Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the most common irreversible brain diseases in the elderly. Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is an early symptom of AD, and the early intervention of MCI may slow down the progress of AD. However, due to the subtle neuroimaging differences between MCI and normal control (NC), the clinical diagnosis is subjective and easy to misdiagnose. Machine learning can extract depth features from neural images, and analyze and label them to assist the diagnosis of diseases. This paper combines diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and support vector machine (SVM) to classify AD, MCI, and NC. First, the white matter connectivity network was constructed based on DTI. Second, the nodes with significant differences between groups were screened out by the two-sample t-test. Third, the optimal feature subset was selected as the classification feature by recursive feature elimination (RFE). Finally, the Gaussian kernel support vector machine was used for classification. The experiment tested and verified the data downloaded from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database, and the area under the curve (AUC) of AD/MCI and MCI/NC are 0.94 and 0.95, respectively, which have certain competitive advantages compared with other methods.
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the most influential neurological diseases in the world. According to the statistics, AD accounts for 60–80% of all dementia cases [1]. Although the incidence of AD is high, its pathophysiological mechanism is still unclear. Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) lies between normal control (NC) and AD. Studies have indicated that people with MCI are progressing to AD at a pace of about 10–15% annually [2], and that appropriate therapeutic interventions can slow the progression of the disease if taken at the MCI stage [3]. Therefore, the early recognition of MCI is of great significance for timely intervention and delaying the progression of AD.
Due to subtle changes in the brain structure of MCI patients, the characteristics of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are not obvious, so it is difficult to distinguish MCI from AD and NC. Studies have shown that microstructural changes in white matter (WM) appear earlier than aberrant modifications in gray matter and functional connectivity during AD progression [4]. Therefore, WM degeneration is an effective biomarker for MCI. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an important tool for studying the microstructure of the brain, which can examine the fine structural changes in WM fibers and provide highly specific anatomical information [5,6,7]. DTI diffusion tensor parameters include fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), radial diffusivity (RD), and so on. Among them, FA and MD are the main parameters used by DTI to assess the integrity and degree of damage of WM fiber bundles [8]. Dalboni et al. [9] conducted a voxel-based analysis of FA in AD, MCI, and NC, and found that the bilateral intersection of the hippocampal cingulum and parahippocampal gyrus was the most differentiated area in AD. Jung et al. [10] applied DTI to the memory-related WM fiber tracts of MCI subjects and found that MCI subjects had decreased FA values and increased MD values in the cingulate gyrus tract, superior longitudinal fasciculus, and other regions compared to the NC group. Bergamino et al. [11] compared the free water DTI of AD and MCI subjects and found significant differences in the WM fibers in multiple regions between the two groups. Among them, higher FA values were found in the anterior thalamic and corticospinal tracts of the AD group, while the fornix had lower FA values and higher MD values, which may be related to a decrease in cognitive ability. Wurst et al. [12] used DTI to study changes in the WM structure of motor basal ganglia in AD and NC. The results indicated that, compared with the NC group, the FA in the right caudate nucleus of the AD group decreased significantly, while the FA in the left and right putamen increased significantly.
The human brain is one of the most sophisticated systems in nature, consisting of a complex and vast network of billions of neurons, which is the physiological basis for information processing and cognitive expression [13]. Extensive studies have shown that the pathogenesis of AD is not only limited to a single brain region but that there is a problem with the synergy between multiple regions of the brain. Therefore, experiments need to study AD from a holistic perspective using complex network theory [14,15,16,17,18,19]. Machine learning is a pattern recognition technology. While producing a classification, it can also train a large number of historical data through algorithms and learn the characteristic rules from them, to realize the recognition of new sample data and some predictions for the future [20]. Machine learning can greatly improve the efficiency of diagnosis. If given enough training data, the system can be trained in a short time and a lot of feature information can be obtained, and finally, reliable classification results can be made. In recent years, the combination of various machine learning-based classification techniques like support vector machine (SVM) [21] and brain networks have gradually been widely used in the early diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases [22,23,24]. SVM is a two-classification generalized linear classifier based on supervised learning. The appearance of the kernel method broadens the application scope of SVM, which enables SVM to deal with nonlinear problems and high-dimensional data (such as MRI, DTI, and other neuroimaging data). Brain networks can analyze abnormal changes in brain function and structure. Therefore, researchers often use DTI and fiber bundle imaging technology to construct a whole brain white matter connection network, use various feature extraction methods to extract effective feature information from the white matter connection network, and use SVM to classify. Gao et al. [25] utilized the complex network visualization method [26] to construct functional brain networks related to AD and used the topological features of brain network regions as classifier samples to construct SVM models. Meanwhile, this study further explored the local topological abnormalities of AD brain networks and found that the brain regions with abnormal functional connectivity caused by AD involved the left insula region, the right posterior cingulate region, and other cortical regions. Dai et al. [27] used DTI’s automated fiber quantification method [28] to track 20 WM fiber bundles from the whole brain to classify and predict different subtypes of MCI using SVM models. Zhao et al. [29] extracted blood oxygen level-dependent time series from white and gray matter, constructed functional connectivity brain networks with static and dynamic between white and gray matter as well as static and dynamic within gray matter, and assessed these features using SVM. Li et al. [30] used the network clustering coefficient, global efficiency, and average node degree as features to distinguish amnesia MCI from NC, and established an SVM classification model.
This study aims to identify the effective features in white matter connectivity networks to improve the classification performance. The main contributions are as follows:
- (1)
- Calculate the DTI index of the WM connectivity between the brain regions of the whole brain and construct the FA connectivity network as features.
- (2)
- Combine the statistical test and recursive feature elimination (RFE) [31] to screen the combination features with better classification effects. The contribution of features was also calculated using RFE to analyze the pathological mechanisms of AD and MCI.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Experimental Environment
The data used for the experiments came from the open-source medical dataset Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI). The main purpose of ADNI is to investigate whether early progression of MCI and AD can be measured by combining a series of MRI, DTI, other biomarkers, and clinical and neuropsychological evaluations. We randomly selected 140 DTI data, which contained 38 AD data, 46 MCI data, and 56 NC data. All the subjects underwent the mini-mental state examination (MMSE).
The classification experiments conducted in this study were implemented using the TensorFlow 2.4.0 framework and Python 3.8 on an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 GPU with 64 GB of memory.
2.2. System Pipeline
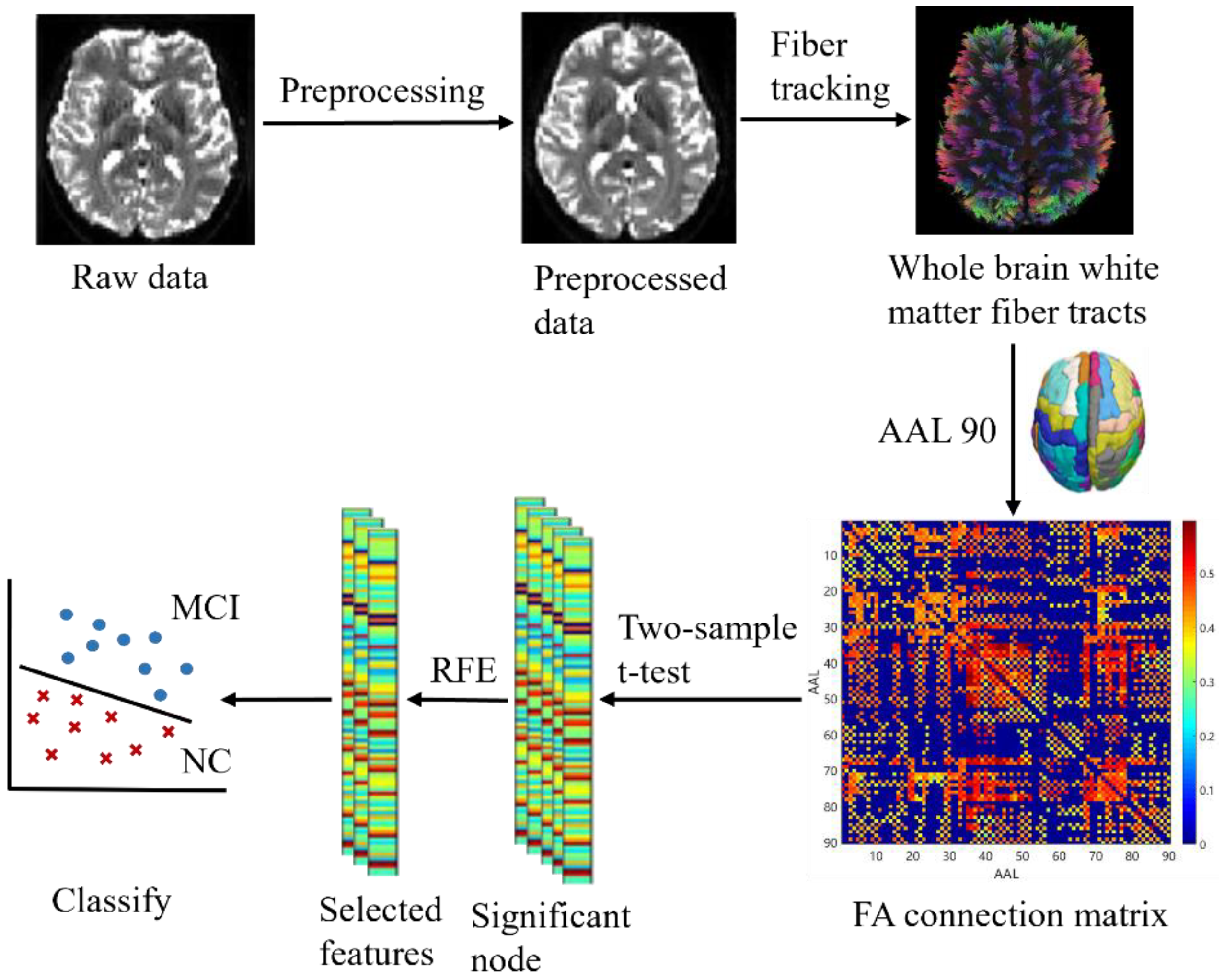
The key to the proposed classification framework is to use FA parameters to provide a rich description of the connected network. The proposed classification process is shown in Figure 1. First, we preprocessed the data and calculated the DTI parameter FA. Second, we tracked the WM fiber bundle, generated the FA connection matrix, and constructed a white matter connectivity network. Third, the FA connectivity matrix was tested by two-sample t-test to select brain region nodes with significant differences between groups. Finally, the optimal feature subset was selected using RFE to train the classifier. The test of classification performance tests showed that our feature extraction method was effective.
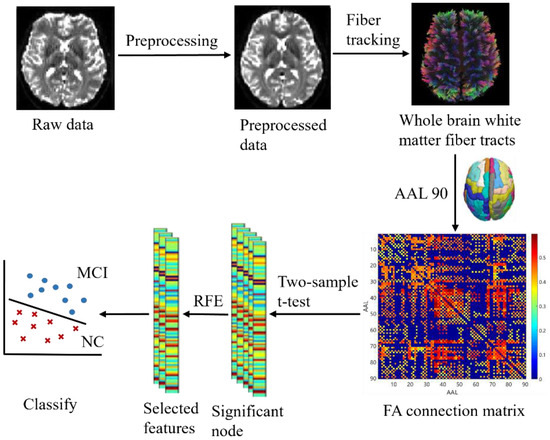
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the proposed methodology.
2.3. Image Processing
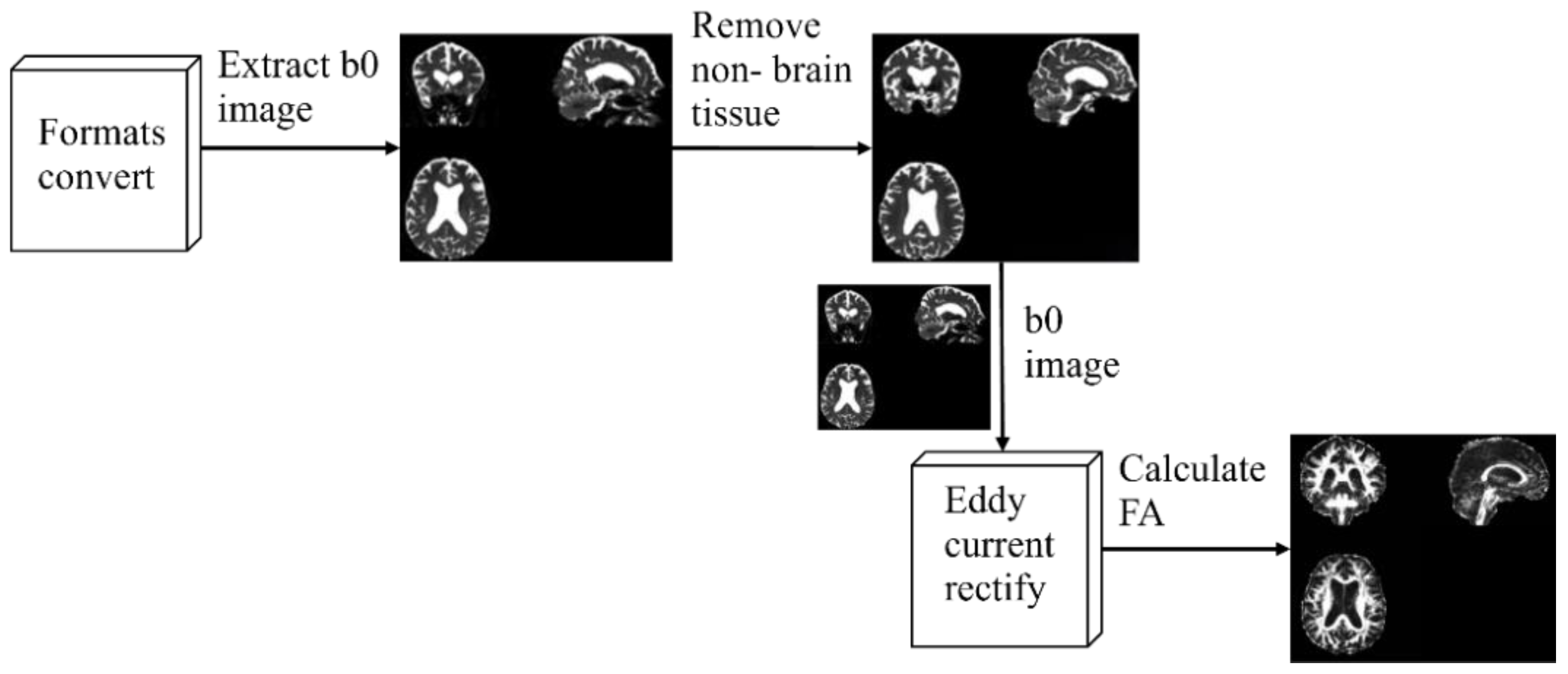
A series of pre-processing of the raw DTI images was required before further analysis. In the experiments, the open-source toolkit FSL 6.0.3 [32] was used to preprocess the data, including image format conversion, b0 images extraction, non-brain tissues removal, eddy current correction, and tensor FA calculation. Figure 2 shows the overall flow of preprocessing.
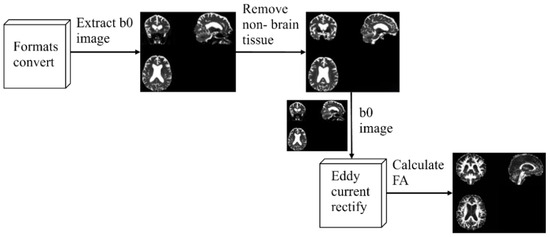
Figure 2.
Pre-processing process.
2.4. White Matter Connectivity Network Construction
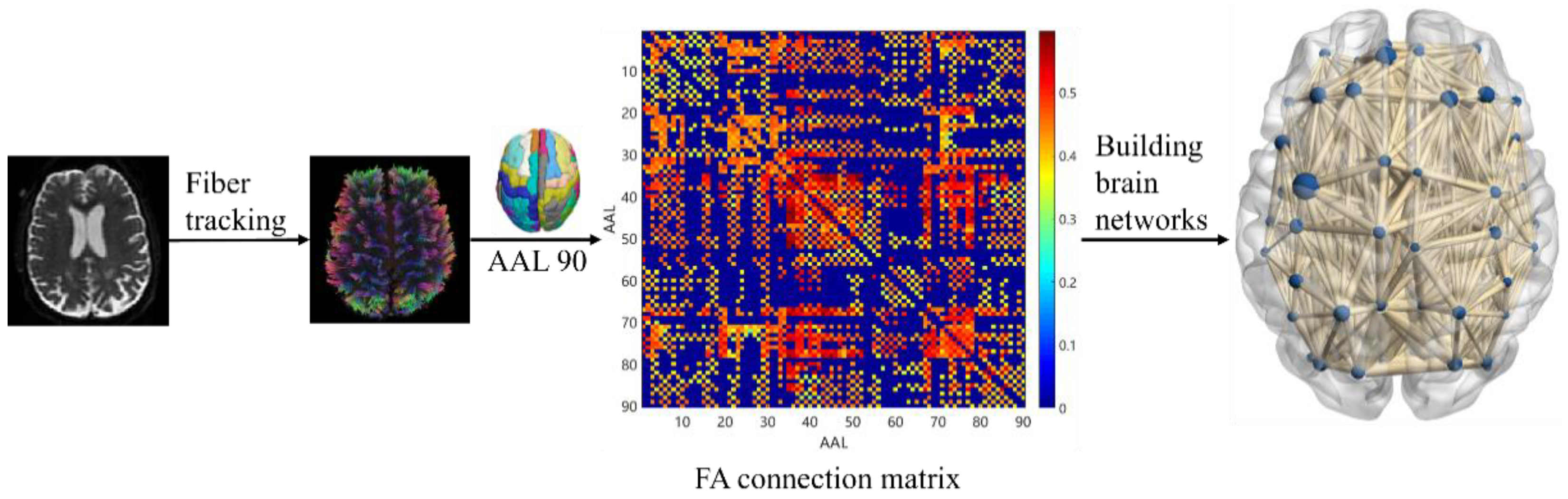
Individual white matter connectivity networks were constructed for each study subject. The experiment used the automated anatomical labeling (AAL) 90 template, a standard template for brain network mapping, to divide the brain into 90 brain regions, each representing a node in the white matter network. Edge represents the characteristics of nerve fiber bundle connections between brain regions of interest, and in this paper, FA values were defined as the edge of the network to describe the strength of connections between nodes. The experiment used DSI Studio software (version 2023.06.05) to track fiber bundles using fiber assignment by continuous tracking (FACT) technology. Tracking imaging was terminated if the FA of each voxel was ≤0.2 or tracking angle was >45° [33], and a complete WM fiber bundle was obtained. Next, the nerve fiber FA connectivity matrix was generated and presented using a hotspot map, which can show the connectivity between brain regions. The horizontal and vertical coordinates were the serial numbers of the brain regions, and the dots in the graph were the connectivity strengths of the two brain regions the horizontal and vertical coordinates of which correspond to the serial numbers, the color of the points in the graph is redder, indicating stronger intensity. Conversely, the color of the points is bluer, indicating lower intensity. Finally, the BrainNet Viewer 1.7 toolkit was used to construct and visualize the white matter connectivity network. Figure 3 shows the basic process of white matter connectivity network construction.
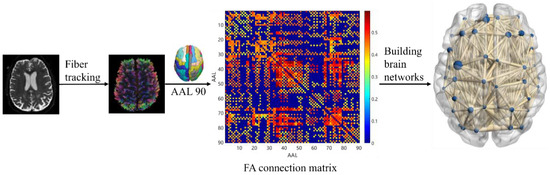
Figure 3.
White matter connectivity network construction.
2.5. Gaussian Kernel Support Vector Machine
SVM is a kind of machine learning algorithm that is used to solve binary classification problems by finding the partition hyperplane that separates different types of samples in the sample space, maximizing the minimum distance from two-point sets to this plane, and maximizing the distance from edge points in two-point sets to this plane.
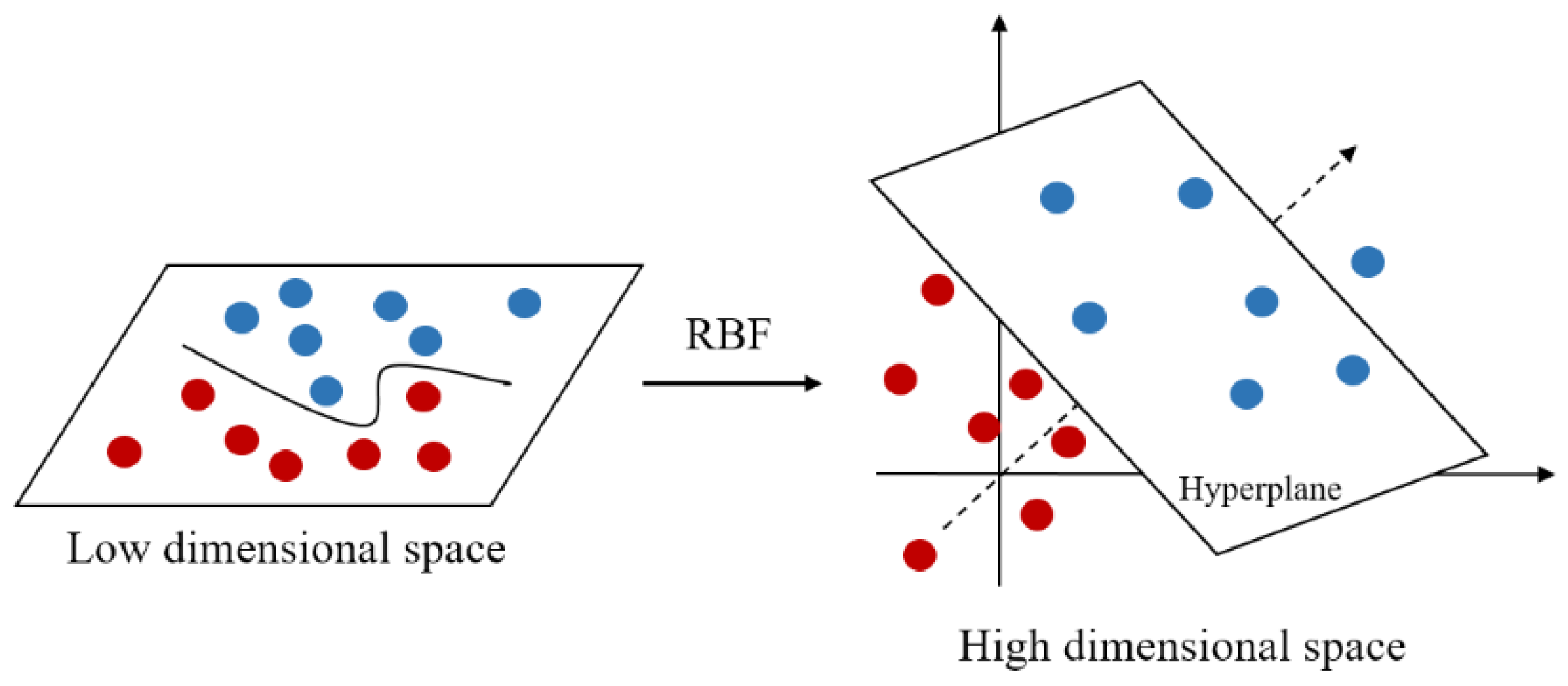
The kernel function is an important part of SVM, especially the Gaussian kernel function which is widely used in practice. Gaussian kernel function, also known as radial basis function (RBF), is a nonlinear function that can map data into higher dimensional space. As shown in Figure 4, it can transform low-dimensional data into high-dimensional data, thus making it easier for data to be separated in higher space [34].
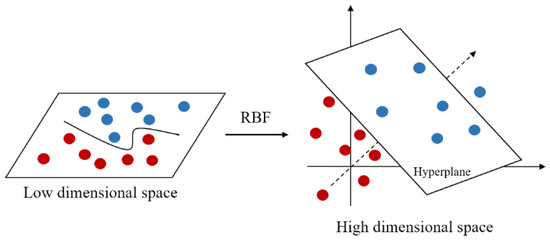
Figure 4.
Gaussian kernel function mapping.
The expression of the RBF function is
where and are sample vectors, is the parameter of the Gaussian kernel function. is the square of the Euclidean distance between the sample vectors. SVM-RBF can learn more complex models, thus improving the classification performance of the model.
2.6. Statistical Processing
The experiment was conducted using SPSS software (version 26.0) to analyze differences between groups in the basic information of each group. χ2 test was used for gender, and a one-way ANOVA was used for age, years of education, and MMSE scores. p < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference between groups. A two-sample t-test was conducted on the FA values of all fiber bundles using MATLAB software (version R2023a), fiber nodes that were statistically different between groups were screened using p < 0.01 as a condition.
2.7. Evaluation Indicators
To evaluate the classification effect of the optimal feature subset, the accuracy (ACC), sensitivity (SEN), and specificity (SPE) are chosen as evaluation indexes in this paper.
where , , , and represent true positive, true negative, false positive, and false negative, respectively. represents the number of positive samples, represents the number of negative samples, represents the prediction score for positive samples, and represents the prediction score for negative samples.
The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was also plotted, with the horizontal axis indicating the false positive rate (SPE), the vertical axis indicating the true positive rate (SEN), and the area under the curve (AUC) representing the efficacy of correct classification.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Demographic Information
The demographic data and neuropsychological scores of each group are shown in Table 1. There was no statistically notable variations in gender (p = 0.053), age (p = 0.270), education attainment (p = 0.068), and MMSE (p = 0.303) among the groups.

Table 1.
Results of demographic characteristics and scale scores of the subjects.
3.2. Comparison of FA Values
Table 2 shows the nodes with notable variations in the FA values between the MCI and NC groups. A total of 16 FA values were selected based on the results of the statistical comparison between the groups. Compared with the NC group, the FA values of the WM were significantly lower in the brain regions such as the bilateral superior parietal gyrus, bilateral supraorbital frontal gyrus, left posterior cingulate gyrus, left cuneiform lobe, right medial supraorbital gyrus, and right angular gyrus in the MCI group.

Table 2.
Nodes with significant differences in FA values between MCI and NC groups.
Table 3 shows the nodes that have significant differences in FA values between the MCI and AD groups. A total of 16 FA values were selected based on the results of the statistical comparison between the groups. Compared with the MCI group, the FA values of the WM in brain regions such as the bilateral lenticular nucleus, bilateral thalamus, left precuneus, left medial superior frontal gyrus, right insula, and right sub frontal gyrus of insula were significantly lower in the AD group.

Table 3.
Nodes with significant differences in FA values between the MCI and AD groups.
In this study, we found that there was a left–right brain asymmetry in the areas of reduced FA values in some fiber tracts in the AD and MCI groups, and both of them had larger areas of reduced FA on the left side compared to the right side, and this result reveals that the left hemisphere of the brain in the patients with AD and MCI is more severely damaged in the WM. In addition, this study also found significant differences in the brain regions between these groups, which is more consistent with the findings of existing studies [35,36,37], that cognitive dysfunction in patients with MCI is not caused by damage to a few brain regions, but rather, multiple brain regions throughout the whole brain have different degrees of damage.
3.3. Feature Extraction
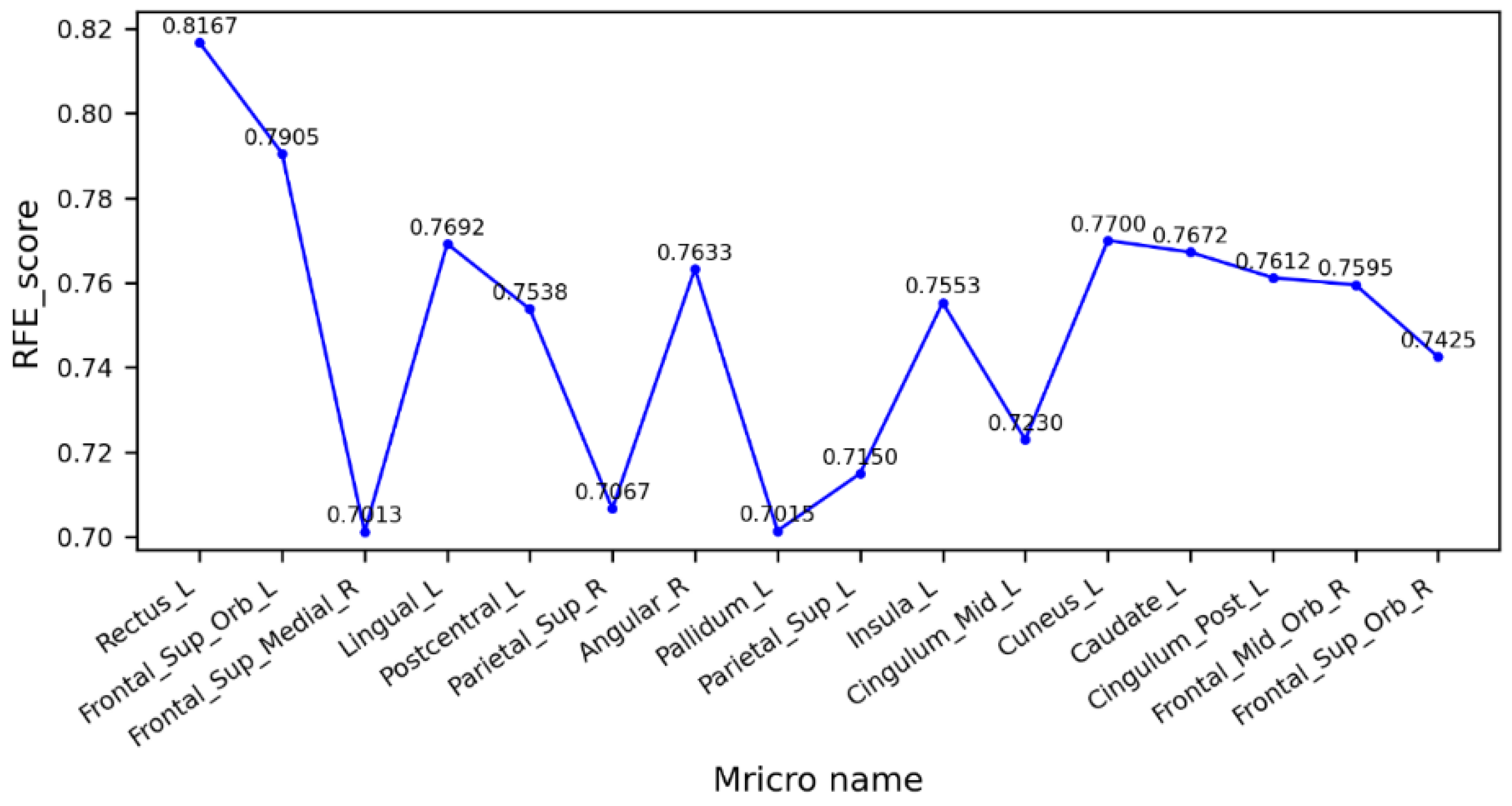
Figure 5 shows the cross-validation scores of the feature factor RFE between the MCI and NC groups. As can be seen from the figure, the left gyrus rectus had the highest score, the model had the best performance, and the prediction accuracy was 81.67%. Several brain regions with higher scores were highly correlated with visual function, so it is hypothesized that there may be a direct or indirect relationship between the degradation of visual function and cognitive dysfunction in patients with MCI, which is consistent with previous studies on the association of visual networks with cognitive dysfunction [38]. It also reveals that the MCI stage is already potentially at risk for impaired motor levels.
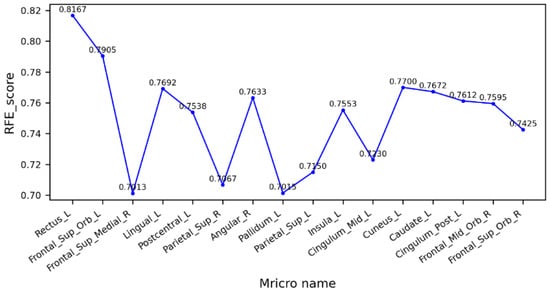
Figure 5.
Cross-validation scores of eigenvectors between MCI and NC groups.
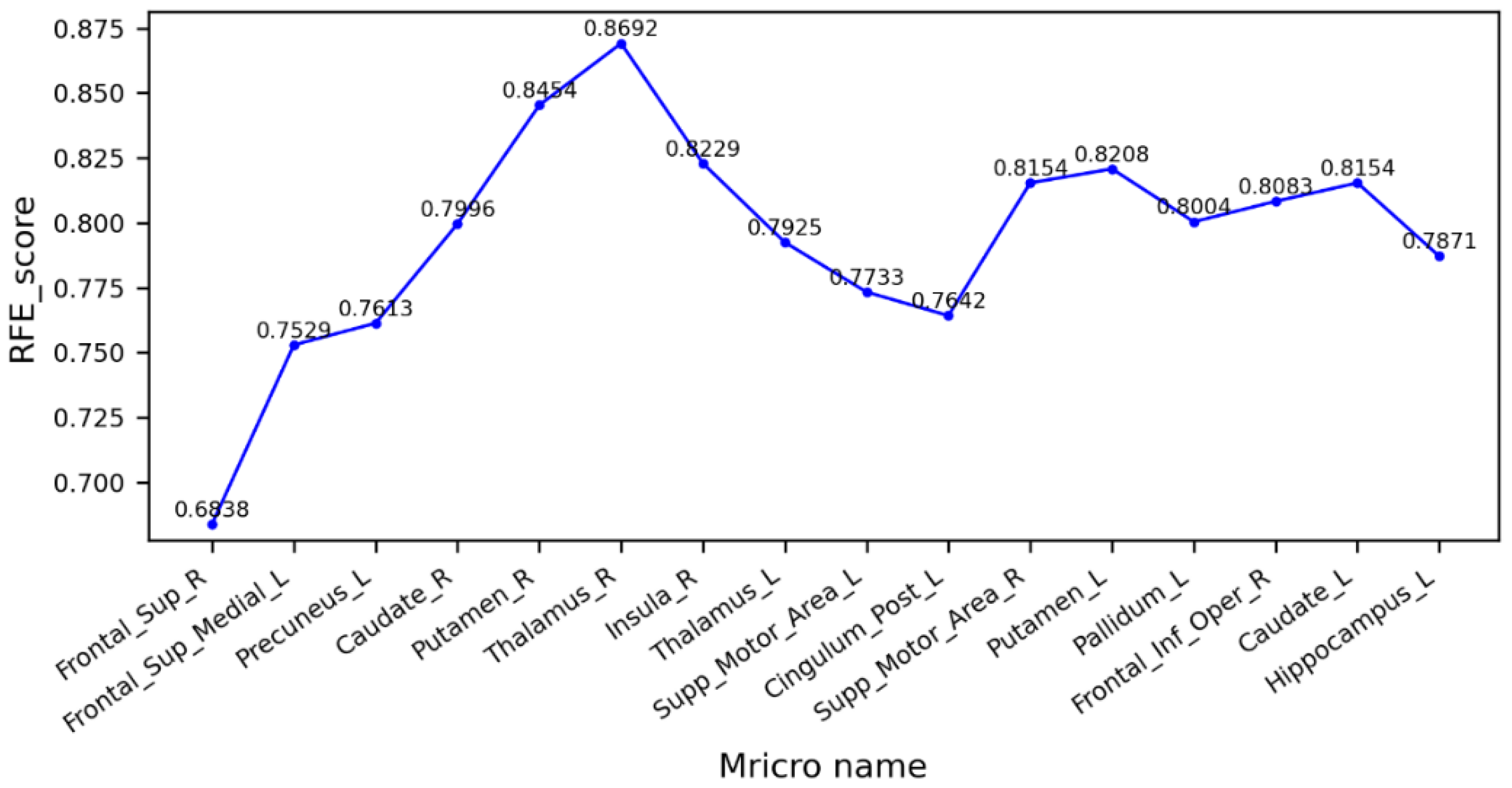
Figure 6 shows the cross-validation scores after the RFE of the trait factors between the MCI and AD groups. As can be seen from the figure, the right thalamus has the highest score, the model had the best performance, and the prediction accuracy was 86.92%. The several brain regions with higher scores are highly correlated with motor and sensory functions. Therefore, we believe that the decrease in motor ability in AD patients may be affected by changes in the WM fiber bundle, and during the MCI stage, the fiber bundle may have partially changed, but not enough to affect the patient’s motor level. At the same time, declines in sensory abilities, and a wide range of brain functions including sensory processing, attention, decision-making, and memory, are consistent with the early symptoms exhibited by AD patients [39].
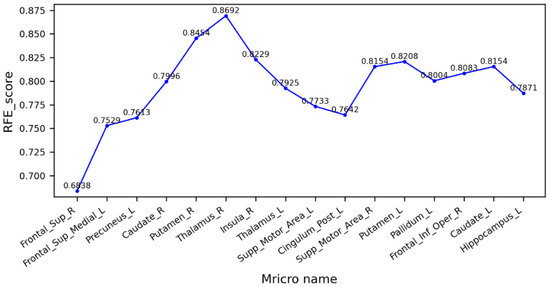
Figure 6.
Cross-validation scores of eigenvectors between MCI and AD groups.
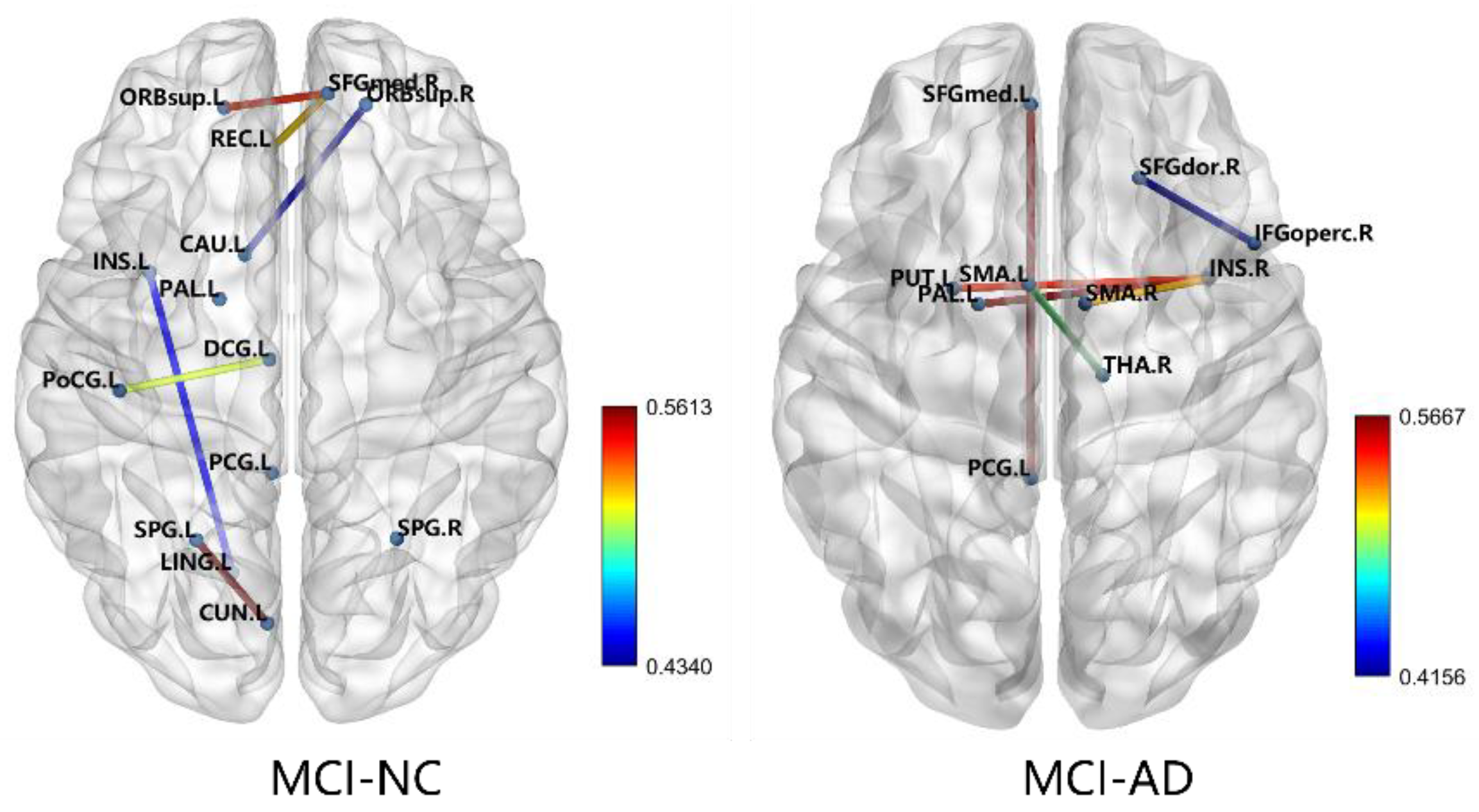
The features selected for the RFE between the MCI and NC groups were the left supplementary motor area-right thalamus, left medial superior frontal gyrus-left posterior cingulate gyrus, right insula-right supplementary motor area, right insula-left lenticular nucleus, right insula-left pallidum lenticular nucleus, and right dorsolateral superior frontal gyrus-right opercular part inferior frontal gyrus. The features selected for the RFE between the MCI and AD groups were the left orbitofrontal gyrus-right medial superior frontal gyrus, left gyrus rectus-right medial superior frontal gyrus, left insula-left lingual gyrus, left cuneate lobe-left superior parietal gyrus, left postcentral gyrus-left medial and para-cingulate cingulate gyrus, right orbitofrontal gyrus-left caudate nucleus, right posterior cingulate gyrus-right posterior cingulate gyrus, and left leguminous pallidum-left posterior cingulate gyrus. The FA values of these inter-brain interval fibers were used as the optimal feature subset for SVM-RBF classification. Figure 7 shows the schematic diagram of the connections between each group of brain regions.
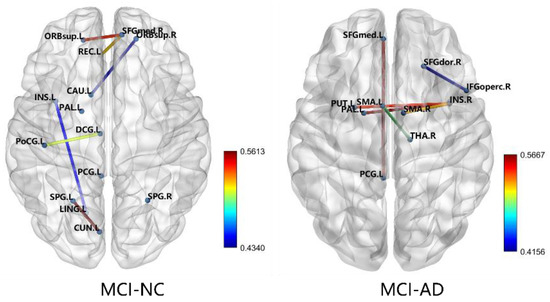
Figure 7.
Characteristics of the RFE selection.
3.4. Results and Discussion
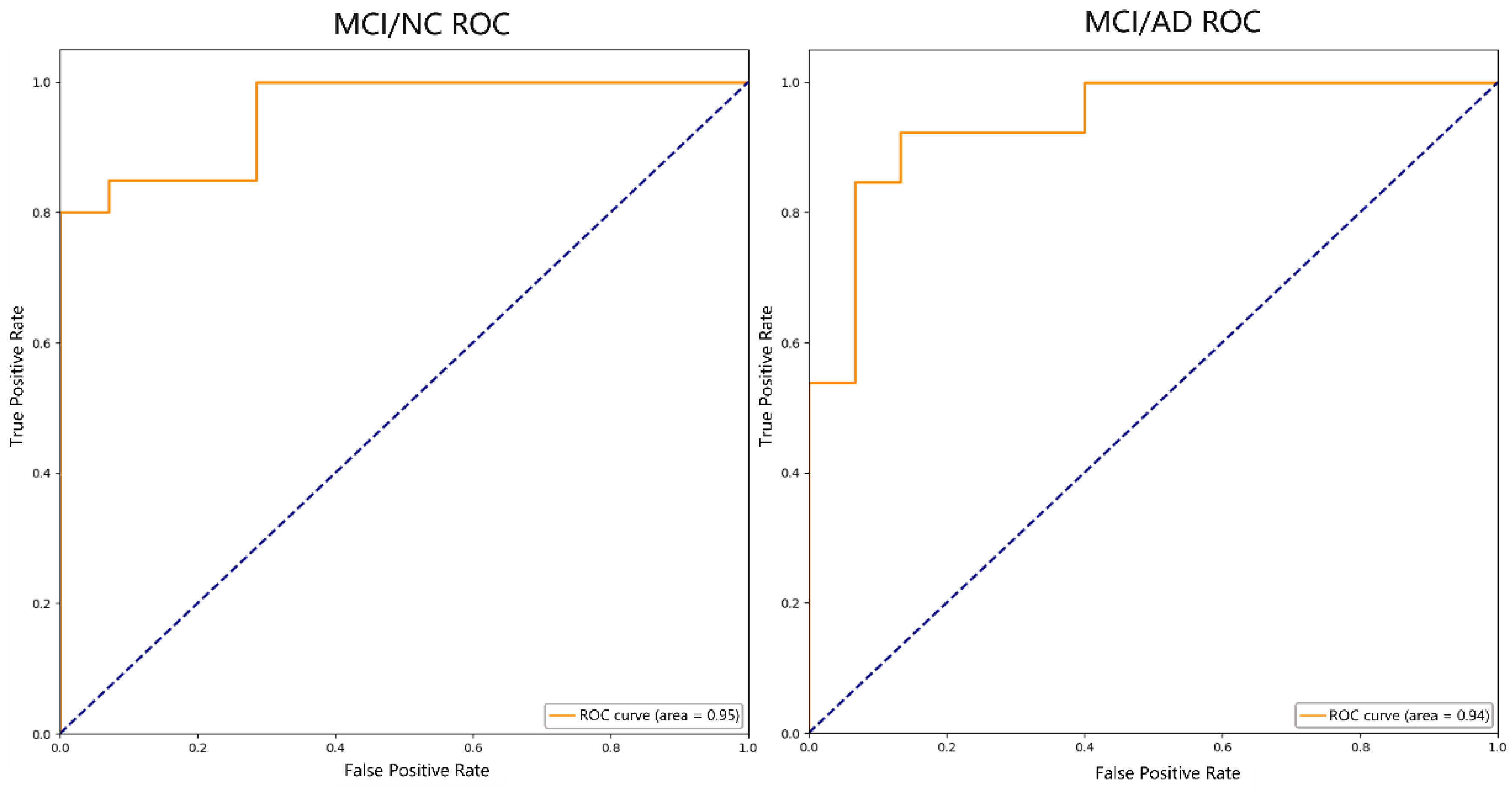
Based on the results of the RFE feature selection, the SVM-RBF classification algorithm was used to classify two subject groups of AD and MCI, and NC and MCI, and Table 4 shows the results. Figure 8 shows the ROC curves for each group.

Table 4.
Classification results of SVM-RBF.
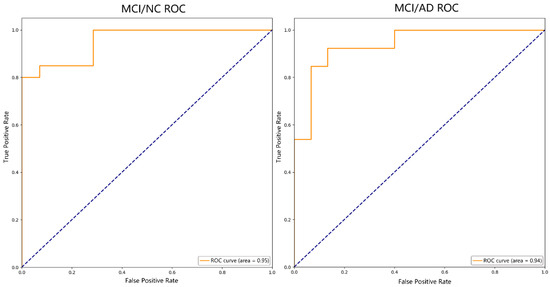
Figure 8.
ROC curve.
In the classification of AD, MCI, and NC, Table 5 demonstrates the relevant studies on DTI-based classification tasks in recent years using different classification methods. Khvostikov et al. [40] fused the ROI of structural MRI and DTI, extracted the MD of the hippocampus (HIP), and classified AD, MCI, and NC by using a convolutional neural network (CNN). The experiment only used an evaluation index of ACC, and it was low, with the ACC of AD/MCI being 80% and MCI/NC being 63%. Dalboni et al. [9] selected the FA value of bilateral para-hippocampal gyrus and used linear SVM to classify AD, MCI, and NC. Although the ACC of the AD/MCI and MCI/NC classification was high, both of which were 90%, the evaluation index of the experiment was relatively single and the dataset was small, which made it easy to overfit. Marzban et al. [41] selected the MD values of the HIP and the entrepreneurial cortex (EC), and classified MCI and NC using a CNN. Although ACC, SPE, and AUC were selected as evaluation indexes, the results were not very good. The ACC was 71.1%, the SPE was 81.8%, and the AUC was 0.68, which were lower than the results of our study. Zhou et al. [42] also used SVM-RFE to classify MCI and NC. Although the selected evaluation indexes were the same as ours, all the indexes were lower than our results, with an ACC of 79.8%, SEN of 84.1%, SPE of 73.8%, and AUC of 0.901. The reason may be that only the FA value related to the HIP was selected as the classification feature, and the influence of other fiber bundles in the development of AD was ignored. Bigham et al. [43] classified AD, MCI, and NC according to the DTI features in superficial WM, extracted the FA, MD, and RD values of the whole brain, and used quadratic SVM as the classifier. Although the SPE of AD/MCI and the SEN of MCI/NC were higher than our results, which were 86.3% and 94.4%, respectively, the other indexes were lower than our results, and the experimental data were also less than ours. In this study, we calculated the FA values of the whole brain WM, and selected the nodes with significant differences as the classification features using statistical tests and RFE. The ACC for AD/MCI was 89.29%, the SEN was 92.86%, the SPE was 85.71%, and the AUC was 0.94; for MCI/NC, the ACC was 91.18%, the SEN was 92.31%, the SPE was 90.48%, and the AUC was 0.95. Compared with these studies, our method has a competitive advantage in classification performance.

Table 5.
Comparison with the previous studies.
4. Conclusions
DTI is currently the only noninvasive technique that can display the microstructure of WM fiber bundles in the living brain, and previous studies have shown that the application of DTI technology combined with machine learning has great potential in the classification of AD, MCI, and NC. In this study, the white matter connectivity network of AD, MCI, and NC was constructed based on DTI data. Statistical tests and RFE were used to select the features of the nodes between the groups, and the FA values of the nodes with significant differences were used as the combination of classification features. The SVM-RBF algorithm was utilized to categorize AD, MCI, and NC. The experiment has achieved good classification results, and it was also found that the changes in the FA values of the fiber bundles in the cortical visual area, cortical motor area, and cortical sensory area are more significant during the progress of AD, especially the WM degeneration in the cortical motor area, which may play a decisive role in AD progression. This will provide some support and help for a more in-depth study of the pathophysiological mechanisms of AD development and new targets for its diagnosis and treatment, which are of great clinical significance for an early and timely intervention to slow down the progression of AD.
However, there are still some limitations in this study. This study only discusses the differences in the FA values among AD, MCI, and NC, and does not analyze and compare the parameters such as MD and RD. After this, we will study other parameters of DTI and compare them with the results of this study. At the same time, the current study only uses the neuroimaging technology of DTI, in the future, we will try to carry out pattern recognition and intelligent diagnosis by combining other neuroimaging technologies. Based on the existing research results, we will improve the generalization ability by using deep learning technology to further promote the early diagnosis of AD and MCI.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.X. and X.Y.; methodology, Y.X.; software, Y.X.; validation, Y.X., X.Y. and Z.L.; investigation, L.L., Z.F. and J.Z.; data curation, Y.X.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.X.; writing—review and editing, X.Y. and Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: http://adni.loni.usc.edu/ (accessed on 30 March 2023).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the ADNI (http://adni.loni.usc.edu/ (accessed on 30 March 2023)) investigators for publicly sharing their valuable neuroimaging data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Prince, M.; Comas-Herrera, A.; Knapp, M.; Guerchet, M.; Karagiannidou, M. World Alzheimer Report 2016: Improving Healthcare for People Living with Dementia. Coverage, Quality and Costs Now and in the Future; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Ge, X.; Han, H.; Cui, J.; Bai, W.; Yu, H. Research progress on reversal of mild cognitive impairment to cognitive normal. Chin. Fam. Med. 2021, 24, 3506–3509. [Google Scholar]
- Odusami, M.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Damaševičius, R. An Intelligent System for Early Recognition of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Neuroimaging. Sensors 2022, 22, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Si, X.P.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chao, Y.; Lin, C.-P.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Ming, D.; Li, Q. Hippocampus- and Thalamus-Related Fiber-Specific White Matter Reductions in Mild Cognitive Impairment. Cereb. Cortex 2022, 32, 3159–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caranova, M.; Soares, J.F.; Batista, S.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Duarte, J.V. A systematic review of microstructural abnormalities in multiple sclerosis detected with NODDI and DTI models of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 104, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Shi, Z.; Chen, X.; Han, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Alterations in White Matter Fiber Tracts Characterized by Automated Fiber-Tract Quantification and Their Correlations with Cognitive Impairment in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Patients. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 904309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Ko, N.; Kim, B.-R.; Moon, W.-J.; Choi, D.-H.; Lee, J. Correlation of Hemispatial Neglect with White Matter Tract Integrity: A DTI Study. Brain NeuroRehabil. 2022, 15, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.R.; Wang, X.C.; Zhang, H.; Tan, Y. Research progress of magnetic resonance diffusion imaging in mild cognitive impairment. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 12, 70–72+84. [Google Scholar]
- Dalboni da Rocha, J.L.; Bramati, I.; Coutinho, G.; Moll, F.T.; Sitaram, R. Fractional Anisotropy changes in Parahippocampal Cingulum due to Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.S.; Um, Y.H.; Kang, D.W.; Lee, C.U.; Woo, Y.S.; Bahk, W.-M.; Lim, H.K. Diagnostic Validity of an Automated Probabilistic Tractography in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2018, 16, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamino, M.; Walsh, R.R.; Stokes, A.M. Free-Water Diffusion Tensor Imaging Improves the Accuracy and Sensitivity of White Matter Analysis in Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurst, Z.; Kuchtová, B.B.; Křemen, J.; Lahutsina, A.; Ibrahim, I.; Tintěra, J.; Bartoš, A.; Brabec, M.; Rai, T.; Zach, P.; et al. Basal Ganglia Compensatory White Matter Changes on DTI in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.; Wei, S.-M.; Martinez, P.E.; Gregory, M.D.; Kippenhan, J.S.; Kohn, P.D.; Nieman, L.K.; Yanovski, J.A.; Schmidt, P.J.; Berman, K.F. Changes in Brain Structure Associated with Adrenarche in Typically Developing Prepubertal Children. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2023, 153, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamino, M.; Schiavi, S.; Daducci, A.; Walsh, R.R.; Stokes, A.M. Analysis of Brain Structural Connectivity Networks and White Matter Integrity in Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 793991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzolo, L.; Narbutas, J.; Van Egroo, M.; Chylinski, D.; Besson, G.; Baillet, M.; Bahri, M.A.; Salmon, E.; Maquet, P.; Vandewalle, G.; et al. Relationship between brain AD biomarkers and episodic memory performance in healthy aging. Brain Cogn. 2021, 148, 105680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borna, B.; Clara, T. Brain Networks, Clinical Manifestations, and Neuroimaging of Cognitive Disorders: The Role of Computed Tomography (CT), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Positron Emission Tomography (PET), and Other Advanced Neuroimaging Tests. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2023, 39, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, X.; Qi, S.; Xu, X.; Fu, Z.; Hong, L.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Fu, Y.; et al. Neuropsychiatric symptoms associated multimodal brain networks in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2023, 44, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Guo, Z.; Gao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Fu, J. Multiscale Brain Network Models and Their Applications in Neuropsychiatric Diseases. Electronics 2022, 11, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, S.; Han, L.; Yao, X. Coupling analysis between functional and structural brain networks in Alzheimer’s disease. Math. Biosci. Eng. MBE 2022, 19, 8963–8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billeci, L.; Badolato, A.; Bachi, L.; Tonacci, A. Machine Learning for the Classification of Alzheimer’s Disease and Its Prodromal Stage Using Brain Diffusion Tensor Imaging Data: A Systematic Review. Processes 2020, 8, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, J. Sequential Minimal Optimization: A Fast Algorithm for Training Support Vector Machines; Microsoft Research: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Tao, L.; Xiao, P.; Gui, H.; Xu, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; He, W.; et al. Combined brain network topological metrics with machine learning algorithms to identify essential tremor. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1035153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Hong, Y.; An, S.; Park, U.; Shin, J.; Lee, J.; Oh, M.S.; Lee, B.-C.; Yu, K.-H.; Lim, J.-S.; et al. Machine learning-based prediction of post-stroke cognitive status using electroencephalography-derived brain network attributes. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1238274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer, C.; Stumme, J.; da Costa Campos, L.; Rubbert, C.; Caspers, J.; Caspers, S.; Jockwitz, C. Classification and prediction of cognitive performance differences in older age based on brain network patterns using a machine learning approach. Netw. Neurosci. 2023, 7, 122–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Feng, Y.; Ma, C.; Ma, K.; Cai, Q. Disrupted Time-Dependent and Functional Connectivity Brain Network in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Resting-State fMRI Study Based on Visibility Graph. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2020, 17, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacasa, L.; Luque, B.; Ballesteros, F.; Luque, J.; Nuño, J.C. From time series to complex networks: The visibility graph. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4972–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, K.; Lu, J.M.; Li, W.P.; Zhang, X.; Qing, Z.; Zhang, B. Classification prediction study of mild cognitive impairment based on diffusion tensor imaging automated fiber quantitative analysis. J. Clin. Radiol. 2022, 41, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, X.; Yao, H.; Feng, F.; Wang, P.; Zhou, B.; Jin, D.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; et al. Characterizing white matter connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: An automated fiber quantification analysis with two independent datasets. Cortex 2020, 129, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ding, X.; Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Men, G. Functional connectivity between white matter and gray matter based on fMRI for Alzheimer’s disease classification. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, C.; Xie, P.; Han, Y.; Su, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y. The diagnosis of amnestic mild cognitive impairment by combining the characteristics of brain functional network and support vector machine classifier. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 363, 109334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene Selection for Cancer Classification using Support Vector Machines. Mach. Learn. 2002, 46, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Bannister, P.R.; Beckmann, C.; Brady, M.; Clare, S.; Flitney, D.; Hansen, P.; Jenkinson, M.; Leibovici, D.; Ripley, B.; et al. FSL: New tools for functional and structural brain image analysis. NeuroImage 2001, 13, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Duan, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, C.; Dong, H.; Ye, J.; He, Y. Diffusion tensor tractography reveals disrupted topological efficiency in white matter structural networks in multiple sclerosis. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 2565–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, J. Differential privacy fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm based on gaussian kernel function. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, M.; Wagner, G.; de la Cruz, F.; Köhler, S.; Schultz, C.C. Resilience and cortical thickness: A MRI study. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 270, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaee, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Babajani-Feremi, A. Classification of patients with MCI and AD from healthy controls using directed graph measures of resting-state fMRI. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 322, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Shrestha, S.; Sun, M.; Wu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, J.; Ni, H. Microstructural White Matter Alterations in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: Study Based on Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging (NODDI). Clin. Neuroradiol. 2020, 30, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, G.K.; Sundgren, M.; Brismar, T. Mechanism of visual network dysfunction in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis and its relation to cognition. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Gauthier, S.; Jia, J. Alzheimer’s disease: Current status and perspective. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2494–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khvostikov, A.; Aderghal, K.; Benois-Pineau, J.; Krylov, A.; Catheline, G. 3D CNN-based classification using sMRI and MD-DTI images for Alzheimer disease studies. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.05968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzban, E.N.; Eldeib, A.M.; Yassine, I.A.; Kadah, Y.M. Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegenerative Initiative. Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis from diffusion tensor images using convolutional neural networks. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Si, X.; Chao, Y.-P.; Chen, Y.; Lin, C.-P.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Ming, D.; Li, Q. Automated Classification of Mild Cognitive Impairment by Machine Learning with Hippocampus-Related White Matter Network. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 866230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigham, B.; Zamanpour, S.A.; Zare, H. Features of the superficial white matter as biomarkers for the detection of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).