Abstract
Phaeocystis globose (P. glo) are the most frequent harmful algae responsible for red tides in Qinzhou Bay, Guangxi. They pose a significant threat to the coastal marine ecosystem, making it essential to develop an efficient indicator method tailored to P. glo outbreaks. In remote sensing water quality monitoring, there is a strong correlation between P. glo and cyanobacteria, with phycocyanin (PC) serving as an indicator of cyanobacterial biomass. Consequently, existing research has predominantly focused on remote sensing monitoring of medium to high PC concentrations. However, it is still challenging to monitor low PC concentrations. This paper introduced the BP neural network (BPNN) and particle swarm optimization algorithm (PSO). It selects spectral bands and indices sensitive to PC concentrations and constructs a PC concentration retrieval model, in combination with meteorological factors, offering a comprehensive exploration of the indicative role of low PC concentrations in predicting P. glo red tide outbreaks in Qinzhou Bay. The results demonstrated that the PC concentration retrieval model, based on the backpropagation neural network optimized by the particle swarm optimization algorithm (PSO-BPNN), demonstrated better performance (MAE = 0.469, RMSE = 0.615). In Qinzhou Bay, PC concentrations were mainly concentrated around 2~5 μg/L. During the P. glo red tide event, the area with undetectable PC concentrations (PC < 0.04 μg/L) increased by 4.97 km2, with regions below 0.9 μg/L experiencing exponential growth. Considering the variations in PC concentrations along with meteorological factors, we proposed a straightforward early warning threshold for P. glo red tides: PC < 0.9 μg/L and T < 20 °C. This method, from a remote sensing perspective, analyzes the process of P. glo outbreaks, simplifies PC concentration monitoring, and provides a reasonably accurate prediction of the risk of P. glo red tide disasters.
1. Introduction
Phaeocystis globose [1] (P. glo) is a photosynthetic autotrophic planktonic alga belonging to the phylum Chrysophyceae and the order Flagellates. It exists in two forms of life: unicellular and colonial gelatinous cysts. During mass reproduction, it transforms from unicellular to more dominant cysts and produces harmful substances, such as haemolytic toxins, capable of killing fish and shellfish [2]. This leads to damage in the environment of marine water bodies, potentially resulting in the severe degradation of marine ecosystems in both structure and function [3]. Since 2015, P. glo red tides have frequently occurred in Qinzhou Bay, Guangxi, China (Table 1). A red tide not only affects marine fisheries and the ecological environment, but also leads to the blockage of cooling water intake systems in nuclear power plants [4]. As a result, many scholars have investigated the morphology [5,6], growth history [7,8], and genome sequence [9] of P. glo. They found that, compared to other algae, P. glo is more adaptable to low temperatures and can survive in low-light environments. Consequently, P. glo tends to aggregate in deep water and remains suspended in seawater after forming cysts. It only floats to the sea surface when its density is high. This phenomenon leads to the detection of P. glo in surface seawater, indicating that the P. glo red tide has already reached a high blooming stage, causing potentially irreversible harm to marine organisms and the ecological environment. Therefore, the development of effective early warning methods for P. glo red tides is of paramount importance. In a study of Zhao et al. [10], it was pointed out that there exists a significant negative correlation between the concentration changes in Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus and P. glo. This finding offers a potential early warning indicator for P. glo red tides. Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus belong to the same group of cyanobacteria, which are algae with a high phytoplankton abundance in the ocean [11,12], whereas cyanobacteria are prokaryotic organisms with intracellular phycobilisomes. The phycobilisomes contain phycocyanin (PC), distinguishing them from other algae [13]. PC concentrations are usually utilized as markers for monitoring the concentration of cyanobacteria.

Table 1.
Statistical table of P. glo red tide events in Qinzhou Bay, Guangxi.
Because PC has a strong absorption property at 620 nm, most water quality sensors use 620 nm fluorescence photometry to monitor the PC concentration [14]. The traditional manual monitoring methods are not only time-consuming and labor-intensive, but the monitored points are also difficult to represent the changes in PC concentration in the entire sea surface. Remote sensing monitoring can make up for the shortcomings of manual monitoring. It does so by analyzing the correlation between PC concentration and spectral characteristics of the water body. This involves the use of empirical, semi-empirical, and analytical methods to establish a mapping relationship between PC concentration and spectral features of water bodies. For example, Simis et al. [15] developed a semi-analytical, nested band ratio-based algorithm and verified the feasibility of the method for PC retrieval in turbid water bodies dominated by cyanobacteria. Qi et al. [16] proposed the band-subtraction algorithm for cyanobacterial bloom in Lake Taihu, China, where the remote sensing reflectivity at 620 nm was deduced from the baseline height between 560 nm and 665 nm, and then the obtained value was used to estimate the PC concentration. In addition to using the band ratio as independent variables for the input of the model, researchers have also proposed an enhanced three-band empirical model based on a three-band algorithm [17,18] framework to detect high PC concentrations (PC ∈ [68.13, 3032.47] μg/L) in inland water bodies. This algorithm experienced a significant decrease in predictive accuracy when the PC concentrations are below 300 μg/L, with the model’s coefficient of determination (R2) dropping from 0.99 to 0.65 [19]. These empirical algorithms or semi-analytical algorithms showed high errors in predicting PC concentration, such as the model proposed by Mishra [19], which had a relative error of up to 30.7% for PC concentration prediction. Recent comparative studies between empirical statistical models and machine learning models indicated that machine learning algorithms achieve higher prediction accuracy for PC concentration [20,21]. Moreover, these algorithms demonstrate improved capability in capturing the mapping relationship between PC concentrations and spectral characteristics. It is worth considering whether the accuracy of the model is higher when using high spatial resolution and high spectral resolution images for PC concentration retrieval [22,23,24].
It is well known that many inland lakes are severely affected by cyanobacterial blooms. Previous studies on PC concentration retrieval have mainly focused on areas with high PC concentrations in inland waters bodies, leading to the poor performance of these models in the low PC concentration range. In the absence of exogenous input, PC concentration in nearshore waters is usually low ([0, 20] μg/L), resulting in limited investigation of PC concentration retrieval in these nearshore areas. Combining machine learning algorithms has the potential to fill the research gap in remote sensing monitoring of low PC concentrations in nearshore regions.
To address the issue of low PC concentration in Qinzhou Bay, Guangxi, we attempted to construct a series of spectral indices based on the bands after image preprocessing. Subsequently, we comprehensively analyzed the correlation between these spectral indices and PC concentrations. Ultimately, we identified the optimal spectral bands/indices to be used as independent variables for input into the Particle Swarm Optimization-based Backpropagation Neural Network model (PSO-BPNN). This model utilized high spatial resolution data from Sentinel-2 MSI for accurate prediction of PC concentrations. Based on these findings, the paper proposed an early warning threshold for predicting P. glo red tide outbreaks in Qinzhou Bay. This method can roughly infer the risk of P. glo red tide outbreak based on the distribution of PC concentration, providing a scientific basis for water environmental management in coastal areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Qinzhou Bay is located on the southern coast of Guangxi, China. It consists of three parts: the inner bay, the neck of the bay, and the outer bay, forming a typical gourd-shaped bay (Figure 1). The bay’s formation could be attributed to the rise in sea level during the late Quaternary ice age and the submergence of ancient river valleys by seawater [25,26]. The Bay has a subtropical monsoon climate characterized by high annual rainfall, with an average annual temperature of about 23 °C. Factors such as runoff from the Qin and Maoling rivers, as well as the region’s topography, limit water exchange capacity. These conditions facilitate the accumulation of nutrients, resulting in the frequent occurrence of red tide phenomena in Qinzhou Bay.
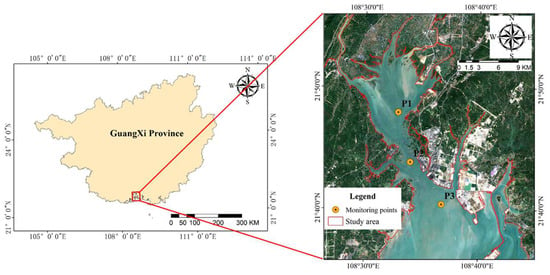
Figure 1.
Study area and monitoring site.
2.2. Dataset
2.2.1. PC Concentration Monitoring Data
PC concentration monitoring data were obtained from three automatic monitoring stations located in the waters of Qinzhou Bay (Figure 1). The latitudes and longitudes of each monitoring point are provided in Table 2. The water quality sensors at each point were positioned at depths approximately 0.5 to 1 m below the water surface to capture surface seawater conditions. The concentration of PC was determined using the phycocyanin fluorescence spectrophotometric method. This method involves measuring the fluorescence intensity of phycocyanin under optimal excitation and emission wavelengths, with a detection limit of 0.04 μg/L. Based on daily water quality data collected by the automatic monitoring stations from 2015 to 2019, PC concentration data corresponding to the imaging time of Sentinel-2 images were selected and the statistical data of the measured PC concentration are presented in Table 3.

Table 2.
Latitude and longitude of automatic monitoring stations.

Table 3.
Statistical analysis of PC concentration.
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Image Data
The Sentinel-2 MSI satellite image data are part of the Copernicus Program, operated by the European Space Agency (ESA). These satellite images offer a wealth of spectral information, as depicted in Table A1. The imaging resolution of Sentinel-2 MSI is exceptionally high, reaching up to 10 m. Its applications span a wide range, including natural disaster monitoring, land cover surveys, and nearshore environmental monitoring. The first Sentinel-2 satellite (S2A) was successfully launched in June 2015, and the second one (S2B) in March 2017, forming a double-star network. The synergistic effect of these two satellites has shortened the revisit period of the satellites to 2~5 days. This high frequency observation capability provides a stable data source for water quality retrieval. Detailed information regarding the matched images and monitoring times for PC concentration can be found in Table A2.
2.2.3. Other Data
The study collected meteorological data, including total rainfall and sea surface temperature, from ERA5 (https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-single-levels?tab=form (accessed on 19 July 2023)) hourly reanalysis data with a resolution of 0.25° × 0.25°. Furthermore, the inorganic salt data were collected on-site along with the PC concentration as part of the automatic monitoring data. It was measured using an in situ nutrient analyzer, which employs the method of diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) reduction colorimetry.
2.3. Methods
To evaluate the performance of the PSO-BPNN model, we compared it with the traditional backpropagation neural network (BPNN) and the support vector machine regression model (SVR). After confirming the high retrieval accuracy of the PSO-BPNN model, we applied it to analyze the changes in PC concentration using Sentinel-2 MSI images taken before and after the 2017 red tide outbreak of P. glo in Qinzhou Bay. For a comprehensive understanding, the analysis incorporated additional environmental variables such as sea surface temperature, precipitation, and inorganic salt concentration. Finally, the indicators for the P. glo red tide outbreak in Qinzhou Bay were established. The technical route of the study is shown in Figure 2.
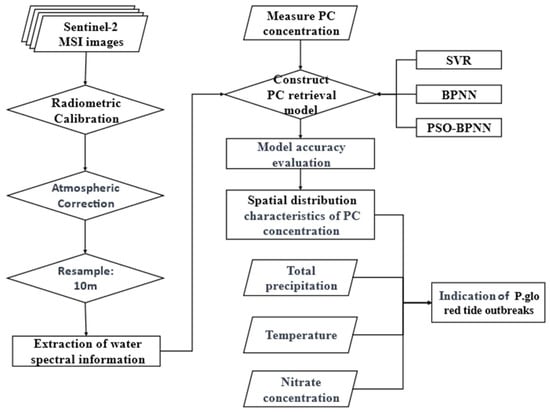
Figure 2.
Research technical route.
2.3.1. Image Preprocessing
The latest version of Sen2Cor V2.11, provided by ESA, allows for radiometric calibration and atmospheric correction of collected Sentinel-2 L1C class images. It adopts higher precision Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data (30 m), enhancing support for the improved radiometric calibration and atmospheric correction of Sentinel-2 images. The Sentinel-2 MSI images encompass 13 effective bands, each containing rich spectral information. Resample images from a total of 13 bands, B1 to B12, into images with a 10-m resolution. To accurately extract the water body boundaries, the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) was applied within the study area [27,28]. NDWI is a normalized ratio index based on the green and near-infrared spectral bands. It is used to highlight water bodies within images. The formula for calculating NDWI is as follows:
where RrsGreen represents the reflectance values in the green spectral band; RrsNIR represents the reflectance values in the near-infrared spectral band; NDWI values typically range from −1 to 1, with higher values indicating a higher likelihood of water presence.
2.3.2. Feature Preference
Feature optimization is the process of screening feature factors that respond well to water quality parameters (PC) for modeling. Cross-validation was employed on the chosen feature factors, with data randomly divided into 60% for model training and 40% for validation. Keeping the independent validation results separate from the model’s training provided a more objective assessment of the model’s performance.
2.3.3. Model Building
BPNN is a feed-forward neural network composed of an input layer, hidden layers, and an output layer. It iteratively adjusts network weights and thresholds to approximate the target function, thereby achieving the intended model output. The structure of a single hidden layer is shown in Figure 3. Feature variables are input into the left side of the input layer, passed through Equation (1) to enter the hidden layer, where they undergo activation through Equations (2) and (3) before being transmitted to the output layer. After passing through another activation function (Equation (4)), the predicted values are generated. Model predictive capabilities are optimized based on the Mean Squared Error (MSE) between predicted and actual values. The BPNN possesses strong self-learning and self-adjustment capabilities, enabling it to exhibit robust fitting and adaptability when dealing with complex data [29,30]. In cases where predicted values deviate from expected values, the error is backpropagated using the gradient descent method to update weights and thresholds. This process influences the final prediction result of BPNN and can be one of the reasons why BPNN is prone to getting stuck in local minima [31].
where Ij and Ik represent the input values of the hidden layer and output layer, respectively; yj and yt stand for the output values of the hidden layer and output layer, respectively; ω correspond to the weights; β is the thresholds; f is the activation functions, with each neuron in the same layer sharing the same activation function; n and h refer to the number of nodes in the input layer and hidden layer, respectively.
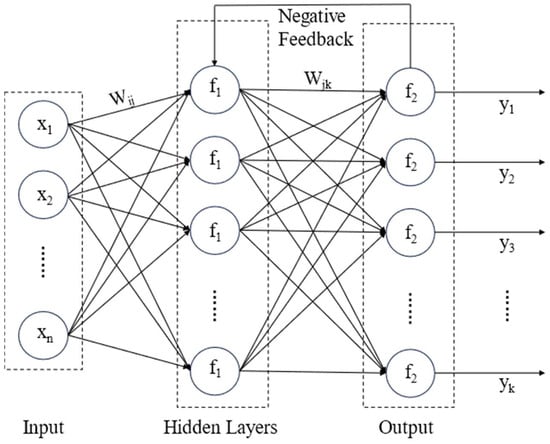
Figure 3.
Structure of BPNN with a hidden layer.
To address the issue of BPNN being susceptible to local minima, many scholars have developed intelligent optimization algorithms such as the Genetic Algorithm (GA) [32], Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm (ACO) [33], and the Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm (PSO) [34]. These optimization algorithms aim to transition the initial weights and thresholds of BPNN from a random state to a well-established state. Compared with other intelligent optimization algorithms, the position of each particle in PSO is updated based on the historical experience of both individual particles and entire group, and the introduction of the inertia weight ω of the speed as in Equation (6). The speed of movement of the particle decreases with an increasing number of iterations. This ensures that particles explore a broader range of possibilities during the early optimization stages while accurately converging to the optimal position in the later stages. At this point, the particle’s position represents the optimally initialized weights and thresholds for BPNN [35,36]. This process can be expressed by Equations (7) and (8).
where ω is the inertia weight; ωmax, ωmin represent the maximum and minimum inertia weight; t is the number of current iterations; tmax is the total number of iterations; Vi is the velocity of the particle; r1 and r2 are random numbers distributed in the interval [0, 1]; c1 and c2 are the acceleration factors, which are non-negative constants; Pi is the current local optimal position of the ith particle; Gi is the global optimal position of the particle swarm; and represents the position of the ith particle in the tth iteration.
In this study, a PSO-optimized BPNN was constructed using 30 particles, with a maximum of 100 iterations at a speed of 1, and using inertia weights in the range of [0.4, 0.9]. The optimization process is shown in Figure 4. Simultaneously, both a BPNN and an SVR model were constructed. Model accuracy validation was conducted, followed by a comparative analysis to assess the performance of the PSO-optimized BPNN and evaluate its capacity for PC concentration retrieval. Detailed information regarding the code and hyperparameter settings for constructing PSO-BPNN can be found in Table A3.
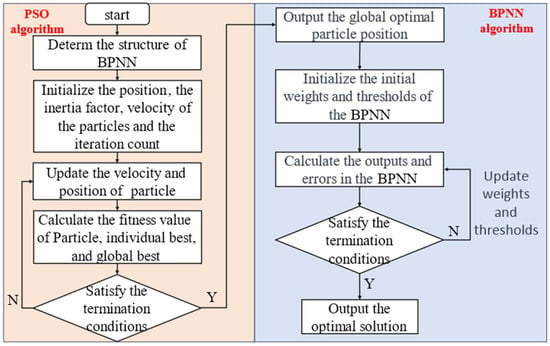
Figure 4.
Flowchart of BPNN optimized with PSO.
2.3.4. Model Validation and Evaluation
The coefficient of determination (R2), mean absolute error (MAE), and root mean square error (RMSE) were used to evaluate the performance of the PC concentration retrieval model, and the formulas for each evaluation metric are as follows:
where yi is the measured PC concentration; yi,pre is the predicted PC concentration; and ymean is the average of the measured PC concentrations.
3. Results
3.1. Results of Correlation Analysis
The acquired bands and spectral indices were subjected to a Pearson correlation analysis with measured PC concentrations. A strong correlation between two variables is indicated by a Pearson correlation coefficient closer to 1 in absolute value. The statistical results are presented in Table 4. Among the single bands, B4 had the highest correlation of 0.646. Following closely were B1 and B3 with correlations of 0.633 and 0.640, respectively. This differs from previous researchers [37,38,39], who based their monitoring of PC concentration on the prominent absorption valley of PC in the spectral curve at 620 nm. At very low PC concentrations, the spectral characteristics of PC appear at 665 nm. This precisely demonstrates that the spectral feature position of PC changes with variations in the PC concentration [17], rather than consistently residing at 620 nm. Among the spectral indices, the correlation was strongest for (B2 + B8)/B4, measuring −0.651. Notably, the spectral indices with strong correlations to measured PC concentrations were associated with the B1, B3, and B4 bands. Therefore, the retrieval model was constructed using B1, B3, and B4 bands as input feature vectors.

Table 4.
Statistical analysis of band and spectral index correlations with PC concentrations. NDVI stands for Normalized Difference Vegetation Index; NDWI stands for Normalized Difference Water Index; MNDWI refers to Modified Normalized Difference Water Index.
3.2. PC Retrieval Results and Validation
Selecting automatically monitored data with good weather conditions and the corresponding satellite overpass times reduced systematic errors caused by data mismatches. The samples were randomly divided into a 6:4 ratio using cross-validation, with 60% utilized for model training and the remaining data used to assess the generalization ability of each PC concentration retrieval model. The retrieval results for each model are presented in Table 5, while the scatter plot depicting the retrieval values against the measured values for model validation is shown in Figure 5.

Table 5.
Retrieval results of PC concentration model.
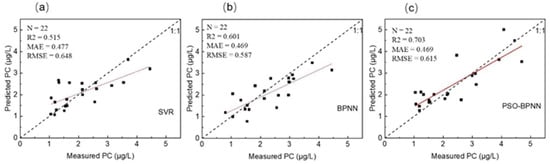
Figure 5.
Evaluation of PC concentration retrieval model performance. (a) SVR model; (b) BPNN model; (c) PSO-BPNN model.
The results indicate that both PSO-BPNN and BPNN outperformed SVR in terms of retrieval performance. This could be attributed to SVR’s heightened sensitivity to noise in the data [40]. The objective of SVR regression is to maximize the margin while maintaining the predicted values within a certain range. However, noisy data can have a greater impact, leading to overfitting and insufficient generalization during model training. Compared to all the machine learning models, BPNN showed better performance in terms of RMSE. However, the model displayed underestimation when the PC concentration exceeded 2.5 μg/L, resulting in suboptimal fitting. PSO-BPNN improved the model’s fitting capability by 17% compared to BPNN and outperformed SVR by 36.5%. The predicted values closely matched the measured values, predominantly distributed around the 45-degree line, showing a better fit as well as stronger generalization capabilities (R2 = 0.703, MAE = 0.469, RMSE = 0.615). This illustrates that PSO can optimize BPNN, mitigating the problem of getting stuck in local minima and providing a distinct advantage for low PC concentration remote sensing retrieval in complex coastal optical environments. Consequently, PSO-BPNN was chosen as the optimal PC retrieval model.
3.3. Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of PC Concentration
Based on the 2017 Qinzhou Municipal State of the Marine Environment Bulletin, the PSO-BPNN inversion model was employed to track the PC concentration during the P. glo red tide event in Qinzhou Bay from November to December 2017. The distribution of PC concentrations is shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
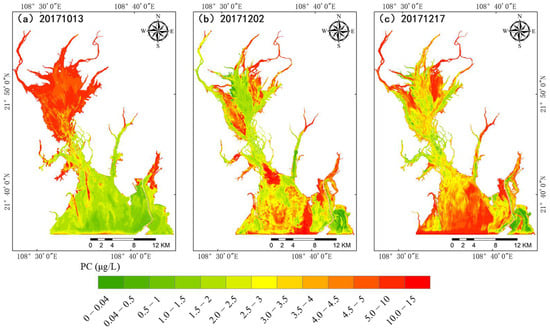
Figure 6.
Retrieval map of PC concentration in Qinzhou Bay. (a) The image PC retrieval concentration distribution map obtained on 13 October 2017; (b) the image PC retrieval concentration distribution map obtained on 2 December 2017; (c) the image PC retrieval concentration distribution map obtained on 17 December 2017.
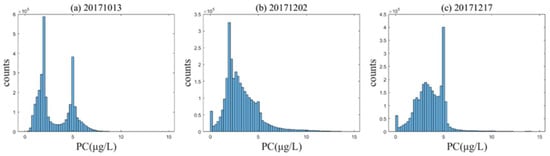
Figure 7.
Histogram of PC concentrations. (a–c) are images from 13 October 2017, 2 December 2017, and 17 December 2017, respectively.
According to Figure 6 and Figure 7, it is evident that the maximum PC concentration in Qinzhou Bay was 14.81 μg/L. PC concentrations below 1 μg/L were more prevalent in the outer bay, especially near coastal ports. The majority of the water areas maintained PC concentrations between 2 and 5 μg/L. Generally, the PC concentration was higher in the inner bay, gradually decreasing from the inner bay towards the outer bay. However, the PC concentration is influenced by external environmental factors, such as rainfall, oyster culture, hydrodynamic changes, and the outbreak of P. glo red tides, amongst others. As shown in Figure 8, on 2 December 2017, there was a generally low PC concentration around the oyster raft culture area. This phenomenon may be attributed to oysters competing for nutrient resources with cyanobacteria during the growth process and even feeding on cyanobacteria [41,42], thereby limiting the survival space of cyanobacteria. During the outbreak of P. glo red tide, it can be clearly seen that the undetected area of PC concentration significantly expanded by 4.97 km2, particularly concentrated around the Sandun Harbor Pier in the southeast area of Qinzhou Bay (coinciding with the location of the outbreak of P. glo). This indicates that the P. glo outbreak can suppress the growth of blue-green algae. Due to the obstructive nature of the reclaimed land in the enclosed sea area, tidal currents are notably weaker. Local tidal currents change direction due to the alteration of the flow direction intersecting with the tidal current in the fairway. The area of the P. glo outbreak resembles a rotating eddy current, suggesting that the formation of this eddy current morphology is likely related to the hydrodynamic environment of Qinzhou Bay.
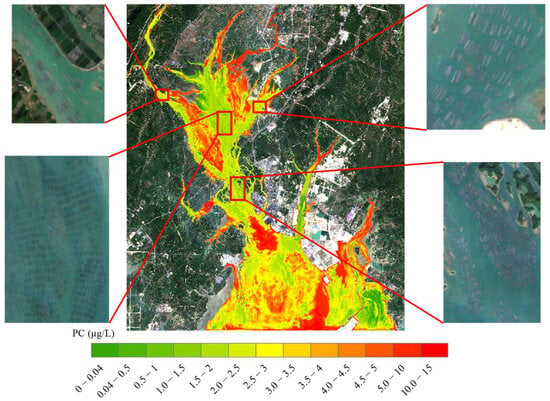
Figure 8.
Retrieval map of PC concentration in Qinzhou Bay on 2 December 2017.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Total Precipitation and Temperature on PC Concentration
The hourly reanalysis data collected from the official website of ERA5 were collated into daily mean meteorological data. Meteorological data for the retrieval image day and the preceding seven days were obtained, as shown in Figure 9.
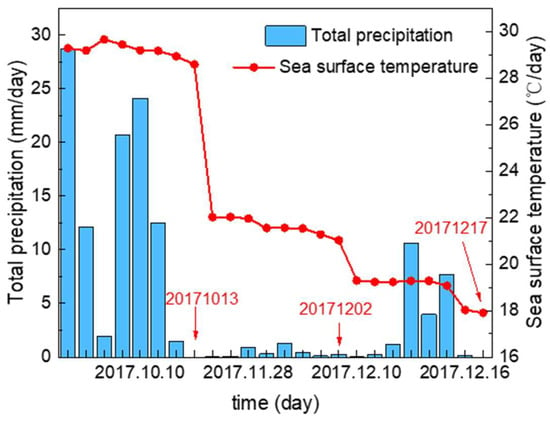
Figure 9.
Daily mean sea surface temperature and total precipitation.
Combined with the PC concentration retrieval results, it can be found that the PC concentration is affected by temperature to a certain extent, as temperature affects the activity of algal cell reproduction and metabolism. When the temperature dropped to 20 °C, the undetected area of PC concentration increased significantly. But in general, the correlation between PC concentration and temperature is not significant. This can potentially be attributed to continuous rainy weather, causing water bodies with high cyanobacterial abundance from inland areas to converge with the river and flow into Qinzhou Bay. This phenomenon is especially obvious on October 13. Before the outbreak of P. glo red tide, the surface PC concentrations in the bay are relatively low. The influence of rainfall relieves the phosphorus limitation for cyanobacterial growth in the inner bay, leading to a rapid increase in PC concentration within the inner bay. As the water flows towards the neck of the bay and the outer bay, PC concentrations gradually decreased. This resulted in a bimodal pattern in PC concentration statistics (Figure 7a). Over time, due to the constraints of low temperatures and the competition succession of P. glo, the undetected area of PC concentration continued to expand in the outbreak area of P. glo. So, low temperatures lead to a decrease in PC concentration, while precipitation causes an increase in PC concentration.
4.2. Effect of Nitrate on PC Concentration
Relevant studies have shown that during P. glo outbreaks, a substantial consumption of nitrates occurs to form cysts [43]. P. glo outbreaks not only compete for the living space of cyanobacteria, but also in the presence of a large number of cysts, float on the surface of the seawater, blocking the sunlight required by cyanobacteria for photosynthesis and leading to a decline in their abundance. This observation aligns with Figure 10, where the best correlation between PC and nitrate is the strongest, reaching 0.71. Compared with 2 December, on 17 December, the continuous rainfall had an impact. It caused inland waters with low inorganic phosphorus and high inorganic nitrogen from the Qin River and Maoling River to flow into Qinzhou Bay [44]. This influx resulted in an overall increase in PC concentration throughout Qinzhou Bay. Near Sandun Harbor (Figure 11), the semi-exchange period of water significantly decreases due to the effects of land reclamation before the rainfall. PC concentrations stay below 1 μg/L, consistent with the findings of Lv et al.’s dye diffusion study [45]. After the rainfall, influenced by surface runoff, the water’s exchange capacity increases, allowing for the replenishment of nutrients in the water. As a result, PC concentrations near the runoff areas significantly increase.
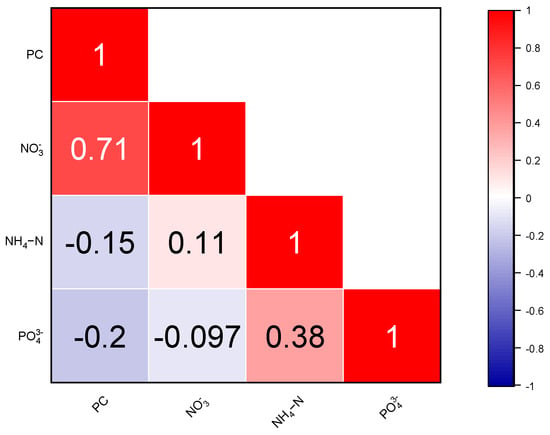
Figure 10.
Correlation analysis of nutrient salt and PC concentrations.
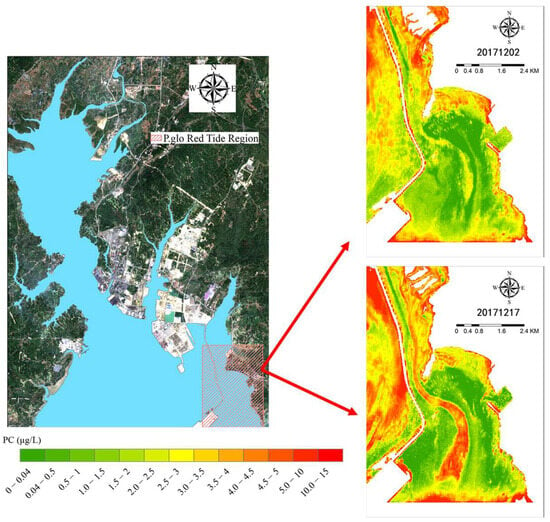
Figure 11.
PC concentration of undetected zone.
4.3. Early Warning of P. glo Red Tide Outbreaks in Qinzhou Bay
In summary, there is a close correlation between P. glo red tides and the spatial distribution pattern of PC concentration. According to the PC statistical results in Figure 7, it is revealed that during the occurrence of P. glo red tide, the area with PC < 0.9 μg/L increased exponentially, the area with undetected PC concentration (PC < 0.04 μg/L) increased by 4.97 km2, and the area with undetected PC concentration aligns with the outbreak area of P. glo red tide. This result indicates that the variation in PC concentration serves as an indicator for P. glo red tide outbreaks. In the P. glo red tide event, rainfall and temperature also play a contributing role, but rainfall is not a necessary condition for P. glo outbreaks, as direct discharge of industrial wastewater can provide the necessary nutrients for P. glo outbreaks. Based on these characteristics, with PC concentration variations as the main factor, and sea surface temperature as the secondary factor, a simple early warning threshold can be proposed for the P. glo red tide outbreak in Qinzhou Bay: PC < 0.9 μg/L and temperature T < 20 °C. Such an early warning system could play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of harmful algal blooms on marine ecosystems, fisheries, and coastal areas.
Building a system capable of directly forecasting P. glo red tide outbreaks is a long-term vision for marine management. To enhance the accuracy of such forecasting, consideration still needs to be given to other factors that influence P. glo outbreaks. For instance, heavy metals in seawater contribute to the synthesis of complexes that accelerate the formation of the cyst outer wall in P. glo. In a study conducted by Xu et al. [46], the concentrations of six heavy metals (Zn, Cd, Cr, Hg, As, Cu) in surface seawater and phytoplankton bodies in Qinzhou Bay were investigated. The results indicated that Cd levels exceeded standards at monitoring points near Sandu Harbor, which could also be one of the factors contributing to P. glo outbreaks.
In areas with low PC concentrations, optical substances like suspended matter and chlorophyll-a have a significant impact on PC concentration inversion. Future research should focus on eliminating the influence of other substances on PC spectral characteristics and developing inversion models better suited for lower PC concentrations. Further exploration is needed for P. glo red tide warning methods, and future studies could investigate seawater salinity, dissolved oxygen levels, and heavy metal concentrations to enhance P. glo red tide forecasting capabilities.
5. Conclusions
(1) Compared with the performance of different models, the BPNN model optimized through PSO significantly enhanced the accuracy of PC concentration retrieval. In the validation set, the mean absolute error (MAE) and the root mean square error (RMSE) were 0.469 and 0.615, respectively, demonstrating that its retrieval accuracy meets the requirements for the remote sensing of low PC concentrations.
(2) The PC concentration is primarily concentrated around 2~5 μg/L, exhibiting a distribution pattern where the inner bay > neck of bay > outer bay in Qinzhou Bay. However, the PC concentration is also affected by the P. glo outbreaks. Therefore, based on algal competition relationships, we propose a simple red alert threshold for predicting P. glo red tide. This approach enables a rapid preliminary assessment of the P. glo red tide risk in Qinzhou Bay and enhances our ability to manage coastal areas effectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Y.; methodology, Y.L.; software, H.C.; validation, M.W.; formal analysis, Z.H.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L.; writing—review and editing, W.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by scientific research capacity building project for Beibu Gulf Marine Ecological Environment Field Observation and Research Station of Guangxi under Grant No. 23-026-271.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The Sentinel-2 MSI Image data sets are available from https://scihub.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 8 March 2023); the ERA5 data are available from https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-single-levels?tab=overview (accessed on 19 July 2023); the codes for building the machine learning regression model are available from the authors; water quality data from automated monitoring stations are not publicly available due to the inclusion of sensitive information.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
The spectral information for Sentinel-2 bands can be found in Table A1.

Table A1.
Sentinel-2 satellite image band information.
Table A1.
Sentinel-2 satellite image band information.
| Bands | Resolution (m) | S2A Central Wavelength (nm) | S2B Central Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1-Aerosols | 60 | 443.9 | 442.3 |
| B2-Blue | 10 | 496.6 | 492.1 |
| B3-Green | 10 | 560 | 559 |
| B4-Red | 10 | 664.5 | 665 |
| B5-Red Edge 1 | 20 | 703.9 | 703.8 |
| B6-Red Edge 2 | 20 | 740.2 | 739.1 |
| B7-Red Edge 3 | 20 | 782.5 | 779.7 |
| B8-NIR | 10 | 835.1 | 833 |
| B8A-Red Edge 4 | 20 | 864.8 | 864 |
| B9-Water vapor | 60 | 945 | 943.2 |
| B10-SWIR/Cirrus | 60 | 1375.5 | 1376.9 |
| B11-SWIR 1 | 20 | 1613.7 | 1610.4 |
| B12-SWIR 2 | 20 | 2202.4 | 2185.7 |
The selected images and the corresponding water quality monitoring times are shown in Table A2.

Table A2.
Data source information on remote sensing images.
Table A2.
Data source information on remote sensing images.
| Monitoring Date | Image Date | Image Quality |
|---|---|---|
| 18 December 2015 | 18 December 2015 | No cloud |
| 2 November 2016 | 2 November 2016 | Less than 10% cloud |
| 13 October 2017 | 13 October 2017 | No cloud |
| 27 November 2017 | 27 November 2017 | Less than 10% cloud |
| 2 December 2017 | 2 December 2017 | No cloud |
| 17 December 2017 | 17 December 2017 | No cloud |
| 22 March 2018 | 22 March 2018 | No cloud |
| 3 October 2018 | 3 October 2018 | Less than 10% cloud |
| 2 November 2018 | 2 November 2018 | No cloud |
| 22 November 2018 | 22 November 2018 | No cloud |
| 17 December 2018 | 17 December 2018 | No cloud |
| 9 August 2019 | 9 August 2019 | No cloud |
| 23 September 2019 | 23 September 2019 | No cloud |
| 28 September 2019 | 28 September 2019 | No cloud |
| 13 October 2019 | 13 October 2019 | No cloud |
| 18 October 2019 | 18 October 2019 | No cloud |
| 7 November 2019 | 7 November 2019 | No cloud |
| 22 November 2019 | 22 November 2019 | No cloud |
| 2 December 2019 | 2 December 2019 | No cloud |
| 7 December 2019 | 7 December 2019 | No cloud |
| 12 December 2019 | 12 December 2019 | No cloud |
| 18 December 2015 | 18 December 2015 | No cloud |
| 2 November 2016 | 2 November 2016 | Less than 10% cloud |
| 13 October 2017 | 13 October 2017 | No cloud |
Please refer to Table A3 for detailed parameter settings of the BPNN model.

Table A3.
BPNN parameter configuration.
Table A3.
BPNN parameter configuration.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Hidden layer | 1 |
| Neurons in hidden layer | 10 |
| Training epochs | 1000 |
| Training goal | 1 × 10−6 |
| Learning rate | 0.01 |
| Activation function | tansig and purelin |
| Training algorithm | Levenberg–Marquardt |
| Loss function | mse |
References
- Rousseau, V.; Chretiennot-Dinet, M.-J.; Jacobsen, A.; Verity, P.; Whipple, S. The Life Cycle of Phaeocystis: State of Knowledge and Presumptive Role in Ecology. Biogeochemistry 2007, 83, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Fu, S.; Song, X.; Tong, M.; Jiang, T. Stress Regulation of Photosynthetic System of Phaeocystis globosa and Their Hemolytic Activity. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 2164–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, O.; Economou, T.; Torres, R.; Ashton, I.; Brown, R. Quantifying Spatio-Temporal Risk of Harmful Algal Blooms and Their Impacts on Bivalve Shellfish Mariculture Using a Data-Driven Modelling Approach. Harmful Algae 2023, 121, 102363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, J. Historical Occurrence of Algal Blooms in the Northern Beibu Gulf of China and Implications for Future Trends. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T. Morphological Characteristics of Colony for Phaeocystis globosa and the Influences of Light and Calcium Ion on Formation and Cell Distribution of Colony. Master’s Thesis, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M. The Key Influencing Factors in Solitary Cell and Colony Stages of Phaeocystis globosa in Beibu Gulf. Ph.D. Thesis, Guangxi University, Nanning, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Shen, P.; Wang, Y. Taxonomy and lifecycle of genus Phaeocystis (prymnesiophyceae). J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2001, 9, 174–184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.-F.; Han, B.-B.; Shi, R.-J.; Wu, F.-X.; Rao, Y.-Y.; Dai, M.; Huang, H.-H. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Key Molecular Events Driving Phaeocystis Globosa Bloom and Dissipation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Lai, J.; Chen, B.; Jinag, F.; Xu, M. Molecular Identification of Phaeocystis from Beibu Gulf Based on 18S rDNA Sequences. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2016, 24, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, F.; Kang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Geng, H.; Guo, W.; Zhou, M. Relationship between seasonal variation of pico-and nano-phytoplankton assemblages and Phaeocystis red tides in Beibu Gulf. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2019, 50, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, D.J.; West, N.J. Molecular Ecology of the Marine Cyanobacterial Genera Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Qi, L.; Chen, B.; Zhao, F.; Bao, Q.; Wu, J. Codon Usage Patterns and Adaptive Evolution of Marine Unicellular Cyanobacteria Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2012, 62, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Tan, S.; Yi, Y.-C.; Hsiang, C.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chang, J.-S.; Ng, I.-S. High-Level Production and Extraction of C-Phycocyanin from Cyanobacteria Synechococcus Sp. PCC7002 for Antioxidation, Antibacterial and Lead Adsorption. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazer, A.N.; Fang, S. Chromophore Content of Blue-Green Algal Phycobiliproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 248, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simis, S.G.H.; Ruiz-Verdu, A.; Antonio Dominguez-Gomez, J.; Pena-Martinez, R.; Peters, S.W.M.; Gons, H.J. Influence of Phytoplankton Pigment Composition on Remote Sensing of Cyanobacterial Biomass. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Duan, H.; Cannizzaro, J.; Ma, R. A Novel MERIS Algorithm to Derive Cyanobacterial Phycocyanin Pigment Concentrations in a Eutrophic Lake: Theoretical Basis and Practical Considerations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 298–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N.; Carvalho, L.; Codd, G.A.; Maberly, S.C. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Cyanobacterial Pigments as Indicators for Cell Populations and Toxins in Eutrophic Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2705–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Gritz, Y.; Merzlyak, M.N. Relationships between Leaf Chlorophyll Content and Spectral Reflectance and Algorithms for Non-Destructive Chlorophyll Assessment in Higher Plant Leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 160, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. A Novel Remote Sensing Algorithm to Quantify Phycocyanin in Cyanobacterial Algal Blooms. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 114003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Yan, S.; Cui, Y.; Wang, H. Annual dynamic remote sensing monitoring of phycocyanin concentration in Lake Chaohu based on Sentinel-3 OLCI images. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Yan, S. Dynamic Monitoring of Phycocyanin Concentration in Chaohu Lake of China Using Sentinel-3 Images and Its Indication of Cyanobacterial Blooms. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Tedesco, L.; Hall, B.; Li, Z. Hyperspectral Retrieval of Phycocyanin in Potable Water Sources Using Genetic Algorithm-Partial Least Squares (GA-PLS) Modeling. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 18, 368–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, J.; Duan, H.; Baek, S.; Kim, M.S.; Jeon, T.; Kwon, Y.S.; Lee, H.; Cho, K.H. A Convolutional Neural Network Regression for Quantifying Cyanobacteria Using Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R.; Xu, M.; Zhan, S.; Johansen, R.; Liu, H.; Tong, S.; Yang, B.; Shu, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; et al. Comparison of Satellite Reflectance Algorithms for Estimating Turbidity and Cyanobacterial Concentrations in Productive Freshwaters Using Hyperspectral Aircraft Imagery and Dense Coincident Surface Observations. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Tang, L.-Q.; Wang, C.-H.; Liu, C.-J.; Dong, Z.-D. Combined Effects of Channel Dredging, Land Reclamation and Long-Range Jetties upon the Long-Term Evolution of Channel-Shoal System in Qinzhou Bay, SW China. Ocean Eng. 2014, 91, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Bao, X.; Zhu, X. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of tidal current in Qinzhou Bay. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2009, 28, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.C. NDWI—A Normalized Difference Water Index for Remote Sensing of Vegetation Liquid Water from Space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Li, Y.; Qian, J.; Liu, Y. A New Accuracy Evaluation Method for Water Body Extraction. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 7311–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Sun, X.; Wu, Q.M.J. Difference Co-Occurrence Matrix Using BP Neural Network for Fingerprint Liveness Detection. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 5157–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Zhang, J. BP Neural Network Prediction Model for Suicide Attempt among Chinese Rural Residents. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 246, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, T. Back Propagation Neural Network with Adaptive Differential Evolution Algorithm for Time Series Forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, D.; Fei, M.; Sorensen, H.; Ren, Y.; Mou, J. Application of GA-BPNN on Estimating the Flow Rate of a Centrifugal Pump. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 119, 105738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, C.; Dong, F.; Wei, P. Numerical Investigation of the Dynamic Responses of Long-Span Bridges with Consideration of the Random Traffic Flow Based on the Intelligent ACO-BPNN Model. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 28520–28529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Xu, L.; Liang, R.; Guo, K.; Cui, B.; Yue, S. Study on internal corrosion rate of oil pipeline based on improved PSO–BPNN. J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2019, 15, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Eberhart, R.C. Empirical Study of Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the 1999 Congress on Evolutionary Computation-CEC99 (Cat. No. 99TH8406), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 July 1999; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 3, pp. 1945–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, C. The Risk of Block Chain Financial Market Based on Particle Swarm Optimization. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 370, 112667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, L.; Song, K. Remote Sensing of Freshwater Cyanobacteria: An Extended IOP Inversion Model of Inland Waters (IIMIW) for Partitioning Absorption Coefficient and Estimating Phycocyanin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R.; Xu, M.; Zhan, S.; Liu, H.; Johansen, R.A.; Tong, S.; Yang, B.; Shu, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; et al. Comparison of Satellite Reflectance Algorithms for Estimating Phycocyanin Values and Cyanobacterial Total Biovolume in a Temperate Reservoir Using Coincident Hyperspectral Aircraft Imagery and Dense Coincident Surface Observations. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddick, C.A.L.; Hunter, P.D.; Dominguez Gomez, J.A.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Presing, M.; Horvath, H.; Kovacs, A.W.; Voros, L.; Zsigmond, E.; Tyler, A.N. Optimal Cyanobacterial Pigment Retrieval from Ocean Colour Sensors in a Highly Turbid, Optically Complex Lake. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Huang, J.; Li, G. On the noise sensitivity of ε-support vector regression. Fire Control Command. Control 2013, 38, 130–132+140. [Google Scholar]
- Avila-Poveda, O.H.; Torres-Arino, A.; Giron-Cruz, D.A.; Cuevas-Aguirre, A. Evidence for Accumulation of Synechococcus elongatus (Cyanobacteria: Cyanophyceae) in the Tissues of the Oyster Crassostrea gigas (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Tissue Cell 2014, 46, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straquadine, N.R.W.; Kudela, R.M.; Gobler, C.J. Hepatotoxic Shellfish Poisoning: Accumulation of Microcystins in Eastern Oysters (Crassostrea virginica) and Asian Clams (Corbicula fluminea) Exposed to Wild and Cultured Populations of the Harmful Cyanobacteria, Microcystis. Harmful Algae 2022, 115, 102236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X. The Key Effect of Nitrate on Phaeocystis globosa Booms in the Beibu Gulf. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Oceanography Researcher, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Qingdao, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D. The Influence Factors for Spatio-Temporal Changes of Nutrients and the Quantitative Reduction of Terrestrial TDN in Qinzhou Bay. Ph.D. Thesis, Guangxi University, Nanning, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, H.; Zhang, S.; Song, D.; Bao, X. The cummulative effect of land reclamation on hydrodynamics in Qinzhou Bay. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2021, 52, 823–833. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Liao, R.; Su, J.; Gong, L. The content and pollution evaluation of six heavy metals in surface water and plankton in the eastern area of Qinzhou Bay. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2017, 48, 960–969. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).