Eggshell-Waste-Derived Calcium Acetate, Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate and Corresponding Eggshell Membranes
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Chemical Transformation of Eggshell Waste by Acetic and o-Phosphoric Acid
2.3. Characterization of Eggshell-Derived Calcium Salts
2.4. Characterization of Eggshell Derived Eggshell Membranes
2.5. Stastitical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Eggshell Waste Transformation using 10% Acetic and 15% o-Phosphoric Acid
3.2. Characterization of Eggshell-Waste-Derived Eggshell Membranes
3.3. Characterization of Eggshell-Waste-Derived Calcium Acetate and Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strelec, I.; Ostojčić, M.; Brekalo, M.; Hajra, S.; Kim, H.-J.; Stanojev, J.; Maravić, N.; Budžaki, S. Transformation of Eggshell Waste to Egg White Protein Solution, Calcium Chloride Dihydrate, and Eggshell Membrane Powder. Green Process. Synth. 2023, 12, 20228151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignardi, S.; Archilletti, L.; Medeghini, L.; De Vito, C. Valorization of Eggshell Biowaste for Sustainable Environmental Remediation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, T.A.E.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Gomaa, A. Editorial: Biotechnology and Bioengineering Applications for Egg-Derived Biomaterials. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 756058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strelec, I.; Ostojčić, M.; Budžaki, S. Transformacija ljuske kokošjih jaja u proizvode dodane vrijednosti. In Neke Mogućnosti Iskorištenja Nusproizvoda Prehrambene Industrije—Knjiga 3; Sveučilište Josipa Jurja Strossmayera u Osijeku, Prehrambeno-tehnološki Fakultet Osijek, Veleučilište u Požegi: Osijek, Croatia, 2021; pp. 303–327. ISBN 978-953-7005-74-0. [Google Scholar]
- Abeyrathne, E.D.N.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Ahn, D.U. Egg White Proteins and Their Potential Use in Food Processing or as Nutraceutical and Pharmaceutical Agents—A Review. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 3292–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, J.; Araujo, J.; Castro, F. Alternative Low-Cost Adsorbent for Water and Wastewater Decontamination Derived from Eggshell Waste: An Overview. Waste Biomass Valorization 2011, 2, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budžaki, S.; Velić, N.; Ostojčić, M.; Stjepanović, M.; Rajs, B.B.; Šereš, Z.; Maravić, N.; Stanojev, J.; Hessel, V.; Strelec, I. Waste Management in the Agri-Food Industry: The Conversion of Eggshells, Spent Coffee Grounds, and Brown Onion Skins into Carriers for Lipase Immobilization. Foods 2022, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Lala, S.; Deb, P.; Barua, E.; Deoghare, A.B.; Chatterjee, S. Characterization of Hydroxyapatite Derived from Eggshells for Medical Implants. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 15, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinska, B.; Jelinska, M.; Szulc-Musiol, B.; Ryszka, F. Use of Eggshells as a Raw Material for Production of Calcium Preparations. Czech. J. Food Sci. 2016, 34, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannan, M.B.; Ronan, K. Conversion of Biowastes to Biomaterial: An Innovative Waste Management Approach. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.-S.; Lee, S.-J. Fabrication of Calcium Phosphate Glass Using Eggshell and Its Crystallization Behavior. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2017, 54, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, T.S.S.; Madhumathi, K.; Jayasree, R. Eggshell Waste: A Gold Mine for Sustainable Bioceramics. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2022, 102, 599–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, A.; Isa, N.M.; Adzila, S. Synthesis of Calcium Phosphate Extracted from Eggshell Waste through Precipitation Method. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 15058–15067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, A.; Najah, M.; Munirah; Adzila, S. Review on Eggshell Waste in Tissue Engineering Application. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2022, 14, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, N.; Habte, L.; Thenepalli, T.; Ahn, J.W. Effect of Eggshell Powder on the Hydration of Cement Paste. Materials 2019, 12, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waheed, M.; Butt, M.S.; Shehzad, A.; Adzahan, N.M.; Shabbir, M.A.; Suleria, H.A.R.; Aadil, R.M. Eggshell Calcium: A Cheap Alternative to Expensive Supplements. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleoni, A.C.C. Albumen Protein and Functional Properties of Gelation and Foaming. Sci. Agric. 2006, 63, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baláž, M. Eggshell Membrane Biomaterial as a Platform for Applications in Materials Science. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3827–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláž, M.; Zorkovská, A.; Fabián, M.; Girman, V.; Briančin, J. Eggshell Biomaterial: Characterization of Nanophase and Polymorphs after Mechanical Activation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, X.; Cai, C.; He, W.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J. Characteristics of Glycosaminoglycans in Chicken Eggshells and the Influence of Disaccharide Composition on Eggshell Properties. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, L.; Li, G.; He, W.; Linhardt, R.J. Compositional Analysis and Structural Elucidation of Glycosaminoglycans in Chicken Eggs. Glycoconj. J. 2014, 31, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, N.; Xu, Q.; Harlina, P.W.; Ma, M. An Efficient Method for Co-Purification of Eggshell Matrix Proteins OC-17, OC-116, and OCX-36. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2016, 36, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walton, H.V.; Cotterill, O.J.; Vandepopuliere, J.M. Composition of Shell Waste from Egg Breaking Plants1. Poult. Sci. 1973, 52, 1836–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Teotia, M.; Soni, R.K.; Mittal, J. Applications of Egg Shell and Egg Shell Membrane as Adsorbents: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.; Manso, M.A.; López-Fandiño, R.; Ramos, M. Comparative Study of Egg White Proteins from Different Species by Chromatographic and Electrophoretic Methods. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 221, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réhault-Godbert, S.; Guyot, N.; Nys, Y. The Golden Egg: Nutritional Value, Bioactivities, and Emerging Benefits for Human Health. Nutrients 2019, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acevedo-Davila, J.L.; Lopez-Cuevas, J.; Vargas-Gutierrez, G.; Rendon-Angeles, J.C.; Mendez-Nonell, J. Chemical Synthesis of Bone-like Carbonate Hydroxyapatite from Hen Eggshells and Its Characterization. Bol. Soc. Esp. Ceram. Vidr. 2007, 46, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A.A.; Rahman, M.K.A. The Environmental Sustainability of Calcined Calcium Phosphates Production from the Milling of Eggshell Wastes and Phosphoric Acid. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.W.; Wong, Y.H.; Singh, R.S.K.; Chandran, H.; Wong, S.K.; Lee, K.Y.S. Irradiation Time-Dependent Study of Eggshell-Derived Hydroxyapatite Powder Synthesized by Microwave-Assisted Wet Chemical Precipitation Method. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2022, 23, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbarczyk, M.; Szczes, A.; Kantor, I.; May, Z.; Sternik, D. Synthesis and Characterization of Calcium Phosphate Materials Derived from Eggshells from Different Poultry with and without the Eggshell Membrane. Materials 2022, 15, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbarczyk, M.; Szczes, A.; Sternik, D. The Preparation of Calcium Phosphate Adsorbent from Natural Calcium Resource and Its Application for Copper Ion Removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.S.; Kwak, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-J. Effects of PH and Temperature on Synthesis of Calcium Phosphate Derived from Calcined Eggshell. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2016, 17, 925–929. [Google Scholar]
- Kunam, D.; Sampath, V.; Manimaran, S.; Sekar, M. Effect of Indigenously Developed Nano-Hydroxyapatite Crystals from Chicken Egg Shell on the Surface Hardness of Bleached Human Enamel: An In Vitro Study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2019, 10, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Oh, S.H. Synthesis of Biocompatible Calcium Phosphate Powders by Using an Eggshell. In Bioceramics 15; BenNissan, B., Sher, D., Walsh, W., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2003; Volume 240–242, pp. 35–38. ISBN 978-0-87849-911-3. [Google Scholar]
- Natasha, A.N.; Ramesh, S.; Bang, L.T.; Koay, M.H. P Influence of Calcination Temperature in Synthesizing Eggshell-Derived Calcium Phosphate. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 48, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu’ad, N.A.S.M.; Alipal, J.; Abdullah, H.Z.; Idris, M.I.; Lee, T.C. Synthesis of Eggshell Derived Hydroxyapatite via Chemical Precipitation and Calcination Method. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, S.; Natasha, A.N.; Tan, C.Y.; Bang, L.T.; Ramesh, S.; Ching, C.Y.; Chandran, H. Direct Conversion of Eggshell to Hydroxyapatite Ceramic by a Sintering Method. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 7824–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopavath, U.K.; Sah, M.K.; Panigrahi, B.B.; Rath, S.N. Mechanochemically Synthesized Phase Stable and Biocompatible Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate from Avian Eggshell for the Development of Tissue Ingrowth System. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 12910–12919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, Y.W.; Saputra, A.; Bahtiar, A.; Nuzulia, N.A. Effects of Microwave Processing Parameters on the Properties of Nanohydroxyapatite: Structural, Spectroscopic, Hardness, and Toxicity Studies. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 30061–30070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.; Giroto, A.S.; Klaic, R.; Wypych, F.; Ribeiro, C. Mechanochemical Synthesis of Eco-Friendly Fertilizer from Eggshell (Calcite) and KH2PO4. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 4070–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Chun, S.Y. Fabrication of Calcium Based Fine Ceramic Materials by Recycling Eggshell. In Eco-Materials Processing & Design Vi; Kim, H.S., Park, S.Y., Hur, B.Y., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2005; Volume 486–487, pp. 293–296. ISBN 978-0-87849-966-3. [Google Scholar]
- Laohavisuti, N.; Boonchom, B.; Boonmee, W.; Chaiseeda, K.; Seesanong, S. Simple Recycling of Biowaste Eggshells to Various Calcium Phosphates for Specific Industries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopyan, I.; Adlina, S.F.; Mohamad, S.A. Preparation of Dense Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Ceramics Using Eggshell Derived Nanopowders. In Applied Mechanics and Materials; Fan, W., Ed.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 110–116, pp. 3645–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Shi, Y.; An, P.; Hu, X.; Wan, Y. Optimization of Preparation of Calcium Acetate from Eggshell by Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e114421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, L.C.S.; Santos, S.; Palavra, A.M.F.; Calvete, M.J.F.; de Castro, C.A.N.; Nobre, B.P. Supercritical Antisolvent Precipitation of Calcium Acetate from Eggshells. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2020, 163, 104862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Mansilla, A.; Delgado-Mejía, E. Influence of Separation Techniques with Acid Solutions on the Composition of Eggshell Membrane. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2017, 16, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Communities. European Communities First Commision Directive of 28 July 1981 Laying down Community Methods of Analysis for Verifying That Certain Additives Used in Foodstuffs Satisfy Criteria of Purity. Off. J. Eur. Communities L257 1981, 24, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Publications Office of the EU. European Union Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 of 9 March 2012 Laying Down Specifications for Food Additives Listed in Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/a42dd9b2-b63f-438b-a790-1fa5995b7d41 (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations GSFA Online Food Additive Details for Calcium Acetate. Available online: https://www.fao.org/gsfaonline/additives/details.html?id=317 (accessed on 13 May 2023).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations GSFA Online Food Additive Details for Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate. Available online: https://www.fao.org/food/food-safety-quality/scientific-advice/jecfa/jecfa-additives/details-simple/en/?ins_id=341(ii) (accessed on 13 May 2023).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Combined Compendium of Food Additive Specification; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006; Volume 4, ISBN 92-5-105569-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lizhong, W. Preparation of Food-Level Calcium Acetate by Using Egg Shell and Other Biological Waste as Raw Material. CN1274712A, 29 November 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, D.; Xin, G. Method for Producing Calcium Acetate with Egg Shell. Chinese Patent CN101172942A, 7 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-J.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Lee, M.-H.; Oh, N.-S. Highly Sinterable Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Synthesized from Eggshells. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, J.A.; Scheideler, S.E. Eggshell Derived Monocalcium and Dicalcium Phosphate. US Patent WO2002060274A1, 8 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Thoroski, J.H. Eggshell Processing Methods and Apparatus. US Patent US6649203B1, 18 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Movasaghi, Z.; Rehman, S.; ur Rehman, D.I. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy of Biological Tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2008, 43, 134–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belbachir, K.; Noreen, R.; Gouspillou, G.; Petibois, C. Collagen Types Analysis and Differentiation by FTIR Spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, S.A.; da Silva, B.C.; Riegel-Vidotti, I.C.; Urbano, A.; de Sousa Faria-Tischer, P.C.; Tischer, C.A. Production and Characterization of Bacterial Cellulose Membranes with Hyaluronic Acid from Chicken Comb. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yang, X.; Ji, Z.; Zhu, L.; Ma, N.; Chen, D.; Jia, X.; Tang, J.; Cao, Y. DFT-Calculated IR Spectrum Amide I, II, and III Band Contributions of N-Methylacetamide Fine Components. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8572–8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musumeci, A.W.; Frost, R.L.; Waclawik, E.R. A Spectroscopic Study of the Mineral Paceite (Calcium Acetate). Spectroc. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectr. 2007, 67, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, S.H.; Jun, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, H.E. Synthesis and Dissolution Behavior of Beta-TCP and HA/Beta-TCP Composite Powders. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 23, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Lugo, V.; Karthik, T.V.K.; Mendoza-Anaya, D.; Rubio-Rosas, E.; Villasenor Ceron, L.S.; Reyes-Valderrama, M.I.; Salinas-Rodriguez, E. Wet Chemical Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Hydroxyapatite Flakes: Effect of PH and Sintering Temperature on Structural and Morphological Properties. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 180962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Destainville, A.; Champion, E.; Bernache-Assollant, D.; Laborde, E. Synthesis, Characterization and Thermal Behavior of Apatitic Tricalcium Phosphate. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 80, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiers, J.L.; Bult, J.H.F. Mildly Processed Natural Eggshell Membrane Alleviates Joint Pain Associated with Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Med. Food 2021, 24, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
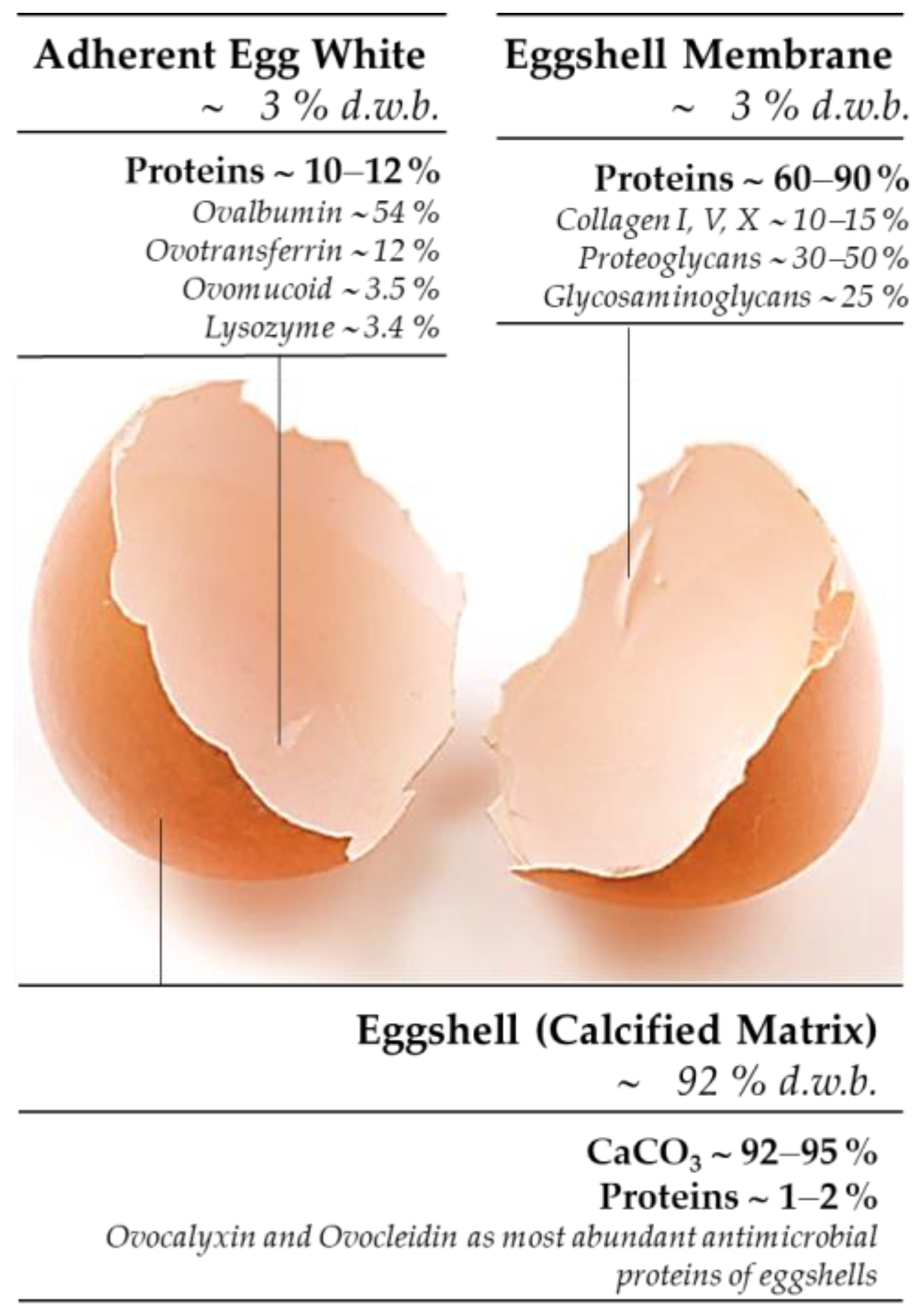



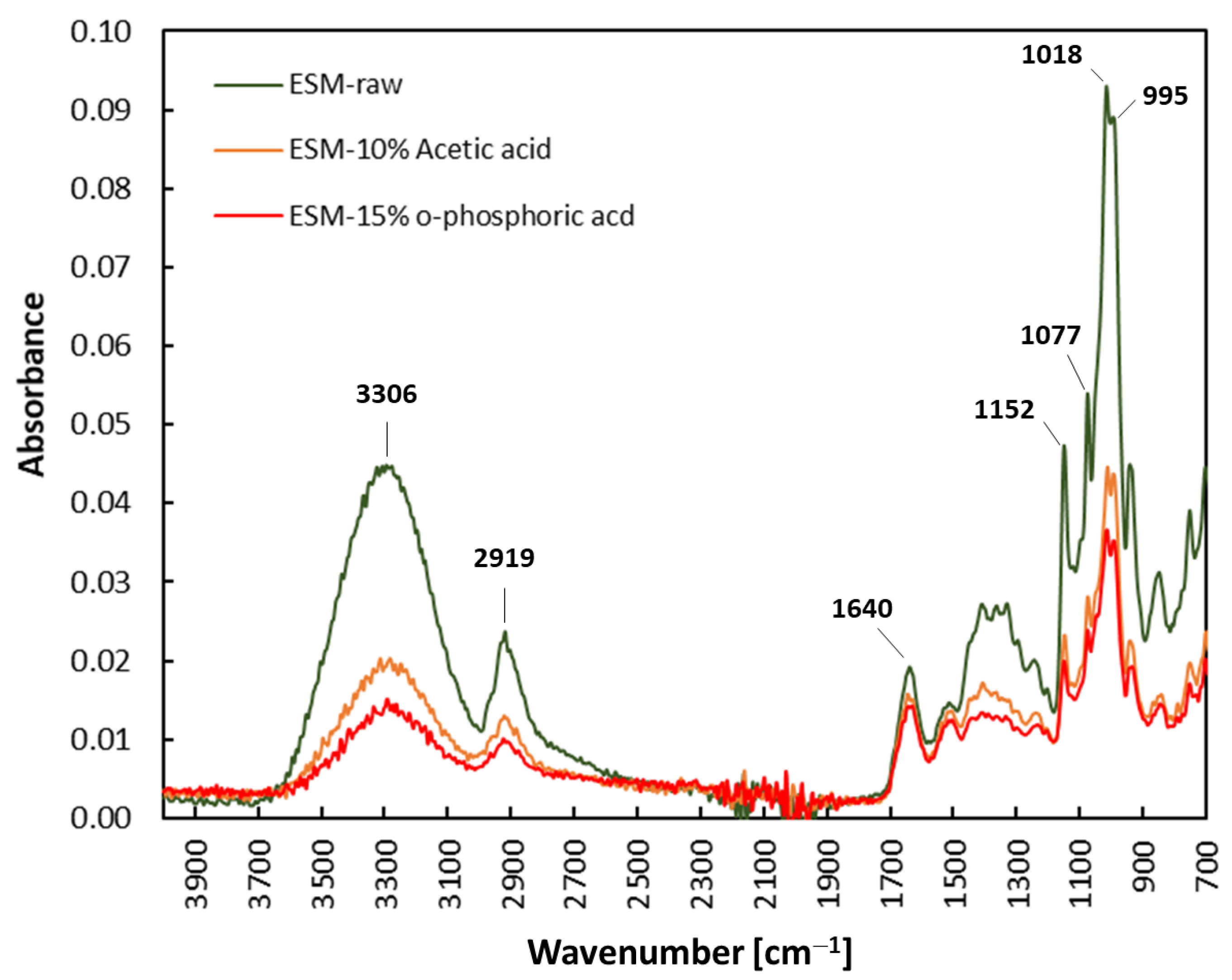

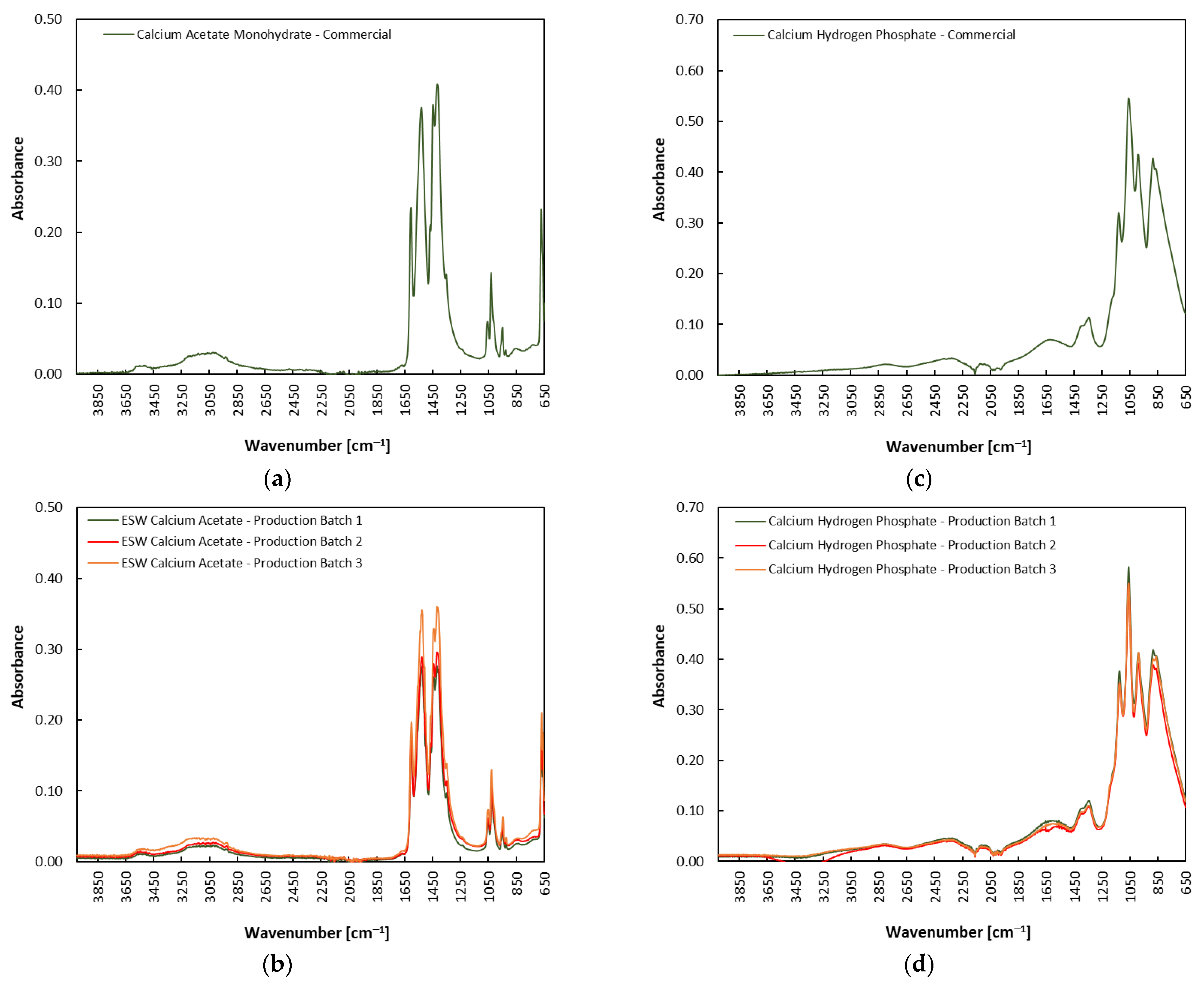
| Eggshell-Waste-Derived Product | Mass Yield [g/100 g ESW] 1,2 | Chemical Yield [%] |
|---|---|---|
| 10% (w/v) acetic-acid-derived ESM | 2.90 ± 0.14 | n. a. 3 |
| 15% (w/v) o-phosphoric-acid-derived ESM | 2.94 ± 0.08 | n. a. 3 |
| ESW-derived Calcium Acetate Monohydrate | 111.41 ± 2.13 | 79.16 ± 1.18 4 |
| ESW-derived Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate | 77.06 ± 6.21 | 71.36 ± 5.58 5 |
| Content | Raw ESM | 10% Acetic-Acid-Derived ESM | 15% o-Phosphoric-Acid-Derived ESM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry matter [g/100 g] | 91.45 ± 0.36 | 90.85 ± 0.12 | 90.45 ± 0.10 |
| Proteins [g/100 g d.w.b.] 2 | 84.26 ± 0.77 | 96.48 ± 1.75 | 93.36 ± 1.69 |
| Lipids [g/100 g d.w.b.] | 0.57 ± 0.06 | 0.42 ± 0.11 | 0.26 ± 0.09 |
| Parameter | Value | Food Additive Criteria 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Dry matter [%] | 98.78 ± 0.94 | n. c. 2 |
| Calcium [% d.w.b.] 3 | 22.46 ± 0.43 | n. c. |
| pH of 10% solution | 7.01 ± 0.26 | 6–9 |
| Soluble proteins [g/100 g d.w.b.] | 0.15 ± 0.09 | n. c. |
| Loss on Drying [%] | 2.60 ± 1.39 | <11 |
| Water insoluble [%] | 0.6 ± 0.08 | <0.3 |
| Formic acid and oxidizable impurities [mg/kg] | 4392.42 ± 337.86 | <1000 |
| Fluoride [mg/kg] | <10 | n. c. |
| As [mg/kg] | <1 | <3 |
| Pb [mg/kg] | <1 | <2 |
| Hg [mg/kg] | <0.015 | <1 |
| Parameter | Value | Food Additive Criteria 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Dry matter [%] | 99.47 ± 0.19 | n. c. 2 |
| Calcium [% d.w.b.] 3 | 25.64 ± 0.68 | n. c. |
| Calcium [% d.w.b.] 4 | 23.57 ± 0.07 | n. c. |
| Phosphorus [% d.w.b.] 4 | 17.25 ± 0.20 | n. c. |
| pH of 10% solution | 4.13 ± 0.15 | n. c. |
| Soluble proteins [g/100 g d.w.b.] | not detected | n. c. |
| Loss on Drying [%] | 1.40 ± 0.16 | <2 |
| Loss on Incineration [%] | 8.43 ± 0.31 | <8.5 (anhydrous) <26.5 (dihydrate) |
| Fluoride [mg/kg] | <10 | <50 |
| As [mg/kg] | <0.36 | <1 |
| Cd [mg/kg] | <0.04 | <1 |
| Pb [mg/kg] | <1 | <1 |
| Hg [mg/kg] | <0.01 | <1 |
| Al [mg/kg] | <26.99 | <80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strelec, I.; Tomičić, K.; Zajec, M.; Ostojčić, M.; Budžaki, S. Eggshell-Waste-Derived Calcium Acetate, Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate and Corresponding Eggshell Membranes. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7372. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137372
Strelec I, Tomičić K, Zajec M, Ostojčić M, Budžaki S. Eggshell-Waste-Derived Calcium Acetate, Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate and Corresponding Eggshell Membranes. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(13):7372. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137372
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrelec, Ivica, Klara Tomičić, Marko Zajec, Marta Ostojčić, and Sandra Budžaki. 2023. "Eggshell-Waste-Derived Calcium Acetate, Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate and Corresponding Eggshell Membranes" Applied Sciences 13, no. 13: 7372. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137372
APA StyleStrelec, I., Tomičić, K., Zajec, M., Ostojčić, M., & Budžaki, S. (2023). Eggshell-Waste-Derived Calcium Acetate, Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate and Corresponding Eggshell Membranes. Applied Sciences, 13(13), 7372. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137372







