Case Study: Validation of the Spectral-Analysis-of-Surface-Waves Method for Concrete Pavement Condition Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The SASW Method
2.1. The Field Arrangement of SASW Method
2.2. The Data Processing of SASW Method
3. The Field Testing on Concrete Pavement
3.1. The Field Measurement of SASW Method
3.2. The Field Measurement of the FWD Method
3.3. The Axial Compressive Strength Laboratory Test
4. Results and Discussion
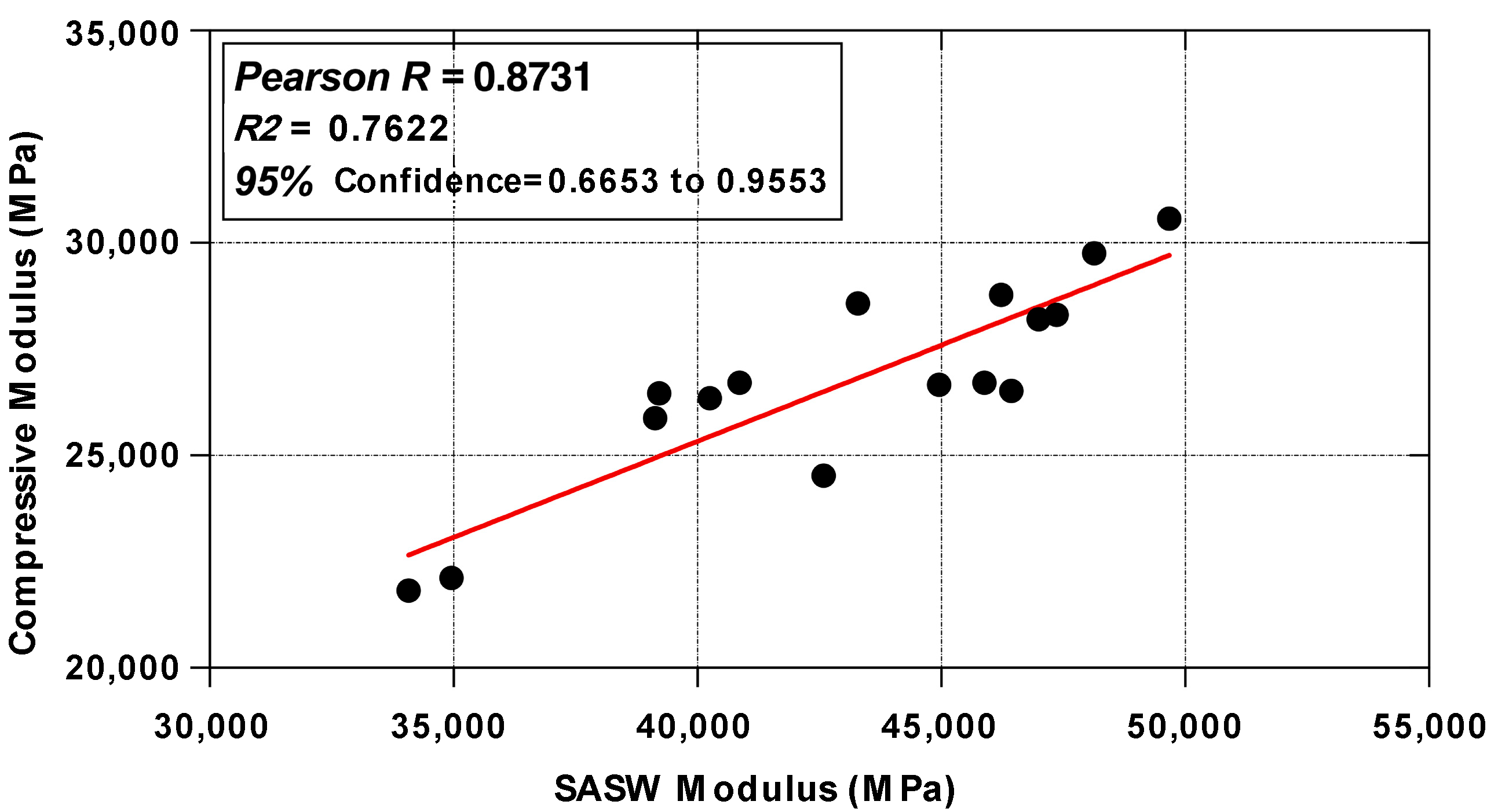
4.1. The Comparative Analysis of SASW Modulus and Compressive Modulus Results
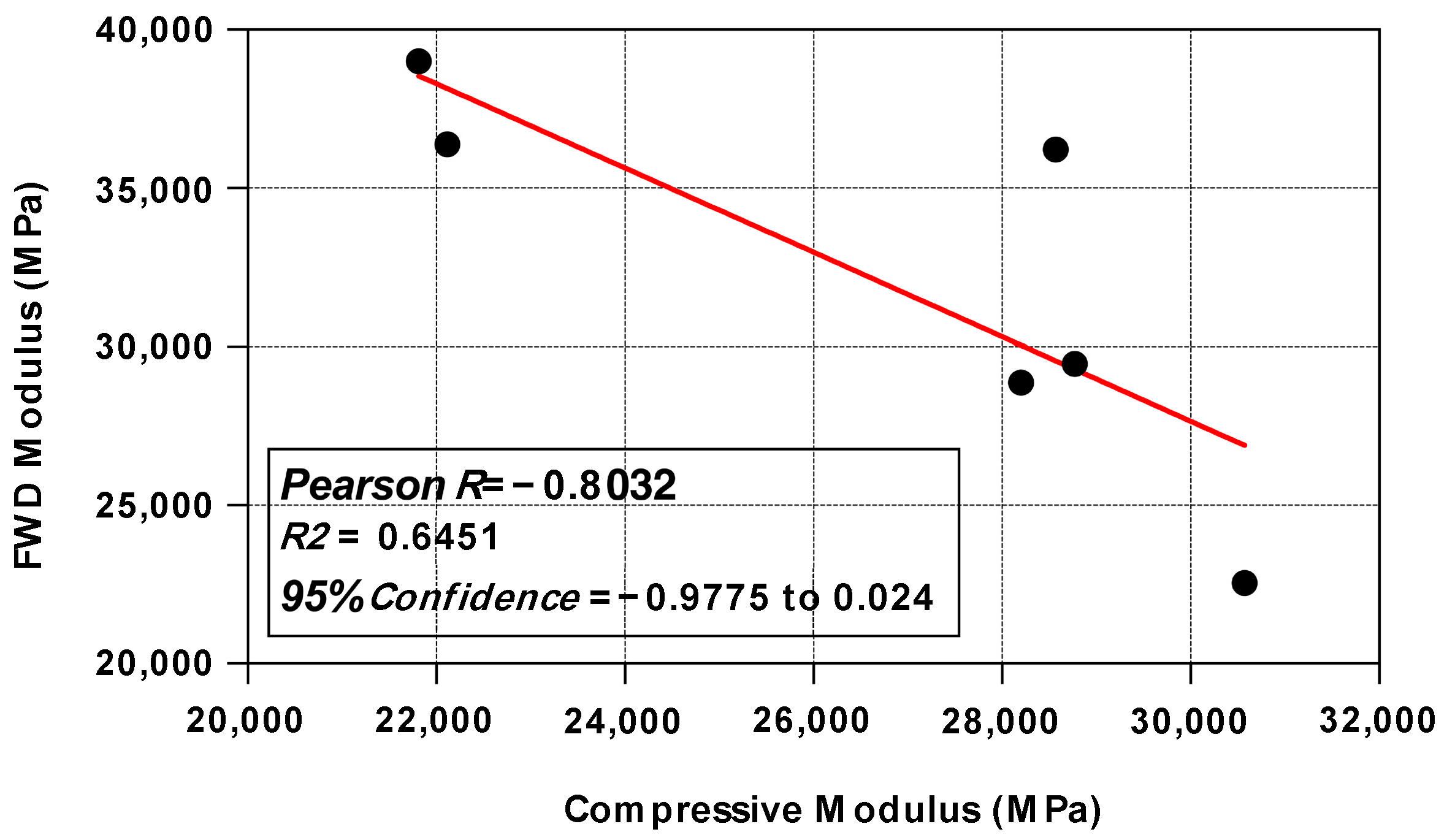
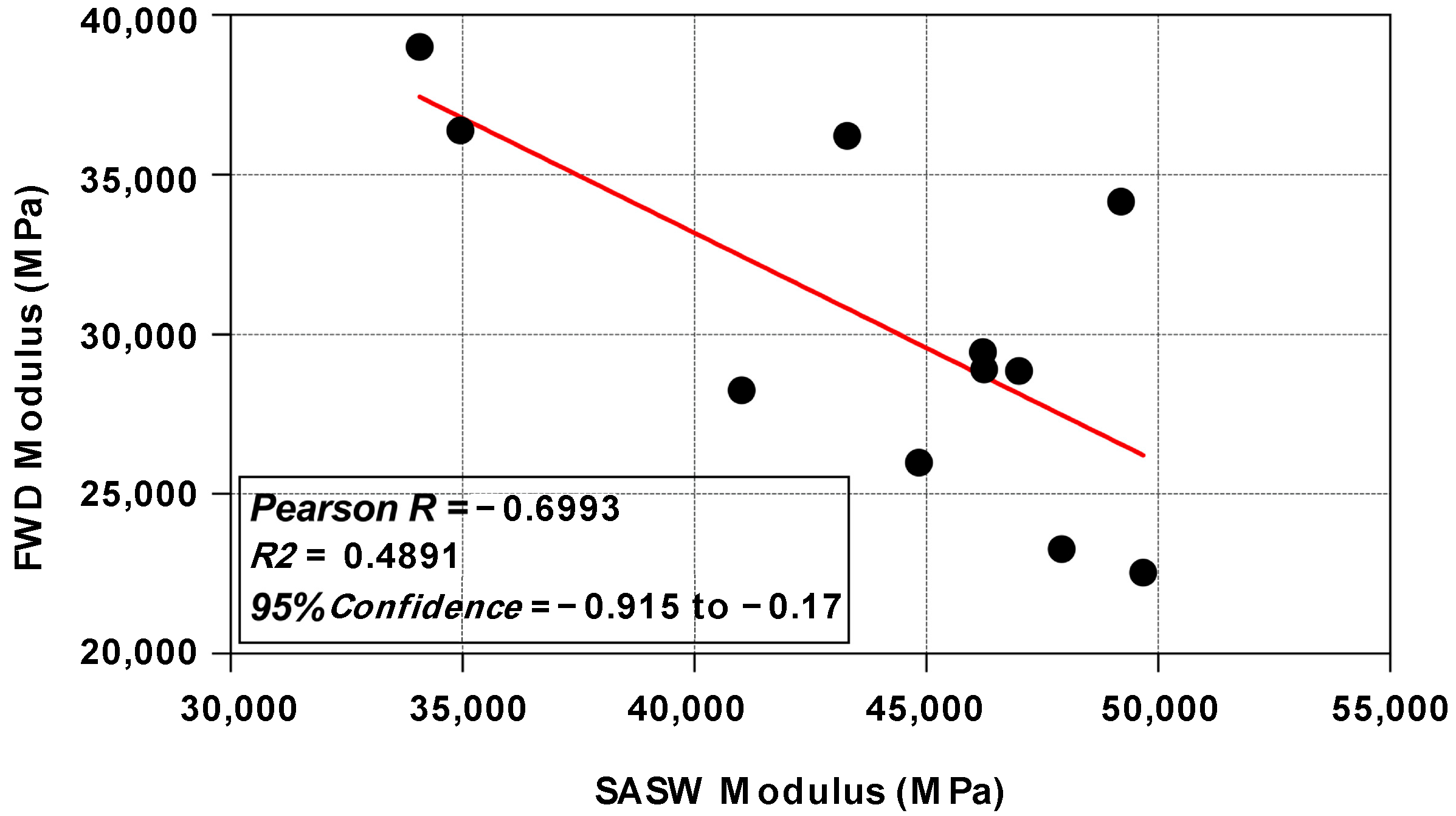
4.2. The Comparative Analysis of SASW Modulus and FWD Modulus
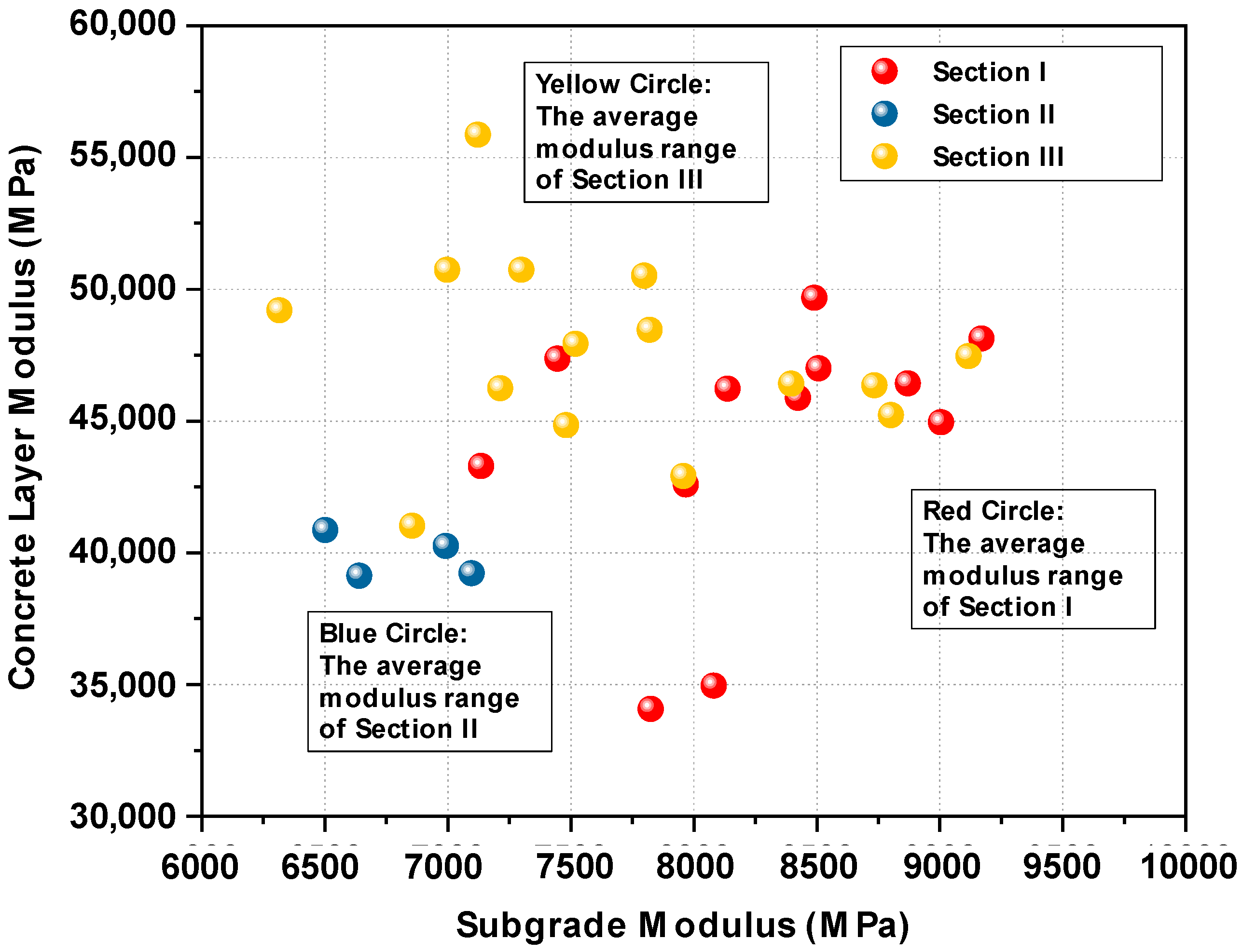
4.3. The Modulus of Three In-Service Pavements
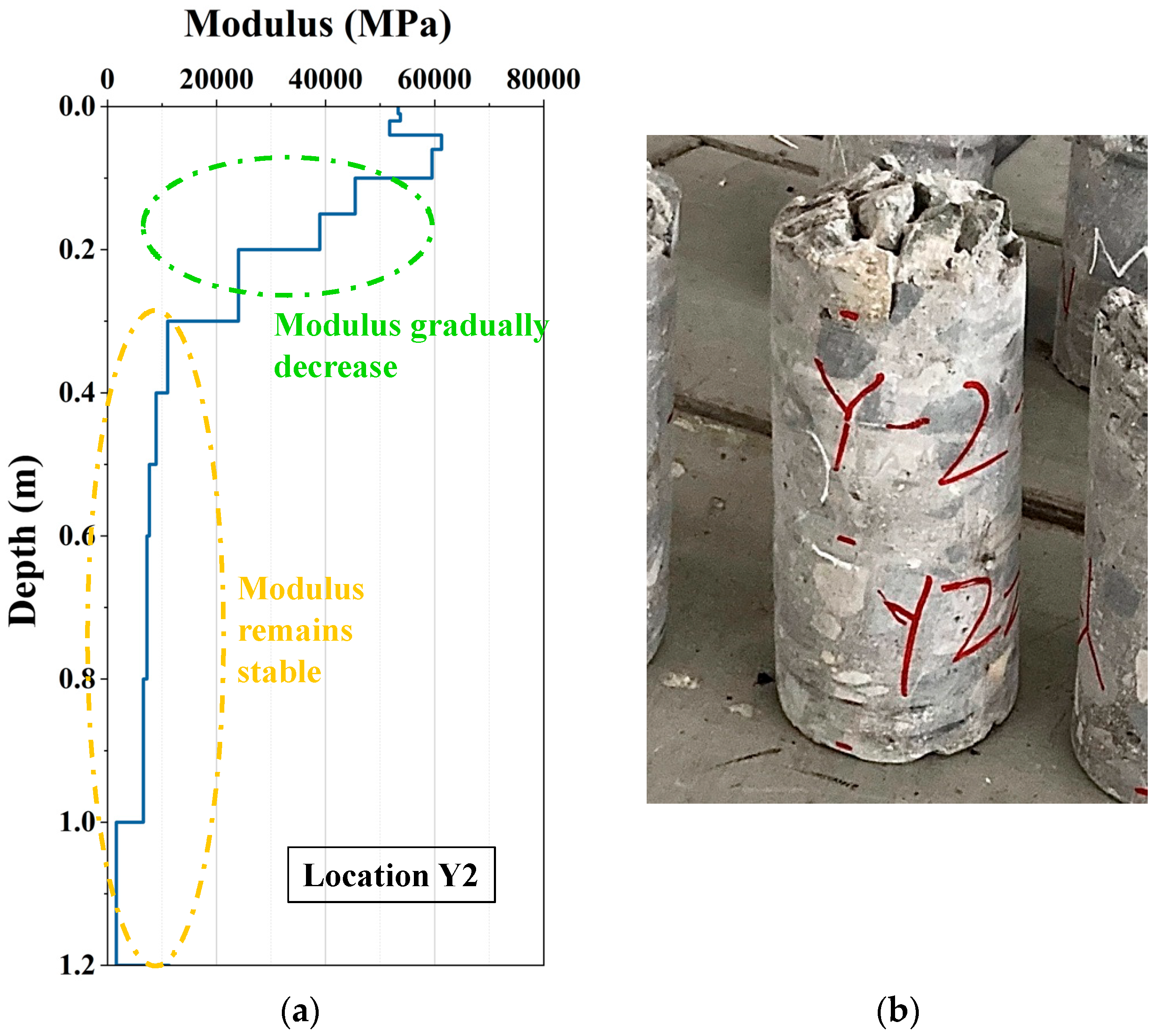
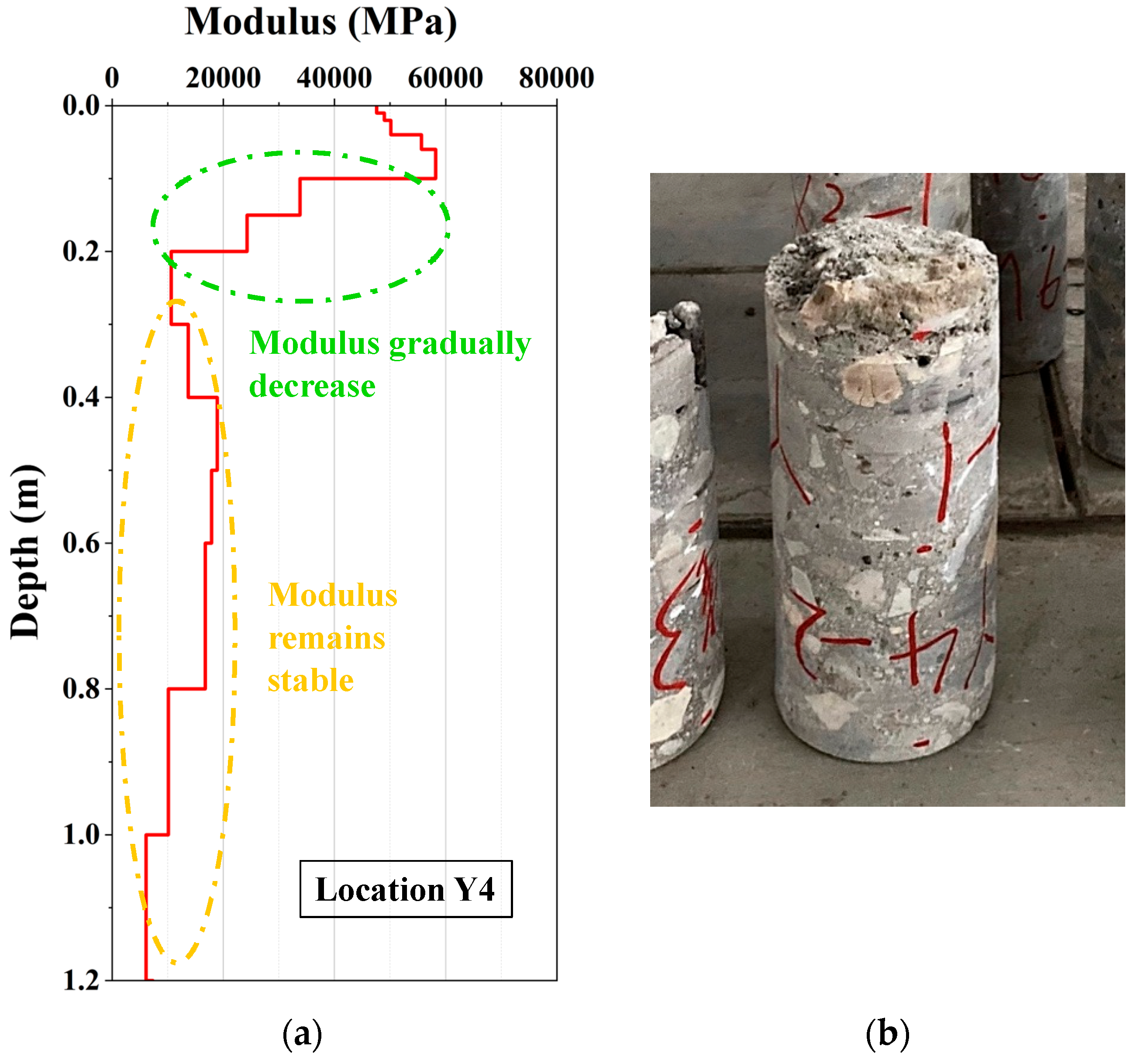
4.4. The Gradient Modulus Analysis from the SASW Method
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salour, F. Moisture Influence on Structural Behaviour of Pavements: Field and Laboratory Investigations; KTH Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tayabji, S.D.; Brown, J.L.; Mack, J.W.; Hearne, T.M., Jr.; Anderson, J.; Murrell, S.; Noureldin, A.S. Pavement Rehabilitation. TRB Committee on Pavement Rehabilitation, TRB Millennium Paper Series; Texas Pavement Preservation Center: Anderson, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gulen, S.; Samy Noureldin, A. Evaluation of Concrete Pavement Rehabilitation Techniques on I-65 in Indiana. Transp. Res. Rec. 2000, 1730, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Eng, P.; Works, P. Concrete Pavement Rehabilitation Techniques and Canadian Based Case Studies; SWOV: Hague, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, F. Local Calibration of Pavement ME and Performance Evaluation of Pavement Rehabilitation and Preservation Asphalt Overlays in Louisiana; Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2021; ISBN 9798845453112. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, F.; Chen, D.-H. Effects of Surface Preparation, Thickness, and Material on Asphalt Pavement Overlay Transverse Crack Propagation. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2009, 36, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Das, A. Nondestructive Testing of Asphalt Pavements for Structural Condition Evaluation: A State of the Art. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 2008, 23, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouad, M.F.; Stokoe, K.H.; Roesset, J.M. Evaluation of Flexible Pavements and Subgrades Using the Spectral-Analysis-of-Surface-Waves (SASW) Method; FHWA, U.S. Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 148–158. [Google Scholar]
- Tarefder, R.A.; Ahmed, M.U. Consistency and Accuracy of Selected FWD Backcalculation Software for Computing Layer Modulus of Airport Pavements. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 7, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarian, S.; Stokoe, K.H.; Hudson, W.R. Use of Spectral Analysis of Surface Waves Method for Determination of Moduli and Thicknesses of Pavement Systems; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1983; Volume 930, pp. 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarian, S.; Stokoe, K.H. In Situ Determination of Elastic Moduli of Pavement Systems by Spectral-Analysis-of-Surface-Waves Method: Practical Aspects; FHWA/TX-86/L3+368-Lf; FHWA, U.S. Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarian, S.; Stokoe, K.H. Nondestructive Testing of Pavements Using Surface Waves. Transp. Res. Rec. 1984, 993, 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, J.; Naskar, T. Effects of Site Stiffness and Source to Receiver Distance on Surface Wave Tests’ Results. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. J. 2015, 77, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, S.; Hollender, F.; Garofalo, F.; Albarello, D.; Asten, M.; Bard, P.-Y.; Comina, C.; Cornou, C.; Cox, B.; Di Giulio, G. Guidelines for the Good Practice of Surface Wave Analysis: A Product of the InterPACIFIC Project. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 16, 2367–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, M.A.; Madun, A.; Zainalabidin, M.H.; Dan, M.F.M.; Talib, M.K.A.; Zahari, M.N.H.; Ambak, K.; Ismail, M.A.M. Soil Compaction Assessment Using Spectral Analysis of Surface Waves (SASW); IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 995, p. 12119. [Google Scholar]
- Ghani, N.A.F.A.; Ismail, N.N.; Azahar, W.N.A.W.; Rahman, F.A.; Azman, A.W.; Yusoff, N.I.M.d.; Rosyidi, S.A.P. Classification of Rigid Pavement at Airport Taxiway Using Shear Wave Velocity and Elastic Modulus Derived from Spectral Analysis of Surface Waves (SASW) Method. J. Fail. Anal. Preven. 2022, 22, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosyidi, S.A.P.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Ismail, N.N.; Yazid, M.R.M. Integrated Time-Frequency Wavelet Analysis and Impulse Response Filtering on SASW Test for Rigid Pavement Stiffness Prediction. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2020, 12, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joh, S.H.; Rahman, N.A.; Magno, K.; Ph, D.; Rahman, N.A.; Ph, D.; Magno, K. Pavement Integrity Assessed by Leaky Surface Waves with Wave Group Interpretation. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2018, 144, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokoe, K.H.; Hwang, S.; Joh, S.-H. Spectral-Analysis-of-Surface-Waves (SASW) Testing to Evaluate vs. Profiles at Geotechnical and Geological Sites. In Proceedings of the 16th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Santiago, Chile, 8–13 January 2017; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, N.N.; Yusoff, N.I.; Anuar, K.; Nayan, M.; Rahman, N.A.; Rosyidi, S.A.P.; Ismail, A. Effect of Input Source Energy and Measurement of Flexible Pavement Deflection Using the SASW Method. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2019, 20, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrell, R.G.; Cox, B.R.; Ii, K.H.S.; Allen, J.J.; Lewis, D. Field Evaluation of the Stiffness of Unbound Aggregate Base Layers in Inverted Flexible Pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. 2003, 1837, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widodo, W. Experimental Investigation of Seismic Parameters and Bearing Capacity of Pavement Subgrade Using Surface Wave Method. Semesta Tek. 2016, 12, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Rosyidi, S. Measurement of Subgrade Stiffness Using the SASW Method. In Proceedings of the Malaysian Geotechnical Conference, Petalingjaya, Malaysia, 14–16 March 2004; pp. 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Shen, S.; Jin, G.; Mao, Q.; Lu, H. Characterization of In Situ Modulus of Asphalt Pavement and Its Relation to Cracking Performance Using SASW Method. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2020, 146, 04020039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walubita, L.F.; Hugo, F.; Epps, A.L. Performance of Rehabilitated Lightweight Aggregate Asphalt Concrete Pavements under Wet and Heated Model Mobile Load Simulator Trafficking: A Comparative Study with the TxMLS; University of Texas at Austin, Center for Transportation Research: Austin, TX, USA, 2000; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Gucunski, N.; Ganji, V.; Maher, M.H. Effects of Obstacles on Rayleigh Wave Dispersion Obtained from the SASW Test. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 1996, 15, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.; Cascante, G.; Hutchinson, D.J. The Innovative Use of Seismic Surface Waves for Void Detection and Material Characterization. In Proceedings of the 15th EEGS Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, Las Vegas, NA, USA, 10–14 February 2002; p. CAV8. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Zhang, J.; Song, S.J.; Kim, H.J. Numerical Simulation of Rayleigh Wave Interaction with Surface Closed Cracks under External Pressure. Wave Motion 2015, 57, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Z. Quantitative Assessment of the Pavement Modulus and Surface Crack Using the Rayleigh Wave Dispersion Curve. Transp. Res. Rec. 2020, 2674, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarian, S.; Stokoe, K.H. In Situ Determination of Elastic Moduli of Pavement Systems by Spectral-Analysis-of-Surface-Waves Method (Theoretical Aspects); Interim Report. No. FHWA/Tx-87/46+ 437-2; U.S. Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; p. 134. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.S.; Lin, F.-B. Spectral Analysis of Surface Wave Response of Multi-Layer Thin Cement Mortar Slab Structures with Finite Thickness. NDT E Int. 2001, 34, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-S.; Seo, W.-S.; Lee, K. IE–SASW Method for Nondestructive Evaluation of Concrete Structure. NDT E Int. 2006, 39, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R. Surface Wave Technique for Measuring the Elastic Properties and Thickness of Roads: Theoretical Development. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 1962, 13, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidale, R.F. The Dispersion of Stress Waves in Layered Media Overlying a Half Space of Lesser Acoustic Rigidity; University of Wisconsin-Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Joh, S.-H.; Stokoe, K.H. Advances in Interpretation and Analysis Techniques for Spectral-Analysis-of-Surface-Waves (SASW) Measurements; Offshore Technology Research Center: College Station, TX, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.; Nazarian, S. Automated Surface Wave Method: Inversion Technique. J. Geotech. Eng. 1993, 119, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTGE30; Testing Methods of Cement and Concrete for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Communications of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2005.
- ACI Committee. Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete (ACI 318-05) and Commentary (ACI 318R-05); American Concrete Institute: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, K.; Shen, S. Falling Weight Deflectometer Dispersion Curve Method for Pavement Modulus Calculation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2023, 381, 20220167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
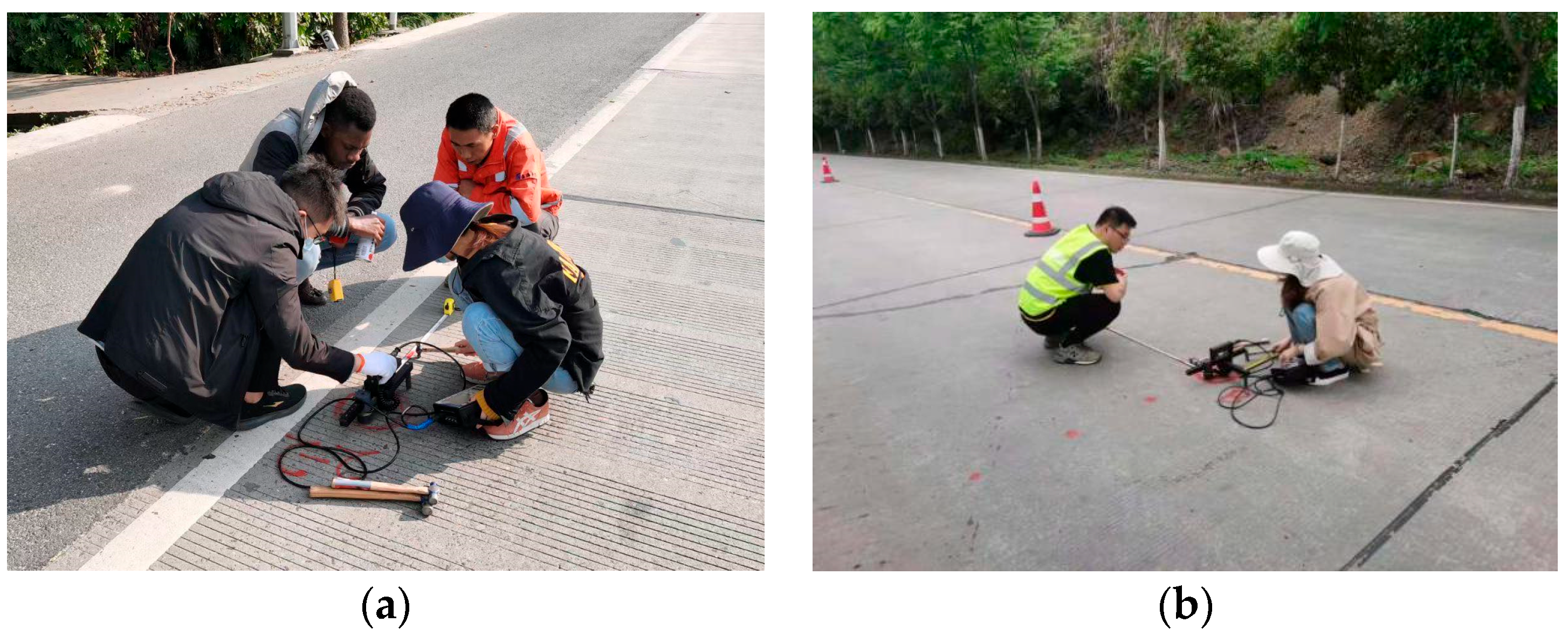
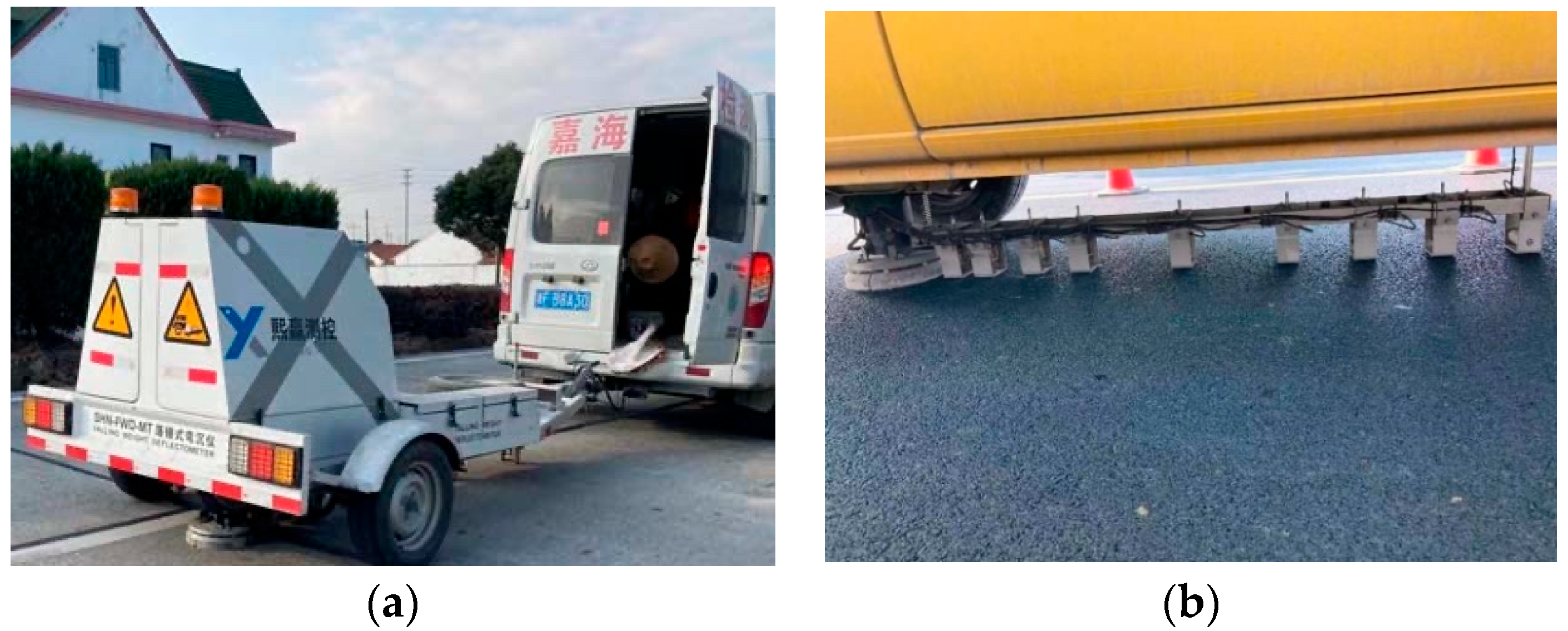
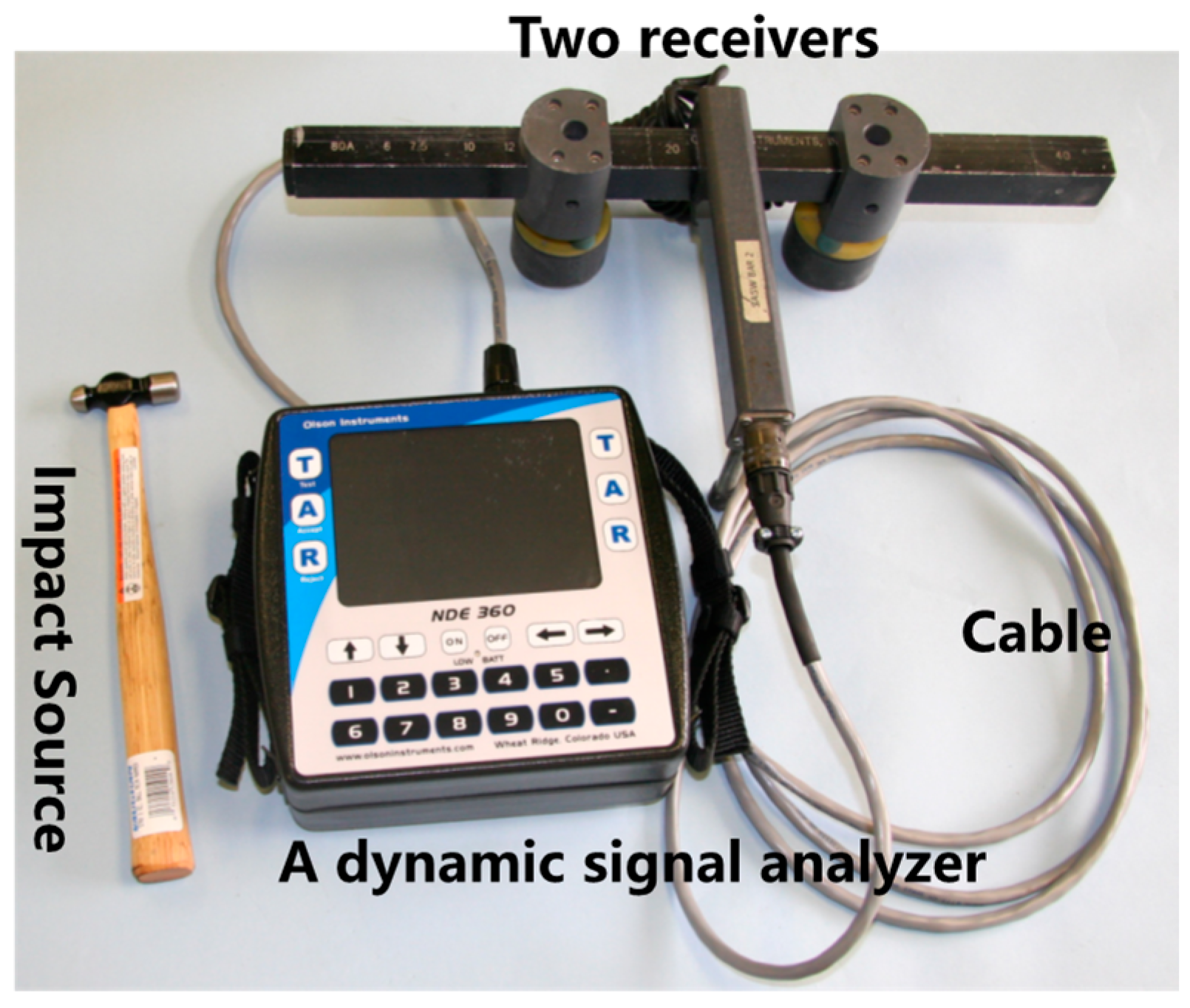



| Pavement | Measurement Location | SASW Method | FWD Method | Core Taking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section I | X1/X2/X3 | |||
| Y1/Y2/Y3 | ||||
| Z1/Z2/Z3 | ||||
| M | ||||
| L | ||||
| N | ||||
| Section II | AA | |||
| BA | ||||
| CA | ||||
| DA | ||||
| Section III | JX1-JX10 | |||
| A | ||||
| B | ||||
| C | ||||
| D | ||||
| E |
| Pavement Section | Measurement Location | SASW (MPa) | Compressive Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Section I | X1 | 43,291 | 28,571 |
| X2 | 34,075 | 21,814 | |
| X3 | 34,958 | 22,118 | |
| Y1 | 49,675 | 30,571 | |
| Y2 | 46,224 | 28,773 | |
| Y3 | 46,996 | 28,201 | |
| Z1 | 46,433 | 26,523 | |
| Z2 | 47,363 | 28,302 | |
| Z3 | 42,591 | 24,521 | |
| M | 45,881 | 26,715 | |
| L | 44,956 | 26,667 | |
| N | 48,131 | 29,759 | |
| Section II | AA | 40,861 | 26,715 |
| BA | 39,218 | 26,467 | |
| CA | 39,131 | 25,881 | |
| DA | 40,254 | 26,344 |
| Pavement Section | Measurement Location | SASW (MPa) | FWD (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Section I | X1 | 43,291 | 36,217 |
| X2 | 34,075 | 39,003 | |
| X3 | 34,958 | 36,384 | |
| Y1 | 49,675 | 22,541 | |
| Y2 | 46,224 | 29,460 | |
| Y3 | 46,996 | 28,870 | |
| Section III | A | 47,922 | 23,277 |
| B | 49,196 | 34,155 | |
| C | 41,020 | 28,259 | |
| D | 44,844 | 25,993 | |
| E | 46,246 | 28,918 |
| Pavement Section | Elastic Modulus (MPa) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section I | Location | X1 | X2 | X3 | Y1 | Y2 |
| Concrete Layer | 43,291 | 34,075 | 34,958 | 49,675 | 46,224 | |
| Subgrade | 7135 | 7825 | 8081 | 8490 | 8137 | |
| Location | Y3 | Z1 | Z2 | Z3 | M | |
| Concrete Layer | 46,996 | 46,433 | 47,363 | 42,591 | 45,881 | |
| Subgrade | 8507 | 8870 | 7445 | 7968 | 8423 | |
| Location | L | N | ||||
| Concrete Layer | 44,956 | 48,131 | ||||
| Subgrade | 9005 | 9170 | ||||
| Section II | Location | AA | BA | CA | DA | |
| Concrete Layer | 40,861 | 39,218 | 39,131 | 40,254 | ||
| Subgrade | 6501 | 7096 | 6640 | 6992 | ||
| Section III | Location | JX-1 | JX-2 | JX-3 | JX-4 | JX-5 |
| Concrete Layer | 46,352 | 48,462 | 47,457 | 42,912 | 46,419 | |
| Subgrade | 8734 | 7820 | 9117 | 7958 | 8396 | |
| Location | JX-6 | JX-7 | JX-8 | JX-9 | JX-10 | |
| Concrete Layer | 45,227 | 50,514 | 50,735 | 55,867 | 50,737 | |
| Subgrade | 8802 | 7798 | 6997 | 7122 | 7299 | |
| Location | A | B | C | D | E | |
| Concrete Layer | 47,922 | 49,196 | 41,020 | 44,843 | 46,246 | |
| Subgrade | 7519 | 6315 | 6855 | 7481 | 7213 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, M.; Wang, X.; Hou, R. Case Study: Validation of the Spectral-Analysis-of-Surface-Waves Method for Concrete Pavement Condition Evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011410
Qiao M, Wang X, Hou R. Case Study: Validation of the Spectral-Analysis-of-Surface-Waves Method for Concrete Pavement Condition Evaluation. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(20):11410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011410
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Ming, Xue Wang, and Rui Hou. 2023. "Case Study: Validation of the Spectral-Analysis-of-Surface-Waves Method for Concrete Pavement Condition Evaluation" Applied Sciences 13, no. 20: 11410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011410
APA StyleQiao, M., Wang, X., & Hou, R. (2023). Case Study: Validation of the Spectral-Analysis-of-Surface-Waves Method for Concrete Pavement Condition Evaluation. Applied Sciences, 13(20), 11410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011410






