Bi-LS-AttM: A Bidirectional LSTM and Attention Mechanism Model for Improving Image Captioning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We proposed a trainable model incorporating a bidirectional LSTM and attention mechanism. This model embeds image captions and scores into a region by capitalizing on the long-term forward and backward context.
- We upgraded the feature extraction mechanism, replacing the conventional CNN and RCNN with a Fast RCNN. This improvement enhances the model’s ability to rapidly detect and extract features from items within an image’s regions of interest.
- We verified the efficiency of the framework on two datasets Flickr30K and MSCOCO. The evaluation demonstrated that the Bi-LSTM and attention mechanism model achieved highly competitive performance results relative to current techniques in the tasks of generating captions and image sentence retrieval.
2. Related Works
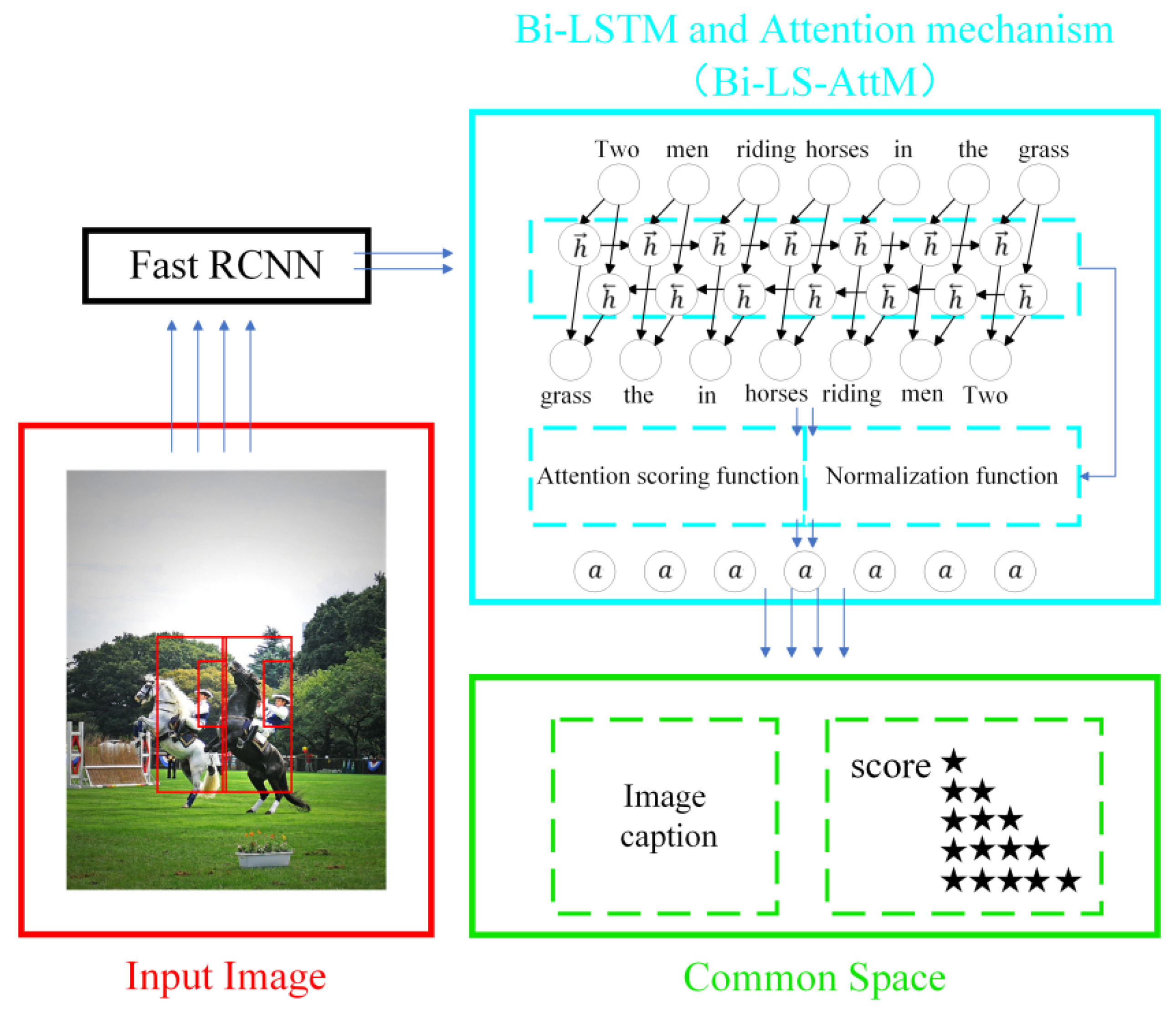
3. Methodology
3.1. Detect Object by Fast RCNN
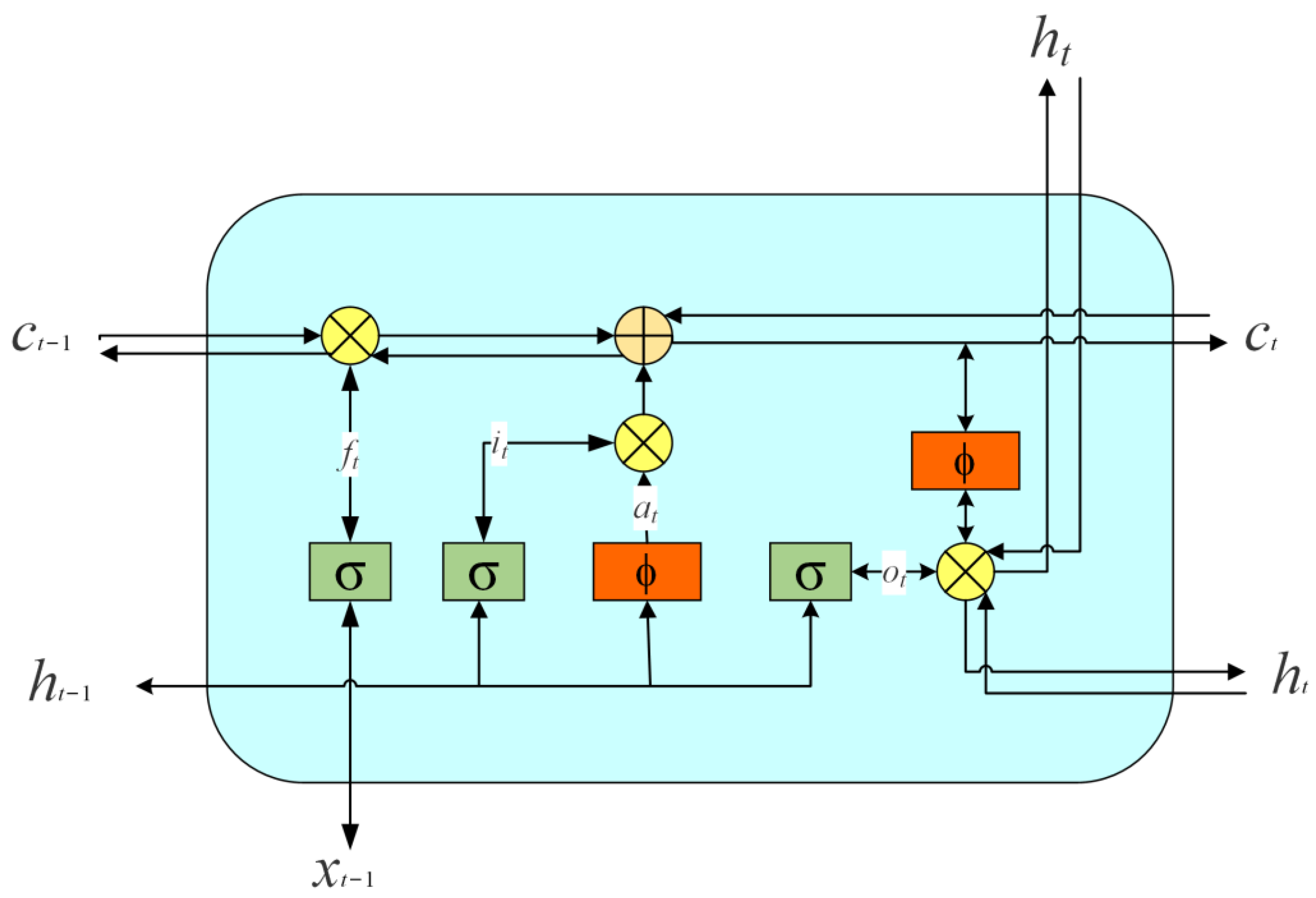
3.2. Long Short-Term Memory
3.3. Bi-LSTM
3.4. Architecture Model
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Experimental Results on the Generated Image Caption
4.5. Experimental Results on the Retrieval of Image-Sentence
4.6. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CV | Computer Vision |
| NPL | Natural Language Processing |
| Bi-LSTM | Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| Bi-LS-AttM | Bidirectional LSTM and Attention Mechanism |
| Fast RCNN | Fast Region-based Convolutional Network |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| RoI | Region of Interest |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| CRF | Conditional Random Field |
| NDE | Nonparametric Density Estimation |
| VggNet | Visual geometry group Net |
| Deep VS | Deep Visual Semantic |
| m-RNN | Multimodal Recurrent Neural Network |
| BULE | Bilingual Evaluation Understudy |
| MSCOCO | Microsoft Common Objects in Context |
| METEOR | Metric for Evaluation of Translation with Explicit Ordering |
| CIDEr | Consensus-based Image Description Evaluation |
| R@K | Recall@K |
References
- Lu, J.; Xiong, C.; Parikh, D.; Socher, R. Knowing when to look: Adaptive attention via a visual sentinel for image captioning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3242–3250. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D. Neural Baby Talk. In Proceedings of the Name of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6566–7296. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Lv, X.; Li, L.-J. Deep reinforcement learning-based captioning with embedding reward. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1151–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Sohel, F.; Shiratuddin, M.F.; Laga, H.A. Comprehensive Survey of Deep Learning for Image Captioning. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 51, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, N.; Hu, X.; Song, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Topic-Oriented Image Captioning Based on Order-Embedding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2743–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhu, M.; Fang, Y.; Shi, G.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y. Visual Cluster Grounding for Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 3920–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Bartz, C.; Meinel, C. Image captioning with deep bidirectional LSTMs. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 15–19 October 2016; pp. 988–997. [Google Scholar]
- Vahid, C.; Fadaeieslam, J.; Yaghmaee, F. Improvement of image description using bidirectional LSTM. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2018, 7, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Saif, A.; Hanif, M.; Shakil, M.; Jaman, M.; Haque, M.; Shawkat, S.; Hasan, J.; Sonok, B.; Rahman, F. Att-BiL-SL: Attention-Based Bi-LSTM and Sequential LSTM for Describing Video in the Textual Formation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Oh, H. Generalized Image Captioning for Multilingual Support. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, J.; Lu, S.; Lu, H. Show, Tell, and Polish: Ruminant Decoding for Image Captioning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 22, 2149–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zou, Z. Image captioning via proximal policy optimization. Image Vis. Comput. 2021, 108, 104126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Chan, A. On Distinctive Image Captioning via Comparing and Reweighting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 2088–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, A.; Hejrati, S.; Sadeghi, M.; Young, P.; Forsyth, D. Every picture tells a story: Generating sentences from images. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; pp. 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Lin, C.; Schlkopf, B. A tutorial on ν-support vector machines. Appl. Stoch. Model. Bus. Ind. 2005, 21, 111–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Lin, C. Libsvm: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kulkarni, G.; Berg, T.; Berg, A.; Choi, Y. Composing simple image descriptions using web-scale n-grams. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, Portland Oregon, OR, USA, 23–24 June 2011; pp. 220–228. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, G.; Premraj, V.; Dhar, S.; Li, S.; Berg, T. Baby talk: Understanding and generating simple image descriptions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 2891–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Q.; Szummer, M.; Minka, T. Bayesian conditional random fields. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Bridgetown, Barbados, 6–8 January 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, C.; Rohanimanesh, K.; McCallum, A. Dynamic conditional random fields: Factorized probabilistic models for labeling and segmenting sequence data. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2007, 8, 693–723. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, P.; Ordonez, V.; Berg, T.; Choi, Y. Treetalk: Composition and compression of trees for image descriptions. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2014, 2, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.; Charniak, E. Nonparametric Method for Data-driven Image Captioning. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Baltimore, MA, USA, 23–24 June 2014; pp. 592–598. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Gan, C.; Nevatia, R. Automatic concept discovery from parallel text and visual corpora. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2596–2604. [Google Scholar]
- Kiros, R.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Zemel, R. Multimodal Neural Language Models. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China, 21–26 June 2014; pp. 595–603. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Ba, J.; Kiros, R.; Cho, K.; Courville, A.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Zemel, R.; Bengio, Y. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 2048–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, D.; Fidler, S.; Urtasun, R.; Lin, D. Towards diverse and natural image descriptions via a conditional gan. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2989–2998. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub, S.; Gulzar, Y.; Reegu, F.A.; Turaev, S. Generating Image Captions Using Bahdanau Attention Mechanism and Transfer Learning. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Jafar, A.; Ghneim, N. Image captioning model using attention and object features to mimic human image understanding. J. Big Data 2022, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.; Yamane, T.; Maemura, Y. A deep learning-based image captioning method to automatically generate comprehensive explanations of bridge damage. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2022, 37, 1387–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Y. Switchable Novel Object Captioner. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Plummer, B.; Wang, L.; Cervantes, C.; Caicedo, J.; Lazebnik, S. Flickr30k Entities: Collecting Region-to-Phrase Correspondences for Richer Image-to-Sentence Models. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vinyals, O.; Toshev, A.; Bengio, S.; Erhan, D. Show and Tell: Lessons Learned from the 2015 MSCOCO Image Captioning Challenge. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W. Bleu: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Denkowski, M.; Lavie, A. Meteor universal: Language specific translation evaluation for any target language. In Proceedings of the 9th Workshop on statistical machine translation (WMT 2014), Baltimore, MD, USA, 26–27 June 2014; pp. 376–380. [Google Scholar]
- Vedantam, R.; Zitnick, C.; Parikh, D. CIDEr: Consensus-based Image Description Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4566–4575. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, H.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Shah, T.; Ranjan, R. Towards brain big data classification: Epileptic eeg identification with a lightweight vggnet on global mic. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 14722–14733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthiah, M.; Logashamugam, E.; Nandhitha, N. Performance evaluation of googlenet, squeezenet, and resnet50 in the classification of herbal images. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2021, 69, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; Yuille, A. Deep captioning with multimodal recurrent neural networks (m-rnn). arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6632. [Google Scholar]
- Karpathy, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3128–3137. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zitnick, C. Mind’s eye: A recurrent visual representation for image caption generation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 2422–2431. [Google Scholar]







| Parameters | Descriptions | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Emb-dim | Dimension of word embeddings. | 256 |
| Attention-dim | Dimension of Bi-LSTM attention linear layers. | 256 |
| Frcnn-dim | Dimension of fast RCNN. | 128 |
| Dropout | The phenomenon of learning to adapt can be considerably reduced by training batches. | 0.5 |
| Cudnn-benchmark | Set to true only if inputs to model are fixed size; otherwise, lots of computational overhead. | True |
| Parameters | Descriptions | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Lay-Num | Number of layers | 3 |
| Time-fore | Time of data used to make the forecast. | 5 |
| Hidden-size | The size of the featured area in the hidden status. | 8 |
| Epoch | Displaying the number of forward and backward calculations that could be performed. | 120 |
| Batch-size | The amount of data transferred to the trainer. | 0.5 |
| Learning-rate | Adjustment of the network weighting rate by the loss gradient. | 0.002 |
| Optimizer | Training and parameter tuning to reduce the loss of function. | Adam |
| Parameters | Descriptions | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Lay-Num | Number of layers. | 3 |
| Hidden-dim | Size of the featured area in the hidden status. | 8 |
| Epoch | Displaying the number of forward and backward calculations that could be performed. | 120 |
| Batch-size | The amount of data transferred to the trainer. | 64 |
| Learning-rate | Adjustment of the network weighting rate by the loss gradient. | 0.004 |
| Optimizer | Training and parameter tuning to reduce the loss function. | Adam |
| Grad-clip | Clipping to threshold, and gradient to update weights. | 5 |
| Alpha-c | Regularization parameter for attention mechanisms. | 1 |
| Model | Flickr30K | MSCOCO | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-1 | B-2 | B-3 | B-4 | B-1 | B-2 | B-3 | B-4 | |
| Deep VS [41] | 57.3 | 36.9 | 24.0 | 15.7 | 62.5 | 45.0 | 32.1 | 23.0 |
| m-RNN(AlexNet) [40] | 54.0 | 36.0 | 23.0 | 15.0 | - | - | - | - |
| m-RNN(VGGNet) [40] | 60.0 | 41.0 | 28.0 | 19.0 | 67.0 | 49.0 | 35.0 | 25.0 |
| Hard-attention [26] | 66.9 | 43.9 | 29.6 | 19.9 | 71.8 | 50.4 | 35.7 | 25.0 |
| Bi-LSTM [9] | 62.1 | 42.6 | 28.1 | 19.3 | 67.2 | 49.2 | 35.2 | 24.4 |
| Deep Bi-LSTM [8] | 63.1 | 44.2 | 29.7 | 20.0 | 67.5 | 49.0 | 35.5 | 24.9 |
| Our model (Bi-LSTM and attention mechanism) | 64.5 | 44.6 | 29.8 | 20.2 | 68.8 | 51.0 | 35.9 | 25.2 |
| Model | METEOR | CIDEr |
|---|---|---|
| Muhammad’s model [29] | 16.3 | 39.0 |
| Wu’s model (SNOC) [31] | 21.9 | 39.5 |
| Our model (Bi-LSTM) | 17.8 | 34.5 |
| Our model (Bi-LS-AttM) | 21.5 | 41.2 |
| Model | Flickr30K | MSCOCO | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-1 | B-2 | B-3 | B-4 | METEOR | B-1 | B-2 | B-3 | B-4 | METEOR | |
| Baseline models (without attention) | 56.2 | 38.9 | 23.0 | 14.8 | 14.7 | 59.6 | 45.8 | 28.4 | 19.7 | 15.9 |
| Our model (Bi-LS-AttM) | 64.5 | 44.6 | 29.8 | 20.2 | 18.6 | 68.8 | 51.0 | 35.9 | 25.2 | 21.5 |
| Dataset | Model | Image to Sentence | Sentence to Image | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R@1 | R@2 | R@3 | Medr | R@1 | R@2 | R@3 | Medr | ||
| Flickr30k | Deep VS [41] | 22.2 | 48.2 | 61.4 | 4.8 | 15.2 | 37.7 | 50.5 | 9.2 |
| m-RNN(AlexNet) [40] | 18.4 | 40.2 | 50.9 | 10.0 | 12.6 | 31.2 | 41.5 | 16.0 | |
| Mind’s Eye [42] | 18.5 | 45.7 | 58.1 | 7.0 | 16.6 | 42.5 | 58.9 | 8.0 | |
| Bi-LSTM [9] | 28.1 | 53.1 | 64.2 | 4.0 | 19.6 | 43.8 | 55.8 | 7.0 | |
| Deep Bi-LSTM [8] | 29.2 | 54.0 | 64.9 | 3.8 | 20.8 | 44.5 | 56.7 | 6.7 | |
| Our model (Bi-LSTM and attention mechanism) | 29.5 | 53.8 | 65.0 | 3.6 | 21.0 | 44.7 | 57.3 | 6.5 | |
| MSCOCO | Deep VS [41] | 16.5 | 39.2 | 52.0 | 9.0 | 10.7 | 29.6 | 42.2 | 14.0 |
| m-RNN(AlexNet) [40] | 12.4 | 29.3 | 48.6 | 15.0 | 9.5 | 25.4 | 38.2 | 18.0 | |
| Mind’s Eye [42] | 12.8 | 35.6 | 50.1 | 11.0 | 11.6 | 33.7 | 48.5 | 10.0 | |
| Bi-LSTM [9] | 13.4 | 33.1 | 44.7 | 13.0 | 9.4 | 26.5 | 37.7 | 19.0 | |
| Deep Bi-LSTM [8] | 16.6 | 39.4 | 52.4 | 9.0 | 11.6 | 30.9 | 43.4 | 13.0 | |
| Our model (Bi-LSTM and attention mechanism) | 17.2 | 40.0 | 53.6 | 8.0 | 12.2 | 35.6 | 49.8 | 11.0 | |
| Task | Bi-LSTM | Deep Bi-LSTM | Our Models |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caption creation | 1.04s | 1.07 s | 0.67 s |
| Image-Sentence Retrieval | 5.78 s | 5.81 s | 4.28 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, T.; Ding, W.; Zhang, J.; Wan, X.; Wang, J. Bi-LS-AttM: A Bidirectional LSTM and Attention Mechanism Model for Improving Image Captioning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7916. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137916
Xie T, Ding W, Zhang J, Wan X, Wang J. Bi-LS-AttM: A Bidirectional LSTM and Attention Mechanism Model for Improving Image Captioning. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(13):7916. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137916
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Tian, Weiping Ding, Jinbao Zhang, Xusen Wan, and Jiehua Wang. 2023. "Bi-LS-AttM: A Bidirectional LSTM and Attention Mechanism Model for Improving Image Captioning" Applied Sciences 13, no. 13: 7916. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137916
APA StyleXie, T., Ding, W., Zhang, J., Wan, X., & Wang, J. (2023). Bi-LS-AttM: A Bidirectional LSTM and Attention Mechanism Model for Improving Image Captioning. Applied Sciences, 13(13), 7916. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137916







