Study on Cl− Erosion of Concrete under the Combined Effect of Fatigue Load and Wet–Dry Cycles: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Coupling Action of Fatigue Load and Cl− Erosion
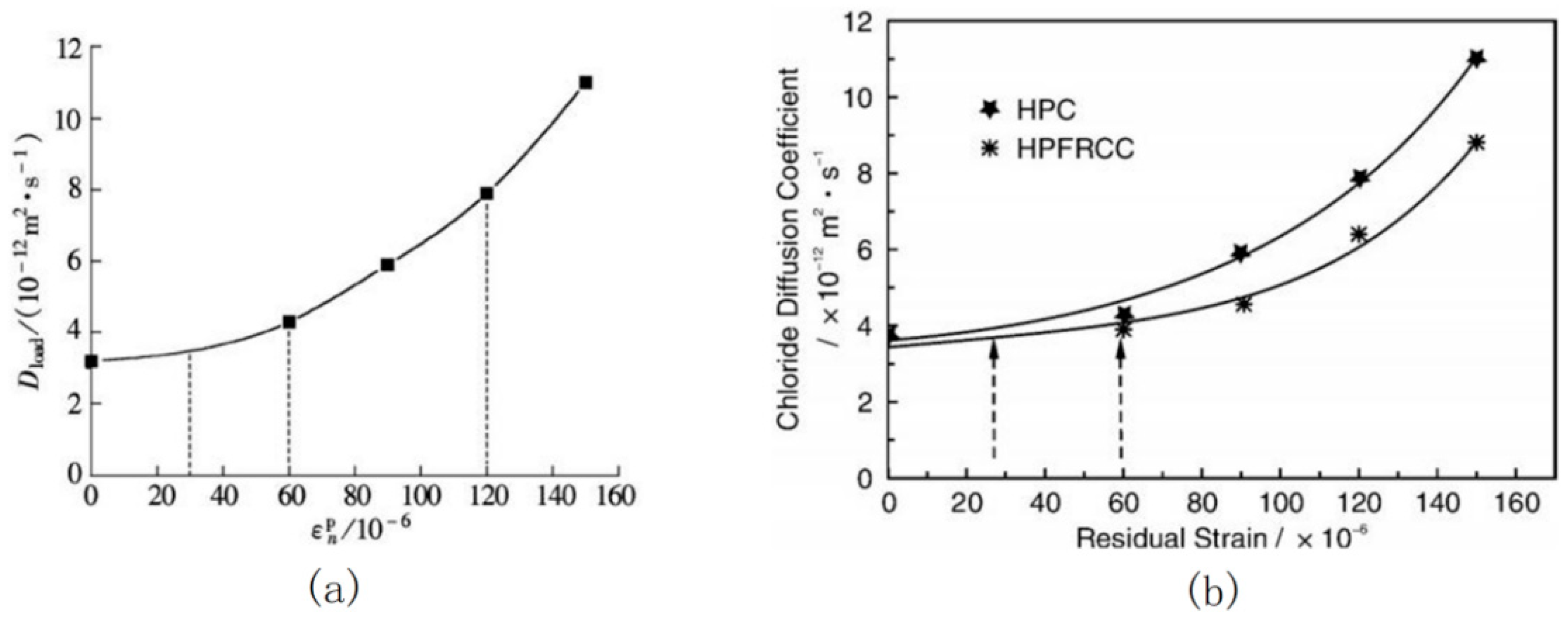
2.1. Transport Properties of Cl− under Fatigue Loading
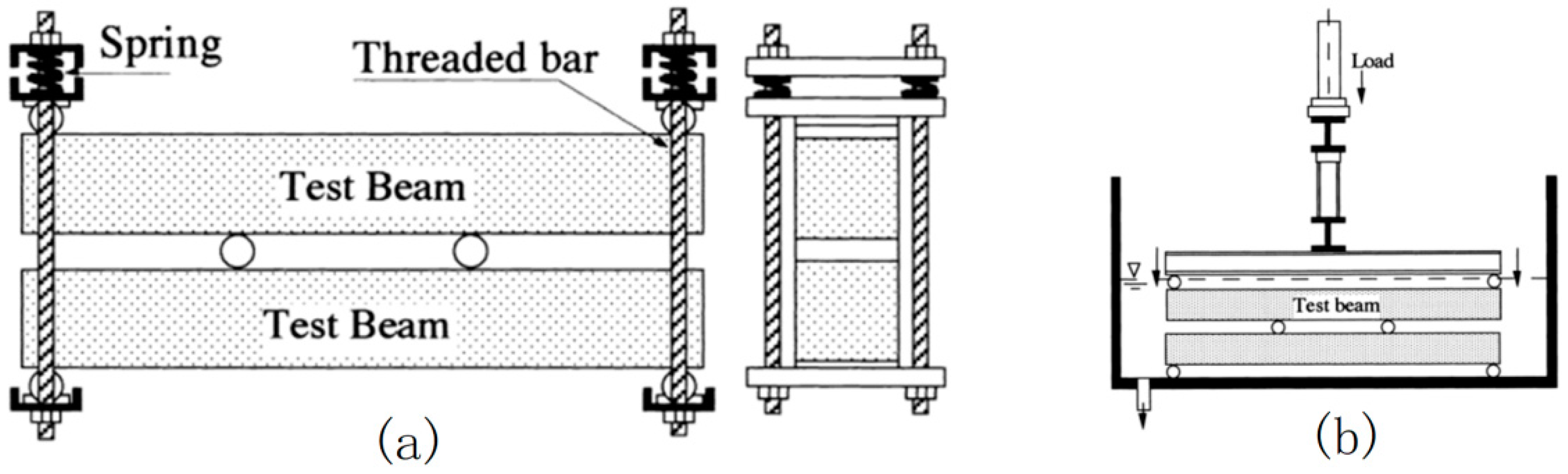
2.2. Durability Performance of Reinforced Concrete under Fatigue Load Coupled with Cl−
3. Coupling of Dry–Wet Cycles and Cl−
3.1. Transport Properties of Cl− under the Action of Dry–Wet Cycles
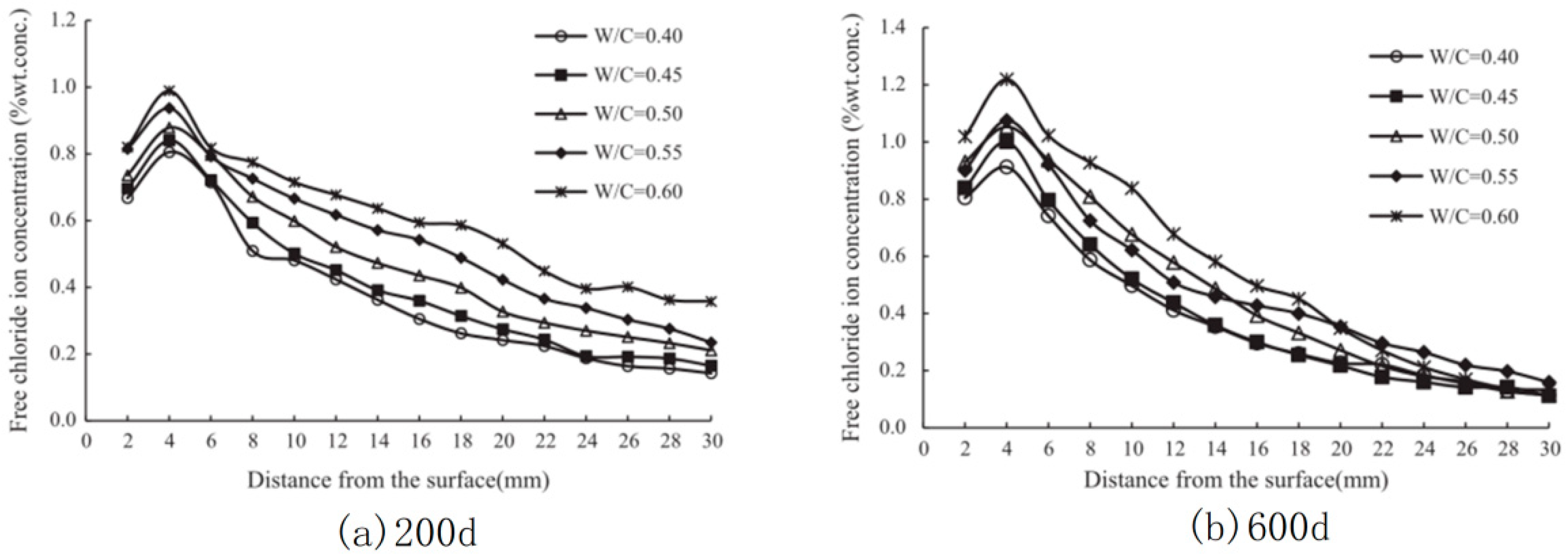
3.2. Durability Performance of Reinforced Concrete under the Coupling Action of Dry–Wet Cycles and Cl− Erosion
4. Durability of Concrete under Dry–Wet Cycles, Fatigue Load, and Cl− Erosion
5. Conclusions and Further Reflections
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neville, A. Chloride attack of reinforced concrete: An overview. Mater. Struct. 1995, 28, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xie, N.; Fortune, K.; Gong, J. Durability of steel reinforced concrete in chloride environments: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, L.; Elsener, B.; Pedeferri, P.; Redaelli, E.; Polder, R.B. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete: Prevention, Diagnosis, Repair; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hoseini, M.; Bindiganavile, V.; Banthia, N. The effect of mechanical stress on permeability of concrete: A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.J.; Zhang, W.M.; Gao, X.J. Influence of Water to Cement Ratio and Stress Level on Chloride Penetration Resistance of Concrete. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2006, 28, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.M.; Ba, H.J.; Gao, X.J. CInfluence of fly ash and stress level on permeability of concrete. J. Jiangsu Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2008, 29, 356–359. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.H. Experimental Study on Permeability of Concrete under Cyclic Loadings. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Lv, Y.G.; Yu, Z.J. Experimental Study on Diffusion Behavior of Chlorine Ion in Concrete Subjected to Fatihue Loading. J. Exp. Mech. 2017, 32, 517–524. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q. Investigation on water absorption in concrete after subjected to compressive fatigue loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, G.; Maso, J.C. Microstructure evolution of concrete under low-frequency cyclic loading: Determination of the porosity variations. In Fracture 84; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1984; pp. 2817–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Q.Y.; Sun, J.Z.; Liu, X.L. Chloride ion diffusion of structural concrete under the coupled effect of bending fatigue load and chloride. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19 (Suppl. 1), S1-181–S1-184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, A.; Lyu, Z.; Guo, Y. Investigations of chloride ions permeability of pavement concrete under coupled effect of fatigue loading and hydrodynamic pressure. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 23, 1659–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.T.; Lu, X.Y.; Miao, Y.Y.; Zhou, Y. Diffusion of chloride ions into fatiigue-damaged concrete in salt spray environment. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2015, 47, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhi, A.E.; Xi, Y.; Willam, K.; Frangopol, D.M. The effect of fatigue loading on chloride penetration in non-saturated concrete. In Proceedings of the European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering, Barcelona, Spain, 11–14 September 2000; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gontar, W.A.; Martin, J.P.; Popovics, J.S. Effects of cyclic loading on chloride permeability of plain concrete. In Condition Monitoring of Materials and Structures, Proceedings of the Engineering Mechanics Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 21–24 May 2000; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2000; pp. 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.M.; Stitmannaithum, B.; Nawa, T. Prediction of chloride diffusion coefficient of concrete under flexural cyclic load. Comput. Concr. 2011, 8, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. Resistance to chloride ion diffusion of structural concrete under bending fatigue load. J. Southeast Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2010, 40, 362–366. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Jiang, J.Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.H. Resistance to Chloride Ion Diffusion of HPC and HPFRCC under Bending Fatigue Load. Mater. China 2009, 28, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Horii, H.; Shin, H.C.; Pallewatta, T.M. Mechanism of fatigue crack growth in concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1992, 14, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, B.; Marchand, J. Influence of cracking on the diffusion properties of cement-based materials: Part I: Influence of continuous cracks on the steady-state regime. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, F. Analytical model for load dependence of chloride penetration into concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04016279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Guan, B.; Liu, G.; Jia, Y. Modeling of chloride ion diffusion in concrete under fatigue loading. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Zhao, R. Reliability evaluation of chloride diffusion in fatigue damaged concrete. Eng. Struct. 2007, 29, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hime, W.G.; Backus, L.A.; Li, C.Q. Modeling time-to-corrosion cracking in chloride contaminated reinforced concrete structures. Discussions and closure. ACI Mater. J. 1999, 96, 611–613. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, W.; Reddy, D.V. Galvanostatic testing for the durability of marine concrete under fatigue loading. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Diao, B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, W. Effects of the reinforcement ratio and chloride corrosion on the fatigue behavior of RC beams. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 131, 105299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, S.; Yin, X.; Cao, Z. Experimental study on fatigue performance of reinforced concrete beams in corrosive environment with cyclic loads. Struct. Durab. Health Monit. 2020, 14, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Meng, X.H.; Liu, Y. Research on residual strength of concrete under fatigue loading and corrosion of chloride. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 94, 1369–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Fang, C.; Parsaeimaram, M.; Yang, S. Cyclic behavior of corroded reinforced concrete bridge piers. J. Bridge Eng. 2017, 22, 04017020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Li, H.; Ba, X.; Guan, X.; Li, H. Experimental investigation on the cyclic performance of reinforced concrete piers with chloride-induced corrosion in marine environment. Eng. Struct. 2015, 105, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nanukuttan, S.V.; Basheer, P.A.; Bai, Y. Influence of micro and macro cracks due to sustained loading on chloride-induced corrosion of reinforced concrete beams. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Durability of Concrete Structures, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 24–26 July 2014; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Jin, N.; Ye, H.; Jin, X.; Dai, W. Corrosion characteristics of a 4-year naturally corroded reinforced concrete beam with load-induced transverse cracks. Corros. Sci. 2017, 117, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, L.; Mancini, G.; Tondolo, F. Reinforced concrete members subjected to cyclic tension and corrosion. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2011, 9, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffer, S.J.; Hansson, C.M. The influence of cracks on chloride-induced corrosion of steel in ordinary Portland cement and high performance concretes subjected to different loading conditions. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 3343–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffer, S.J.; Hansson, C.M. Chloride-induced corrosion products of steel in cracked-concrete subjected to different loading conditions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.K. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Chloride Transport and Steel Corrosion under the Coupling of Chloride and Fatigue Load. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.S.; Lepech, M.D.; Kiremidjian, A.S.; Sun, X.-Y. Simplified structural deterioration model for reinforced concrete bridge piers under cyclic loading. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 13, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurumatani, M.; Anzo, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Okazaki, S.; Hirose, S. Damage model for simulating chloride concentration in reinforced concrete with internal cracks. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 84, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorato, D.; Fiorentino, G.; Pelle, A.; Rasulo, A.; Bergami, A.V.; Briseghella, B.; Nuti, C. A corrosion model for the interpretation of cyclic behavior of reinforced concrete sections. Struct. Concr. 2020, 21, 1732–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Q.; Liu, L.X.; Dai, D.H. Experimental study of concrete corroding in brine and fresh water under dry-wet circulation. J. Qinghai Univ. 2006, 2006, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Ma, X.; Fang, L.; Zhang, J. Effects of additives on water permeability and chloride diffusivity of concrete under marine tidal environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 320, 126217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, C.; Bioubakhsh, S.; Vassie, P. Chloride penetration in concrete subject to wet/dry cycling: Influence of moisture content. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Struct. Build. 2014, 167, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polder, R.B.; Peelen WH, A. Characterisation of chloride transport and reinforcement corrosion in concrete under cyclic wetting and drying by electrical resistivity. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2002, 24, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, E.P.; Geiker, M.R. Chloride diffusion in partially saturated cementitious material. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Mei, K.; Xue, Q.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L. Study on the process of chloride invasion and deposition in concrete under dry-wet cycles and continuous loading. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Surakarta, Indonesia, 24–25 August 2021; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 861, p. 072013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhuang, H.-X.; Zhang, J.-Z. Time dependence and similarity analysis of peak value of chloride concentration of concrete under the simulated chloride environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 181, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xing, F.; Dong, B.Q.; Ma, H.Y.; Pan, D. New equation for description of chloride ions diffusion in concrete under shallow immersion condition. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Mu, S.; Xie, D.; Wang, P. Influence of pore structure and moisture distribution on chloride “maximum phenomenon” in surface layer of specimens exposed to cyclic drying-wetting condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.H.; Sun, Y.Y. Cl-penetration resistance of concrete with nano-particles under the action of dry-wet cycle. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2019, 51, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Gao, Y.; Cui, Z.; Liu, R. Experimental analysis of chloride penetration into concrete subjected to drying–wetting cycles. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04015036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xu, K.; Su, Y.B.; Wang, Y.M. Transport Characteristics of Chloride Ion in Concrete under Dry-Wet Cycles. J. Build. Mater. 2014, 17, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, K.; Hooton, R.D. Effects of cyclic chloride exposure on penetration of concrete cover. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutrisno, W.; Suprobo, P.; Wahyuni, E. Experimental Test of Chloride Penetration in Reinforced Concrete Subjected to Wetting and Drying Cycle. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2016, 851, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Heede, P.; De Keersmaecker, M.; Elia, A.; Adriaens, A.; De Belie, N. Service life and global warming potential of chloride exposed concrete with high volumes of fly ash. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 80, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.H.; Jang, S.Y. Effects of material and environmental parameters on chloride penetration profiles in concrete structures. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababneh, A.; Benboudjema, F.; Xi, Y. Chloride penetration in nonsaturated concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2003, 15, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soive, A.; Tran, V.Q.; Baroghel-Bouny, V. Requirements and possible simplifications for multi-ionic transport models–Case of concrete subjected to wetting-drying cycles in marine environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Jun, W.; Jing, Y. Model analysis of the transportation of chloride into concrete under dry-wet cyclic conditions. Int. J. Model. Identif. Control 2009, 7, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Jin, N.; Jin, X.; Fu, C. Model of chloride penetration into cracked concrete subject to drying–wetting cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Tian, Y.; Jin, N.; Jin, X.; Fu, C. Influence of cracking on chloride diffusivity and moisture influential depth in concrete subjected to simulated environmental conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, F.G.; Ma, X.X.; Ding, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, X. Durability analysis of RC piles exposed naturally in coastal saline soil environment for 17 years. Build. Struct. 2011, 41, 148–151+144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.F.; Chen, C.; Yu, B. Multi-factor Time-varying Model of M arine Environmental Action on Concrete in Splash Zone. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 47, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.T.; Liu, S.Q.; Niu, D.T.; Xu, W. Critical Chloride Concentration of Rebar Corrosion under Dry-Wet Cycles. J. Build. Mater. 2016, 19, 385–389. [Google Scholar]
- Yuma, K.; Tomoda, Y.; Ohtsu, M. AE monitoring of corrosion process in cyclic wet–dry test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2353–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, T.; Dong, R.Z. Influencing research of chloride on reinforced concrete material under dry-wet cycle. Concrete 2010, 224, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.W.; Xie, J.H.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.-L. Bond-slip behaviors of BFRP-to-concrete interfaces exposed to wet/dry cycles in chloride environment. Compos. Struct. 2019, 219, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, S.-P.; Lv, H.-L. Performance of interface between TRC and existing concrete under a chloride dry-wet cycle environment. J. Cent. South Univ. 2020, 27, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, M.; Golden, G.; Alexander, M.G.; Beushausen, H. Acceleration of steel corrosion in concrete by cyclic wetting and drying: Effect of drying duration and concrete quality. Mater. Struct. 2019, 52, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.C.; van Zijl GP, A.G.; Babafemi, A.J.; Tan, M.J. Chloride ingress in cracked and uncracked SHCC under cyclic wetting-drying exposure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käthler, C.B.; Angst, U.M.; Ebell, G.; Elsener, B. Chloride-induced reinforcement corrosion in cracked concrete: The influence of time of wetness on corrosion propagation. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlström, J.; Tidblad, J.; Sederholm, B.; Wadsö, L. Influence of chloride and moisture content on steel rebar corrosion in concrete. Mater. Corros. 2016, 67, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.R. Effect of moisture variation on oxygen consumption rate of corroding steel in chloride contaminated concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T. Electrochemical behavior of steel in concrete under wet and dry condition with NaCl solution. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Ann, K.Y. Corrosion risk of reinforced concrete structure arising from internal and external chloride. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 8, 7539349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, R. Experimental studies on chloride penetration and steel corrosion in cracked concrete beams under drying-wetting cycles. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Lin, C. Chloride diffusion analysis of concrete members considering depth-dependent diffusion coefficients and effect of reinforcement presence. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28, 04015183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Kim, M.W. Evaluate the concrete mix by type accelerated corrosion test and chloride penetration analysis with artificial seawater cyclic wet and dry condition. J. Korean Recycl. Constr. Resour. Inst. 2013, 1, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, Z. Numerical modeling for predicting service life of reinforced concrete structures exposed to chloride environments. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ming, J.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y. Corrosion performance of reinforcing steel in concrete under simultaneous flexural load and chlorides attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Ye, H.; Jin, X.; Yan, D.; Jin, N.; Peng, Z. Chloride penetration into concrete damaged by uniaxial tensile fatigue loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Diao, B.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J. Effects of pre-fatigue damage on high-cycle fatigue behavior and chloride permeability of RC beams. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 122, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Diao, B.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D. Chloride diffusivity and service life prediction of fatigue damaged RC beams under seawater wet-dry environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Transport model of chloride ions in concrete under loads and drying-wetting cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Jia, K.; Wu, F.; Chen, W.; Zhu, D. Corrosion cracking process of reinforced concrete under the coupled effects of chloride and fatigue loading. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 3376–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Diao, B.; Ye, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, X. Impact of cyclic loading on chloride diffusivity and mechanical performance of RC beams under seawater corrosion. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1687–8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; Diao, B.; Wu, J.Q. Effect of load upper limit and loading cycles on chloride diffusion of fatigue damaged RC beans. In Proceedings of the 28th National Conference on Structrual Engineering (No.III), Nanchang, China, 19–20 October 2019; pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Z.J.; Zheng, X.N. Experimental study on chloride ion diffusion of fatigue damaged RC beams in seawater wet-dry cycles. J. Build. Struct. 2015, 36, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Wu, J.; Yang, T.; Xu, A.-H.; Sheng, Y.-P.; Chen, H.-X. Developing a model for chloride ions transport in cement concrete under dynamic flexural loading and dry-wet cycles. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 5760512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcherdchoo, A. Closed-form solutions for modeling chloride transport in unsaturated concrete under wet-dry cycles of chloride attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. Probabilistic life prediction for reinforced concrete structures subjected to seasonal corrosion-fatigue damage. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
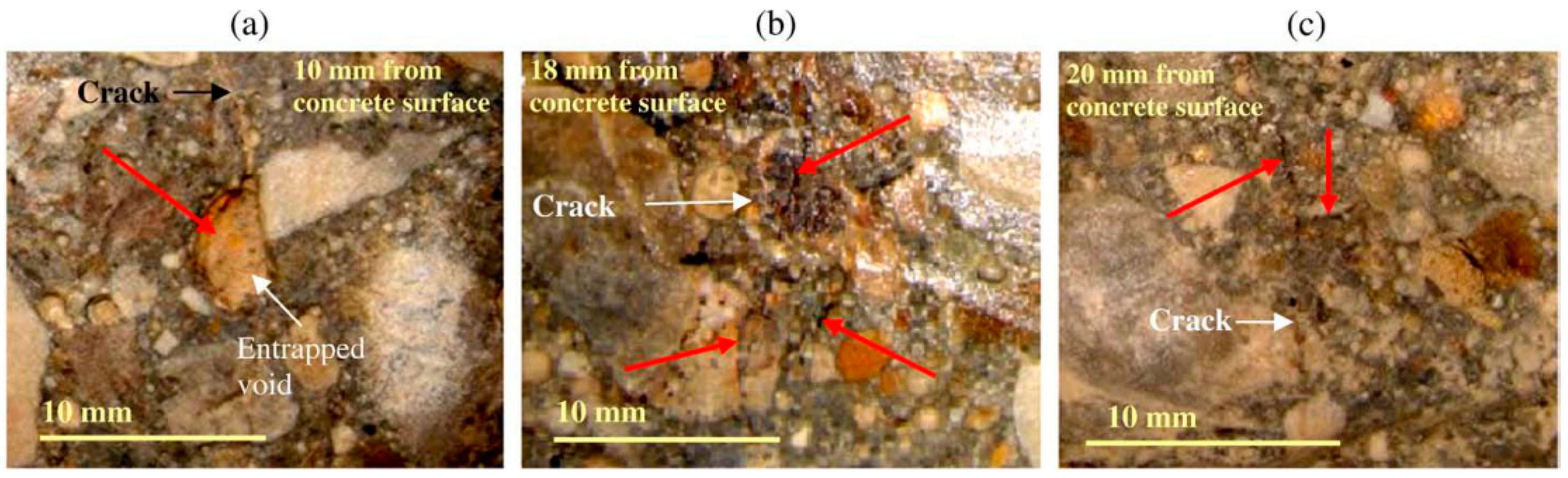



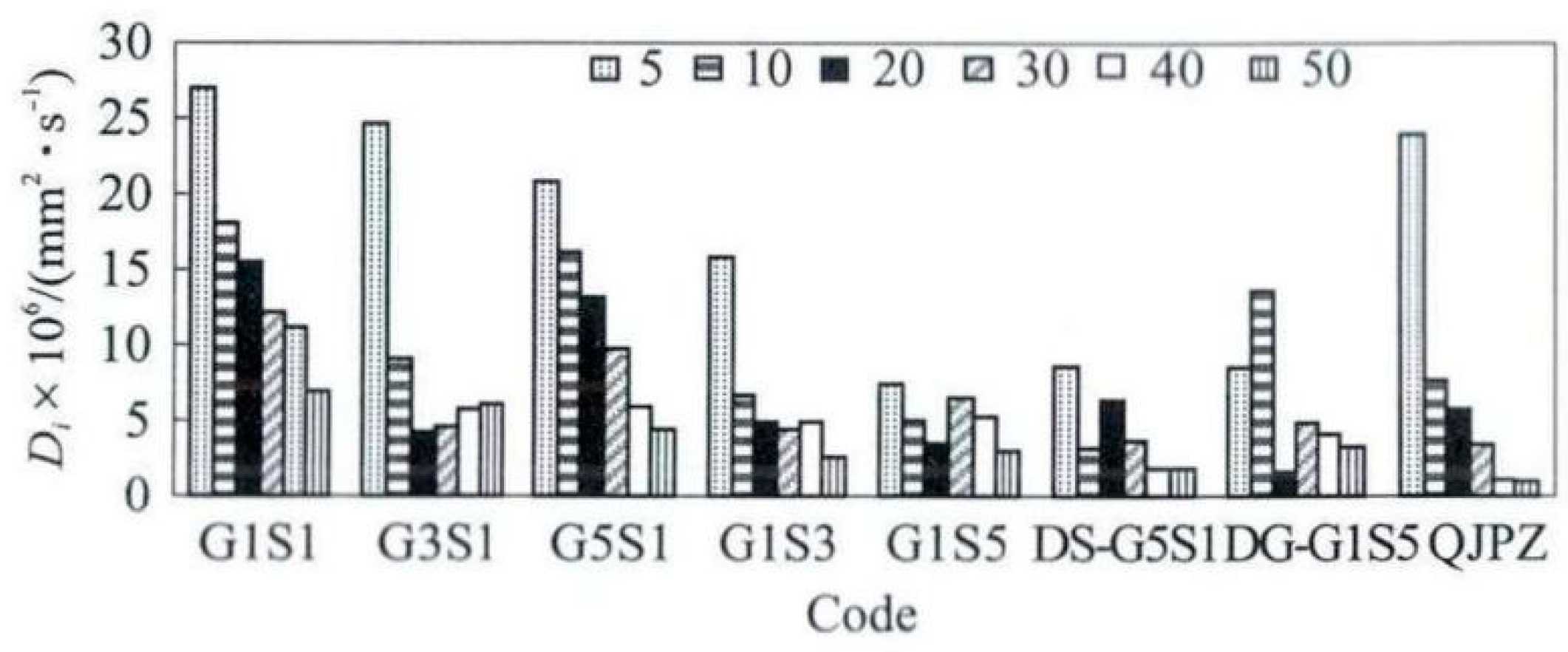
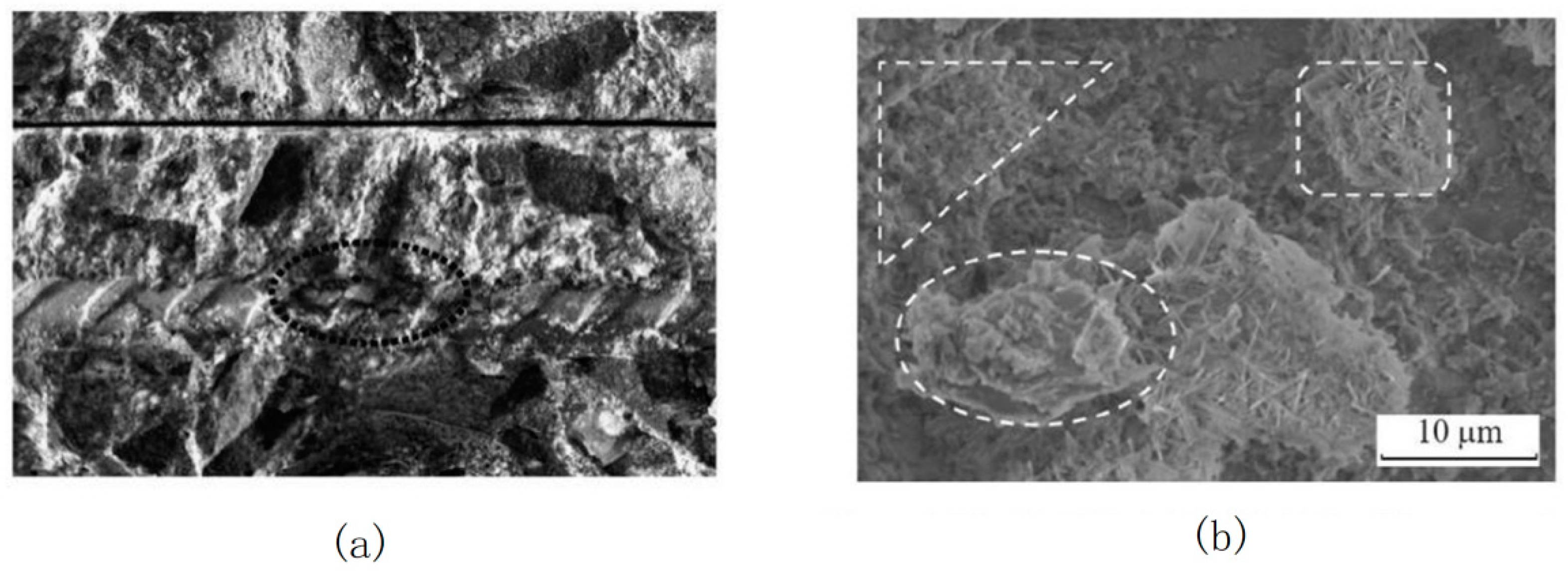
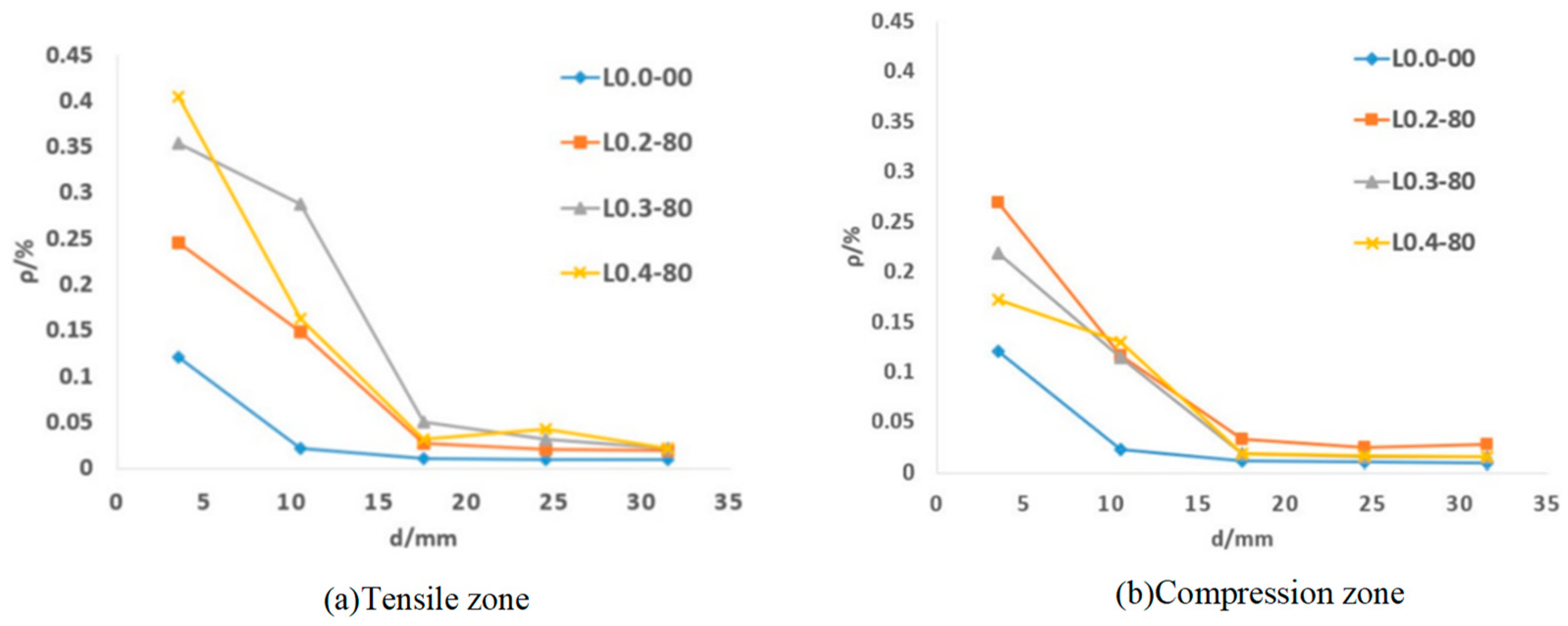
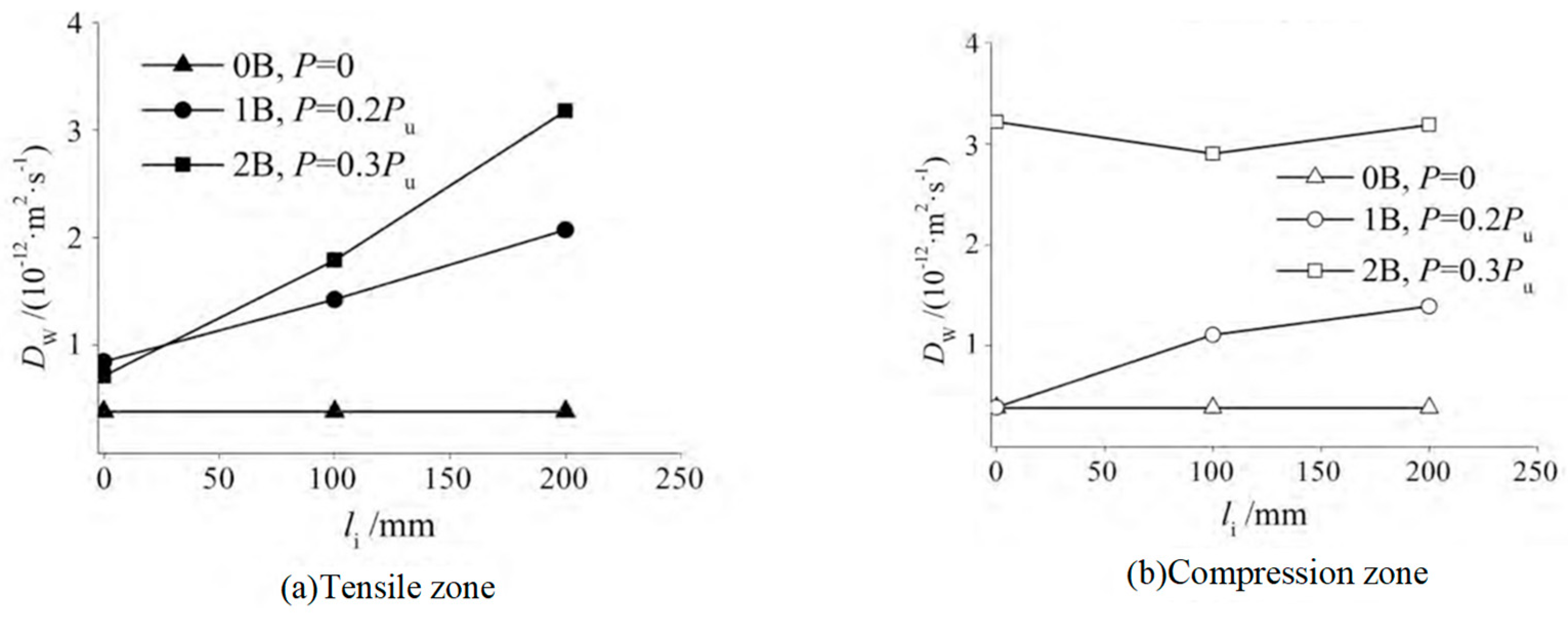
| Code | G1S1 | G3S1 | G5S1 | G1S3 | G1S5 | QJPZ | DS-G5S1 | DG-G1S5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio of dry and wet | 1:1 | 3:1 | 5:1 | 1:3 | 1:5 | 5:1 | 1:5 | |
| Single time ratio/h | 24:24 | 36:12 | 40:8 | 12:36 | 8:40 | 0:48 | 60:12 | 12:60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Cui, J.; Xu, R. Study on Cl− Erosion of Concrete under the Combined Effect of Fatigue Load and Wet–Dry Cycles: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6691. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116691
Zhang M, Li Z, Cui J, Xu R. Study on Cl− Erosion of Concrete under the Combined Effect of Fatigue Load and Wet–Dry Cycles: A Review. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(11):6691. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116691
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Maohua, Zhiyi Li, Jiyin Cui, and Ronghua Xu. 2023. "Study on Cl− Erosion of Concrete under the Combined Effect of Fatigue Load and Wet–Dry Cycles: A Review" Applied Sciences 13, no. 11: 6691. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116691
APA StyleZhang, M., Li, Z., Cui, J., & Xu, R. (2023). Study on Cl− Erosion of Concrete under the Combined Effect of Fatigue Load and Wet–Dry Cycles: A Review. Applied Sciences, 13(11), 6691. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116691





