Abstract
Background. Training muscle capacities in hypoxic conditions increases some manifestations, such as hypertrophy and muscle strength, due to a change in the muscle phenotype as a result of the activation of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF). Despite the proven benefits of resistance training in hypoxic conditions that allow conjecture regarding the effectiveness in facilitating muscular capacities in different populations, there is still controversy regarding the difference between resistance training in hypoxia and normoxia. The objective of this review was to compile the present evidence and update the methods and effectiveness of resistance training in simulated hypoxia for the development of strength and muscle hypertrophy. Methodology. A systematic search for an integrative review was carried out based on the preferred reporting guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA) in 4 stages: identification, data selection, data collection and extraction, and quality evolution. Results. Four studies (92 participants) reported benefits in strength when training in hypoxia, three (101 participants) benefits in hypertrophy, and twelve (327 participants) benefits in strength and hypertrophy. Conclusion. Based on the findings of this systematic review, it is concluded that there are positive effects on muscle size and ability to generate force after a hypoxic training programme. However, some studies did not show a statistically greater benefit than for the normoxia groups, but several methodologies have been identified that promote the benefits of hypoxia.
1. Introduction
Considering the current research developments related to sports and exercise medicine, it is crucial to explore new methods that improve sports performance and optimise health. Studying the novel methods of physical programming is key to proving its effectiveness and impact [1]. In this regard, some interventions focus on muscle strength training as a critical factor that allows the necessary neuromuscular adaptation to maintain optimal physical conditions. Consequently, research on muscle strength training methods and the understanding of adaptations have allowed exploring different interventions that manage intensity, volume, type of exercises, execution sequence, and velocity [2].
Previous evidence has found that even though resistance training in hypoxia increases muscle growth and strength, this modality does not provide additional benefits compared with normal oxygen availability. Furthermore, previous reviews have highlighted that the particularities of the studies concerning sample, methods, exercise programming, and even the level of hypoxia do not allow us to draw accurate conclusions when comparing both methods [2]. This is why recently, the available evidence on hypoxia and strength training has increased significantly without being explored with a new systematic review or meta-analysis.
Even though the muscle is adaptable to different training methods, it adapts to the type of stimulus to a greater or lesser extent. Among the available training methods in exercise and health sciences, exercising under hypoxic conditions has emerged as an alternative to improve strength. Altitude training facilitates physiological and biochemical adaptations in muscles [3,4]. Still, due to the lack of evidence, there is increasing interest in how hypoxia could boost exercise interventions. The challenge is to determine which hypoxic conditions are more suitable to achieve the necessary adaptations efficiently and effectively for a specific population [5].
Some research on hypoxia in sports and exercise medicine has evidenced an improvement in variables related to skeletal muscle function. This method has shown an increase in the maximum voluntary contraction, increased muscle size in the cross-sectional area, and improved muscular endurance and mitochondrial angiogenesis and biogenesis [6]. Hypoxia training also offers special conditions for strength training through muscle hypertrophy due to a change in muscle phenotype by activation of hypoxia-inducible factors (hypoxia-inducible factor, HIF), which in turn affects the expression of genes in charge of the functional part of skeletal muscle tissue, as well as the gene transcription related to erythropoiesis and angiogenesis [7].
The benefits and muscular adaptations to strength training under hypoxia vary from changes in blood volume leading to haemoconcentration (a reduction in plasma volume) to improved muscle mechanical function. Training muscle strength under hypoxic conditions has increased intramuscular metabolic stress, enhanced hypertrophic signalling and muscle hypertrophy, and increased anabolic hormone concentration. In the long term, this method causes improvements in oxygen transport and uptake, which expose the muscle to metabolic stress that facilitates adaptation and increases the recruitment of motor units so that a larger portion of the muscle is stimulated [8].
In addition, positive results have been explored using hypoxic low-intensity strength training, leading to an observed increase in motor unit recruitment and muscular endurance. [9,10]. One of the reasons why hypoxia can increase muscle hypertrophy at high rates compared to normoxia conditions is the greater amount of metabolic stress during training caused by the lack of oxygen availability [11]. This response can be associated with the higher hypoxic intramuscular environment that results from training; for that reason, there is greater dependence on anaerobic processes and, therefore, a greater accumulation of metabolic by-products, such as blood lactate, that stimulate muscle growth.
Despite the proven benefits of resistance training in hypoxic conditions that allow conjectures regarding its effectiveness in facilitating muscular capacities in different populations, there is still controversy on the difference between resistance training in hypoxic vs. normoxic conditions. Thus, interest has increased in systematising the available evidence related to clinical studies centred on analysing the benefits of strength training in hypoxia to increase muscle size and strength [2]. Due to the growing interest in the study of this topic, the new evidence recently published, and to redirect future scientific efforts in this regard, this systematic review aimed to compile the evidence concerning strength training in simulated hypoxia and update knowledge regarding the methods used and its effectiveness in the improvement of strength and muscular hypertrophy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
This systematic literature review was prepared following the PRISMA guidelines [12] (see Figure 1). The authors selected the inclusion criteria and included experimental and quasi-experimental studies exploring the effectiveness of muscle strength training in hypoxia under simulated conditions to improve muscle strength and hypertrophy. The decision to perform a document review related to the aim of the present study is based on clear guidelines for the replication and updating of systematic reviews [13,14].
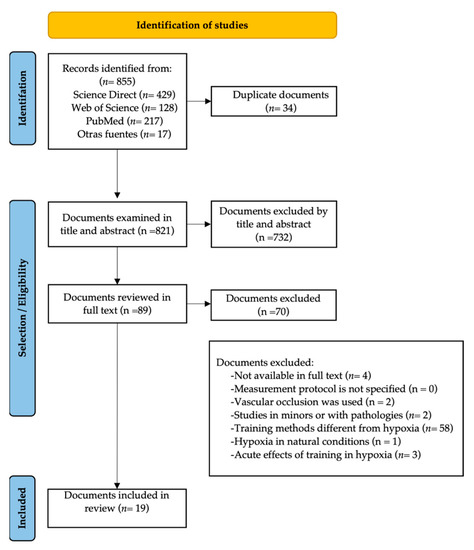
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the identification, selection, and discrimination of documents.
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
For this systematic review, the following inclusion criteria were established: (1) that the study determined the effect of training under simulated hypoxic conditions for at least four weeks on training methodologies for the achievement of strength and muscle hypertrophy; (2) studies had to have an experimental or quasi-experimental design; (3) the study had information on pre-and post-treatment assessments (e.g., one-repetition maximum tests, measurement of cross-sectional muscle area, or lean mass); (4) only studies in the English language were taken into account, to update previous reviews [2], and that were framed within the objective of this review; only studies from the year 2000 onwards were included.
Studies were excluded if: (1) the full text was not available; (2) the measurement protocol and key methodological aspects were not specified in hypoxia conditions (e.g., simulated altitude, intensity, volume, characteristics of participants); (3) vascular occlusion methods were used; (4) they were conducted on minors or people with any pathology; (5) hypoxia training in natural conditions (e.g., altitude training); (7) studies that considered training methods other than hypoxia, and (8) studies that explored acute effects of resistance training.
2.3. Sample
The PubMed, Science Direct and Web of Science electronic databases were chosen to perform a bibliographic search according to the research topic. This search was carried out from 2000 to 15 April 2021. A combination of keywords such as: “Hypoxia AND Resistance”, “Hypoxia AND Strength”, “Altitude AND Resistance”, and “Altitude AND Strength” were used to search for results.
2.4. Study Selection Process and Data Analysis
The main author performed the search. A database was created in a computer programme (Excel, Microsoft, San Francisco, CA, USA) in which each article found in the databases (PubMed, ScienceDirect and Web of Science) was included. This database had the name of the database, the article title, the authors, the journal name in which it was published, and the year of publication. Subsequently, duplicate articles were eliminated, and the title and abstract of the remaining documents were read. The full text was read to verify that the proposed eligibility criteria were met to judge the relevance of the article. From a methodological standpoint, studies were analysed using the PEDro Scale with items described as low risk of bias, unclear risk of bias, or high risk of bias (see Figure 2). Two authors independently assessed the risk of bias. Figure 3 shows the evolution of publications of recent literature related to this review; it is noteworthy that there has been an increase in publications in the last few years.
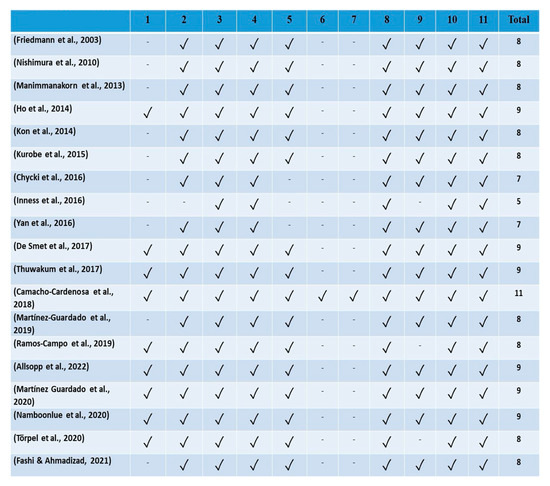
Figure 2.
Methodological classification of studies used in the systematic review. A rating of 9–11 is considered excellent, a rating of 6–8 is good, a rating of 4–5 is acceptable, and a rating of ≤3 shows a lack of methodological quality [6,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32].
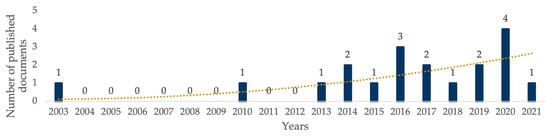
Figure 3.
Evolution of published documents related to hypoxia in strength and hypertrophy variables in recent years.
3. Results
As shown in Figure 1, after evaluating 855 identified studies, 766 were excluded due to title or abstract (n = 732) and duplicity (n = 34) during the search. The remaining 89 studies were examined in full text, of which 19 articles fulfilled the inclusion criteria.
Of the documents included in the systematic review, as shown in Table 1, four studies (21.05%) examined the effect of training in hypoxia on strength, three (15.78%) on hypertrophy and 12 (63.15%) analysed the training effect on both parameters.
Additionally, 527 participants were included, ranging between 12 and 59 participants per study. Of the total participants, 92 (17.45%) were involved in studies investigating the effectiveness of resistance training under hypoxic conditions on muscle strength, 101 (19.16%) were part of protocols identifying the effect on muscle hypertrophy and a total of 327 (62.04%) on both strength and hypertrophy parameters [6,10,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25].
Only two (10.53%) studies [26,27] selected a female population to determine the effect of hypoxia on strength and hypertrophy. Additionally, two (10.53%) [15,25] investigated the effect of hypoxia on the elderly population. Participants reported an average age of 27.37 ± 30.22 years (elderly included) and an average weight of 71.45 ± 3.25 kg.
The papers included healthy participants (n = 188, 35.67%) [15,16,19,21,25,28], trained or athletes (n = 183, 34.72%) [6,22,24,27,29,30,31] and a sedentary or untrained population (n = 156, 29.60%) [17,18,20,23,26,32]. The studies analysed the effect of resistance exercise in hypoxia with a frequency of two to four times per week during 4 to 12 weeks, with a total of ten to 36 sessions. The training sessions consisted of two to six series and three to 30 repetitions. Only four studies used muscle failure methods during intervention sessions [19,20,27,32].
Six documents (31.57%) based their prescribed load on 1RM percentages less than 50% [16,17,18,25,27,32]. On the other hand, two articles (10.59%) used loads higher than 80% of the 1RM [21,24], one (5.26%) [26] used maximal power as the reference value, and the remaining ten studies (52.63%) used a training load between 50 and 80% of 1RM [6,15,19,20,22,23,28,29,30,31].
Ten documents (52.63%) used lower limb exercises exclusively [16,17,18,22,26,27,28,30,31,32], two papers (10.52%) focused on the upper limb [19,23], and seven articles (36.84%) combined lower and upper limb exercises [6,15,20,21,24,25,29].
In Figure 4a,b, the 19 papers showed improvements in the percentage of change in at least one of the two groups.
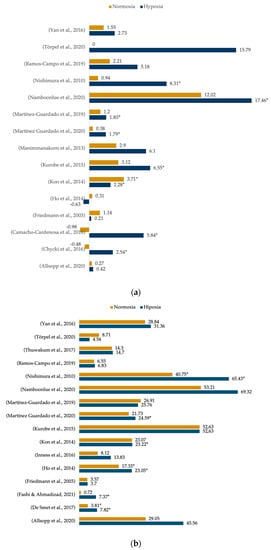
Figure 4.
Percentages of change in hypertrophy (a) and strength (b) before and after training by group. * Significant difference.
Of 15 documents that measured the hypertrophy variable, only three presented significant improvements in the control group [6,17,18], while the remaining 12 [15,19,20,21,22,23,24,24,25,26,27,28,29] showed a greater percentage of change in the hypertrophy group concerning measurements 1 and 2 (Figure 4a).
Sixteen documents measured the muscle strength variable, and only two showed significant improvements in the control group; two studies had an increase in the percentage of change but without differences between the groups, while the remaining 12 [15,16,17,18,20,22,23,24,28,30,31,32] showed a higher percentage of change in the hypoxia group for the force variable concerning measurement 1 and 2 (Figure 4b). Moreover, 57.89% (n = 11) report significant differences between the groups [6,16,18,19,20,21,22,23,26,29,32].
Considering the muscle hypertrophy variable, four documents presented a percentage of change between 5 and 10% between groups [22,23,25,26], four manuscripts presented change percentages between 2 and 4.9% [19,24,27,29] and seven studies under 2% [6,15,17,18,20,21,28]. One paper [18] reported adverse results in the hypoxia group due to training (see Figure 4a).
The documents presented between 5 and 10% percentage change in the muscle hypertrophy variable. For example, studies by Namboonlue et al. and Törpel et al. [22,23,25] based their training schedule on 4–7 weeks. These papers included loads of 3–4 sets with 10–15 repetitions [22,23,25]; and applied a percentage of effort between 50 to 70% of 1RM [22,23].
Of the comprehensive studies on the strength variable, six presented a percentage of change between 5 and 25% between groups [15,16,22,25,29,30], three presented a rate of change between 2 and 4.9% [16,20,28], and seven studies less than 2% [6,17,19,21,24,25,31], two documents reported a higher percentage of change in the strength variable in the control group (Figure 4b) [21,25].
Finally, the studies that reported between a 5 and 25% percentage change in muscle strength [15,18,22,23,30,32] based their intervention on a four to 8-week training programme [15,18,22,23,30] and used training loads of three to four sets with six to 15 repetitions and a percentage effort of 50–70% of 1RM.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the selected documents for the systematic review.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the selected documents for the systematic review.
| Reference | FiO2 | Number of Participants | Physical State | Age (years) | Weight (kg) | Modality | W | Ses | Ses/W | Repetitions | Series | Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | HYP:12 | 19 (♂) | Sedentary | 24.3 ± 2.5 25.1 ± 2.9 | 72.9 ± 9.0 77.0 ± 9.0 | Knee Ext + knee flex | 4 | 12 | 3 | 25 | 6 | 30% RM |
| [23] | HYP:16 NOR: 21 | 14 (♂) | Sedentary | 21.4 ± 1.1 | 65.9 ± 8.1 | French Press + elbow flex | 6 | 12 | 2 | 10 | 4 | 70% RM |
| [27] | SpO2 al 80% | 30 (♀) | Netball players | 20.2 ± 3.3 | 65.2 ± 6.5 | Knee Ext + knee flex | 5 | 15 | 3 | Muscle failure | 6 | 20% RM |
| [18] | HYP:15 NOR: 21 | 18 (♂) | Sedentary | 21.3 ± 2.0 | 67.3 ± 9.7 | Squat | 6 | 18 | 3 | 10 | 3 | 50% RM |
| [6] | HYP:14.4 | 16 (♂) | Recreational training | 28.4 ± 1.6 28.2 ± 1.4 | 68.2 ± 2.2 65.8 ± 3.7 | Bench press + Squat press | 8 | 16 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 70% RM |
| [19] | HYP:12.7 NOR: 20.9 | 13 (♂) | Healthy | 23.0 ± 1.0 | 60.2 ± 1.6 | Elbow ext | 8 | 24 | 3 | Muscle failure | 3 | 10 RM |
| [29] | HYP:12.9 | 12 (♂) | Trained | 21.0 ± 2.4 22.0 ± 1.5 | 80.6 ± 12.3 81.1 ± 7.5 | Bench press | 6 | 12 | 2 | 10 | 8 | 70% RM |
| [30] | HYP:14.5 NOR: 20 | 20 (♂) | Trained | Squat + deadlift | 7 | 21 | 3 | 3–6 | 2–4 | 50–70% RM | ||
| [28] | HYP:16 HYP:12.6 | 25 (♂) | Healthy | 22.2 ± 2.6 | 70.5 ± 10.0 | Squat | 5 | 10 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 70% RM |
| [16] | HYP: 12.3–16.4 | 18 (♂) | Healthy | 23.9 ± 3.0 | 70.1 ± 6.6 | Knee Ext | 5 | 15 | 3 | 30 | 4–6 | 20–25% RM |
| [31] | HYP:14 NOR: 20.9 | 40 (♂) | Trained | 20.2 ± 1.7 | Knee Ext + knee flex | 5 | 15 | 3 | 15 | 6 | 30–80% RM | |
| [26] | HYP:17.2 NOR: 20.9 | 59 (♀) | Sedentary | 41 ± 3.15 | 78.2 ± 14.8 | HIIT | 12 | 36 | 3 | 30 s–3 min | 3–6 | 90–130 Wmax |
| [21] | HYP:15 NOR: 20.9 | 28 (♂) | Healthy | 24.6 ± 6.8 23.2 ± 5.2 | 74.9 ± 11.5 69.4 ± 7.4 | Full body strength programme | 8 | 16 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 85–90% RM |
| [24] | HYP:15 NOR: 20.9 | 28 (♂) | Trained | 24.6 ± 6.8 23.2 ± 5.2 | 74.9 ± 11.5 69.4 ± 7.4 | Full body strength programme | 8 | 16 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 85–90% RM |
| [15] | HYP: 14.4 NOR:20.93 | 12 (♂) 8 (♀) | Healthy | 65.9 ± 1.1 64 ± 0.8 | 70.7 ± 4.4 71.9 ± 4.3 | Full body strength programme | 8 | 16 | 2 | 10 | 4 | 70% RM |
| [20] | HYP:13 NOR: 21 | 32 (♂) | Sedentary | 25.7 ± 6.42 | 78.4 ± 12.1 | Bench Press + biceps flex + French press + pendlay + Squat | 7 | 21 | 3 | Muscle failure | 3 | 65% RM |
| [22] | HYP:13.6 HYP:15.8 | 37 (♂) | Trained | 19.5 ± 1.1 | Knee Ext + knee flex | 5 | 15 | 3 | 15 | 3 | 50–80% RM | |
| [25] | SpO2 al 80–88% | 84 | Healthy | 24.25 ± 4.05 67.95 ± 4.35 | 75.9 ± 11.6 | Full body strength programme | 5 | 20 | 4 | 15 | 3 | 25–40% RM |
| [32] | HYP: 12.7 NOR: 20.9 | 14 (♂) | Sedentary | 21 ± 4 | Squat | 4 | 12 | 3 | Muscle failure | 3 | 50% 10RM |
Note. HYP: Hypoxia; NOR: Normoxia; ♂: men; ♀: women; W: Weeks; Ses: Sessions.
4. Discussion
This systematic review aimed to compile the present evidence regarding resistance training in hypoxia and update knowledge of the methods used and their effectiveness in developing strength and muscle hypertrophy. The results concord with previous systematic review results [2]. This manuscript confirms that, in most cases, resistance training under hypoxic conditions significantly improves strength and muscle hypertrophy. However, some documents do not report substantial differences compared to training in normoxia. This suggests that a greater quantity and quality of scientific evidence should be reported until convincing results are obtained regarding the effectiveness of this training. It should be noted that some studies with more significant improvements in the percentage of change in the hypoxia group have highlighted several methodological similarities, so recommendations can be made to improve the quality of future studies and thus permit the comparability of results, as well as to encourage carrying out a meta-analysis on this topic when the volume of documents allows strong conclusions.
It is known that muscular strength training leads to structural or neural adaptations and that these improvements influence muscle growth and the effectiveness of the muscle in generating force [33,34]. In addition, strength training contributes to sports performance [6,22,24,27,29,30,31] and is also beneficial to health [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,23,25,26,28,32]. Resistance training leads to morphological muscle adaptations such as hypertrophy and increased strength due to changes in muscle fibre diameter, protein synthesis of myofibrils and increased anaerobic capacity [7,33,34]. In addition, it causes changes in metabolic characteristics such as mitochondrial synthesis, increases in lactate tolerance, and improvements in oxidative function and muscle endurance capacity [7].
Therefore, strength training induces these changes due to the metabolic stress it generates since the energy pathways used in this type of training generate an anabolic situation that, in turn, causes an increase in anabolic signalling proteins, giving way to the creation of metabolites that promote myofibrillar protein synthesis. Consequently, these muscle proteins balance with satellite cells and bind to the muscle fibre. This balance is only achieved when the protein synthesis rate exceeds its breakdown because of the work carried out by satellite cells in muscle hypertrophy [7,35].
Hypoxic training on muscle hypertrophy and strength development is an issue that has become relevant in recent years. Part of the theory is associated with greater metabolic stress than normoxic training since there is more dependence on the anaerobic metabolism, which contributes to muscular adaptations [24,36]. Training in hypoxia has been postulated as a factor that stimulates capillary growth through increased nitric oxide production and greater vasodilation, as well as increased expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene (VEGF). This factor is induced by HIF-1; these signals, due to the activation of the HIF factor, affect the expression of a greater number of genes. Most of these genes have functional relevance in muscle tissue adaptations and are related to erythropoiesis, angiogenesis, pH and glycolysis regulation [7,16].
4.1. Changes in Muscle Size Due to Hypoxia
Hypoxia was observed to provoke some positive results concerning muscle growth [15,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. However, in some papers, no substantial change was proven between groups (normoxia vs. hypoxia), suggesting that one training method is neither more nor less effective. Those studies that presented statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) in the hypoxia group [19,20,21,22,23,26,29], can be due to methodological particularities, and no strong recommendations could be made so far based on this evidence.
Some documents found greater benefits in the hypoxic group. These studies share certain methodological characteristics, such as training programmes of between 4 to 7 weeks [22,23,25], which can be considered a relatively moderate training time. Evidence [23] suggests that chronic exposure to altitude could lead to an adverse effect on hypertrophy since prolonged exposure can generate a reduction in the cross-sectional area of the muscle (CSA), and a decrease in the size of the muscle fibres. Furthermore, there is a similarity in the analysed documents where substantial improvements were found in the percentage of change for the hypoxia group [22,23]. These studies applied moderate loads of 50–70% of 1RM, while other interventions [17,18], used percentages less than 50% of 1RM. These manuscripts reported an adverse effect, since the control group had an improvement in one normoxic environment.
The three studies with the highest percentage of change in the hypoxia group selected a programme of three to four series with ten to fifteen repetitions [22,23,25]; contrary to studies that used six sets with many repetitions >15 [17]. Furthermore, this evidence suggested using different body segments in the study designs, showing that hypertrophy gains under hypoxic conditions can be achieved regardless of the stimulated body area [22,23,25].
4.2. Changes in Muscle Strength Due to Hypoxia
Strength training in hypoxic conditions is a new horizon for training programmes to improve strength capacity, as proposed in some studies [21]. Furthermore, some contrasting evidence suggests that strength training under hypoxic conditions has or has not greater benefits than under normoxia [2]. Consequently, these systematic review results are inconclusive, regardless of suggesting a significantly greater benefit of hypoxia than normoxia. Anecdotally, compared to hypertrophy variables, in strength, almost all the studies reported a positive change, and only one study presented a slightly greater improvement in the control group [21]. Furthermore, some significant improvements (p < 0.05) were found in the hypoxia group in some studies [6,16,18,20,23,32].
Methodological consistency was found in the hypertrophy-selected variables. Regarding strength variables results, in some studies, a higher percentage of change was found [15,18,22,23,30,32]. These studies shared the duration of the intervention (4–8 weeks) [15,18,22,23,30] and reported a load intensity of 50–70%, considering a low-moderate load. Additionally, increased strength was reported when a low training load was applied under hypoxic conditions [22]. This can also be noted when intensities of 85–90% of 1RM were used [21].
The physiological mechanisms caused by the low load in strength training are not entirely understood. Type I muscle fibres are thought to fatigue earlier in a low-load, hypoxic environment and are highly recruited. The recruitment of type II fibres can cause growth hormone alterations and testosterone because of hypertrophy and muscle strength [19,28].
Finally, regarding the training volume, in those studies reporting the highest percentage of change, a total of three to four series and six to fifteen repetitions were programmed Falta algo. [15,18,22,23,30]. Another study used three sets to failure, and the results had a small impact on the hypoxia group compared to the control group [19]. In addition, there was a small impact on the percentage of change between groups, using >25 repetitions [17]. Concerning the body segments used, the highest rate of change was found in those studies where different body segments were involved [15,18,22,23,30,32]. There is no clear methodological consistency among studies, and no evidence-based recommendation can be given based on this review at this time. Based on particular data, strength training under hypoxia could be performed using three to four series, six to fifteen repetitions and large muscle groups.
5. Limitations
An important limitation of this systematic review is the lack of previous studies that allow a consensus to be established on the training methodology used since there is a certain heterogeneity in the design and methods of the studies, which causes little clarity about which is the best exercise design and programming to trigger significant training improvements in hypoxic compared to normoxic conditions.
6. Practical Applications
Since 2018, study flow has increased by 52.63%. This evidence regarding the effect of resistance training in hypoxic conditions is still growing, and more research should be devoted to this topic. The research results clarify the panorama about the methodological considerations of the programming and prescription of the resistance exercise in conditions of normobaric hypoxia. This systematisation could serve as a basis for recommending and guiding researchers and professionals of human movement in their practical interventions. Furthermore, there are certain studies where effectiveness seems greater, and their designs have certain methodological similarities.
The effects observed in the different investigations suggest that the changes in strength and hypertrophy are more effective if you work at moderate intensities of 50 to 70% of RM, between 4 to 6 series and repetitions not greater than 15 (considered reasonable). These findings suggest that individual differences (e.g., genetic, morphological, physiological) exist in certain participants, leading to greater benefits under hypoxic conditions.
The potential difference in the effectiveness of hypoxic strength training between participants considering genetics, sex, age, physical condition, previous activity, and the morphology and particular conditions of certain age groups could be a starting point for new scientific studies. Therefore, it is essential to find the optimum training load to take advantage of this training modality.
7. Conclusions
This systematic review shows positive effects on muscle size and force-generating capacity due to normobaric hypoxia training. However, some studies did not show a statistically greater benefit than normoxia groups, six for hypertrophy [15,17,18,24,25,27,28] and ten for strength [15,17,19,21,22,24,25,28,30,31]. This difference in results arises because of the methodological heterogeneity of the studies selected. In addition, a pattern in the exercise schedule was identified. However, relatively few scientific documents still test this training methodology. Finally, the systematic review results suggest the importance of continuing with studies in this line of research and considering the present results to assess the methodological design of future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, J.V., I.M.-G., J.M.G. and D.R.-V.; methodology, J.V., B.S.-U., C.A.-M. and D.R.-V.; software, J.V., B.S.-U., C.A.-M., J.M.G. and D.R.-V.; validation, J.V., J.M.G. and D.R.-V.; formal analysis, J.V., J.M.G., I.M.-G. and D.R.-V.; investigation, J.V., B.S.-U., C.A.-M. and D.R.-V.; resources, B.S.-U., S.J.I. and D.R.-V.; data curation, J.V., J.M.G. and D.R.-V.; writing—original draft preparation, J.V., B.S.-U., C.A.-M. and D.R.-V.; writing—review and editing, I.M.-G., C.A.-M., B.S.-U., S.J.I., J.M.G. and D.R.-V.; supervision, C.A.-M., B.S.-U., S.J.I. and D.R.-V.; project administration, S.J.I. and D.R.-V.; funding acquisition, C.A.-M., B.S.-U., S.J.I. and D.R.-V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was partially funded by the GOERD of University of Extremadura and the Research Vice-rectory of Universidad Nacional. This work has been partially supported by the funding for research groups (GR21149) granted by the Government of Extremadura (Employment and infrastructure office—Consejería de Empleo e Infraestructuras), with the contribution of the European Union through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) by the Group for the Optimisation of Training and Sports Performance (GOERD) of the Faculty of Sports Sciences of the University of Extremadura. In addition, the author José M. Gamonales was supported by a grant from the Requalification Programme of the Spanish University System, Field of Knowledge: Biomedical (MS-18).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Capote Lavandero, G.; Torres, Á.; Analuiza, E.; Sánchez, C.; Rendón Morales, P. El Deporte, El Entrenamiento Deportivo y Los Entrenadores. Lect. Educ. Física Deportes 2017, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Scott, B.R.; Alcaraz, P.E.; Rubio-Arias, J.A. The Efficacy of Resistance Training in Hypoxia to Enhance Strength and Muscle Growth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Nieto, C.Y.; Pérez Labrada, C.; de la, C.; López Nieto, C.G.; Garcés Banqueris, R.E. Entrenamiento de fuerza y resistencia en hipoxia: Efecto en la hipertrofia muscular. Biomédica 2020, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cenia de la Caridad, P.L.; Claudia Gracil, L.N.; Raúl Enrique, G.B. Entrenamiento de fuerza y resistencia en hipoxia: Efecto en la hipertrofia muscular. In Proceedings of the I Congreso Virtual de Ciencias Básicas Biomédicas de Granma, Granma, Cuba, 22 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Parodi, A.; Capuccio, Á.; Magallanes, C. Efectos de 20 semanas de utilización de máscaras de entrenamiento en altura durante un programa de entrenamiento funcional. Evista Univ. De La Educ. Física Y El Deporte 2020, 21, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kon, M.; Ohiwa, N.; Honda, A.; Matsubayashi, T.; Ikeda, T.; Akimoto, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Hirano, Y.; Russell, A.P. Effects of Systemic Hypoxia on Human Muscular Adaptations to Resistance Exercise Training. Physiol. Rep. 2014, 2, e12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Lázaro, D.; Díaz, J.; Caballero, A.; Córdova, A. Entrenamiento de fuerza y resistencia en hipoxia: Efecto en la hipertrofia muscular. Biomédica 2019, 39, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cáceres, S.A. Entrenamiento Hipóxico y Su Relación En El Rendimiento Deportivo En Atletas de Las Modalidades de Fondo y Semifondo de Federación Deportiva de Chimborazo. Master’s Thesis, University of Quito, Quito, Ecuador, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Rubio-Arias, J.A.; Dufour, S.; Chung, L.; Ávila-Gandía, V.; Alcaraz, P.E. Biochemical Responses and Physical Performance during High-Intensity Resistance Circuit Training in Hypoxia and Normoxia. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Rubio-Arias, J.Á.; Freitas, T.T.; Camacho, A.; Jiménez-Diaz, J.F.; Alcaraz, P.E. Acute Physiological and Performance Responses to High-Intensity Resistance Circuit Training in Hypoxic and Normoxic Conditions. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.R.; Slattery, K.M.; Sculley, D.V.; Lockhart, C.; Dascombe, B.J. Acute Physiological Responses to Moderate-Load Resistance Exercise in Hypoxia. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, T.P. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, P.; Hopewell, S.; Chandler, J.; MacLehose, H.; Akl, E.A.; Beyene, J.; Chang, S.; Churchill, R.; Dearness, K.; Guyatt, G.; et al. When and How to Update Systematic Reviews: Consensus and Checklist. BMJ 2016, 354, i3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.A.; Karunananthan, S.; Maxwell, L.J.; Akl, E.A.; Avey, M.T.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brouwers, M.C.; Clark, J.P.; Cook, S.; et al. When to Replicate Systematic Reviews of Interventions: Consensus Checklist. BMJ 2020, 370, m2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fashi, M.; Ahmadizad, S. Short-Term Hypoxic Resistance Training Improves Muscular Performance in Untrained Males. Sci. Sport. 2021, 36, S0765159721000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inness, M.W.H.; Billaut, F.; Walker, E.J.; Petersen, A.C.; Sweeting, A.J.; Aughey, R.J. Heavy Resistance Training in Hypoxia Enhances 1RM Squat Performance. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manimmanakorn, A.; Hamlin, M.J.; Ross, J.J.; Taylor, R.; Manimmanakorn, N. Effects of Low-Load Resistance Training Combined with Blood Flow Restriction or Hypoxia on Muscle Function and Performance in Netball Athletes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2013, 16, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuwakum, W.; Hamlin, M.J.; Manimmanakorn, N.; Leelayuwat, N.; Wonnabussapawich, P.; Boobpachat, D.; Manimmanakorn, A. Low-Load Resistance Training with Hypoxia Mimics Traditional Strength Training in Team Sport Athletes. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2017, 17, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Lai, X.; Yi, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y. Effects of Five-Week Resistance Training in Hypoxia on Hormones and Muscle Strength. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Cardenosa, A.; Camacho-Cardenosa, M.; Burtscher, M.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Timon, R.; Brazo-Sayavera, J.; Olcina, G. High-Intensity Interval Training in Normobaric Hypoxia Leads to Greater Body Fat Loss in Overweight/Obese Women than High-Intensity Interval Training in Normoxia. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chycki, J.; Czuba, M.; Gołaś, A.; Zając, A.; Fidos-Czuba, O.; Młynarz, A.; Smółka, W. Neuroendocrine Responses and Body Composition Changes Following Resistance Training Under Normobaric Hypoxia. J. Hum. Kinet. 2016, 53, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsopp, G.L.; Hoffmann, S.M.; Feros, S.A.; Pasco, J.A.; Russell, A.P.; Wright, C.R. The Effect of Normobaric Hypoxia on Resistance Training Adaptations in Older Adults. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2022, 36, 2306–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, S.; van Herpt, P.; D’Hulst, G.; Van Thienen, R.; Van Leemputte, M.; Hespel, P. Physiological Adaptations to Hypoxic vs. Normoxic Training during Intermittent Living High. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, B.; Kinscherf, R.; Borisch, S.; Richter, G.; Bärtsch, P.; Billeter, R. Effects of Low-Resistance/High-Repetition Strength Training in Hypoxia on Muscle Structure and Gene Expression. Pflüg. Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2003, 446, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.-Y.; Kuo, T.-Y.; Liu, K.-L.; Dong, X.-Y.; Tung, K. Combining Normobaric Hypoxia With Short-Term Resistance Training Has No Additive Beneficial Effect on Muscular Performance and Body Composition. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurobe, K.; Huang, Z.; Nishiwaki, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Kanehisa, H.; Ogita, F. Effects of Resistance Training under Hypoxic Conditions on Muscle Hypertrophy and Strength. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2015, 35, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez Guardado, I.; Sánchez Ureña, B.; Camacho Cardenosa, A.; Camacho Cardenosa, M.; Olcina Camacho, G.; Timón Andrada, R. Effects of Strength Training under Hypoxic Conditions on Muscle Performance, Body Composition and Haematological Variables. Biol. Sport 2020, 37, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Guardado, I.; Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Olcina, G.J.; Rubio-Arias, J.A.; Chung, L.H.; Marín-Cascales, E.; Alcaraz, P.E.; Timón, R. Effects of High-Intensity Resistance Circuit-Based Training in Hypoxia on Body Composition and Strength Performance. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namboonlue, C.; Hamlin, M.J.; Sirasaporn, P.; Manimmanakorn, N.; Wonnabussapawich, P.; Thuwakum, W.; Sumethanurakkhakun, W.; Manimmanakorn, A. Optimal Degree of Hypoxia Combined with Low-Load Resistance Training for Muscle Strength and Thickness in Athletes. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2020, 20, 828–838. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, A.; Sugita, M.; Kato, K.; Fukuda, A.; Sudo, A.; Uchida, A. Hypoxia Increases Muscle Hypertrophy Induced by Resistance Training. Int. J. Sport. Physiol. Perform. 2010, 5, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Rubio-Arias, J.A.; Freitas, T.T.; Othalawa, S.; Andreu, L.; Timón, R.; Alcaraz, P.E. Muscle Architecture and Neuromuscular Changes After High-Resistance Circuit Training in Hypoxia. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019. Publish Ahead of Print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Törpel, A.; Peter, B.; Schega, L. Effect of Resistance Training Under Normobaric Hypoxia on Physical Performance, Hematological Parameters, and Body Composition in Young and Older People. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Magallanes, C. Effects of Traditional Strength Training vs CrossFit on Different Expressions of Strength. Retos Nuevas Tend. En Educ. Física Deporte Recreación 2021, 42, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Mosteiro-Muñoz, F.; Domínguez, R. Efectos del entrenamiento con sobrecargas isoinerciales sobre la función muscular / Effects of Inertial Overload Resistance Training on Muscle Function. Rev. Int. Med. Cienc. Act. Física Deporte 2017, 17, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito Jiménez, C. Volumen de entrenamiento como variable principal para la hipertrofia muscular. University of Basque Country. 2020. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10810/43518 (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- Scott, B.R.; Goods, P.S.R.; Slattery, K.M. High-Intensity Exercise in Hypoxia: Is Increased Reliance on Anaerobic Metabolism Important? Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).