Application of Biogas from Quinoa, Wheat, and Andean Guinea Pig Residuals as Biofuels for Gas Turbines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biogas Production
2.2. Studied Gas Turbine
2.3. Biogas Characterization
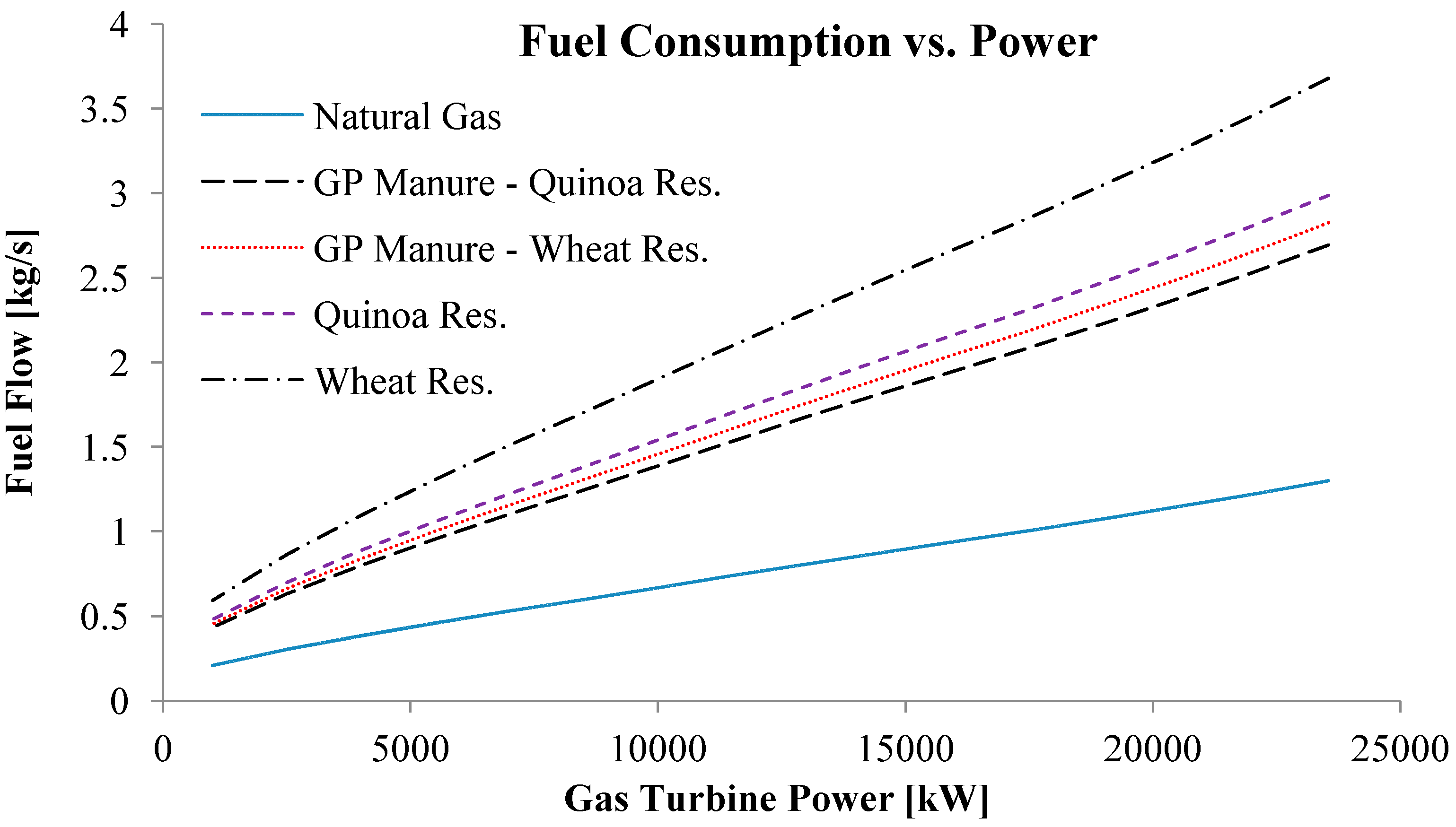
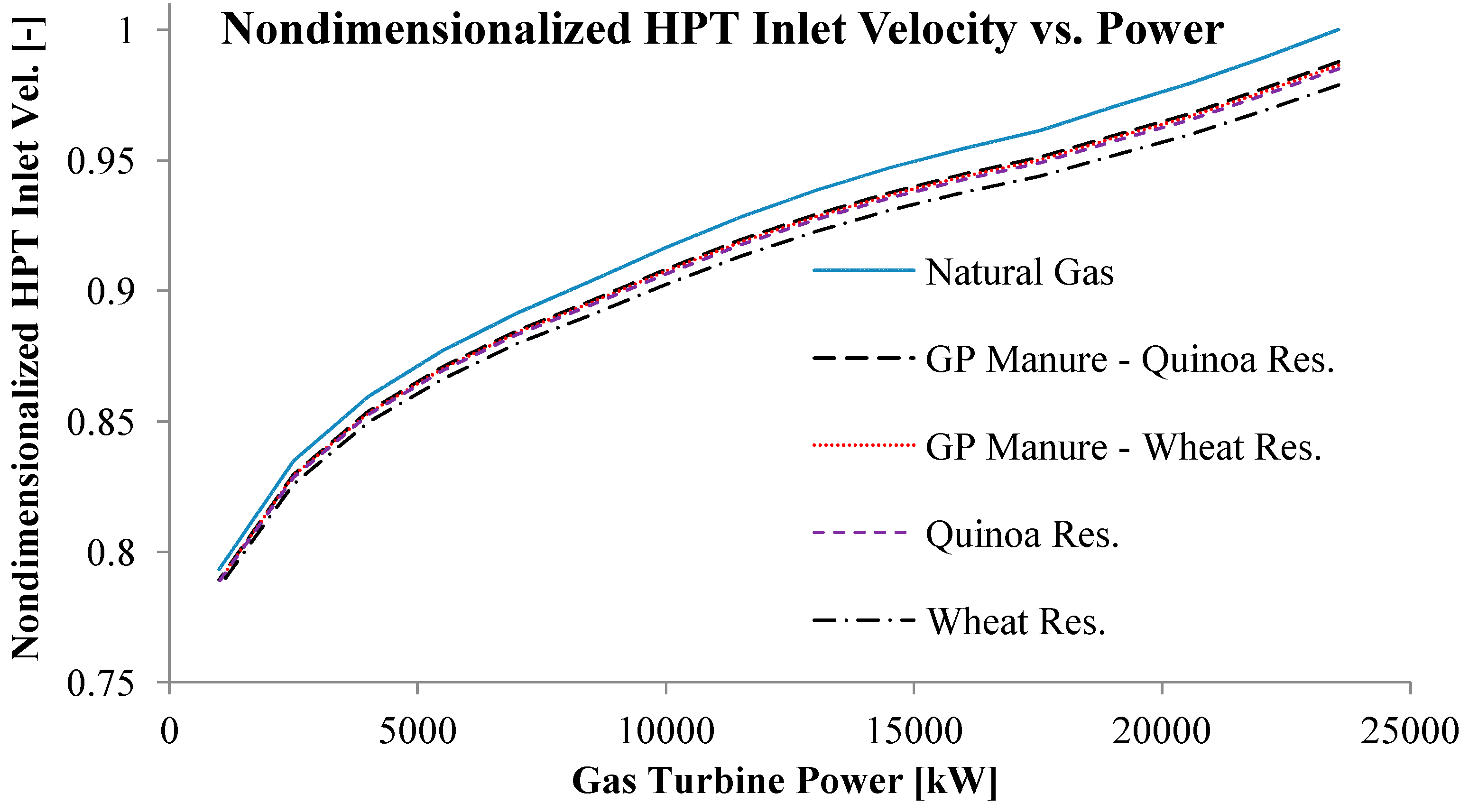
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Omambia, A.N.; Shemsanga, C.; Hernandez, I.A.S. Climate change impacts, vulnerability, and adaptation in East Africa (EA) and South America (SA). In Handbook of Climate Change Mitigation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 749–799. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Lei, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, D. Co-benefits from energy policies in China. Energy 2010, 35, 4265–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfí, M.; Martí-Herrero, J.; Garwood, A.; Ferrer, I. Household anaerobic digesters for biogas production in Latin America: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheinbaum-Pardo, C.; Ruiz, B.J. Energy context in Latin America. Energy 2012, 40, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo-Ramos, C.; Moutinho, P. No man’s land in the Brazilian Amazon: Could undesignated public forests slow Amazon deforestation? Land Use Policy 2018, 73, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, I.; Garfí, M.; Cadena, E.; Ferrer, I. Technical, economic and environmental assessment of household biogas digesters for rural communities. Renew. Energy 2014, 62, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igliński, B.; Pietrzak, M.B.; Kiełkowska, U.; Skrzatek, M.; Kumar, G.; Piechota, G. The assessment of renewable energy in Poland on the background of the world renewable energy sector. Energy 2022, 261, 125319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechota, G. Biogas/Biomethane Quality and Requirements for Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Units/Gas Grids with a Special Focus on Siloxanes-a Short Review. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechota, G. Siloxanes in Biogas: Approaches of Sampling Procedure and GC-MS Method Determination. Molecules 2021, 26, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobslaw, D.; Engesser, K.-H.; Störk, H.; Gerl, T. Low-cost process for emission abatement of biogas internal combustion engines. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfí, M.; Castro, L.; Montero, N.; Escalante, H.; Ferrer, I. Evaluating environmental benefits of low-cost biogas digesters in small-scale farms in Colombia: A life cycle assessment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Parra, J.L.; Peña-Loyola, P.J. Potential high-quality growing tea regions in Ecuador: An alternative cash crop for Ecuadorian small landholders. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melby, C.L.; Orozco, F.; Averett, J.; Muñoz, F.; Romero, M.J.; Barahona, A. Agricultural Food Production Diversity and Dietary Diversity among Female Small Holder Farmers in a Region of the Ecuadorian Andes Experiencing Nutrition Transition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Góngora, J.C. Beneficios y Costos de Políticas Públicas Ambientales en la Gestión de Residuos Sólidos: Chile y Países Seleccionados; United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 71, ISBN 9213222688. [Google Scholar]
- Garfí, M.; Ferrer-Martí, L.; Villegas, V.; Ferrer, I. Psychrophilic anaerobic digestion of guinea pig manure in low-cost tubular digesters at high altitude. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6356–6359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kouakou, N.D.V.; Grongnet, J.-F.; Assidjo, N.E.; Thys, E.; Marnet, P.-G.; Catheline, D.; Legrand, P.; Kouba, M. Effect of a supplementation of Euphorbia heterophylla on nutritional meat quality of Guinea pig (Cavia porcellus L.). Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedano-Castro, J.I.; Jiménez, R.; Huamán, A.; Fuerst-Waltl, B.; Wurzinger, M.; Gutiérrez, G. Estimation of genetic parameters for four Peruvian guinea pig lines. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 53, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.E. Death of a Guinea Pig: Grief and the Limits of Multispecies Ethnography in Peru. Environ. Humanit. 2019, 11, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Salazar, M.A.; Morini, M.; Pinelli, M.; Spina, P.R.; Venturini, M.; Finkenrath, M.; Poganietz, W.-R. Methodology for estimating biomass energy potential and its application to Colombia. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meneses-Quelal, O.; Velázquez-Martí, B.; Gaibor-Chávez, J.; Niño-Ruiz, Z. Effect of the co-digestion of agricultural lignocellulosic residues with manure from South American camelids. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2021, 15, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Alvarez, J.; Macé, S.; Llabrés, P. Anaerobic digestion of organic solid wastes. An overview of research achievements and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 74, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses Quelal, W.O.; Velázquez-Martí, B.; Gaibor Chávez, J.; Niño Ruiz, Z.; Ferrer Gisbert, A. Evaluation of methane production from the anaerobic co-digestion of manure of guinea pig with lignocellulosic Andean residues. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 2227–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VDI. 4630: Fermentation of Organic Materials-Characterisation of the Substrate, Sampling, Collection of Material Data, Fermentation Tests; VDI Handbu; Verein Deutscher Ingenieure (VDI): Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mattingly, J.D. Elements of Propulsion: Gas Turbines and Rockets; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Warnatz, J.; Maas, U.; Dibble, R.W. Combustion; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, N. Turbulent Combustion; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Energy General Electric Gas Turbine and Combined Cycle Products. Available online: http://www.gepower.com/prod_serv/products/gas_turbines_cc/en/downloads/gasturbine_cc_products.Pdf (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Kluiters, S.; Visser, W.; Rademaker, E. A New Combustor and Emission Model for the Gas Turbine Simulation Program GSP; National Aerospace Laboratory: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nikpey Somehsaraei, H.; Mansouri Majoumerd, M.; Breuhaus, P.; Assadi, M. Performance analysis of a biogas-fueled micro gas turbine using a validated thermodynamic model. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 66, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Mofijur, M.; Tarannum, K.; Chowdhury, A.T.; Rafa, N.; Nuzhat, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Biogas upgrading, economy and utilization: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 4137–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahed, P.; Avami, A. Techno-economic optimization of biogas-fueled micro gas turbine cogeneration systems in sewage treatment plant. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 218, 112965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Jash, T. Performance analysis of micro turbine-based grid-connected biogas power plant in Purulia in West Bengal, India. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2015, 17, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera-Medina, A.; Giles, A.; Pugh, D.; Morris, S.; Pohl, M.; Ortwein, A. Investigation of Combustion of Emulated Biogas in a Gas Turbine Test Rig. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 27, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazooyar, B.; Gohari Darabkhani, H. The design strategy and testing of an efficient microgas turbine combustor for biogas fuel. Fuel 2021, 294, 120535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zeng, W.; Wang, C. Experimental study of biogas combustion and emissions for a micro gas turbine. Fuel 2020, 267, 117312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Liu, H.; Cai, W.; Weng, S. Effect of carbon dioxide content in biogas on turbulent combustion in the combustor of micro gas turbine. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, K.; Rhim, S.; Park, J. Mechanical characteristics evaluation of biogas micro turbine power systems. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2009, 22, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Chow, T.-T.; Lee, C.-K. Performance analysis of biogas-fueled maisotsenko combustion turbine cycle. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 195, 117247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, W.; Jia, Y.; Tang, J. Numerical Analysis of the Combustion in Micro Gas Turbine with Methane/Biogas Fuels. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 11897–11907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Álvarez, J.F.; Gonzalo de Grado, J. Study of a modern industrial low pressure turbine for electricity production employed in oxy-combustion cycles with CO2 capture purposes. Energy 2016, 107, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Álvarez, J.F.; Alonso Fernández, E. Oxy-combustion flow field study under power-generating and CO2-capturing Matiant cycle conditions and its influence on the turbine inlet conditions. Fuel 2021, 303, 121172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, O.O. Gas-turbine performance improvements. Appl. Energy 1999, 64, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Luyben, W.L. Dynamic simulation and control of a combustion turbine process for biogas derived methane. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2021, 144, 107121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

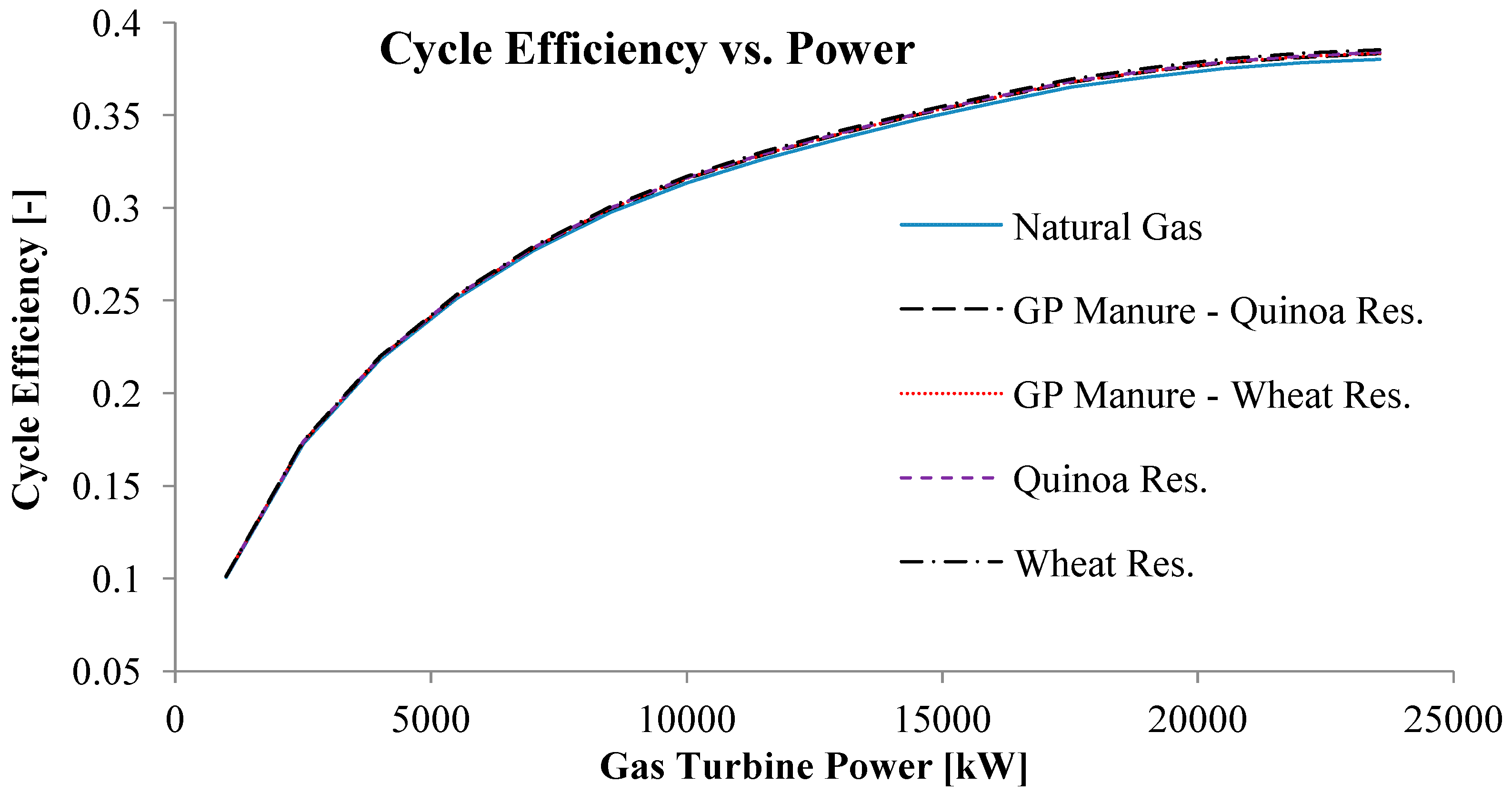
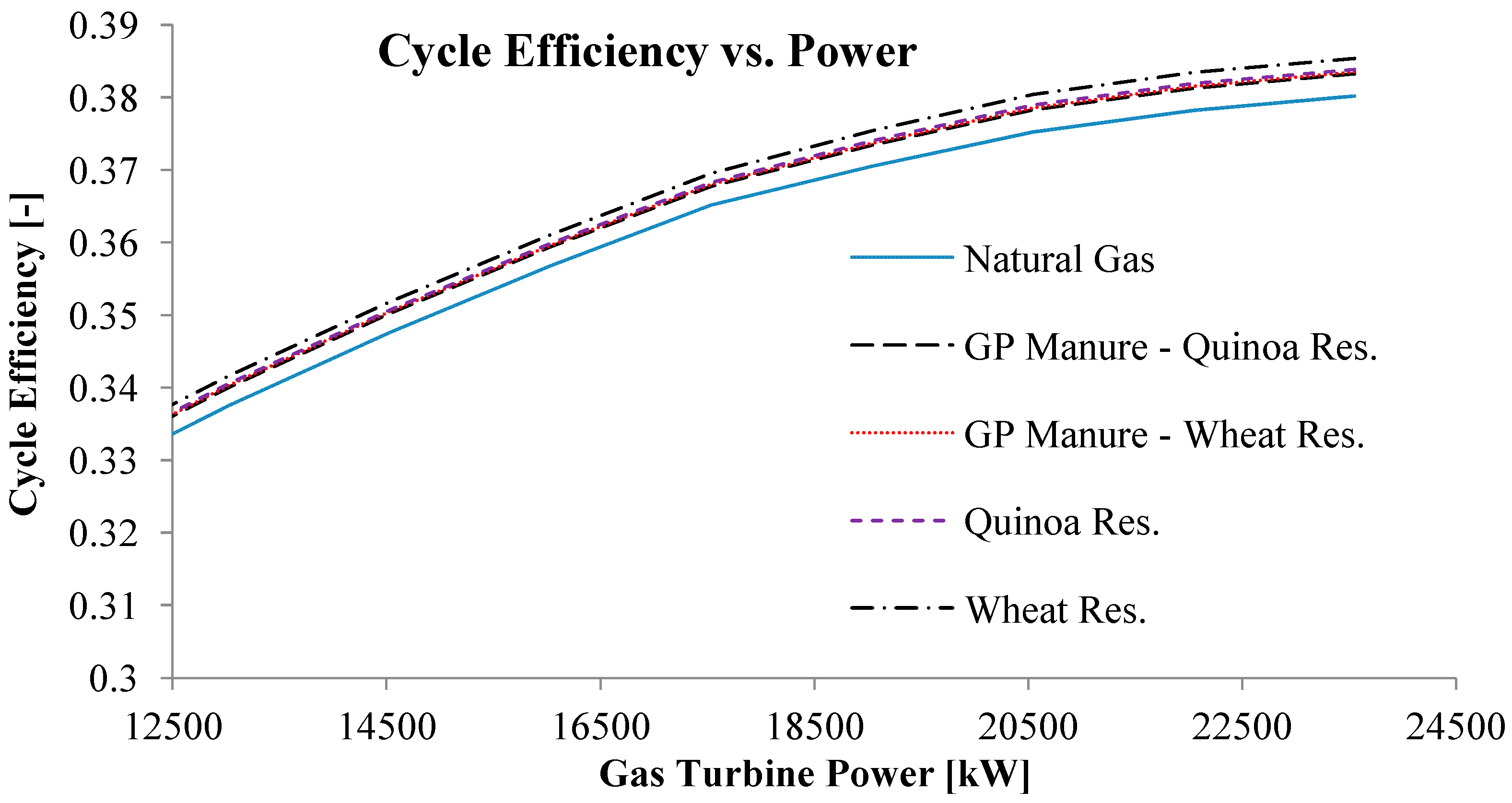
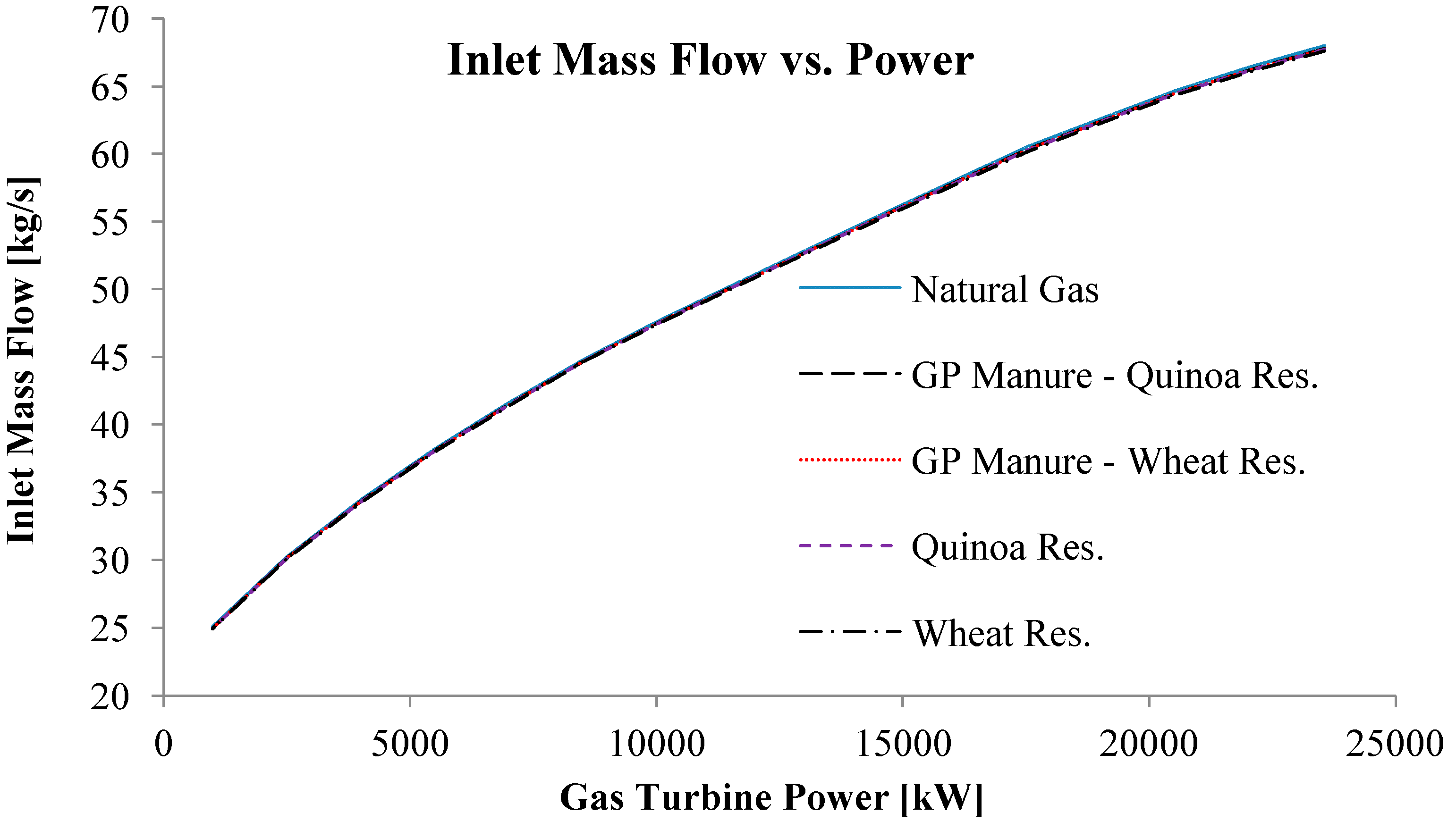
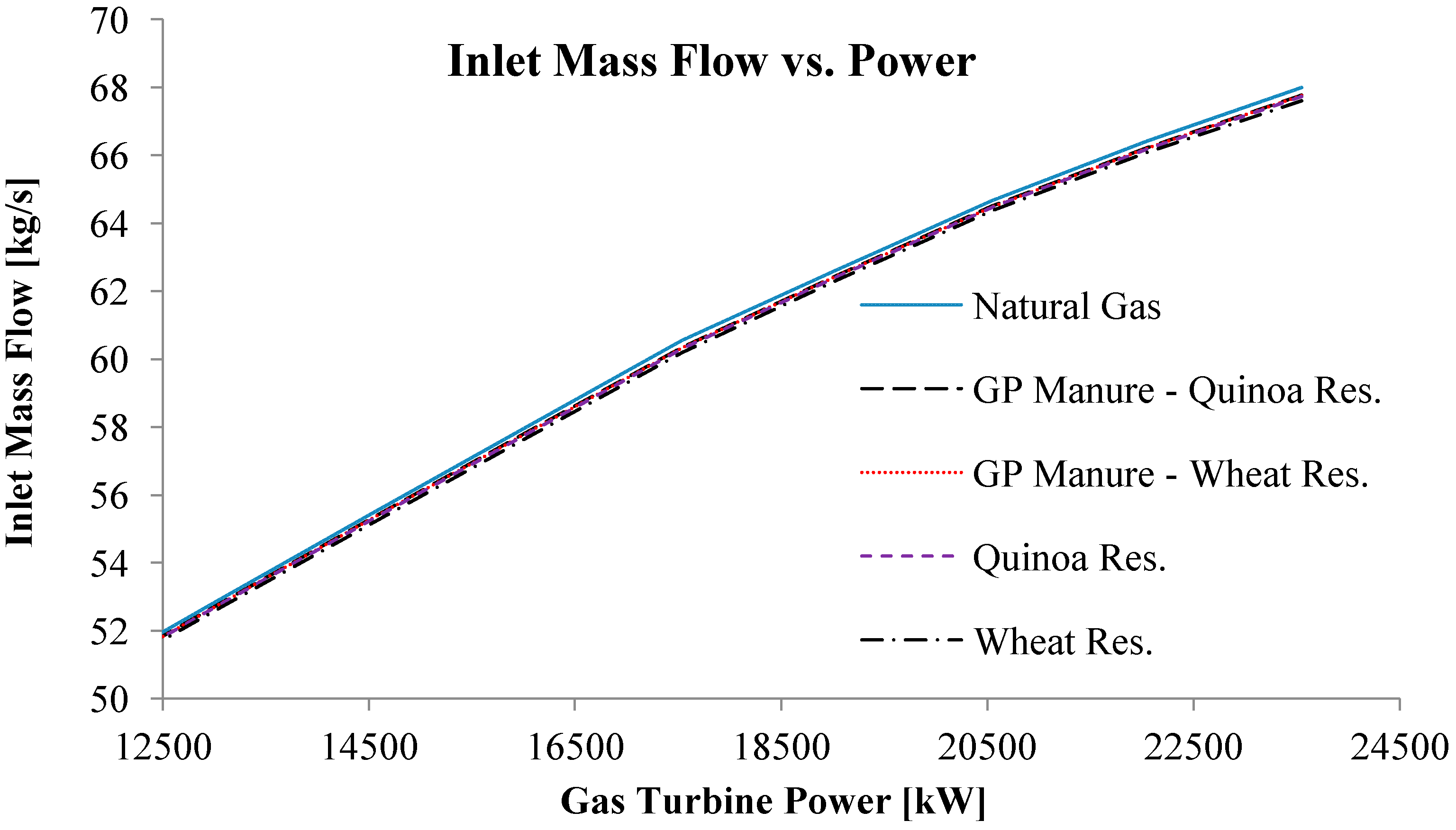
| Power [kW] | Exhaust Mass Flow [kg/s] | Exhaust Temperature [K] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LM2500PE | 23,292 | 69 | 806.15 |
| Model | 23,550.59 | 69.30 | 786.93 |
| Deviation % | 1.11 | 0.43 | 2.38 |
| % Volume CH4 | % Volume CO2 | % Volume H2S | % Volume N2 | Lower Heating Value (LHV) [kJ/kg] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat Residuals | 57.00 ± 1.26 | 42.42 ± 2.36 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | 0.31 ± 0.12 | 16,604.88 |
| Quinoa Residuals | 65.08 ± 0.98 | 33.95 ± 2.36 | 0.35 ± 0.09 | 0.62 ± 0.11 | 20,541.66 |
| Guinea Pig Manure—Wheat Res. 75:25 | 66.73 ± 2.11 | 32.14 ± 0.25 | 0.32 ± 0.08 | 0.81 ± 0.22 | 21,746.17 |
| Guinea Pig Manure–Quinoa Res. 50:50 | 69.00 ± 1.02 | 29.9 ± 0.99 | 0.38 ± 0.12 | 0.72 ± 0.32 | 22,822.33 |
| Parameters | Units | GPM | QS | WS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS | % | 33.9 (1.7) | 87.0 (0.1) | 92.6 (0.1) |
| VS (% ST) | % | 72.6 (1.1) | 58.4 (1.5) | 77.2 (0.9) |
| Ashes | % | 13.1 (0.1) | 30.3 (1.4) | 11.8 (0.1) |
| N | % | 2.3 (1.0) | 2.2 (0.9) | 1.7 (0.7) |
| C | % | 39.5 (1.2) | 30.7 (1.7) | 48.9 (1.6) |
| H | % | 4.6 (0.5 | 6.4 (0.9) | 6.1 (0.5) |
| O | % | 39.7 (1.2) | 29.8 (1.7) | 31.1 (1.6) |
| S | % | 0.4 (0.0) | 0.6 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.0) |
| C/N | - | 15.3 (0.8) | 12.0 (0.9) | 29.6 (0.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González Álvarez, J.F.; Velázquez-Martí, B.; Gaibor-Chávez, J.; Franco Rodríguez, J.E.; Rico, C. Application of Biogas from Quinoa, Wheat, and Andean Guinea Pig Residuals as Biofuels for Gas Turbines. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7802. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137802
González Álvarez JF, Velázquez-Martí B, Gaibor-Chávez J, Franco Rodríguez JE, Rico C. Application of Biogas from Quinoa, Wheat, and Andean Guinea Pig Residuals as Biofuels for Gas Turbines. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(13):7802. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137802
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález Álvarez, José Francisco, Borja Velázquez-Martí, Juan Gaibor-Chávez, John Eloy Franco Rodríguez, and Carlos Rico. 2023. "Application of Biogas from Quinoa, Wheat, and Andean Guinea Pig Residuals as Biofuels for Gas Turbines" Applied Sciences 13, no. 13: 7802. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137802
APA StyleGonzález Álvarez, J. F., Velázquez-Martí, B., Gaibor-Chávez, J., Franco Rodríguez, J. E., & Rico, C. (2023). Application of Biogas from Quinoa, Wheat, and Andean Guinea Pig Residuals as Biofuels for Gas Turbines. Applied Sciences, 13(13), 7802. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137802








