Influence of Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction on Resorption of a Large-Volume Free-Fat Transplant Evaluated Using T3D Optical Scanning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Fat Tissue Source
2.3. Preparation of Fat Tissue for Transplantation
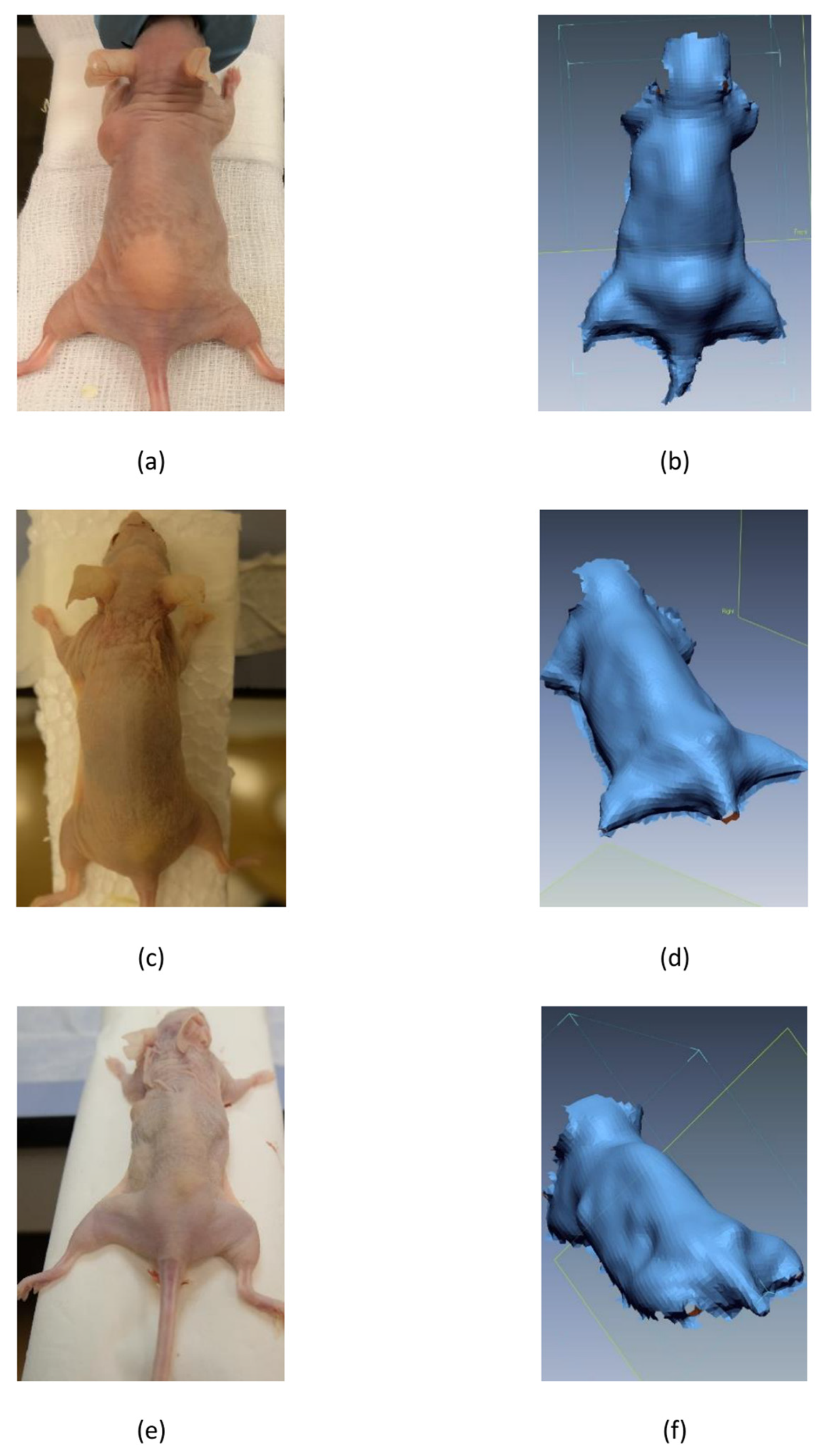
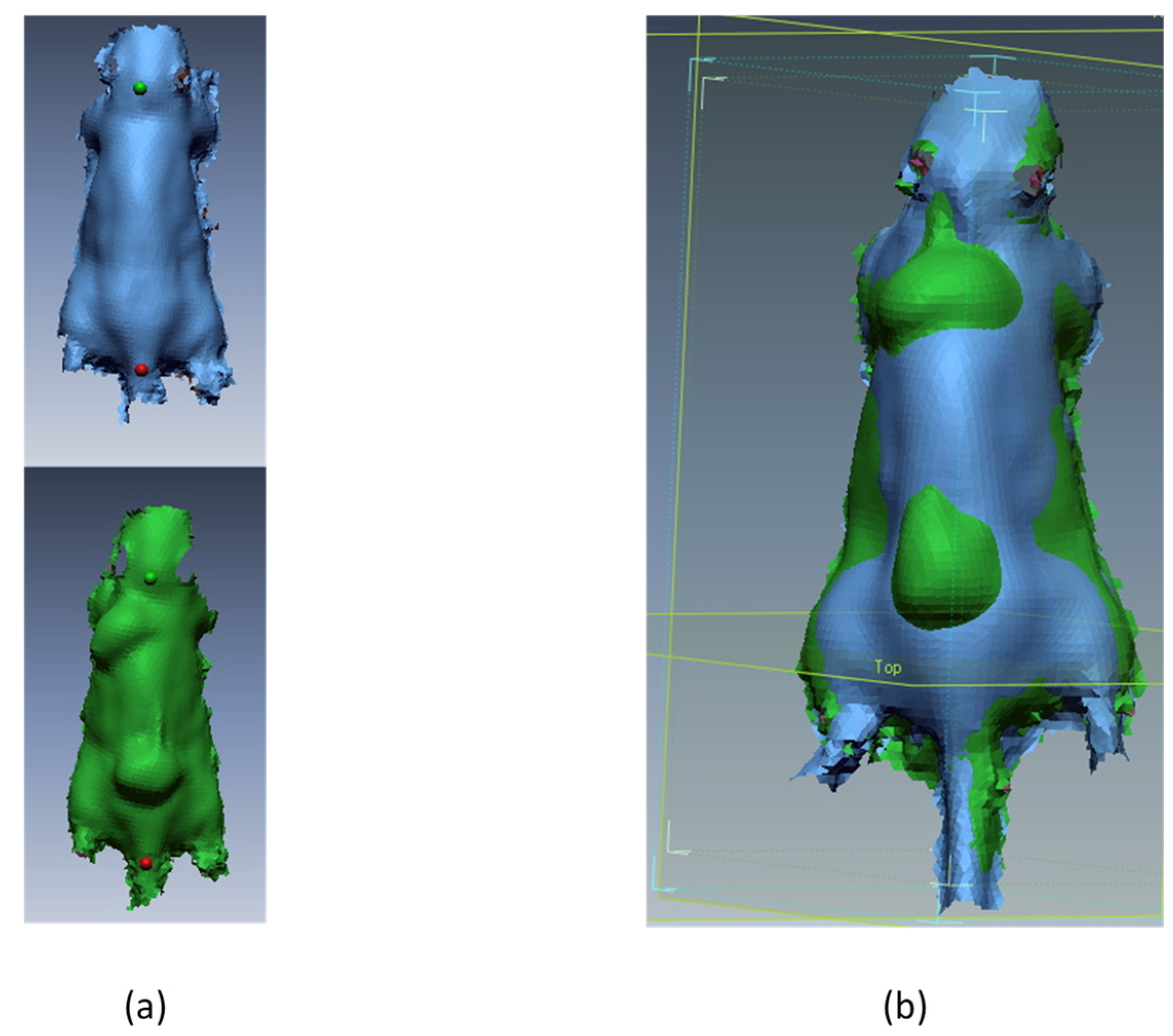
2.4. 3D Scanning
2.5. Statistical Analysis
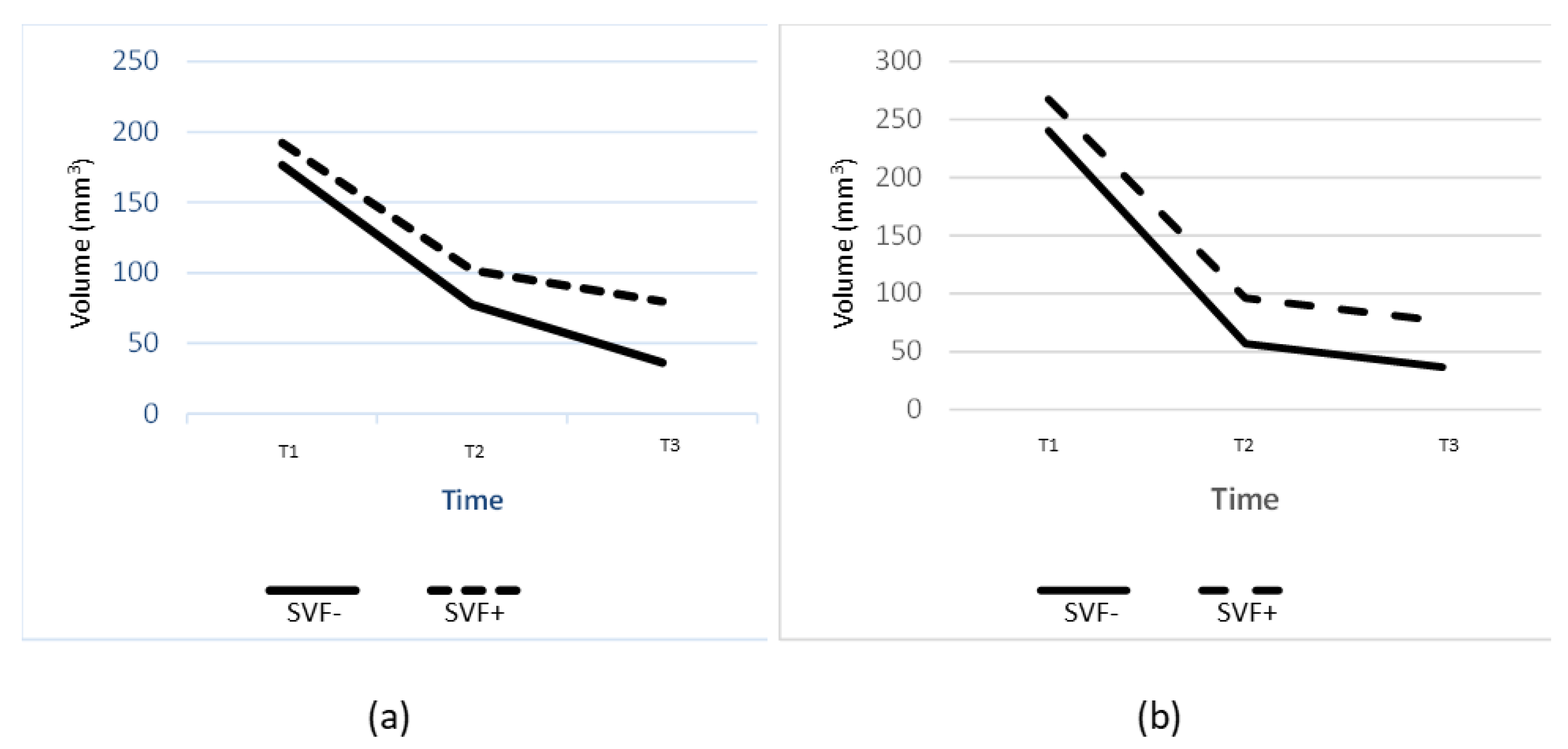
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Billings, E., Jr.; May, J.W., Jr. Historical review and present status of free fat graft autotransplantation in plastic and reconstructive surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1989, 83, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, E.; Grieco, M.P.; Raposio, E. The science behind autologous fat grafting. Ann. Med. Surg. 2017, 24, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, S.R. Structural fat grafting: More than a permanent filler. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 108s–120s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocchi, M.L.; Zuliani, F. Bicompartmental breast lipostructuring. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2008, 32, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposio, E.; Caruana, G.; Petrella, M.; Bonomini, S.; Grieco, M.P. A Standardized Method of Isolating Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for Clinical Applications. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigotti, G.; Marchi, A.; Galie, M.; Baroni, G.; Benati, D.; Krampera, M.; Pasini, A.; Sbarbati, A. Clinical treatment of radiotherapy tissue damage by lipoaspirate transplant: A healing process mediated by adipose-derived adult stem cells. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 119, 1409–1422. discussion 1423–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aust, L.; Devlin, B.; Foster, S.J.; Halvorsen, Y.D.; Hicok, K.; du Laney, T.; Sen, A.; Willingmyre, G.D.; Gimble, J.M. Yield of human adipose-derived adult stem cells from liposuction aspirates. Cytotherapy 2004, 6, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, H.; Kato, H.; Suga, H.; Aoi, N.; Doi, K.; Kuno, S.; Yoshimura, K. The fate of adipocytes after nonvascularized fat grafting: Evidence of early death and replacement of adipocytes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimble, J.M.; Katz, A.J.; Bunnell, B.A. Adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno, S.; Yoshimura, K. Condensation of Tissue and Stem Cells for Fat Grafting. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2015, 42, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, D.; Sato, K.; Gonda, K.; Takaki, Y.; Shigeura, T.; Sato, T.; Aiba-Kojima, E.; Iizuka, F.; Inoue, K.; Suga, H.; et al. Cell-assisted lipotransfer: Supportive use of human adipose-derived cells for soft tissue augmentation with lipoinjection. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 3375–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gormley, D.E.; Eremia, S. Quantitative Assessment of Augmentation Therapy. J. Dermatol. Surg. Oncol. 1990, 16, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niechajev, I.; Sevcuk, O. Long-term results of fat transplantation: Clinical and histologic studies. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1994, 94, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, L.A. Loss of Weight and Volume in Human Fat Grafts: With Postulation of A “Cell Survival Theory”. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1950, 5, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.H.; Radwanski, H.N. Fat grafting of the buttocks and lower limbs. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 1996, 20, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpaneda, C.A.; Ribeiro, M.T. Percentage of graft viability versus injected volume in adipose autotransplants. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 1994, 18, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillaert, F.; Findlay, M.; Palmer, J.; Idrizi, R.; Cheang, S.; Messina, A.; Abberton, K.; Morrison, W.; Thompson, E.W. Host rather than graft origin of Matrigel-induced adipose tissue in the murine tissue-engineering chamber. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 2291–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolle, S.F.; Fischer-Nielsen, A.; Mathiasen, A.B.; Elberg, J.J.; Oliveri, R.S.; Glovinski, P.V.; Kastrup, J.; Kirchhoff, M.; Rasmussen, B.S.; Talman, M.L.; et al. Enrichment of autologous fat grafts with ex-vivo expanded adipose tissue-derived stem cells for graft survival: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2013, 382, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frueh, F.S.; Später, T.; Scheuer, C.; Menger, M.D.; Laschke, M.W. Isolation of Murine Adipose Tissue-Derived Microvascular Fragments as Vascularization Units for Tissue Engineering. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 55721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Li, X.; Qi, Y.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, G.-e. Volume Retention after Facial Fat Grafting and Relevant Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2021, 45, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.L.Q.; Coleman, S.R.; Cui, X.; Ferguson, R.E.H., Jr.; Vasconez, H.C. Autologous fat grafts harvested and refined by the Coleman technique: A comparative study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolderer, J.H.; Thompson, E.W.; Slavin, J.; Trost, N.; Cooper-White, J.J.; Cao, Y.; O’Connor, A.J.; Penington, A.; Morrison, W.A.; Abberton, K.M. Long-term stability of adipose tissue generated from a vascularized pedicled fat flap inside a chamber. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkham, J.C.; Lee, J.H.; Medina, M.A., 3rd; McCormack, M.C.; Randolph, M.A.; Austen, W.G., Jr. The impact of liposuction cannula size on adipocyte viability. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2012, 69, 479–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsoy, Z.; Kul, Z.; Bilir, A. The role of cannula diameter in improved adipocyte viability: A quantitative analysis. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2006, 26, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivisonno, A.; Di Rocco, G.; Cannistra, C.; Finocchi, V.; Torres Farr, S.; Monti, M.; Toietta, G. Harvest of superficial layers of fat with a microcannula and isolation of adipose tissue-derived stromal and vascular cells. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2014, 34, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condé-Green, A.; de Amorim, N.F.; Pitanguy, I. Influence of decantation, washing and centrifugation on adipocyte and mesenchymal stem cell content of aspirated adipose tissue: A comparative study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. JPRAS 2010, 63, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallua, N.; Pulsfort, A.K.; Suschek, C.; Wolter, T.P. Content of the growth factors bFGF, IGF-1, VEGF, and PDGF-BB in freshly harvested lipoaspirate after centrifugation and incubation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 123, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonacci, F.; Bertozzi, N.; Grieco, M.P.; Grignaffini, E.; Raposio, E. Procedure, applications, and outcomes of autologous fat grafting. Ann. Med. Surg. 2017, 20, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, O.; Karakol, P.; Bozkurt, M.; Tuglu, M.I. The Effect of Centrifuge Duration on Fat Graft Survival. Indian J. Plast. Surg. Off. Publ. Assoc. Plast. Surg. India 2023, 56, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.; Suga, H.; Eto, H. Adipose-derived stem/progenitor cells: Roles in adipose tissue remodeling and potential use for soft tissue augmentation. Regen. Med. 2009, 4, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Ogawa, R.; Ou, C.; Yang, B.; Fu, B. Improvement of the survival of human autologous fat transplantation by using VEGF-transfected adipose-derived stem cells. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.; Sato, K.; Aoi, N.; Kurita, M.; Hirohi, T.; Harii, K. Cell-assisted lipotransfer for cosmetic breast augmentation: Supportive use of adipose-derived stem/stromal cells. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2008, 32, 48–55. discussion 56–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domergue, S.; Bony, C.; Maumus, M.; Toupet, K.; Frouin, E.; Rigau, V.; Vozenin, M.C.; Magalon, G.; Jorgensen, C.; Noel, D. Comparison between Stromal Vascular Fraction and Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Remodeling Hypertrophic Scars. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Park, M.; Kang, L.W.; Lee, S.H. Current use of autologous adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction cells for orthopedic applications. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, M.J.; Birnbaum, Z.E.; Kurtz, L.G.; Aronowitz, J.A. Review: Proposed Methods to Improve the Survival of Adipose Tissue in Autologous Fat Grafting. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2018, 6, e1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.; Sato, K.; Aoi, N.; Kurita, M.; Inoue, K.; Suga, H.; Eto, H.; Kato, H.; Hirohi, T.; Harii, K. Cell-assisted lipotransfer for facial lipoatrophy: Efficacy of clinical use of adipose-derived stem cells. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2008, 34, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Schreiber, R.; Ransom, J.T.; Fraser, J.K.; Hedrick, M.H.; Pinkernell, K.; Kuo, H.C. Supplementation of fat grafts with adipose-derived regenerative cells improves long-term graft retention. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2010, 64, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, S.L.; Wilson, H.B.; Lockwood, M.D. Fat injection to correct contour deformities in the reconstructed breast. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 116, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, P.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, C.; Huang, R.; Liu, K.; Li, Q. The second fat graft has significantly better outcome than the first fat graft for Romberg syndrome: A study of three-dimensional volumetric analysis. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. JPRAS 2016, 69, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, L.A. Cell Survival Theory versus Replacement Theory. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1955, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdenik, M.; Ihan Hren, N. Differences in three-dimensional soft tissue changes after upper, lower, or both jaw orthognathic surgery in skeletal class III patients. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 43, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettl, S.; Arold, O.; Yang, Z.; Häusler, G. Flying triangulation—An optical 3D sensor for the motion-robust acquisition of complex objects. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübbers, H.T.; Medinger, L.; Kruse, A.; Grätz, K.W.; Matthews, F. Precision and accuracy of the 3dMD photogrammetric system in craniomaxillofacial application. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2010, 21, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, O.M.; Small, K.H.; Unger, J.G.; Feldman, D.L.; Kumar, N.; Choi, M.; Karp, N.S. 3D analysis of breast augmentation defines operative changes and their relationship to implant dimensions. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2009, 62, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, C.; Ueberreiter, K.; Busche, M.N.; Vogt, P.M. Autologous Fat Transplantation: Volumetric Tools for Estimation of Volume Survival. A Systematic Review. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2013, 37, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, G.; Bertozzi, N.; Boschi, E.; Grieco, M.; Grignaffini, E.; Raposio, E. Role of adipose-derived stem cells in chronic cutaneous wound healing. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2015, 86, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bowles, A.; Strong, A.; Wise, R.; Thomas, R.; Gerstein, B.; Dutreil, M.; Hunter, R.; Gimble, J.; Bunnell, B. Adipose Stromal Vascular Fraction-Mediated Improvements at Late-Stage Disease in a Murine Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Stem Cells 2016, 35, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SundarRaj, S.; Deshmukh, A.; Priya, N.; Krishnan, V.S.; Cherat, M.; Majumdar, A.S. Development of a System and Method for Automated Isolation of Stromal Vascular Fraction from Adipose Tissue Lipoaspirate. Stem Cells Int. 2015, 2015, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; He, X.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, M.; Du, H.; Zhong, X. Effect of fat particle-to-SVF ratio on graft survival rates in rabbits. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2015, 74, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delay, E.; Garson, S.; Tousson, G.; Sinna, R. Fat injection to the breast: Technique, results, and indications based on 880 procedures over 10 years. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2009, 29, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panettiere, P.; Accorsi, D.; Marchetti, L.; Sgro, F.; Sbarbati, A. Large-breast reconstruction using fat graft only after prosthetic reconstruction failure. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2011, 35, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, L.A. The neglected free fat graft, its behavior and clinical use. Am. J. Surg. 1956, 92, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouri, R.K.; Rigotti, G.; Cardoso, E.; Khouri, R.K., Jr.; Biggs, T.M. Megavolume autologous fat transfer: Part I. Theory and principles. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 133, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boemi, I.; Lisa, A.V.E.; Vitali, E.; Liman, N.; Battistini, A.; Barbera, F.; Maione, L.; Vinci, V.; Klinger, M.E.A.; Lania, A.G.A. Evaluation of the Ex Vivo Effects of Tamoxifen on Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: A Pilot Study. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 555248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, B.S.; Lykke Sorensen, C.; Vester-Glowinski, P.V.; Herly, M.; Trojahn Kolle, S.F.; Fischer-Nielsen, A.; Drzewiecki, K.T. Effect, Feasibility, and Clinical Relevance of Cell Enrichment in Large Volume Fat Grafting: A Systematic Review. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2017, 37, S46–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullmann, Y.; Hyams, M.; Ramon, Y.; Beach, D.; Peled, I.J.; Lindenbaum, E.S. Enhancing the Survival of Aspirated Human Fat Injected into Nude Mice. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1998, 101, 1940–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, L.L.; Li, J.X.; Liu, H.W.; Li, S.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; Liao, X.; Rao, C.Q. Improved fat transplantation survival by using the conditioned medium of vascular endothelial growth factor transfected human adipose-derived stem cells. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieck, B.; Schlaak, S. Measurement in vivo of the survival rate in autologous adipocyte transplantation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2003, 111, 2315–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervelli, D.; Gasparini, G.; Grussu, F.; Moro, A.; Matteo Marianetti, T.; Foresta, E.; Azzuni, C.; Pelo, S. Autologous fat transplantation for the temporalis muscle flap donor site: Our experience with 45 cases. Head Neck 2014, 36, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SVF- | SVF+ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | |
| Scapula region | ||||||
| Mean (mm3) | 176.6 | 77.5 | 36.2 | 192.3 | 101.8 | 79.6 |
| SD | 64.5 | 43.9 | 22.2 | 70.6 | 24.0 | 35.7 |
| n | 12 | 12 | 10 | 13 | 12 | 12 |
| Sacrum region | ||||||
| Mean (mm3) | 240.6 | 56.8 | 36.7 | 286.8 | 96.1 | 70.3 |
| SD | 93.7 | 30.5 | 33.0 | 90.2 | 43.5 | 29.1 |
| n | 14 | 12 | 10 | 14 | 13 | 12 |
| Animal weight | ||||||
| Mean (g) | 26.1 | 27.7 | 28.1 | 25.4 | 27.3 | 26.0 |
| SD | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 2.9 |
| n | 14 | 12 | 10 | 14 | 13 | 12 |
| p-Value SVF-:SVF+ | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Border | Upper Border | ||
| Scapula region | |||
| T1 | 0.56 | −72.15 | 40.09 |
| T2 | 0.11 | −54.30 | 5.65 |
| T3 | 0.003 | −70.45 | −16.19 |
| Sacrum region | |||
| T1 | 0.2 | −117.76 | 25.29 |
| T2 | 0.01 | −68.87 | −9.69 |
| T3 | 0.02 | −59.86 | −7.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koren, M.; Brezar, S.K.; Dovšak, T.; Sersa, G.; Kansky, A.; Ihan Hren, N. Influence of Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction on Resorption of a Large-Volume Free-Fat Transplant Evaluated Using T3D Optical Scanning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127100
Koren M, Brezar SK, Dovšak T, Sersa G, Kansky A, Ihan Hren N. Influence of Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction on Resorption of a Large-Volume Free-Fat Transplant Evaluated Using T3D Optical Scanning. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(12):7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127100
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoren, Matic, Simona Kranjc Brezar, Tadej Dovšak, Gregor Sersa, Andrej Kansky, and Nataša Ihan Hren. 2023. "Influence of Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction on Resorption of a Large-Volume Free-Fat Transplant Evaluated Using T3D Optical Scanning" Applied Sciences 13, no. 12: 7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127100
APA StyleKoren, M., Brezar, S. K., Dovšak, T., Sersa, G., Kansky, A., & Ihan Hren, N. (2023). Influence of Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction on Resorption of a Large-Volume Free-Fat Transplant Evaluated Using T3D Optical Scanning. Applied Sciences, 13(12), 7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127100






