The Effect of Non-Newtonian Fluid Midsole Footwear on Lower Limb Biomechanics after 5 km of Running in High Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
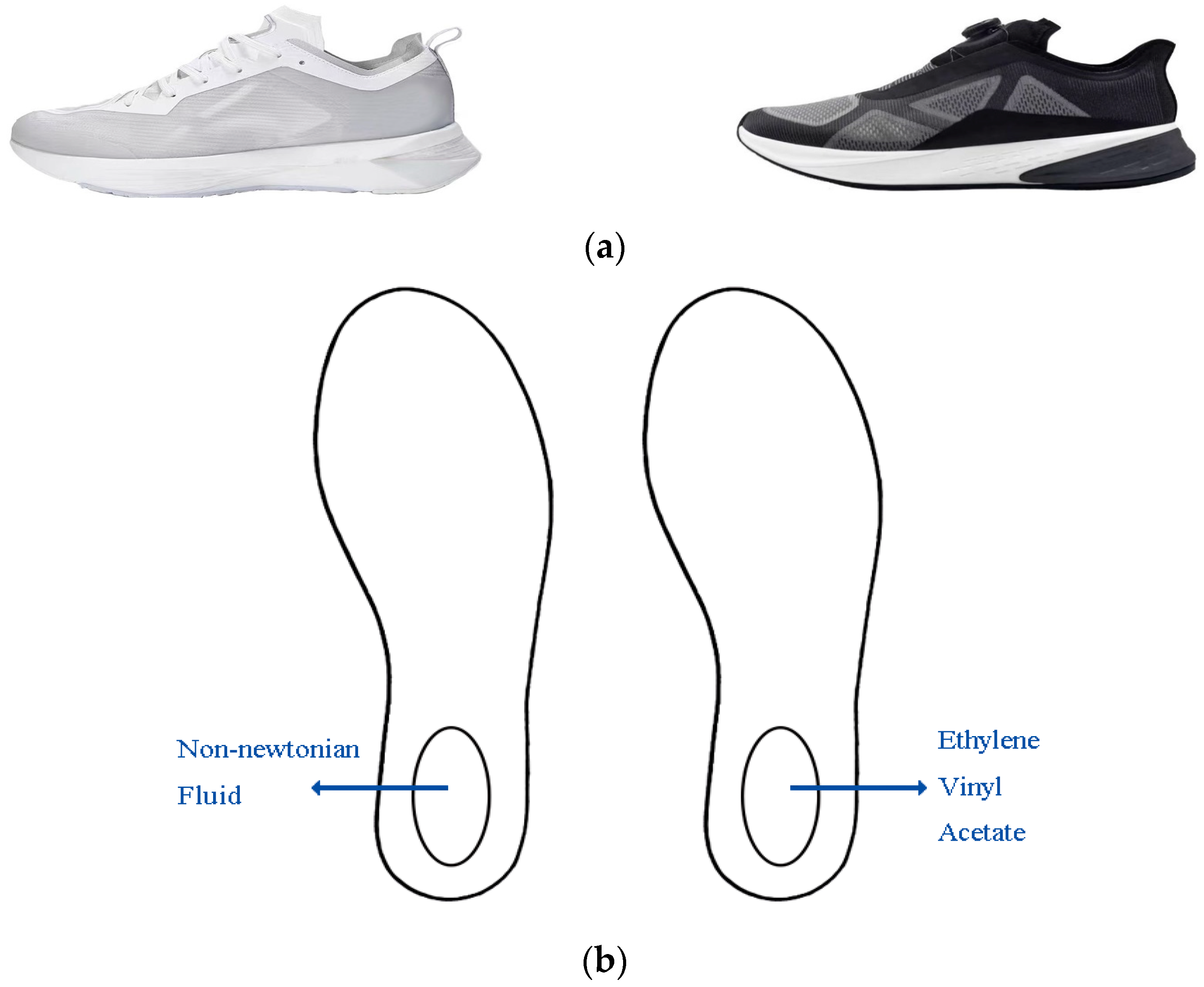
2.2. Experimental Shoes
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
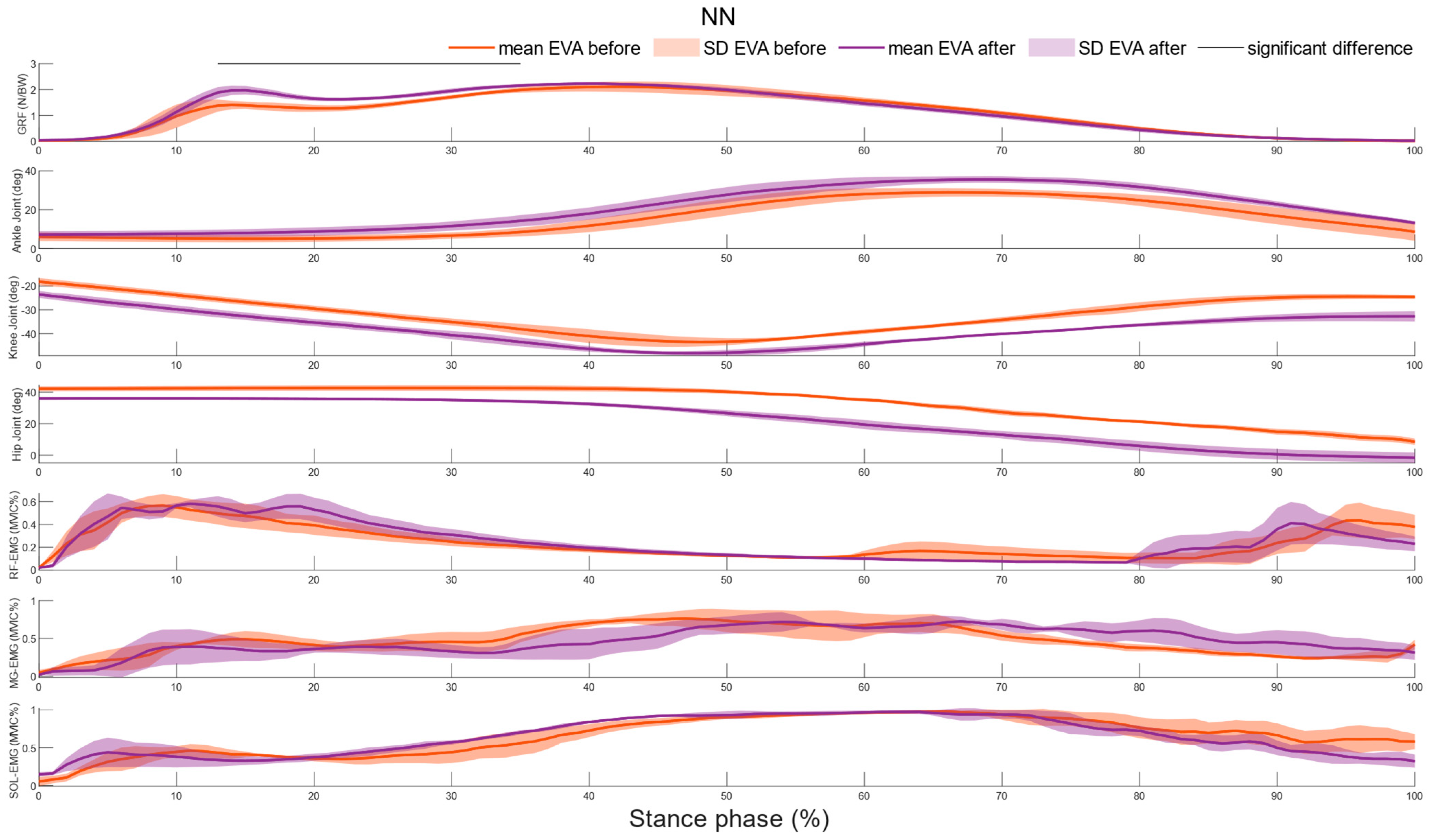
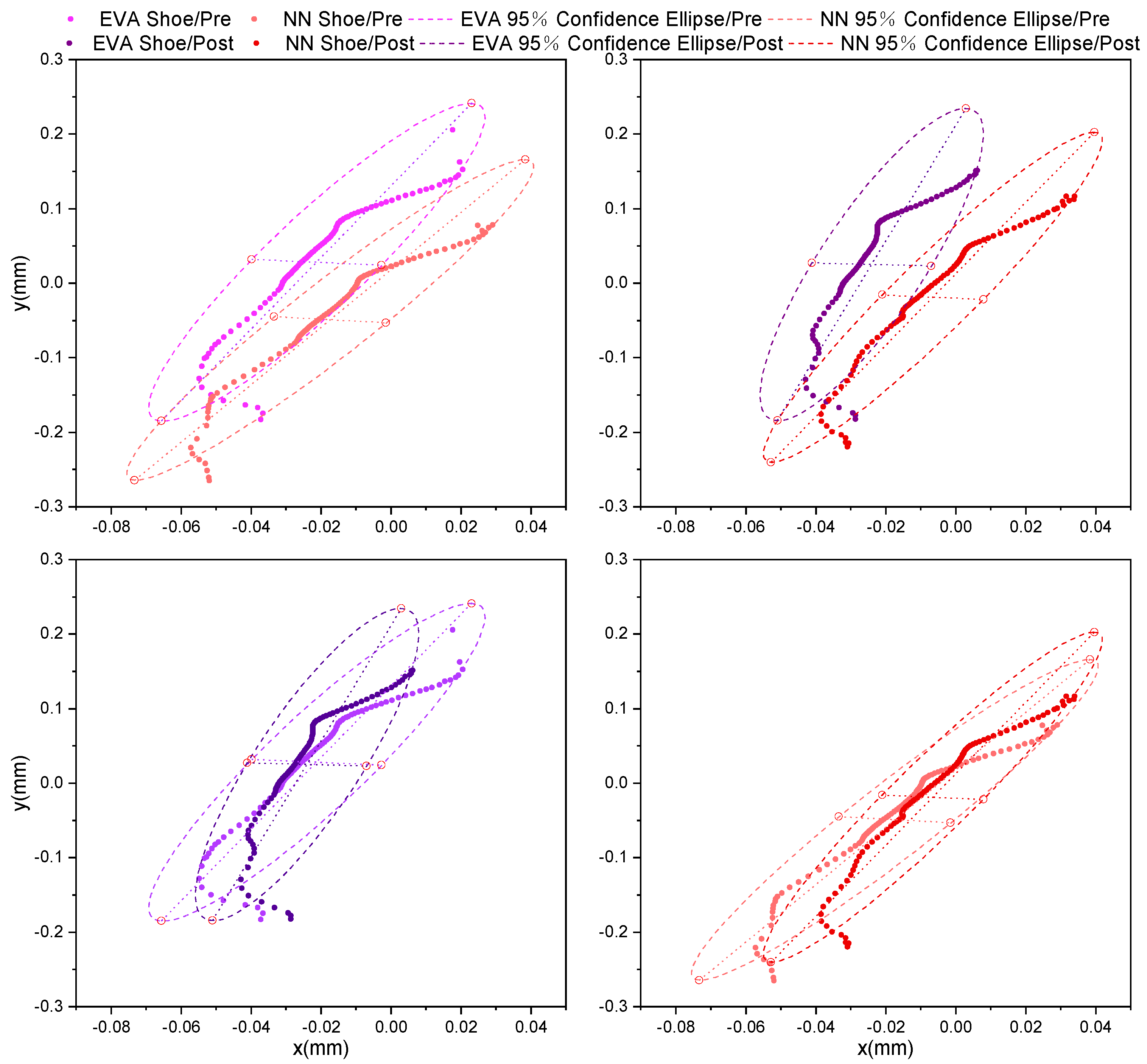
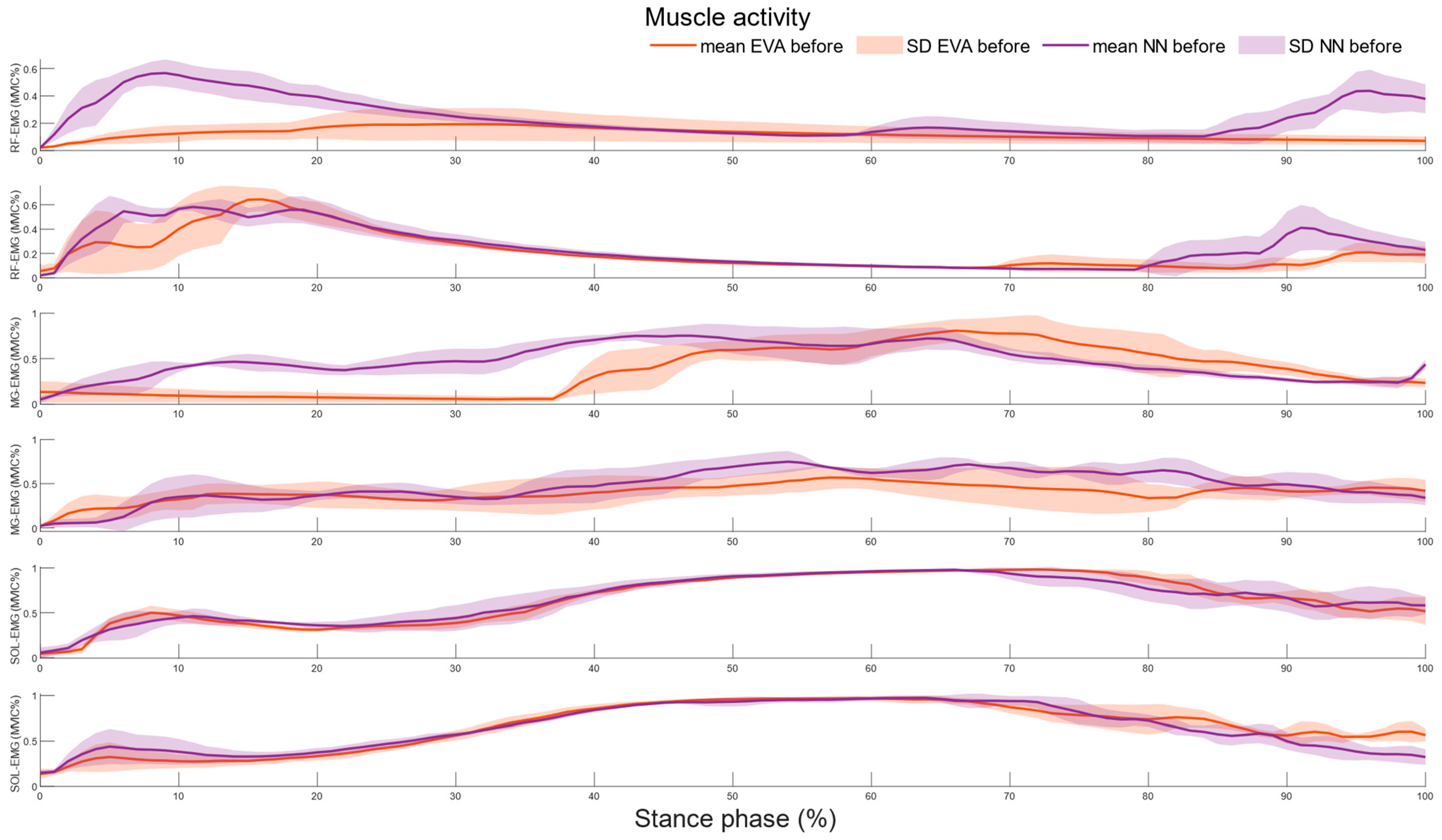
3.1. Effects of the Shoe Conditions
3.2. Effects of the Temperature
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dib, M.Y.; Smith, J.; Bernhardt, K.A.; Kaufman, K.R.; Miles, K.A. Effect of environmental temperature on shock absorption properties of running shoes. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2005, 15, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Mohamad, N.I. Development of Badminton-specific Footwork Training from Traditional Physical Exercise to Novel Intervention Approaches. Phys. Act. Health 2022, 6, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, B. Lower limb biomechanics related to running injuries. Physiotherapy 1992, 78, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, I.; Pradhan, D.; Ghosh, S.; Kar, S.K.; Dhara, P. A comparative study of foot dimension between adult male and female and evaluation of foot hazards due to using of footwear. J. Physiol. Anthropol. Appl. Hum. Sci. 2001, 20, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Song, Y.; Cen, X.; Bálint, K.; Fekete, G.; Sun, D. The Implications of Sports Biomechanics Studies on the Research and Development of Running Shoes: A Systematic Review. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoitz, F.; Mohr, M.; Asmussen, M.; Lam, W.-K.; Nigg, S.; Nigg, B. The effects of systematically altered footwear features on biomechanics, injury, performance, and preference in runners of different skill level: A systematic review. Footwear Sci. 2020, 12, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, G.K.; Hunt, M.A.; Reid, A.L.; Esculier, J.-F. What are the perceptions of runners and healthcare professionals on footwear and running injury risk? BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2020, 6, e000767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, I.; McLeod, A.; Valentine, D.; Low, T.; Ward, J.; Hager, R. Running economy, mechanics, and marathon racing shoes. J. Sport. Sci. 2019, 37, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isherwood, J.; Rimmer, E.; Fu, F.; Xie, Z.; Sterzing, T. Biomechanical and perceptual cushioning sensitivity based on mechanical running shoe properties. Footwear Sci. 2021, 13, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S. Use of pressure insoles to compare in-shoe loading for modern running shoes. Ergonomics 2008, 51, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.W.; Candelaria, N.G.; Smith, D.R. Running in new and worn shoes: A comparison of three types of cushioning footwear. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2009, 43, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatmadari, M.; English, R.; Rothwell, G. Effects of Temperature on the Performance of Footwear Foams: Review of Developments. In Proceedings of the 26th Southern Biomedical Engineering Conference SBEC 2010, College Park, MD, USA, 30 April–2 May 2010; pp. 409–413. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, S.D.; Kester, M.A.; Brunet, M.E. Shock absorption characteristics of running shoes. Am. J. Sport. Med. 1985, 13, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamill, J.; Bates, B. A kinetic evaluation of the effects of in vivo loading on running shoes. J. Orthop. Sport. Phys. Ther. 1988, 10, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hong, Y.; Li, J.X. Durability of running shoes with ethylene vinyl acetate or polyurethane midsoles. J. Sport. Sci. 2012, 30, 1787–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Quan, W.; Zhou, H.; Sun, D.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Explaining the differences of gait patterns between high and low-mileage runners with machine learning. Sci Rep. 2022, 12, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, C.-M.; Birs, I.R.; Copot, D.; Muresan, C.; Caponetto, R. Mathematical modelling with experimental validation of viscoelastic properties in non-Newtonian fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2020, 378, 20190284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjat, M.; Etemad, S.G.; Bagheri, R.; Thibault, J. Rheological characteristics of non-Newtonian nanofluids: Experimental investigation. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.R.; Toghraie, D.; Abdulkareem, L.A.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Barnoon, P.; Afrand, M. The rheological behavior of MWCNTs–ZnO/Water–Ethylene glycol hybrid non-Newtonian nanofluid by using of an experimental investigation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 8401–8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Trenberth, K.E. Modern global climate change. Science 2003, 302, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H.; Bates, B.T. The effect of environmental temperature on the properties of running shoes. J. Appl. Biomech. 1996, 12, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, J.; Dutheil, F.; Ugbolue, U.C. The Prevalence of Lower Extremity Injuries in Running and Associated Risk Factors: A Systematic Review. Phys. Act. Health 2021, 5, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnoon, P.; Toghraie, D.; Dehkordi, R.B.; Afrand, M. Two phase natural convection and thermal radiation of Non-Newtonian nanofluid in a porous cavity considering inclined cavity and size of inside cylinders. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 108, 104285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, N. Polymer Foams Handbook: Engineering and Biomechanics Applications and Design Guide; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.; Rodrigues, J.; Pinto, V.; Ferreira, M.; Russo, R.; Pereira, C. Evaluation of shock absorption properties of rubber materials regarding footwear applications. Polym. Test. 2009, 28, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbiss, C.R.; Burnett, A.; Nosaka, K.; Green, J.P.; Foster, J.K.; Laursen, P.B. Effect of hot versus cold climates on power output, muscle activation, and perceived fatigue during a dynamic 100-km cycling trial. J. Sport. Sci. 2010, 28, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menant, J.C.; Perry, S.D.; Steele, J.R.; Menz, H.B.; Munro, B.J.; Lord, S.R. Effects of shoe characteristics on dynamic stability when walking on even and uneven surfaces in young and older people. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, J.; Pollard, C.D. Differences in running biomechanics between a maximal, traditional, and minimal running shoe. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2020, 23, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, H.; Quan, W.; Hu, Q.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Ground reaction force differences between bionic shoes and neutral running shoes in recreational male runners before and after a 5 km run. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Song, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ren, F.; Bíró, I.; Gu, Y. Gender Effects on Lower Limb Biomechanics of Novice Runners before and after a 5 km Run. J. Men’s Health 2022, 18, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, A.; Dekerle, J. Reciprocal versus nonreciprocal assessment of knee flexors and extensors in concentric actions using the CON-TREX multijoint isokinetic dynamometer: A reliability study. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2019, 23, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, W.; Wang, M.; Liu, G.; Fekete, G.; Baker, J.S.; Ren, F.; Gu, Y. Comparative Analysis of Lower Limb Kinematics between the Initial and Terminal Phase of 5km Treadmill Running. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 161, e61192. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Lu, Z.; Liang, M.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Influence of Different Load Conditions on Lower Extremity Biomechanics during the Lunge Squat in Novice Men. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, X.; Xuan, R.; Song, Y.; Bíró, I.; Liang, M.; Gu, Y. Effect of Heel Lift Insoles on Lower Extremity Muscle Activation and Joint Work during Barbell Squats. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, B.; Kóbor, I.; Sebestyén, Ö.; Tihanyi, J. Longer Achilles tendon moment arm results in better running economy. Physiol. Int. 2021, 107, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creps, J.M. An Investigation of Simulated Core Muscle Activation during Running and Its Effect on Knee Loading and Lower Extremity Muscle Activation Using Opensim. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, R.P. Wavelet transform theory and its application in EMG signal processing. In Proceedings of the 2010 Seventh International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Yantai, China, 10–12 August 2010; pp. 2234–2238. [Google Scholar]
- Friston, K.J.; Holmes, A.P.; Worsley, K.J.; Poline, J.P.; Frith, C.D.; Frackowiak, R.S. Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: A general linear approach. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1994, 2, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.J.; Taylor, J.E. Random Fields and Geometry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 80. [Google Scholar]
- Wearing, S.; Hooper, S.; Dubois, P.; Smeathers, J.; Dietze, A. Force-deformation properties of the human heel pad during barefoot walking. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2014, 46, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdejo, R. Gas Loss and Durability of EVA Foams Used in Running Shoes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Malisoux, L.; Gette, P.; Urhausen, A.; Bomfim, J.; Theisen, D. Influence of sports flooring and shoes on impact forces and performance during jump tasks. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, Z.; Woo, J.; Liebenberg, J.; Park, S.-K.; Ryu, J.; Lam, W.-K. Kinetics and perception of basketball landing in various heights and footwear cushioning. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinyoka, T. Comparative response of Newtonian and Non-Newtonian fluids subjected to exothermic reactions in shear flow. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 2021, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-A.; Liao, W.-H.; Wu, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-L.; Tung, Y.-C. Electrofluidic circuit-based microfluidic viscometer for analysis of Newtonian and non-Newtonian liquids under different temperatures. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2317–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, E.; Bertrand, F.; Chaouki, J. Development of a granular normal contact force model based on a non-Newtonian liquid filled dashpot. Powder Technol. 2013, 237, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cen, X.; Chen, H.; Sun, D.; Munivrana, G.; Bálint, K.; Bíró, I.; Gu, Y. The influence of running shoe with different carbon-fiber plate designs on internal foot mechanics: A pilot computational analysis. J. Biomech. 2023, 153, 111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.E. Biomechanical measurement of running shoe cushioning properties. Biomech. Asp. Sport Shoes Play. Surf. 1983, 25, 126–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kovács, B.; Csala, D.; Sebestyén, Ö.; Matlák, J.; Groszmann, Á.; Tihanyi, J.; Petridis, L. Arm Swing during Vertical Jumps does not Increase EMG Activity of the Lower Limb Muscles. Phys. Act. Health 2023, 7, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, D.E.; Warrener, A.G.; Wang, J.; Castillo, E.R. Effects of stride frequency and foot position at landing on braking force, hip torque, impact peak force and the metabolic cost of running in humans. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 3406–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Vieira, T.M.; Gallina, A.; Kouzaki, M.; Moritani, T. Novel insights into biarticular muscle actions gained from high-density electromyogram. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2021, 49, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, D.C.; Franz, J.R.; Keenan, G.S.; Dicharry, J.; Della Croce, U.; Wilder, R.P. The effect of running shoes on lower extremity joint torques. PmR 2009, 1, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdok, A.E.; Biewener, A.A.; McMahon, T.A.; Weyand, P.G.; Herr, H.M. Energetics and mechanics of human running on surfaces of different stiffnesses. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 92, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Joint (x°) | Variables | EVA (Pre) | EVA (Post) | NN (Pre) | NN (Post) | Main Effect Shoe | Main Effect Temp | Interaction Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip | ROM | 34.0 ± 1.7 | 34.2 ± 3.8 | 34.2 ± 3.3 | 37.8 ± 3.4 | F = 69.708; p = 0.001 | F = 1.785; p = 0.252 | F = 1.640; p = 0.270 |
| Knee | ROM | 25.7 ± 2.9 | 27.2 ± 2.6 | 25.6 ± 2.4 | 24.9 ± 2.0 | F = 1.237; p = 0.328 | F = 0.137; p = 0.730 | F = 0.600; p = 0.482 |
| Ankle | ROM | 25.8 ± 3.3 | 28.1 ± 4.9 | 24.7 ± 1.7 | 28.9 ± 1.7 | F = 0.013; p = 0.916 | F = 14.307; p = 0.019 | F = 0.657; p = 0.463 |
| Joint Torque (N·m·kg−1) | EVA (Pre) | EVA (Post) | NN (Pre) | NN (Post) | Main Effect Shoe | Main Effect Temp | Interaction Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip-flexion torque | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.02 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | F = 0.173; p = 0.718 | F = 7.867; p = 0.107 | F = 21.078; p = 0.044 |
| Knee-flexion torque | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.03 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | F = 47.701; p = 0.002 | F = 31.750; p = 0.006 | F = 0.205; p = 0.674 |
| Ankle-dorsiflexion torque | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.04 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | F = 0.424; p = 0.550 | F = 3.642; p = 0.129 | F = 2.178; p = 0.214 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Gao, L.; Shao, E.; Kovács, B.; Li, J.; Gu, Y. The Effect of Non-Newtonian Fluid Midsole Footwear on Lower Limb Biomechanics after 5 km of Running in High Temperature. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8024. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148024
Ye J, Gao L, Shao E, Kovács B, Li J, Gu Y. The Effect of Non-Newtonian Fluid Midsole Footwear on Lower Limb Biomechanics after 5 km of Running in High Temperature. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(14):8024. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148024
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Jingyi, Lidong Gao, Enze Shao, Bálint Kovács, Jiao Li, and Yaodong Gu. 2023. "The Effect of Non-Newtonian Fluid Midsole Footwear on Lower Limb Biomechanics after 5 km of Running in High Temperature" Applied Sciences 13, no. 14: 8024. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148024
APA StyleYe, J., Gao, L., Shao, E., Kovács, B., Li, J., & Gu, Y. (2023). The Effect of Non-Newtonian Fluid Midsole Footwear on Lower Limb Biomechanics after 5 km of Running in High Temperature. Applied Sciences, 13(14), 8024. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148024








