Fundamental Investigations of the Deformation Behavior of Single-Crystal Ni-Mn-Ga Alloys and Their Polymer Composites via the Introduction of Various Fields
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Ingot Fabrication (Polycrystalline Ni-Mn-Ga Alloys)
2.3. Preparations of the SC Ni-Mn-Ga alloys
2.3.1. SC Ni-Mn-Ga Particles via Mechanical Crushing
2.3.2. SC Ni-Mn-Ga Flakes via Stress-Assisted Thermal Crushing
2.3.3. SC Ni-Mn-Ga Cubes via a Floating Zone Method
2.4. Preparations of the SC Ni-Mn-Ga/Polymer Composites
2.4.1. Epoxy Resin as a Matrix of the Composites
2.4.2. Silicone Rubber as a Matrix of the Composites
2.4.3. Integration of Polymer Matrix and SC Ni-Mn-Ga Particles
SC Ni-Mn-Ga Particles/Epoxy Composites
SC Ni-Mn-Ga Particles/Silicone Composites
2.5. Fundamental Analysis of SC Ni-Mn-Ga Alloys
2.5.1. Thermal Analysis
2.5.2. X-ray Diffraction Measurements
2.5.3. Microstructure Observations
2.5.4. Crystallographic Direction Identification
2.5.5. Mechanical Property Evaluations
2.5.6. Magnetic Property Evaluations
2.6. Fundamental Analysis of the SC Ni-Mn-Ga Alloys/Polymer Composites
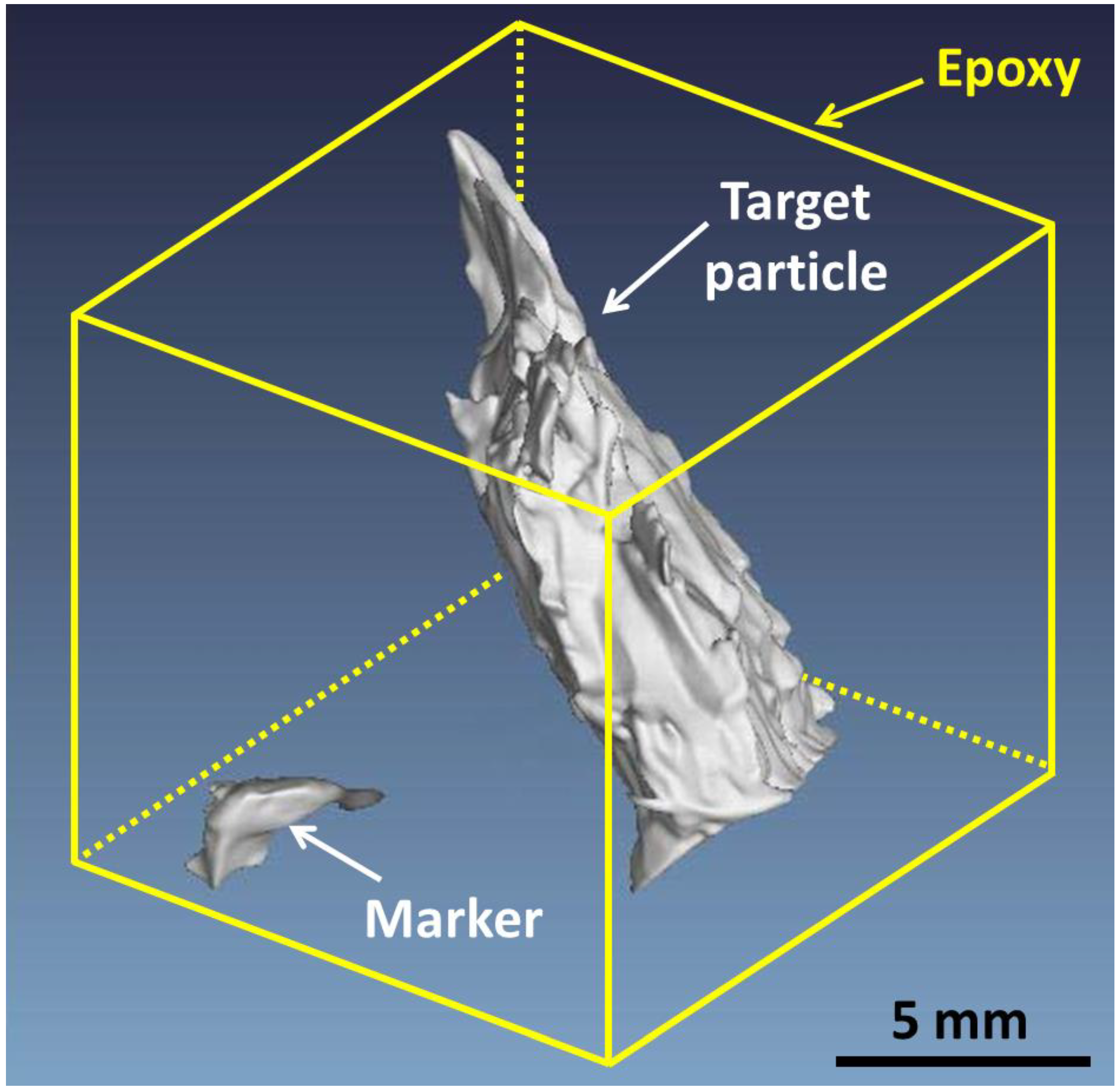
2.6.1. 3D μCT Images
2.6.2. In Situ Deformation Behavior Observations of the Composites
In Situ Compressive Field-Applied Examinations of the Composites
In Situ Magnetic Field-Applied Examinations of the Composites
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fundamental Analysis of the SC Ni-Mn-Ga Alloys
3.1.1. Thermal Analysis
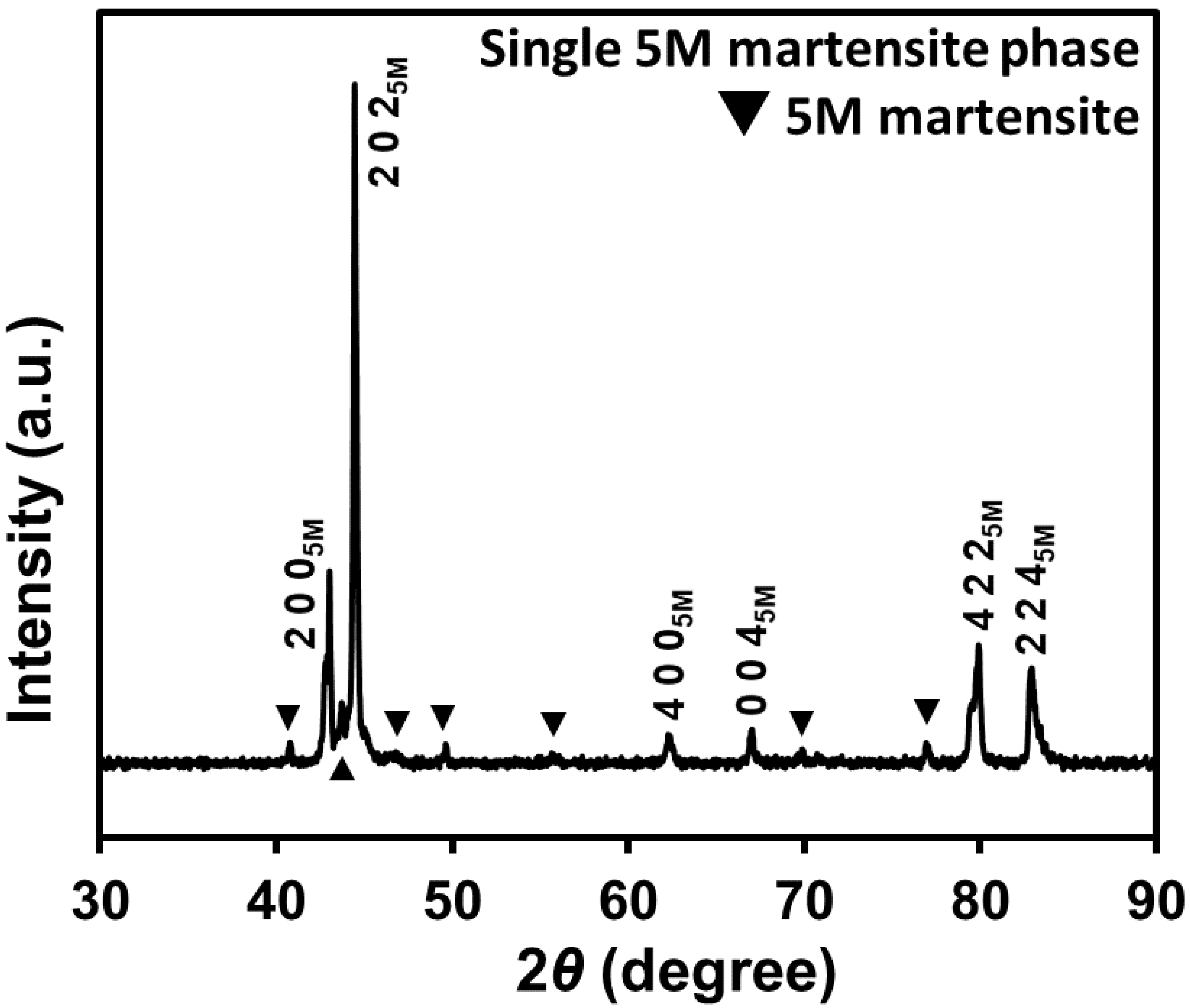
3.1.2. θ-2θ X-ray Diffraction Measurements
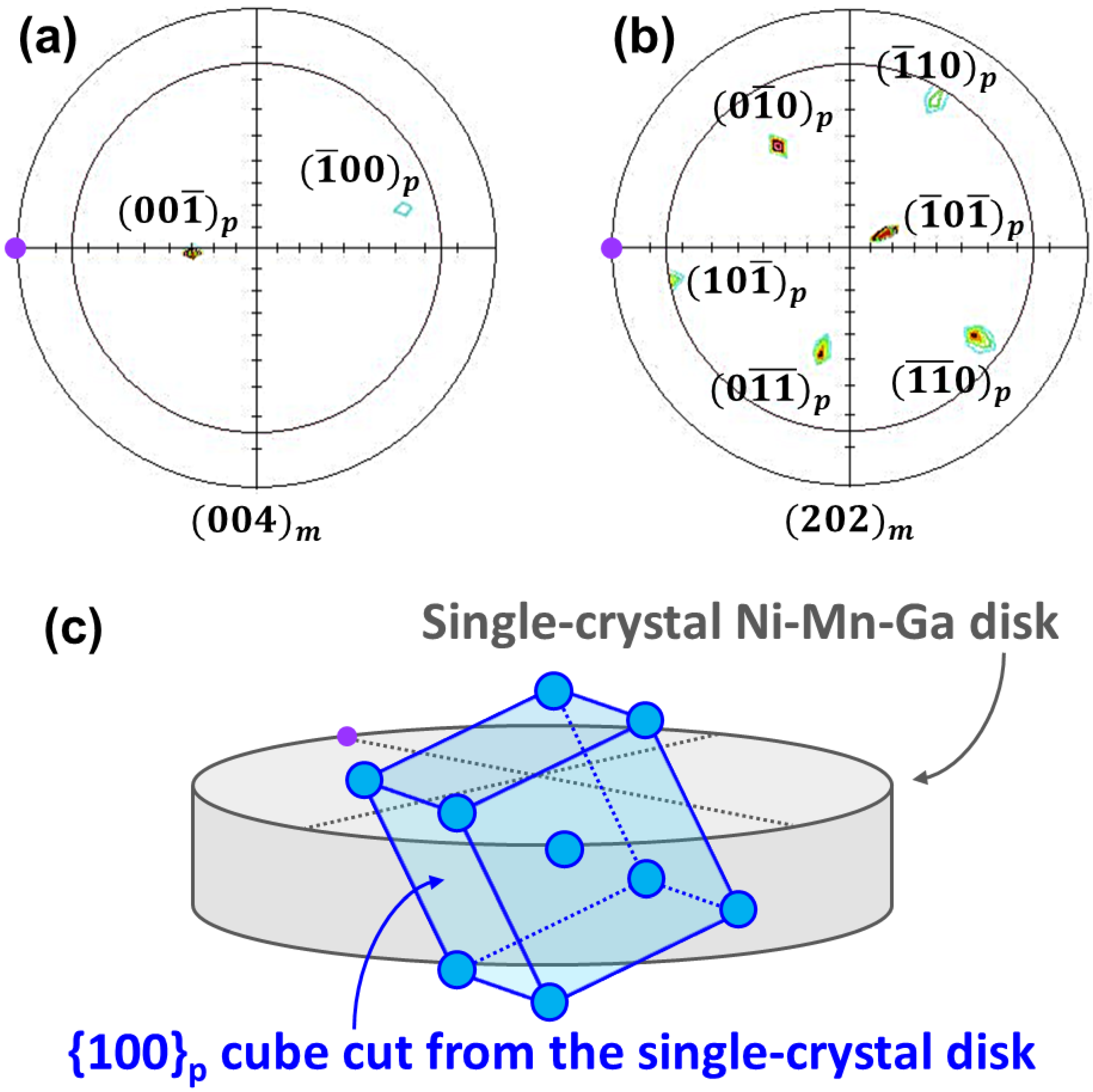
3.1.3. Crystal Direction Identification
3.2. Mechanical and Magnetic Properties of SC Ni-Mn-Ga Cube
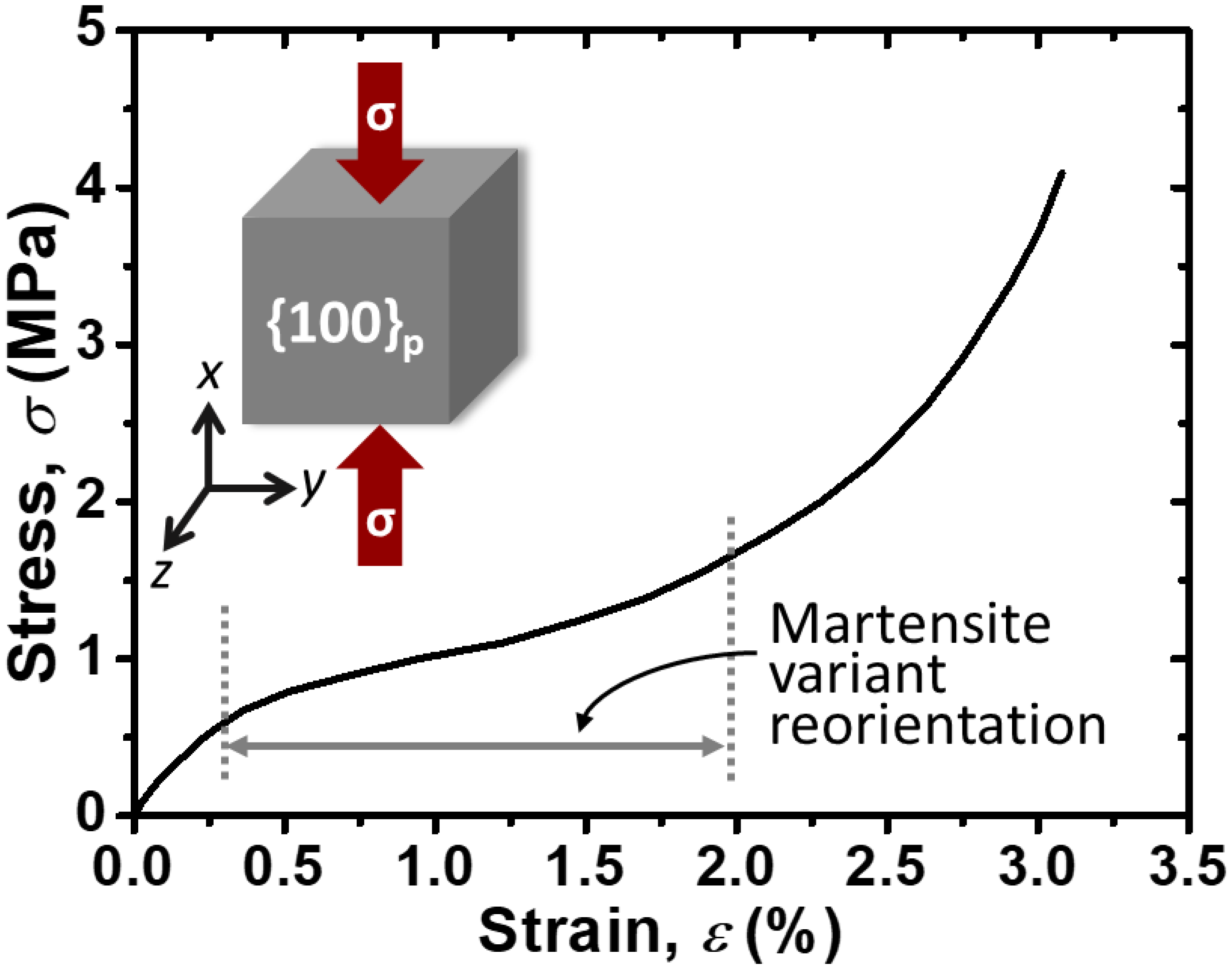
3.2.1. Mechanical Properties
3.2.2. Magnetic Properties
3.3. Fundamental Analysis of the SC Ni-Mn-Ga Alloy/Silicone Rubber Composite
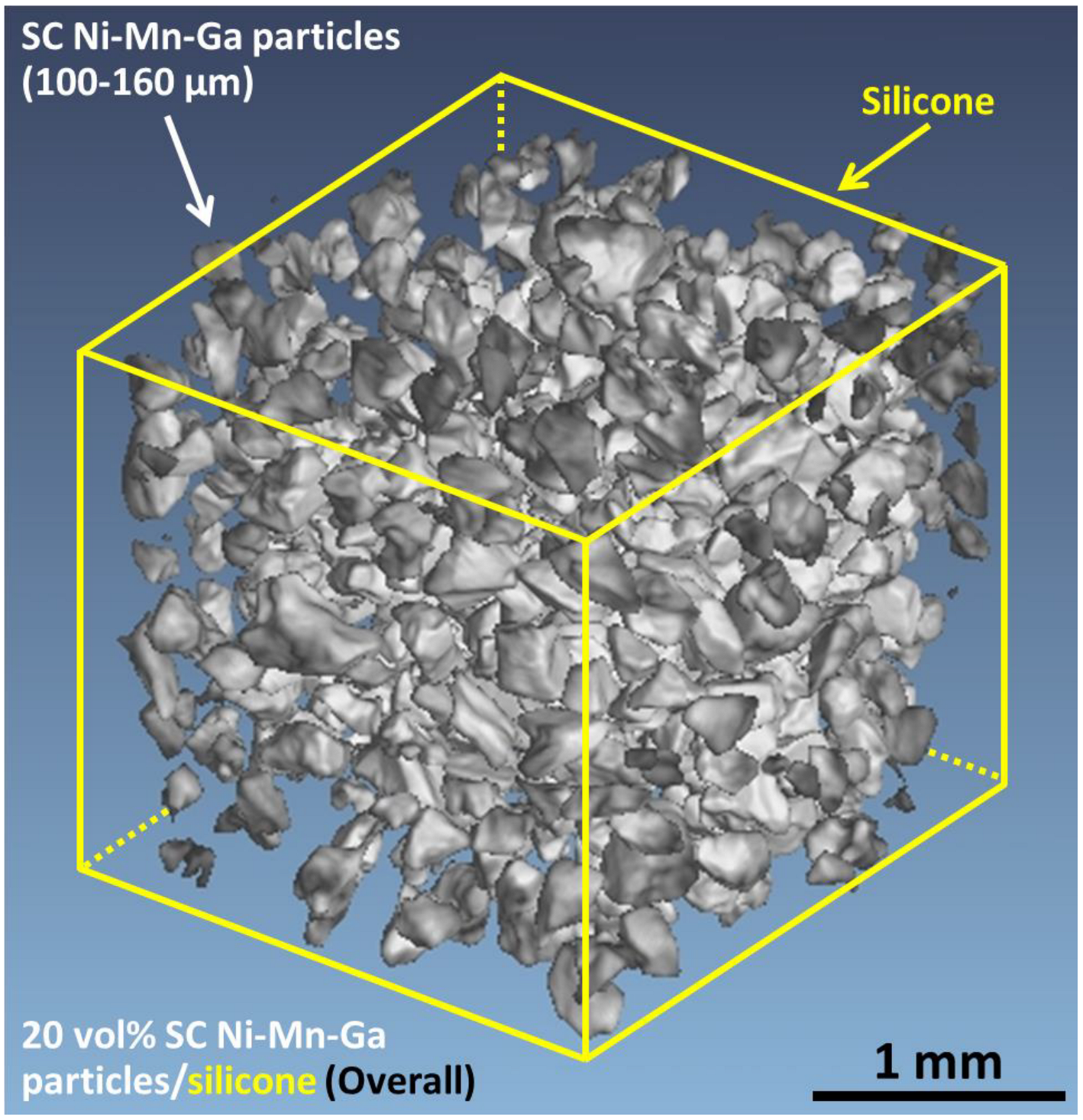
3.3.1. μCT Detection for Microstructure Observations
One SC Ni-Mn-Ga Particle/Epoxy Composite
20 vol.% SC Ni-Mn-Ga Particles/Silicone Composite
3.4. Deformation Behavior of the Composites via a Compressive Force
3.4.1. Compression of One-Particle/Epoxy Composite
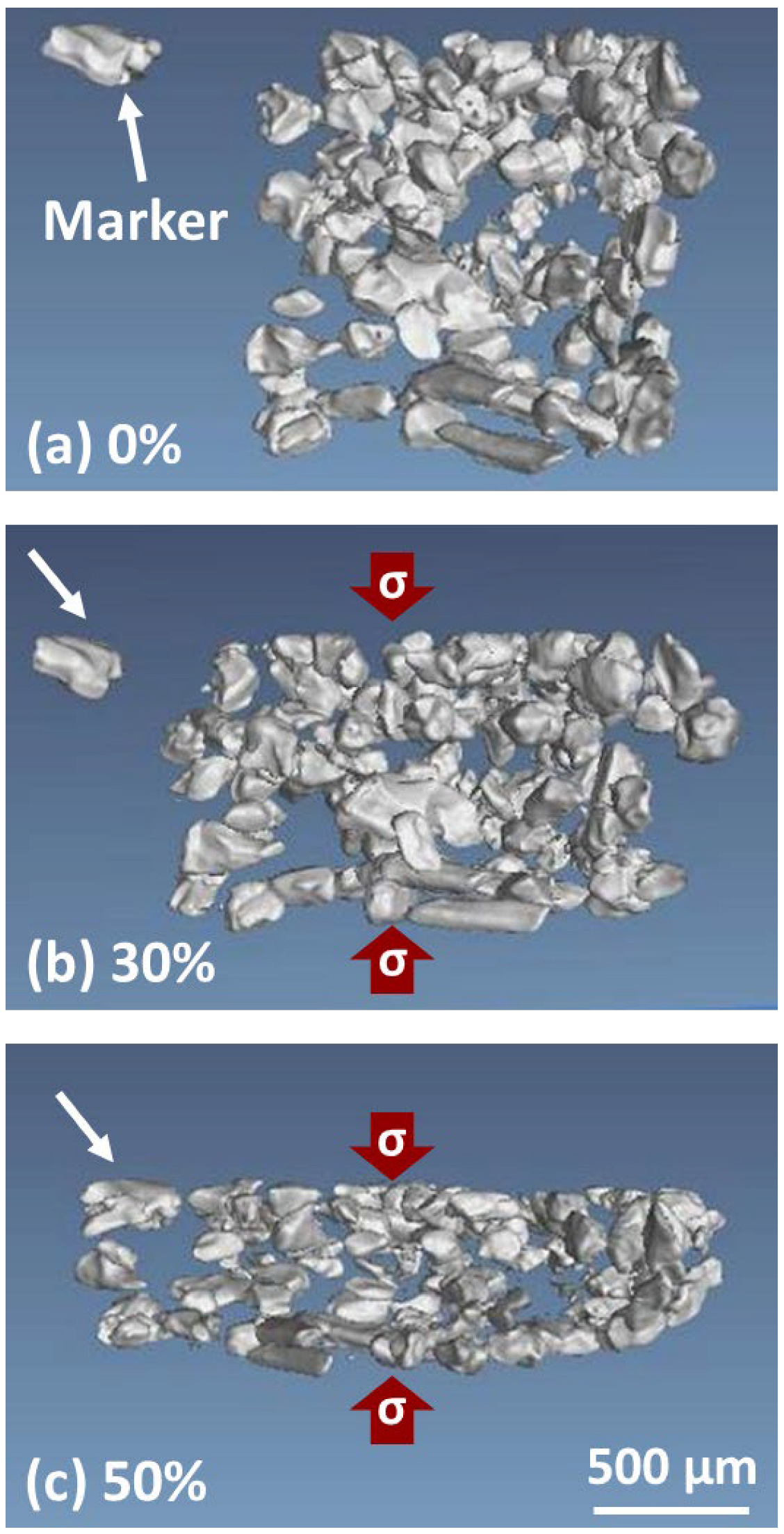
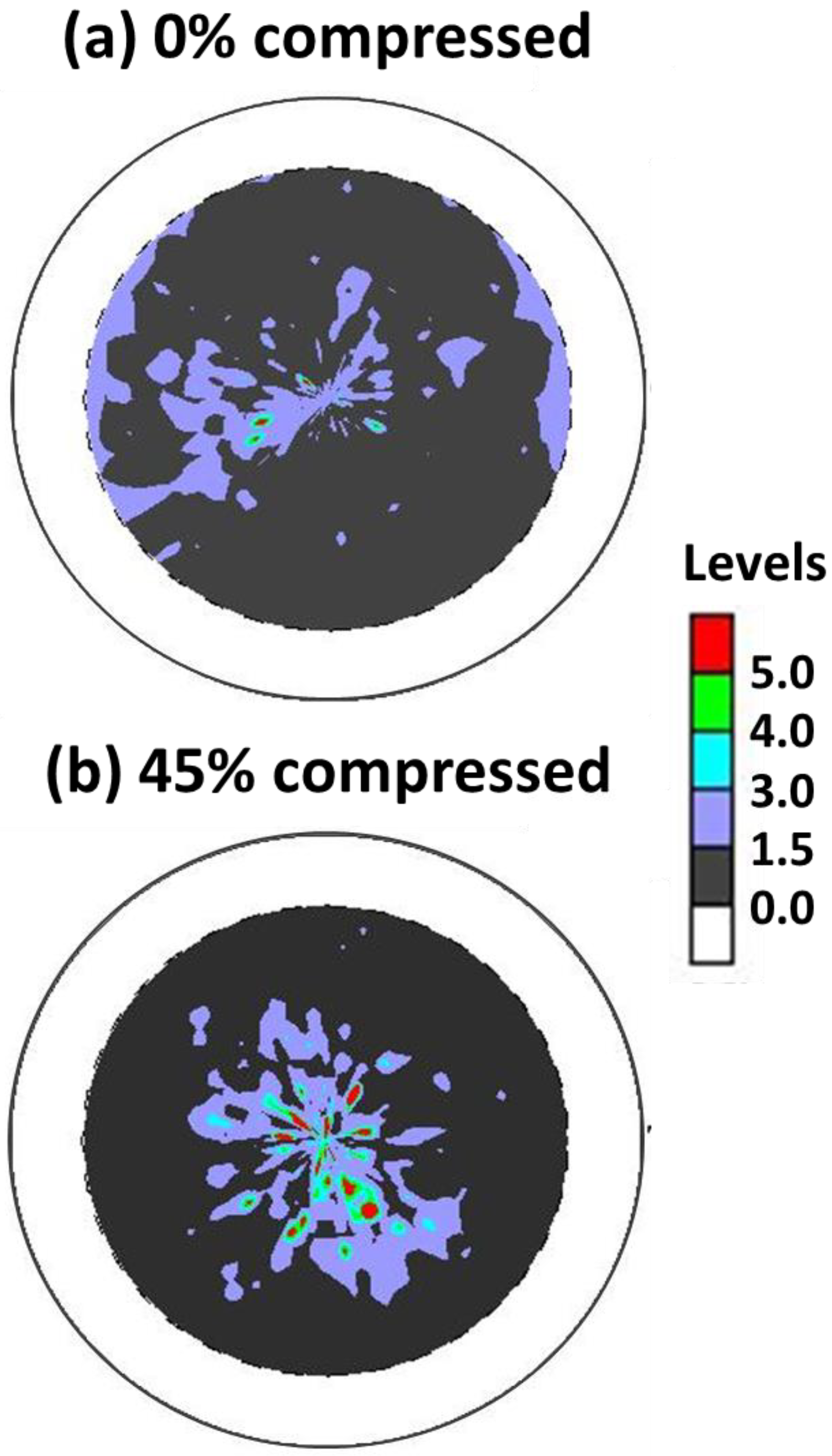
3.4.2. Compression of 10 vol.% SC Ni-Mn-Ga Particles/Epoxy
3.4.3. Compression of 40 vol.% SC Ni-Mn-Ga Particles/Epoxy
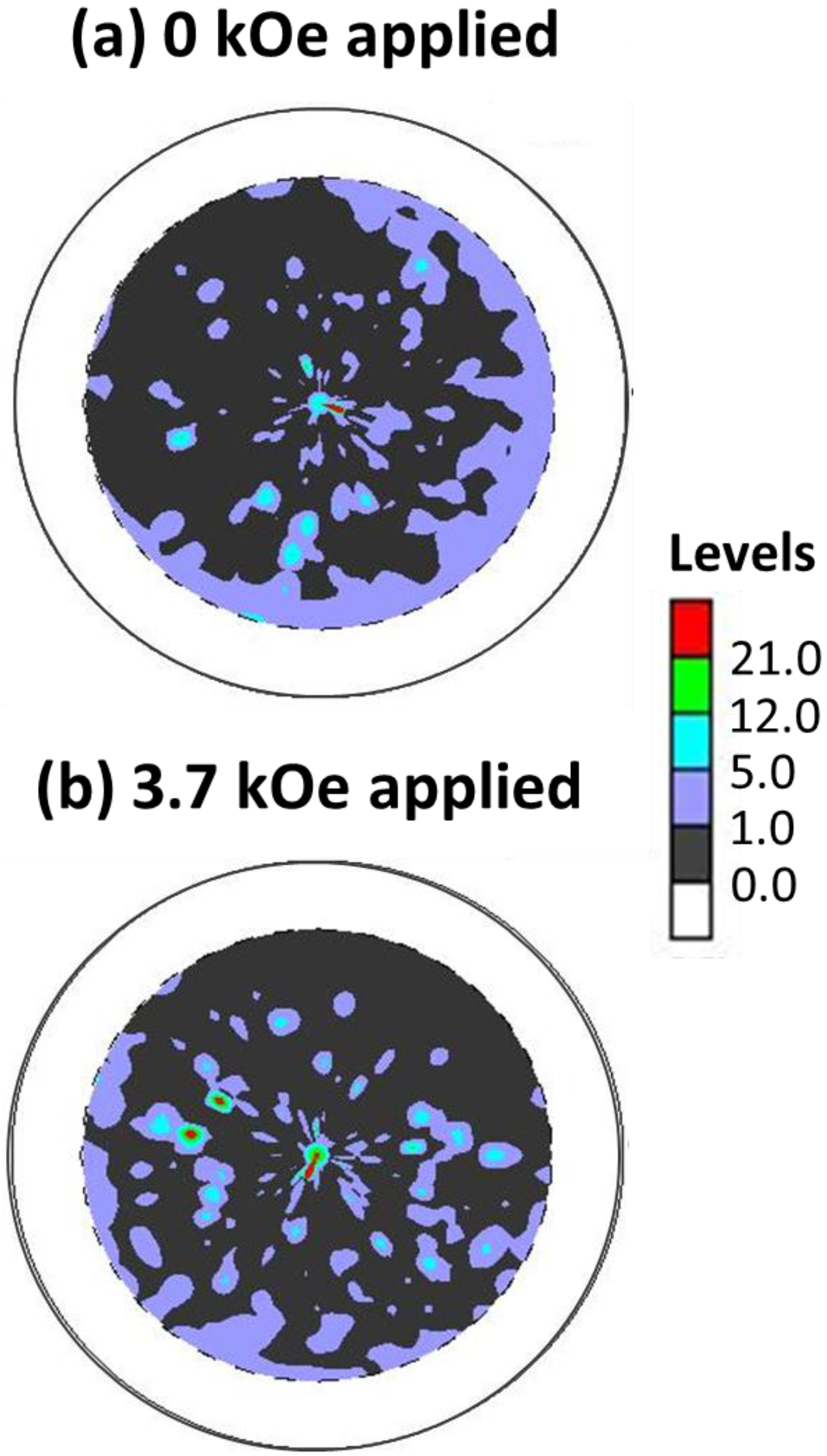
3.5. Deformation Behavior of the Composites via a Magnetic Field
4. Conclusions
- In the thermal analysis of the SC Ni-Mn-Ga particles, the Mf, Ms, As, and Af were determined to be 19 °C, 37 °C, 34 °C, and 53 °C, respectively, which are in good agreement with those found in the literature. A martensite phase at RT was therefore confirmed.
- For the phase identification, it was found that the SC Ni-Mn-Ga particles were composed of the single 5M martensite phase at room temperature.
- The SC Ni-Mn-Ga ingots were successfully fabricated via the floating zone method. These {100}p SC Ni-Mn-Ga cubes with various dimensions were prepared based on the crystallographic identification.
- In the compression test of the {100}p SC Ni-Mn-Ga cubes, it was found that the martensite variant reorientation (MVR) took place from around 0.5 MPa and proceeded until approximately 1.5 MPa. A clear stress plateau, which was discerned in the stress–strain curve, indicates the commencement and proceeding of the MVR. Stress for the MVR is also in good agreement with that found in the literature.
- In the magnetization–magnetic field (M–H) curve, it was observed that a sudden “jump” of the magnetization of the {100}p SC Ni-Mn-Ga cube took place as the magnetic field was increase to around 2.5 kOe. This indicates the MVR was initiated by the introduction of a magnetic field at this specific magnetic field value.
- A relatively large SC Ni-Mn-Ga particle (one-particle/epoxy composite) was integrated with epoxy and served as a preliminary trial for the series of composites. An obvious rotation and a shape deformation were found in this relatively large SC Ni-Mn-Ga particle. The shape deformation through the analysis of the ratios of hx/wx (where x = 0 and 1) can be evidence of the MVR under a compressive field. Following this, the relatively small SC particles composite also confirmed a clear observation by using μCT.
- Following the synthesis and analysis of the one-particle/epoxy composite, the SC Ni-Mn-Ga particles with the dimensions of 100–160 μm were integrated with two different polymers, respectively, in various volume percentages (i.e., 10, 20, and 40 vol.%).
- For the SC Ni-Mn-Ga particles/epoxy composites, it was found that an obvious shape deformation (e.g., triggered by stress-induced MVR) can be found by observing the pole figures as compressive field was applied, while no apparent shape deformation was discerned as the magnetic field was imposed.
- In this study, it can be concluded that the curing process for the alignment of the SC Ni-Mn-Ga particles to render the particle chains in the polymer matrix is a critical process for shape deformation when an external field is applied.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, J.; Gretzel, U.; Pesonen, J. Marketing Robot Services in Hospitality and Tourism: The Role of Anthropomorphism, Future of Tourism Marketing, 1st ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Veale, A.J.; Xie, S.Q. Towards compliant and wearable robotic orthoses: A review of current and emerging actuator technologies. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Wu, W.; Dong, X.; Sang, L. 4D printing of mechanically robust PLA/TPU/Fe3O4 magneto-responsive shape memory polymers for smart structures. Compos. B Eng. 2023, 248, 110382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelecke, S.; Müller, I. Shape memory alloy actuators in smart structures: Modeling and simulation. ASME Appl. Mech. Rev. 2004, 57, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Rogers, C.A. Design of Shape Memory Alloy Actuators. ASME J. Mech. Des. 1992, 114, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, R.; Tannuri, E.A. Modeling, control and experimental validation of a novel actuator based on shape memory alloys. Mechatronics 2009, 19, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krulevitch, P.; Lee, A.P.; Ramsey, P.B.; Trevino, J.C.; Hamilton, J.; Northrup, M.A. Thin film shape memory alloy microactuators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 1996, 5, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullakko, K. Magnetically controlled shape memory alloys: A new class of actuator materials. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 1996, 5, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, N.; Kaur, D. Shape memory alloy thin films and heterostructures for MEMS applications: A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 242, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttig, M.; Li, J.; Craciunescu, C. A new ferromagnetic shape memory alloy system. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 2393–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Handley, R.C.; Murray, S.J.; Marioni, M.; Nembach, H.; Allen, S.M. Phenomenology of giant magnetic-field-induced strain in ferromagnetic shape-memory materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tickle, R.; James, R.D.; Shield, T.; Wuttig, M.; Kokorin, V.V. Ferromagnetic shape memory in the NiMnGa system. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 4301–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, H.E.; Karaman, I.; Basaran, B.; Ren, Y.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Maier, H.J. Magnetic Field-Induced Phase Transformation in NiMnCoIn Magnetic Shape-Memory Alloys—A New Actuation Mechanism with Large Work Output. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 983–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, H.E.; Karaman, I.; Basaran, B.; Lagoudas, D.C.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Maier, H.J. On the stress-assisted magnetic-field-induced phase transformation in Ni2MnGa ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4253–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, H.E.; Karaman, I.; Basaran, B.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Maier, H.J. Magnetic field and stress induced martensite reorientation in NiMnGa ferromagnetic shape memory alloy single crystals. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Liang, T.; Xu, H. Superhigh strains by variant reorientation in the nonmodulated ferromagnetic NiMnGa alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heczko, O.; Scheerbaum, N.; Gutfleisch, O. Magnetic Shape Memory Phenomena. In Nanoscale Magnetic Materials, and Applications; Liu, J., Fullerton, E., Gutfleisch, O., Sellmyer, D., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Karamana, I.; Basaran, B.; Karaca, H.E. Energy harvesting using martensite variant reorientation mechanism in a NiMnGa magnetic shape memory alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 172505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Yang, B.; Yan, H.; Gan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Unconventional twin deformation of Ni-Mn-Ga 7M martensite under tension mediated by the collective lattice reorientation from a-c twin to b-c twin. Acta Mater. 2022, 227, 117729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, P.; Ma, G.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.; Zhou, T.; Wang, D.; Du, Y. Large reversible magnetic-field-induced strain in a trained Ni49.5Mn28Ga22.5 polycrystalline alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 792, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Chattopadhyay, M.K.; Chouhan, A.; Roy, S.B. Temperature and magnetic field induced strain in Ni50Mn34In16 alloy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 185005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Kang, G.; Rao, W.; Song, D. Modelling the stress-induced multi-step martensite transformation of single crystal NiMnGa ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Mech. Mater. 2019, 134, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, P.; Szczerba, M.J.; Chulist, R.; Bałanda, M.; Przewoźnik, J.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Schell, N.; Kapusta, C.; Maziarz, W. Martensitic transition, structure and magnetic anisotropy of martensite in Ni-Mn-Sn single crystal. Acta Mater. 2016, 118, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.H.; Yu, C.H.; Meng, L.Q.; Chen, J.L.; Yang, F.M.; Qi, S.R.; Zhan, W.S. Giant magnetic-field-induced strains in Heusler alloy NiMnGa with modified composition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 75, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Zhan, X. Enhanced interfacial joining strength of laser wobble joined 6061-T6 Al alloy/CFRTP joint via interfacial bionic textures pre-construction. Compos. B Eng. 2023, 261, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saren, A.; Laitinen, V.; Vinogradova, M.; Ullakko, K. Twin boundary mobility in additive manufactured magnetic shape memory alloy 10M Ni-Mn-Ga. Acta Mater. 2023, 246, 118666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahelin, M.; Aaltio, I.; Heczko, O.; Söderberg, O.; Ge, Y.; Löfgren, B.; Hannula, S.-P.; Seppälä, J. DMA testing of Ni–Mn–Ga/polymer composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafaei, A.; Kimes, K.A.; Stevens, E.L.; Toman, J.; Krimer, Y.L.; Ullakko, K.; Chmielus, M. Microstructural evolution and magnetic properties of binder jet additive manufactured Ni-Mn-Ga magnetic shape memory alloy foam. Acta Mater. 2017, 131, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielus, M.; Zhang, X.X.; Witherspoon, C.; Dunand, D.C.; Müllner, P. Giant magnetic-field-induced strains in polycrystalline Ni–Mn–Ga foams. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.D.; Lin, J.P.; Dahmen, K.A.; Wang, Z.L.; Liaw, P.K. Superelasticity and Serration Behavior in Small-Sized NiMnGa Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2014, 16, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseghini, S.; Villa, E.; Passaretti, F.; Pini, M.; Bonfanti, F. Plastic deformation of NiMnGa polycrystals. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 378, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.-T.; Sratong-on, P.; Tahara, M.; Chernenko, V.; Hosoda, H. Aging behavior of Ni-Mn-Ga/silicone particulate composites exhibiting large recoverable magnetostrain. Scr. Mater. 2023, 227, 115277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Tian, B.; Xu, J.; Tong, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, L. Investigation on porous NiMnGa alloy and its composite with epoxy resin. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 892, 162248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, H.; Lazarczyk, J.; Sratong-on, P.; Tahara, M.; Chernenko, V. Elaboration of magnetostrain-active NiMnGa particles/polymer layered composites. Mater. Lett. 2021, 289, 129427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sratong-on, P.; Chernenko, V.A.; Feuchtwanger, J.; Hosoda, H. Magnetic field-induced rubber-like behavior in Ni-Mn-Ga particles/polymer composite. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheerbaum, N.; Hinz, D.; Gutfleisch, O. Compression-induced texture change in NiMnGa-polymer composites observed by synchrotron radiation. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 09C501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakιr, A.; Righi, L.; Albertini, F.; Acet, M.; Farle, M.; Aktürk, S. Extended investigation of intermartensitic transitions in Ni-Mn-Ga magnetic shape memory alloys: A detailed phase diagram determination. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 183912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.-T.; Sratong-on, P.; Chang, T.-F.M.; Tahara, M.; Sone, M.; Chernenko, V.; Hosoda, H. Bi-doping engineering of Ni-Mn-Ga polycrystals and resulting grain particles for smart Ni-Mn-Ga/polymer composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.-T.; Goto, A.; Tahara, M.; Inamura, T.; Hosoda, H. Effects of volume fraction between single crystal Ni-Mn-Ga ferromagnetic shape memory alloy and silicone rubber on the martensite variant reorientation. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 926, 166862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, M.; Inamura, T.; Kanetaka, H.; Hosoda, H. Compression Behavior and Texture Development of Polymer Matrix Composites Based on NiMnGa Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloy Particles. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 654–656, 2103–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.-T.; Sratong-on, P.; Tahara, M.; Chernenko, V.; Hosoda, H. Large magnetostrains of Ni-Mn-Ga/silicone composite containing system of oriented 5M and 7M martensitic particles. Scr. Mater. 2022, 207, 114265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.-T.; Ishigaki, T.; Nohira, N.; Umise, A.; Tahara, M.; Hosoda, H. Effect of 3D transition metal additions on the phase constituent, mechanical properties, and shape memory effect of near–eutectoid Ti–4Au biomedical alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 857, 157599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.J.; Marioni, M.; Allen, S.M.; O’Handley, R.C. 6% magnetic-field-induced strain by twin-boundary motion in ferromagnetic Ni–Mn–Ga. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heczko, O.; Straka, L. Magnetic properties of stress-induced martensite and martensitic transformation in Ni–Mn–Ga magnetic shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 378, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, P.; Sittner, P.; Novak, V.; Prokleska, J.; Sechovsky, V.; Ouladdiaf, B.; Hanulla, S.P.; Heczko, O. In situ neutron diffraction study of magnetic field induced martensite reorientation in Ni–Mn–Ga under constant stress. J. Condens. Matter Phys. 2008, 20, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.-T.; Goto, A.; Tahara, M.; Inamura, T.; Hosoda, H. Investigation of the martensite variant reorientation of the single crystal Ni–Mn-Ga alloy via training processes and a modification with a silicone rubber. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 297, 127390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.-T.; Okuno, M.; Tahara, M.; Inamura, T.; Hosoda, H. Investigations of the Crystallographic Orientation on the Martensite Variant Reorientation of the Single-Crystal Ni-Mn-Ga Cube and Its Composites for Actuator Applications. Actuators 2023, 12, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Chiu, W.-T.; Tahara, M.; Chernenko, V.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Hosoda, H. Framework of magnetostrain responsive Ni–Mn–Ga microparticles driving magnetic field induced out-of-plane actuation of laminate composite. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| (a) Composites Prepared in This Study | Epoxy | Silicone |
| Volume percentages of Ni-Mn-Ga particles (vol.%) | One particle | 10 |
| 10 | 20 | |
| 40 | 40 | |
| (b) Physical Properties of Two Polymers | Epoxy | Silicone |
| Density, ρ (g cm−3) | 1.10 | 1.27 |
| Young’s modulus, E (MPa) | 200~800 | 2~4 |
| Flow stress, σ (MPa) | 15~40 | <3 MPa |
| Applied Fields | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Field | Magnetic Field | |
| Quantity | 0~50% | 0 and 3.7 kOe |
| Methodology | In-house compression cell | Magnet |
| Externally Applied Field | Corresponding Figure | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Compressive | Magnetic | |
| SC Ni-Mn-Ga cube | σMVR = ~0.5 MPa | HMVR = ~2.5 kOe | Figure 5 and Figure 6 |
| One-particle composite | Rotation and MVR Free: h0/w0 = 1.34 Pressed: h1/w1 = 1.31 | -- | Figure 9 and Figure 10 |
| SC Ni-Mn-Ga particles/polymer composite | Obvious MVR | No clear MVR | Figure 12 and Figure 13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, W.-T.; Okuno, M.; Tahara, M.; Inamura, T.; Hosoda, H. Fundamental Investigations of the Deformation Behavior of Single-Crystal Ni-Mn-Ga Alloys and Their Polymer Composites via the Introduction of Various Fields. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8475. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148475
Chiu W-T, Okuno M, Tahara M, Inamura T, Hosoda H. Fundamental Investigations of the Deformation Behavior of Single-Crystal Ni-Mn-Ga Alloys and Their Polymer Composites via the Introduction of Various Fields. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(14):8475. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148475
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Wan-Ting, Motoki Okuno, Masaki Tahara, Tomonari Inamura, and Hideki Hosoda. 2023. "Fundamental Investigations of the Deformation Behavior of Single-Crystal Ni-Mn-Ga Alloys and Their Polymer Composites via the Introduction of Various Fields" Applied Sciences 13, no. 14: 8475. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148475
APA StyleChiu, W.-T., Okuno, M., Tahara, M., Inamura, T., & Hosoda, H. (2023). Fundamental Investigations of the Deformation Behavior of Single-Crystal Ni-Mn-Ga Alloys and Their Polymer Composites via the Introduction of Various Fields. Applied Sciences, 13(14), 8475. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148475







