Abstract
The proliferation of smartphones and internet connectivity has provided the opportunity to use crowdsourced data in traffic management. Nowadays, many people use navigation apps such as Google Maps, Waze, and Flitsmeister to obtain real-time travel information and provide feedback on road conditions, such as reporting police speed checks. As an accurate traffic speed prediction is of great significance for road users and traffic managers, different models have been proposed and widely used to predict traffic speed considering the spatio-temporal dependence of traffic data and external factors such as the weather, accidents and points of interest. This study investigates the impact of crowdsourced data about police enforcement from navigation apps on traffic speed. In addition, we examine whether the police enforcement report affects the accuracy of the deep learning prediction model. The authors extract crowdsourced police enforcement information from navigation apps, collect the corresponding historical traffic speed data, and predict traffic speed in several corridors in The Netherlands using a GCN-GRU traffic speed prediction model. The results show that the crowdsourced data for police enforcement cause the average vehicle speed to drop between 1 [km/h] and 3 [km/h] when passing the road segments marked with police activity. Moreover, the prediction performance of the GCN-GRU model during the periods without police enforcement is better than the periods with reported police activity, showing that police speed check reports can decrease the accuracy of speed prediction models.
1. Introduction
These days, most people use navigation apps such as Google Maps, Waze, and Flitsmeister to find the best route for their trip due to the proliferation of smartphones and internet connectivity [1,2]. These apps utilize the users’ GPS data known as crowdsourced data to estimate and provide real-time travel information. Recently, these apps also enabled a feature where users can provide feedback and share their experiences; for instance, users can report traffic accidents and police speed checks. This information not only can help these apps predict future travel times more accurately but also can warn other app users about the conditions and help travelers adjust their routes or driving behaviors accordingly.
The 3Es approach, which comprises engineering, education, and enforcement, has been used for decades to improve road safety. The traffic safety level is expected to increase through educating people about safety knowledge and driving skills, as well as improving road infrastructure and vehicle standards. In addition, traffic enforcement can influence the behavior of high-risk drivers and is still an integral part of safety improvement. For instance, around 3 million traffic fines were issued in The Netherlands in the second half of 2021, of which 512,277 were issued by police flashing along the roads [3]. However, the report of police activity on navigation apps may nullify the impact of enforcement. Intuitively drivers who receive crowdsourced data from the app could potentially adjust their driving behavior, which otherwise may be different. This means that police activity reports in navigation apps could impact the driving speed in certain locations, and as a result, may influence the overall traffic condition.
Traffic speed is one of the three imperative traffic parameters, which could reflect the traffic state and has become the key component of traffic prediction research. Forecasting traffic speed is of great significance for road users and urban managers, which could help to reasonably plan travel routes and manage urban traffic. Urban traffic speed prediction has always been one of the most challenging parts of intelligent transportation systems (ITSs) due to the complicated spatial and temporal correlations of urban road networks. Many predictive models have been proposed to capture the spatio-temporal dependence of traffic data, and their effectiveness has been proved using real traffic data [4,5,6]. Moreover, to increase the prediction accuracy, the influence of external factors, such as social attributes [7], accidents [8], weather [9], and point of interest (POI) [10] have been investigated. However, the impacts of external factors on traffic speed are unclear. In particular, the impact of crowdsourced data about police activity on traffic speed has not been investigated yet. Capturing such temporary impacts is important for traffic management because the induced speed changes at enforcement locations may impact the overall traffic situation.
Therefore, the purpose of this research is to examine to what extent the reported police enforcement on navigation apps affects traffic speed and the accuracy of traffic speed prediction models.
To achieve these goals, this research extracts police enforcement information from crowdsourced data from navigation apps in The Netherlands, collects historical traffic speed data on the same road segments where enforcement happened, and predicts the speed based on a deep learning prediction model. The impact of police speed checks reported in navigation apps on drivers’ behaviors, as well as the accuracy of deep learning predictive models in the presence of police enforcement, are examined. Our analysis shows that the average actual traffic speed is 1–3 [km/h] lower compared to the predicted speed. In addition, the accuracy of the speed prediction model is lower during reported police enforcement periods than the periods without police enforcement.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the related literature. Section 3 presents the used methods and discusses the data, followed by the analyses and discussion of findings in Section 4. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper and presents the future research directions.
2. Literature Review
Many researchers have delved into the matter of how police enforcement influences drivers’ driving speeds. Ref. [11] investigated factors influencing speed choices on rural roads in Norway with an 80 km/h speed limit. It looked at how drivers’ perceptions of police enforcement, penalties for speeding, and other drivers’ speeds affect their choices. The study found that making most other drivers slow down or increasing law enforcement had the most significant impact on reducing individual speed choices, while stricter penalties had only a minor effect. Ref. [12] examined the impact of police presence on speeding in urban areas using a realistic-looking police cut-out named “Constable Scarecrow” in British Columbia, Canada. The findings showed that deploying the cut-out along major roads helped reduce speeding among motorists. Ref. [13] looked at how police saturation enforcement impacts speeding on a highway corridor in Western Canada. They used radar devices at different locations to measure speeds during enforcement and non-enforcement periods. The results showed that police saturation enforcement effectively reduced average vehicle speeds and the proportion of speeding vehicles in the enforcement area, contributing to discussions on policing and road safety. However, there is still a scarcity of relevant research on crowdsourced data for police enforcement.
2.1. Crowdsourced Data Usage in ITS
Crowdsourced data from social media apps such as Twitter have become an emerging data source to provide new support for predicting or managing traffic issues due to the rapid growth of smartphone users. An increasing number of research has investigated the application of such crowdsourced data in traffic management. Ref. [14] used crowdsourced data from smartphone applications, GIS-based web interfaces, and weather sensors to model the individual mobility decision processes. The model is regarded as a potential platform for personalized travel management in smart cities, as well as a communication tool between cities and users. Ref. [15] mined crowdsourced media data from Twitter and Foursquare to look into the spatial and temporal patterns of human activities in a city, and showed the importance and usefulness of crowdsourced data in analyzing people’s activities. Ref. [16] proposed that mining social media data can be a basic low-cost supplement and convenient solution for ITS. More than 1 million tweets were collected over 3 months, and an Arabic Twitter content analysis framework was proposed to tackle the problem of missing the location information of traffic-related incidents in the tweets. Ref. [17] developed a machine learning method to predict traffic evolution after accidents based on the user-generated crowdsourced data (UGCD) provided by navigation apps that have interfaced for users to report traffic incidents, and showed the efficiency of using UGCD for the real-time analysis of traffic accidents. Ref. [18] assessed the speed data based on a crowdsourced navigation system, Waze, and conducted a case study in Sevierville. They showed that the posted speed on Waze is a good representation of actual speed. Ref. [19] proposed an innovative machine learning framework to extract traffic-related information from social network crowdsourced data for traffic incident detection. These studies and others [20,21,22] indicate that crowdsourced data from social media or smartphone applications are one of the promising data sources for managing smart cities and transportation systems.
2.2. Traffic Speed Prediction
Accurate traffic speed prediction is an important component in ITS, as it offers useful information to reduce traffic congestion by providing route guidance to travelers [23]. Extensive research has been conducted on using available datasets to predict traffic evolution. The difficulty of predicting traffic speed in urban road networks lies in (i) accurately extracting temporal and spatial features of traffic networks, and (ii) adequately considering the impact of external factors on traffic flow from multiple sources of data, such as weather, social events, accidents, etc.
Traditionally, researchers use mathematical statistics to analyze and predict traffic states, such as the ARIMA model [24,25], the Kalman filter algorithm [26], the hidden Markov model [27], the Bayesian network [28], etc. These statistical techniques could model the traffic conditions using relatively small-scale datasets but have limited ability to capture the nonlinear characteristics of traffic data.
With the development of data collection and computing power, most recent works have focused on data-driven models, particularly from traditional machine learning models [29,30] to deep learning models [31,32] that could perform the prediction task well based on historical traffic databases. The advantages of machine learning models are the ability to handle multidimensional data, implementation flexibility, generality, and strong predictive capabilities [33]. However, they cannot capture the spatial correlations of road networks well. In addition, compared with deep learning methods, the prediction accuracy of machine learning is relatively lower due to the shallow structure.
Recently, more advanced and powerful deep learning models have been applied to traffic prediction. Ref. [34] represented large-scale traffic networks as images, and adopted the deep learning architecture of convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract the spatio-temporal traffic features contained in the images. The traditional CNN can use a fixed-size learnable convolution kernel, which effectively describes the spatial characteristics of Euclidean data, such as text, sound, and images, and extracts useful information from them [35]. However, real road networks are difficult to meet the approximate grid shape in space, and a large amount of traffic data is complex non-Euclidean data [36].
In order to incorporate the topology of road networks and exploit graph structure information, the graph convolutional neural network (GCN) is extended and applied to traffic prediction [37,38]. The principles of GCN are to regard the transportation network as a graph and recognize the connectivity of roads by an adjacency matrix, then extend the convolution operation on the graph structure to aggregate the information of each node, which is proved to be more effective than a grid-type convolution on capturing topology features of transportation networks and forecasting traffic speed [39]. In order to take into account the temporal characteristics of traffic data simultaneously, the gated recurrent unit (GRU) is also widely used in traffic speed prediction combined with GCN [31]. GRU is an improved version of the recurrent neural network (RNN), which could process sequence data and can reduce the vanishing gradient problem, while preserving long-term sequence information [40]. The efficiency of GCN and GRU as traffic prediction models has widely been proved using real traffic data [39,41].
In addition, traffic forecasting is more challenging than other spatiotemporal forecasting problems because it involves many external factors, which affect traffic states. Ref. [42] constructed the traffic speed prediction model considering the day of the week and POI. Ref. [43] proposed a model with bidirectional long short-term memory (LSTM) and a complex attention mechanism to predict the urban traffic volume, combined with weather conditions and event information as external features to further improve the prediction precision. A traffic graph convolution operator was proposed in [44] in order to extract the local features and combine the physical features of the road network. Ref. [45] modeled external factors as dynamic and static attributes, and designed an attribute augmentation unit to encode and integrate these factors into a spatio-temporal graph convolution model, and demonstrated the effectiveness of considering external information in the traffic speed prediction task. However, due to the complexity of built environment, there are various types of latent factors which affect the driver behavior, thereby affecting the traffic speed and adding uncertainty to traffic prediction problems.
To summarize, works in the existing literature do not fully consider the influence of external factors on traffic. In particular, how the crowdsourced data about police speed checks report in navigation apps influence drivers’ driving behavior and overall traffic speed on the road network has not been investigated yet.
3. Methodology
In order to study the driver’s response to the police enforcement information from users’ feedback on navigation apps, it is firstly necessary to accurately predict the driving speed. This research uses a graph convolutional–gated recurrent network (GCN-GRU) model proposed by [39] to implement the speed prediction task. We use this model because it can well capture the spatial correlation between sensors and the time-series features of historical speed data, with high computational efficiency and prediction accuracy. For the sake of completeness, we briefly introduce the model in the next subsection.
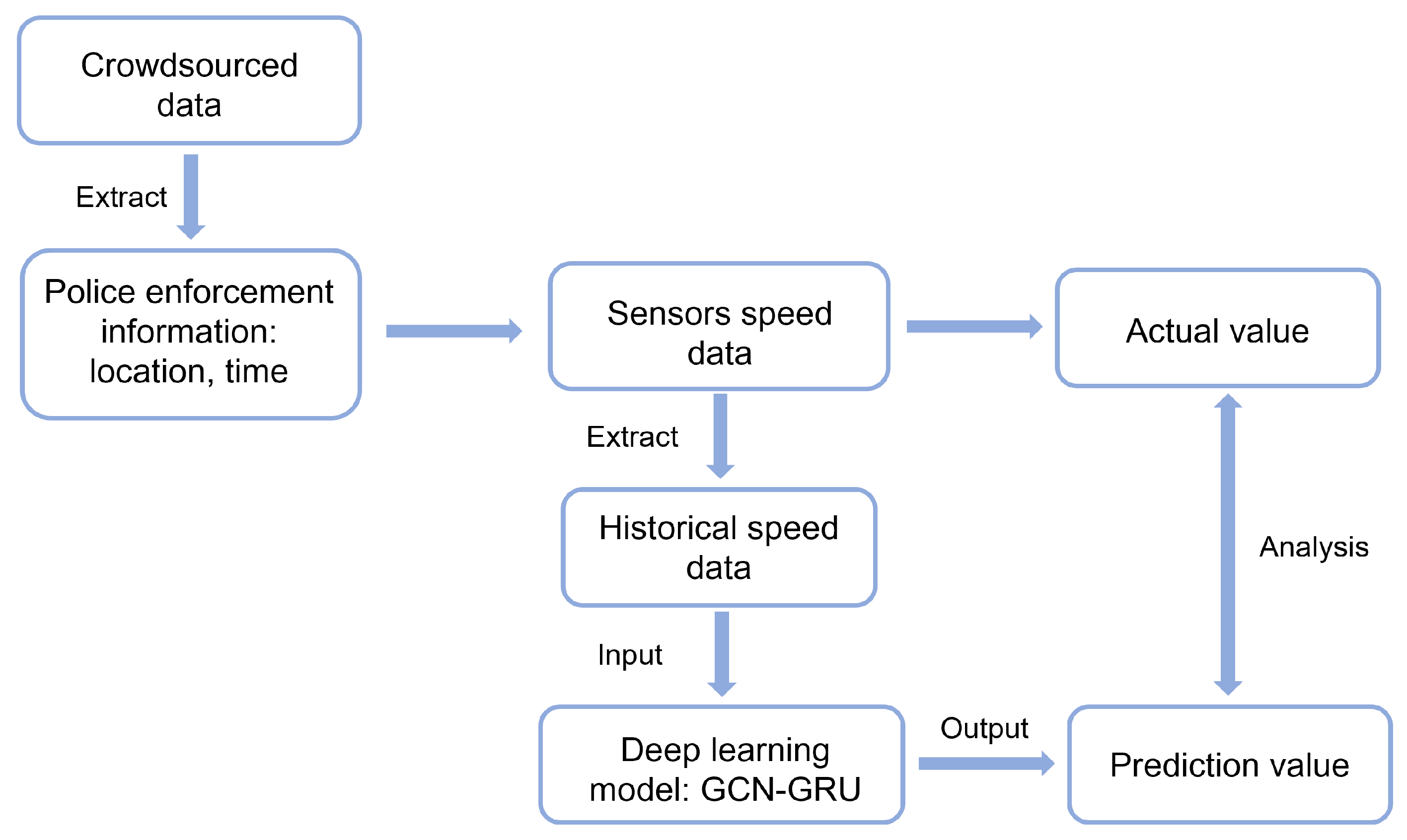
Then, we obtain the crowdsourced data of police enforcement in The Netherlands, including the time and location of police activity reported by users. According to this information, we select the road segments around speed check points, collect the historical speed data of all the sensors on these corridors, and use the aforementioned deep learning model to predict the traffic speed at the target locations during the police enforcement period to analyze whether the actual driving speed is different from predicted speed and the potential speed change induced by the police enforcement information. Figure 1 shows the framework of our approach.
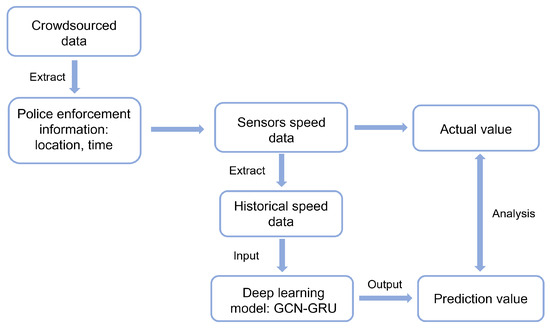
Figure 1.
Proposed research framework.
3.1. Speed Prediction
3.1.1. GCN
This research mainly aims at the traffic speed prediction problem. The essence is to learn function f to predict the traffic state of all nodes in the future time period according to the historical data and the corresponding road structure.
Since the target road segments of this study are all unidirectional, an undirected unweighted graph is constructed to describe the topological structure of the road network. The position of sensors is treated as nodes set V in the graph, and the connection relationship between the sensors are treated as edges E. Assuming that the current time is t, the traffic information X at time can be expressed as:
where T represents the length of the input historical time series; represents the traffic information of each sensor at time t.
The GCN is a neural network that extends the convolution operation to the graph structure [46]. The core idea is that the central node performs information aggregation on its neighbor nodes. The node feature is regarded as a signal, which is transformed into the frequency domain space through Fourier transform, and finally the graph domain convolution is obtained through inverse Fourier transform. Each layer of convolution only processes the first-order neighborhood information, and the information transfer of multi-order neighborhoods can be realized by stacking several convolutional layers [47]. The propagation rules for each convolutional layer are as follows:
where represents adjacency matrix A with a self-connection structure, I is the identity matrix, and represents the degree matrix of . X represents the input, and is the convolution kernel. The adjacency matrix A, which contains elements of 0 and 1, is used to describe the connection between nodes. The element is 1 if the sensors are connected, and 0 otherwise. Traffic speed is treated as a feature of nodes.
3.1.2. GRU
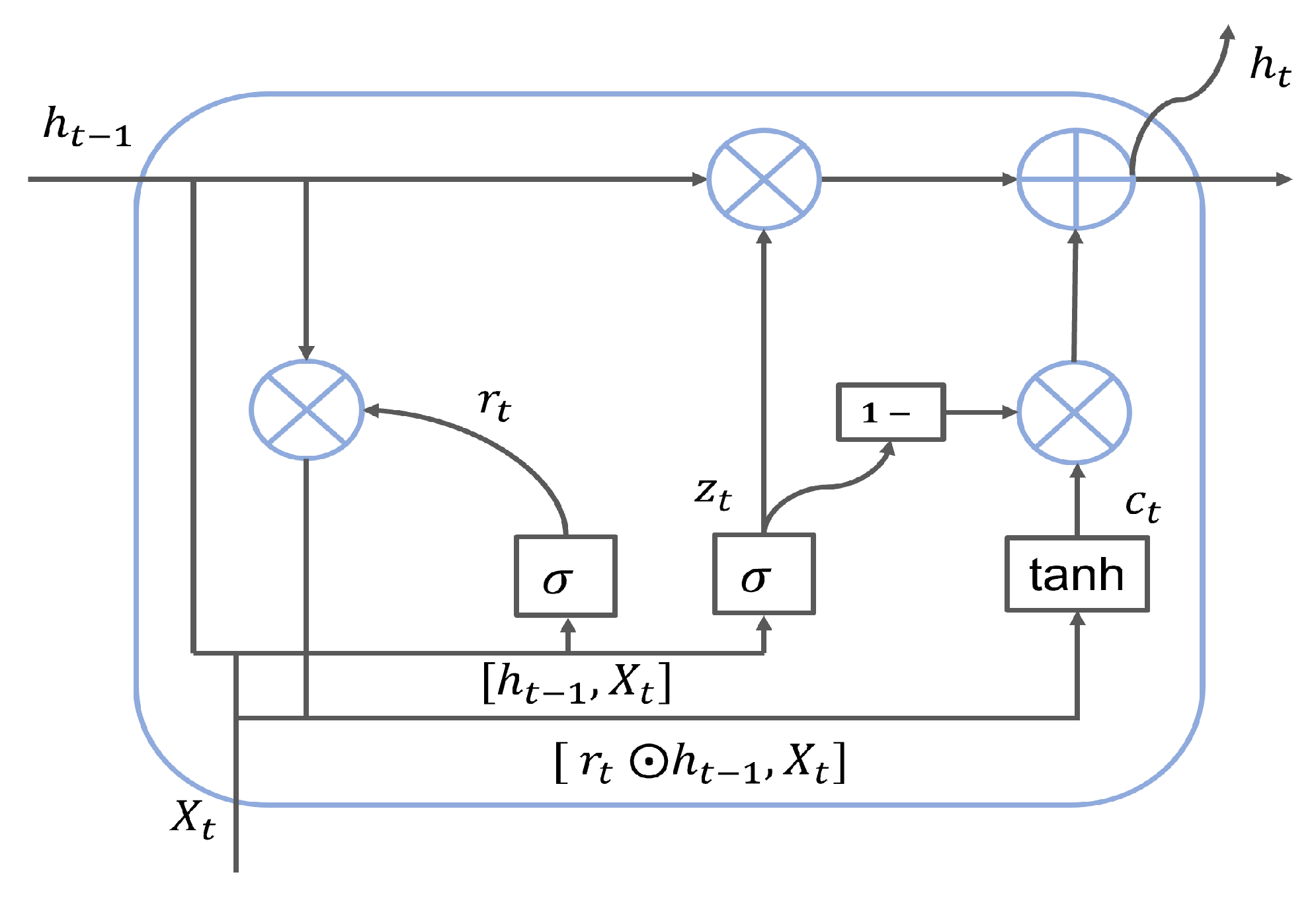
GRU is an improved model based on RNN and LSTM. Compared with RNN, it can solve problems such as long-term memory and gradient disappearance in back propagation. In comparison with LSTM, using GRU could achieve comparable results, and is easier to train. So the training efficiency could be greatly improved. The hidden unit in GRU is a special cell structure rather than a node of a traditional neural network. There are two gates inside it, a reset gate and an update gate. Intuitively, the reset gate determines how the new input information is combined with the previous memory, and the update gate determines the amount of the previous memory saved to the current time step. The cell structure of GRU is shown in Figure 2, and each gate is calculated as follows:
where and represent the reset and update gates, which control the input data at time t and the hidden state transmitted from the previous layer at time . is the memory content at time t. denotes the output at time t. W represents the weight of the model in the training process. is the nonlinear activation function, and ⊙ is the element-wise multiplication of the two vector groups.
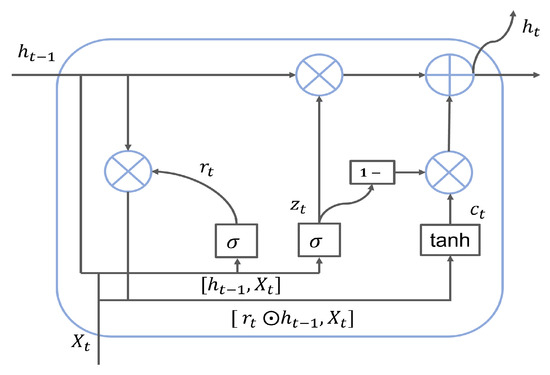
Figure 2.
The internal structure of GRU.
3.1.3. GCN-GRU
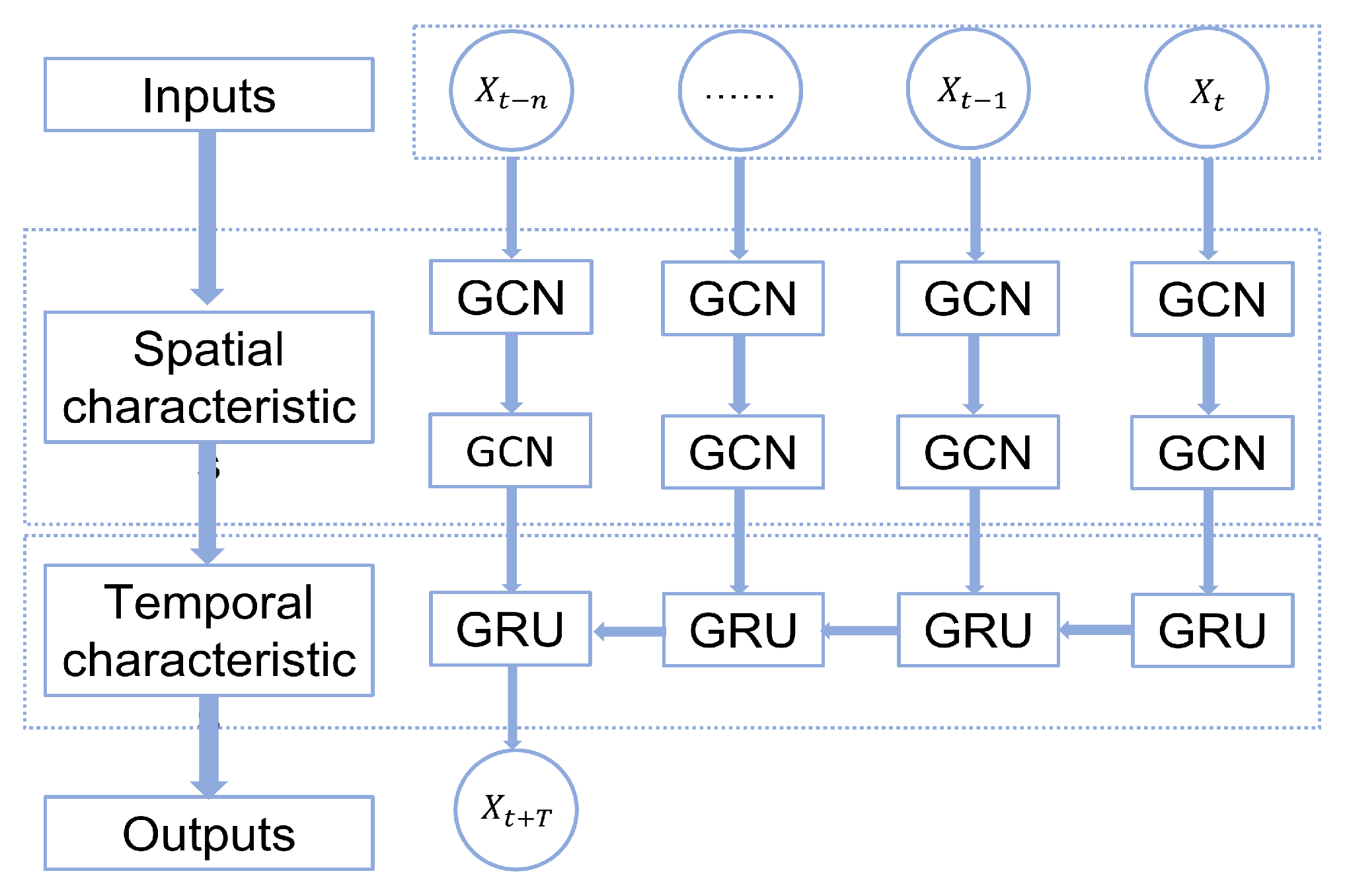
In order to simultaneously capture the spatial and temporal correlations of traffic data, this research uses a combined GCN-GRU model to implement the prediction task. The principle of the model is shown in Figure 3 and is as follows: (1) Use a two-layer graph convolutional network to aggregate the spatial information of first- and second-order neighbors to capture the spatial correlation of traffic flow. (2) Incorporate a gated recurrent unit model to capture the temporal correlation through information transfer between units. (3) Obtain the prediction results through the fully connected layer.
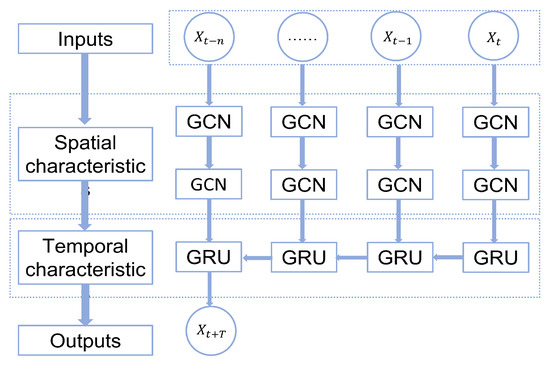
Figure 3.
The structure of GCN-GRU.
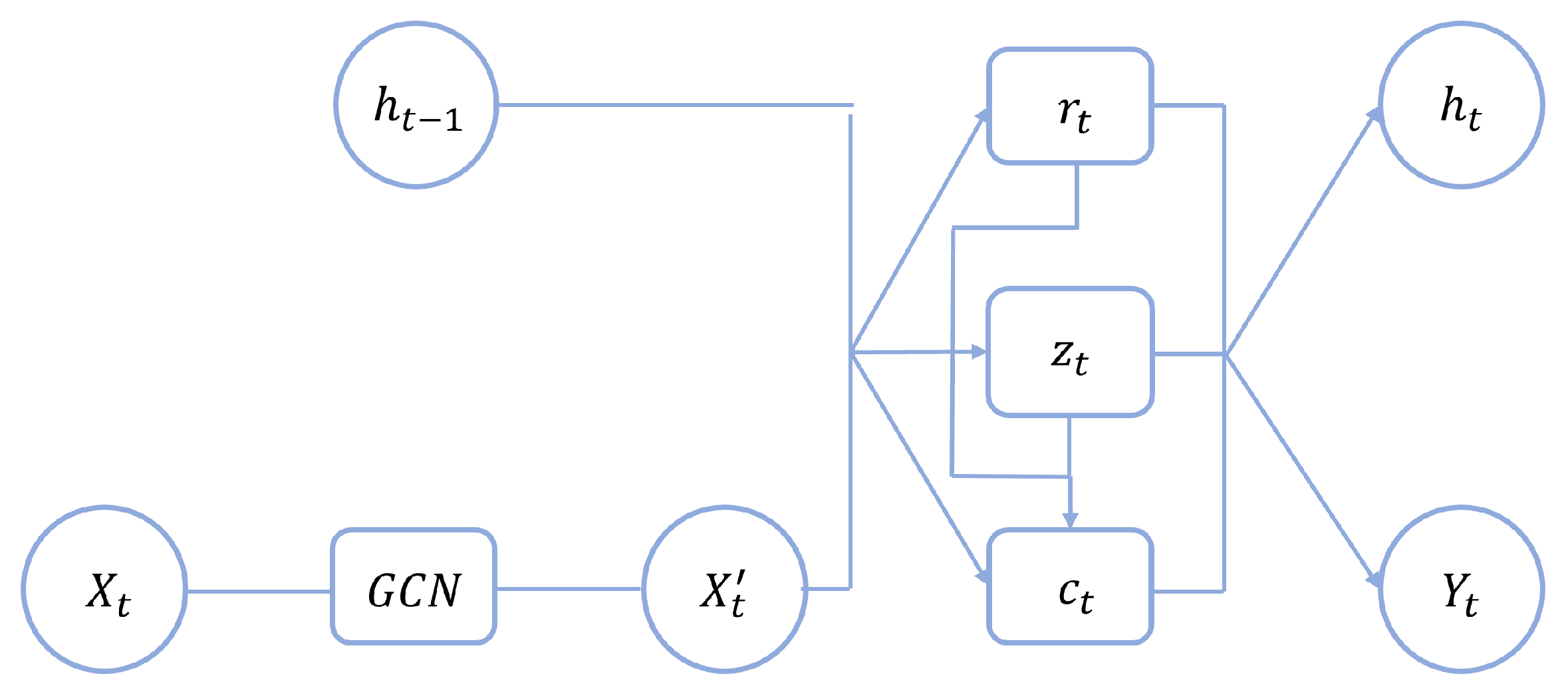
The internal structure of GCN-GRU is shown in Figure 4, where is the final predicted speed value. The graph convolution operation is calculated as follows:
where and denote the weight matrix in the first and second layers, and represents the activation function.
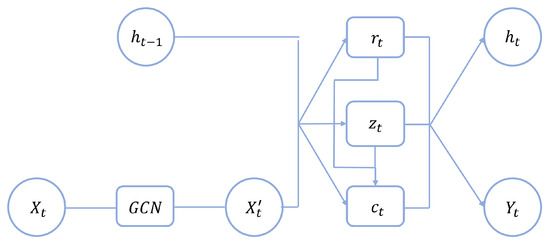
Figure 4.
The internal unit of GCN-GRU.
Then, combined with a gated recurrent unit model, the temporal correlations are captured through information transfer between memory units, and the specific process is as follows:
where denotes the graph convolution process defined in Equation (4), and b represents the deviation of the model in the training process.
Overall, through the effective combination of GCN and GRU, the spatio-temporal dependence of traffic data is well modeled to predict traffic speed.
4. Numerical Experiment
In this section, we investigate the influence of police enforcement crowdsourced data from navigation apps on traffic speed in The Netherlands. We selected corridors that met two conditions: (a) there are both police speed enforcement records and speed loop detectors; and (b) the number of speed cameras on the corridor is relatively small to ensure that the reports are all about police activity.
Two datasets, namely, the speed dataset and the crowdsourced dataset of The Netherlands, are used in our experiment:
- -
- The speed data are provided by the national data warehouse for traffic information (http://opendata.ndw.nu/, accessed on 26 October 2023). The raw speed data are collected from loop detectors on the highways every 5 min interval, and the samples are shown in Table 1.
 Table 1. Sample of loop detectors data.
Table 1. Sample of loop detectors data. - -
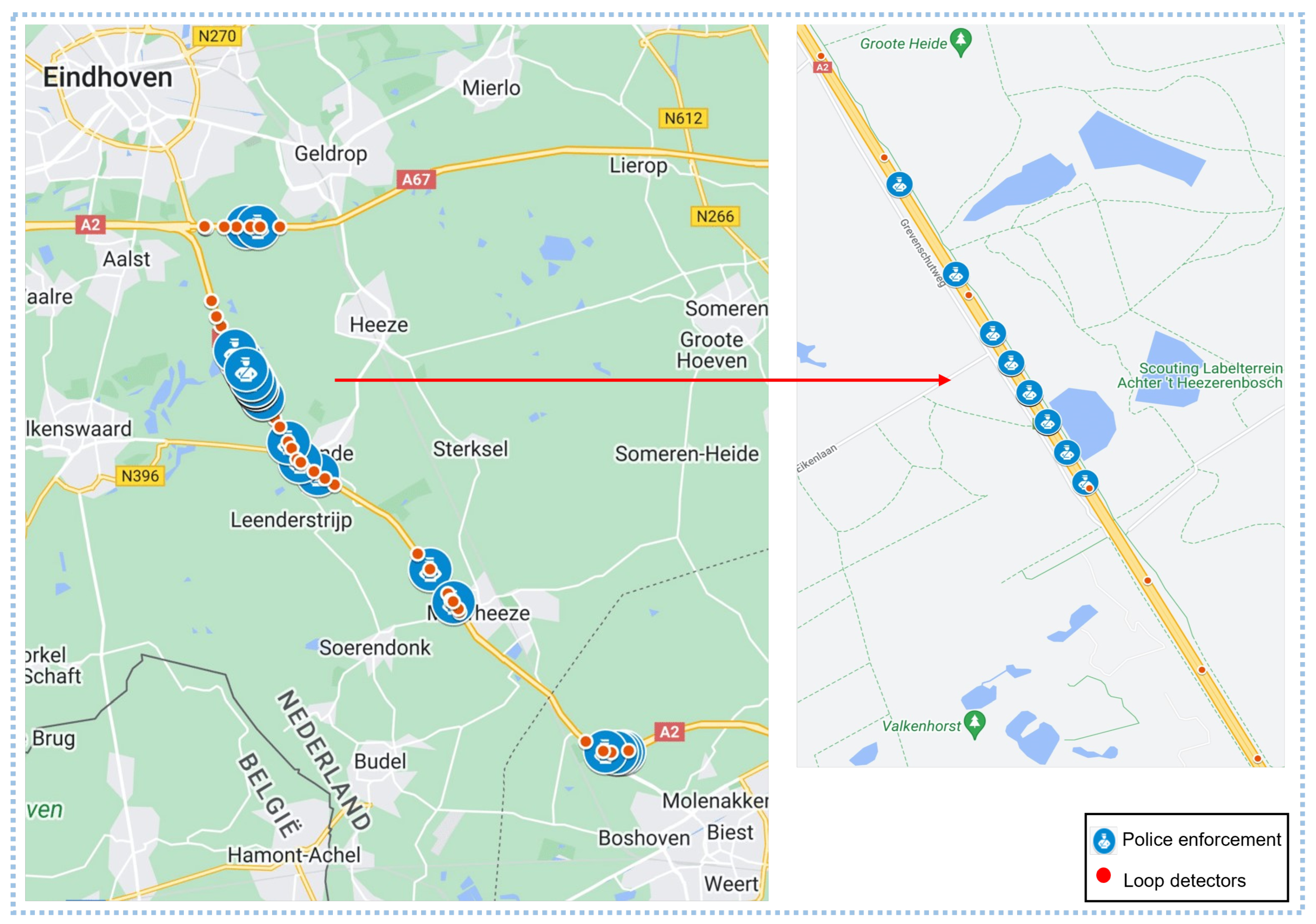
- The crowdsourced data of police speed enforcement reported between September and December 2021 in The Netherlands are provided by a navigation app. The dataset includes the latitude, longitude, and start and end time information reported by users on the navigation apps, and a sample of the data is provided in Table 2. Erroneous reports were removed, and reported police activities were accurately mapped to specific road segments using their location information. Figure 5 shows the study area and the location of speed loop detectors and reported police activities.
 Table 2. Sample of speed check data.
Table 2. Sample of speed check data.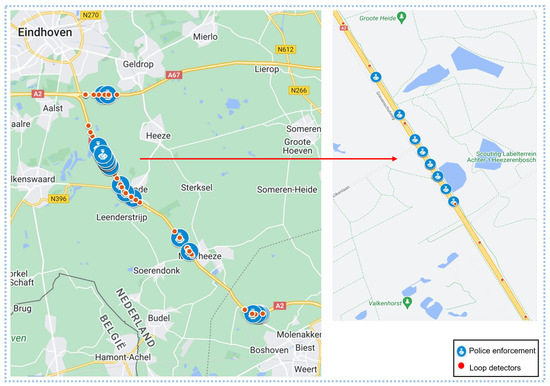 Figure 5. Study area.
Figure 5. Study area.
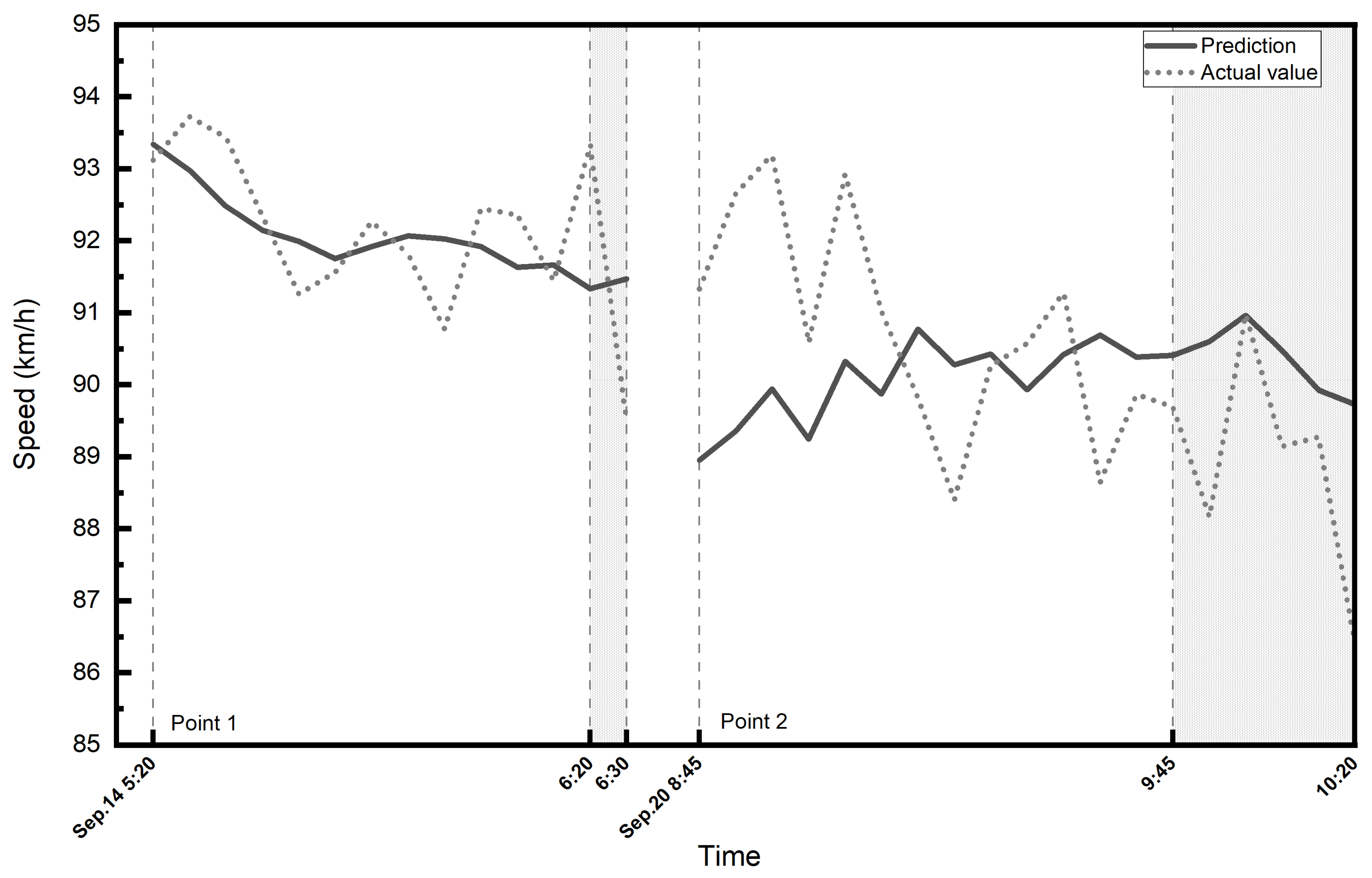
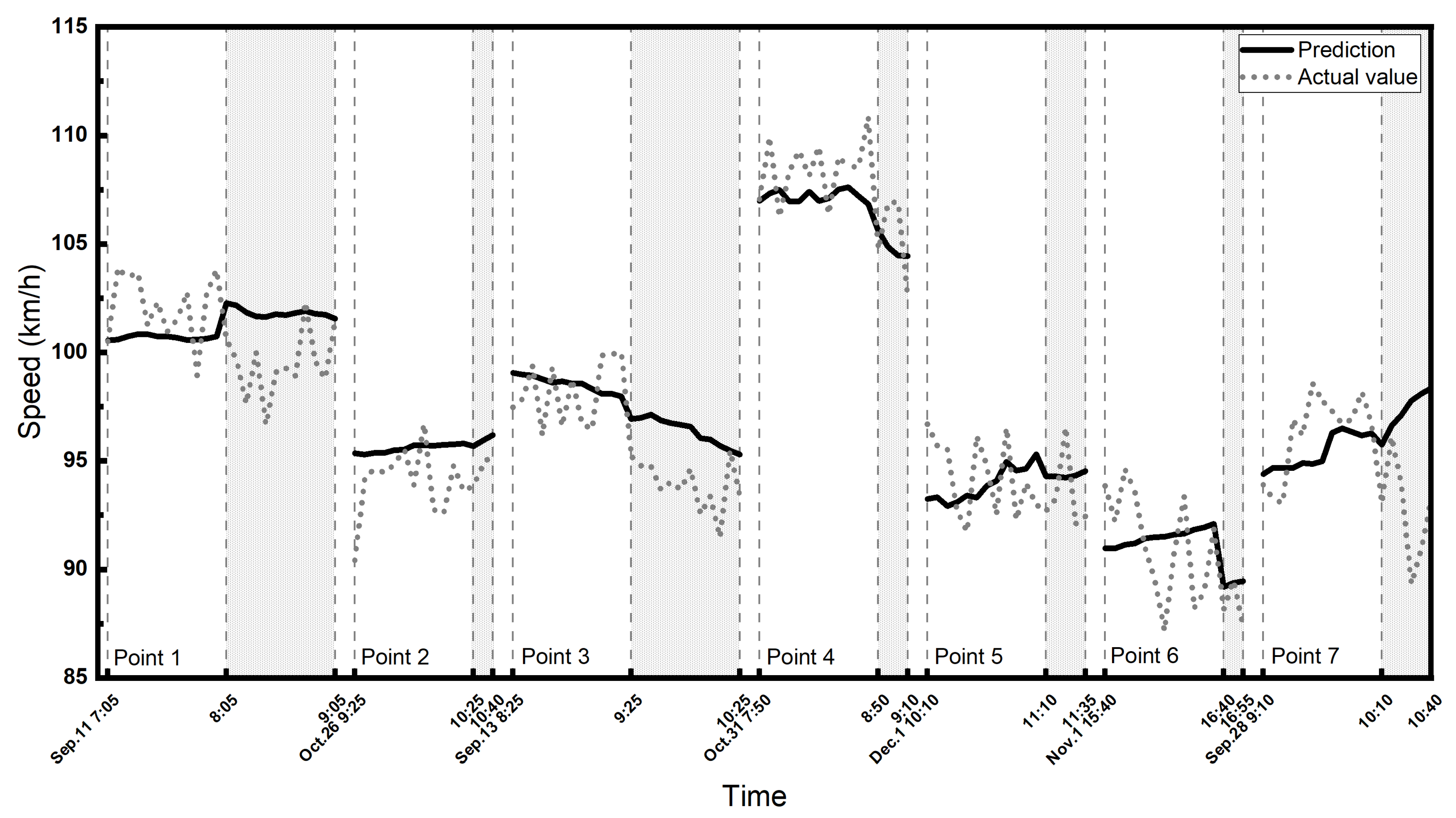
A section of the A67 highway on the south of Eindhoven from west to east was investigated first. It is a two-lane highway and the speed limit on express lane is 120 [km/h] and on the local lane is 100 [km/h]. There are two speed check points in this section. We collected the historical traffic speed data of the past 7 days for every 5 min interval of each check time period. The speed data are all from local lanes since there are plenty of missing data from loop detectors on express lanes. Then, we make predictions by the GCN-GRU model for each point and its corresponding inspection time; 80% of the input data was used as the training set and the remaining 20% was used as the testing set. Figure 6 shows the predicted and actual speeds during the reported police enforcement periods and an hour before the start of police enforcement as a comparison.
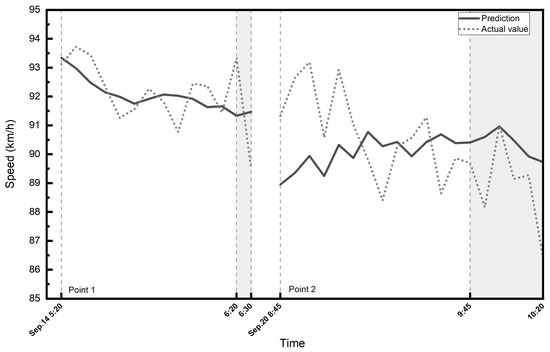
Figure 6.
The predicted and actual speeds on the A67 highway. The shaded area shows the enforcement period.
We performed the one factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) test to determine whether there are any statistically significant differences between the means of the predicted and actual speeds. In addition, in order to compare the performance of the GCN-GRU model in predicting traffic speed during the periods with and without police enforcement, three evaluation indicators were used:
- (i)
- Mean absolute error (MAE):
- (ii)
- Root mean square error (RMSE):
- (iii)
- Accuracy (ACC):where represents the actual traffic speed at time t, represents the predicted speed, n is the total number of test samples, and represents the Frobenius norm. MAE and RMSE can well reflect the deviation between the predicted values and the actual values, and smaller values of them indicate better prediction. ACC is used to detect the prediction precision, and larger values represent better prediction.
Table 3 shows the test results of the A67 highway. A one-factor ANOVA test with a significance level of 0.05 is performed. The p-values of the groups with and without police enforcement are 0.1502 and 0.2289, respectively, which means that the differences between the actual and predicted speed means are not statistically significant. Comparing the prediction evaluation indicators of the model with and without police enforcement shows that the model performs slightly better when there is no enforcement.

Table 3.
The test result of the A67 highway.
We note that there are only two speed check points on this corridor, and relatively small samples might be the reason for not seeing a statistically significant difference. However, the actual average speed is 1 [km/h] lower than the predicted average speed during the police enforcement periods, while it is slightly higher when no police enforcement is reported.
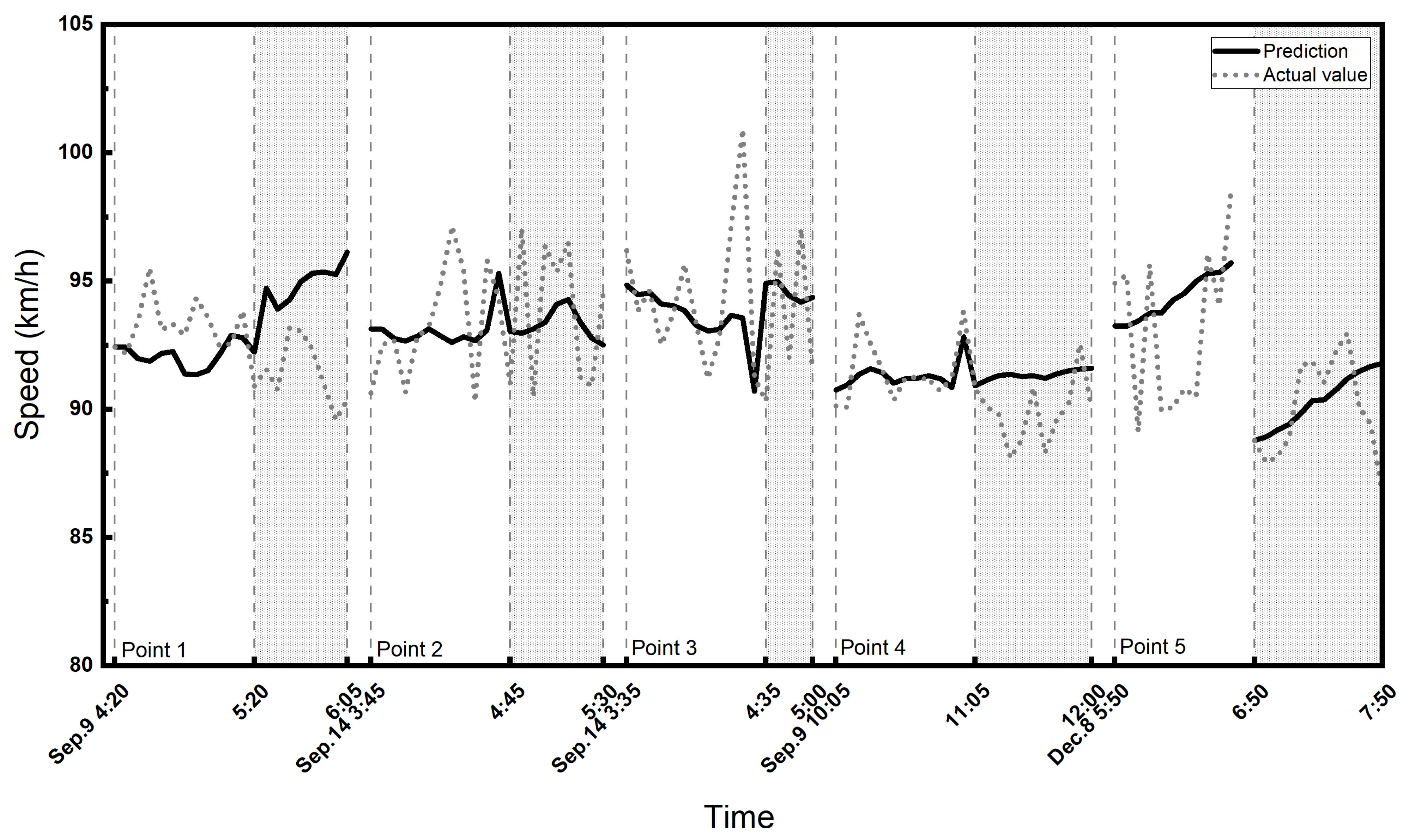
Then, we selected a section of A2, one of the busiest highways in The Netherlands. This section is located in the south of Eindhoven, and connects Eindhoven to Weert. We first analyzed the south-to-north driving direction on A2. It is a two-lane highway, and the speed limit is again 120 [km/h] on the express lane and 100 [km/h] on the local lane. According to the latitude and longitude information of police enforcement, there are eight enforcement points distributed in this direction. Among them, the speed check at two locations occurred during weekends, when the speed datasets had a large amount of missing data, so they were not considered for the analysis. Again, the speed data were collected from local lanes. The predicted and actual speeds with and without police enforcement are shown in Figure 7. The ANOVA test results and the prediction performance of GCN-GRU on this corridor are reported in Table 4.
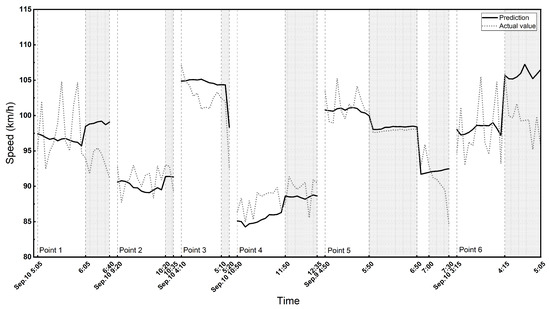
Figure 7.
The predicted and actual speed on A2 highway for the south-to-north driving direction. The shaded area shows the enforcement period.

Table 4.
The test results of A2 highway for the south-to-north driving direction.
It can be seen from Table 4 that the p-value of the with-police group (=0.03) is smaller than the confidence level 0.05, which means that the predicted and the actual speeds have statistically significant differences. On the contrary, no significant differences between the predicted and actual speeds were observed during the time period one hour before the police enforcement. Similar to the A67 corridor, in the presence of the police, the average of the actual speed is smaller than the predicted speed by 2.37 [km/h]; however, the actual average is 0.67 [km/h] larger than the predicted average when there is no police enforcement. Again, we can observe that the performance of the GCN-GRU model during reported police enforcement periods is relatively lower than periods without police enforcement.
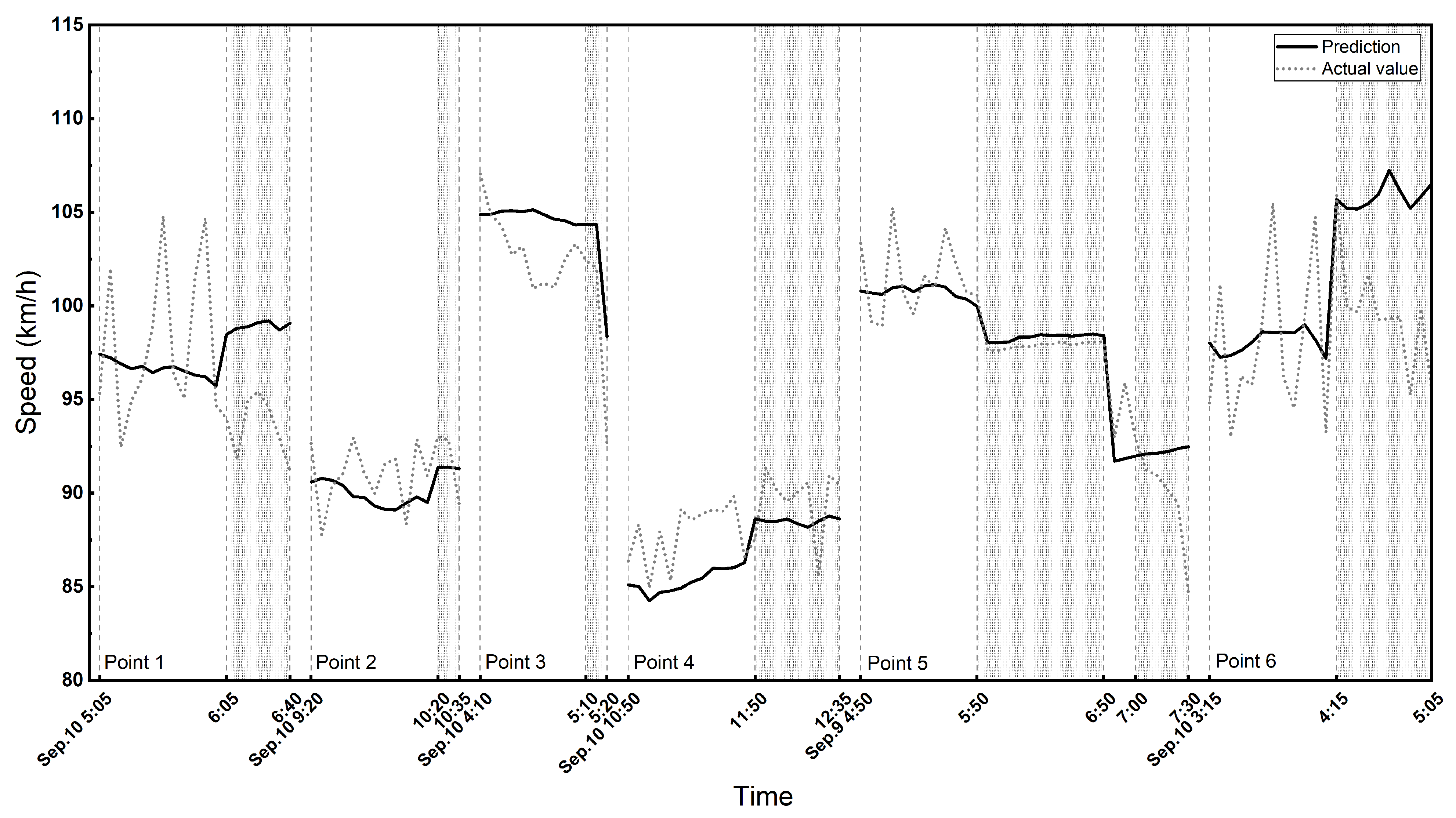
We also analyzed the north-to-south driving direction on A2. There are 15 police enforcement points in this direction. In particular, a part of the road section including five check points is a three-lane highway. As there is too much missing data in the express lane, we conducted the experiments on the local lanes of three lanes (5 points) and two lanes (10 points) on A2 separately. The predicted and actual speeds with and without police enforcement are shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9, and the ANOVA test results and the prediction metrics of the GCN-GRU are shown in Table 5 and Table 6.
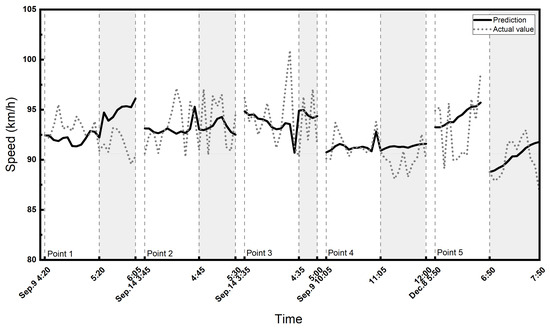
Figure 8.
The predicted and actual speed of three lanes on A2 highway for north-to-south driving direction. The shaded area shows the enforcement period.
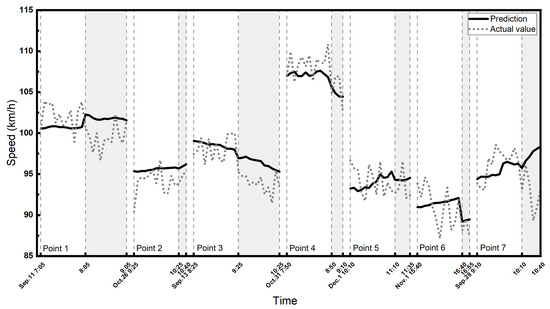
Figure 9.
The predicted and actual speeds of two lanes on the A2 highway for north-to-south driving direction. The shaded area shows the enforcement period.

Table 5.
The test results of three lanes of the A2 highway for the north-to-south driving direction.

Table 6.
The test results of two lanes of the A2 highway for the north-to-south driving direction.
Table 5 and Table 6 show that the difference between the prediction and actual speeds during police enforcement is statistically significant, while the two values are statistically the same when there is no police enforcement. The actual speeds are 1.1 [km/h] and 2.1 [km/h] in the case of three lanes and two lanes, respectively, and both are lower than the predicted speed during the police enforcement period. Similar to the other corridors, the model prediction accuracy is decreased during police enforcement compared to the time without any police activity. Furthermore, all the results consistently demonstrate that in the absence of police, the F-score exhibits a higher value, while in the presence of police, the F-score is generally much lower. This indicates that when police are present, the model’s performance tends to decline.
5. Conclusions and Future Research
In recent years, using crowdsourced data for traffic management has become increasingly possible due to smart devices and internet connectivity. The report of police activity in navigation apps by users is an example of such crowdsourced data. The traffic speed prediction models have considered the effect of external factors, such as accidents, weather, and POI, to increase prediction accuracy. In this research, the potential impact of the crowdsourced data of police enforcement on traffic speed and the prediction accuracy of a speed prediction model using real data from The Netherlands were investigated. The analyses showed that in most cases, there are significant statistical differences between the predicted speed and actual speed when there exist police enforcement reports, and the actual average speed is lower than the predicted average speed by 1–3 [km/h] during the presence of a police enforcement report. This suggests that the drivers adjust their speed as a result of such reports on navigation apps, which can nullify the enforcement effort by police. In addition, we find that the report of police activity lessens the performance of the speed prediction model GCN-GRU. Existing models considered the influence of external factors, such as weather and accidents on traffic speed. However, the presence of police enforcement on a road segment also affects the performance of deep learning prediction models. Therefore, during the model training phase, it is necessary to incorporate the impact of external factors related to the reported police activity. Furthermore, the existence of crowdsourced police activity data allows drivers to be aware of the locations and times of police presence in advance. While this might somewhat diminish the effectiveness of law enforcement, such as reducing the number of traffic citations, it can encourage drivers to slow down in advance, which is also a safety-enhancing measure.
A limitation of this study is selecting road segments that have both police activity reports as well as speed loop detectors. Most of the reported police enforcement takes place on rural or secondary roads, where few or no speed sensors, and consequently speed data, exist to conduct such investigations. Moreover, this study investigates the impact of police activity reported in one navigation app in The Netherlands. Hence, it is worth performing similar analyses in other locations and using data from more navigation apps to examine if the same results can be made. In addition, there is a limitation in performing traffic forecasting on large-scale road networks because of the randomness of the time and location of reported police enforcement. In this study, we perform the analysis based on the single enforcement location in different corridors because the enforcement on the same roads may occur several weeks apart. For a future study, we plan to collect more crowdsourced police enforcement data and speed data based on an entire road network, using police activity as an influencing factor, and integrate it into the speed prediction models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L.; Methodology, Y.L.; Software, Y.L.; Validation, Y.L.; Supervision, T.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cabannes, T.; Shyu, F.; Porter, E.; Yao, S.; Wang, Y.; Vincentelli, M.A.S.; Hinardi, S.; Zhao, M.; Bayen, A.M. Measuring regret in routing: Assessing the impact of increased app usage. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 2589–2594. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Bahrami, S.; Feng, T.; Rasouli, S. Impact of Crowdsourced Speed Check Data on Traffic Speed: A Case Study of The Netherlands. Available online: https://rstrail.nl/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Liu-Yutian.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Times, P. These Are the Most Dangerous Speed Cameras in The Netherlands (For Your Wallet). 2021. Available online: https://pledgetimes.com/these-are-the-most-dangerous-speed-cameras-in-the-netherlands-for-your-wallet/ (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Min, W.; Wynter, L. Real-time road traffic prediction with spatio-temporal correlations. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2011, 19, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X. Spatiotemporal recurrent convolutional networks for traffic prediction in transportation networks. Sensors 2017, 17, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Tang, X.; Wei, H.; Zheng, G.; Li, Z. Revisiting spatial-temporal similarity: A deep learning framework for traffic prediction. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 29–31 January 2019; Volume 33, pp. 5668–5675. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; McIlwraith, D.; Chen, T.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Wu, F. Deep sequence learning with auxiliary information for traffic prediction. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 537–546. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Guo, T.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B.Y. Deep graph convolutional networks for incident-driven traffic speed prediction. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Virtual Event, 19–23 October 2020; pp. 1665–1674. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, X.; Jiang, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, H. An improved deep belief network for traffic prediction considering weather factors. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Hong, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, T.; Zhu, T.; Ji, S. Temporal multi-graph convolutional network for traffic flow prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 3337–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryeng, E.O. The effect of sanctions and police enforcement on drivers’ choice of speed. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2012, 45, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.; McCutcheon, M.; Lal, D. Reducing speeding via inanimate police presence: An evaluation of a police-directed field study regarding motorist behavior. Criminol. Public Policy 2020, 19, 997–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.; Frewing, Q.; Bayer, J. The Effects of Saturation Enforcement on Speed(ing) along a Highway Corridor: Results from a Police-Directed Field Study. Justice Eval. J. 2023, 6, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semanjski, I.; Gautama, S. Smart city mobility application—Gradient boosting trees for mobility prediction and analysis based on crowdsourced data. Sensors 2015, 15, 15974–15987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, L. Crowdsourcing functions of the living city from Twitter and Foursquare data. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 43, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumoud, S. Twitter analysis for intelligent transportation. Comput. J. 2019, 62, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Li, R. Real-time traffic accidents post-impact prediction: Based on crowdsourcing data. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 145, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinzadeh, N.; Liu, Y.; Han, L.D.; Brakewood, C.; Mohammadnazar, A. Quality of location-based crowdsourced speed data on surface streets: A case study of Waze and Bluetooth speed data in Sevierville, TN. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2020, 83, 101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Ali, A.; Imran, M.; Naqvi, R.A.; Siddiqi, M.H.; Kwak, K.S. Traffic accident detection and condition analysis based on social networking data. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 151, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.; El-Diraby, T.; Shalaby, A. Supporting sustainable system adoption: Socio-semantic analysis of transit rider debates on social media. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Arjona, J.; Horak, J.; Svoboda, R.; García-Ruíz, Y. Social media semantic perceptions on Madrid Metro system: Using Twitter data to link complaints to space. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbani, O. Leveraging Twitter Data to Support Transit Planning and Operations. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toronto (Canada), Toronto, ON, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liebig, T.; Piatkowski, N.; Bockermann, C.; Morik, K. Dynamic route planning with real-time traffic predictions. Inf. Syst. 2017, 64, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Cook, A.R. Analysis of Freeway Traffic Time-Series Data by Using Box-Jenkins Techniques; Number 722; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Dong, S.; Qian, Z.; Wei, H. A novel work zone short-term vehicle-type specific traffic speed prediction model through the hybrid EMD–ARIMA framework. Transp. B Transp. Dyn. 2016, 4, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hinsbergen, C.P.; Schreiter, T.; Zuurbier, F.S.; Van Lint, J.; Van Zuylen, H.J. Localized extended kalman filter for scalable real-time traffic state estimation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2011, 13, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Ishak, S. A Hidden Markov Model for short term prediction of traffic conditions on freeways. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2014, 43, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sun, J. A dynamic Bayesian network model for real-time crash prediction using traffic speed conditions data. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 54, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzeszótko, J.; Nguyen, S.H. Machine learning for traffic prediction. Fundam. Inform. 2012, 119, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukerche, A.; Wang, J. Machine Learning-based traffic prediction models for Intelligent Transportation Systems. Comput. Netw. 2020, 181, 107530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Xu, J.; Zheng, K.; Yin, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, X. Lc-rnn: A deep learning model for traffic speed prediction. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; Volume 2018, p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Wu, G.; Wei, J.; Shen, Y.; Qi, H.; Yin, B. Deep learning on traffic prediction: Methods, analysis and future directions. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 4927–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csikós, A.; Viharos, Z.J.; Kis, K.B.; Tettamanti, T.; Varga, I. Traffic speed prediction method for urban networks—An ANN approach. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS), Budapest, Hungary, 3–5 June 2015; pp. 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Dai, Z.; He, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Learning traffic as images: A deep convolutional neural network for large-scale transportation network speed prediction. Sensors 2017, 17, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, W.; Wang, Z. Deep convolutional neural networks for image classification: A comprehensive review. Neural Comput. 2017, 29, 2352–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, F.; Long, G.; Zhang, C.; Philip, S.Y. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Lee, Y.; Sohn, K. Forecasting road traffic speeds by considering area-wide spatio-temporal dependencies based on a graph convolutional neural network (GCN). Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 114, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, M.; Zhao, A. Traffic prediction based on GCN-LSTM model. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet of Things and Smart City (IoTSC 2021), Kunming, China, 4–6 June 2021; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1972, p. 012107. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Lin, T.; Deng, M.; Li, H. T-gcn: A temporal graph convolutional network for traffic prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 3848–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Ma, C.; Xu, X. Short-term traffic flow prediction method for urban road sections based on space–time analysis and GRU. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 143025–143035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Pan, C.; Yang, L.; Gu, X. AGG: A Novel Intelligent Network Traffic Prediction Method Based on Joint Attention and GCN-GRU. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 7751484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, A. Temporal graph convolutional networks for traffic speed prediction considering external factors. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM), Hong Kong, China, 10–13 June 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 234–242. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, W.; Sun, Y.; Tian, C. An effective dynamic spatiotemporal framework with external features information for traffic prediction. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 3159–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Henrickson, K.; Ke, R.; Wang, Y. Traffic Graph Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network: A Deep Learning Framework for Network-Scale Traffic Learning and Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 4883–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Q.; Tao, C.; Deng, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, H. AST-GCN: Attribute-augmented spatiotemporal graph convolutional network for traffic forecasting. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 35973–35983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niepert, M.; Ahmed, M.; Kutzkov, K. Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Graphs. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 20–22 June 2016; Balcan, M.F., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Volume 48, pp. 2014–2023. [Google Scholar]
- Defferrard, M.; Bresson, X.; Vandergheynst, P. Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2016/hash/04df4d434d481c5bb723be1b6df1ee65-Abstract.html (accessed on 26 October 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).