Abstract
Multimodal emotion classification (MEC) has been extensively studied in human–computer interaction, healthcare, and other domains. Previous MEC research has utilized identical multimodal annotations (IMAs) to train unimodal models, hindering the learning of effective unimodal representations due to differences between unimodal expressions and multimodal perceptions. Additionally, most MEC fusion techniques fail to consider the unimodal–multimodal inconsistencies. This study addresses two important issues in MEC: learning satisfactory unimodal representations of emotion and accounting for unimodal–multimodal inconsistencies during the fusion process. To tackle these challenges, the authors propose the Two-Stage Conformer-based MEC model (Uni2Mul) with two key innovations: (1) in stage one, unimodal models are trained using independent unimodal annotations (IUAs) to optimize unimodal emotion representations; (2) in stage two, a Conformer-based architecture is employed to fuse the unimodal representations learned in stage one and predict IMAs, accounting for unimodal–multimodal differences. The proposed model is evaluated on the CH-SIMS dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that Uni2Mul outperforms baseline models. This study makes two key contributions: (1) the use of IUAs improves unimodal learning; (2) the two-stage approach addresses unimodal–multimodal inconsistencies during Conformer-based fusion. Uni2Mul advances MEC by enhancing unimodal representation learning and Conformer-based fusion.
1. Introduction
Emotion classification is a crucial subtask that has been extensively studied in domains such as human–computer interaction, healthcare, and medicine. Early research on emotion classification primarily utilized unimodal data, such as text [1,2], audio [3], or visual cues [4], and achieved notable success. Recently, researchers have started incorporating two or more modalities to achieve multimodal emotion classification (MEC) [5,6,7]. MEC (explanations for all abbreviations in Appendix A Table A1) can furnish salient clues to more accurately discern the genuine emotional states of the opinion holder and enhance the precision of outcomes [8]. With the burgeoning of short video applications, MEC has become an active area of research [9].
The two most salient components in MEC tasks are unimodal emotion representation learning and multimodal fusion. In many scenarios, unimodal emotion expression differs from multimodal emotion perception, and multimodal annotation stems from the interaction between each modality. Taking a video clip from the CH-SIMS dataset as an exemplar, as illustrated in Figure 1, the text “Isn’t it about to go bankrupt”, with an emotional annotation of −0.8, indicates a negative emotion, and the audio modality annotation is also −0.8. The visual modality expression includes a smile and corresponds to a positive emotional annotation of 1.0. The combination of these three modalities results in a multimodal emotional annotation of 0.6, indicating a positive emotion for the video clip.
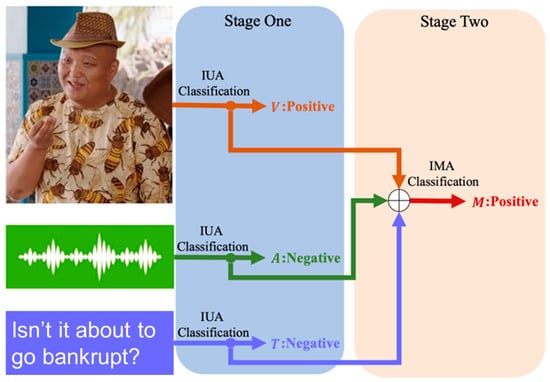
Figure 1.
An example of inconsistency between unimodal emotion expression and multimodal emotion perception. Stage One: unimodal emotion recognition, Stage Two: multimodal fusion for emotion recognition. M: Multimodal, V: Vision, A: Audio, T: Text, ⊕: multimodal fusion.
The majority of existing research employs identical multimodal annotations (IMAs) for unimodal model pretraining and multimodal fusion [10,11,12]. The unimodal models trained using IMAs cannot learn satisfactory representations but rather those of forced alignment. The representation of forced alignment will contain certain discrepancies in the distribution of each modality and form an irregular semantic space, as depicted in Figure 2a. Multimodal fusion grounded on this will generate distorted and convoluted classification boundaries (see Figure 2c). If the unimodal models are trained using independent unimodal annotations (IUAs), the representations for each modality are roughly within a unified region and harbor certain differences (see Figure 2b). Leveraging unimodal representations with certain differences such as this for multimodal fusion will contribute to superior fusion outcomes [13]. Meanwhile, the multimodal fusion strategy is also imperative to achieve a comprehensive MEC model. A satisfactory fusion strategy can fully harness the information from each modality and can capture the differences and interactions between modalities. Building upon this, the distributions of each emotion category are uniform, and the classification boundaries are also relatively systematic (see Figure 2d). Most current studies on fusion pay less attention to the unimodal–multimodal emotions’ inconsistency [14,15,16,17] and struggle to learn the differences between different modalities [13].
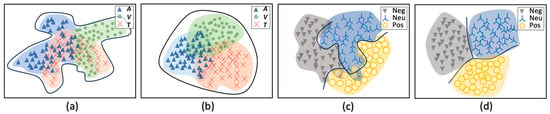
Figure 2.
Hypothesized unimodal and multimodal emotion representation. In (a,b), the markers of different colors represent different modalities, and shapes with dotted curves of different colors represent semantic spaces of respective modalities. The black solid curves indicate the envelope of these colored lines. In (c,d), the markers of different colors represent different emotion categories, and the black solid curves represent classification boundaries. V: Vision, A: Audio, T: Text.
The CH-SIMS dataset encompasses not only IMAs for each clip but also IUAs for each modality [13], which is consistent with our stance and endeavors to train the unimodal model with IUAs, but does not delve deeply enough into the two aforementioned problems: unimodal representation learning and multimodal fusion strategy.
Problem Statement: In most existing multimodal datasets with IMAs:
where represents different modalities, is the data, and is the IMAs. MEC models based on these datasets take as input and as output in the whole training stage. This process can be expressed as
where is responsible for both unimodal representation and multimodal fusion.
We define CH-SIMS as
where represents IUAs and represents IMAs. We express the training process based on CH-SIMS as
where is responsible for unimodal representation and for multimodal fusion.
To find optimal and , we propose a Conformer-based MEC model (Uni2Mul), which integrates a sub-task to predict IUAs and IMAs. We argue that to achieve a satisfactory unimodal representation, it is necessary to not only design a suitable feature extraction network, but also train it with the correct IUAs rather than IMAs. Moreover, a satisfactory fusion strategy can better leverage the effectiveness of the unimodal representation under a multi-task framework.
The contributions of this work can be summarized as follows:
The key contributions are using IUAs for better unimodal learning (see Figure 2b) and the two-stage approach to account for unimodal–multimodal inconsistencies during fusion (see Figure 2d). Uni2Mul advances MEC by improving unimodal representation learning and fusion.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the related work, Section 3 discusses the proposed methods and overall architecture of the Uni2Mul model, Section 4 explains the experimental setup and results, Section 5 presents the discussion, and Section 6 summarizes our work.
2. Related Work
2.1. Visual Emotion Classification
Facial expressions are one of the important bases for human emotional expression. The feature extraction methods for facial expressions mainly include traditional methods and deep learning methods.
Traditional methods for facial expression recognition rely on low-level or artificially designed features, necessitating significant human involvement. These methods commonly include global feature extraction methods [18,19], which obtain overall information regarding facial images; local feature extractions [20], which better capture local details; mixed feature extraction methods [21,22], which combine the benefits of global and local features; and optical-flow-based methods [23], which capture the dynamics and changes in facial images. While these traditional, handcrafted methods for feature extraction have achieved noticeable success, they may not be applicable in complex scenes with large amounts of data.
Deep learning networks, such as the convolutional neural network (CNN) [24,25] and recurrent neural network (RNN) [26], have demonstrated strong performance in the recognition of facial expressions, leading researchers to gradually shift away from traditional methods and toward deep learning approaches [27,28,29].
Saravanan et al. [24] noted the effectiveness of CNNs for image recognition tasks as these networks are able to capture spatial features due to their large number of filters. They proposed a model comprising six convolutional layers, two max pooling layers, and two fully connected layers, which outperformed decision trees and feed-forward neural networks on the FER-2013 dataset. Yu et al. [25] proposed a model comprising a face detection module based on the ensemble of three face detectors and a classification module that utilized an ensemble of multiple deep CNNs. To combine the multiple CNN models, they presented two schemes for learning the ensemble weights of the network responses: by minimizing the log likelihood loss and by minimizing the hinge loss. Their model achieved excellent results on both the FER and SFEW datasets.
For modeling the spatiotemporal evolution of visual information, Kahou [26] presented the application of an RNN for modeling this spatiotemporal evolution via the aggregation of facial features to perform emotion recognition in video. Li [30] trained a CNN to extract both geometric and appearance features, and a long short-term memory (LSTM) to capture temporal and contextual information regarding facial expressions. The CNN-LSTM architecture enables a more comprehensive representation of facial expressions as it combines both spatial and temporal information.
To more effectively utilize information regarding the key parts that convey emotion, Ming et al. [31] proposed a facial expression recognition method incorporating an attention mechanism based on a CNN and LSTM. This model mined information regarding important regions more effectively than general CNN-LSTM-based models.
2.2. Audio Emotion Classification
Speech contains rich emotional information, including features such as tone and rhythm, which can convey emotions in addition to the textual information present. Acoustic features may be divided into low-level and high-level categories.
Low-level features refer to those extracted via time and frequency algorithms, which are usually categorized into three types: prosodic features [32], spectral features [33], and voice quality features [34]. Each single feature can only express emotional information from a particular aspect of speech and, as such, cannot effectively represent speech emotions. To improve the recognition of speech emotions, researchers typically fuse multiple single features [35].
High-level features refer to those extracted directly from the raw speech signal or via low-level features [36] using deep learning techniques, such as CNN [37] and LSTM [38,39]. These methods are capable of directly learning optimal feature representations from raw data and forming more abstract high-level features by combining low-level features, thereby effectively capturing hidden features within the data without the cumbersome task of manually extracting features.
Mao et al. [37] proposed the use of CNN for speech emotion recognition (SER) by learning affect-salient features. They divided the CNN training into two stages: the learning of local invariant features and the learning of affect-salient, discriminative features. Their approach led to robust recognition performance in complex scenes and outperformed several well-established SER features, such as spectrogram representation and local invariant features.
Lee et al. [38] proposed an RNN-based speech emotion recognition framework capable of accounting for long contextual effects in emotional speech. The weighted accuracy of this framework improved by up to 12% compared to the baseline. For effective classification and learning of multidimensional complex data (speech features that can be used for analysis, such as pitch, energy, formants, linear predictor coefficients (LPCs), linear frequency cepstral coefficients (LFCCs), MFCCs, and TEO), Kumbhar et al. [39] presented a speech emotion recognition system using the LSTM model and MFCC features. This model yields an observed area under the ROC curve of 0.55.
To reduce the dimensionality of the acoustic data and extract high-level features, Etienne et al. [40] employed a mixed CNN-LSTM architecture. They transformed the audio signal into a spectrogram, which served as input to the convolutional layers followed by recurrent ones. The best results were achieved with a choice of 4 convolutional and 1 Bi-directional LSTM (BiLSTM) layers.
CNN and RNN may lose some context information when dealing with long sequence data and fail to fully capture emotional features. The introduction of an attention mechanism helps these neural networks highlight important information. Atila et al. [41] proposed a novel attention-based 3D CNN-LSTM network for accurate speech-based emotion prediction. The network comprises six 3D convolutional layers, two batch normalization (BN) layers, five Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) layers, three 3D max pooling layers, one attention layer, one LSTM layer, one flatten layer, one dropout layer, and two fully connected layers. The attention layer is connected to the 3D convolution layers, and the proposed method is highly efficient.
In recent years, some excellent self-supervised models have emerged in the field of speech [42,43,44,45], among which Wav2vec can capture information about the speaker and performs particularly well in ultra-low-resource cases [46].
2.3. Textual Emotion Classification
The Word2Vec model, proposed in 2013 [47,48], realized the distributed representation of words, and the resulting general features of words have been widely used for textual features. Meanwhile, LSTM has been employed to obtain deep emotional representation by capturing long-term context dependencies. Javed et al. [49] proposed two LSTM-based models: simple LSTM and emotion lexicon boost LSTM. The simple LSTM architecture comprised two hidden LSTM layers and a dense layer with softmax activation for emotion analysis. The emotion lexicon boost model enhanced the simple LSTM architecture by incorporating the NRC Hashtag emotion lexicon. Both LSTM networks show promising results. With the emergence of Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformers (BERT) [50], BERT has been introduced for textual features in emotion analysis and has achieved good results. Gou et al. [51] generated word-level and sentence-level vectors for text using BERT, inserted the word-level feature into BiLSTM for processing, and connected the output of BiLSTM with sentence-level features for emotion analysis of dialogue. Their method significantly outperformed the baselines.
CNN models can extract local features. Gui [52] learned representations of users and products, reviewed words using heterogeneous network embedding techniques, and employed CNN to detect product review sentiment polarity with the learned representations, achieving state-of-the-art performance. Chen [53] constructed a novel weakly supervised multimodal deep learning framework and trained a discriminative model from cheaply available emoticon annotations for multimodal prediction.
Even with the hybrid approach that leverages the powers of LSTM and CNN, the important information cannot always be better selected from word embeddings. Therefore, the attention mechanism is used with these neural networks. The attention mechanism can highlight important information from contextual information by assigning different weights [54]. Xie et al. [55] calculated attention scores using both the word vectors themselves and the feature of word vectors extracted by the LSTM network. They then integrated the word vectors with attention scores to input them into CNN for calculating emotion intensity. The multi-head attention mechanism from Transformer [56] enables the model to jointly attend to information from different representation subspaces at different positions. Akula et al. [57] enhanced word embeddings of input text with an attention module using L self-attention layers and H heads per layer. They passed the resultant features through a Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) and a feed-forward layer for sarcasm detection.
2.4. Multimodal Emotion Classification
Unimodal emotion recognition has limitations in accurately detecting human emotions because of its reliance on a single type of sensory input. MEC combines multiple sources of data, such as facial expressions, voice, body posture, and linguistic cues, to more accurately detect and differentiate various emotional states. Multimodal fusion methods aim to combine information from multiple modalities to improve the performance of various tasks. Some popular multimodal fusion methods include early fusion [58,59,60], late fusion [15], and hybrid fusion [14,15].
Early fusion concatenates features from each modality and inputs the resultant joint representation into a classifier for emotion classification. Pérez-Rosas et al. [58] combined linguistic, acoustic, and visual features into a single feature vector, which was used to make a decision about the sentiment orientation of the utterance. Xu et al. [59] used the Object-VGG and Scene-VGG models to detect visual semantic features and extracted words that were important to sentiment with the visual-feature-guided attention mechanism. The visual and textual features were aggregated by using an early fusion layer to obtain the final multimodal representation for MEC.
Late fusion employs and trains a separate classifier for each modality and combines the output of each classifier to obtain the final prediction. Poria et al. [61] presented early and late fusion methods. In the case of early fusion, they concatenated textual and visual features and fed the resulting long vector into a Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier. In the case of late fusion, they fed features of each modality into separate SVM classifiers and then combined their decisions with weights chosen experimentally. Yu et al. [62] used logistic regression to perform emotion prediction of the text and related images individually and performed late fusion for the probabilistic results using the average strategy.
The mixed fusion method integrates the advantages of early and late fusion methods and considers both the individual features of different modalities and the relevance among them. Cimtay et al. [15] used a hybrid fusion of faces with early fusion on electroencephalogram (EEG) and galvanic skin response (GSR) modalities. EEG and GSR modalities were used for estimating the level of arousal, and late fusion of EEG, GSR, and face modalities was used.
The mixed fusion method requires more computing resources and needs a more refined feature extraction and classifier construction for different modalities, which increases the difficulty and cost of implementation. Recently, many research works have focused on attention-based fusion [63,64,65] and its variants, such as self-attention [66,67], multi-head attention [68,69], and Transformer [70,71]. The attention-based fusion integrates the advantages of early fusion and late fusion and compensates for their shortcomings [64]. Li et al. [63] proposed an attention-based multimodal fusion approach. They first fused the audio and visual modalities, and then fused the resultant fusion result with the text modality. Their approach resolved the problem of asynchronous inputs by using two attention layers to align the inputs and learn their relatedness in an orderly manner. Thao et al. [67] designed a self-attention-based neural network for predicting the affective responses of movie viewers from different input modalities. They implemented a self-attention mechanism using N identical layers, each of which included two sublayers: a multi-head self-attention followed by a feed-forward layer. Each of these sublayers was enclosed by a residual connection, accompanied by layer normalization. Wang et al. [64] proposed a cross-attention asymmetric fusion module, which utilized information matrices of the acoustic and visual modality as weights to strengthen the textual modality. Xie et al. [70] employed a transformer-based cross-modality fusion with a robust deep learning architecture to estimate the emotion during a conversation.
The aforementioned studies reported varying fusion methods and achieved great successes while having a common limitation: insufficient consideration of the differences between IMAs and IUAs, as well as the impacts they may have on emotion classification models. In this paper, we further discuss the impacts of IMAs and IUAs based on existing research and propose a new multimodal fusion method.
3. Methods
Given a video clip that contains multimodal information such as text, audio, and vision, the task aims to predict emotional annotation of the clip, i.e., positive, negative, and neutral. The key is to extract and fuse the representations of each modality. To achieve this, we propose a Conformer-based MEC model (Uni2Mul). Figure 3 provides a detailed illustration of our model. The visual, acoustic, and textual features are extracted from the video data using CLIP (ViT-B/32), Wav2Vec, and BERT (bert-base-chinese), three pre-trained models, respectively. These features are then fed into unimodal neural networks to predict IUAs. Meanwhile, hidden representations are fetched from these unimodal neural networks and fused to predict IMAs. More details about our model are provided below.
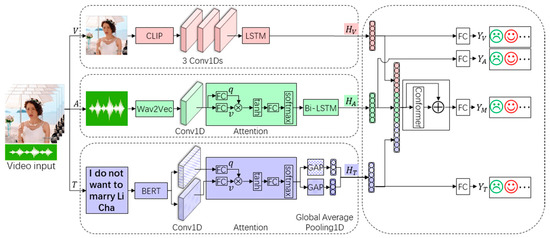
Figure 3.
Conformer-based MEC model (Uni2Mul). The model contains two stages: emotional classification models for each modality (left part) aim to optimize unimodal representation, and multi-task fusion network with Conformer (right part) performs multimodal fusion and MEC. The different colors correspond to different modalities. Pink, green, and purple represent the visual, acoustic, and textual modalities respectively. : Multimodal, : Vision, : Audio, : Text, : representation from hidden layer, : emotional annotation, : query, : value, FC: Fully Connected layer. GAP: Global Average Pooling1D, ⊗: operation of multiplication, ⊕: operation of addition.
3.1. Unimodal Neural Networks
3.1.1. Vision
CLIP is a transferable visual model trained from 400 million (image, text) pairs collected from the internet [72]. We use this pre-trained model as a visual feature extractor to make full use of its prior knowledge, which includes not only visual but also textual information. To extract better unimodal emotional representations, we construct an emotion classification model for the visual modality using CNN and LSTM, inspired from [30].
Specifically, we use CLIP to extract features from images and define the visual feature as . We then feed into three CNN layers, whose operation process can be formulated as
where represents the output of CNNs and can be defined as , where is the timestep. denotes the weight matrix and represents the bias vector.
Next, the LSTM layer takes the outputs of CNNs as input and performs the following operations:
where , , and represent the output of the input gate, forget gate, and output gate, respectively, in the LSTM; represents the current moment cell state; and represents the hidden output of the LSTM and can be defined as (where is timestep). denotes the sigmoid activation function and is the hyperbolic tangent function. , and represent the weight matrices, while , and represent the bias vectors.
Finally, we define the hidden representation as , which is fed into a fully connected layer for visual emotional classification. The operation process of the visual emotional classification can be formulated as
where represents the annotation of the visual modality, represents the weight matrix, and represents the bias vector.
3.1.2. Audio
Wav2Vec 2.0 is a self-supervised framework for speech representation learning. It can capture the information about the speaker and performs well in speech recognition tasks, especially in ultra-low-resource cases [46]. Therefore, we use it as a feature extractor for acoustic data. Inspired by Atila et al. [41], we propose a network that consists of a CNN, followed by a self-attention mechanism and a Bi-LSTM.
Firstly, we employ Wav2Vec 2.0 to extract acoustic features from the waveform signal and define the acoustic feature as . We then feed into a CNN layer:
where represents the CNN output, represents the weight matrix, and represents the bias vector.
We use the “Scaled Dot-Product Attention” from [56] as the attention mechanism. The matrix of outputs is computed as
where , , and stand for query, key, and value, respectively. is equal to , and represents the weight on the value. is the softmax function, and is the hyperbolic tangent function. is the output of the attention module and can be defined as , where is the timestep. is fed into BiLSTM to extract deep representations. , and represent the weight matrices. The outputs of BiLSTM can be computed as follows:
where , , and represent outputs of the input gate, forget gate, and output gate, respectively, in LSTM; represents the current moment cell state; and represents the hidden output of LSTM and can be defined as , where is the timestep. denotes the sigmoid activation function and is the hyperbolic tangent function. , and represent the weight matrices and , and represent the bias vectors.
Finally, we feed the output of BiLSTM into a fully connected layer for acoustic emotional classification. The operation process of the acoustic emotional classification can be formulated as
and represent hidden representation and annotation of the acoustic modality, respectively. represents the weight matrix, and represents the bias vector.
3.1.3. Text
We use BERT to obtain embeddings from texts. We do not use word segmentation tools, due to the characteristics of BERT. We add two unique tokens to indicate the beginning and the end for each text. We define the textual feature extracted by BERT as .
During the training of the unimodal emotional classification models, we find that the performance of the textual modality emotional classification model is superior to the other modalities, so we want to extract more information from the textual modality. Inspired by [54], we design the CNN-attention-based model.
Specifically, we generate the query and key for the textual modality using two 1D CNNs. We use the “Scaled Dot-Product Attention” from [56] as the attention mechanism, too. The matrix of outputs is computed as
where , , and stand for query, key, and value, respectively. is equal to , and represents the weight on the value. is the softmax function and is the hyperbolic tangent function. is the output of the attention module. , and represent the weight matrices. and represent the bias vectors.
Subsequently, we conduct a global average pooling operation on and , and concatenate them together to formulate the textual representation, . is computed as follows:
where represents the global average pooling operation.
Lastly, we send to a fully connected layer for emotional classification. We formulate the classification operation as follows:
where represents the annotation of the textual modality, represents the weight matrix, and represents the bias vector.
These networks for each modality are trained with IUAs to ensure the difference of representation between the inter-modal information, and are then saved to construct Uni2Mul framework.
3.2. Multi-Task Multimodal Fusion Network with Conformer
Inspired by Gulati et al. [73], we propose the Conformer-based fusion method. The Conformer [73] (see Figure 4) is a convolution-augmented Transformer for speech recognition. It can combine convolution neural networks and Transformers to model both local and global dependencies of audio sequences in a parameter-efficient way. The model exhibits better accuracy with fewer parameters than previous work on the LibriSpeech dataset.
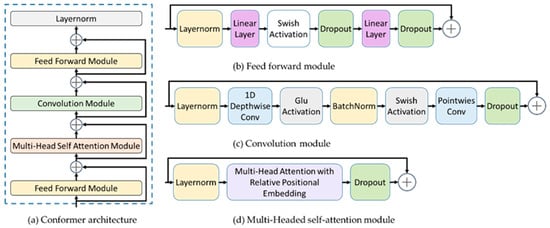
Figure 4.
Conformer architecture. (a) is Conformer architecture, (b) is feed-forward module, (c) is convolution module, and (d) is multi-head self-attention module. ⊕: operation of addition.
The Conformer block (see Figure 4a) is composed of four modules stacked together, i.e., a feed-forward module, a self-attention module, a convolution module, and a second feed-forward module at the end. In the multi-head self-attention module (see Figure 4d), we employ pre-norm residual units with dropout, which helps in training and regularizing deeper models. The convolution module (see Figure 4c) is stacked in the order of layernorm layer, convolution layer, gated linear unit (GLU), and so on. Batchnorm is deployed just after the convolution for training deep models. As for the feed-forward module (see Figure 4b), it starts with a layernorm layer, which is followed by two interleaved linear layers and dropout layers. We also apply Swish activation to regularize the network.
Especially, we first load the unimodal models saved above and set these models as untrainable to obtain unimodal representations from their hidden layers. We then concatenate these representations to form the multimodal representation, which can be formulated as
We use a Conformer-based method to fuse the multimodal representation and predict the emotional annotation of video. Especially, we send into the first feed-forward module and define the result as , which is fed into the multi-head self-attention module. The operation of the multi-head self-attention module in the Conformer can be formulated as follows:
where is the layer normalization operation, and , , and stand for query, key, and value, respectively. is equal to , and represents the weight on the value. is the softmax function and is the hyperbolic tangent function. is the output of the attention module of one head and is the output of the multi-head attention module. , and represent the weight matrices. represents the concatenate operation and represents the dropout operation.
is then fed into the convolution module, and the operations in the convolution module can be formulated as
where is the layer normalization operation, represents the gated linear unit operation, is the batch normalization operation, and represents the dropout operation. and are convolution operation results. and represent the weight matrices, and and represent the bias vectors. We feed into the second feed-forward module and define the result as .
Based on the research results of CH-SIMS, the accuracy of the textual and visual modalities in unimodal emotion recognition models is relatively high, which we refer to as the dominant modalities. In contrast, the accuracy of the acoustic modality is relatively low, which we refer to as the less salient modality. During the process of multimodal fusion, in order to avoid neglecting information from less salient modalities, we utilize a multi-task framework for multimodal fusion. In other words, our multimodal model has four outputs, which include the unimodal classification results for the visual, acoustic, and textual modalities, as well as the overall MEC result. The operation process of the MEC can be formulated as
where represents the annotation for each video clip; and represent the weight matrices; and , and represent the bias vectors. represents the global average pooling operation.
4. Experiment
4.1. Dataset
The CH-SIMS [13] dataset collects 60 videos from movies, TV series, and variety shows, and divides these videos into 2281 video clips. Each video clip has three unimodal annotations and one multimodal annotation. Given that there are only a few datasets containing unimodal annotations currently available, we only conduct experiments on the CH-SIMS dataset.
4.2. Parameters’ Setting
All experiments are carried out using a single NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA) Quadro P520 card. We adopt Adam as the optimizer with a learning rate of 1 × 10−4, and set the number of epochs to 30 and batch size to 32. All models are trained using sparse categorical cross-entropy on each softmax output. We evaluate the models with accuracy (Acc.) and F1 score. Acc. is equal to the proportion of correctly classified samples to the total number of samples, and can be formulated as follows:
is true positives, is true negatives, is false positives, and is false negatives.
Precision is the ability of the classifier not to label as positive a sample that is negative, and recall is the ability of the classifier to find all the positive samples. The F1 score can be interpreted as a weighted harmonic mean of the precision and recall, and can be formulated as follows:
Higher values of Acc. and F1 score represent better performance. We use the “save_best_only = True” parameter in Keras to save only the best model during training. This parameter ensures that the model weights are saved whenever the monitored metric improves and overwrites the previously saved weights only if there is an improvement. Thus, at the end of training, the saved weights correspond to the best performing model on the validation set.
In addition to the general parameters mentioned above, personalized parameters for unimodal and multimodal models are set as follows:
Vision: In the process of selecting the visual timestep, we conduct several pilot experiments to access the impact of different timesteps on the performance of the visual models. We observe that increasing the timestep results in a larger memory footprint for the feature matrix, without a significant improvement in model performance. To strike a balance between computational complexity and performance, we decide to set the visual timestep to 10. The output length of CLIP is 512. Therefore, the input shape of the visual modality is . The following three 1D convolution layers have 64 filters, and the kernel sizes are set to 3, 1, and 3, respectively, with strides being set to 1. The subsequent BiLSTM has 32 units.
Audio: Similarly, in line with our previous findings for the visual timestep, our pilot experiments demonstrate that setting the acoustic timestep to 128 not only maintains a good level of performance but also showcases the effectiveness of this parameter. As a result, we set the acoustic timestep to 128. The output length of Wav2Vec 2.0 is 512. Thus, the input shape of the acoustic modality is . The following 1D convolution layer has 64 filters, and the kernel size and strides are set to 3 and 2, respectively. The subsequent BiLSTM has 32 units, and dropout is used with a rate of 0.5 to prevent overfitting.
Text: The longest sentence in the CH-SIMS dataset has 36 tokens. The output length of BERT used in this paper is 512. Hence, the input shape of the textual modality is . The subsequent two 1D convolution layers have 64 filters, and both the kernel size and strides are set to 1.
Multimodal: The number of attention heads in our multi-head attention module in Conformer is 2. Dropout is used with a rate of 0.5 to prevent overfitting. The convolution layer in Conformer has 64 filters, and the kernel size is set to 3. The loss weights for multimodal, vision, audio, and text are 0.3, 0.2, 0.2, and 0.3, respectively.
4.3. Experimental Results
We employ the models described in [13] as our initial benchmark. Following established research practices, we conduct experiments involving single-task and multi-task scenarios to evaluate the fusion of multimodal data. We test two variations of unimodal models, namely pre-trained and without pre-training, within both the single-task and multi-task frameworks. The evaluation of these models is based on the Acc. metric, and the outcomes are presented in Table 1, comparing our models to the baseline performance on the CH-SIMS dataset.

Table 1.
The results of the baseline and our models on the CH-SIMS dataset. The models with * are multi-task models, extended from single-task models by introducing independent unimodal annotations. “S” in model names stands for “Single-task”, while “M” denotes “multi-task”. The model names with “w/o pre-train” indicate that the corresponding unimodal models have not been pre-trained, while the ones without “w/o pre-train” indicate that the unimodal models have been pre-trained. “Conformer” in model names means the fusion method of the models.
The results indicate that all four of our models outperform the baseline models mentioned in the CH-SIMS paper in terms of Acc. Particularly, the Uni2Mul-M-Conformer model exhibits an accuracy improvement of 7.75 points compared to the MLF-DNN∗ baseline.
We can observe that the pre-training method in stage one improves the performance of the MEC models. For example, Uni2Mul-S-Conformer demonstrates a higher Acc. than Uni2Mul-S-Conformer (w/o pre-train), and Uni2Mul-M-Conformer shows a higher Acc. than Uni2Mul-M-Conformer (w/o pre-train). These results suggest that pre-trained unimodal models can capture good representations and pass them unchanged to the fusion network for MEC.
Additionally, a multi-task framework can achieve complementary information among multiple related tasks, improving the generalization ability of the MEC models. For example, Uni2Mul-M-Conformer (w/o pre-train) outperforms Uni2Mul-S-Conformer (w/o pre-train), and Uni2Mul-M-Conformer outperforms Uni2Mul-S-Conformer.
These findings demonstrate that Uni2Mul models can achieve superior performance, and our proposed methods for representation extraction and fusion strategy prove effective for MEC.
5. Discussion
5.1. Ablation Study
5.1.1. Unimodal Representation
To validate our hypotheses, we conducted the following experiments to examine the impact of different feature extraction methods and neural network structures on the performance of unimodal emotion classification models. We trained individual models for each modality, utilizing two types of annotations: IMAs and IUAs. The evaluation of these models was based on the Acc. and F1 score. The results are shown in Table 2. To compare the performance differences more clearly between IMA and IUA models, we plotted Figure 5 based on the data in Table 2.

Table 2.
Performance of unimodal models in stage one. “ATTN” in the model names represents attention mechanism. Mel is the Mel spectrogram feature.
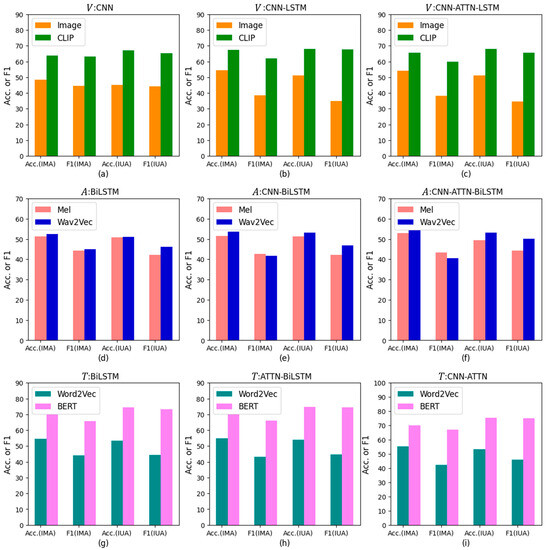
Figure 5.
Performance comparison chart of unimodal models in stage one. (a–c) depict the model performance metrics, Acc. and F1 score, of three visual models: CNN, CNN-LSTM, and CNN-ATTN-LSTM. (d–f) depict the model performance metrics, Acc. and F1 score, of three acoustic models: BiLSTM, CNN-BiLSTM, and CNN-ATTN-BiLSTM. (g–i) depict the model performance metrics, Acc. and F1 score, of three textual models: BiLSTM, ATTN-BiLSTM, and CNN-ATTN. V: Vision, A: Audio, T: Text.
In the visual modality, we compared our unimodal model, the CNN-LSTM-based model, with the CNN-based and CNN-ATTN-LSTM-based models. Two types of features were tested for each model: video images and the outputs of CLIP. As presented in Table 2 and Figure 5a–c, the Acc. (IUAs) consistently outperformed Acc. (IMAs), and our CNN-LSTM-based model yielded the highest performance among the three models. Specifically, the CNN-LSTM-based model demonstrated a 0.65 percentage point improvement in Acc. (IUAs) and a 5.53 percentage point improvement in F1 (IUAs) when compared to Acc. (IMAs) and F1 (IMAs). Furthermore, CLIP proved to be an effective method for visual feature extraction. Taking the CNN-LSTM model trained using IUAs as an example, employing the output of CLIP as the input feature resulted in a 16.85 percentage point increase in Acc. and a 32.52 percentage point increase in F1 score, compared to using images as the input. This improvement can be attributed to the ability of CLIP to leverage prior knowledge of both vision and text, allowing it to extract textual information along with visual information.
For the acoustic modality, we compared our unimodal model, the CNN-ATTN-BiLSTM-based model, with the BiLSTM-based and CNN-BiLSTM-based models. Two types of features were examined for each model: Mel features and outputs of Wav2vec. As indicated in Table 2 and Figure 5d–f, most models exhibited higher F1 score for IUAs compared to IMAs, and our CNN-ATTN-BiLSTM-based model delivered the best performance among the three models. Additionally, Wav2Vec 2.0 proved to be an effective method for acoustic feature extraction. Although the CNN-ATTN-BiLSTM-based model had a 1.1 percentage point lower Acc. (IUAs) compared to Acc. (IMAs), it demonstrated a 9.58 percentage point higher F1 score for IUAs compared to F1 score for IMAs.
In the textual modality, we compared our unimodal model, the CNN-ATTN-based model, with the BiLSTM-based and ATTN-BiLSTM-based models. Two types of features were tested for each model: outputs of Word2Vec and BERT. As depicted in Table 2 and Figure 5g–i, in most cases, the F1 score for IUAs outperformed the F1 score for IMAs, and in some instances, the Acc. (IUAs) surpassed Acc. (IMAs). Our CNN-ATTN-based model yielded the best performance among the three models. As expected, BERT proved to be an effective method for textual feature extraction.
5.1.2. Multimodal Fusion
We compared four fusion strategies: concatenate, multi-head attention, Transformer, and Conformer. The evaluation of these fusion strategies was conducted using Acc. (accuracy) and F1 score. The results are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Results for MEC with different fusion strategies in stage two.
Based on the overall trend observed in Table 3, Conformer emerged as the most effective fusion method, followed by Transformer, multi-head attention, and concatenate. Specifically, the Uni2Mul-M-Conformer model achieved an Acc. (IUAs) that was 0.22, 0.44, and 1.76 percentage points higher than those of Uni2Mul-M-Transformer, Uni2Mul-M-Attention, and Uni2Mul-M-Concatenate, respectively.
In most cases, Acc. (IUAs) outperformed Acc. (IMAs), and F1 (IUAs) outperformed F1 (IMAs). The Uni2Mul-M-Conformer model demonstrated an Acc. (IUAs) that was 3.72 percentage points higher than that of Acc. (IMAs), while F1 (IUAs) was 3.58 percentage points higher than that of F1 (IMAs). These results align precisely with our expectations.
Furthermore, the multimodal fusion models constructed using pre-trained unimodal models exhibited higher Acc. and F1 score compared to those built without pre-training. Additionally, the multi-task framework outperformed the single-task framework, which is consistent with previous research findings.
5.2. Visualization
5.2.1. Visualization of Hidden Representations
To assess the impact of IMAs and IUAs on model feature extraction, we utilized t-SNE to visualize the hidden representations of our models (refer to Figure 6).
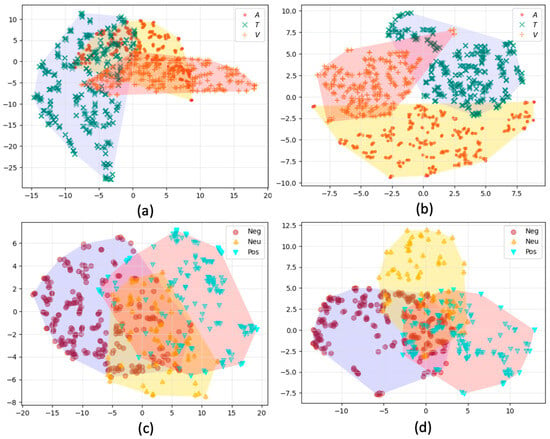
Figure 6.
Unimodal and multimodal representation. (a,b) are the results from unimodal models trained using IMAs and IUAs, respectively; (c,d) are the results from models trained using IMAs and IUAs with Conformer-based fusion strategy. In (a,b), the markers of different colors represent different modalities, and shapes filled with different colors represent semantic spaces of different modalities. In (c,d), the markers of different colors represent different emotional categories, and shapes filled with different colors represent classification distribution. V: Vision, A: Audio, T: Text.
For unimodal representations, models trained using IMAs displayed irregular clustering in the semantic space with diffuse distributions (see Figure 6a). Conversely, models trained using IUAs formed more regular, spherical-like clusters (see Figure 6b) that adhered to a uniform Gaussian distribution.
In terms of multimodal representations, the Conformer-based fusion model trained with IMAs were not well concentrated, with multiple overlapping regions, resulting in suboptimal classification performance and limited generalizability (Figure 6c). In contrast, the model trained with IUAs exhibited distinct classification boundaries and minimal overlap in the classification distribution, yielding comparatively superior classification performance and adequate generalizability (see Figure 6d).
5.2.2. Visualization of Attention Weights
In stage one, we obtained a 64-dimensional visual feature vector, a 64-dimensional acoustic feature vector, and a 128-dimensional textual feature vector. In stage two, we concatenated these three vectors into a 256-dimensional multimodal vector and fed it into the fusion network. To explore the differences in fusion methods, we visualized the attention weights of three fusion strategies: multi-head attention (see Figure 7a), Transformer (see Figure 7b), and Conformer (see Figure 7c). In Figure 7a–c, we constructed an attention weight matrix for the aforementioned 256-dimensional multimodal feature vectors. The horizontal axis positions correspond to visual, acoustic, and textual feature components from left to right, and the vertical axis positions correspond to them from top to bottom. The numerical values (different colors) of each position in the matrix represent the degree of correlation of the corresponding positions, and the diagonal represents autocorrelation. The higher the value, the brighter the color. The weights of different heads were averaged.
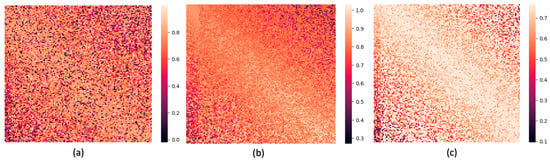
Figure 7.
Attention weights of three fusion methods: (a) for “multi-head attention”, (b) for “Transformer”, and (c) for “Conformer”. The lighter the color, the higher the weight.
In Figure 7a, we observed a few scattered regions with relatively high weights in the distribution, indicating that the multi-head attention fusion model successfully identified important emotional features. In Figure 7b, the weights were predominantly higher along the main diagonal, suggesting that the Transformer model discovered significant intra-modal relationships. Although there were a few high weight regions near the bottom left corner, their weights were lower compared to those along the main diagonal. This implies that the model had less proficiency in fusing inter-modal information and primarily focused on intra-modal relationships. Moving on to Figure 7c, we notice that the main diagonal had a wider area of prominence compared to Figure 7b. Additionally, some vertical highlight regions appeared at the bottom left of the main diagonal. These observations indicate that the Conformer model, benefiting from its convolutional kernel, assigns higher weights to intra-modal relationships and exhibits greater confidence in inter-modal relationships. These findings align with our expectations and suggest that the Conformer network serves as an effective fusion model.
5.2.3. Visualization of Confusion Matrix
To provide a more intuitive representation of the impact of IMAs, IUAs, and fusion strategies on the performance of multi-modal fusion models, we visualize the confusion matrices of these models. The results are shown in Figure 8.
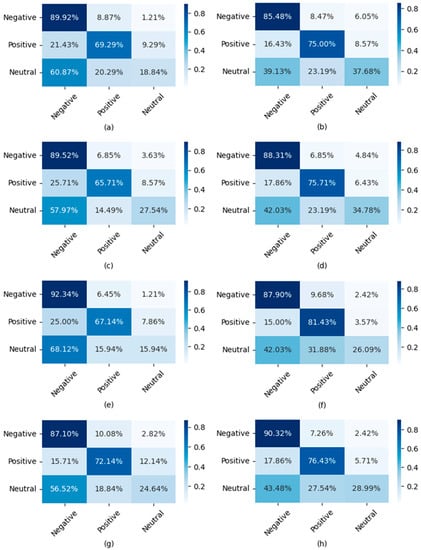
Figure 8.
Confusion matrix for MEC models. (a,c,e,g) are from models trained with IMAs, while (b,d,f,h) are from models trained with IUAs. (a,b) belong to the concatenate-based fusion models, (c,d) belong to the multi-head attention-based fusion models, (e,f) belong to the transformer-based fusion models, and (g,h) belong to the Conformer-based fusion models.
Comparing the left side of Figure 8a,c,e,g with the right side Figure 8b,d,f,h, it can be observed that regardless of the fusion strategy employed, models trained with IUAs outperform those trained with IMAs. Models trained with IMAs tend to have higher recognition accuracy for the negative class but lower accuracy for the positive and neutral classes. On the other hand, models trained with IUAs exhibit better recognition capabilities for both the positive and neutral classes, especially those based on the Conformer fusion method, which show improvements in recognition accuracy for all three classes.
This research, however, has several limitations. The first limitation is the lack of additional datasets for extensive validation. The second limitation is that CH-SIMS is a dataset with imbalanced samples, specifically a small number of positive, especially neutral emotion samples. The adaptability of the model to imbalanced data can also be improved.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a robust Conformer-based MEC model called Uni2Mul, which focuses on optimizing unimodal representation and multimodal fusion. We divide the implementation of Uni2Mul into two stages. In stage one, we construct individual unimodal neural networks for each modality and train them using IUAs to optimize the unimodal representations. This results in pre-trained unimodal models with superior performance. In stage two, we concatenate the hidden representations of these pre-trained unimodal models and feed the concatenated feature into the Conformer-based fusion network. This fusion network includes a sub-task that predicts IUAs for MEC. We also perform ablation experiments for the two stages separately. For stage one, we construct three different neural network structures for each modality and train these networks using IUAs and IMAs, respectively. For stage two, we try four fusion methods: concatenate, multi-head attention, Transformer, and Conformer. We summarize our overall findings as follows:
- (1)
- Unimodal models trained using IUAs can learn more differentiated information and improve the complementarity between modalities compared to those trained using IMAs.
- (2)
- The hidden representations of the pre-trained unimodal models serve as effective inputs for the fusion network. This ensures that the differentiated information learned using the unimodal models is passed unchanged to the fusion network.
- (3)
- The Conformer module, with its multi-head attention mechanism and convolutional kernel, excels in paying attention to important intra-modal information and capturing inter-modal relationships. It is the best among the four fusion strategies mentioned above.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z.; Funding Acquisition, N.J.; Methodology, L.Z.; Resources, N.J.; Software, L.Z.; Validation, C.L.; Visualization, C.L.; Writing—Original Draft, L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Doctoral Research Innovation Program of China People’s Police University, grant number BSKY202201; 2022 Humanities and Social Science Research Youth Foundation Project of Ministry of Education, grant number 22YJC860014; and Hebei Province Science and Technology Support Program, grant number 18215601. The APC was funded by the 2022 Humanities and Social Science Research Youth Foundation Project of the Ministry of Education.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
https://github.com/thuiar/MMSA, accessed on 6 March 2023.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Abbreviations used in this paper. Each abbreviation retains the underlined letter from its corresponding phrase.
Table A1.
Abbreviations used in this paper. Each abbreviation retains the underlined letter from its corresponding phrase.
| Abbreviations | Stand for |
|---|---|
| Uni2Mul | Unimodal to Multimodal |
| MEC | Multimodal Emotion Classification |
| IUAs | Independent Unimodal Annotations |
| IMAs | Identical Multimodal Annotations |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| SER | Speech Emotion Recognition |
| LFCC | Linear Frequency Cepstral Coefficients |
| MFCC | Mel-scale Frequency Cepstral Coefficients |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| BiLSTM | Bidirectional LSTM |
| BN | Batch Normalization |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformers |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| VGG | Visual Geometry Group |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| EEG | electroencephalogram |
| GSR | Galvanic Skin Response |
| CLIP | Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training |
| GLU | Gated Linear Unit |
| LN | Layer Normalization |
| DP | Dropout Operation |
| GAP | Global Average Pooling1D |
References
- Taboada, M.; Brooke, J.; Tofiloski, M.; Voll, K.; Stede, M. Lexicon-Based Methods for Sentiment Analysis. Comput. Linguist. 2011, 37, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelwall, M.; Buckley, K.; Paltoglou, G. Sentiment Strength Detection for the Social Web. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigeorgis, G.; Ringeval, F.; Brueckner, R.; Marchi, E.; Nicolaou, M.A.; Schuller, B.; Zafeiriou, S. Adieu Features? End-to-End Speech Emotion Recognition Using a Deep Convolutional Recurrent Network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 5200–5204. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, H.; Kessler, H.; Eppel, T.; Rukavina, S.; Traue, H.C. Expression Intensity, Gender and Facial Emotion Recognition: Women Recognize Only Subtle Facial Emotions Better than Men. Acta Psychol. 2010, 135, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collignon, O.; Girard, S.; Gosselin, F.; Roy, S.; Saint-Amour, D.; Lassonde, M.; Lepore, F. Audio-Visual Integration of Emotion Expression. Brain Res. 2008, 1242, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Pappagari, R.; Kulkarni, P.; Villalba, J.; Carmiel, Y.; Dehak, N. Deep Neural Networks for Emotion Recognition Combining Audio and Transcripts. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pampouchidou, A.; Simantiraki, O.; Fazlollahi, A.; Pediaditis, M.; Manousos, D.; Roniotis, A.; Giannakakis, G.; Meriaudeau, F.; Simos, P.; Marias, K.; et al. Depression Assessment by Fusing High and Low Level Features from Audio, Video, and Text. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 16 October 2016; pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Dardagan, N.; Brđanin, A.; Džigal, D.; Akagic, A. Multiple Object Trackers in OpenCV: A Benchmark. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 30th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Kyoto, Japan, 20–23 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Deep Multimodal Representation Learning: A Survey. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 63373–63394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, E.; Niehues, J.; Asteriadis, S. Multimodal Attention-Mechanism For Temporal Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 25–28 October 2020; pp. 251–255. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.J.; Leung, C.H.C.; Li, Y. Multimodal Emotion Recognition Using Transfer Learning on Audio and Text Data. In Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2021; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Gervasi, O., Murgante, B., Misra, S., Garau, C., Blečić, I., Taniar, D., Apduhan, B.O., Rocha, A.M.A.C., Tarantino, E., Torre, C.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 12951, pp. 552–563. ISBN 978-3-030-86969-4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Chao, Y.; Liu, X.; Meng, H. Context-Aware Multimodal Fusion for Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2022, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 18 September 2022; pp. 2013–2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Xu, H.; Meng, F.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, J.; Zou, J.; Yang, K. CH-SIMS: A Chinese Multimodal Sentiment Analysis Dataset with Fine-Grained Annotations of Modality. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gunes, H.; Piccardi, M. Bi-Modal Emotion Recognition from Expressive Face and Body Gestures. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2007, 30, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimtay, Y.; Ekmekcioglu, E.; Caglar-Ozhan, S. Cross-Subject Multimodal Emotion Recognition Based on Hybrid Fusion. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 168865–168878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, R.-H.; Shu, J.; Bao, S.-L.; Liang, R.-H.; Chen, P.; Chi, K.-K. Video Multimodal Emotion Recognition Based on Bi-GRU and Attention Fusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 8213–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Jin, X. Gated Attention Fusion Network for Multimodal Sentiment Classification. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 240, 108107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabid, T. Robust Facial Expression Recognition Based on Local Directional Pattern. ETRI J. 2010, 32, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, G. Face Expression Recognition Based on Equable Principal Component Analysis and Linear Regression Classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI), Shanghai, China, 19–21 November 2016; pp. 876–880. [Google Scholar]
- Barman, A.; Dutta, P. Facial Expression Recognition Using Distance Signature Feature. In Advanced Computational and Communication Paradigms; Bhattacharyya, S., Chaki, N., Konar, D., Chakraborty, U.K., Singh, C.T., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 706, pp. 155–163. ISBN 978-981-10-8236-8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Tian, Y. Facial Expression Recognition Method Based on Gabor Wavelet Features and Fractional Power Polynomial Kernel PCA. In Advances in Neural Networks—ISNN 2010; Zhang, L., Lu, B.-L., Kwok, J., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 6064, pp. 144–151. ISBN 978-3-642-13317-6. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, W.-L.; Ding, J.-J.; Liu, J.-Z. Facial Expression Recognition Based on Improved Local Binary Pattern and Class-Regularized Locality Preserving Projection. Signal Process. 2015, 117, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Ruiz, J.V.; Moreno, A.B.; Montemayor, A.S.; Hernández, J.; Pantrigo, J.J. Differential Optical Flow Applied to Automatic Facial Expression Recognition. Neurocomputing 2011, 74, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Perichetla, G.; Gayathri, D.K.S. Facial Emotion Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Networks. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 2, 446. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, C. Image Based Static Facial Expression Recognition with Multiple Deep Network Learning. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Seattle, WA, USA, 9 November 2015; pp. 435–442. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi Kahou, S.; Michalski, V.; Konda, K.; Memisevic, R.; Pal, C. Recurrent Neural Networks for Emotion Recognition in Video. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Seattle, WA, USA, 9 November 2015; pp. 467–474. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Zhou, S.K.; Chellappa, R. FaceNet2ExpNet: Regularizing a Deep Face Recognition Net for Expression Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, M.; Kobori, H.; Nakashima, Y.; Takemura, N.; Nagahara, H. Facial Expression Recognition with Skip-Connection to Leverage Low-Level Features. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Ciftci, U.; Yin, L. Facial Expression Recognition by De-Expression Residue Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2168–2177. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.-H.S.; Kuo, P.-H.; Tsai, T.-N.; Luan, P.-C. CNN and LSTM Based Facial Expression Analysis Model for a Humanoid Robot. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 93998–94011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Y.; Qian, H.; Guangyuan, L. CNN-LSTM Facial Expression Recognition Method Fused with Two-Layer Attention Mechanism. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliou, T.; Anagnostopoulos, C.-N. Statistical Evaluation of Speech Features for Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2009 Fourth International Conference on Digital Telecommunications, Colmar, France, 20–25 July 2009; pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; An, N.; Li, B.N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L. Speech Emotion Recognition Using Fourier Parameters. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2015, 6, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahaie, O.; Lefebvre, R.; Gournay, P. Influence of Audio Bandwidth on Speech Emotion Recognition by Human Subjects. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Montreal, QC, USA, 22 July 2017; pp. 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bandela, S.R.; Kumar, T.K. Stressed Speech Emotion Recognition Using Feature Fusion of Teager Energy Operator and MFCC. In Proceedings of the 2017 8th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Delhi, India, 3–5 July 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Yu, D.; Tashev, I. Speech Emotion Recognition Using Deep Neural Network and Extreme Learning Machine. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2014, Singapore, 14–18 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Q.; Dong, M.; Huang, Z.; Zhan, Y. Learning Salient Features for Speech Emotion Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2014, 16, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Tashev, I. High-Level Feature Representation Using Recurrent Neural Network for Speech Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2015, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbhar, H.S.; Bhandari, S.U. Speech Emotion Recognition Using MFCC Features and LSTM Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference On Computing, Communication, Control And Automation (ICCUBEA), Pune, India, 19–21 September 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Etienne, C.; Fidanza, G.; Petrovskii, A.; Devillers, L.; Schmauch, B. CNN+LSTM Architecture for Speech Emotion Recognition with Data Augmentation. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Speech, Music and Mind (SMM 2018), Hyderabad, India, 1 September 2018; pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Atila, O.; Şengür, A. Attention Guided 3D CNN-LSTM Model for Accurate Speech Based Emotion Recognition. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 182, 108260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baevski, A.; Zhou, H.; Mohamed, A.; Auli, M. Wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations 2020. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 12449–12460. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, Y.-A.; Hsu, W.-N.; Tang, H.; Glass, J. An Unsupervised Autoregressive Model for Speech Representation Learning. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2019, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.T.; Li, S.-W.; Lee, H. TERA: Self-Supervised Learning of Transformer Encoder Representation for Speech. IEEEACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 2351–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.T.; Yang, S.; Chi, P.-H.; Hsu, P.; Lee, H. Mockingjay: Unsupervised Speech Representation Learning with Deep Bidirectional Transformer Encoders. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6419–6423. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Li, M.; Zhou, S.; Xu, B. Exploring Wav2vec 2.0 on Speaker Verification and Language Identification 2021. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2021, Brno, Czechia, 30 August–3 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space 2013. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2–4 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and Their Compositionality 2013. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2–4 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, N.; Muralidhara, B.L. Emotions During COVID-19: LSTM Models for Emotion Detection in Tweets. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Recent Trends in Machine Learning, IoT, Smart Cities and Applications; Gunjan, V.K., Zurada, J.M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 237, pp. 133–148. ISBN 9789811664069. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the NAACL-HLT 2019, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, Z.; Li, Y. Integrating BERT Embeddings and BiLSTM for Emotion Analysis of Dialogue. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2023, 2023, 6618452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, R.; He, Y.; Lu, Q. Learning Representations from Heterogeneous Network for Sentiment Classification of Product Reviews. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2017, 124, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ji, R.; Su, J.; Cao, D.; Gao, Y. Predicting Microblog Sentiments via Weakly Supervised Multimodal Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 20, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Guo, J. Bidirectional LSTM with Attention Mechanism and Convolutional Layer for Text Classification. Neurocomputing 2019, 337, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Feng, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y. A Novel Attention Based CNN Model for Emotion Intensity Prediction. In Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Zhang, M., Ng, V., Zhao, D., Li, S., Zan, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11108, pp. 365–377. ISBN 978-3-319-99494-9. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need 2017. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Akula, R.; Garibay, I. Interpretable Multi-Head Self-Attention Architecture for Sarcasm Detection in Social Media. Entropy 2021, 23, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rosas, V.; Mihalcea, R.; Morency, L.-P. Utterance-Level Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Sofia, Bulgaria, 4–9 August 2013; pp. 973–982. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Mao, W. MultiSentiNet: A Deep Semantic Network for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Singapore, 6 November 2017; pp. 2399–2402. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, D.; Zhou, Y.; Pi, J.; Shi, B.E. Multimodal Utterance-Level Affect Analysis Using Visual, Audio and Text Features. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.00625. [Google Scholar]
- Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Gelbukh, A. Deep Convolutional Neural Network Textual Features and Multiple Kernel Learning for Utterance-Level Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; pp. 2539–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Lin, H.; Meng, J.; Zhao, Z. Visual and Textual Sentiment Analysis of a Microblog Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Algorithms 2016, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, T.; Shen, X. Attention-Based Multimodal Fusion for Estimating Human Emotion in Real-World HRI. In Proceedings of the Companion of the 2020 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, Cambridge, UK, 23 March 2020; pp. 340–342. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J.; Fu, Z.; Liu, F. SCANET: Improving Multimodal Representation and Fusion with Sparse-and Cross-attention for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 2022, 33, e2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, X. Multimodal Fusion with Co-Attention Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Rustenburg, South Africa, 6–9 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Hua, Y.; Xu, G.; Deng, L. Multimodal Fusion Method Based on Self-Attention Mechanism. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, H.T.P.; Balamurali, B.T.; Roig, G.; Herremans, D. AttendAffectNet–Emotion Prediction of Movie Viewers Using Multimodal Fusion with Self-Attention. Sensors 2021, 21, 8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Wang, J.; Cai, S.; Yang, C.; Song, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, L.; Wang, H. Targeted Aspect-Based Multimodal Sentiment Analysis: An Attention Capsule Extraction and Multi-Head Fusion Network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 157329–157336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.-S.; Kasun, C.; Sivadas, S.; Rajapakse, J. Recurrent Multi-Head Attention Fusion Network for Combining Audio and Text for Speech Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2022, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 18 September 2022; pp. 744–748. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Sidulova, M.; Park, C.H. Robust Multimodal Emotion Recognition from Conversation with Transformer-Based Crossmodality Fusion. Sensors 2021, 21, 4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Guo, X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; He, L.; Luo, X. TETFN: A Text Enhanced Transformer Fusion Network for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 136, 109259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision 2021. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual Event, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, A.; Qin, J.; Chiu, C.-C.; Parmar, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Han, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. Conformer: Convolution-Augmented Transformer for Speech Recognition 2020. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2020, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.; Kleinegesse, S.; Comanescu, R.; Radu, O. Recognizing Emotions in Video Using Multimodal DNN Feature Fusion. In Proceedings of the Grand Challenge and Workshop on Human Multimodal Language (Challenge-HML), Melbourne, Australia, 20 July 2018; pp. 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, A.; Liang, P.P.; Mazumder, N.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.-P. Memory Fusion Network for Multi-View Sequential Learning 2018. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y.-H.H.; Bai, S.; Liang, P.P.; Kolter, J.Z.; Morency, L.-P.; Salakhutdinov, R. Multimodal Transformer for Unaligned Multimodal Language Sequences. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 6558–6569. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lakshminarasimhan, V.B.; Liang, P.P.; Zadeh, A.; Morency, L.-P. Efficient Low-Rank Multimodal Fusion with Modality-Specific Factors. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, A.; Chen, M.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.-P. Tensor Fusion Network for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 9–11 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).