Improving a Fuel Cell System’s Thermal Management by Optimizing Thermal Control with the Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and an Artificial Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
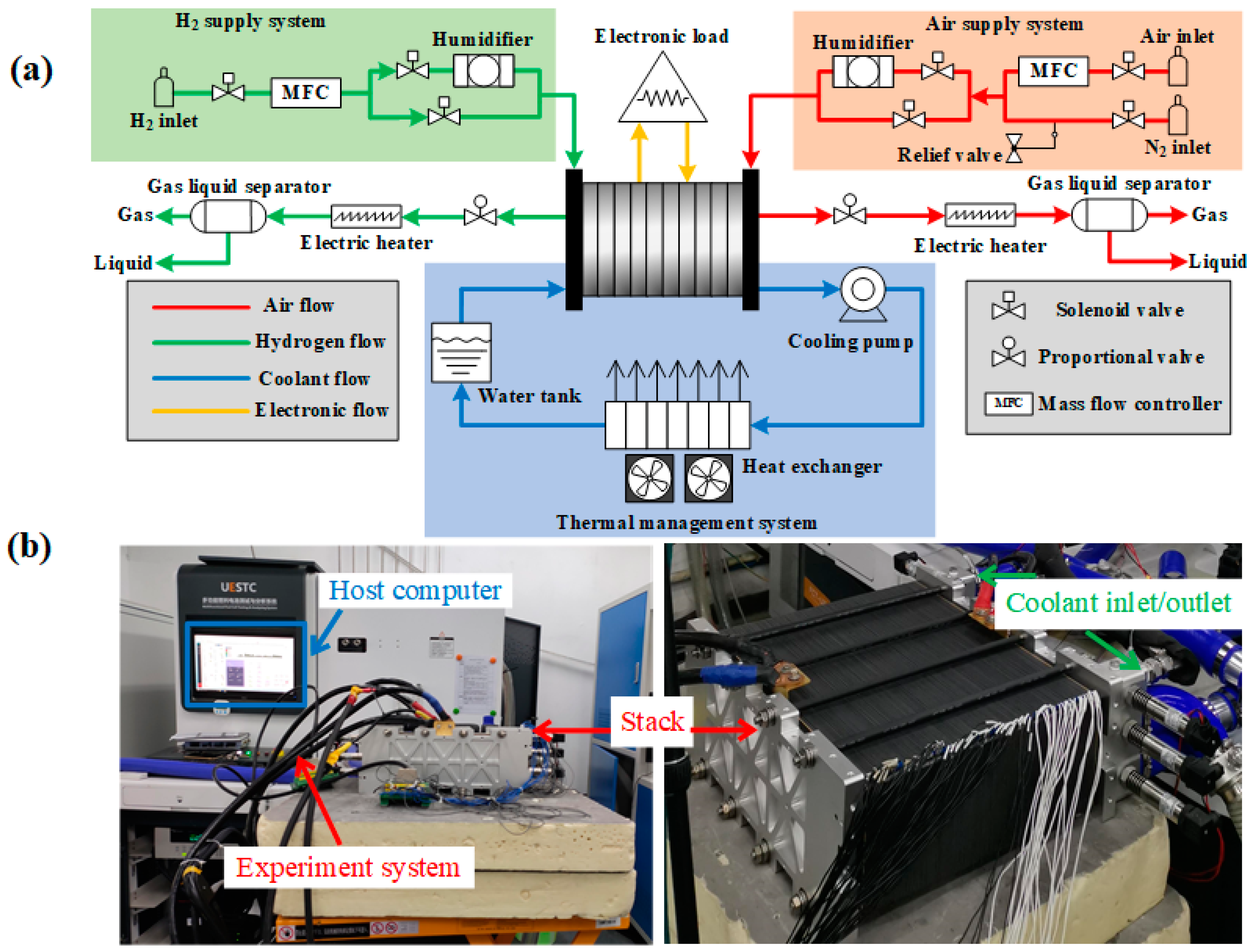
2. Experiment
3. Model Development
3.1. Model Structure
3.2. Dynamic Mechanistic Model
3.2.1. Stack Voltage Model
3.2.2. Water Flow in the Cathode and Anode
- (1)
- Gas behaves as an ideal gas and conforms to the ideal gas law.
- (2)
- The gas temperature inside the flow channel equals the stack temperature.
- (3)
- The temperature, pressure, and humidity inside the flow channel and at the exit are equal.
- (4)
- When the relative humidity of the gas is above 100%, the vapor condenses to liquid form but does not leave the stack. The liquid water evaporates into the gas or accumulates in the flow channel.
- (5)
- The flow channel volume is constant.
3.2.3. Membrane Hydration
- (1)
- The water mass flow is distributed uniformly across the membrane.
- (2)
- The membrane water content is the average of the cathode water content and anode water content , , and can be expressed as
3.2.4. Stack Heat Exchange
3.2.5. Radiator
3.2.6. Piping
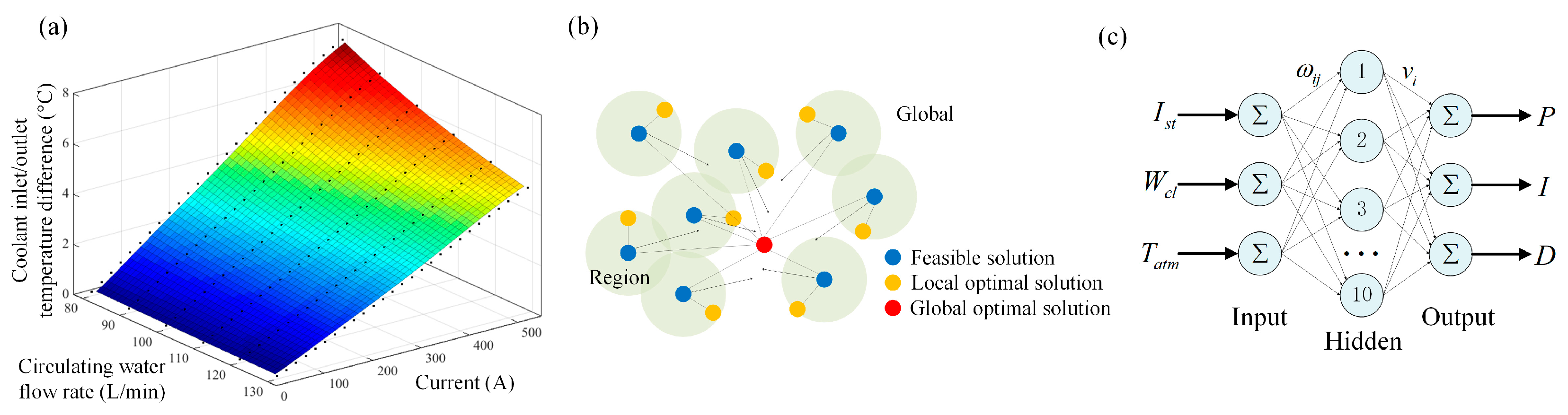
3.3. Control Model
4. Results and Discussion
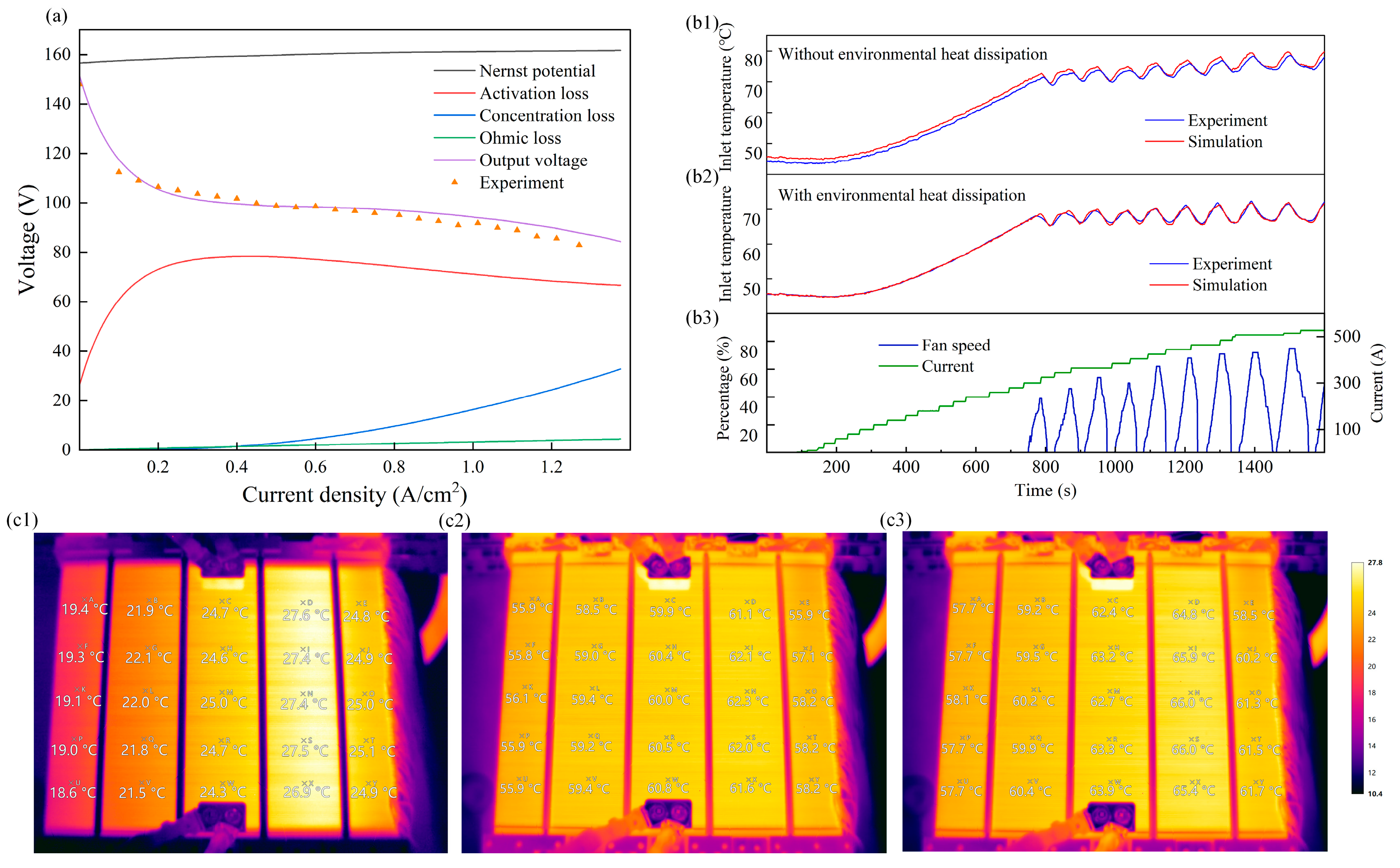
4.1. Model Validation
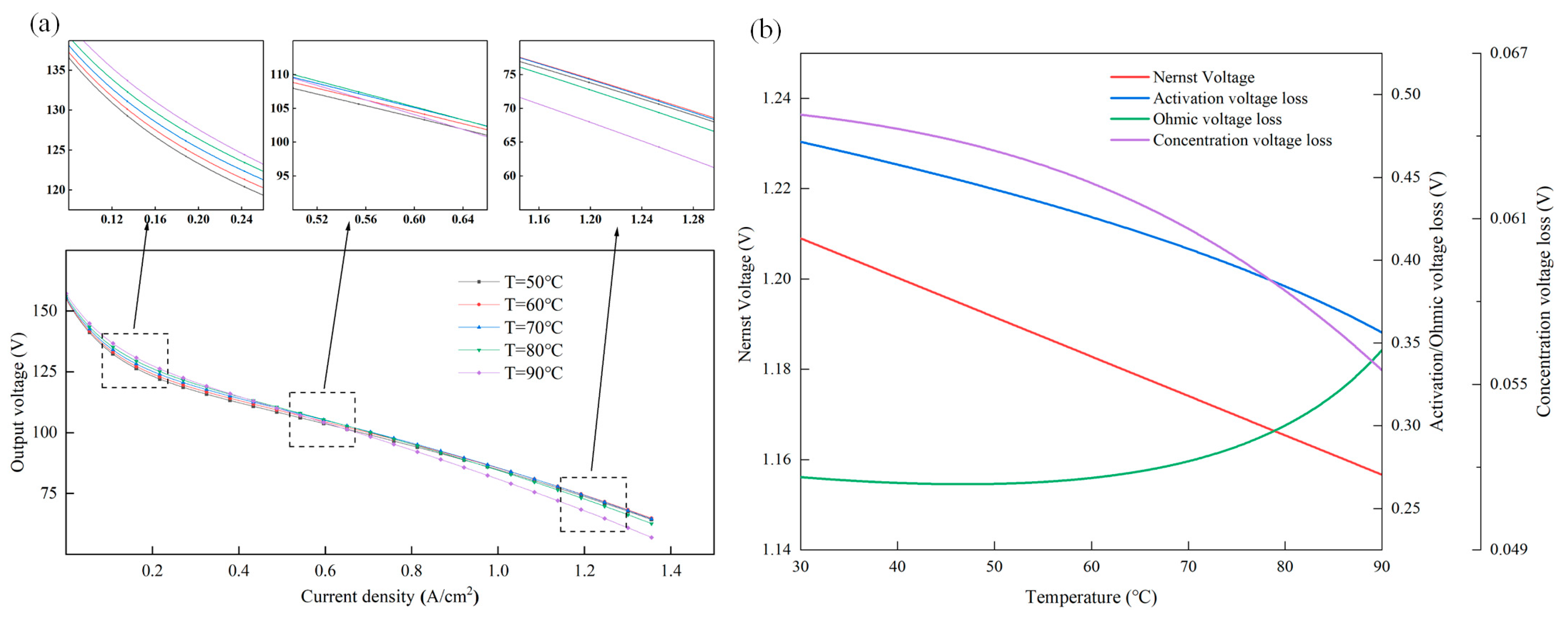
4.2. Parametric Effect Analysis of Temperature
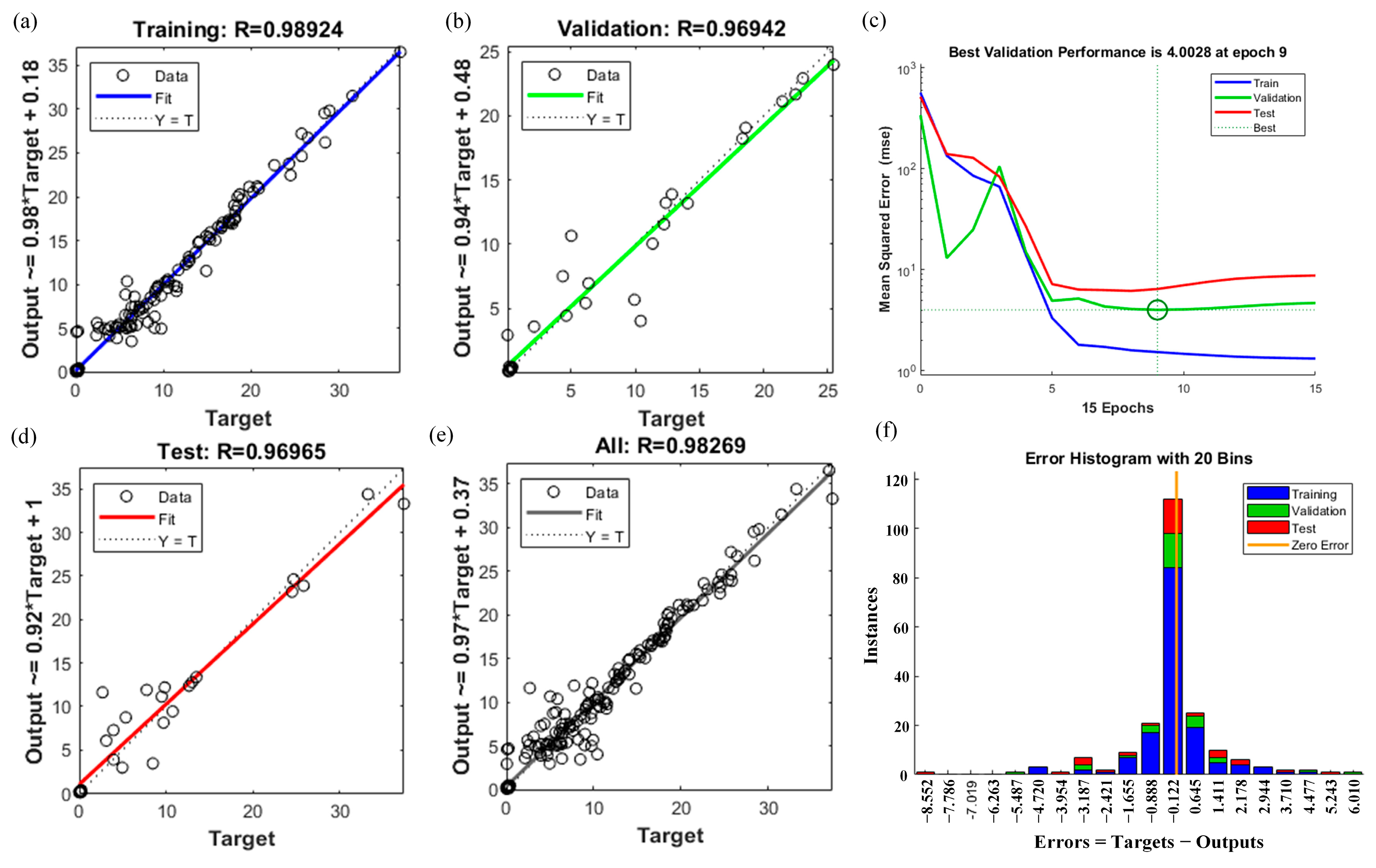
4.3. Training Results
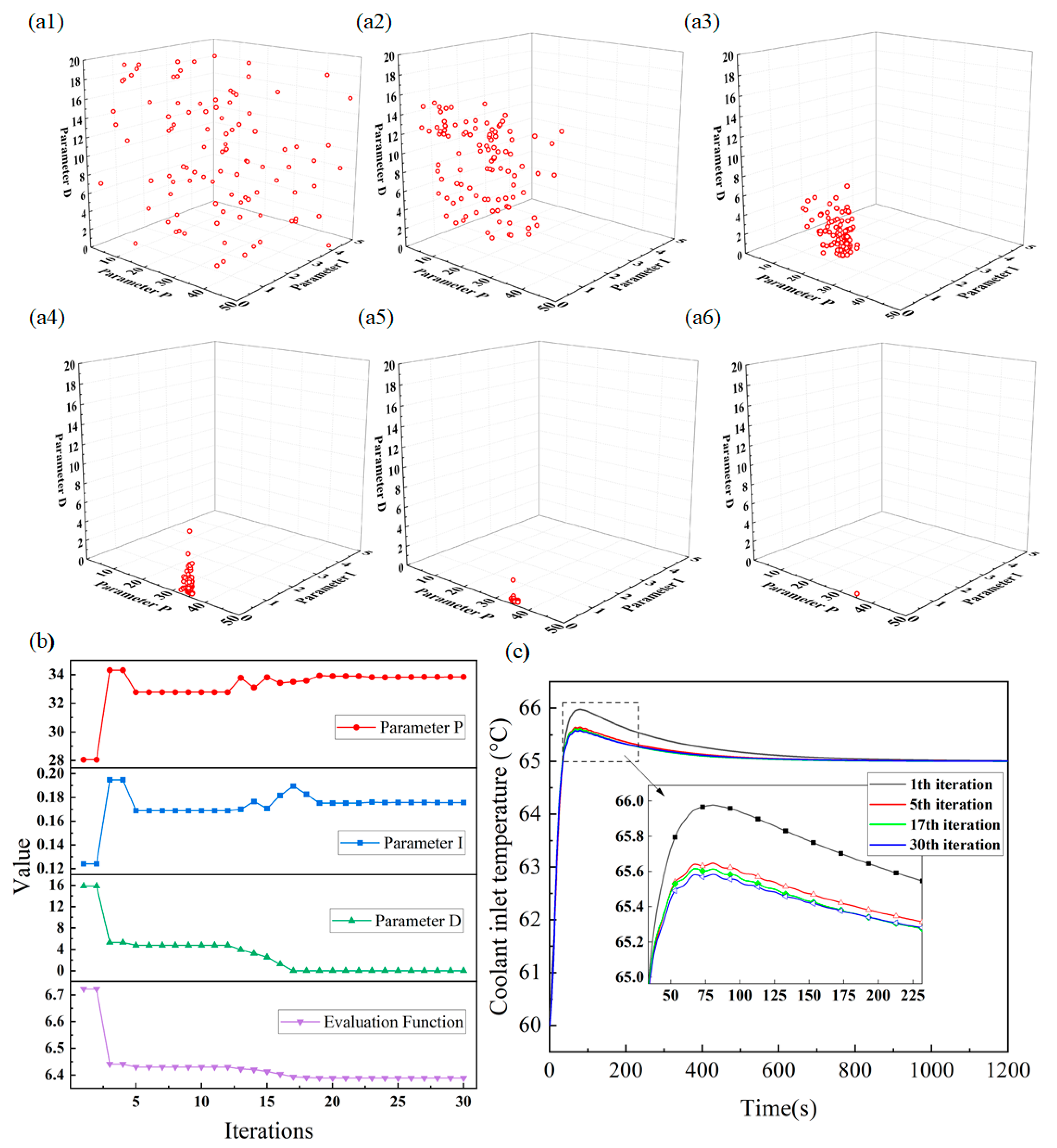
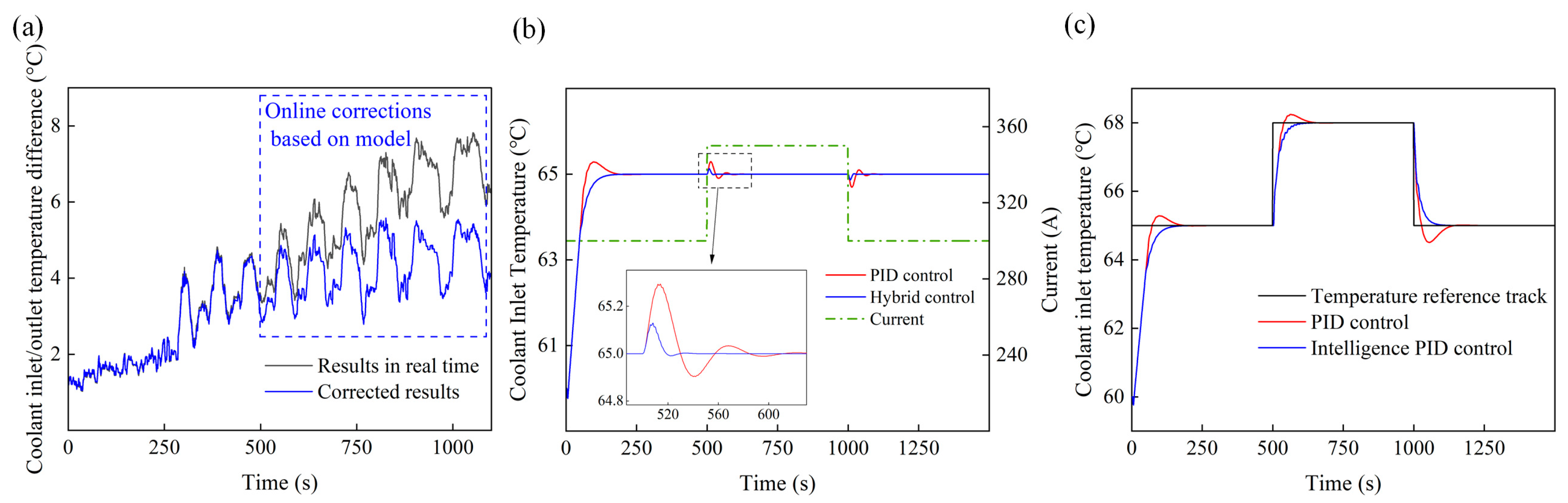
4.4. Control Model Effectiveness
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Ruiz Diaz, D.F.; Chen, K.S.; Wang, Z.; Adroher, X.C. Materials, Technological Status, and Fundamentals of PEM Fuel Cells—A Review. Mater. Today 2020, 32, 178–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ling, C.-Y.; Han, M.; Yong, R.-Y.; Sun, D.; Chen, J. Review on Current Research of Materials, Fabrication and Application for Bipolar Plate in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 29832–29847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Gong, C.; Wen, S.; Wang, X.; Tu, Z. Progress on Design and Development of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Systems for Vehicle Applications: A Review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 179, 203–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Nawaz, T.; Ali, A.; Orhan, M.F.; Samreen, A.; Kannan, A.M. An Overview of Proton Exchange Membranes for Fuel Cells: Materials and Manufacturing. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 19086–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zeng, K.; Shu, H.; Cao, P.; Ren, Y. A Critical Survey of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell System Control: Summaries, Advances, and Perspectives. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 9986–10020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittinger, W.; Vahidi, A. A Review of the Main Parameters Influencing Long-Term Performance and Durability of PEM Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2008, 180, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.-M.; Chen, F.; Wu, H.-Y.; Soong, C.-Y.; Chu, H.-S. Analysis of Thermal and Water Management with Temperature-Dependent Diffusion Effects in Membrane of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2004, 129, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yang, S.; Deng, C. A Review on Temperature Control of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Processes 2021, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Kandlikar, S.G. A Critical Review of Cooling Techniques in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Stacks. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 2412–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Xu, L.; Cheng, S.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Ouyang, M. Sliding-Mode-Based Temperature Regulation of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Test Bench. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 11745–11757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jiao, K. Multi-Phase Models for Water and Thermal Management of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell: A Review. J. Power Sources 2018, 391, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jung, D. Thermal Management Strategy for a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell System with a Large Active Cell Area. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 2540–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Ouyang, M. Performance Prediction of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Engine Thermal Management System Using 1D and 3D Integrating Numerical Simulation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 1736–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Maranzana, G.; Didierjean, S.; Dillet, J.; Lottin, O. Measurements of Electrode Temperatures, Heat and Water Fluxes in PEMFCs: Conclusions about Transfer Mechanisms. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, F191–F204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahgoshay, S.M.; Ranjbar, A.A.; Ramiar, A.; Alizadeh, E. Thermal Investigation of a PEM Fuel Cell with Cooling Flow Field. Energy 2017, 134, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.-F.; Lin, H.; Chen, L.; He, Y.-L.; Tao, W.-Q. Numerical Investigation of the Coupled Water and Thermal Management in PEM Fuel Cell. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, E.; Rokni, M.; Rabbani, A.; Mortensen, H.H. Thermal and Water Management of Low Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell in Fork-Lift Truck Power System. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, J.; Kolodziej, J. Modeling of an Automotive Fuel Cell Thermal System. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 4743–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, W. Thermal Management System Modeling of a Water-Cooled Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 3048–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liso, V.; Nielsen, M.P.; Kær, S.K.; Mortensen, H.H. Thermal Modeling and Temperature Control of a PEM Fuel Cell System for Forklift Applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 8410–8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; He, L.; Niu, Z.; Liu, Z. A Review and Prospect for Temperature Control Strategy of Water-Cooled PEMFC. In Proceedings of the 2017 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 9062–9068. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Fang, C.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Ouyang, M. Model-Based Temperature Regulation of a PEM Fuel Cell System on a City Bus. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 13566–13575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygili, Y.; Eroglu, I.; Kincal, S. Model Based Temperature Controller Development for Water Cooled PEM Fuel Cell Systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yu, Y.; Gao, Y. Temperature Control for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Based on Current Constraint with Consideration of Limited Cooling Capacity. Fuel Cells 2017, 17, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huang, J. Applications of Heuristic Dynamic Programming in the Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Temperature Control. In Proceedings of the 2012 Power Engineering and Automation Conference, Wuhan, China, 18–20 September 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Saadi, A.; Becherif, M.; Hissel, D.; Ramadan, H.S. Dynamic Modeling and Experimental Analysis of PEMFCs: A Comparative Study. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 1544–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-J.; Liu, J.-J. Nonlinear Modeling and Identification of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 9452–9461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.-M.; Cheng, S.-J.; Wu, S.-J. Metamodel Based Design Optimization Approach in Promoting the Performance of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 15283–15294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilberforce, T.; Olabi, A.G. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Performance Prediction Using Artificial Neural Network. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 6037–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.-S.; Park, S.-K.; Chung, C.-B. Modeling and Operation Optimization of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell System for Maximum Efficiency. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 113, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Liu, X.; Luo, K.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Deep Learning from Three-Dimensional Multiphysics Simulation in Operational Optimization and Control of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell for Maximum Power. Appl. Energy 2021, 288, 116632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, C. PEM Fuel Cell Modeling and Simulation Using Matlab; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-12-374259-9. [Google Scholar]
- Amphlett, J.C.; Baumert, R.M.; Mann, R.F.; Peppley, B.A.; Roberge, P.R.; Harris, T.J. Performance Modeling of the Ballard Mark IV Solid Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell: I. Mechanistic Model Development. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyezhai, R.; Mathur, B.L. Mathematical Modeling of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 20, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amphlett, J.C.; Baumert, R.M.; Mann, R.F.; Peppley, B.A.; Roberge, P.R.; Harris, T.J. Performance Modeling of the Ballard Mark IV Solid Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell: II. Empirical Model Development. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Chamberlin, C.E. Modeling of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Performance with an Empirical Equation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 2670–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, T.E.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Gottesfeld, S. Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Model. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1991, 138, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Ouyang, M.; Yi, B. Modeling and Control of Air Stream and Hydrogen Flow with Recirculation in a PEM Fuel Cell System—I. Control-Oriented Modeling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2006, 31, 1879–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Shimpalee, S.; Van Zee, J.W. Numerical Prediction of Mass-Exchange between Cathode and Anode Channels in a PEM Fuel Cell. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2001, 44, 2029–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawodzinski, T.A.; Derouin, C.; Radzinski, S.; Sherman, R.J.; Smith, V.T.; Springer, T.E.; Gottesfeld, S. Water Uptake by and Transport through Nafion® 117 Membranes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhou, B.; Sobiesiak, A. Water and Thermal Management for Ballard PEM Fuel Cell Stack. J. Power Sources 2005, 147, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Cao, G.-Y.; Zhu, X.-J.; Hu, M. Coolant Circuit Modeling and Temperature Fuzzy Control of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 9110–9123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, A.; Rokni, M. Dynamic Characteristics of an Automotive Fuel Cell System for Transitory Load Changes. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2013, 1, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Stack cell number | 140 |
| Material of bipolar plate | Graphite |
| Active area | 406 cm2 |
| Thickness of PEM | 0.0018 cm |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Load current | 467 A-487 A-507 A |
| Coolant flow rate | 90 L/Min |
| Relative humidity | 95% |
| Cathode inlet pressure | 40 kPa |
| Anode inlet pressure | 50 kPa |
| Ambient temperature | 20 °C |
| Target temperature | 65 °C |
| Maximum temperature | 68 °C |
| Parameter | Symbol | Parameter | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating temperature | Cell number | ||
| O2 inlet partial pressure | Water’s molar mass | ||
| H2 inlet partial pressure | Cathode flow channel volume | ||
| Load current | Vapor’s gas constant | ||
| Cathode inlet pressure | PEM thickness |
| Parameter | Symbol | Step | Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load current | 20 A | 0~550 A | |
| Coolant flow rate | 10 L/Min | 80~130 SLPM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, B.; Zhang, X.; Yin, C.; Luo, Y.; Tang, H. Improving a Fuel Cell System’s Thermal Management by Optimizing Thermal Control with the Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and an Artificial Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12895. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312895
Deng B, Zhang X, Yin C, Luo Y, Tang H. Improving a Fuel Cell System’s Thermal Management by Optimizing Thermal Control with the Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and an Artificial Neural Network. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(23):12895. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312895
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Bo, Xuefeng Zhang, Cong Yin, Yuqin Luo, and Hao Tang. 2023. "Improving a Fuel Cell System’s Thermal Management by Optimizing Thermal Control with the Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and an Artificial Neural Network" Applied Sciences 13, no. 23: 12895. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312895
APA StyleDeng, B., Zhang, X., Yin, C., Luo, Y., & Tang, H. (2023). Improving a Fuel Cell System’s Thermal Management by Optimizing Thermal Control with the Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and an Artificial Neural Network. Applied Sciences, 13(23), 12895. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312895






