Optical Particle Visualization Technique Using Red–Green–Blue and Core Storage Shed Flow Field Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Introduction of Latest Technologies and Research
3. Methodology
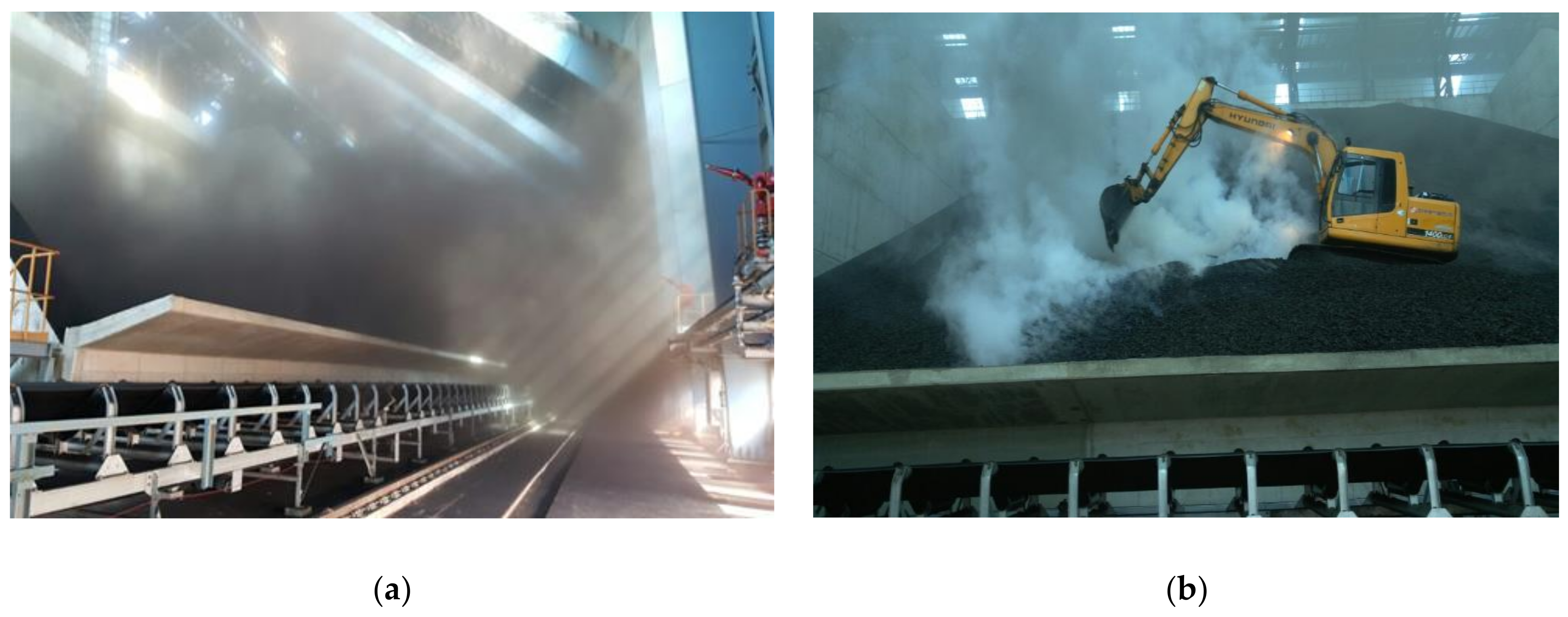
3.1. Description of Shad-Type CSS
3.2. Computational Analysis
3.2.1. Control Equation for CFD
3.2.2. Modeling and Boundary Conditions
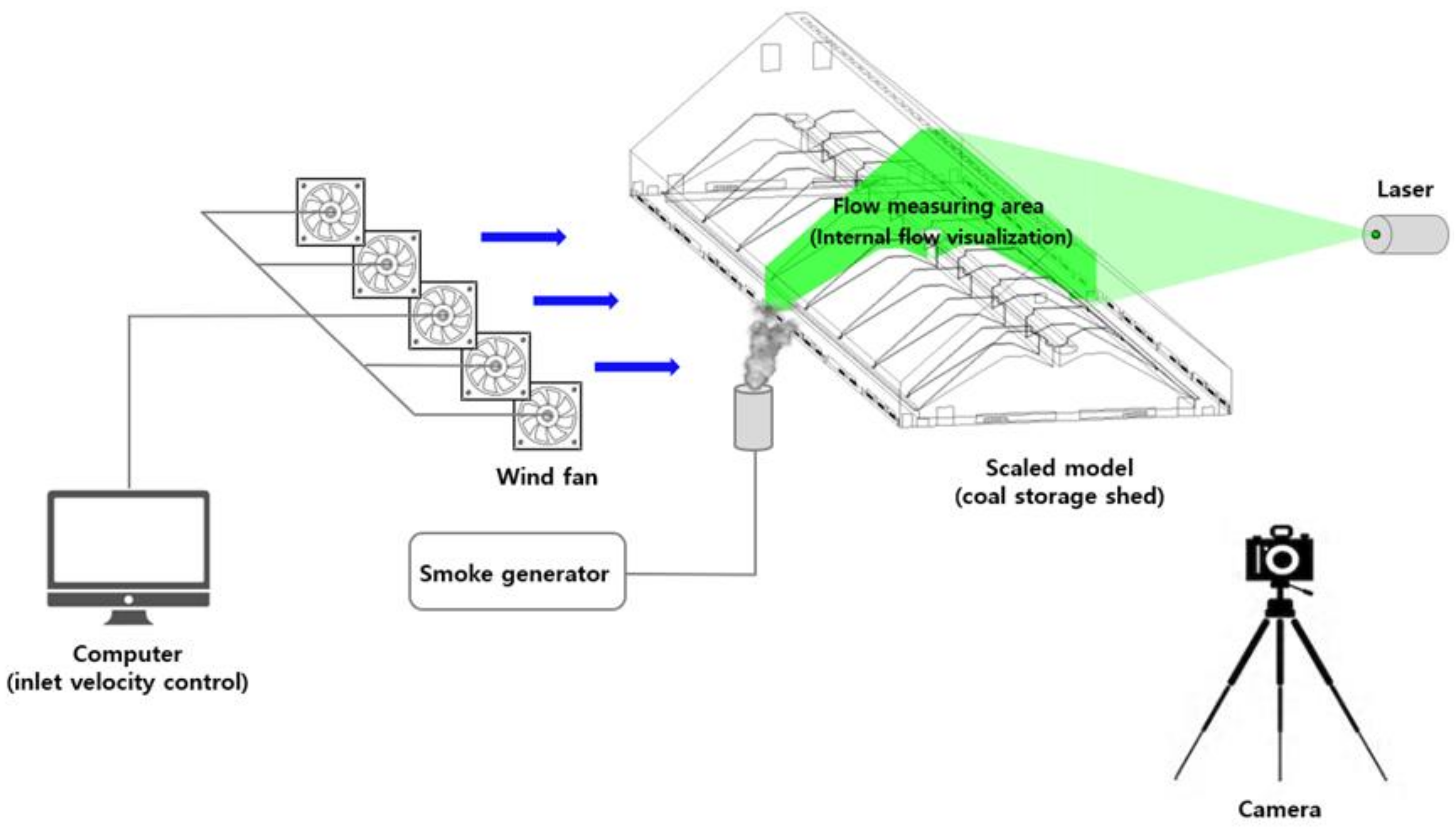
3.3. Verification Experiment Using the Flow Visualization Method
3.3.1. Flow Visualization Experiment Using a Laser
3.3.2. Laser Source and Wind Device
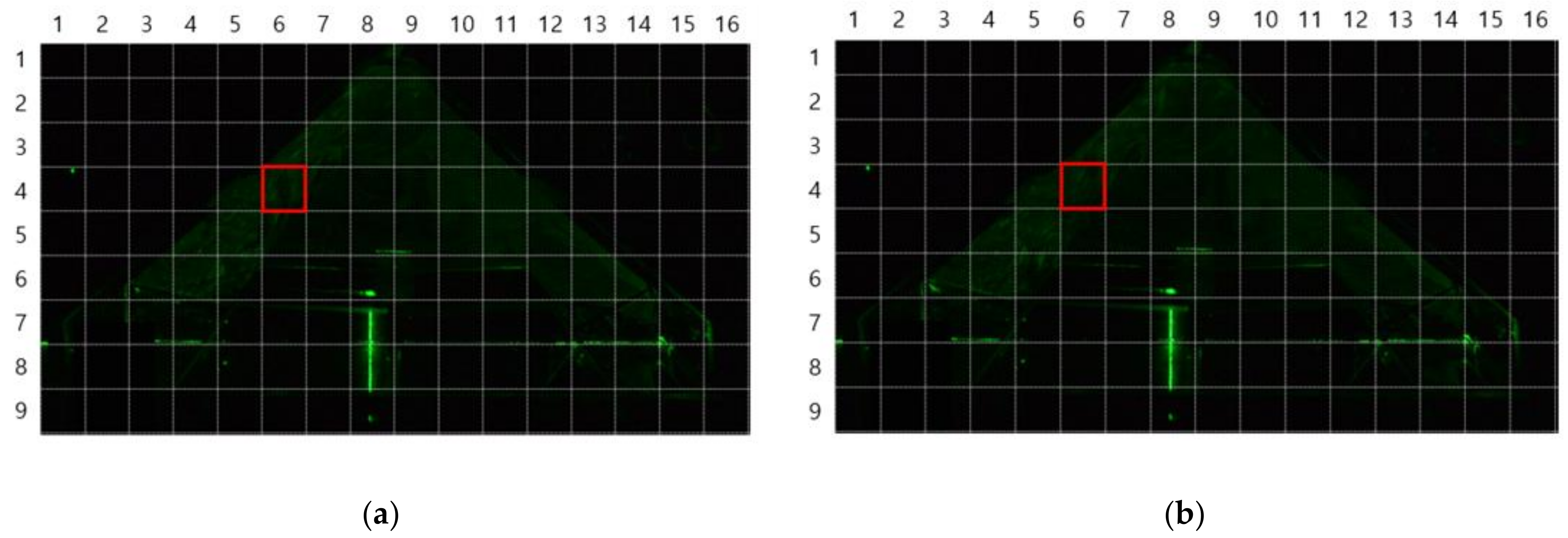
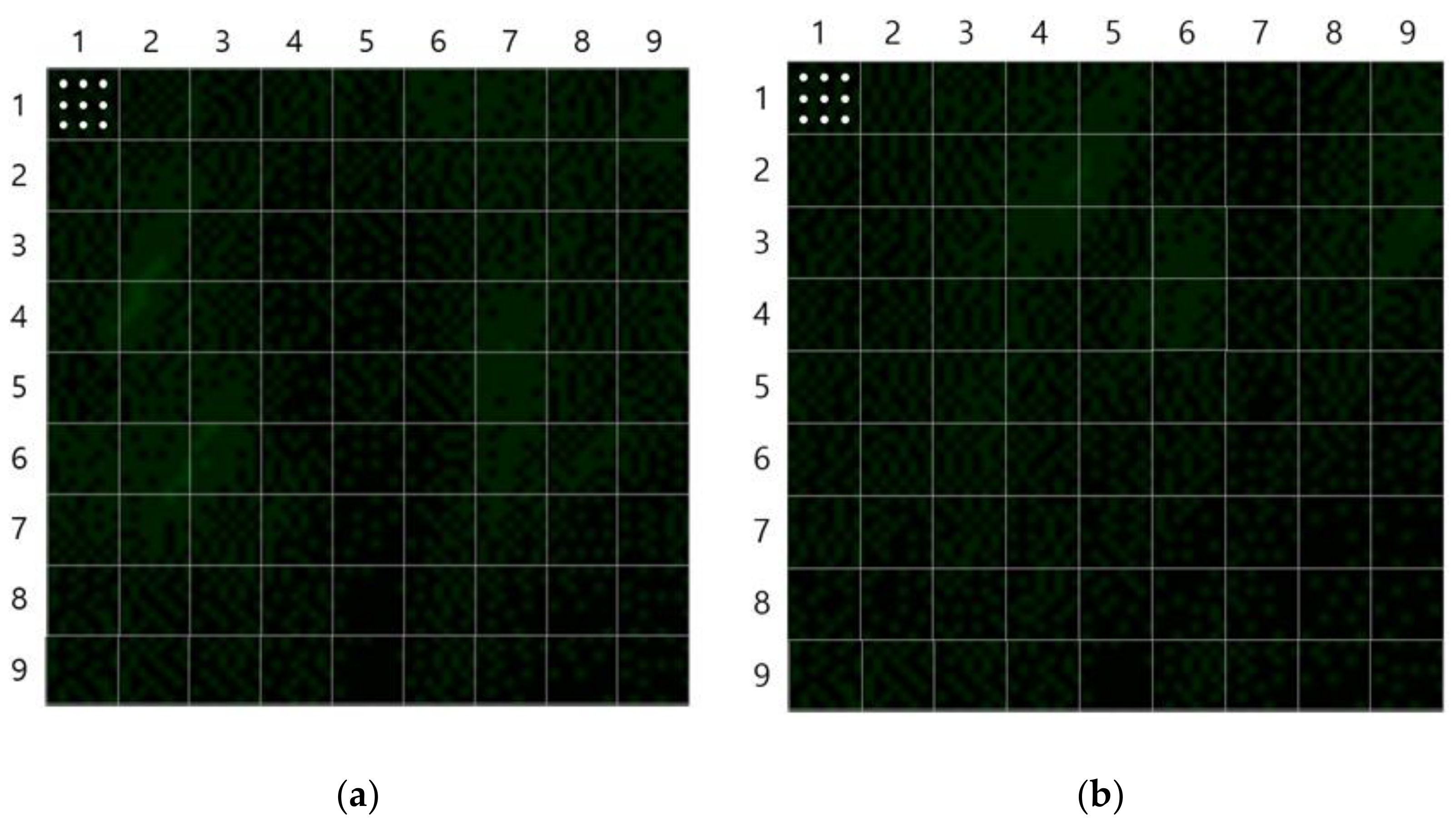
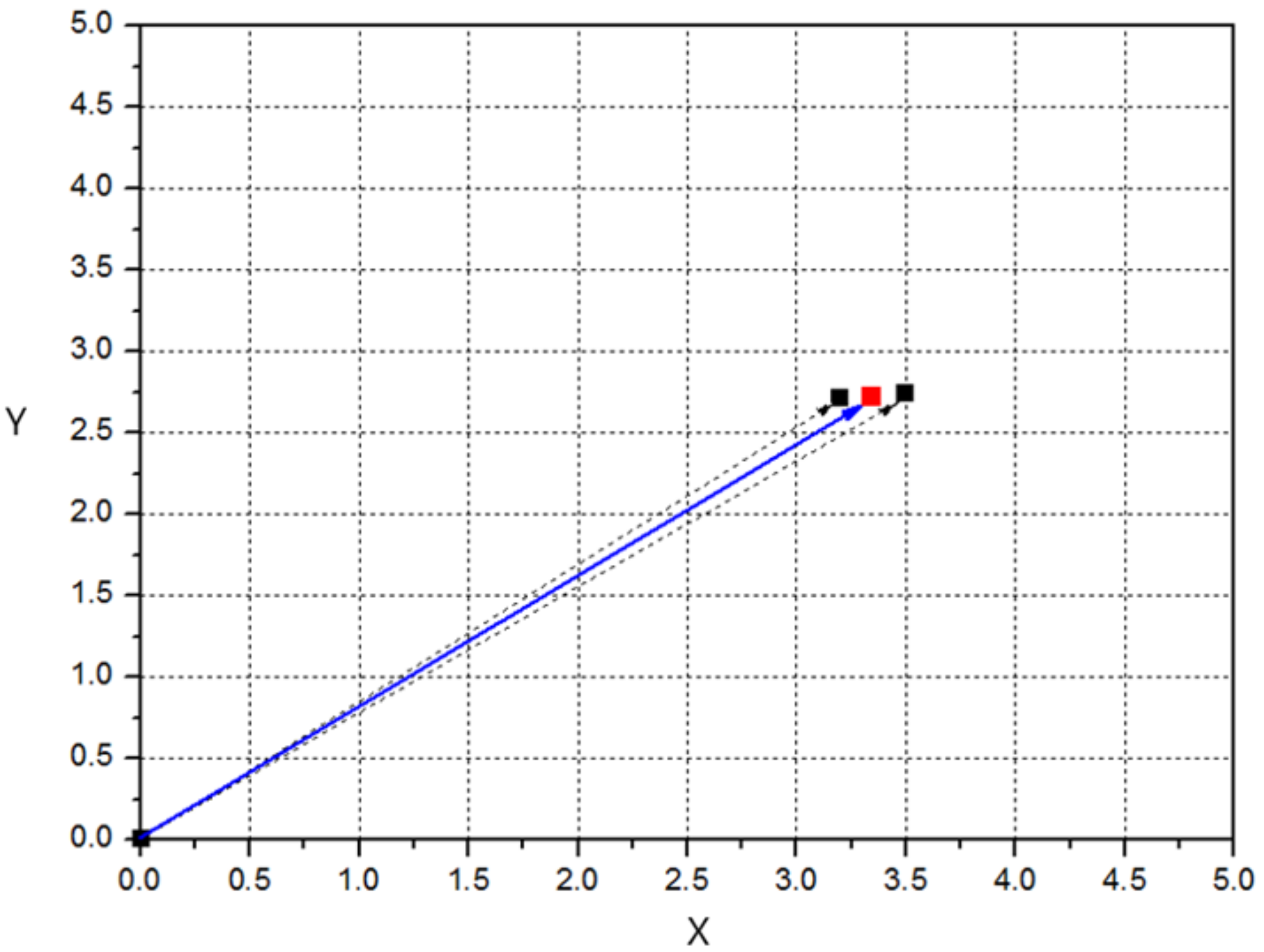
3.3.3. Flow Field Extraction Method
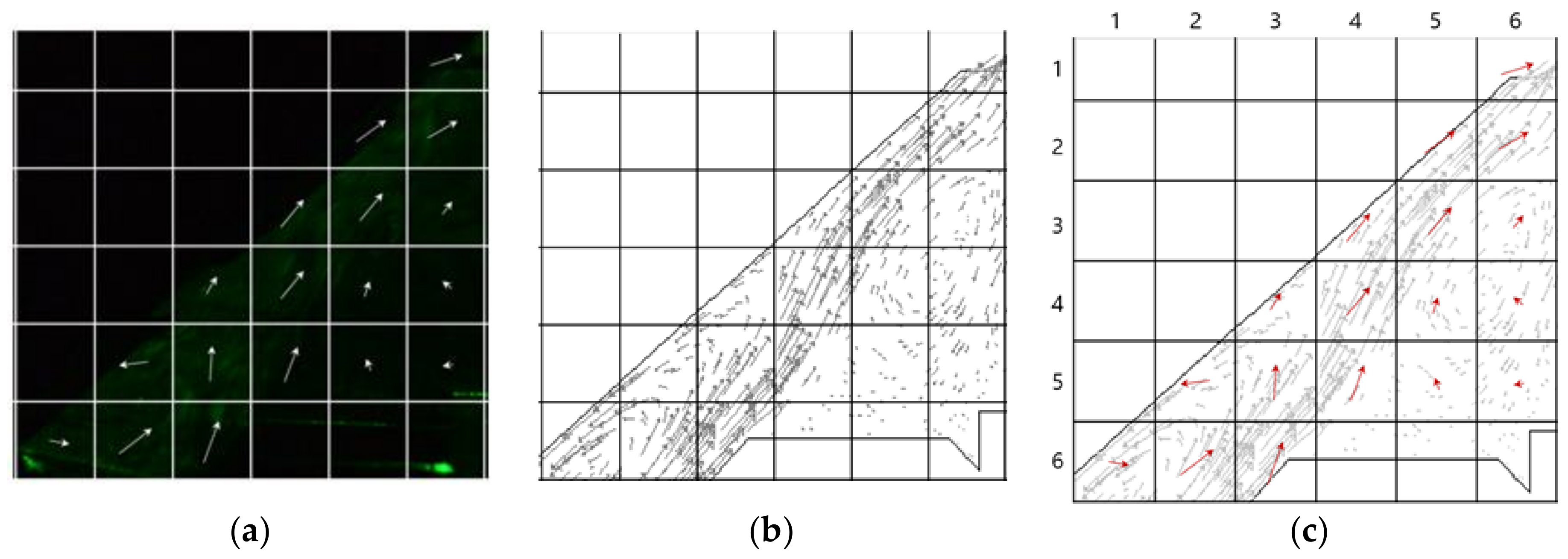
4. Results of Flow Characteristics Analysis
4.1. Experimental Results Using the Flow Visualization Method
4.2. Comparison of Results of Flow Visualization Experiment and Computational Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, F.; Ji, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Tao, R.; Su, C.; Niu, G. Analysis of the Current Status and Hot Technologies of Coal Spontaneous Combustion Warning. Processes 2023, 11, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçük, A.; Kadıoğlu, Y.; Gülaboğlu, M.Ş. A study of spontaneous combustion characteristics of a Turkish lignite: Particle size, moisture of coal, humidity of air. Combust. Flame 2003, 133, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadioglu, Y.; Varamaz, M. The effect of moisture content and air-drying on spontaneous combustion characteristics of two Turkish lignites. Fuel 2003, 82, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ren, T.; Zhong, X.; Wang, J. Study of the Oxidation Characteristics and CO Production Mechanism of Low-Rank Coal Goaf. Energies 2023, 16, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, S.R.; Kwiatek, L.M. Physical properties of selected block Argonne Premium bituminous coal related to CO2, CH4, and N2 adsorption. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2009, 77, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.S.; Busch, A.; Krooss, B.M.; Liu, Z.Y.; Yang, J.L. CH4 and CO2 sorption isotherms and kinetics for different size fractions of two coals. Fuel 2013, 108, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Sun, H.T.; Zhang, D.M.; Yang, K.; Wang, D.K.; Li, X.L.; Long, K.; Li, Y.N. Nuclear magnetic resonance study on the influence of liquid nitrogen cold soaking on the pore structure of different coals. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.B.; Wang, H.A. Experimental investigation on microstructure evolution and spontaneous combustion properties of secondary oxidation of lignite. Process Saf. Environ. 2019, 124, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Zhuang, X.; Font, O.; Izquierdo, M.; Alastuey, A.; Castro, I.; van Drooge, B.L.; Moreno, T.; Grimalt, J.O.; Elvira, J.; et al. Influence of soil cover on reducing the environmental impact of spontaneous coal combustion in coal waste gobs: A review and new experimental data. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2011, 85, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 88th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Das, M.; Salinas, V.; LeBoeuf, J.; Khan, R.; Jacquez, Q.; Camacho, A.; Hovingh, M.; Zychowski, K.; Rezaee, M.; Roghanchi, P.; et al. A Toxicological Study of the Respirable Coal Mine Dust: Assessment of Different Dust Sources within the Same Mine. Minerals 2023, 13, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine. Monitoring and Sampling Approaches to Assess Underground Coal Mine Dust Exposure; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Du, W.; Guo, J.; Wu, S.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z. Dust Dispersion Characteristics of Open Stockpiles and the Scale of Dust Suppression Shed. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.K. PIV Measurements of Open-Channel Turbulent Flow under Unconstrained Conditions. Fluids 2023, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Li, K.; Pang, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, B. Study on Water Jet Characteristics of Square Nozzle Based on CFD and Particle Image Velocimetry. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Yang, X. Design, Heat Transfer, and Visualization of the Milli-Reactor by CFD and ANN. Processes 2022, 10, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mičko, P.; Hečko, D.; Kapjor, A.; Nosek, R.; Kolková, Z.; Hrabovský, P.; Kantová, N.Č. Impact of the Speed of Airflow in a Cleanroom on the Degree of Air Pollution. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Hu, W. Two-Dimensional Flow Field Measurement Method for Sediment-Laden Flow Based on Optical Flow Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Salazar, D.M.; Fagehi, H.; Ghazwani, H.; Montefort, J.; Merati, P. Hybrid Optical-Flow-Cross-Correlation Method for Particle Image Velocimetry. J. Fluids Eng. 2020, 142, 054501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Liang, Y.; Tian, F.; Guo, B. Analytical Prediction of Coal Spontaneous Combustion Tendency: Pore Structure and Air Permeability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallikivi, M.; Hultmark, M.; Smits, A. Turbulent boundary layer statistics at very high Reynolds number. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 779, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G. Optical Design Optimization for LED Chip Bonding and Quantum Dot Based Wide Color Gamut Displays; University of California: Irvine, CA, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/optical-design-optimization-led-chip-bonding/docview/2031612971/se-2 (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Masaoka, K.; Nishida, Y.; Sugawara, M.; Nakasu, E. Design of Primaries for a Wide-Gamut Television Colorimetry. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2010, 56, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Conditions | Value | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| Coal storage | 100% | Porous zone Laminar flow zone |
| Angle of repose | 40° | |
| Coal diameter | 0.01 m | |
| Porosity | 0.2 | |
| Inlet velocity | 2.0 m/s | 1st floor Louver and window |
| Initial temperature | 20 °C | |
| Turbulent model | Standard k-ε model |
| Flow Object (Objn-m) | X-Y Coordinates | Gpeak Value | Coordinates Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obj1-1 | (2.159, −5.305) | 30 |  |
| Obj1-2 | (5.359, −2.584) | 27 | 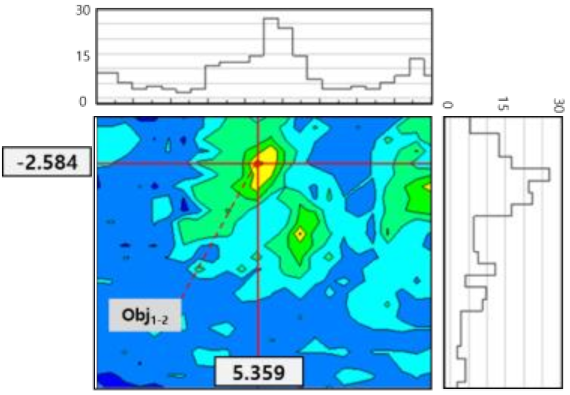 |
| Obj2-1 | (3.008, −7.649) | 27 |  |
| Obj2-2 | (6.497, −4.899) | 26 |  |
| CFD Results | Flow Visualization Experiment | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of Vector | Direction of Vector | Length of Vector | Direction of Vector | ||||||
| a | b | c | a | b | c | ||||
| High velocity area | A(6,3) | 0.85 | 0.83 | 1.18 | 45.68 | 1.22 | 0.52 | 1.32 | 66.91 |
| A(5,3) | 0.77 | 0.59 | 0.97 | 52.54 | 1.02 | 0.07 | 1.02 | 86.07 | |
| A(5,4) | 0.90 | 0.60 | 1.08 | 56.31 | 1.02 | 0.48 | 1.13 | 64.79 | |
| A(4,4) | 0.77 | 0.46 | 0.89 | 59.14 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 1.06 | 46.14 | |
| A(3,4) | 0.51 | 0.38 | 0.63 | 53.31 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 1.11 | 44.63 | |
| A(3,5) | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.88 | 48.20 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 1.14 | 46.41 | |
| A(2,5) | 0.52 | 0.66 | 0.84 | 38.23 | 0.66 | 0.99 | 1.19 | 33.69 | |
| A(2,6) | 0.61 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 38.75 | 0.48 | 1.00 | 1.11 | 25.64 | |
| A(1,6) | 0.43 | 0.66 | 0.78 | 33.08 | 0.30 | 1.09 | 1.13 | 15.38 | |
| Recirculation Area (inlet) | A(6,1) | 0.66 | 0.83 | 1.06 | 218.49 | 0.06 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 354.73 |
| A(6,2) | 0.83 | 0.73 | 1.10 | 48.67 | 0.77 | 1.13 | 1.36 | 34.27 | |
| A(5,2) | 0.43 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 219.58 | 0.09 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 185.35 | |
| A(5,3) | 0.77 | 0.59 | 0.97 | 52.54 | 1.02 | 0.07 | 1.02 | 86.07 | |
| A(4,3) | 0.10 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 195.12 | 0.47 | 0.34 | 0.58 | 54.12 | |
| Recirculation Area (wall) | A(5,5) | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 180.00 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 0.35 | 115.12 |
| A(5,6) | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 228.24 | 0.06 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 191.69 | |
| A(4,5) | 0.39 | 0.27 | 0.47 | 55.30 | 0.44 | 0.15 | 0.46 | 71.17 | |
| A(4,6) | 0.39 | 0.24 | 0.45 | 238.39 | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 148.00 | |
| A(3,6) | 0.20 | 0.38 | 0.43 | 27.77 | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.51 | 49.76 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, M.-L.; Ha, J.-S. Optical Particle Visualization Technique Using Red–Green–Blue and Core Storage Shed Flow Field Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910997
Cho M-L, Ha J-S. Optical Particle Visualization Technique Using Red–Green–Blue and Core Storage Shed Flow Field Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(19):10997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910997
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Mok-Lyang, and Ji-Soo Ha. 2023. "Optical Particle Visualization Technique Using Red–Green–Blue and Core Storage Shed Flow Field Analysis" Applied Sciences 13, no. 19: 10997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910997
APA StyleCho, M.-L., & Ha, J.-S. (2023). Optical Particle Visualization Technique Using Red–Green–Blue and Core Storage Shed Flow Field Analysis. Applied Sciences, 13(19), 10997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910997






