Abstract
Recent legislations, such as the European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), require user data holders to guarantee the individual’s right to be forgotten. This means that user data holders must completely delete user data upon request. However, in the field of machine learning, it is not possible to simply remove these data from the back-end database wherein the training dataset is stored, because the machine learning model still retains this data information. Retraining the model using a dataset with these data removed can overcome this problem; however, this can lead to expensive computational overheads. In order to remedy this shortcoming, we propose two effective methods to help model owners or data holders remove private data from a trained model. The first method uses an elastic weight consolidation (EWC) constraint term and a modified loss function to neutralize the data to be removed. The second method approximates the posterior distribution of the model as a Gaussian distribution, and the model after unlearning is computed by decreasingly matching the moment (DMM) of the posterior distribution of the neural network trained on all data and the data to be removed. Finally, we conducted experiments on three standard datasets using backdoor attacks as the evaluation metric. The results show that both methods are effective in removing backdoor triggers in deep learning models. Specifically, EWC can reduce the success rate of backdoor attacks to 0. IMM can ensure that the model prediction accuracy is higher than 80% and keep the success rate of backdoor attacks below 10%.
1. Introduction
The explosion in the amount of data generated, recorded and processed as a result of huge advances in data storage and transmission technologies has led to the vast amount of private personal data now available on the Internet. For example, approximately 4 billion YouTube videos are viewed every day [1]. Many Internet service providers collect these data to improve the user experience, provide tailored services or identify potential business opportunities. Such an abundance of data has fueled the development of artificial intelligence (AI), such as machine learning (ML) [2,3,4]. ML refers to the process of training an algorithm to make predictions or decisions based on data [5].
On the other hand, these data threaten users’ privacy and increase the risk of data leakage [6,7,8,9]. Furthermore, privacy regulations, such as the European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) [10], allow users to request the deletion of their personal data from learning models as part of the “right to be forgotten”. It is also useful to remove certain training data from the model when they are no longer valid.
For these reasons, some users may choose to remove their data from a system altogether, especially those sensitive systems related to finance or healthcare. In the field of machine learning, data deletion is not limited to simply removing the corresponding records from the back-end database, but should also include any entities that indirectly use that data [11]. For example, a machine learning model that performs a high-level abstraction through given train data. Therefore, the most naive way to delete data is to delete these from the training dataset and then retrain the model. However, retraining can be time-consuming and computationally expensive. To solve this dilemma, researchers have proposed a paradigm called machine unlearning [11].
Machine unlearning has become a popular research topic with the aim of allowing users to completely remove personal data from a trained model. As a remedy for retraining, Bourtoule et al. [12] proposed a machine unlearning framework called Sharded, Isolated, Sliced, and Aggregated training (SISA). SISA effectively reduces the time cost of retraining, but this method degenerates into retraining if the deleted data include all sub-datasets. Other existing methods address the time cost issue, but have their own limitations: some are only applicable to specialized problems, such as Ginart et al. [13], who propose an unlearning method for softmax classifiers based on linear filtering; and Izzo et al. [14], who propose an approximate unlearning method in linear and logistic models based on the influence function; or some other schemes require the introduction of additional random perturbations, leading to non-standard training algorithms [15].
Catastrophic forgetting is a problem of neural networks losing information about the first task after training on a second task. Models using stochastic gradient descent often forget information about the previous task after being trained on a new task. Therefore, it is a fundamental challenge for neural network-based artificial intelligence. The researchers have proposed a paradigm called continual learning to overcome this problem [16]. Clearly, machine unlearning is the reverse process of continual learning and can be realized using the process of reversing continual learning.
This motivates us to propose two effective unlearning methods that can delete data from most deep learning models. First, we modify the loss function to use elastic weight adjustment (EWC) [17] to constrain the significant weights, and then train further on the trained model. During further training, we force the model to forget the corresponding data to be removed and retain other data as much as possible. Second, we propose decreasing moment matching (DMM), which assumes that the posterior parameters of the model follow a Gaussian distribution. DMM decreasingly matches the moment of the posterior distribution of the neural network trained with all data and with the data to be deleted, respectively [18]. Specifically, we train a model with the data to be removed and then merge the parameters of the two networks using the Laplace approximation.
In general, our contributions can be summarized as follows:
- We propose an oblivious learning method using EWC, which allows for further training of the model. EWC is able to constrain model parameters that are important for the remaining data and can be applied with only one or two epochs.
- We propose a unlearning learning method using DMM, which approximates the model parameters as a Gaussian distribution and achieves unlearning by closed updating of the model parameters.
- We have conducted experiments on realistic and commonly used standard datasets, and the results support our theoretical research.
2. Related Work
2.1. Machine Unlearning
The concept of machine unlearning was first introduced by Cao et al. [11], who represented machine learning models as a closed sum form. When a sample of training data is removed, only a small part of the sum needs to be updated, making it faster than retraining from scratch. However, the algorithm only applies to traditional machine learning methods that can be transformed into a summation form. Bourtoule et al. [12] proposed an unlearning framework named Sharded, Isolated, Sliced, and Aggregated training (SISA). Their main idea is to slice the dataset, train a sub-model for each sub-dataset, and generate the final prediction by aggregating the sub-models. SISA effectively reduces the time cost of retraining, but degrades to retraining when the deleted data affect all sub-datasets.
Guo et al. [15] proposed a certified deletion framework that theoretically ensures that an adversary cannot extract information about the training data removed from the model. However, they only apply to linear models with convex losses. As a remedy to [15], Golatkar et al. [19] introduced computable upper bounds for SGD-based learning algorithms, in particular for deep neural networks. However, these theoretical guarantees rely on a tailor-made loss function, which can be seen as a perturbed version of the traditional regularized empirical risk, where the added noise comes from a specified normal distribution.
2.2. Continual Learning
Kirkpatrick et al. [17] found that synaptic consolidation in the brain allows for continual learning by reducing synaptic plasticity, which is critical for previously learned tasks. They performed a similar operation in an artificial neural network, using EWC to add regular terms to the loss function to constrain the significant weights, overcoming the problem of catastrophic unlearning in continual learning. Lee et al. [18] proposed incremental moment matching (IMM) to address the problem of catastrophic unlearning. They stated that IMM incrementally matches the posterior distribution moments of the neural network trained on the first task and the second task, respectively. IMM approximates the Gaussian posterior mixture representing the parameters of a single task as a Gaussian distribution for the combined task.
3. Preliminaries
3.1. Machine Unlearning
We consider an original dataset , where n is the number of data points, and is the pair of input image and image class. Let A be a (stochastic) machine learning algorithm that updates the parameters and outputs an optimal model based on the optimization objective:
In our work, we want to remove the subset of D and make the deep learning model M unlearn the subset of data extracted from D. We set the subset that the individual wants to remove as and the remaining dataset as . In this case, machine unlearning reconstructs M to obtain a model in which is neutralized so that the performance of on is equivalent to a random guess. The simplest method of unlearning is to retrain from scratch, so the ideal model should be approximately equal to . Finally, C denotes the number of classes in the dataset D and w denotes the optimal weight parameter of the model.
3.2. Continual Learning
Continual learning is particularly challenging for neural networks because knowledge from previously learned tasks (e.g., task A) is often suddenly lost when it is merged with the current task (e.g., task B). This phenomenon is known as catastrophic forgetting, and multitask learning to overcome these problems is called continual learning.
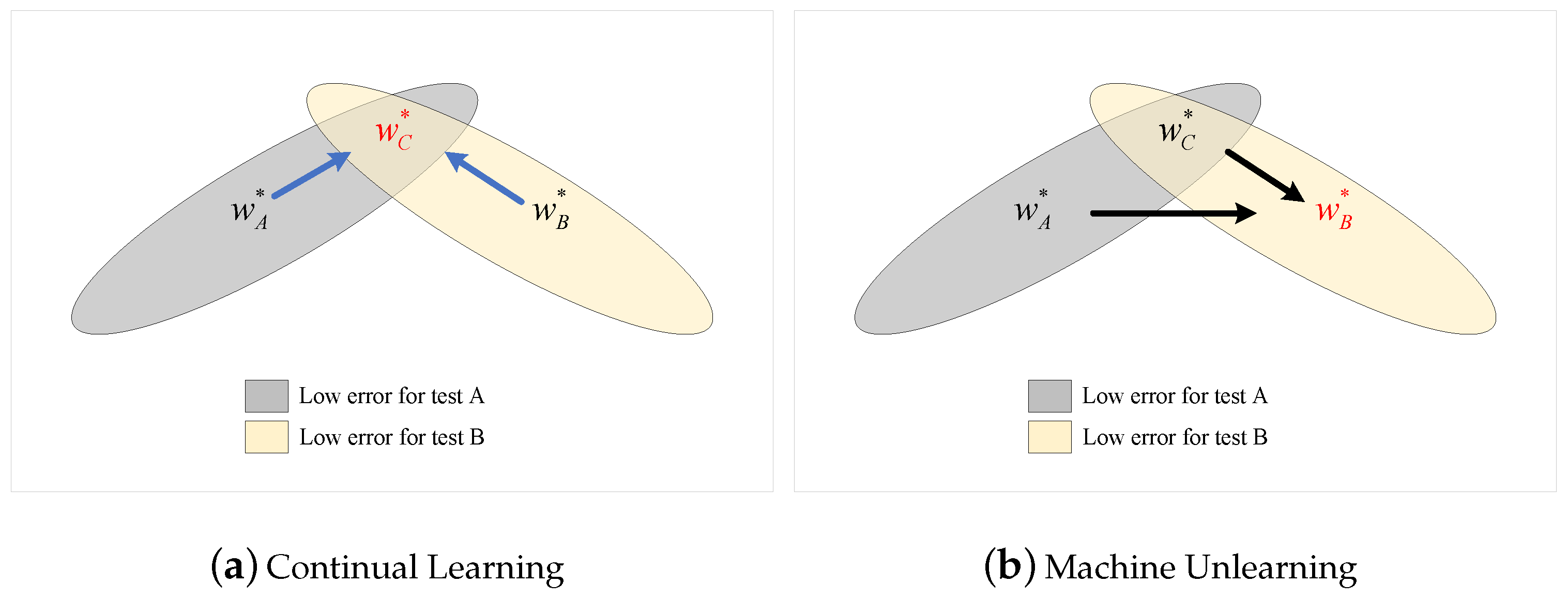
Learning a task requires adjusting the parameter weights w of the model to optimize performance. Different w can lead to the same performance [20]. This overparameterization allows for the existence of a solution for task B that is close to the previously found solution for task A. Continual learning ensures that task A is remembered when further training for task B. Training trajectories are shown in a schematic parameter space, with parameter regions leading to good performance on task A (gray) and on task B (cream color), as shown in Figure 1. In other words, continual learning is learning task B on the model trained on task A to obtain task C (including A and B). Intuitively, continual learning is about finding the intersection of the parameter space of multiple tasks.
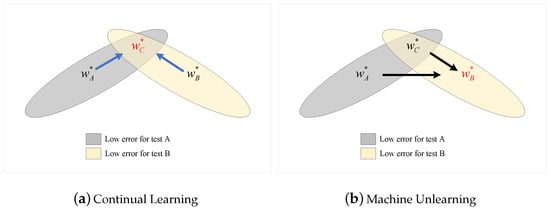
Figure 1.
A schematic view of continual learning and machine unlearning.
When learning task B, EWC protects the performance of task A by restricting the parameters to a low error region around task A. The EWC explicitly calculates the importance of the parameters for task A and finds a corresponding solution for task B, provided that it does not significantly compromise task A. Specifically, EWC approximates the posterior as a Gaussian distribution whose mean is determined by the parameter .The importance of each parameter is measured by the diagonal accuracy given by the diagonal of the Fisher information matrix F. Given this approximation, the function that we minimize in EWC is
where F is the Fisher information matrix for the new task B and i labels each parameter.
In addition, IMM has been proposed to solve the catastrophic forgetting. Unlike the EWC-based approach, the IMM first learns the new task B separately and then averages the parameters of the two networks for the old and new tasks. Specifically, IMM minimizes the average of the KL divergence between an approximated posterior distribution for the combined task and each Gaussian posterior for the single task. As shown in Figure 1, the IMM finds the intersection of the two task parameter spaces by averaging and as follows:
where q denotes an approximation of the true posterior distribution for the task, while and are the mean and covariance in the posterior distribution for task c.
4. Machine Unlearning by Reversing the Continual Learning
4.1. Overview
Removing the knowledge of Task B from Task C is the opposite process of continual learning. It corresponds to the removal of specific data from a trained model in machine unlearning. In continual learning, and are known (in red font), whereas the unlearning process can only access and . Figure 1a illustrates the continual learning process by finding the intersection region from the parameter space of the old and new tasks, whereas Figure 1b illustrates the unlearning process by finding the parameter space of one of the tasks from the parameter space of the other task and merged task.
4.2. Unlearning with EWC
We start by recalling the concept of machine unlearning, which Kim et al. [21] loosely define as the boundary of machine unlearning as the accuracy of on which should be the same as , where is the number of classes in the dataset . They argue that, if a deep learning model is more accurate on than a random model, it can be assumed that the deep learning model has prior knowledge on the corresponding dataset . This suggests that we can achieve our goal by inverting the loss function, but since the loss function is not lower-bounded after inversion, this will result in the model losing information about the remaining dataset while neutralizing . An unlearning method is only of practical use if it keeps the performance as close to the original model as possible.
We now consider the parametric structure of a deep neural network, which consists of several layers of linear transformations and elemental-level nonlinearities. When training the neural network on a dataset, the set of weights and biases w are adjusted to optimize performance. Different values of w will result in the same performance, and this over-parameterization gives us ideas on how to solve the above problems. Our aim is to find a such that the prediction accuracy for dataset is close to that of a random guess and should be close to .
The key to solving this problem is how to constrain the model weights that are important to the remaining data. Inspired by Kirkpatrick et al. [17], we used EWC to correct for the inverse loss function. Specifically, we approximate the importance of the model to the remaining data by the diagonal accuracy given by the diagonal of the Fisher information matrix F. The exact proof procedure can be found in [17]. Therefore, calculating the Fisher information matrix F for the remaining data and then adding a canonical term to the loss function. The modified loss function is as follows:
where is the loss of the dataset , which usually is the cross-entropy; sets the importance of the remaining data compared to the data to be removed, and then i marks each parameter.
4.3. Unlearning with DMM
We first consider continual learning with IMM, given task A (dataset ) and task B (dataset ), and a model that has learnt task A (trained with ). The objective of continual learning is to build on to learn task B while retaining knowledge of task A. In short, one wants to obtain the model M that has learned task C (dataset ). In IMM, the moments of posterior distributions are matched in an incremental way.
We denote the true posterior parameter distribution of M as p, the true posterior parameter distribution of as , and the true posterior parameter distribution of as . Assuming that the posterior parameters of all models follow Gaussian distribution, then the true distributions and can be approximated by and , respectively:
where is the mean of the distribution and is the covariance matrix in the distribution.
The dimension of is d and the dimension of is , where d is the dimension of w. Since , the model M can be calculated from and . The specific idea is to minimize the weighted sum of the KL-divergence between the two sub-distributions and the overall distribution h:
where . Equation (8) has a closed solution:
where and are solutions of Equation (8).
Recall our problem: delete the data from M to obtain , and make sure that has no residual information about . We propose the DMM, in which the moments of posterior distributions are matched in a decreasing way. We can approximate M as the solution of Equations (9) and (10); then, we can calculate and according to the following equation:
where .
Since is the optimal , the model owner can complete the deletion request according to Equations (11) and (12). Specifically, after receiving a deletion request from a user, the model owner trains the model on the dataset to be removed, calculates and according to Equations (11) and (12), and finally uses and to generate the parameters of . Note that our method does not require covariance information, since the calculation of does not require .
5. Evaluation
5.1. Experimental Setup
5.1.1. Test Bench
Experiments are performed using PyTorch on a workstation running Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS, equipped with a 2.60 GHz 8358P CPU, 80 G RAM and NVIDIA RTX A5000 GPU card.
5.1.2. Datasets
We consider three benchmark datasets of different size and complexity, namely MNIST [22], CIFAR-10 [23] and CIFAR-100 [23] to conduct our experiments. MNIST is a gray-scale image dataset consisting of 70,000 handwritten digits, including 60,000 images from the training set and 10,000 images from the test set. The dataset divides the images into 10 classes representing 10 different digits. The CIFAR-10 dataset consists of 60,000 color images in 10 classes of 6000 images each. There are 50,000 training images and 10,000 test images. CIFAR-100 is exactly the same as CIFAR-10 except that it has 100 classes, each containing 600 images. Each class has 500 training images and 100 test images.
5.1.3. Metrics
We use backdoor triggers [24] as an efficient way to evaluate the performance of unlearning methods, similar to [25,26]. Backdoor attack is one of the main attacks against machine learning models. Backdoor attacks do not affect the model’s performance on benign inputs and only produce incorrect results when triggered by a specific sample with a trigger. We add fixed triggers to benign samples to cause the model to produce incorrect prediction results, which are then removed using a machine unlearning algorithm. In other words, we study the ability of the proposed scheme to remove backdoor triggers. Therefore, the data to be removed should be those contaminated samples with backdoor triggers. An unlearning algorithm is successful if it produces a model that reduces the accuracy of the backdoor trigger samples while maintaining good performance on the regular (clean) samples. The prediction accuracy of the model on the remaining dataset was chosen as the ability of the model to retain old knowledge.
5.2. Results and Discussion
We tested the first method on the MNIST dataset and the second on the CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets. As mentioned above, we used backdoor attacks during the training of the MNIST classification model in order to visualize the unlearning effect based on the success rate of the attacks on the post-unlearning model. The backdoor attack is triggered by a backdoor pattern in the input image. The user changed a number of pixels in the benign image to create a backdoor pattern. Backdoor targets in the experiment included predicting the number “1” (class 1) as the number “9” (class 9) in MNIST, predicting a car (class 1) as a truck (class 9) in CIFAR-10 and predicting a dolphin (class 1) as a tractor (class 99) in CIFAR-100. This is achieved by adding a pattern of four pixels in the lower right corner of the benign image. The clean prediction accuracy is the model’s prediction accuracy for samples without triggers, and the backdoor prediction accuracy is the model’s accuracy in predicting samples with triggers as the specified class.
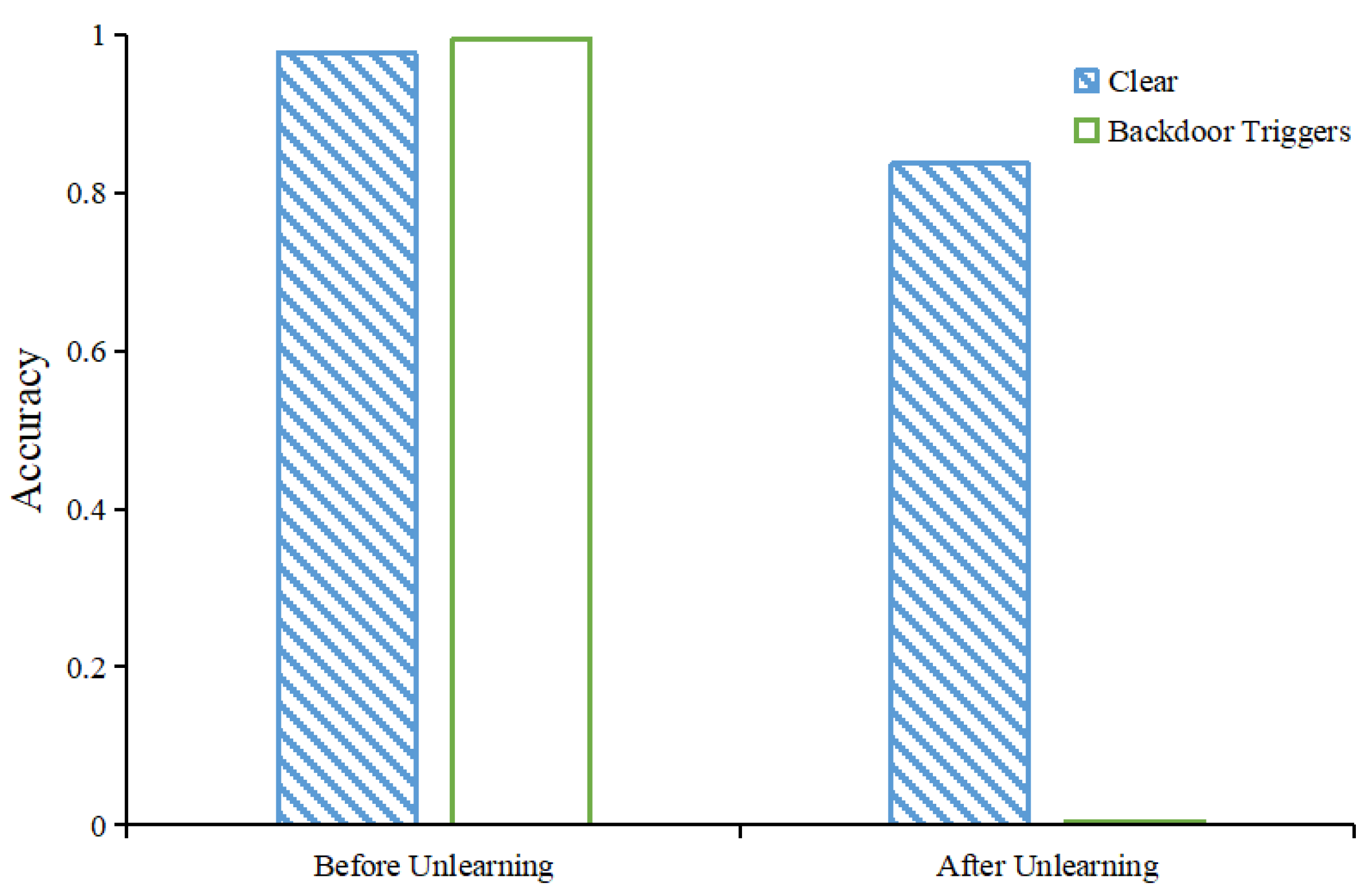
We trained a fully connected neural network model with three layers using the MNIST dataset with a backdoor trigger that tricks the model into classifying the number “1” as the number “9”. Our fully connected network consists of three layers, and the number of neurons is 784 × 100, 100 × 100, and 100 × 10, respectively. In addition, there are ReLu activation functions between every two layers. We evaluated the unlearning effect of our first unlearning method. We show the clean prediction accuracy and the backdoor prediction accuracy of the model before and after unlearning, respectively, as shown in Figure 2. The figure shows that the prediction accuracy of the model for clean data changes from 97.66% to 84.67%, while the success rate of backdoor attacks decreases from 99.47% to 0.18%. This shows that our approach can completely remove backdoor triggers from the model with only a small degradation in model performance. Model performance can be recovered after a small number of epochs of knowledge distillation [27]. Specifically, we used the old model as a teacher to train the unlearned model.
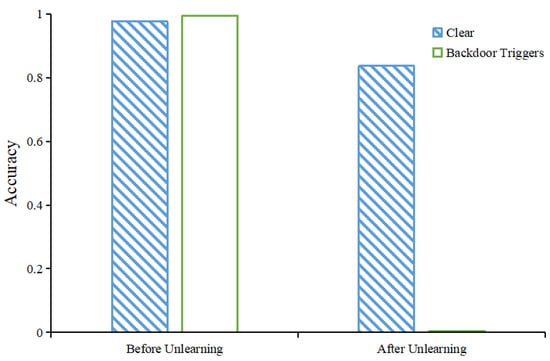
Figure 2.
The clean prediction accuracy and the backdoor prediction accuracy of the model before and after unlearning using EWC, respectively.
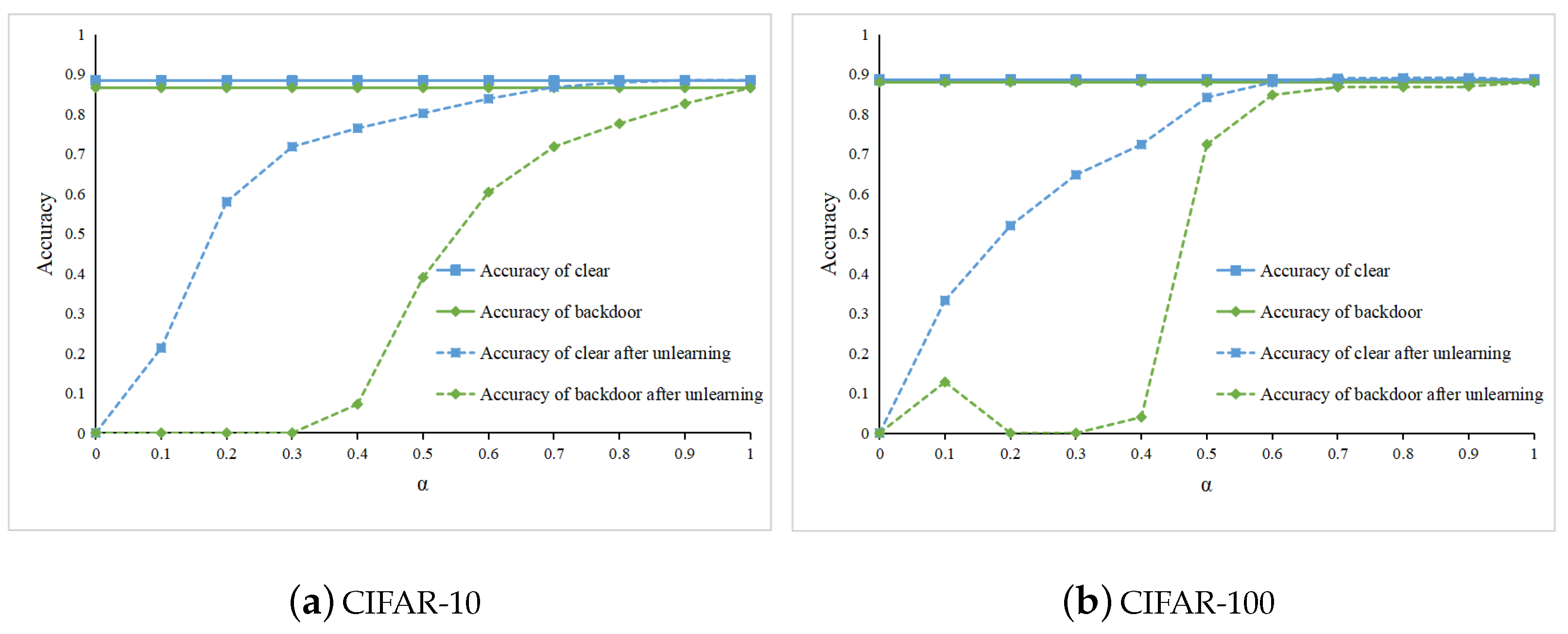
Resnet [28] is a residual network that can handle more complex image data, like CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 [29]. We then trained two ResNet neural networks using the CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets with the addition of backdoor triggers. We evaluated the unlearning effect of our second unlearning method on these two models. We show the effect of on clean prediction accuracy and backdoor prediction accuracy before and after unlearning, as shown in Figure 3. The solid line in the figure is used as a baseline to show the two accuracies before unlearning, while the dashed line shows the accuracy after unlearning. It can be seen from the figure that both the accuracy of the clean data and the backdoor data after unlearning decrease with the value of . Therefore, the value of indicates the importance of the remaining data. However, the decrease in backdoor data accuracy after unlearning is greater than the decrease in clean data accuracy. Therefore, the best unlearning results can be achieved by selecting the appropriate . Figure 3a shows the ResNet neural network trained on CIFAR-10 and Figure 3b shows the ResNet neural network trained on CIFAR-100; it can be seen that both models have higher clean data accuracy and lower backdoor data accuracy when is between 0.4 and 0.5.
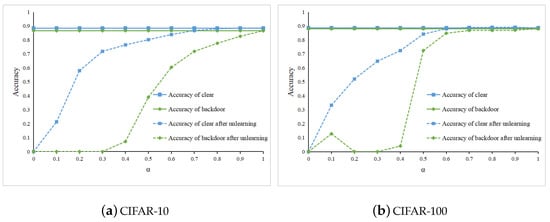
Figure 3.
The clean prediction accuracy and the backdoor prediction accuracy of the model before and after unlearning using DMM, respectively.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we present two methods that can effectively remove parts of the training data from a neural network model. EWC allows the model to retain knowledge of the remaining data during the process of neutralizing the data to be removed, thus guaranteeing the performance of the corrected model. We applied DMM to deep neural networks for machine unlearning, where DMM removes information from one model to another through moment matching of model parameter distributions. Experimental results show that EWC and DMM tend to improve the performance of the unlearned model. Specifically, EWC can guarantee model performance above 84%; DMM can guarantee model performance above 80% when is around 0.45. Overall, we have achieved advanced performance on a variety of machine unlearning datasets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z., H.W. and Z.L.; methodology, Z.L., Y.Z. and F.Z.; investigation, F.Z. and H.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.L. and S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this paper can be found at https://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/ and http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html (accessed on 21 April 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sari, W.; Samosir, B.; Sahara, N.; Agustina, L.; Anita, Y. Learning mathematics “Asyik” with Youtube educative media. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1477, 022012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheisari, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, F.; Rahimi, M.; Moazzamigodarzi, M.; Liu, Y.; Dutta Pramanik, P.K.; Heravi, M.A.; Mehbodniya, A.; Ghaderzadeh, M.; Feylizadeh, M.R.; et al. Deep learning: Applications, architectures, models, tools, and frameworks: A comprehensive survey. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2023; Early View. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaderzadeh, M.; Asadi, F.; Hosseini, A.; Bashash, D.; Abolghasemi, H.; Roshanpour, A. Machine learning in detection and classification of leukemia using smear blood images: A systematic review. Sci. Program. 2021, 2021, 9933481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderzadeh, M.; Aria, M. Management of COVID-19 detection using artificial intelligence in 2020 pandemic. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Medical and Health Informatics, Kyoto, Japan, 14–16 May 2021; pp. 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, I.H. Machine learning: Algorithms, real-world applications and research directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, N.; Liu, C.; Erlingsson, Ú.; Kos, J.; Song, D. The Secret Sharer: Evaluating and Testing Unintended Memorization in Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the USENIX Security Symposium, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 11–13 August 2019; Volume 267. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Liang, H.; Zhao, M.; Lv, Q.; Liang, T.; Wang, Y. Label-only membership inference attacks on machine unlearning without dependence of posteriors. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 9424–9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, R.; Stronati, M.; Song, C.; Shmatikov, V. Membership inference attacks against machine learning models. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Jose, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2017; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Backes, M.; Humbert, M.; Zhang, Y. When machine unlearning jeopardizes privacy. In Proceedings of the 2021 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Virtual Event, 15–19 November 2021; pp. 896–911. [Google Scholar]
- Magdziarczyk, M. Right to be forgotten in light of regulation (eu) 2016/679 of the european parliament and of the council of 27 April 2016 on the protection of natural persons with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data, and repealing directive 95/46/ec. In Proceedings of the 6th International Multidisciplinary Scientific Conference on Social Sciences and Art SGEM 2019, Balchik, Bulgaria, 24 August–2 September 2019; pp. 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Yang, J. Towards making systems forget with machine unlearning. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, CA, USA, 18–20 May 2015; pp. 463–480. [Google Scholar]
- Bourtoule, L.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Choquette-Choo, C.A.; Jia, H.; Travers, A.; Zhang, B.; Lie, D.; Papernot, N. Machine unlearning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–27 May 2021; pp. 141–159. [Google Scholar]
- Baumhauer, T.; Schöttle, P.; Zeppelzauer, M. Machine unlearning: Linear filtration for logit-based classifiers. Mach. Learn. 2022, 111, 3203–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, Z.; Smart, M.A.; Chaudhuri, K.; Zou, J. Approximate data deletion from machine learning models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Virtual, 13–15 April 2021; pp. 2008–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Goldstein, T.; Hannun, A.; Van Der Maaten, L. Certified data removal from machine learning models. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 3832–3842. [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey, M.; Cohen, N.J. Catastrophic interference in connectionist networks: The sequential learning problem. In Psychology of Learning and Motivation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 24, pp. 109–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, J.; Pascanu, R.; Rabinowitz, N.; Veness, J.; Desjardins, G.; Rusu, A.A.; Milan, K.; Quan, J.; Ramalho, T.; Grabska-Barwinska, A.; et al. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3521–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Jun, J.; Ha, J.W.; Zhang, B.T. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting by incremental moment matching. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Golatkar, A.; Achille, A.; Soatto, S. Eternal sunshine of the spotless net: Selective forgetting in deep networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9304–9312. [Google Scholar]
- Sussmann, H.J. Uniqueness of the weights for minimal feedforward nets with a given input-output map. Neural Netw. 1992, 5, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Woo, S.S. Efficient two-stage model retraining for machine unlearning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4361–4369. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/ (accessed on 21 April 2023).
- Available online: https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html/ (accessed on 21 April 2023).
- Gu, T.; Dolan-Gavitt, B.; Garg, S. Badnets: Identifying vulnerabilities in the machine learning model supply chain. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.06733. [Google Scholar]
- Halimi, A.; Kadhe, S.R.; Rawat, A.; Angel, N.B. Federated Unlearning: How to Efficiently Erase a Client in FL? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Xie, X.; Qi, H. Federated unlearning via class-discriminative pruning. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, Lyon, France, 25–29 April 2022; pp. 622–632. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Zhu, S.; Mitra, P. Federated unlearning with knowledge distillation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.09441. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Thudi, A.; Deza, G.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Papernot, N. Unrolling sgd: Understanding factors influencing machine unlearning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 7th European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), Genoa, Italy, 6–10 June 2022; pp. 303–319. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).