Maximum Correntropy Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter with State Estimation for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Vehicle and Tire Model
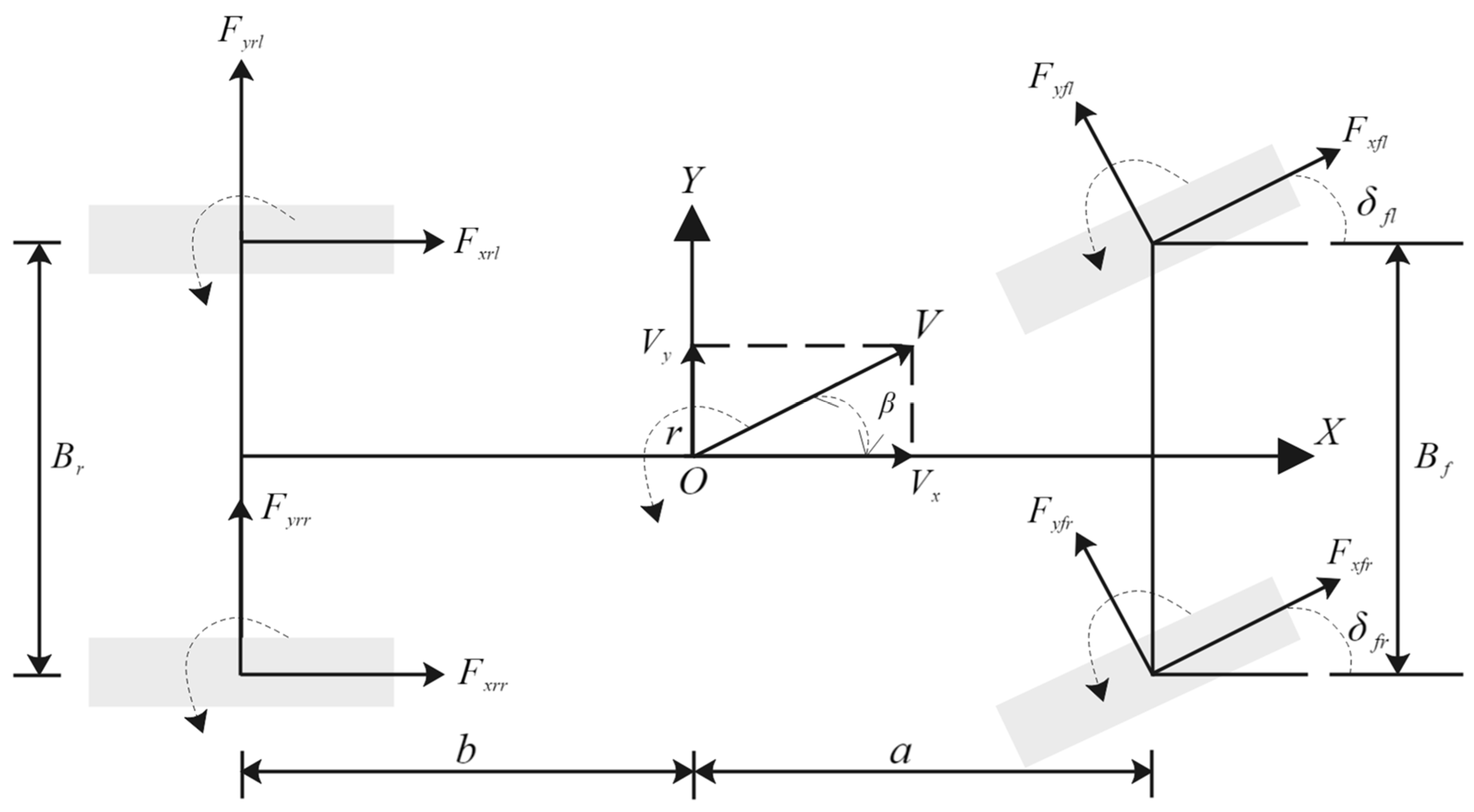
2.1. Vehicle Model
- (a)
- The vehicle model’s centroid coincides with the original point of the vehicle coordinate system;
- (b)
- Ignore the freedom of the vehicle in pitch, roll, and vertical;
- (c)
- Make the suspension a rigid body and the drivetrain a linear system to simplify the system;
- (d)
- Neglecting the influence of longitudinal friction resistance on state estimation.
2.2. Nonlinear Dugoff Tire Model
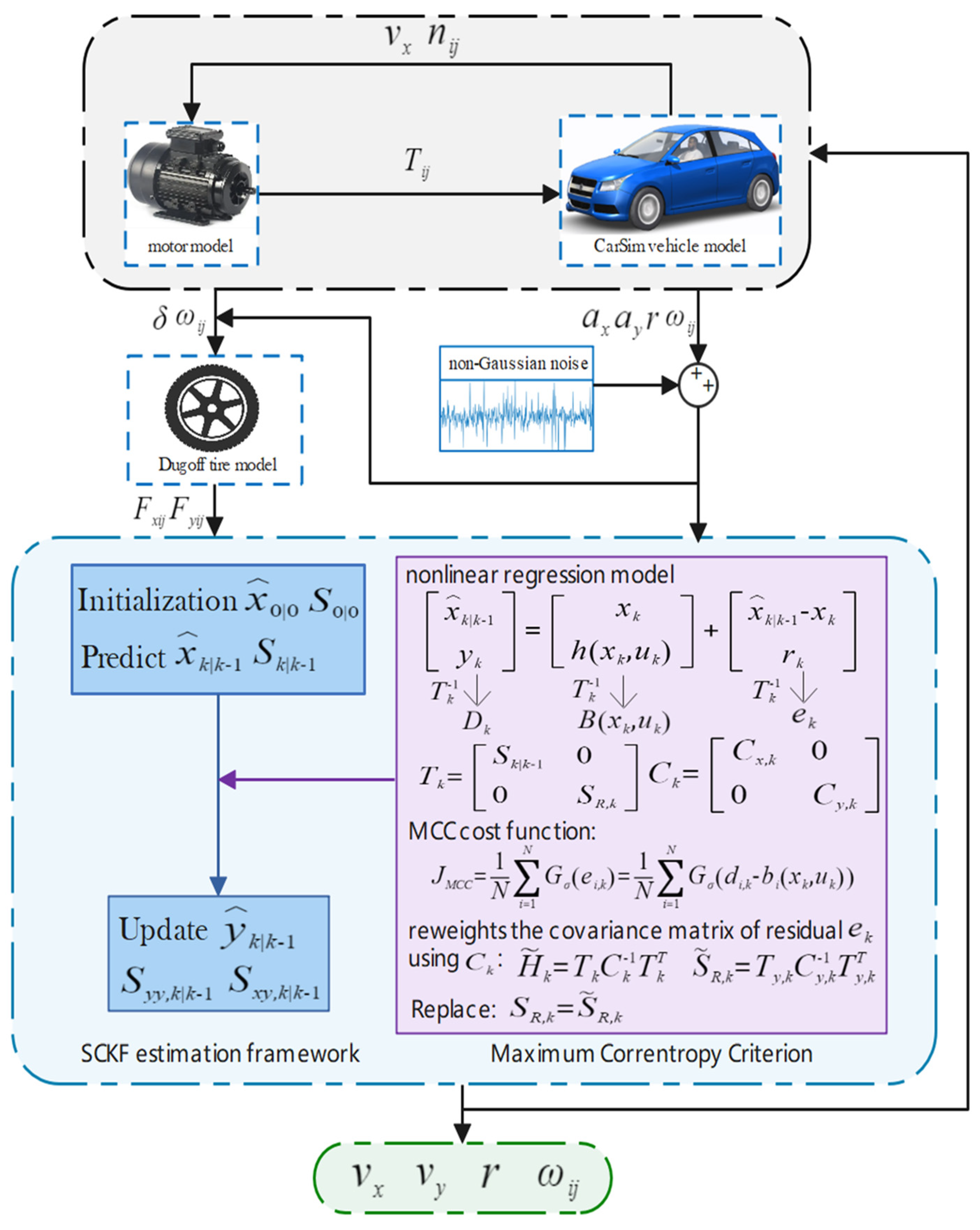
3. Distributed Drive Vehicles Based on MCSRCKF
3.1. Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter
3.1.1. Initialization
3.1.2. Predict
3.1.3. Update
3.2. Maximum Correntropy Criterion
3.3. Derivation of the MCSRCKF
3.4. Algorithm Complexity
4. Simulation and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Environment Settings
4.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
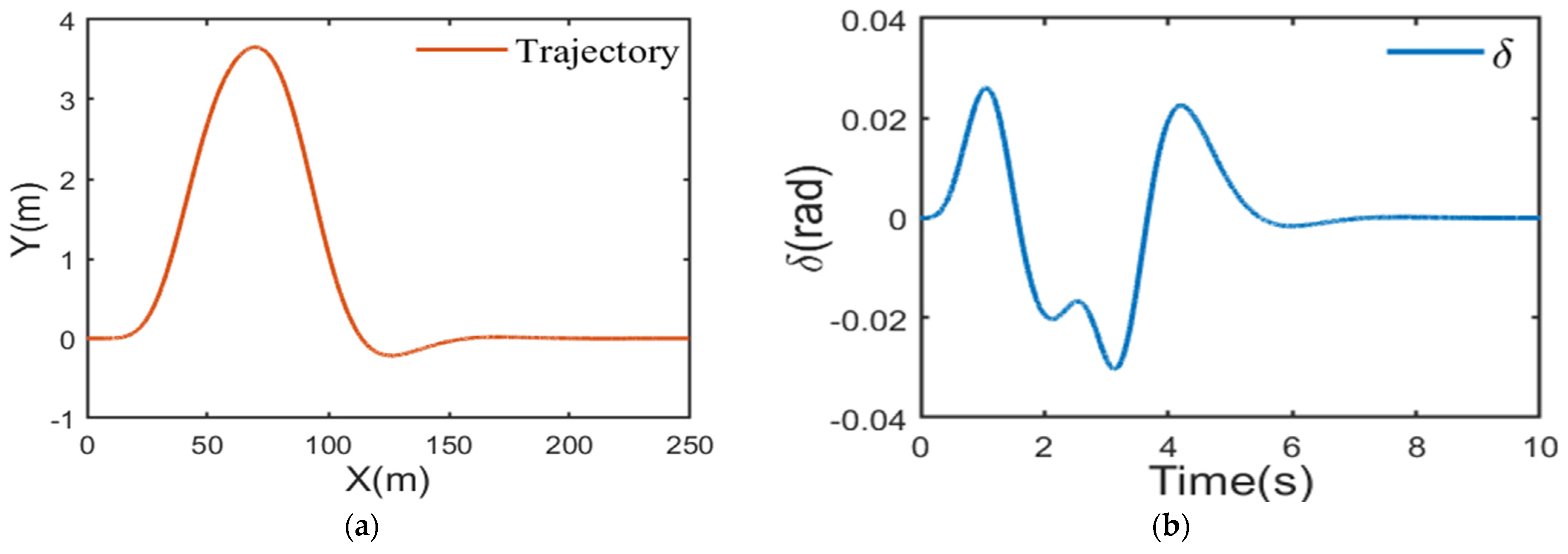
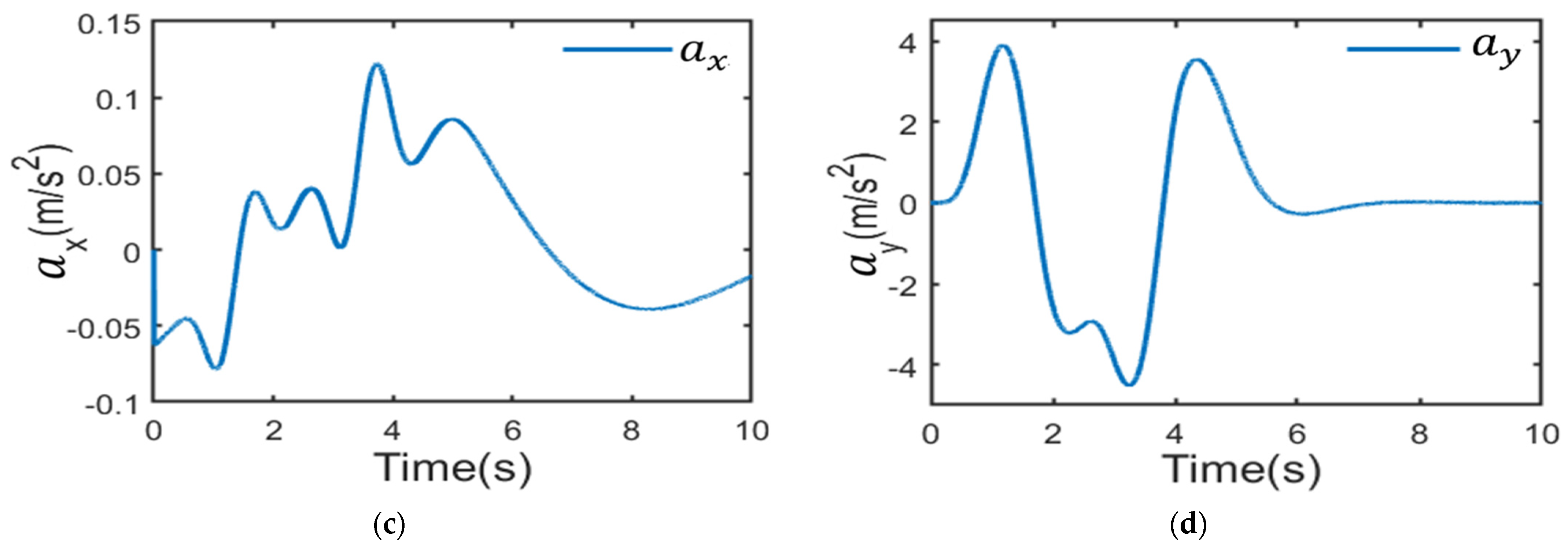
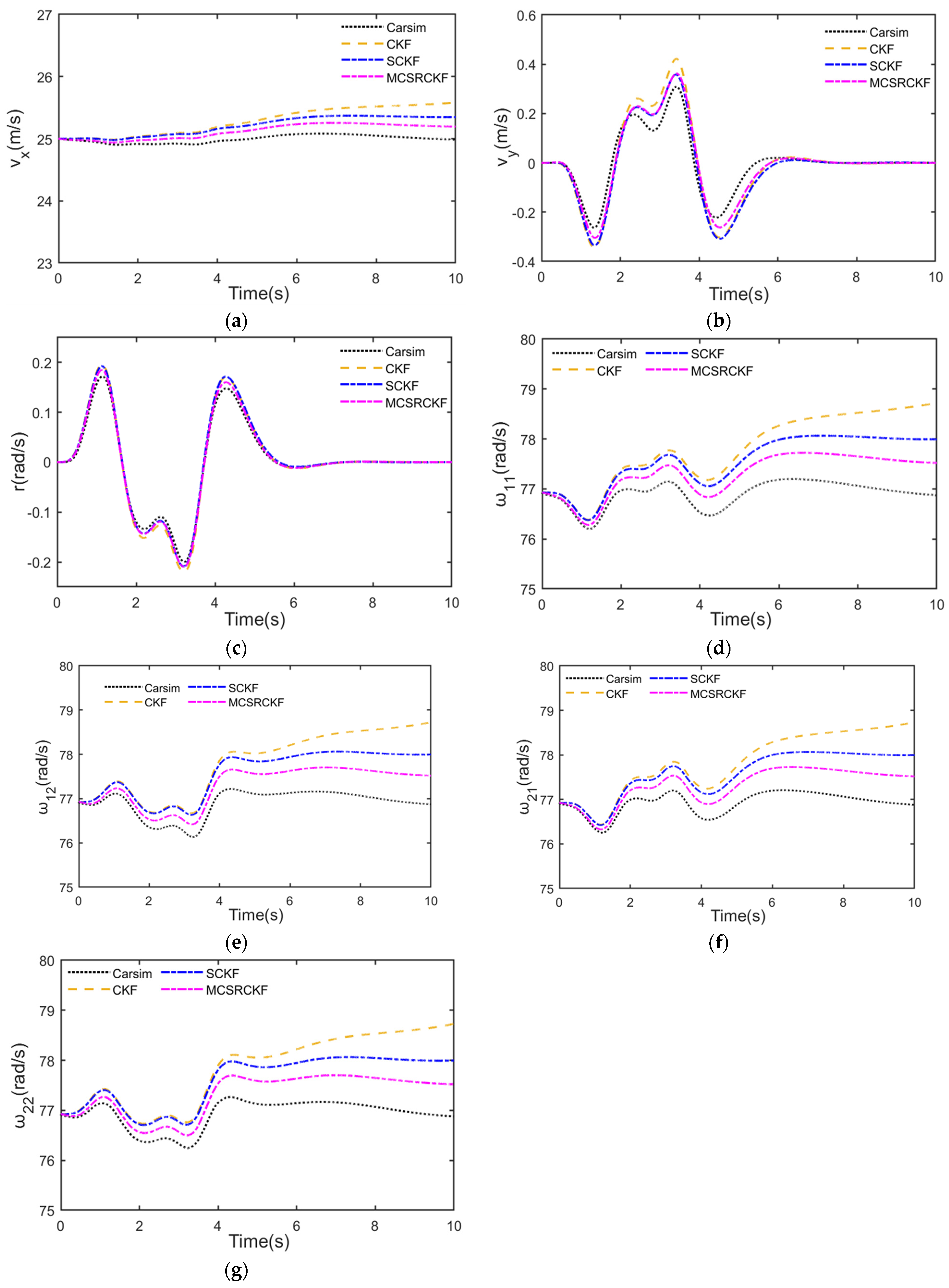
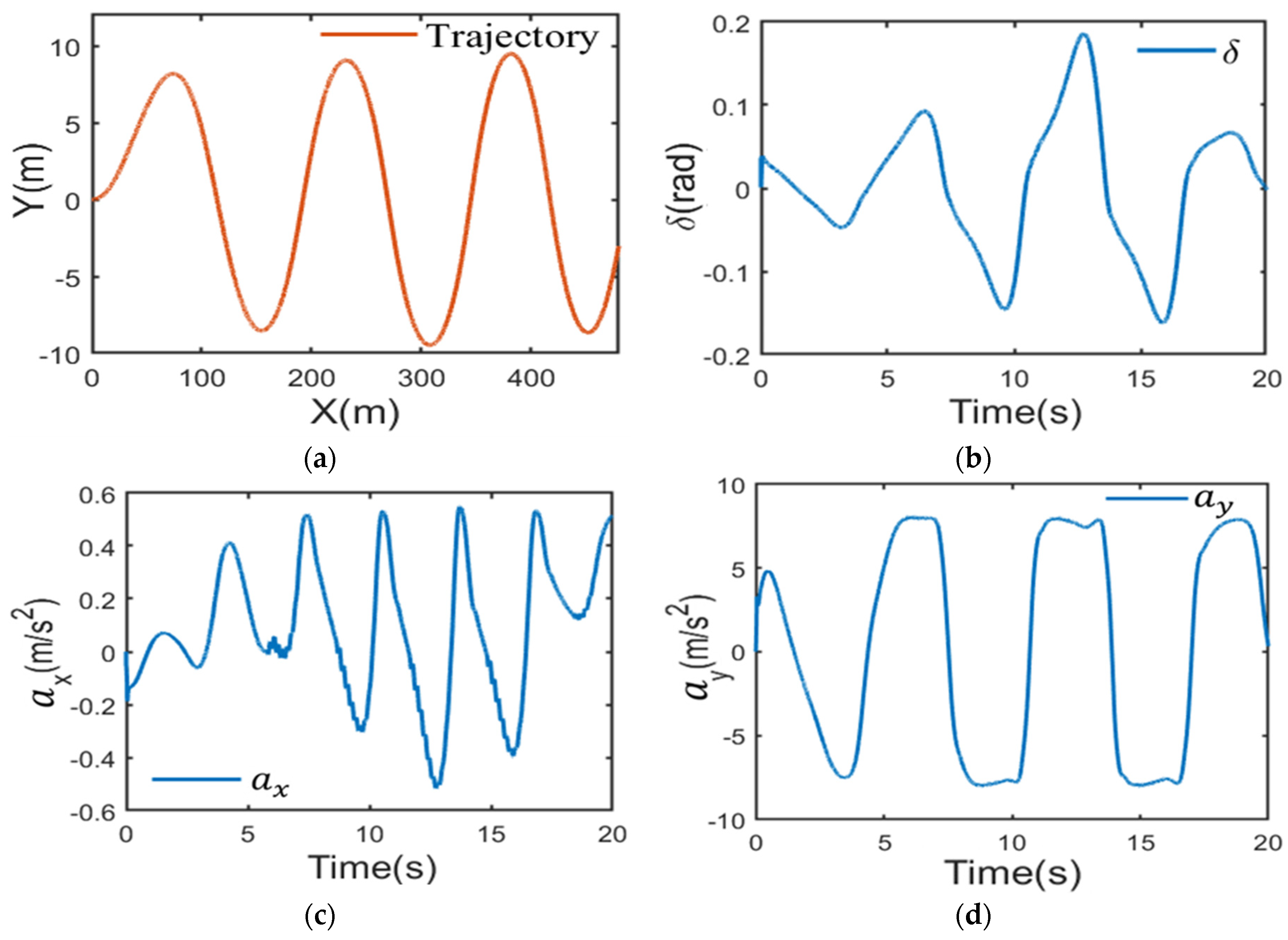
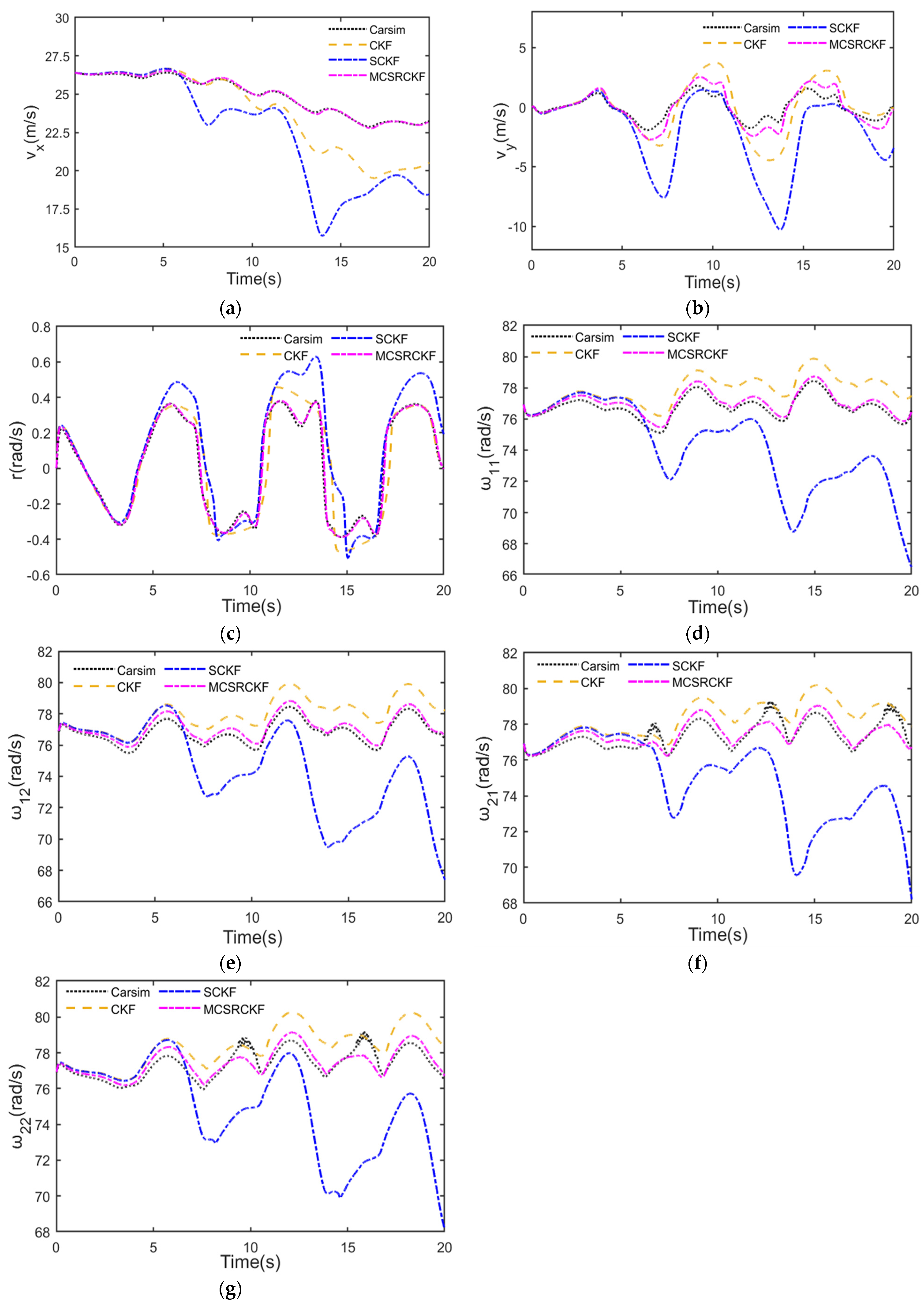
4.2.1. Double-Lane Change Condition
4.2.2. Serpentine Condition
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahangarnejad, A.H.; Radmehr, A.; Ahmadian, M. A review of vehicle active safety control methods: From antilock brakes to semiautonomy. J. Vib. Control 2021, 27, 1683–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, Y. Multi-sensor integrated navigation/positioning systems using data fusion: From analytics-based to learning-based approaches. Inf. Fusion 2023, 95, 62–90. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Xiong, L.; Huang, Y. Estimation on IMU yaw misalignment by fusing information of automotive onboard sensors. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 162, 107993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, V.R.; Kalkkuhl, J.; Raisch, J. Multi-modal sensor fusion for highly accurate vehicle motion state estimation. Control Eng. Pract. 2020, 100, 104409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.J.; Di, K.K.; Bai, S.; Yin, G.D. Vehicle state estimation based on limited memory random weighted extended Kalman filter. J. Southeast Univ. 2022, 2, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Julier, S.J.; Uhlmann, J.K. New extension of the Kalman filter to nonlinear systems. Signal processing, sensor fusion, and target recognition VI. SPIE 1997, 3068, 182–193. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, W.; Feng, J.; Song, B.; Li, X. Huber-Based Robust Unscented Kalman Filter Distributed Drive Electric Vehicle State Observation. Energies 2021, 14, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, D.; Wu, M. A numerical-integration perspective on Gaussian filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 2910–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasaratnam, I.; Haykin, S. Cubature kalman filters. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 1254–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Qi, J. Robust cubature Kalman filter for dynamic state estimation of synchronous machines under unknown measurement noise statistics. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 29139–29148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Jingan, F.; Bao, S.; Xinxin, L. Vehicle state estimation using interacting multiple model based on square root cubature Kalman filter. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10772. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Li, G.; Fan, D. Joint estimation of driving state and road adhesion coefficient for distributed drive electric vehicle. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 75460–75469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufadene, M.; Belkheiri, M.; Rabhi, A. Vehicle longitudinal force estimation using adaptive neural network nonlinear observer. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2019, 79, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, C.; Cheng, L.; Ming-Gang, G.A.N. Extension of SGMF using Gaussian sum approximation for nonlinear/non-Gaussian model and its application in multipath estimation. Acta Autom. Sin. 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek, K.; Domański, P.D. Study on outlier robustness of minimum variance control performance assessment. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2021, 35, 2175–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ren, Z.; Lyu, H. Linear and nonlinear regression-based maximum correntropy extended Kalman filtering. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 3093–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y. Maximum correntropy generalized high-degree cubature Kalman filter with application to the attitude determination system of missile. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 95, 105441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Q. Non-Gaussian Pseudolinear Kalman Filtering-Based Target Motion Analysis with State Constraints. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. A novel robust Gaussian–Student’s t mixture distribution based Kalman filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 3606–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Liu, M.; Hang, L. A novel distribution system state estimator based on robust cubature particle filter used for non-gaussian noise and bad data scenarios. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2022, 16, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. Performance enhanced Kalman filter design for non-Gaussian stochastic systems with data-based minimum entropy optimisation. AIMS Electron. Electr. Eng. 2019, 3, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Dang, L.; Gu, Y. Minimum error entropy Kalman filter. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 5819–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, G.; Yu, H. Generalized minimum error entropy Kalman filter for non-Gaussian noise. ISA Trans. 2022, 136, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Wang, G.; Han, J. Interacting multiple model based on maximum correntropy Kalman filter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 3017–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lyu, D.; He, Z. Cauchy kernel-based maximum correntropy Kalman filter. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2020, 51, 3523–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, G.; Guan, X. Robust M-estimation-based maximum correntropy Kalman filter. ISA Trans. 2022, 136, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, J.; Bhaumik, S. Robust Maximum Correntropy Kalman Filter. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.02694. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H. Maximum correntropy Kalman filter. Automatica 2017, 76, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izanloo, R.; Fakoorian, S.A.; Yazdi, H.S. Kalman filtering based on the maximum correntropy criterion in the presence of non-Gaussian noise. In Proceedings of the 2016 Annual Conference on Information Science and Systems (CISS), Princeton, NJ, USA, 16–18 March 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 500–505. [Google Scholar]
- Mohiuddin, S.M.; Qi, J. Maximum correntropy extended Kalman filtering for power system dynamic state estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Atlanta, GA, USA, 4–9 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X. An ultrasonic positioning algorithm based on maximum correntropy criterion extended Kalman filter weighted centroid. Signal Image Video Process 2018, 12, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Iterated maximum correntropy unscented Kalman filters for non-Gaussian systems. Signal Process 2019, 163, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasaratnam, I. Cubature Kalman Filtering Theory & Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Jian, J.; Dong, K. Volume filtering algorithm based on maximum correlation entropy criterion under noise non-Gaussian conditions. J. Ordnance Equip. Eng. 2021, 42, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Xu, B.; Wang, L. Improved maximum correntropy cubature Kalman filter for cooperative localization. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 13585–13595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Liu, Q.; Lu, D. Friction Prediction and Application to Lateral or Longitudinal Slip Force Prediction. Machines 2022, 10, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, X.; Shi, L. Learning with the maximum correntropy criterion induced losses for regression. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2015, 16, 993–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, B.; He, Z.; Li, D.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J. Maximum Correntropy Unscented Kalman Filter for Ballistic Missile Navigation System based on SINS/CNS Deeply Integrated Mode. Sensors 2018, 18, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Hao, Y.; Wu, X. Complexity analysis of three deterministic sampling nonlinear filtering algorithms. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2013, 45, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
| Equation | Addition/Subtraction, Multiplication, Matrix Inversion, Cholesky Decomposition, and QR Decomposition | Equation | Addition/Subtraction, Multiplication, Matrix Inversion, Cholesky Decomposition, and QR Decomposition |
|---|---|---|---|
| (23) | (32) | ||
| (24) | (33) | ||
| (25) | (34) | ||
| (26) | (36) | ||
| (27) | (37) | ||
| (28) | (38) | ||
| (29) | (45) | ||
| (30) | (54) | ||
| (31) |
| Vehicle Parameter Name | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Vehicle mass | 1418 kg | |
| Distance between the front axle and the mass center | 1.016 m | |
| Distance between the rear axle and the mass center | 1.896 m | |
| Wheelbase of front wheels | 1.675 m | |
| Wheelbase of rear wheels | 1.675 m | |
| Yaw moment of inertia | 1536 kg·m2 | |
| Wheel rolling radius | 0.325 m | |
| Centroid height | 0.54 m | |
| Maximum motor power | 68 kw | |
| Maximum motor torque | 140 N·m |
| Index | Parameters | CKF | SCKF | MCSCKF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 0.2911 | 0.2128 | 0.1247 | |
| 0.0396 | 0.0327 | 0.0262 | ||
| 0.0075 | 0.0063 | 0.0041 | ||
| RMSE | 0.3371 | 0.2375 | 0.1407 | |
| 0.0572 | 0.0486 | 0.0388 | ||
| 0.0113 | 0.0094 | 0.0062 |
| Index | Parameters | CKF | SCKF | MCSCKF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 1.2343 | 2.4148 | 0.0605 | |
| 1.0560 | 2.0644 | 0.4690 | ||
| 0.0689 | 0.1121 | 0.0129 | ||
| RMSE | 1.7582 | 3.3601 | 0.0740 | |
| 1.4914 | 3.3601 | 0.5911 | ||
| 0.1114 | 0.1524 | 0.0209 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, T.; Guo, L.; Xiang, Q. Maximum Correntropy Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter with State Estimation for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158762
Ge P, Zhang C, Zhang T, Guo L, Xiang Q. Maximum Correntropy Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter with State Estimation for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(15):8762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158762
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Pingshu, Ce Zhang, Tao Zhang, Lie Guo, and Qingyang Xiang. 2023. "Maximum Correntropy Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter with State Estimation for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles" Applied Sciences 13, no. 15: 8762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158762
APA StyleGe, P., Zhang, C., Zhang, T., Guo, L., & Xiang, Q. (2023). Maximum Correntropy Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter with State Estimation for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles. Applied Sciences, 13(15), 8762. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158762






