Segmenting Cervical Arteries in Phase Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Convolutional Encoder–Decoder Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Overview
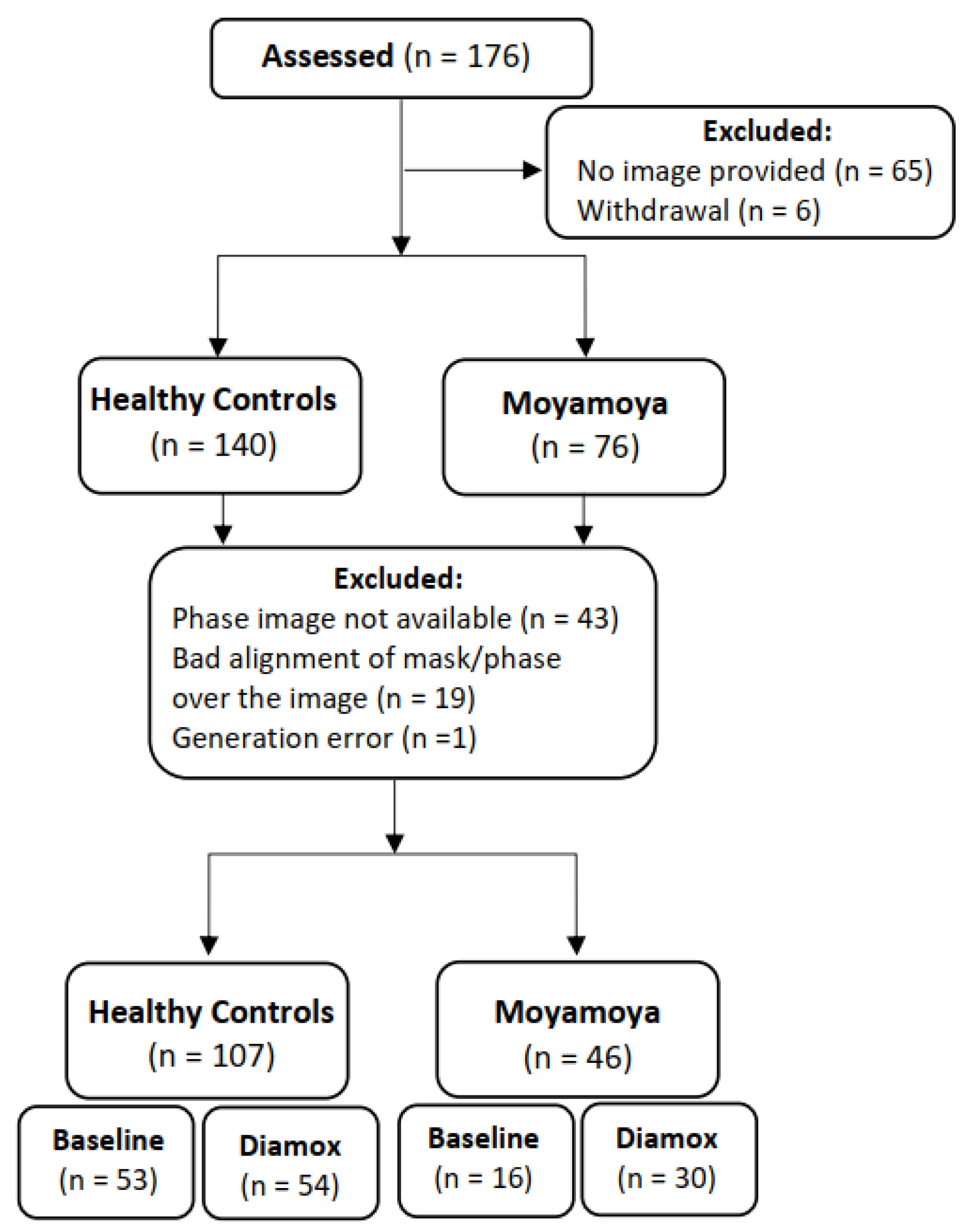
2.2. Study Population
2.3. PC MRI Acquisition and Vessel Segmentation
2.4. Mathematical Description of UNets
2.5. Deep Learning Model Architecture, Training, and Testing
- ±15° rotation of the image;
- ±50 pixels image translation on the x and y axes;
- 0.7 to 1.3 times image scaling;
- ±15° image shear.
2.6. Flow Velocity and Volume Measurements
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
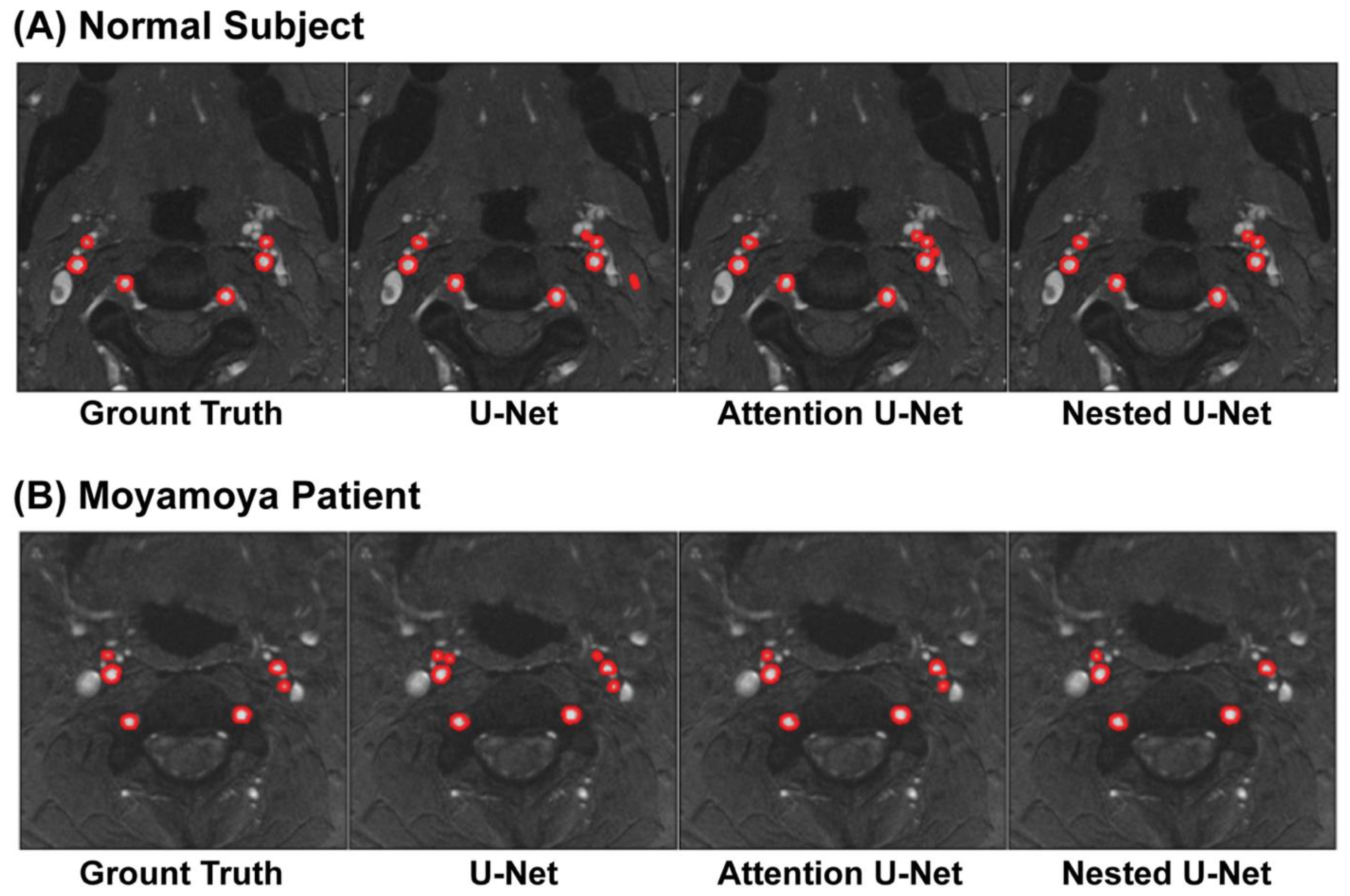
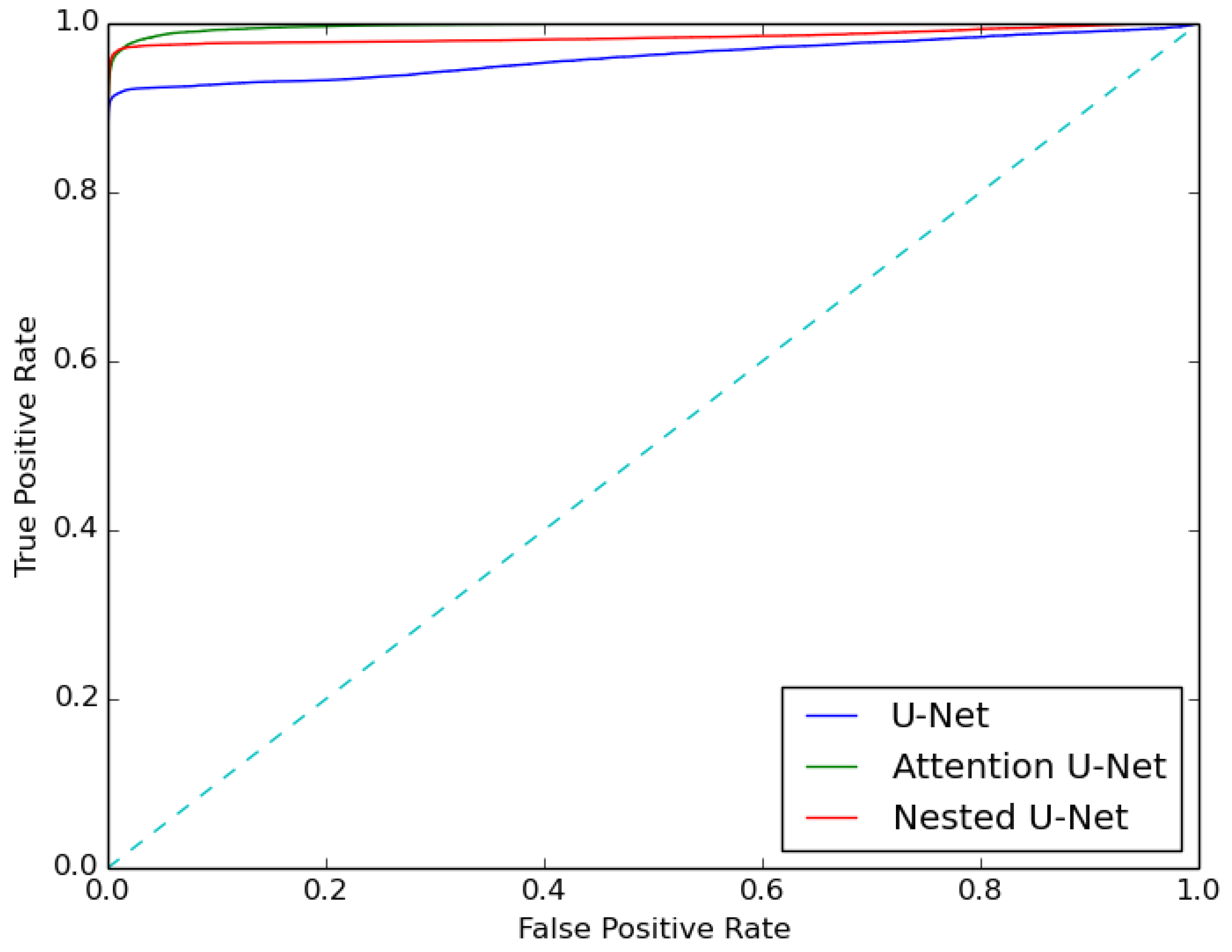
4.1. Segmentation Results
4.2. Flow and Velocity Measurements
5. Discussion
5.1. Performance of the Deep Learning Models
5.2. Flow Volume and Velocity Measurements
5.3. Comparison with Similar Studies on Image Segmentation
5.4. Implications of Results for General Readers
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACZ | acetazolamide |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| CBF | cerebral blood flow |
| CNN | convolutional neural network |
| DSC | Dice similarity coefficient |
| HC | healthy control |
| LECA | left external carotid artery |
| LICA | left internal carotid artery |
| LVA | left vertebral artery |
| MM | moyamoya |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| PC | phase contrast |
| RECA | right external carotid artery |
| RICA | right internal carotid artery |
| ROI | region of interest |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| RVA | right vertebral artery |
References
- De Boorder, M.J.; Hendrikse, J.; van der Grond, J. Phase-Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measurements of Cerebral Autoregulation with a Breath-Hold Challenge: A Feasibility Study. Stroke 2004, 35, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, G.K.; Gooderham, P.A. Intracranial-Extracranial Bypass Surgery for Moyamoya Disease. In Neurovascular Surgery; Kalani, Y., Nakaji, P., Spetzler, R.F., Eds.; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-60406-760-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Zaharchuk, G.; Guzman, R.; Achrol, A.; Bell-Stephens, T.; Steinberg, G.K. Quantitative Hemodynamic Studies in Moyamoya Disease: A Review. Neurosurg. Focus 2009, 26, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Qi, Y.; Lin, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wang, X.; Lu, H. Assessment of Cerebral Blood Flow in Neonates and Infants: A Phase-Contrast MRI Study. NeuroImage 2019, 185, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alperin, N.; Vikingstad, E.M.; Gomez-Anson, B.; Levin, D.N. Hemodynamically Independent Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid and Brain Motion Observed with Dynamic Phase Contrast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 35, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Liu, J.; Tarumi, T.; Lawley, J.S.; Liu, P.; Zhu, D.C.; Lu, H.; Zhang, R. Measurement of Cerebral Blood Flow Using Phase Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Duplex Ultrasonography. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.K.; Greenspan, H.; Davatzikos, C.; Duncan, J.S.; Van Ginneken, B.; Madabhushi, A.; Prince, J.L.; Rueckert, D.; Summers, R.M. A Review of Deep Learning in Medical Imaging: Imaging Traits, Technology Trends, Case Studies with Progress Highlights, and Future Promises. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 820–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.; Valverde, S.; Cabezas, M.; Pareto, D.; Oliver, A.; Salvi, J.; Rovira, À.; Lladó, X. A fully convolutional neural network for new T2-w lesion detection in multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 25, 102149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratt, A.; Kim, J.; Pollie, M.; Beecy, A.N.; Tehrani, N.H.; Codella, N.; Perez-Johnston, R.; Palumbo, M.C.; Alakbarli, J.; Colizza, W.; et al. Machine Learning Derived Segmentation of Phase Velocity Encoded Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance for Fully Automated Aortic Flow Quantification. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2019, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacal, I.; Kılıcarslan, S. Deep Learning-Based Approaches for Robust Classification of Cervical Cancer. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 18813–18828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, O. Cervical Cancer Diagnosis Based on Multi-Domain Features Using Deep Learning Enhanced by Handcrafted Descriptors. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cao, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, P.; Tian, X.; Sun, C.; Wang, W.; Gao, H.; Kang, S.; et al. The Pathological Risk Score: A New Deep Learning-Based Signature for Predicting Survival in Cervical Cancer. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Y.-L.; Ho, C.-Y.; Chiang, H.-J.; Lu, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, J.-J.; Ng, S.-H.; Lai, C.-H.; et al. Generalizable Transfer Learning of Automated Tumor Segmentation from Cervical Cancers toward a Universal Model for Uterine Malignancies in Diffusion-Weighted MRI. Insights Imaging 2023, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, N.; Qin, W.; Krishnan, A. Graph-Based Methods for Cervical Cancer Segmentation: Advancements, Limitations, and Future Directions. AI Open 2023, 4, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Xu, H.; Dong, Y.; Hao, X.; Qin, F.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Cong, F. Automatic Cervical Cancer Segmentation in Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using an EfficientNet Encoder in UNet++ Architecture. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2023, 33, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.Y.; Fan, A.P.; Chen, D.Y.-T.; Sokolska, M.J.; Guo, J.; Ishii, Y.; Shin, D.D.; Khalighi, M.M.; Holley, D.; Halbert, K.; et al. Cerebrovascular Reactivity Measurements Using Simultaneous 15O-Water PET and ASL MRI: Impacts of Arterial Transit Time, Labeling Efficiency, and Hematocrit. NeuroImage 2021, 233, 117955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.10165. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Kihira, S.; Mei, X.; Mahmoudi, K.; Liu, Z.; Dogra, S.; Belani, P.; Tsankova, N.; Hormigo, A.; Fayad, Z.A.; Doshi, A.; et al. U-Net Based Segmentation and Characterization of Gliomas. Cancers 2022, 14, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Agyeman, R.; Rafiq, M.; Chang, M.C.; Choi, G.S. Automated Segmentation of Chronic Stroke Lesion Using Efficient U-Net Architecture. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 42, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saood, A.; Hatem, I. COVID-19 Lung CT Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning Methods: U-Net versus SegNet. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.; Smedsrud, P.H.; Riegler, M.A.; Johansen, D.; de Lange, T.; Halvorsen, P.; Johansen, H.D. ResUNet++: An Advanced Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), San Diego, CA, USA, 9–11 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, S.; Elgohary, K.; Higazy, M.; Mohannad, T.; Selim, S.; Elattar, M. Lung Segmentation Using ResUnet++ Powered by Variational Auto Encoder-Based Enhancement in Chest X-Ray Images. In Medical Image Understanding and Analysis, Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference, MIUA 2022, Cambridge, UK, 27–29 July 2022; Yang, G., Aviles-Rivero, A., Roberts, M., Schönlieb, C.-B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 339–356. [Google Scholar]
- Habijan, M.; Galić, I.; Romić, K.; Leventić, H. AB-ResUNet+: Improving Multiple Cardiovascular Structure Segmentation from Computed Tomography Angiography Images. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| TR/TE | ms | 12.4/4.6 |
| Flip angle | degrees | 20 |
| FOV | mm | 180 × 180 |
| Matrix | 512 × 512 | |
| Voxel size | mm | 0.3516 × 0.3516 × 3 |
| Cardiac phases | 10 | |
| Average time per cardiac phase | ms | 88 |
| Slice thickness | mm | 3 |
| Number of slices | 1 | |
| Velocity encoding | cm/s | 100 |
| Repeats | 2 | |
| Scan duration | min | 1:30 |
| Healthy Control Baseline (n = 53) | Moyamoya Baseline (n = 16) | Healthy Control Diamox (n = 54) | Moyamoya Diamox (n = 30) | All Subjects in All Conditions (n = 153) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 0.92 ± 0.03 | 0.58 ± 0.31 | 0.92 ± 0.05 | 0.73 ± 0.18 | 0.81 ± 0.21 |
| Attention U-Net | 0.87 ± 0.06 | 0.69 ± 0.21 | 0.90 ± 0.05 | 0.76 ± 0.15 | 0.85 ± 0.13 |
| Nested U-Net | 0.85 ± 0.11 | 0.79 ± 0.21 | 0.91 ± 0.06 | 0.80 ± 0.13 | 0.85 ± 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campbell, B.; Yadav, D.; Hussein, R.; Jovin, M.; Hoover, S.; Halbert, K.; Holley, D.; Khalighi, M.; Davidzon, G.A.; Tong, E.; et al. Segmenting Cervical Arteries in Phase Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Convolutional Encoder–Decoder Networks. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111820
Campbell B, Yadav D, Hussein R, Jovin M, Hoover S, Halbert K, Holley D, Khalighi M, Davidzon GA, Tong E, et al. Segmenting Cervical Arteries in Phase Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Convolutional Encoder–Decoder Networks. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(21):11820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111820
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampbell, Britney, Dhruv Yadav, Ramy Hussein, Maria Jovin, Sierrah Hoover, Kim Halbert, Dawn Holley, Mehdi Khalighi, Guido A. Davidzon, Elizabeth Tong, and et al. 2023. "Segmenting Cervical Arteries in Phase Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Convolutional Encoder–Decoder Networks" Applied Sciences 13, no. 21: 11820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111820
APA StyleCampbell, B., Yadav, D., Hussein, R., Jovin, M., Hoover, S., Halbert, K., Holley, D., Khalighi, M., Davidzon, G. A., Tong, E., Steinberg, G. K., Moseley, M., Zhao, M. Y., & Zaharchuk, G. (2023). Segmenting Cervical Arteries in Phase Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Convolutional Encoder–Decoder Networks. Applied Sciences, 13(21), 11820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111820







