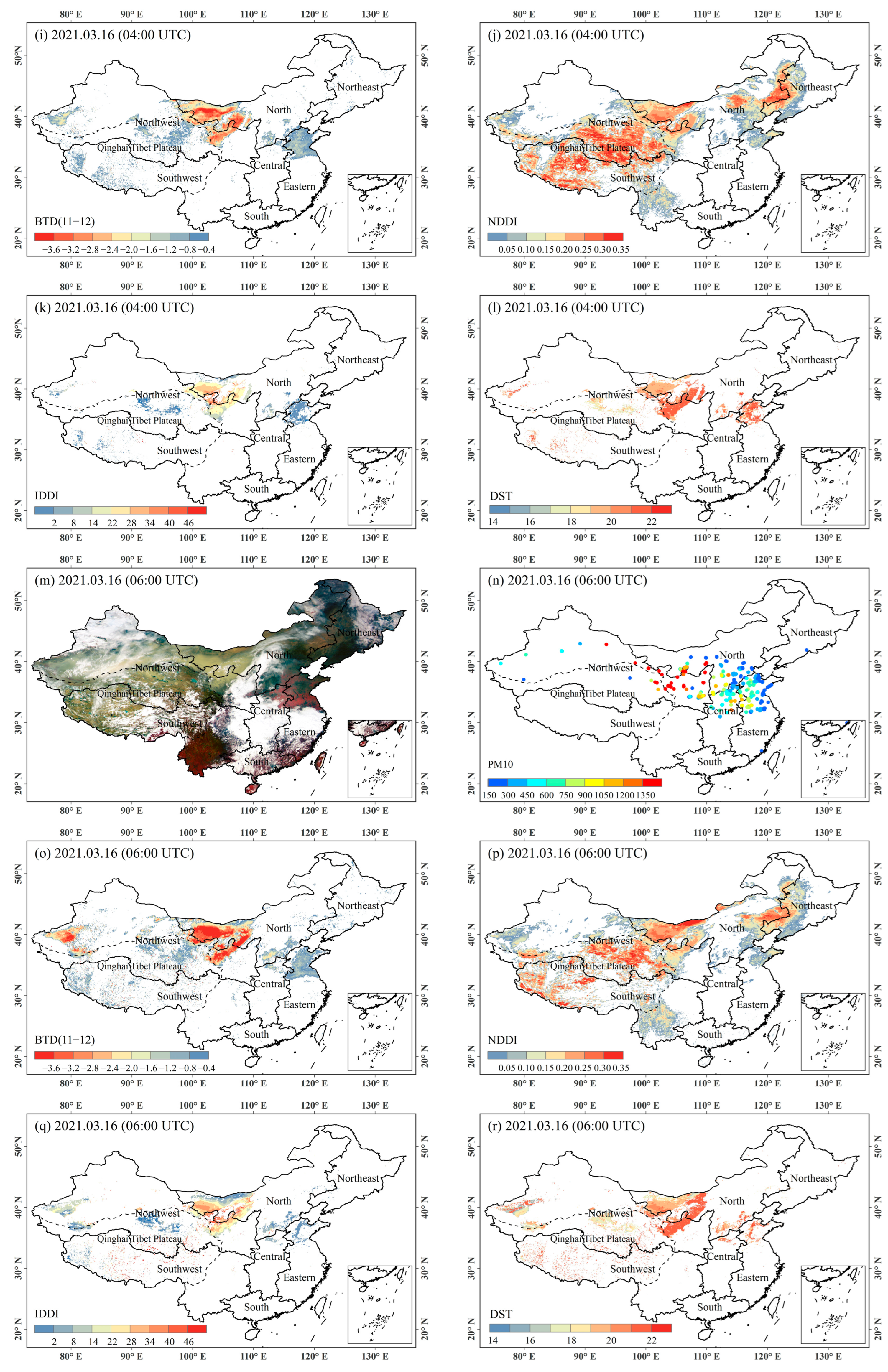
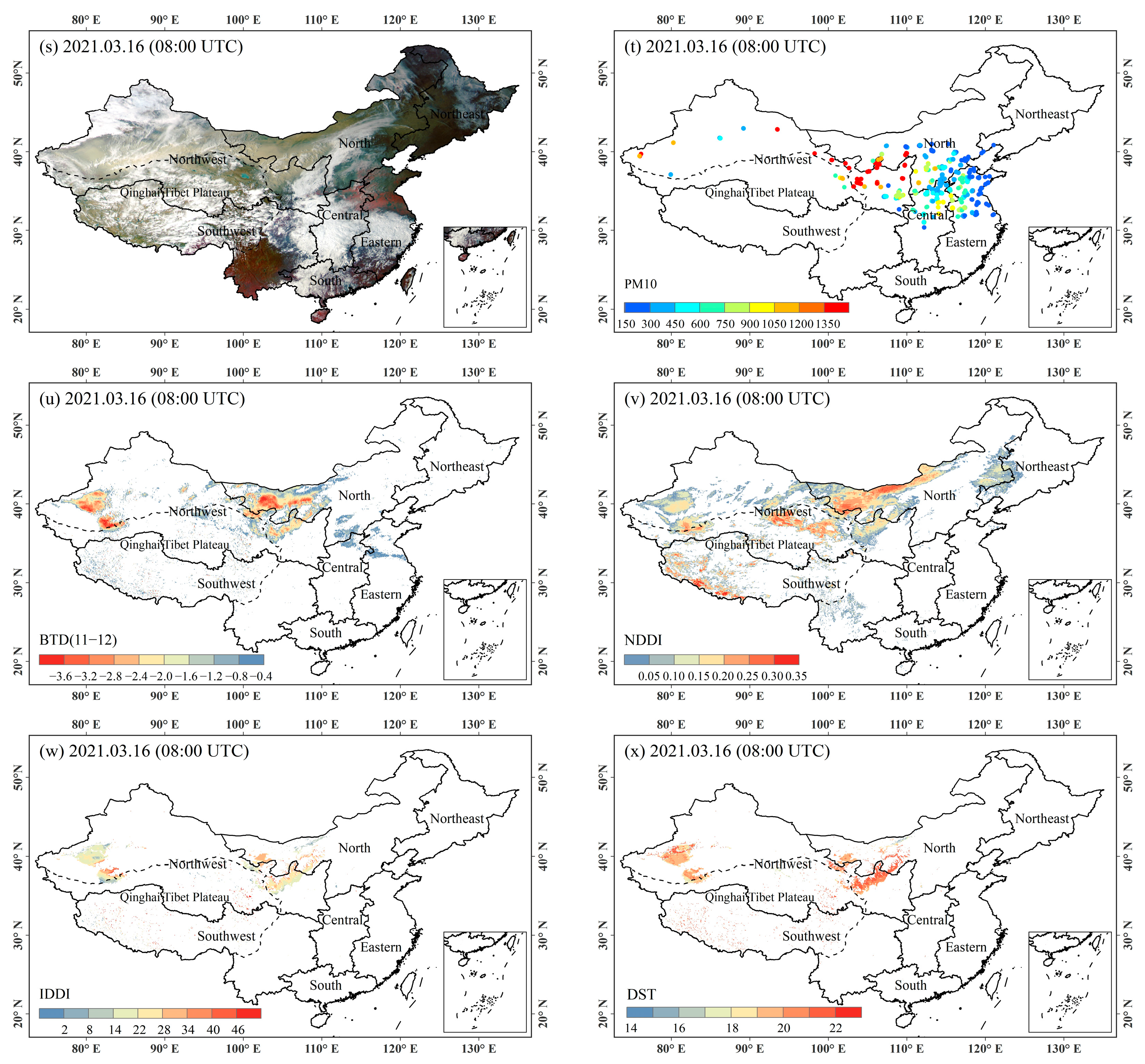
4.1. Analysis of Typical Dust Events
4.2. Validation with Ground-Based PM10 Measurements
4.2.1. Results of the Validation of Four Algorithms
4.2.2. Validation Results of the BTD Overlay IDDI Algorithm
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Bai, W.; Qi, C.; Qi, J. Current status of satellite-based dust aerosol remote sensing and some issues to be concerned. Meteorol. Mon. 2018, 44, 725–736. [Google Scholar]
- Hahnenberger, M.; Nicoll, K. Meteorological characteristics of dust storm events in the eastern Great Basin of Utah, USA. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duce, R.A. Sources, distributions, and fluxes of mineral aerosols and their relationship to climate. Aerosol Clim. 1995, 6, 43–72. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.-T.; Huza, M.A. Filtration and indoor air quality: A practical approach. Ashrae J. 1995, 37, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Aili, A.; Xu, H.; Zhao, X. Health Effects of Dust Storms on the South Edge of the Taklimakan Desert, China: A Survey-Based Approach. Remote Sens. 2022, 19, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababaeian, H.; Ostadtaghizadeh, A.; Ardalan, A.; Asgary, A.; Akbary, M.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Stephens, C. Global Health Impacts of Dust Storms: A Systematic Review. Environ. Health Insights 2021, 15, 11786302211018390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S. Desert dust and human health disorders. Environ Int. 2014, 63, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Tong, D.Q.; Wu, G.; Dan, M.; Teng, B. A systematic review of global desert dust and associated human health effects. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agier, L.; Deroubaix, A.; Martiny, N.; Yaka, P.; Djibo, A.; Broutin, H. Seasonality of meningitis in Africa and climate forcing: Aerosols stand out. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.-H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S. Dust cycle: An emerging core theme in earth system science. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, G.; Phanikumar, D.V.; Kumar, K.N.; Ouarda, T.B.M.J.; Marpu, P.R. Investigation of aerosol optical, physical, and radiative characteristics of a severe dust storm observed over UAE. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-R.; Sohn, E.-H.; Park, K.-H.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Park, N.-Y. Improved dust detection over East Asia using geostationary satellite data. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 57, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaq, M.; Sheltami, T.R.; Mouftah, H.T. A review of techniques and technologies for sand and dust storm detection. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2012, 11, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; He, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, C.; Lv, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Dust storm detection of a convolutional neural network and a physical algorithm based on FY-4A satellite data. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 4288–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Zhang, P.; Min, M. Construction and validation of remote sensing dust recognition algorithm in daytime and nighttime. Meteorol. Mon. 2019, 45, 1666–1679. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Lu, W.; Luo, J. Research on the dust storm monitoring using multi-channel meteorological satellite data. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 5, 300–305+324. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Hu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wang, L.; Han, W.; Yang, Y.; Tao, H.; Wang, J. Detection of a dust storm in 2020 by a multi-observation platform over the Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Han, D.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, W. Dynamic dust detection method based on geostationary meteorological satellite. Remote Sens. Inf. 2018, 33, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhu, J.; Wei, J.; Su, Q.; Sun, W.; Liu, F.; Shu, M. A simplified Suomi NPP VIIRS dust detection algorithm. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2017, 164, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Su, Q.; Sun, L.; Jia, S.; Tian, X.; Zhou, X. Dust monitoring with the Himawari-8 satellite. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol (Nat. Sci). 2018, 37, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolik; Irina, N. The spectral radiative signature of wind-blown mineral dust: Implications for remote sensing in the thermal IR region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 7-1–7-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Tanskanen, A.; Veihelmann, B.; Ahn, C.; Braak, R.; Bhartia, P.K.; Veefkind, P.; Levelt, P. Aerosols, and surface UV products from Ozone Monitoring Instrument observations: An overview. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D24S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Bhartia, P.K.; Herman, J.R.; Ahmad, Z.; Gleason, J. Derivation of aerosol properties from satellite measurements of backscattered ultraviolet radiation: Theoretical basis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 17099–17110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Hao, X.; Kafatos, M.; Wang, L. Asian dust storm monitoring combining Terra and Aqua MODIS SRB measurements. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansell, R.A.; Ou, S.C.; Liou, K.N.; Roskovensky, J.K.; Tsay, S.C.; Hsu, C.; Ji, Q. Simultaneous detection/separation of mineral dust and cirrus clouds using MODIS thermal infrared window data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L11808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmenov, A.; SokolikI, I.N. Identifying the regional thermal-IR radiative signature of mineral dust with MODIS. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, S.A. Remote sensing aerosols using satellite infrared observations. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 17069–17079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, S.A. Using The Radiative Temperature Difference At 3.7 And 11 μm to track dust outbreaks. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 27, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Plana-Fattori, A.; N’doum’e, C. Satellite detection of dust using the IR imagery of Meteosat: 1. Infrared difference dust index. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 18251–18274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lu, N.; Niu, T.; Zhang, P. Operational retrieval of Asian sand and dust storm from FY-2C geostationary meteorological satellite and its application to real-time forecast in Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 7, 8395–8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-M.; Nasiri, S.L.; Yang, P.; Laszlo, I.; Zhao, X.T. Detection of optically thin mineral dust aerosol layers over the ocean using MODIS. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 896–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.X.P.; Ackerman, S.; Guo, W. Dust and Smoke Detection for Multi-Channel Imagers. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2347–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Xue, Y.; Yang, X.; Guang, J.; Li, Y.; Che, Y.; Fan, C.; Xie, Y. Dust Detection and Intensity Estimation Using Himawari-8/AHI Observation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Igbawua, T.; Liu, Y. Developing a dust storm detection method combining Support Vector Machine and satellite data in typical dust regions of Asia. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, A.H.; Vajedian, S. Dust storm detection using random forests and physical-based approaches over the Middle East. J Earth Syst Sci. 2015, 124, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shi, Y.; Cai, C.; Ciren, P.; Wang, J.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Zhang, Z. Machine Learning Based Algorithms for Global Dust Aerosol Detection from Satellite Images: Inter-Comparisons and Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wong, M.S.; Lee, K.H.; Nichol, J.; Chan, P.W. Review of dust storm detection algorithms for multispectral satellite sensors. Atmos. Res. 2021, 250, 105398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciren, P.; Kondragunta, S. Dust aerosol index (DAI) algorithm for MODIS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4770–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Qu, J.J. Saharan dust storm detection using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer thermal infrared bands. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1, 013510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, N.; Moridnejad, A.; Golian, S.; Vali Samani, J.M.; Karimi, D.; Javadi, S. Comparison of dust source identification techniques over land in the Middle East region using MODIS data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 38, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; He, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Q. The brightness temperature adjusted dust index: An improved approach to detect dust storms using MODIS imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth. Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 57, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskovensky, J.K.; Liou, K.N. Differentiating airborne dust from cirrus clouds using MODIS data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L12809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zheng, X.; Lu, J.; Sun, J.; Tu, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Zhou, W. Origin and source of the dust storm influencing Beijing in spring of 2002. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2002, 14, 17–21+81. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; He, Q.; Zeng, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Dou, X. Sand and dust monitoring using FY-4A satellite data based on the random forests and convolutional netural networks. Plateau. Meteorol. 2021, 40, 680–689. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Characteristic analysis of three sand-dust strom process in 2021 based on FY-4A satellite remote sending data. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2022, 50, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ma, X. Analysis of dust vertical and horizontal distribution during dust events in northwest China based on FY-4A, MODIS and CALIPSO satellite data. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2020, 40, 2892–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A. Remote Sensing Mapping of Global Land Cover; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Ban, Y.; Li, S. China: Open access to Earth land-cover map. Nature 2014, 514, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zuo, H.; Min, M. Identify high frequent dust areas and their sources in spring in the northwest of China. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 4065–4073. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Shou, S.; Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Zhu, L. Numerical simulation and diagnostic is of dry intrusion in a dust storm process of Henan province during April 2006. Meteorological 2007, 33, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Operational application of Fengyun satellite in dust weather monitoring. Satell. Appl. 2018, 11, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- GB3095-2012; Ambient Air Quality Standards. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: China, Beijing, 2012.
- Prata, F.; Bluth, G.; Rose, B.; Schneider, D.; Tupper, A. Comments on failures in detecting volcanic ash from a satellite-based technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 78, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Hou, Y.; Liu, G.; He, Y. Dust detection using thermal infrared temperature difference. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 8, 471–474. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Tsunekawa, A.; Tsubo, M.; Zhou, W. An enhanced dust index for Asian dust detection with MODIS images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 6484–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Braun, S.A.; Qu, J.; Hao, X. Simulating the formation of Hurricane Isabel (2003) with AIRS data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L04804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Qu, J.; Niu, S.; Hao, X. Sand and dust storm detection over desert regions in China with MODIS measurements**. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 9365–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.B.; Dash, J.; Roberts, G. An evaluation of satellite dust-detection algorithms in the Middle East region. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 1331–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China General Environmental Monitoring Station. Technical Provisions on Classification of Sandy and Dusty Weather; China General Environmental Monitoring Station: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ryou, H.G.; Heo, J.; Kim, S.-Y. Source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 air pollution, and possible impacts of study characteristics in South Korea. Environ Pollut. 2018, 240, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferm, M.; Sjoberg, K. Concentrations and emission factors for PM2.5 and PM10 from road traffic in Sweden. Atmos Environ. 2015, 119, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeebullah, T.M. An analysis of air pollution in Makkah—A view point of source identification. Environ. Asia 2013, 2, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatoutsidou, S.E.; Kopanakis, I.; Lagouvardos, K.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Torseth, K.; Lazaridis, M. PM10 levels at urban, suburban, and background locations in the eastern Mediterranean: Local versus regional sources with emphasis on African dust. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Askary, H.M.; Sarkar, S.; Kafatos, M.; El-Ghazawi, T.A. A Multisensor Approach to Dust Storm Monitoring over the Nile Delta. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2386–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesh, S.K.; Moorthy, K.K. Radiative Effects of Natural Aerosols: A Review. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 2089–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Channel Type | Dust Index | Algorithm | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIS and NIR | NDDI | (R0.469 − R2.13)/(R0.469 − R2.13) | Qu et al. (2006) [24] |
| Dust aerosol index (DAI) | DAI = −100[log10(R412nm/R440nm) − log10(R′412nm/R′440nm)] Nondust absorbing aerosol index (NDAI) = −10[log10(R412nm/R2130nm)] | Ciren et al. (2014) [38] | |
| TIR | BTD | BTD (11–12 µm) | Ackerman (1997) [28] |
| BTD (3.7–11 µm) | Ackerman (1989) [27] | ||
| BTD (8.5–11 µm) | Ackerman (1997) [28] | ||
| IDDI | BTi − BTj, where i represents the real-time target brightness temperature, j represents the background brightness temperature | Legrand et al. (2001) [29] | |
| Thermal infrared dust index (TDI) | C0 + C1 × BT3.7 +C2 × BT9.7 + C3 ×BT11 + C4 × BT12 | Hao and Qu (2007) [39] | |
| Middle East dust index (MEDI) | (BT11 − BT8.5)/(BT12 − BT8.5) | Karimi et al. (2012) [40] | |
| Brightness temperature adjusted difference index (BADI) | 2/Π×arctan (BDI/BDI0.95), Where BDI = (BT3.9 − BT11.2)2 × (BT12.4 − BT11.2) | Yue et al. (2017) [41] | |
| VIS, NIR, and TIR | D-parameter | Exp (−(R0.54/R0.86 + (BT11 − BT12) − b) | Roskovensky and Liou (2005) [42] |
| Waveband | Spectral Properties | Central Wavelength | Spatial Resolution/km |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOMChannel01 | VIS | 0.47 | 1 |
| NOMChannel02 | 0.65 | 0.5 | |
| NOMChannel03 | NIR | 0.825 | 1 |
| NOMChannel04 | 1.375 | 2 | |
| NOMChannel05 | 1.61 | 2 | |
| NOMChannel06 | 2.225 | 2–4 | |
| NOMChannel07 | IR | 3.75 | 2–4 |
| NOMChannel08 | 3.75 | 4 | |
| NOMChannel09 | 6.25 | 4 | |
| NOMChannel10 | 7.1 | 4 | |
| NOMChannel11 | 8.5 | 4 | |
| NOMChannel12 | 10.8 | 4 | |
| NOMChannel13 | 12 | 4 | |
| NOMChannel14 | 13.5 | 4 |
| BTD | YY | YN | NY | POCD (%) | POFD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02:00 UTC | 724 | 622 | 2023 | 53.79% | 73.64% |
| 04:00 UTC | 638 | 433 | 1630 | 59.57% | 71.87% |
| 06:00 UTC | 628 | 415 | 1965 | 60.21% | 75.78% |
| 08:00 UTC | 469 | 450 | 1452 | 51.03% | 75.59% |
| Average | 56.15% | 74.22% |
| NDDI | YY | YN | NY | POCD (%) | POFD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02:00 UTC | 490 | 856 | 7309 | 36.40% | 93.72% |
| 04:00 UTC | 466 | 605 | 13,098 | 43.51% | 96.56% |
| 06:00 UTC | 398 | 645 | 11,812 | 38.16% | 96.74% |
| 08:00 UTC | 363 | 556 | 5025 | 39.50% | 93.26% |
| Average | 39.39% | 95.07% |
| IDDI | YY | YN | NY | POCD (%) | POFD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02:00 UTC | 441 | 441 | 1001 | 50.00% | 69.42% |
| 04:00 UTC | 575 | 532 | 1714 | 51.94% | 74.88% |
| 06:00 UTC | 547 | 479 | 1968 | 53.31% | 78.25% |
| 08:00 UTC | 308 | 511 | 886 | 37.61% | 74.20% |
| Average | 48.22% | 74.19% |
| DST | YY | YN | NY | POCD (%) | POFD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02:00 UTC | 440 | 802 | 1192 | 35.43% | 73.04% |
| 04:00 UTC | 560 | 523 | 2221 | 51.71% | 79.86% |
| 06:00 UTC | 511 | 481 | 2324 | 51.51% | 81.98% |
| 08:00 UTC | 161 | 172 | 1086 | 48.35% | 87.09% |
| Average | 46.75% | 80.49% |
| BTD_IDDI | YY | YN | NY | POCD (%) | POFD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02:00 UTC | 428 | 478 | 554 | 47.24% | 56.42% |
| 04:00 UTC | 509 | 297 | 691 | 63.15% | 57.58% |
| 06:00 UTC | 476 | 287 | 817 | 62.39% | 63.19% |
| 08:00 UTC | 286 | 316 | 259 | 47.51% | 47.52% |
| Average | 55.07% | 56.17% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; She, L.; Che, Y.; He, X.; Yang, C.; Feng, Z. Analysis of Dust Detection Algorithms Based on FY-4A Satellite Data. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031365
Yang L, She L, Che Y, He X, Yang C, Feng Z. Analysis of Dust Detection Algorithms Based on FY-4A Satellite Data. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(3):1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031365
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lu, Lu She, Yahui Che, Xingwei He, Chen Yang, and Zixian Feng. 2023. "Analysis of Dust Detection Algorithms Based on FY-4A Satellite Data" Applied Sciences 13, no. 3: 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031365
APA StyleYang, L., She, L., Che, Y., He, X., Yang, C., & Feng, Z. (2023). Analysis of Dust Detection Algorithms Based on FY-4A Satellite Data. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031365








