Artificial Neural Network Based Prediction of Long-Term Electric Field Strength Level Emitted by 2G/3G/4G Base Station
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Related Works
1.2. Existing Gaps in Related Works
- A new ANN model with Levenberg–Marquardt (LM) and Bayesian Regulation (BR) learning algorithms was proposed.
- The proposed models were used to predict RF-EMF levels and determine long-term exposure patterns without real-time measurements.
- A performance comparison was made with similar works, and it was shown that the proposed models have higher prediction accuracy.
- Mitigating potential health risks by implementing measures to reduce exposure to RF-EMF.
- Helping regulatory compliance by identifying areas where the maximum allowable levels are likely to be exceeded.
- Supporting the research and development of new technologies that utilize RF-EMF and helping test the effectiveness of new technologies in reducing RF-EMF exposure.
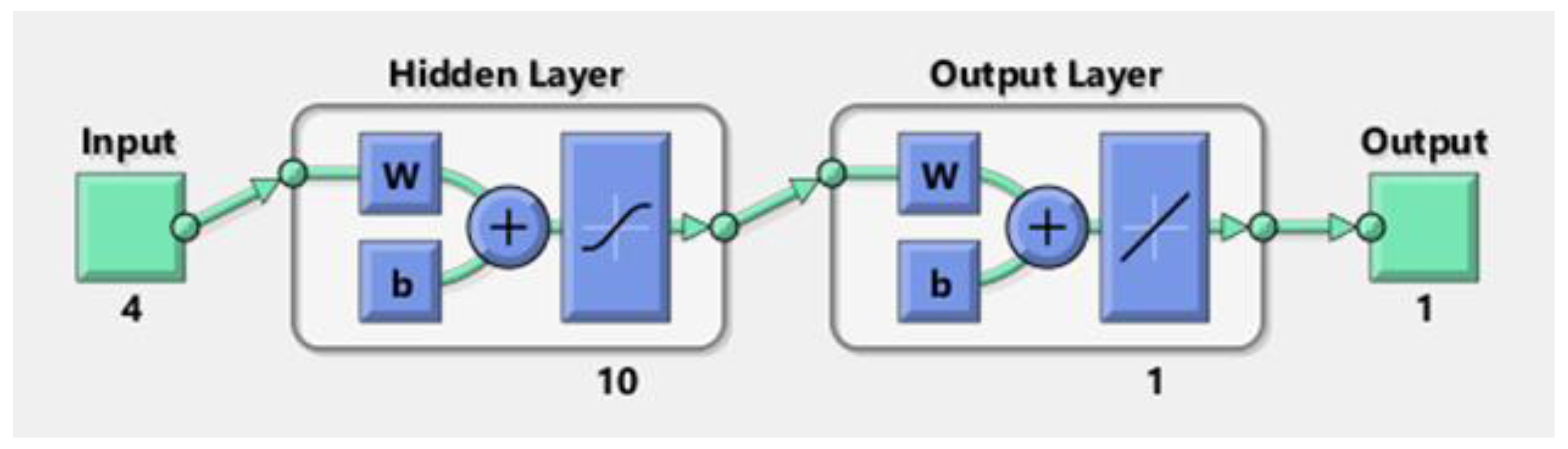
2. Artificial Neural Networks
3. Methodology
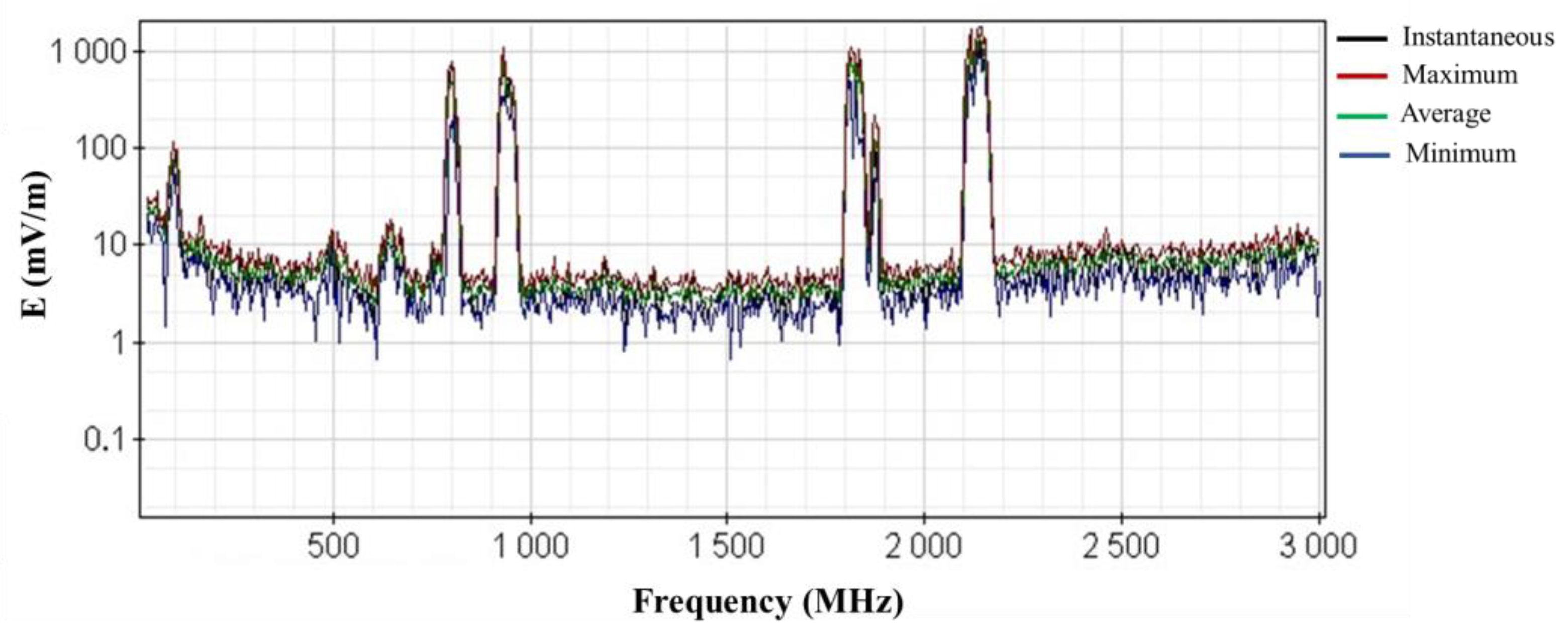
3.1. RF-EMF Data Acquisition
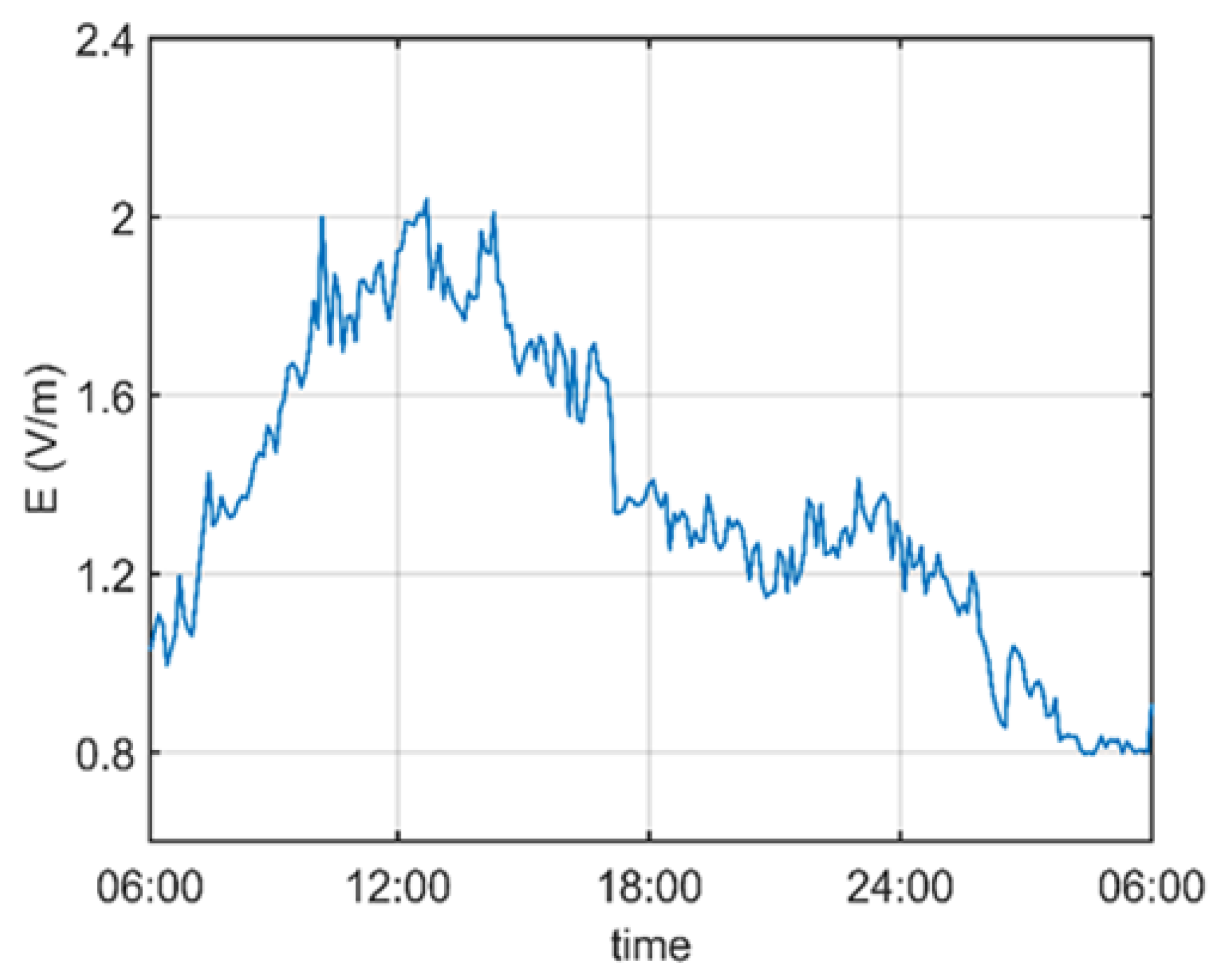
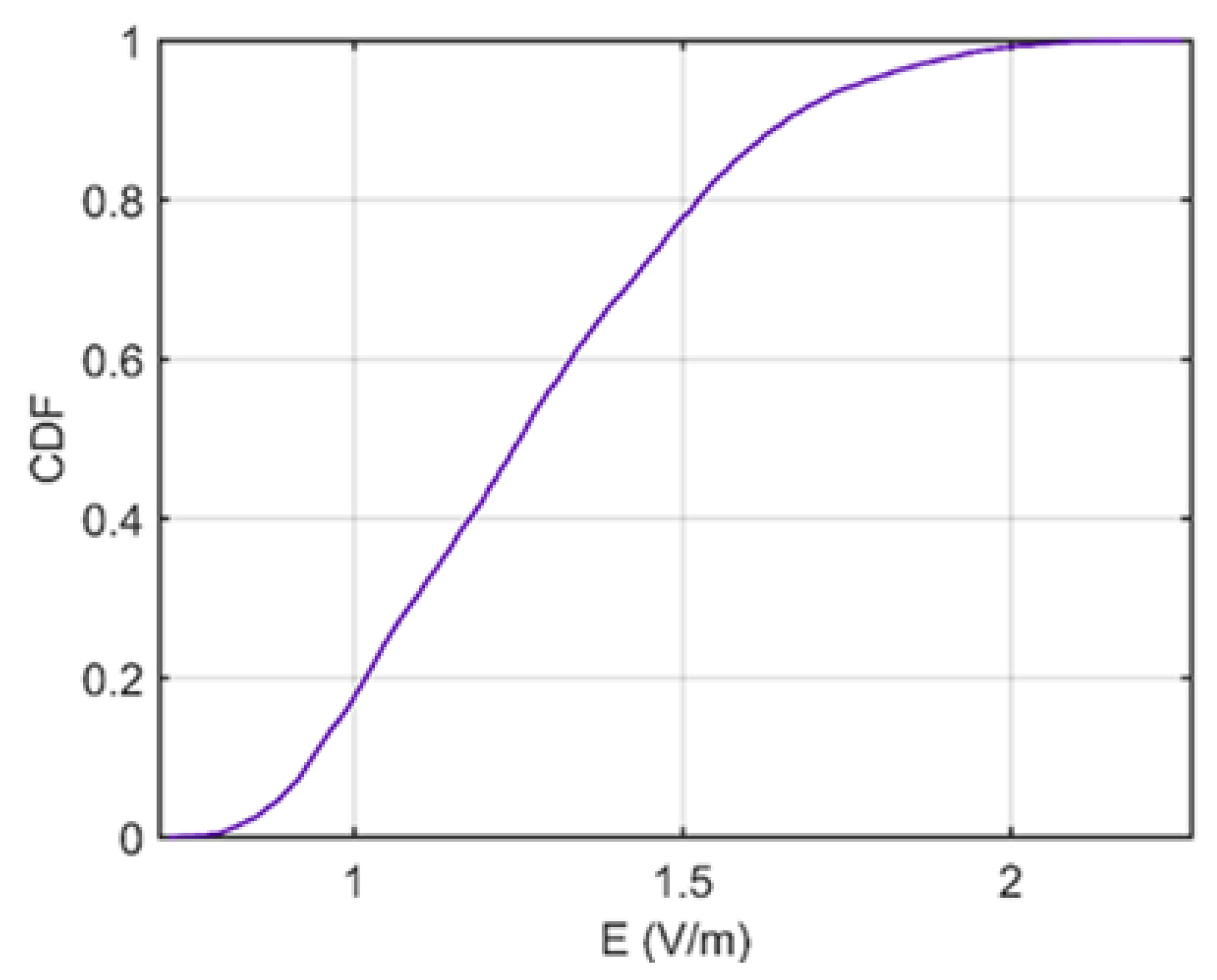
3.2. Data Processing
3.3. RF-EMF Prediction
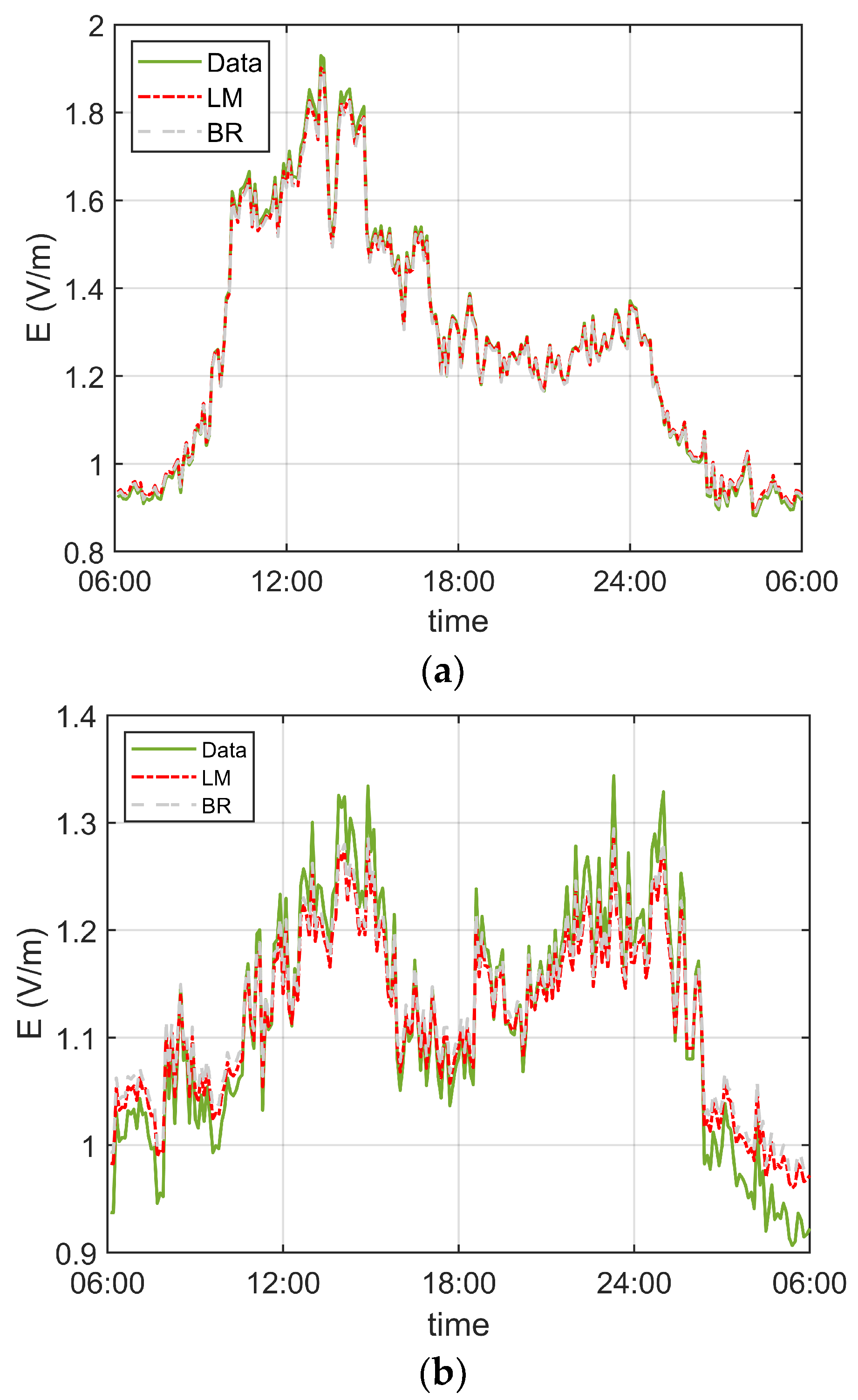
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramarakula, M. An efficient uplink power control algorithm for LTE-advanced relay networks to improve coverage area. Wireless Pers. Commun. 2020, 110, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. In Non-Ionization Radiation, Part 2: Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2013; Volume 102, 461p. [Google Scholar]
- Kaszuba-Zwoińska, J.; Gremba, J.; Gałdzińska-Calik, B.; Wójcik-Piotrowicz, K.; Thor, P.J. Electromagnetic field induced biological effects in humans. Przegl. Lek. 2015, 72, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bilgici, B.; Gun, S.; Avci, B.; Akar, A.; Korunur Engiz, B. What is adverse effect of wireless local area network, using 2.45 GHz, on the reproductive system? Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2018, 94, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkis, M.E.; Bilgin, H.M.; Akpolat, V.; Dasdag, S.; Yegin, K.; Yavas, M.C.; Akdag, M.Z. Effect of 900-, 1800-, and 2100-MHz radiofrequency radiation on DNA and oxidative stress in brain. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2019, 38, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabré-Riera, A.; van Wel, L.; Liorni, I.; Thielens, A.; Birks, L.E.; Pierotti, L.; Joseph, W.; González-Safont, L.; Ibarluzea, J.; Ferrero, A.; et al. Association between estimated whole-brain radiofrequency electromagnetic fields dose and cognitive function in preadolescents and adolescents. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 231, 113659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuermann, D.; Mevissen, M. Manmade electromagnetic fields and oxidative stress—biological effects and consequences for health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICNIRP. Guidelines for limiting exposure to electromagnetic fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 2020, 118, 483–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICTA. Ordinance Change on By-Law on Determination, Control and Inspection of the Limit Values of Electromagnetic Field Force from the Electronic Communication Devices According to International Standards; Law No.30394. 2018. Available online: https://www.resmigazete.gov.tr/eskiler/2018/04/20180417-2.htm/ (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Kurnaz, C.; Engiz, B.K. Measurement and evaluation of electric field strength in Samsun city center. Int. J. Appl. Math. Electron. Comput. 2016, 4, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnaz, C.; Bozkurt, M.C. Measurement and evaluation of electromagnetic pollution levels in Ünye district of Ordu. J. N. Results Sci. 2016, 5, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Yang, C.; Cai, R.S.; Ye, H.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Lin, K.; Song, J.; Huang, X.; et al. Analysis of the relationship between electromagnetic radiation characteristics and urban functions in highly populated urban areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyare, R.N.; Volskiy, V.; Vandenbosch, G.A.E. Study of the correlation between outdoor and indoor electromagnetic exposure near cellular base stations in Leuven, Belgium. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wei, M.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, S. Measurement and mapping of the electromagnetic radiation in the urban environment. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2020, 39, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfi, L. Measurement of electromagnetic radiation with respect to the hours and days of a week at 100 kHz–3GHz frequency band in a Turkish dwelling. Measurement 2013, 46, 3002–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engiz, B.K.; Kurnaz, C. Long-term electromagnetic field measurement and assessment for a shopping mall. Radiat. Prot. Dosimetry 2017, 175, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadag, T.; Yüceer, M.; Abbasov, T. A large-scale measurement, analysis and modelling of electromagnetic radiation levels in the vicinity of GSM/UMTS base stations in an urban area. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2016, 168, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, S.; Wiart, J.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. Assessment of long-term spatio-temporal radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurnaz, C.; Mutlu, M. Comprehensive radiofrequency electromagnetic field measurements and assessments: A city center example. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnaz, C.; Mutlu, M. Monitoring and modelling of long-term radiofrequency electromagnetic field levels. J. Fac. Eng. Archit. Gazi Univ. 2021, 36, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera González, M.X.; Félix González, N.; López, I.; Ochoa Zambrano, J.S.; Miranda Martínez, A.; Maestú Unturbe, C. Compact exposimeter device for the characterization and recording of electromagnetic fields from 78 MHz to 6 GHz with several narrow bands (300 kHz). Sensors 2021, 21, 7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neskovic, A.; Neskovic, N.; Paunovic, D. Indoor electric field level prediction model based on the artificial neural networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2000, 4, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neskovic, A.; Neskovic, N.; Paunovic, D. Macrocell electric field strength prediction model based upon artificial neural networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2002, 20, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neskovic, A.; Neskovic, N. Microcell electric field strength prediction model based upon artificial neural networks. AEU- Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2010, 64, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isabona, J. Wavelet generalized regression neural network approach for robust field strength prediction. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 114, 3635–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraiha Lopes, R.L.; Fraiha, S.G.; Lima, V.D.; Gomes, H.S.; Cavalcante, G.P. Hybrid ARIMA and neural network modelling applied to telecommunications in urban environments in the Amazon region. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2020, 2020, 2671746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alihodzic, A.; Mujezinovic, A.; Turajlic, E. Electric and magnetic field estimation under overhead transmission lines using artificial neural networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 105876–105891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakacı, F.H.; Cerezci, O. Prediction of magnetic pollution with artificial neural network in living areas. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 16, 2701–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yue, Y.; Song, X.; Ji, S. Measurement and prediction of indoor wideband electric field radiation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 6504612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, S.; Vermeeren, G.; Van den Bossche, M.; Aminzadeh, R.; Verloock, L.; Thielens, A.; Leroux, P.; Bergs, J.; Braem, B.; Philippron, A.; et al. Lessons learned from a distributed RF-EMF sensor network. Sensors 2022, 22, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wiart, J. Sensor-aided EMF exposure assessments in an urban environment using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mazloum, T.; Wiart, J. Prediction of RF-EMF exposure by outdoor drive test measurements. Telecom 2022, 3, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpat, E.; Bakcan, M.R. Measurement and prediction of electromagnetic radiation exposure level in a university campus. Teh. Vjesn. 2022, 29, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, M.T.; Menhaj, M.B. Training feedforward networks with the Marquardt algorithm. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, P.; Gupta, N.K.; Ambikapathy, A. Comparative Study of Various Training Algorithms of Artificial Neural Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication Control and Networking (ICACCCN), Greater Noida, India, 12–13 October 2018; pp. 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SRM-3006, Band Selective EMF Meter. Available online: https://www.narda-sts.com/en/selective-emf/srm-3006-field-strength-analyzer/ (accessed on 16 September 2023).
- Kurnaz, C.; Engiz, B.K.; Kose, U. An empirical study: The impact of the number of users on electric field strength of wireless communications. Radiat. Prot. Dosimetry 2018, 182, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






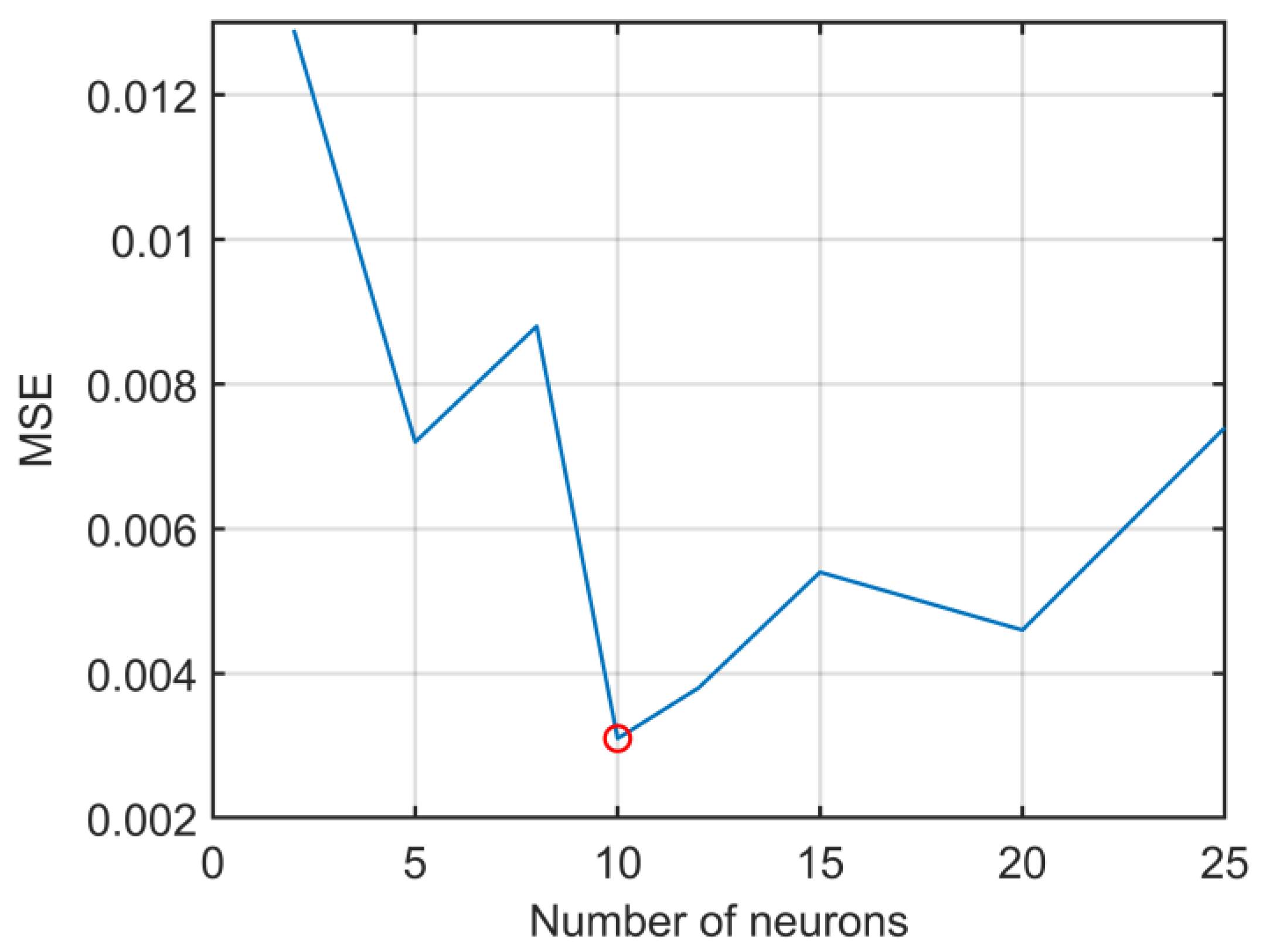
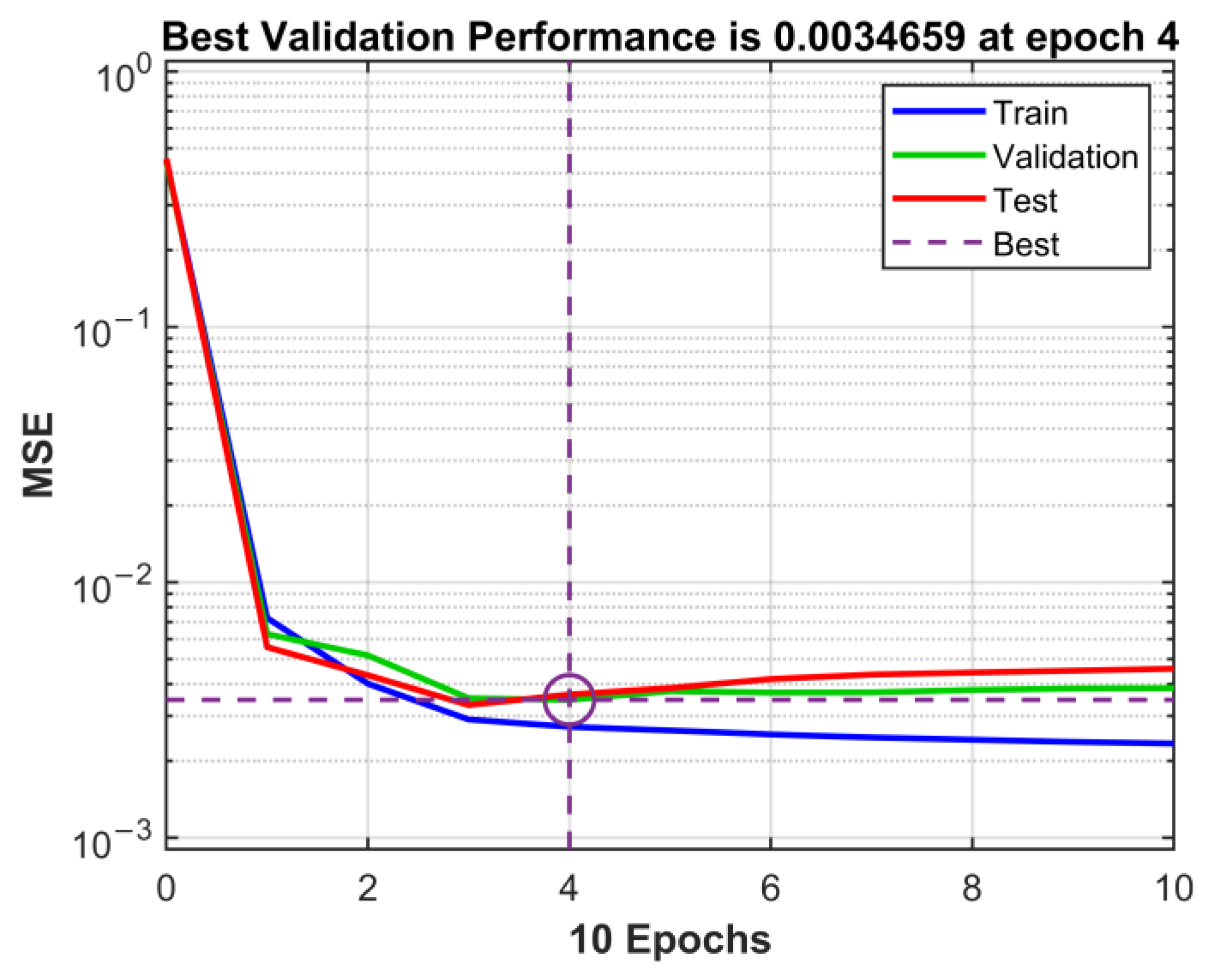
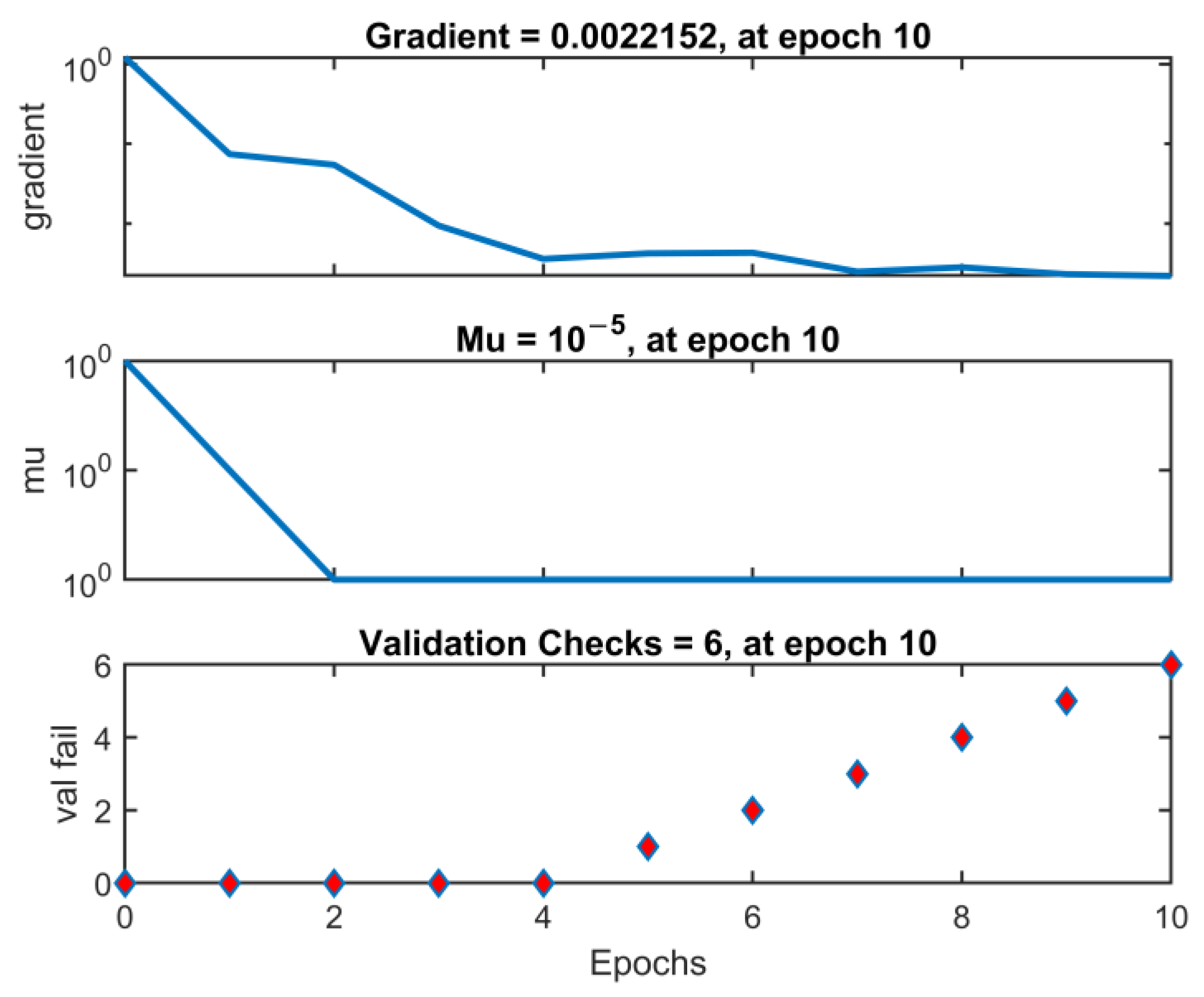
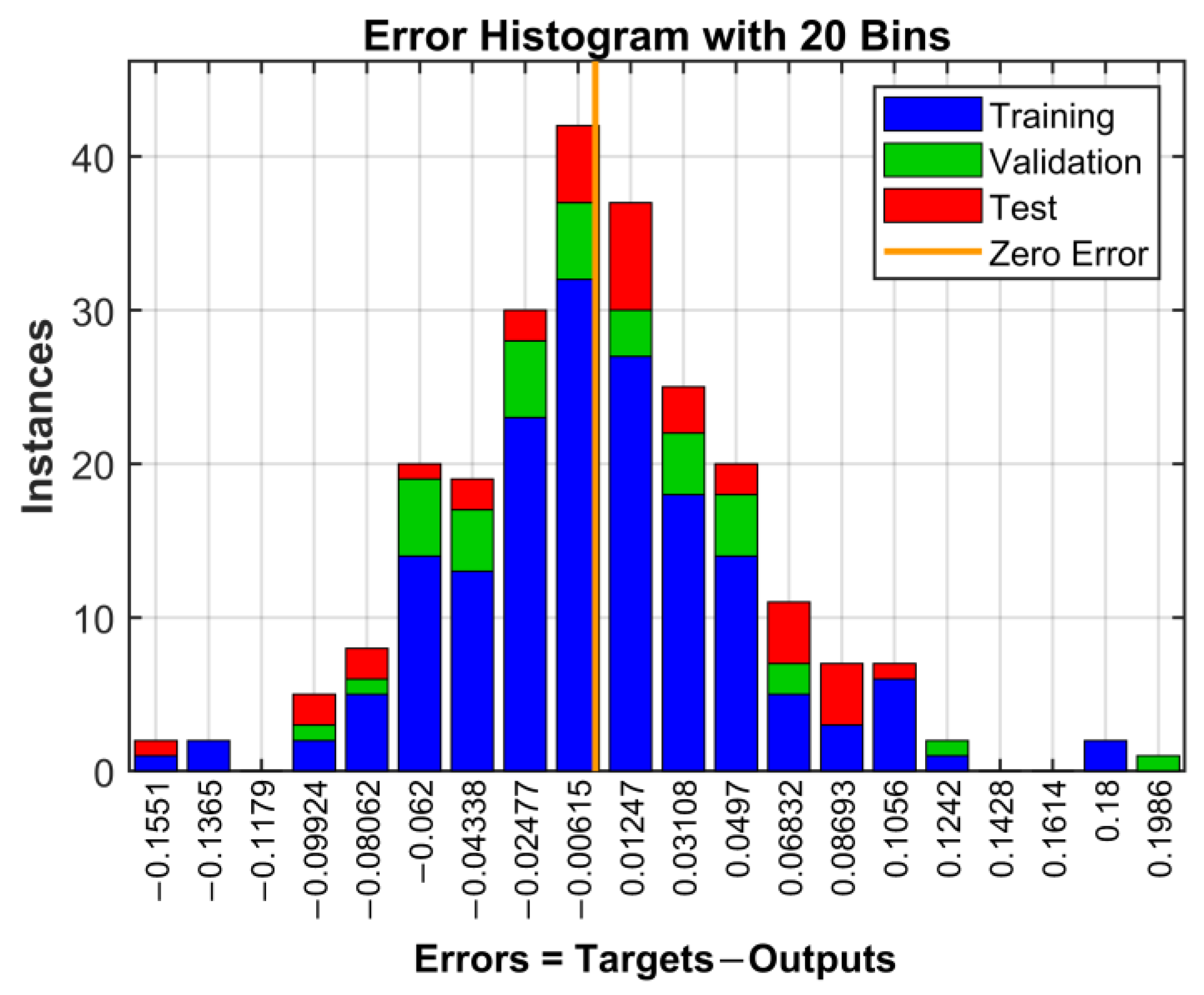

| Frequency (MHz) | E (V/m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ICNIRP | ICTA | ||
| 0.010–0.15 | 87 | 65.25 | |
| 0.15–1 | 87 | 65.25 | |
| 1–10 | 87/f 1/2 | 65.25/f 1/2 | |
| 10–400 | 28 | 21 | |
| 400–789 | 1.375f 1/2 | 1.03f 1/2 | |
| 790–2000 | 1.375f 1/2 | 0.96f 1/2 | |
| 2000–94000 | 61 | 42.93 | |
| Base station using specific frequency | 900 | 41.25 | 28.80 |
| 1800 | 58.33 | 40.72 | |
| 2100 | 61 | 42.93 | |
| 2600 | 61 | 42.93 | |
| f is frequency in MHz | |||
| Service Name | Contribution (%) |
|---|---|
| LTE 800 | 17.04 |
| GSM 900 | 21.02 |
| GSM 1800 | 26.27 |
| UMTS 2100 | 34.99 |
| Others | 0.680 |
| Days | MSE * | Epoch * | Performance * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Validation | Testing | |||
| Mon. | 2.71 × 10−3 | 2.89 × 10−3 | 2.84 × 10−3 | 6.30 | 2.76 × 10−3 |
| Tue. | 3.91 × 10−3 | 4.00 × 10−3 | 4.06 × 10−3 | 6.42 | 3.95 × 10−3 |
| Wed. | 3.55 × 10−3 | 3.66 × 10−3 | 3.85 × 10−3 | 6.38 | 3.61 × 10−3 |
| Thu. | 3.41 × 10−3 | 3.78 × 10−3 | 3.59 × 10−3 | 6.18 | 3.49 × 10−3 |
| Fri. | 2.91 × 10−3 | 2.97 × 10−3 | 3.21 × 10−3 | 6.46 | 2.96 × 10−3 |
| Sat. | 3.77 × 10−3 | 3.85 × 10−3 | 4.08 × 10−3 | 6.24 | 3.83 × 10−3 |
| Sun. | 2.58 × 10−3 | 2.74 × 10−3 | 2.78 × 10−3 | 6.86 | 2.64 × 10−3 |
| Days | MSE * | Epoch * | Performance * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Testing | |||
| Mon. | 2.28 × 10−3 | 4.51 × 10−3 | 473.18 | 2.95 × 10−3 |
| Tue. | 3.41 × 10−3 | 5.72 × 10−3 | 154.34 | 4.11 × 10−3 |
| Wed. | 3.04 × 10−3 | 5.63 × 10−3 | 289.98 | 3.82 × 10−3 |
| Thu. | 3.66 × 10−3 | 4.02 × 10−3 | 120.10 | 3.77 × 10−3 |
| Fri. | 2.60 × 10−3 | 4.94 × 10−3 | 344.52 | 3.30 × 10−3 |
| Sat. | 3.19 × 10−3 | 5.73 × 10−3 | 277.84 | 3.96 × 10−3 |
| Sun. | 2.82 × 10−3 | 3.76 × 10−3 | 335.80 | 3.10 × 10−3 |
| Days | R Value * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Validation | Testing | All | |
| Mon. | 0.981 | 0.982 | 0.977 | 0.980 |
| Tue. | 0.982 | 0.976 | 0.943 | 0.975 |
| Wed. | 0.978 | 0.979 | 0.941 | 0.974 |
| Thu. | 0.975 | 0.976 | 0.960 | 0.972 |
| Fri. | 0.977 | 0.962 | 0.959 | 0.971 |
| Sat. | 0.939 | 0.881 | 0.894 | 0.972 |
| Sun. | 0.885 | 0.826 | 0.853 | 0.868 |
| Days | R Value * | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Testing | All | |
| Mon. | 0.982 | 0.978 | 0.981 |
| Tue. | 0.975 | 0.954 | 0.972 |
| Wed. | 0.973 | 0.965 | 0.972 |
| Thu. | 0.973 | 0.962 | 0.971 |
| Fri. | 0.968 | 0.956 | 0.966 |
| Sat. | 0.929 | 0.944 | 0.932 |
| Sun. | 0.863 | 0.854 | 0.860 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Engiz, B.K. Artificial Neural Network Based Prediction of Long-Term Electric Field Strength Level Emitted by 2G/3G/4G Base Station. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910621
Engiz BK. Artificial Neural Network Based Prediction of Long-Term Electric Field Strength Level Emitted by 2G/3G/4G Base Station. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(19):10621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910621
Chicago/Turabian StyleEngiz, Begum Korunur. 2023. "Artificial Neural Network Based Prediction of Long-Term Electric Field Strength Level Emitted by 2G/3G/4G Base Station" Applied Sciences 13, no. 19: 10621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910621
APA StyleEngiz, B. K. (2023). Artificial Neural Network Based Prediction of Long-Term Electric Field Strength Level Emitted by 2G/3G/4G Base Station. Applied Sciences, 13(19), 10621. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910621





