Multi-Granularity Dilated Transformer for Lung Nodule Classification via Local Focus Scheme
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel Multi-Granularity Dilated Transformer (MGDFormer) to learn pixel-wise global attention of objective region, with an aim to construct a more robust long-range global representation;
- To better focus on local discriminative features for classifying hard samples (i.e., middle-sized nodules), we innovatively design a Local Focus Scheme (LFS) to force networks learning fine-grained local information by modeling channel-wise topology;
- The experimental results on mainstream datasets demonstrate the superiority of our model has a competitive performance compared with the state-of-the-art approaches.
2. Related Work
2.1. Lung Nodule Classification
2.2. Attention Mechanism
3. Methods
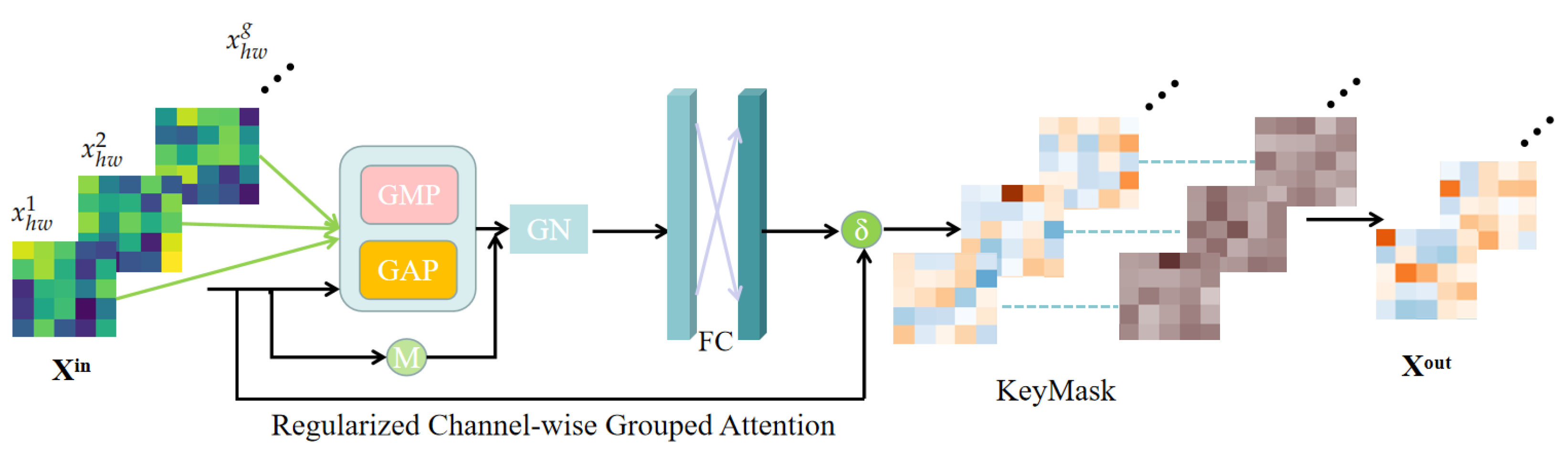
3.1. Local Focus Scheme
3.1.1. Regularized Channel-Wise Grouped Attention
3.1.2. KeyMask
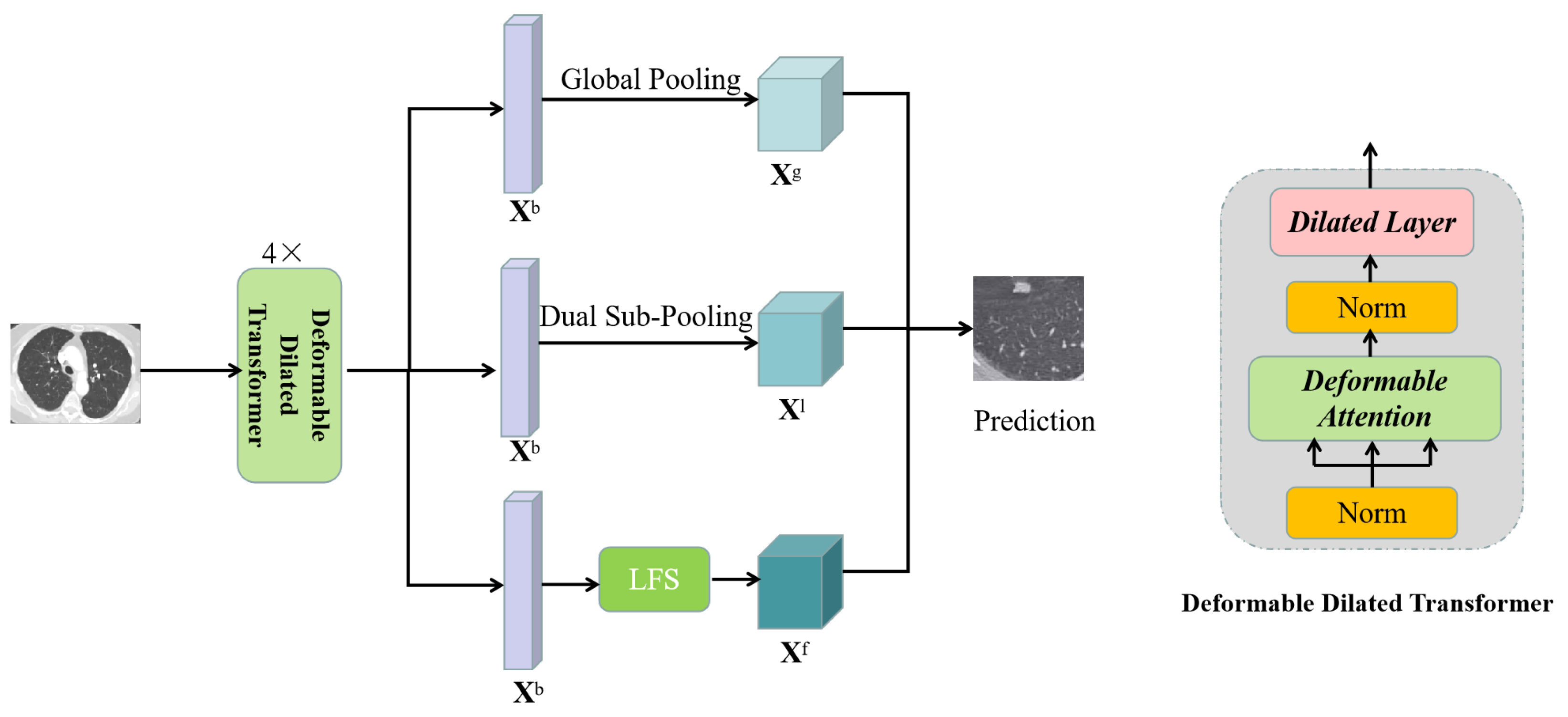
3.2. Deformable Dilated Transformer
3.3. Network Architecture
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Settings
4.3. Data Preprocessing
4.4. Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Effectiveness of the Deformable Dilated Transformer
5.2. Influence of Multi-Granularity Structure
5.3. Performance on Different Size Nodules
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, F.; Song, Y.; Cai, W.; Lee, M.Z.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, H.; Shan, S.; Fulham, M.J.; Feng, D.D. Lung nodule classification with multilevel patch-based context analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 61, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajbakhsh, N.; Suzuki, K. Comparing two classes of end-to-end machine-learning models in lung nodule detection and classification: MTANNs vs. CNNs. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 63, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. Deep learning for image-based cancer detection and diagnosis—A survey. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 83, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Yang, D.; Sun, N.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. Automated pulmonary nodule detection in CT images using deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 85, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabi, M.; Lee, H.K.; Tan, M. Gated-dilated networks for lung nodule classification in CT scans. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 178827–178838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Gan, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Yi, Z. MSCS-DeepLN: Evaluating lung nodule malignancy using multi-scale cost-sensitive neural networks. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 65, 101772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Netto, S.M.B.; Silva, A.C.; Nunes, R.A.; Gattass, M. Automatic segmentation of lung nodules with growing neural gas and support vector machine. Comput. Biol. Med. 2012, 42, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibali, A.; He, Z.; Wollersheim, D. Pulmonary nodule classification with deep residual networks. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.; Cao, K.; Song, Q.; Bagci, U. Risk stratification of lung nodules using 3D CNN-based multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging, Boon, NC, USA, 25–30 June 2017; pp. 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, C.; Fan, W.; Xie, X. Deeplung: Deep 3d dual path nets for automated pulmonary nodule detection and classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 673–681. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Gao, F.; Xu, X.; Huang, F.; Zhu, S. Attentive and ensemble 3D dual path networks for pulmonary nodules classification. Neurocomputing 2020, 398, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, G.L.; da Silva Neto, O.P.; Silva, A.C.; de Paiva, A.C.; Gattass, M. Lung nodules diagnosis based on evolutionary convolutional neural network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 19039–19055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Shen, F.; Gao, F.; Han, W. Learning efficient, explainable and discriminative representations for pulmonary nodules classification. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 113, 107825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabi, M.; Shak, K.; Tan, M. ProCAN: Progressive growing channel attentive non-local network for lung nodule classification. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 122, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable DETR: Deformable Transformers for End-to-End Object Detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Residual attention network for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3156–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Bello, I.; Zoph, B.; Vaswani, A.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Attention augmented convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the PIEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3286–3295. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran, P.; Parmar, N.; Vaswani, A.; Bello, I.; Levskaya, A.; Shlens, J. Stand-alone self-attention in vision models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Hu, H.; Lin, S.; Dai, J. Deformable convnets v2: More deformable, better results. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 9308–9316. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; He, X.; Gao, J.; Deng, L.; Smola, A. Stacked attention networks for image question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Nie, L.; Shao, J.; Liu, W.; Chua, T.S. Sca-cnn: Spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5659–5667. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Heess, N.; Graves, A. Recurrent models of visual attention. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Ba, J.; Kiros, R.; Cho, K.; Courville, A.; Salakhudinov, R.; Zemel, R.; Bengio, Y. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 2048–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; Li, X. Fcanet: Frequency channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 783–792. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.; Kim, H.; Han, B.; Xu, N.; Lee, K.M. Channel attention is all you need for video frame interpolation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 10663–10671. [Google Scholar]
- Bastidas, A.A.; Tang, H. Channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Canu, S.; Ruan, S. Automatic COVID-19 CT segmentation using U-Net integrated spatial and channel attention mechanism. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 31, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Han, X.h. Spatial and channel attention modulated network for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 30 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; He, K. Group normalization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Armato, S.G., III; McLennan, G.; Bidaut, L.; McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Meyer, C.R.; Reeves, A.P.; Zhao, B.; Aberle, D.R.; Henschke, C.I.; Hoffman, E.A.; et al. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): A completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med Phys. 2011, 38, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.; Han, S.X.; Aberle, D.R.; Bui, A.A.; Hsu, W. An interpretable deep hierarchical semantic convolutional neural network for lung nodule malignancy classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 128, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zhou, M.; Yang, F.; Yu, D.; Dong, D.; Yang, C.; Zang, Y.; Tian, J. Multi-crop convolutional neural networks for lung nodule malignancy suspiciousness classification. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabi, M.; Lan, B.L.; Chan, W.Y.; Ng, K.H.; Tan, M. Lung nodule classification using deep local–global networks. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 1815–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Pinho Pinheiro, C.A.; Nedjah, N.; de Macedo Mourelle, L. Detection and classification of pulmonary nodules using deep learning and swarm intelligence. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 15437–15465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Feng, D.; Fulham, M.; Cai, W. Knowledge-based collaborative deep learning for benign-malignant lung nodule classification on chest CT. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2018, 38, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y. Semi-supervised adversarial model for benign–malignant lung nodule classification on chest CT. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 57, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | AUC | Accuracy | Precision | Sensitivity | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSCNN [38] | 85.6 | 84.2 | - | 70.5 | - |
| Multi-Crop [39] | 93.0 | 87.14 | - | 77.0 | - |
| Local-Global [40] | 95.6 | 88.4 | 87.3 | 88.6 | 88.3 |
| Gated-Dilated [5] | 95.1 | 92.5 | 91.8 | 92.2 | 92.6 |
| Swarm [41] | - | 93.7 | 93.5 | 92.9 | - |
| 3D DPN [12] | - | 90.2 | - | 92.0 | 90.4 |
| MV-KBC [42] | 95.7 | 91.6 | 87.7 | 86.5 | 87.1 |
| MSCS-DeepLN [6] | 94.0 | 92.6 | 90.3 | 85.5 | 87.9 |
| MK-SSAC [43] | 95.8 | 92.5 | - | 84.9 | - |
| ProCAN [15] | 97.1 | 94.1 | 94.5 | 93.1 | 93.8 |
| MGDFormer (ours) | 98.5 | 96.1 | 95.9 | 94.4 | 95.2 |
| Method | AUC | Accuracy | Precision | Sensitivity | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA + Dilated Layer | 97.6 | 94.8 | 94.9 | 93.6 | 94.3 |
| RA + MLP | 97.3 | 94.1 | 94.4 | 93.1 | 93.8 |
| DA + MLP | 98.1 | 95.5 | 95.4 | 94.0 | 94.8 |
| DA + Dilated Layer | 98.5 | 96.1 | 95.9 | 94.4 | 95.2 |
| Number | AUC | Accuracy | Precision | Sensitivity | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 97.7 | 94.2 | 94.9 | 93.6 | 94.2 |
| 3 | 98.0 | 94.7 | 95.4 | 94.1 | 94.5 |
| 4 | 98.5 | 96.1 | 95.9 | 94.4 | 95.2 |
| 5 | 98.3 | 95.6 | 95.6 | 94.1 | 95.3 |
| 6 | 98.0 | 94.8 | 95.2 | 93.8 | 94.7 |
| Method | AUC | Accuracy | Precision | Sensitivity | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP | 97.4 | 94.0 | 94.8 | 93.2 | 94.1 |
| DSP | 97.7 | 94.6 | 95.3 | 93.6 | 94.3 |
| LFS | 98.2 | 95.8 | 95.7 | 94.1 | 94.8 |
| GP+DSP | 97.9 | 95.2 | 95.3 | 93.8 | 94.5 |
| GP+DSP+LFS | 98.5 | 96.1 | 95.9 | 94.4 | 95.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, K.; Peng, B.; Zhai, D. Multi-Granularity Dilated Transformer for Lung Nodule Classification via Local Focus Scheme. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010377
Wu K, Peng B, Zhai D. Multi-Granularity Dilated Transformer for Lung Nodule Classification via Local Focus Scheme. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(1):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010377
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Kunlun, Bo Peng, and Donghai Zhai. 2023. "Multi-Granularity Dilated Transformer for Lung Nodule Classification via Local Focus Scheme" Applied Sciences 13, no. 1: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010377
APA StyleWu, K., Peng, B., & Zhai, D. (2023). Multi-Granularity Dilated Transformer for Lung Nodule Classification via Local Focus Scheme. Applied Sciences, 13(1), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010377






