Abstract
We examine the optical absorption in a hybrid structure composed of a metal nanoshell and a semiconductor quantum dot, while interacting with a linearly polarized probe electromagnetic field. First, we derive the equations of motion, in the rotating wave approximation. Then we procced to the derivation of analytical expressions for the linear susceptibility of the metal nanoshell and the semiconductor quantum dot. The imaginary part of the susceptibility expresses the absorption coefficient. We find that by properly engineering the thickness of the metal nanoshell, the material of the dielectric core and the interparticle distance, we may achieve an optimum response. We identify the emergence of two distinct types of hybrid exciton states. One of them emerges in the strong exciton–plasmon coupling regime for low values of the dielectric constant and the radius of the dielectric core. This type of hybrid exciton exhibits an amplified gain without population inversion and a quenched absorption resonance accompanied by a suppressed exciton lifetime. The second type of hybrid exciton emerges in the weak exciton–plasmon coupling regime and presents the opposite spectral characteristics. Here, the exciton lifetime presents a substantial increase, especially for small interparticle distances, in which case the semiconductor quantum dot and the metal nanoshell are strongly coupled with one another.
1. Introduction
During the last fifteen years, hybrid nanostructures which are composed of semiconductor quantum dots (SQDs) and metal nanoparticles have attracted scientific interest [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31] since they exhibit unique optical effects. These novel properties owe their presence to the formation of hybrid excitons and have been extensively investigated in systems where a metal nanosphere is coupled to an SQD [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. The origin of this type of exciton lies in the long-range Coulomb interaction that couples the excitons with the plasmons. The use of nanoparticles with a more complex structure and adjustable characteristics may further reinforce the optical effects that have already been explored in such hybrid systems; it may also give rise to even more interesting phenomena. For instance, the coupling of a metal nanoshell–dielectric core complex with an SQD provides the advantage of tuning the optical properties of the nanosystem more efficiently. This is achieved by properly adjusting the size and the material of the core, as shown in a series of studies where the population inversion [29], the energy absorption rate [29], and the two-photon resonance [30] are examined. It is also known that composite electrochemical coatings can be used in the field of nanostructured metal systems’ formation [31,32]. The coupling of such composite nanoparticles with quantum emitters are ideal candidates for applications in sensing and light harvesting. The linear absorption coefficient has already been investigated thoroughly in the case of an SQD–metal nanosphere hybrid system [6,9,10,28].
This study investigates the novel properties which are associated with the absorption spectra of the coupled nanoparticles when introducing a dielectric core at the center of the metal nanosphere. First, we obtain the density matrix equations and apply a first-order series expansion of the components of the density matrix, with respect to the incident field. Then, we solve the derived equations, in the steady state, and calculate the absorption coefficient for the SQD and the metal nanoshell (MNS). We also present analytical formulas for the calculation of the positions, the widths and the magnitudes of the minima and the maxima of the SQD absorption function. When the dielectric constant of the core is approximately equal to unity, the increase of its radius leads to the enhancement of gain without inversion; it also induces the suppression of both the absorption peak and the exciton lifetime. However, above a specific value of the core radius, the hybrid structure starts exhibiting the opposite trends; the same behavior is detected due to the enhancement of the dielectric constant of the core. For any fixed value of the core radius, the increase of the dielectric constant of the core is found to be responsible for the suppression of gain without inversion, the magnification of the absorption peak and the increase of the exciton lifetime. In the case of an MNS with low thickness, a gain dip appears on the absorption spectrum of the MNS, providing that the dielectric constant of the core tends to unity.
2. Methods
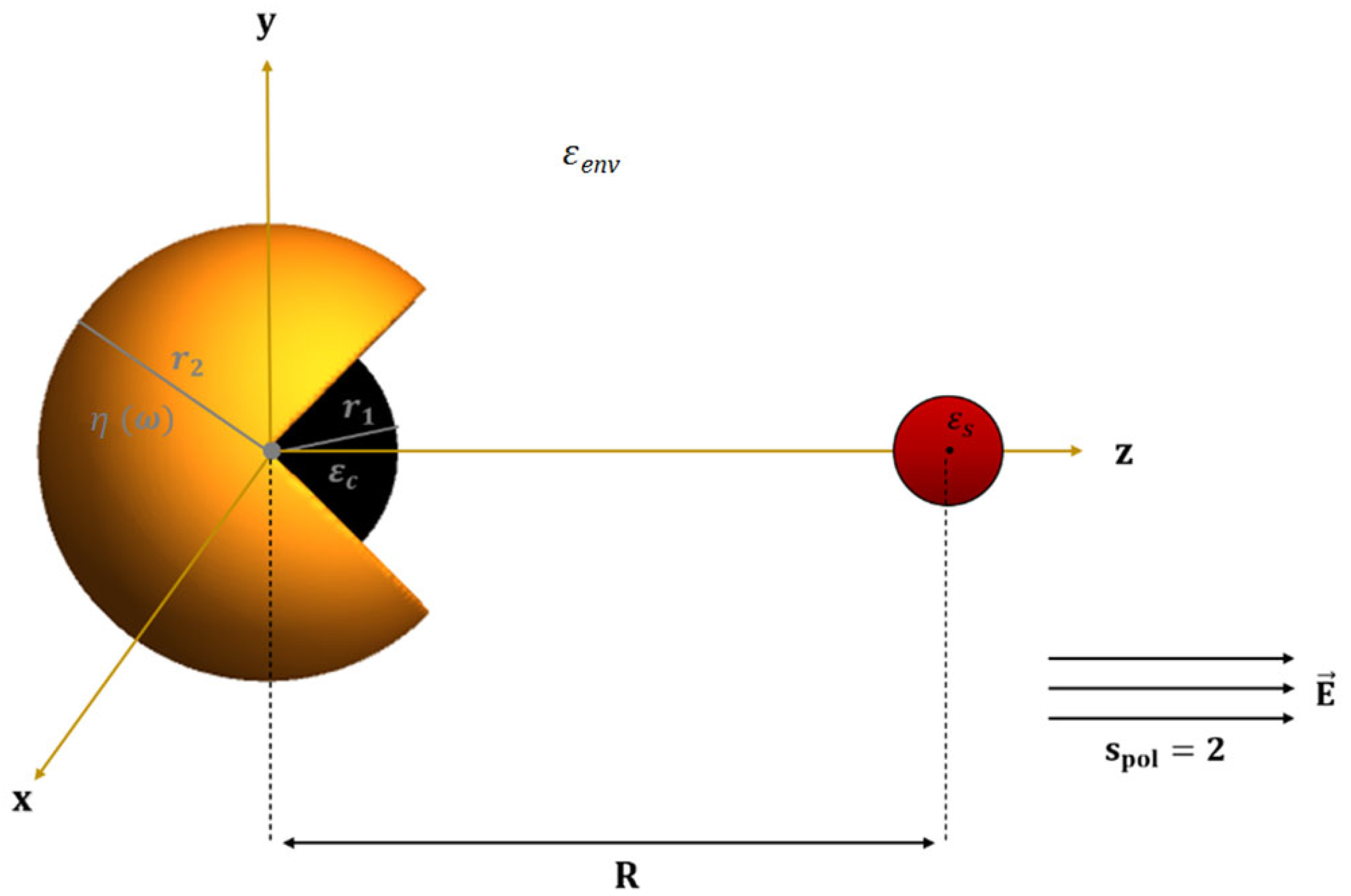
The hybrid nanostructure under study is comprised of an MNS and an SQD, which are coupled to each other via the Coulomb interaction, as illustrated in Figure 1. The distance between the SQD and the center of the MNS is denoted by . The dielectric constants of the SQD and the environment are and , respectively. The MNS has a fixed outer radius and is composed of gold, with dielectric function . The dielectric constant and the radius of the MNS core are symbolized as and ; their values may vary in the present study.

Figure 1.
Schematic configuration of the hybrid system: An SQD with dielectric constant is coupled to an MNS with outer radius and inner radius . The MNS is made of gold with dielectric function . With and we represent the dielectric constants of the core and the environment, respectively.
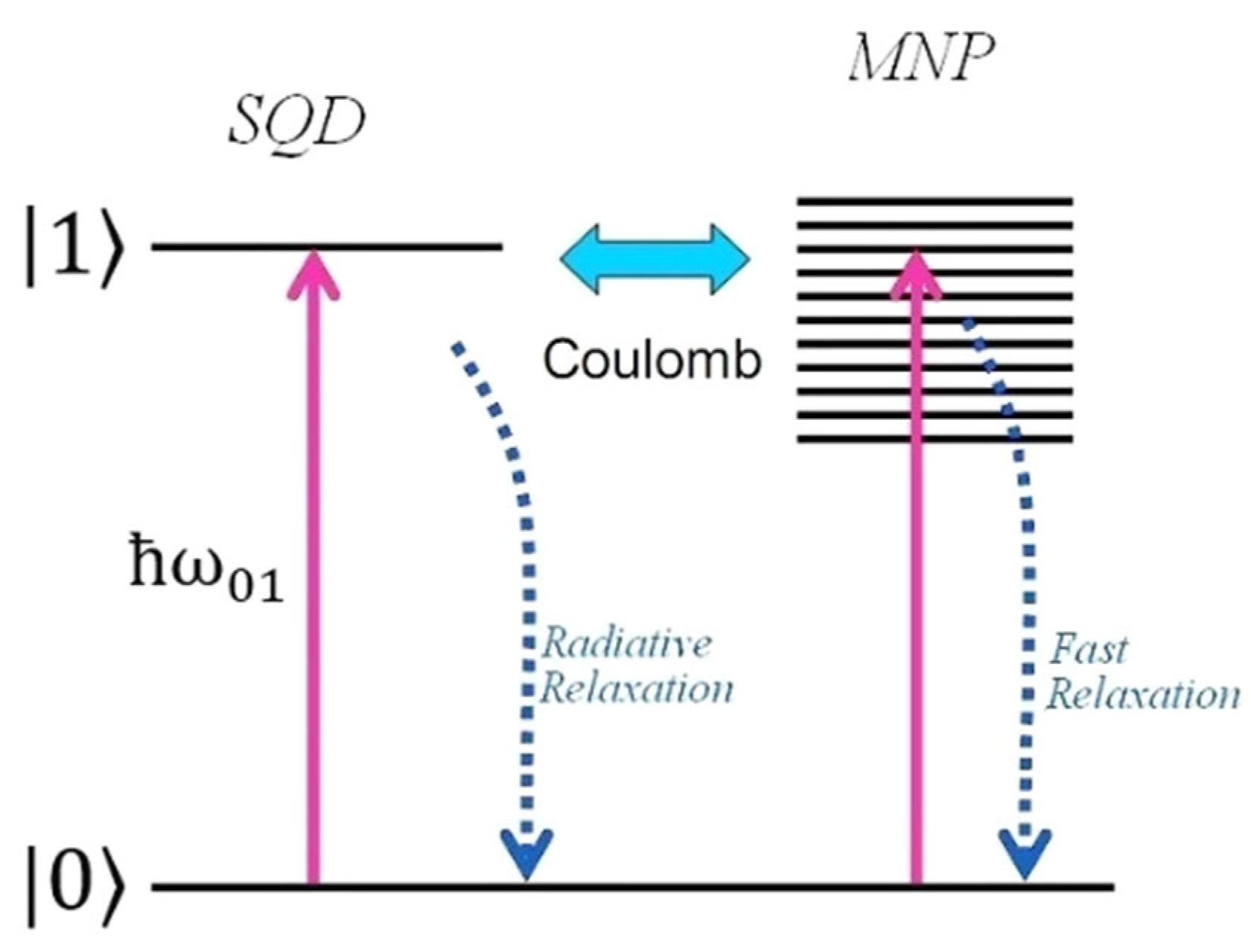
In the present study, we apply the semiclassical approximation, which means that the external electric field is treated classically, while the states of the quantum emitter are quantized. Thus, we assume that the hybrid nanostructure interacts with the external linearly polarized laser field ., with polarization direction lying along the axis defined by the centers of the nanoparticles. We treat the surface plasmons of the MNS as a quantum energy continuum. The SQD is described as a two-level system, as seen in Figure 2, with its ground state and its excited state , respectively, and the probe field is nearly resonant with the interband transition.
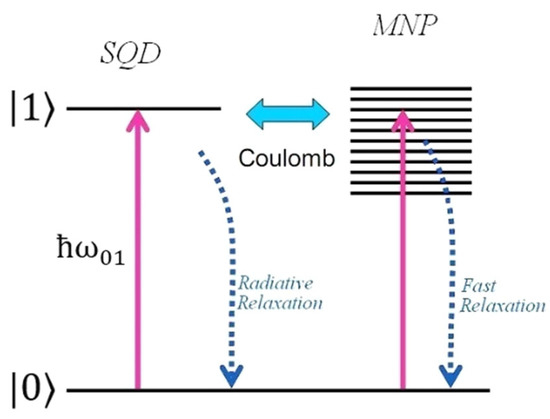
Figure 2.
Energy-level configuration of the hybrid system. The two-level diagram with the ground state and the direct exciton state describes the quantum emitter (SQD) and the electronic continuum states are associated with the MNS.
Taking into consideration that the electric field inside the SQD is expressed as a summation of the external field and the induced internal field [8], we can express the Hamiltonian that determines the equations of motion, in the dipole approximation, as follows:
with
where represents the energy of state (, ) and denotes the non-diagonal density matrix element. In Equation (2), we define the Rabi frequency , where μ represents the transition dipole moment, and (for a polarization direction that lies along the z axis). The first term of this parameter is related to the coupling of the SQD with the probe field and the second term owes its presence to the coupling of the SQD with the field sent back at its position, due to the polarization of the MNS that is purely induced by the probe field. For the derivation of the second term of Equation (2), the first order polarizability of the core-shell nanosystem has been set equal to . The complex function is given in Ref. [30]. The parameter , the exact origin of which is discussed in Ref. [10], expresses the bidirectional interaction between the SQD and the MNS. In the multipole expansion approach, we define the higher-order polarizability as , where an extended mathematical formula is introduced in order to calculate the parameter , as shown in Ref. [33].
The susceptibility of the SQD is proportional to the non-diagonal density-matrix element calculated in the steady state, as in Ref. [10], with V/Γ denoting the ratio of the SQD volume to the optical confinement factor. Next, we expand the density matrix elements in a first-order Taylor series about the weak probe field and substitute these expressions into the equations of motion. After solving the derived equations, in the steady state, we calculate the linear part of the coefficient, based on the following analytical formula:
where and express the real and the imaginary parts of the self-interaction coefficient , respectively, is the detuning of the applied field from resonance and represents the dephasing time. Moreover, the parameter is equal to . In Equation (5), and denote the real and the imaginary parts of , respectively, which can be considered as frequency-independent.
The critical points of the imaginary part of the function are calculated by the analytical expression:
The minimum value of Equation (6) corresponds to the emergence of gain without inversion. If the interparticle distance between the components of the hybrid nanosystem is high enough so that we can practically consider that the interaction between them is infinitesimal, the minimum and the maximum values of converge to zero and , respectively. The absorption resonance arises at
and the corresponding full width at half maximum is calculated by Equation (8):
Next, we determine the first-order optical susceptibility of the core-shell nanoparticle [10]
and we derive an analytical expression for the linear absorption coefficient:
In Equation (10), the parameter is -dependent, is a complex quantity that can be considered as frequency-independent, within the short range of frequencies of interest and symbolizes the imaginary part of the parameter . Based on Equation (10), we can determine the magnitude of the gain peak which arises on the MNS absorption spectrum:
3. Results
Here, we examine the forms of the absorption spectra, with regard to the SQD and the MNS. The MNS has an outer radius and it consists of gold. The value of the corresponding dielectric function , within a short range of frequencies around , can be approximately set equal to , according to Ref. [34]. The hybrid nanosystem is surrounded by vacuum . The dielectric constant of the SQD is , the dephasing time is and / [35]. The dipole moment for the transition is . We also assume that the corresponding energy gap is approximately equal to the excitation energy of the localized MNS surface plasmon.
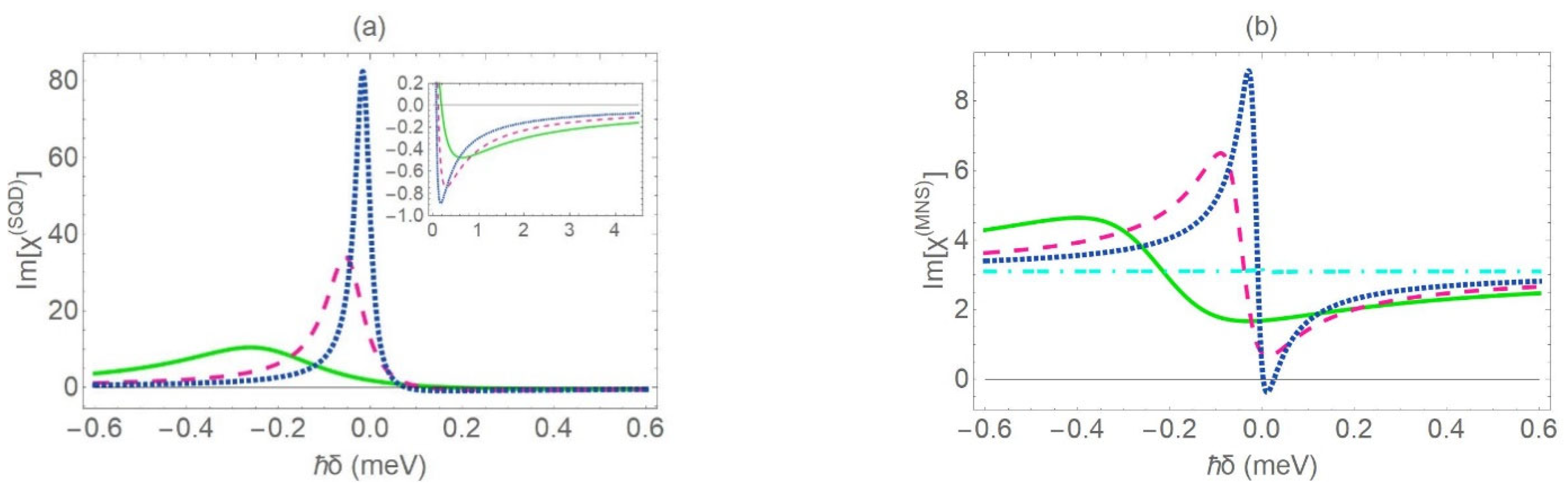
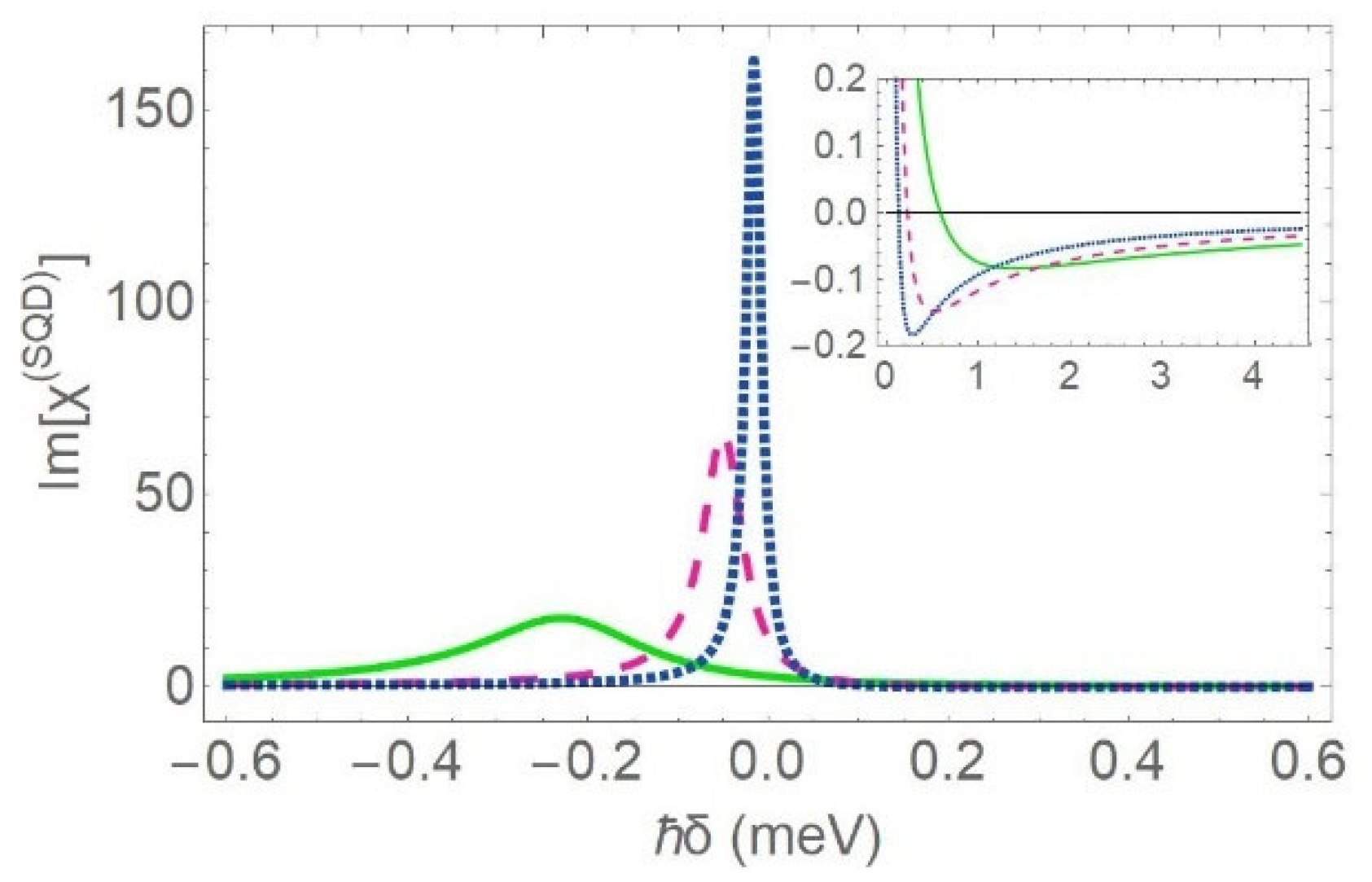
In Figure 3a,b, we present the spectra of the and coefficients, respectively, as a function of the detuning of the weak probe field from resonance , for different values of the center-to-center distance ( = 11.5 nm: green solid curve, 13.5 nm: pink dashed curve and 15.5 nm: blue dotted curved). The radius and the dielectric constant of the core are nm and , respectively. We note that, when the interparticle distance is reduced, the absorption peak becomes highly asymmetric and is transposed to negative values of the detuning parameter, Equation (7); additionally, its magnitude decreases, Equation (6), and the corresponding FWHM expands, Equation (8). Hence, the lifetime of the hybrid exciton is suppressed, and the excitonic energy exhibits a red shift. The previously reported modifications of the spectral characteristics are caused by the enhancement of the coefficients and . In the limiting case where the SQD does not practically interact with the MNS, the profile of the absorption resonance obtains a Lorentzian-like line shape and the gain feature extinguishes, because . The absorption peak has a magnitude and an FWHM equal to and , respectively. This indicates that symmetry is a characteristic of the spectrum, provided that the interaction between both nanoparticles is significantly weakened. The emergence of gain without population inversion on the same spectrum, within a specific range of frequencies, can also be predicted mathematically, based on Equation (6). According to this equation, for any set of the physical parameters, the coefficient is negative, due to the negative sign of the constant . The profile of the spectrum manifests a strong dependence on both the material and the radius of the dielectric core. It is found that the magnitude of the gain dip is maximized for intermediate values of , as long as the dielectric core has a dielectric constant close to the one corresponding to vacuum and the radius of the core is about , as in the case illustrated in Figure 3a. Specifically, for , the increase of leads to the enhancement of the gain dip. However, the characteristics of the absorption resonance are not modified. On the other hand, for , the increase of is responsible for the suppression of the gain dip, as well as for the enhancement and the narrowing of the absorption peak.

Figure 3.
The imaginary part (absorption coefficient) of the linear susceptibility for the SQD (a) and the MNS (b), as a function of the detuning energy of the probe field , for various values of the interparticle distance: (green solid curve), (pink dashed curve), (blue dotted curve) and 100 nm (turquoise dashed-dotted curve). We also set and .
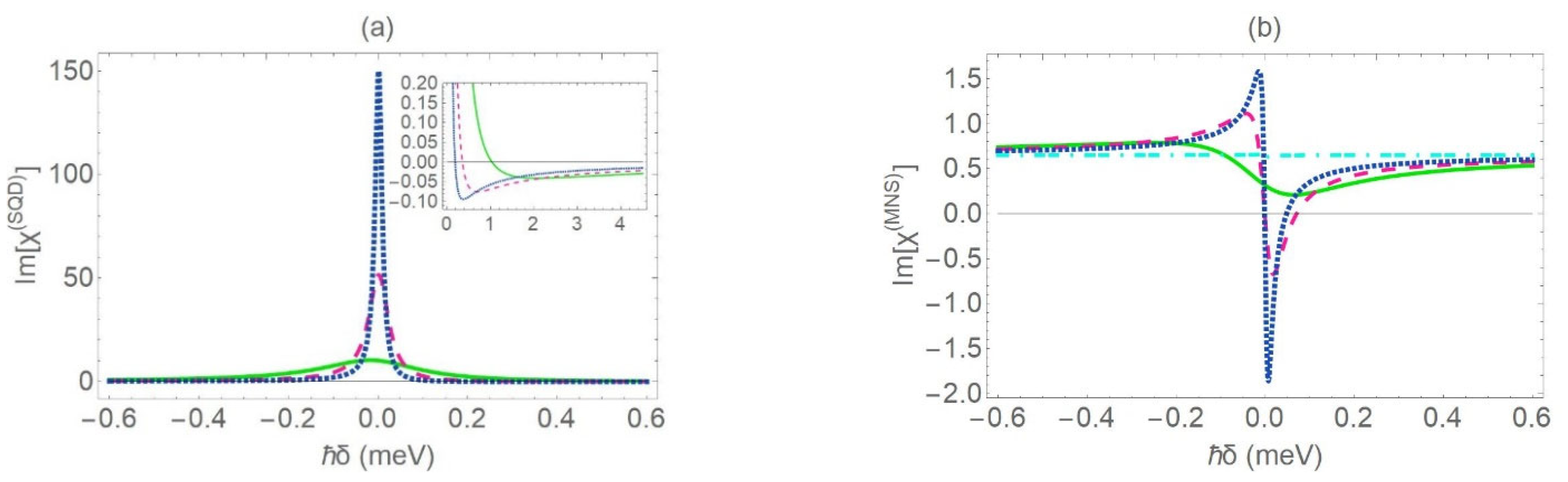
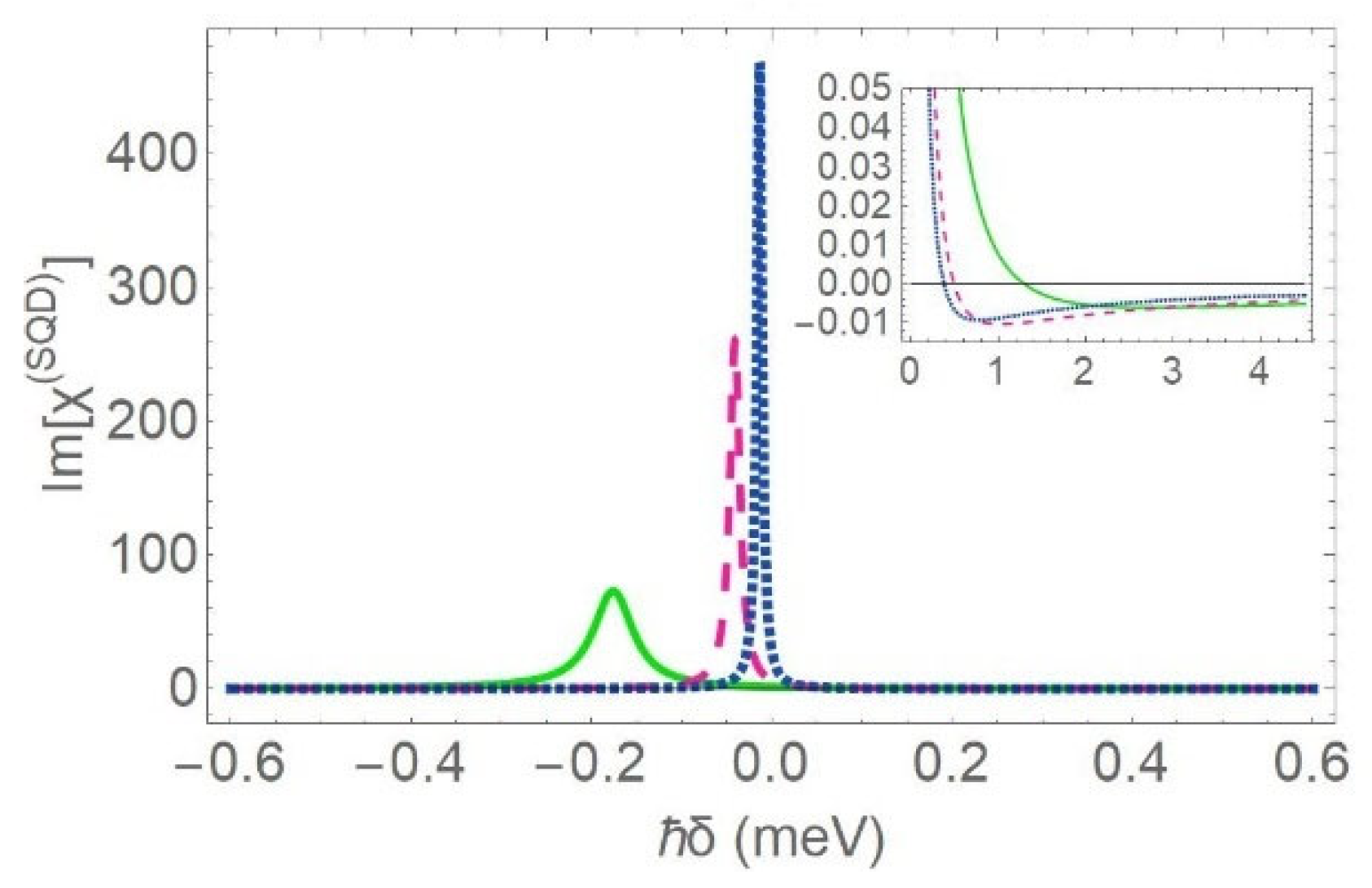
In Figure 4a,b, we present the absorption spectra for the SQD and the MNS, respectively. Here, we assume that r1 = 7 nm. For the rest physical parameters, we use the same values as in Figure 3. As long as the thickness of the MNS is low enough, the increase of the inner radius of the MNS leads to the transposition of the absorption resonance towards the spectral center. This pattern indicates an important attenuation of the exciton–plasmon interaction and was not observed in the case of Figure 3, where the radius of the core was set equal to ; additionally, the gain region that emerges on the spectrum is substantially shrunk. Moreover, the rise of the gain peak on the spectrum, for intermediate values of the interparticle distance, exhibits a strong dependence on the radius and the dielectric constant of the core. Practically, for , a prominent gain dip appears on the spectral form of the MNS absorption coefficient, provided that . Under the same conditions, the spectrum becomes highly asymmetric and manifests a dispersion-like line shape. For an extremely thin metal shell of thickness about , it was found that gain is detected on the MNS absorption spectrum within a much broader range of values of the interparticle distance. Τhis suggests that, when the radius of the core is modified by 5 to 7 nm, the direction of the energy transfer process, due to the coherent interaction between the SQD and MNS, is reversed. This effect can be explained as follows. As we increase the inner radius , the positive factor becomes more and more insignificant and, thus, the R-dependent term is the one that practically determines the value of the coefficient, according to Equation (11). At very high interparticle distances, as in the case with , the second term of Equation (10) vanishes. This happens because the variable , which is inversely proportional to the third order of , converges to zero. The spectral profile of is a horizontal line (turquoise dashed-dotted curve), as the first term of Equation (10), which is constant, determines the value of the absorption coefficient.
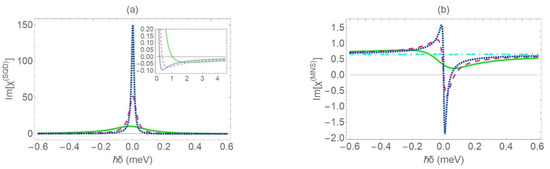
Figure 4.
The linear absorption spectra for the SQD (a) and the MNS (b), for different values of the center-to-center distance (green solid curve: , pink dashed curve: , blue dotted curve: and turquoise dashed-dotted curve: 100 nm). The physical parameters take the same values as in Figure 3, except for the inner radius of the MNS , which is set equal to 7 nm.
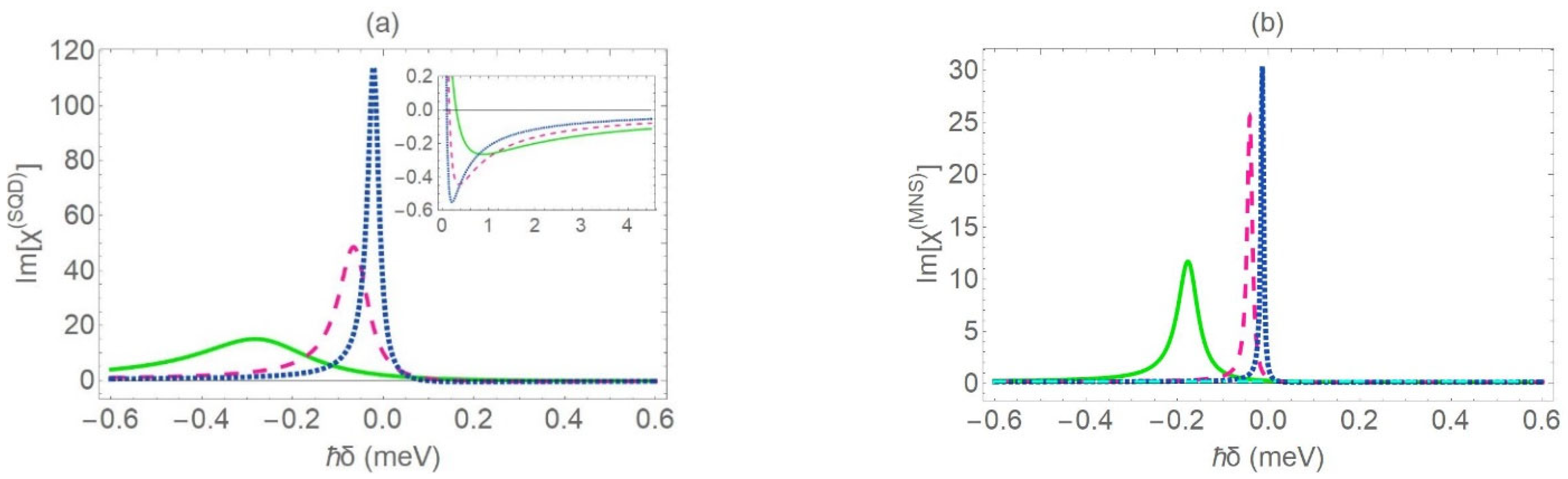
In Figure 5 and Figure 6, we present the absorption spectra for the SQD, for the same values of the distance between the centers of the coupled nanoparticles as those considered in Figure 2. The radius of the core is set equal to , and , in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively, while, in both figures, the dielectric constant of the core is = 7.5. After comparing Figure 5 to Figure 3a and Figure 6 to Figure 4a, we deduce that the increase of is responsible for the enhancement and the narrowing of the absorption resonance and the suppression of the gain dip. This is expected, based on a brief mathematical analysis based on Equation (6). More specifically, the enhancement of leads to the decrease of . As a result, the denominator of Equation (6) decreases, thus leading to the enhancement of the absorption peak. This effect is further intensified, in the limiting case of a quite thin nanoshell (as for ), providing that . In addition, the lifetime of the hybrid exciton is governed by the exact value of the dielectric permittivity of the core. This stems from the fact that the increase of leads to the reduction of the FWHM of the absorption resonance. This effect can be understood in terms of Equation (8), according to which the FWHM is proportional to the parameter , the value of which decreases when the dielectric constant of the core is enhanced. When the dielectric constant of the core is amplified, the magnitude of the gain dip manifests a notable suppression, because, in this case, the factor becomes insignificant. This is consistent with the conclusions that stem from a comparative study of the spectral profiles presented in Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6. However, there is not an explicit pattern that governs the shift of the absorption peak when the dielectric constant of the core is modified. In fact, we can identify two different ranges of values of the inner radius that favor two distinct behaviors with regard to the shift of the resonances. The first one includes values of that lie below ; in this case, the position of the absorption peak exhibits a slight shift towards higher values of the detuning parameter, when the numerical value of is increased. The second one includes values of higher than . In the case of a thin metal nanoshell, the increase of induces a redshift of the absorption resonance. This can be easily observed if we compare Figure 4a to Figure 6. We observe that the absorption resonance moves to the left, as permittivity of the core material is enhanced. To outline, for , the increase of leads to the enhancement and the narrowing of the absorption resonance; it is also responsible for the suppression of the gain dip, in contrast to the case with . All these effects become significant when the radius of the core is enhanced.

Figure 5.
The linear absorption spectra for the SQD, for different values of the center-to-center distance (green solid curve: , pink dashed curve: , blue dotted curve: and turquoise dashed-dotted curve: 100 nm). The dielectric constant of the core is set equal to and the rest physical parameters take the same values as in Figure 3.
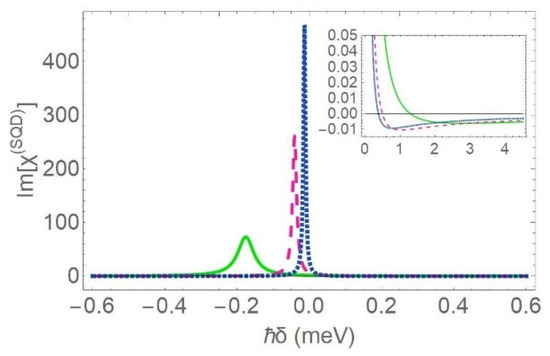
Figure 6.
The linear absorption spectra for the SQD, for different values of the center-to-center distance (green solid curve: , pink dashed curve: , blue dotted curve: and turquoise dashed-dotted curve: 100 nm). The dielectric constant of the core is set equal to , the inner radius of the MNS is set equal to and the rest physical parameters take the same values as in Figure 3.
In Figure 7a, we present the absorption spectrum for the SQD, in the case where the radius of the MNS core is set equal to 2 nm. In Figure 7b, we present the absorption spectrum for the MNS, when r1 = 7 nm. In both cases, we consider that . The rest parameters take the same values as in Figure 2. If we comparatively study Figure 3a and Figure 7a, we note that, for low values of the inner radius, the modification of the dielectric constant of the core subtly affects the spectral characteristics of . On the other hand, the profile of the SQD absorption spectrum presents a strong dependence on the dielectric constant of the core. The same holds with regard to the spectral profile of . When we increase the dielectric constant of the core, the magnitude of the gain dip that arises on the MNS absorption spectrum is suppressed, for any possible value of the inner radius . Above a critical value of , which varies according to the value of , the gain is eliminated, as illustrated in Figure 7b. For , the spectral profile of has a Lorentzian-like line shape, as opposed to the case with shown in Figure 4b, where the spectral profile of the absorption coefficient exhibits a Fano-type line shape. In the limiting case of a quite thick nanoshell (), the characteristic width of the MNS absorption peak is given by the approximate coefficient . Moreover, the gain dip does not practically depend on the dielectric constant of the core. The previously reported effects emerge due to the increase of , which leads to a substantial decrease of the factor that appears in the -dependent term of Equation (10).
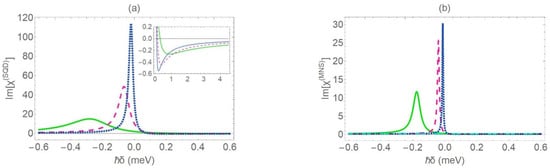
Figure 7.
The linear absorption spectra for the SQD (a) and the MNS (b), for different values of the center-to-center distance (green solid curve: , pink dashed curve: , blue dotted curve: and turquoise dashed-dotted curve: 100 nm). Captions (a) and (b) correspond to the cases in which the inner radius of the MNS is equal to and , respectively. The dielectric constant of the core is set equal to and the rest physical parameters take the same values as in Figure 3.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we present a detailed theoretical analysis of the linear optical response of an SQD–MNS hybrid system. More specifically, we demonstrated that the properties of the MNS core substantially affect the spectral characteristics of the linear absorption coefficient for the MNS and the SDQ, separately. In the present study, we explore how the radius and the dielectric constant of the core affect the absorption spectra of the SQD and the MNS. After deriving the non-linear density matrix equations, we implement a first-order series expansion of the density matrix elements, with respect to the incident field. Next, we obtain analytical expressions for the imaginary part of the linear optical susceptibility of the SQD and the MNS. We also derive analytical expressions for the theoretical prediction of the positions and the magnitudes of the absorption/gain resonances that arise on the absorption spectra; the analytical formula for the FWHM of the absorption peak is presented in the study, which constitutes a measure of the inverse lifetime of the hybrid excitons. More specifically, we have identified two distinct types of hybrid excitons. It is demonstrated that both the dielectric material and the radius of the MNS core determine the type of the hybrid exciton that emerges on the optical absorption spectrum of the SQD.
In particular, the first type of hybrid exciton arises on the absorption spectrum of the quantum emitter, providing that the core of the metal nanoshell is thick and the dielectric constant of its material is close to the one corresponding to vacuum. Under the strong exciton–plasmon coupling regime, the gain without population inversion is importantly enhanced; the absorption peak is also strongly quenched, and the exciton lifetime is importantly shrunk. The second type of hybrid exciton appears under the weak exciton–plasmon coupling regime. Under this regime, the value of the dielectric constant and the radius of the dielectric core are both increased. Typical features of the second type of hybrid exciton are the amplified absorption resonance, the enhanced exciton lifetime, and the suppression of the gain coefficient. The formation of this last type of the hybrid excitons is induced when the dielectric constant of the core is enhanced for any fixed value of the core’s radius. When the core of the MNS has a dielectric constant that tends to unity, the increase of the radius, up until a critical value, leads to the formation of the first type of hybrid exciton. However, above this critical value, the hybrid structure starts exhibiting the characteristics associated with the second type of hybrid exciton. Lastly, the properties of the core govern the absorption response of the MNS, as well. More explicitly, the gain that emerges on the profile of the corresponding spectrum is significantly enhanced, provided that the metal shell becomes exceptionally thin and the dielectric constant of the core tends to unity. Under these conditions, the gain that emerges on the profile of the absorption spectrum of the MNS presents the highest enhancement that can be observed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.G.K. and E.P.; methodology, S.G.K. and E.P.; software, A.K. and S.G.K.; validation, A.K., S.G.K. and E.P.; investigation, S.G.K. and A.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K., S.G.K. and E.P.; writing—review and editing, S.G.K. and E.P.; visualization, A.K., S.G.K. and E.P.; supervision, S.G.K. and E.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We acknowledge funding from an Empeirikion Foundation grant.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sadeghi, S.M. The inhibition of optical excitations and enhancement of Rabi flopping in hybrid quantum dot–metallic nanoparticle systems. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 225401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.M. Plasmonic metaresonances: Molecular resonances in quantum dot–metallic nanoparticle conjugates. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 233309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Govorov, A.O.; Bryant, G.W. Semiconductor-metal nanoparticle molecules: Hybrid excitons and the nonlinear Fano effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 146804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Duan, S.-Q.; Zhao, X.-G.; Govorov, A.O. Optical properties of coupled metal semiconductor and metal-molecule nanocrystal complexes: Role of multipole effects. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 165301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artuso, R.D.; Bryant, G.W. Strongly coupled quantum dot-metal nanoparticle systems: Exciton-induced transparency, discontinuous response, and suppression as driven quantum oscillator effects. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 195419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, M.-C.; Kim, N.-C.; Choe, S. II.; So, G.-H.; Jang, P.-R.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, I.-G.; Li, J.-B. Plasmonic effect on the optical properties in a hybrid V-Type three-level quantum dot-metallic nanoparticle nanosystem. Plasmonics 2017, 13, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyshev, A.V.; Malyshev, V.A. Optical bistability and hysteresis of a hybrid metal-semiconductor nanodimer. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 035314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfo, A.; Di Stefano, O.; Fina, N.; Saija, R.; Savasta, S. Quantum plasmonics with quantum dot-metal nanoparticle molecules: Influence of the Fano effect on photon statistics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 263601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.M. Gain without inversion in hybrid quantum dot–metallic nanoparticle systems. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 455401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosionis, S.G.; Terzis, A.F.; Sadeghi, S.M.; Paspalakis, E. Optical response of a quantum dot-metal nanoparticle hybrid interacting with a weak probe field. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 045304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.-T.; Liu, S.-D.; Zhou, H.-J.; Hao, Z.-H.; Wang, Q.-Q. Coherent exciton–plasmon interaction in the hybrid semiconductor quantum dot and metal nanoparticle complex. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 2125–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño, F.; Antón, M.A.; Paspalakis, E. Nonlinear optical rectification and optical bistability in a coupled asymmetric quantum dot-metal nanoparticle hybrid. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 113107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, A.; Miri, M. Resonance fluorescence of a hybrid semiconductor-quantum-dot-metal-nanoparticle system driven by a bichromatic field. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 99, 115440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.M.; West, R.G. Coherent control of Forster energy transfer in nanoparticle molecules: Energy nanogates and plasmonic heat pulses. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2011, 23, 425302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.M.; Deng, L.; Li, X.; Huang, W.-P. Plasmonic (thermal) electromagnetically induced transparency in metallic nanoparticle–quantum dot hybrid systems. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 365401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosionis, S.G.; Terzis, A.F.; Yannopapas, V.; Paspalakis, E. Nonlocal effects in energy absorption of coupled quantum dot–metal nanoparticle systems. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 23663–23670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindel, D.; Singh, M.R. A study of energy absorption rate in a quantum dot and metallic nanosphere hybrid system. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2015, 27, 345301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapuarachchi, H.; Gunapala, S.D.; Bao, Q.; Stockman, M.I.; Premaratne, M. Exciton behavior under the influence of metal nanoparticle near fields: Significance of nonlocal effects. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 115430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosionis, S.G.; Paspalakis, E. Coherent effects in energy absorption in double quantum dot molecule–Metal nanoparticle hybrids. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2022, 135, 114907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosionis, S.G.; Paspalakis, E. Energy absorption of an exciton-biexciton system in a quantum dot–Metal nanoparticle hybrid. Phys. B Condens. Matt. 2022, 643, 414186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhu, K.-D. Slow light in an artificial hybrid nanocrystal complex. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2009, 42, 0155022009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosionis, S.G.; Paspalakis, E. Pump-probe optical response of semiconductor quantum dot–metal nanoparticle hybrids. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 223104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosionis, S.G.; Paspalakis, E. Modified pump-probe optical effects in asymmetric tunneling-controlled double quantum dot molecule—Metal nanoparticle hybrids. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paspalakis, E.; Evangelou, S.; Kosionis, S.G.; Terzis, A.F. Strongly modified four-wave mixing in a coupled semiconductor quantum dot-metal nanoparticle system. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 083106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosionis, S.G.; Paspalakis, E. Control of self-Kerr nonlinearity in a driven coupled semiconductor quantum dot−metal nanoparticle structure. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 7308–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzis, A.F.; Kosionis, S.G.; Boviatsis, J.; Paspalakis, E. Nonlinear optical susceptibilities of semiconductor quantum dot–metal nanoparticle hybrids. J. Mod. Opt. 2016, 63, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Shen, S.; Ding, C.-L.; Wu, Y. Magnetically induced optical transparency in a plasmon-exciton system. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 053706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinfeld, L.; Cole, J.H.; Hapuarachchi, H. Prospects of utilizing quantum emitters to control the absorption of non-noble plasmonic metal nanoparticles. Ann. Phys. 2022, 535, 2200327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimi, Z.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Miri, M. Optical response of a hybrid system composed of a quantum dot and a core-shell nanoparticle. JOSA B 2019, 36, 2317–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nughoro, B.S.; Iskandar, A.A.; Malyshev, V.A.; Knoester, J. Plasmon-assisted two-photon absorption in a semiconductor quantum dot-metallic nanoshell composite. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 045405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseluikin, V.N. Electrodeposition and properties of composite coatings modified by fullerene С60. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2017, 53, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzutti, A.; Lekka, M.; de Leitenburg, C.; Fedrizzi, L. Effect of pulse current on wear behaviour of Ni matrix micro- and nano-SiC composite coatings at room and elevated temperature. Trib. Int. 2019, 132, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, H.A. Simple derivation of the shell polarizability formula and investigation of the plasmonic behavior of aluminum nanoshells with the Mie theory. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 23501–23507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.B.; Christy, R.W. Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 6, 4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-Hasnain, C.J.; Ku, P.-C.; Kim, J.; Chuang, S.-L. Variable optical buffer using slow light in semiconductor nanostructures. Proc. IEEE 2003, 91, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).