Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Analysis Using Deep Learning to Improve Glaucoma Detection in Eye Disease Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- We proposed an alternative way to detect glaucoma disease by analyzing the damage to the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL). Our proposed method consists of novel step-by-step preprocesses to extract RNFL features from digital fundus images.
- (ii)
- We further analyze our methods by applying them in ORIGA dataset with nine pre-trained CNN and compared them with similar earlier studies about glaucoma classification which used the same dataset.
- (iii)
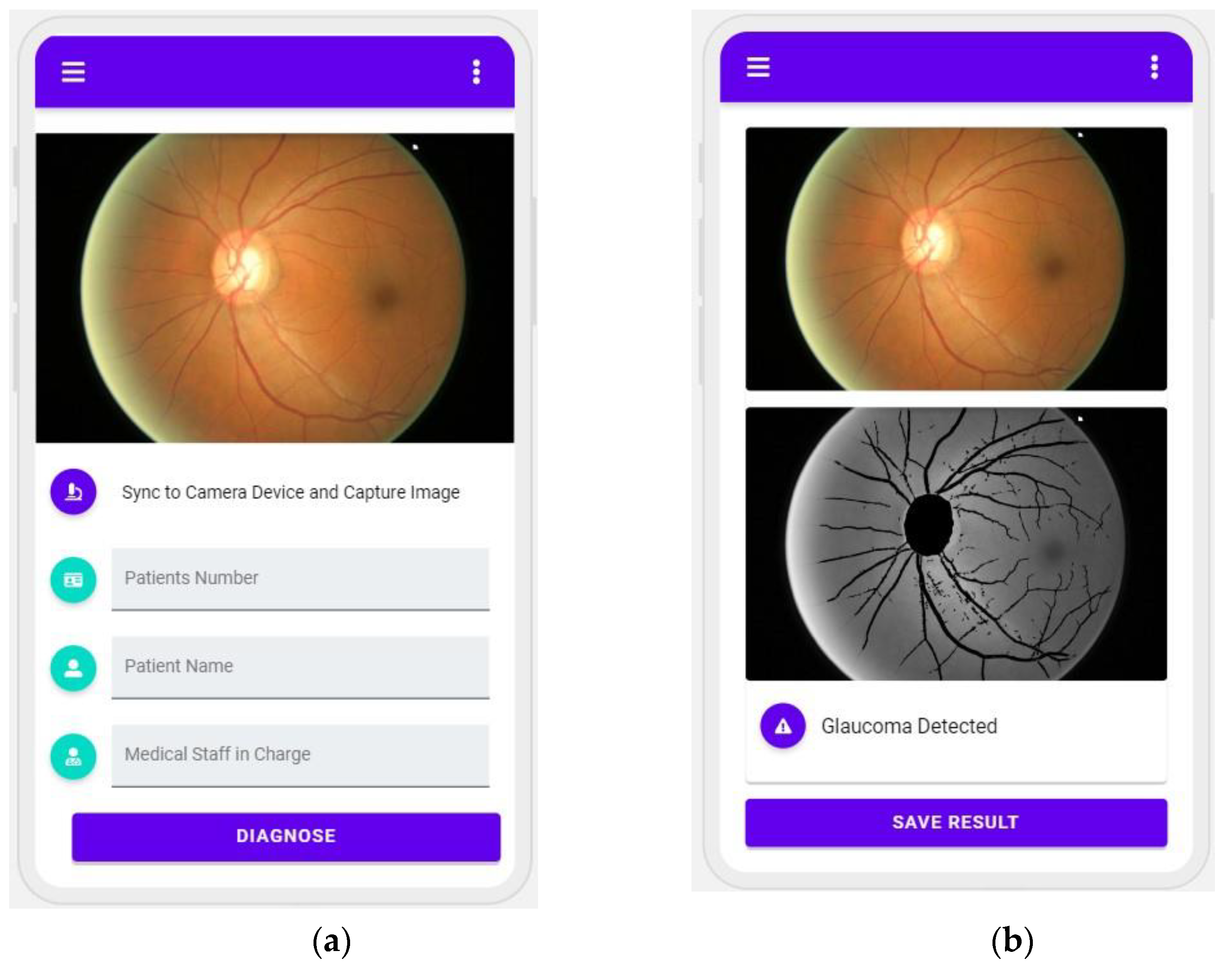
- Finally, we developed a prototype application to categorize fundus images in order to demonstrate the viability of our proposed model. The designed and developed application is expected to be valuable for practitioners and decision-makers as practical guidelines for glaucoma detection and classification.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
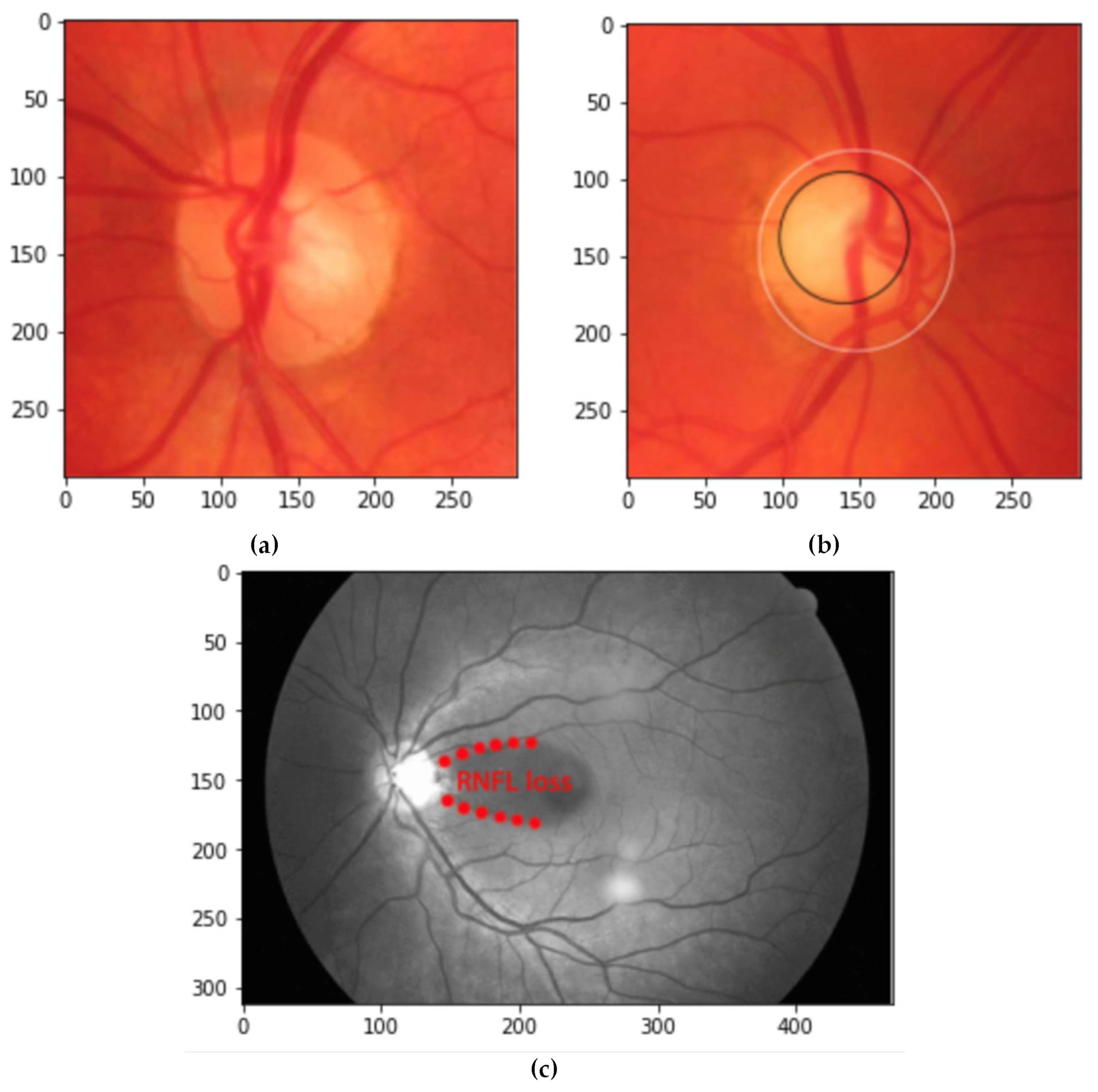
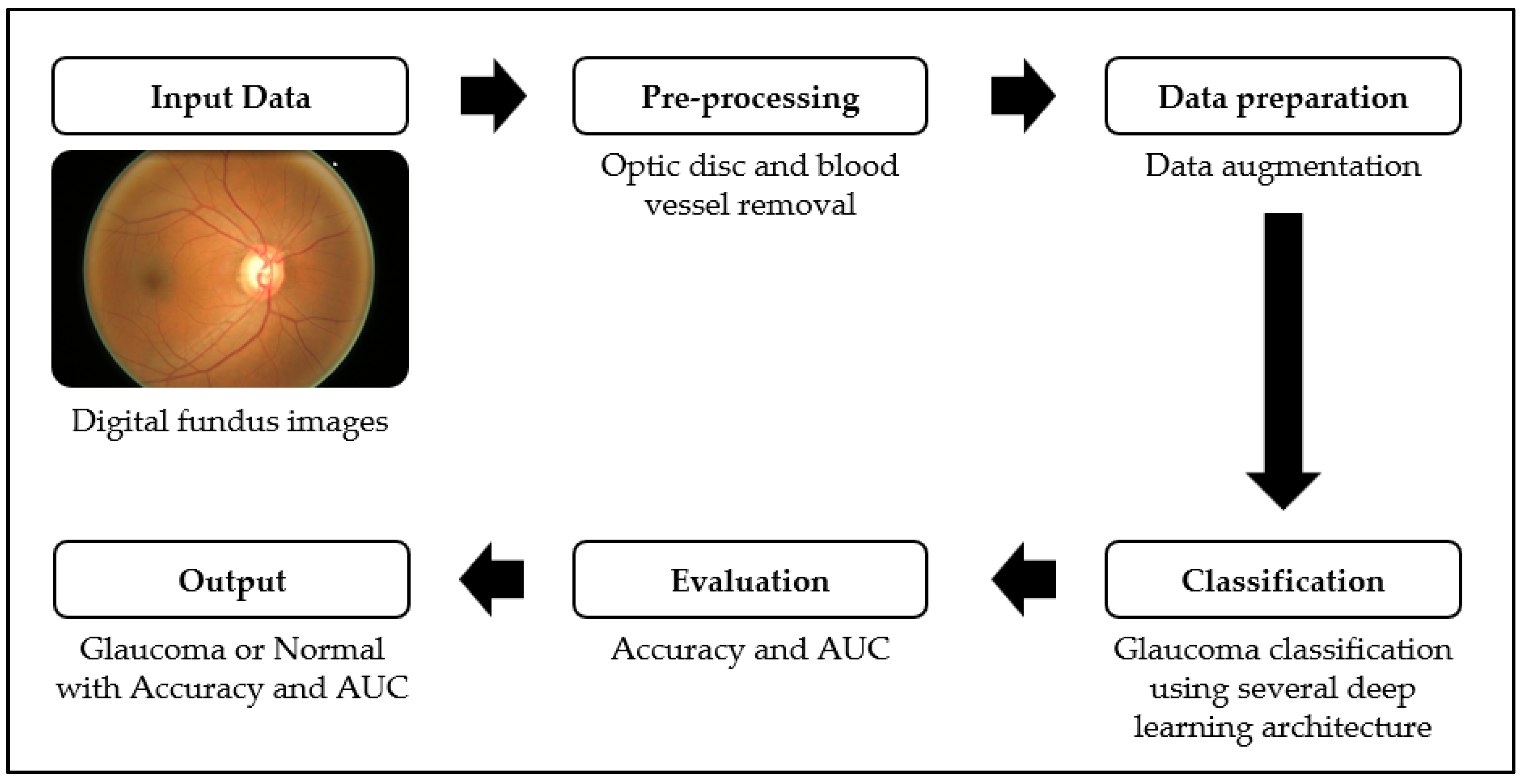
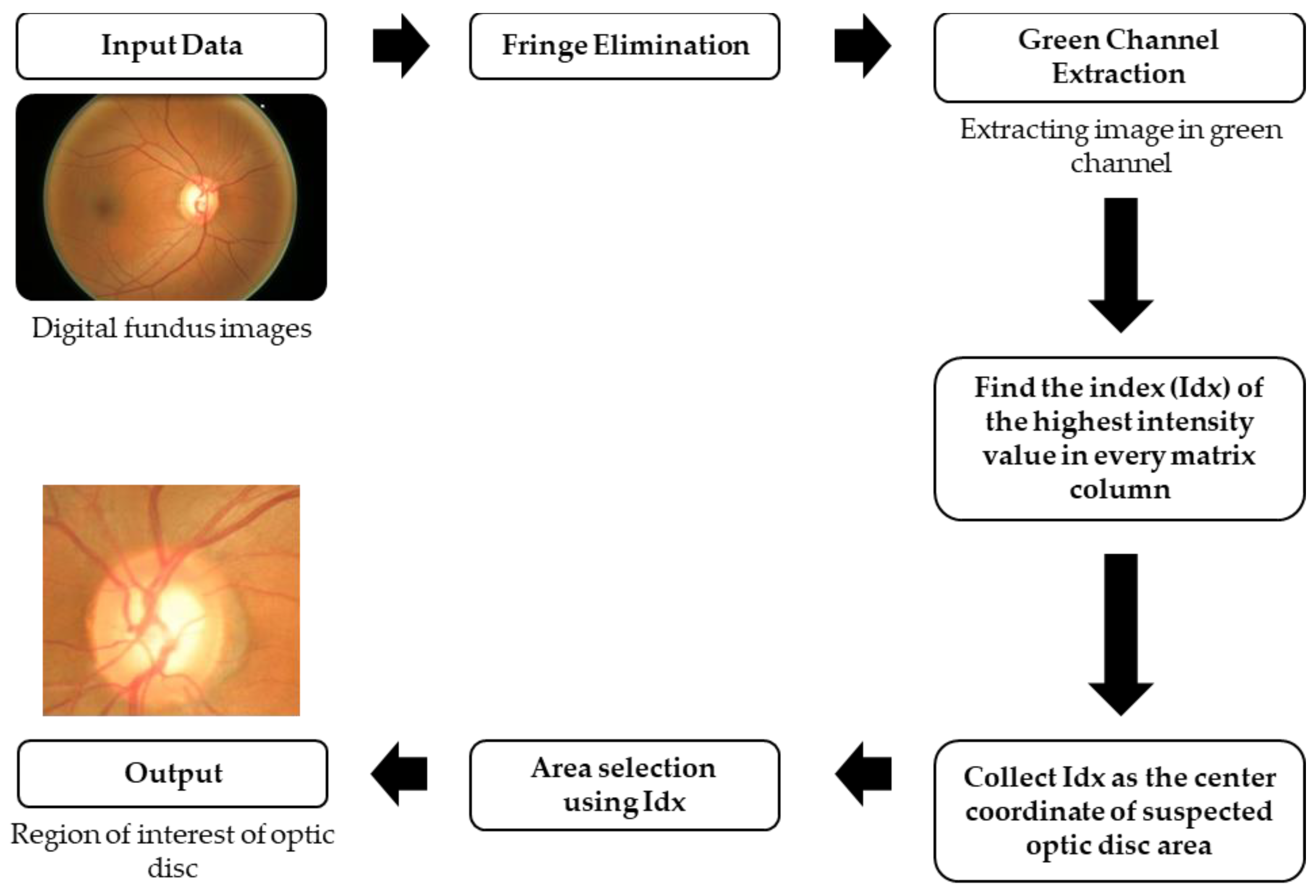
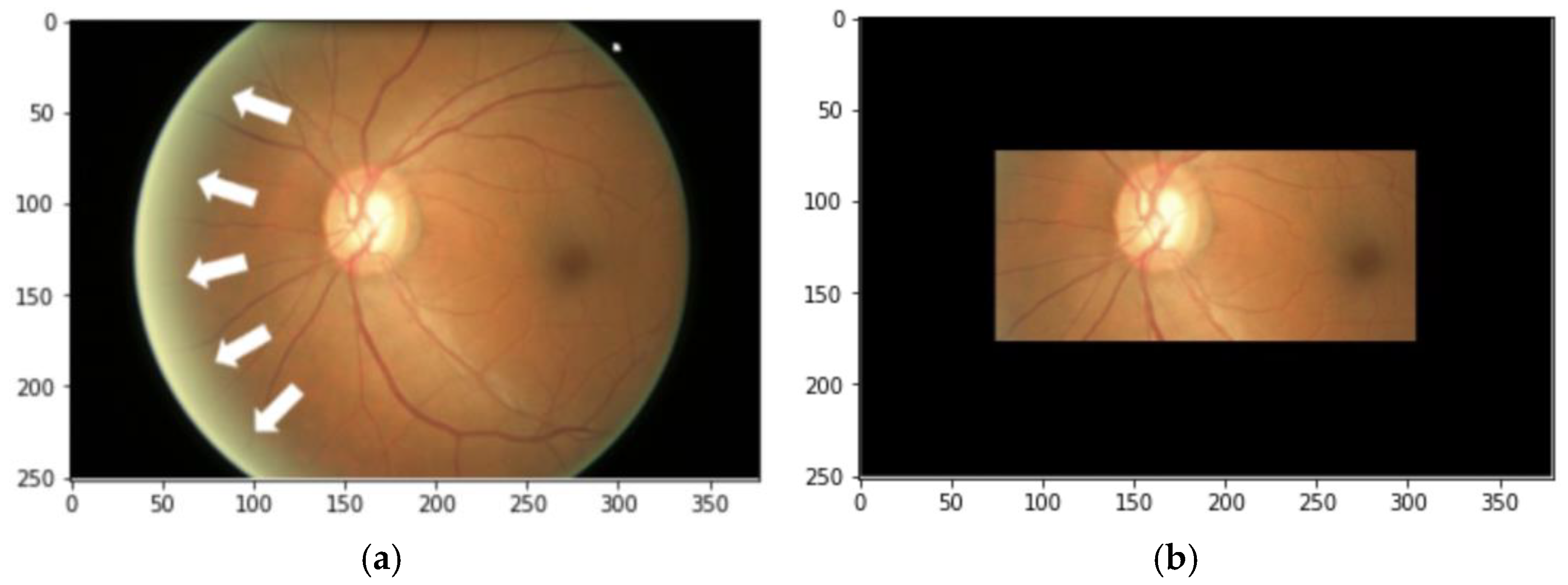
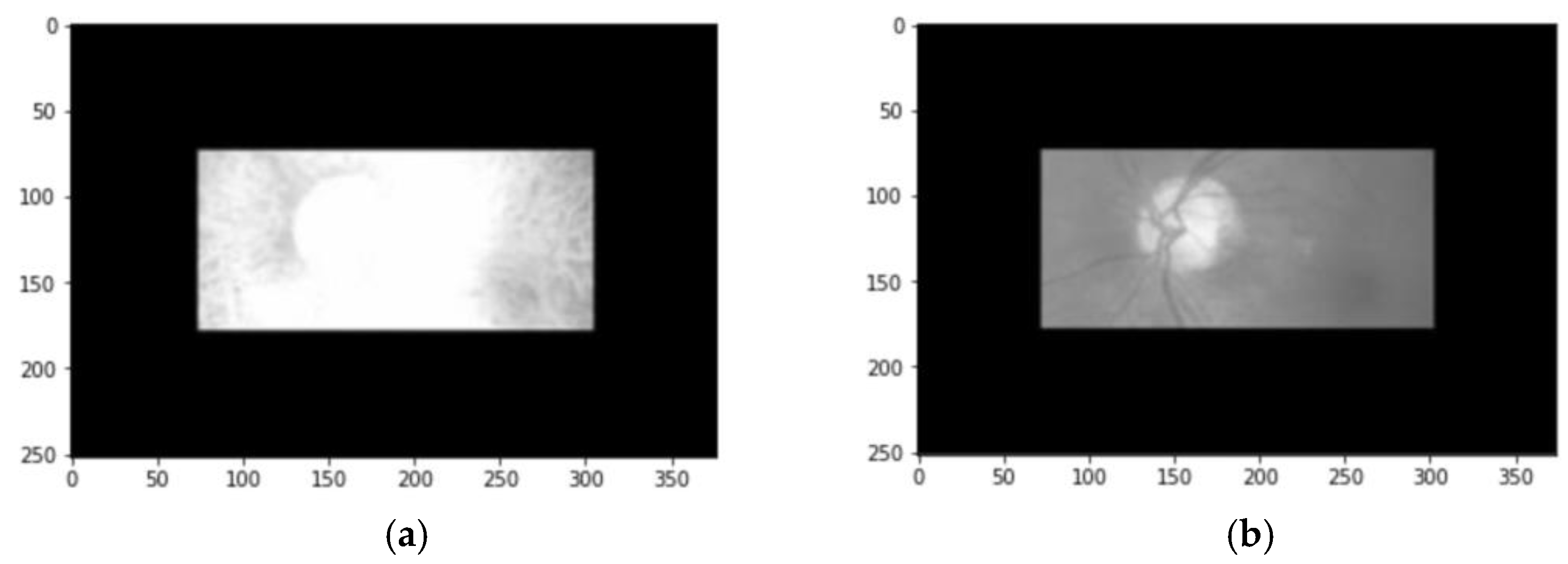
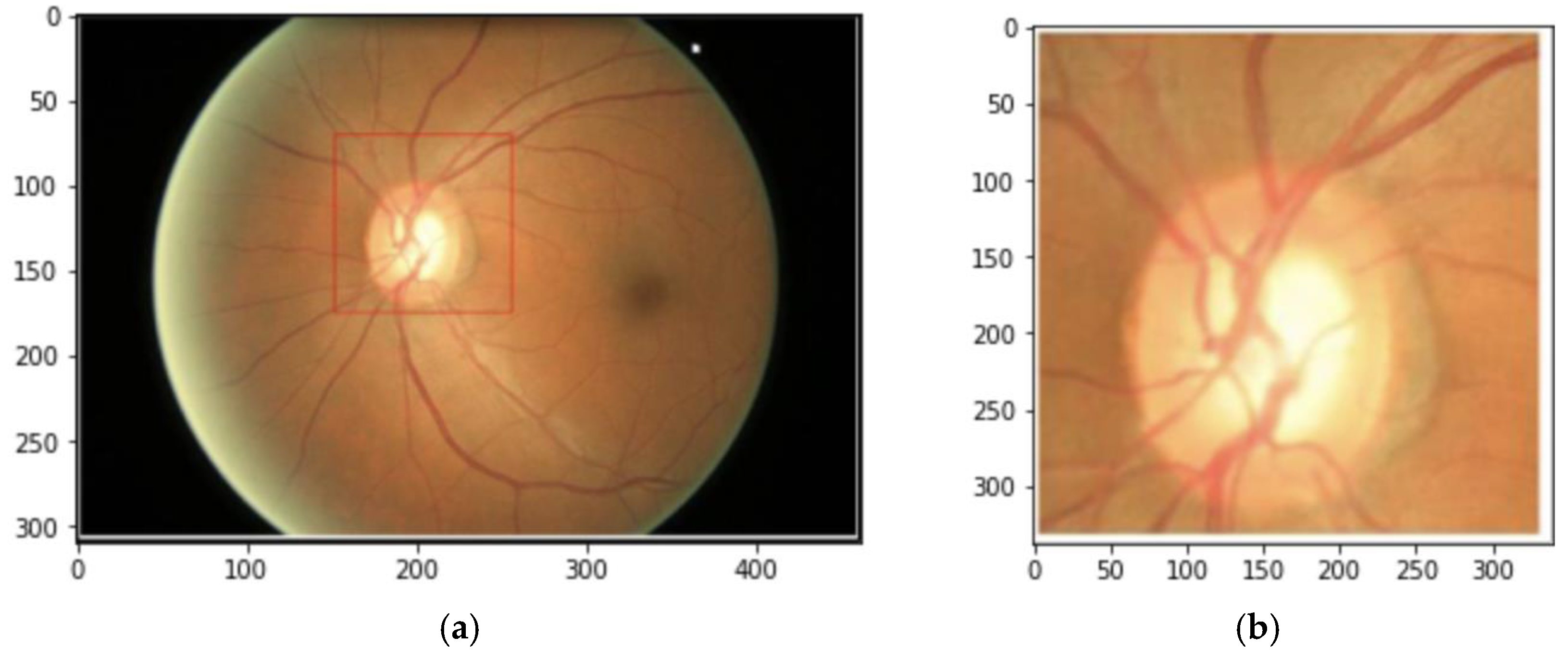
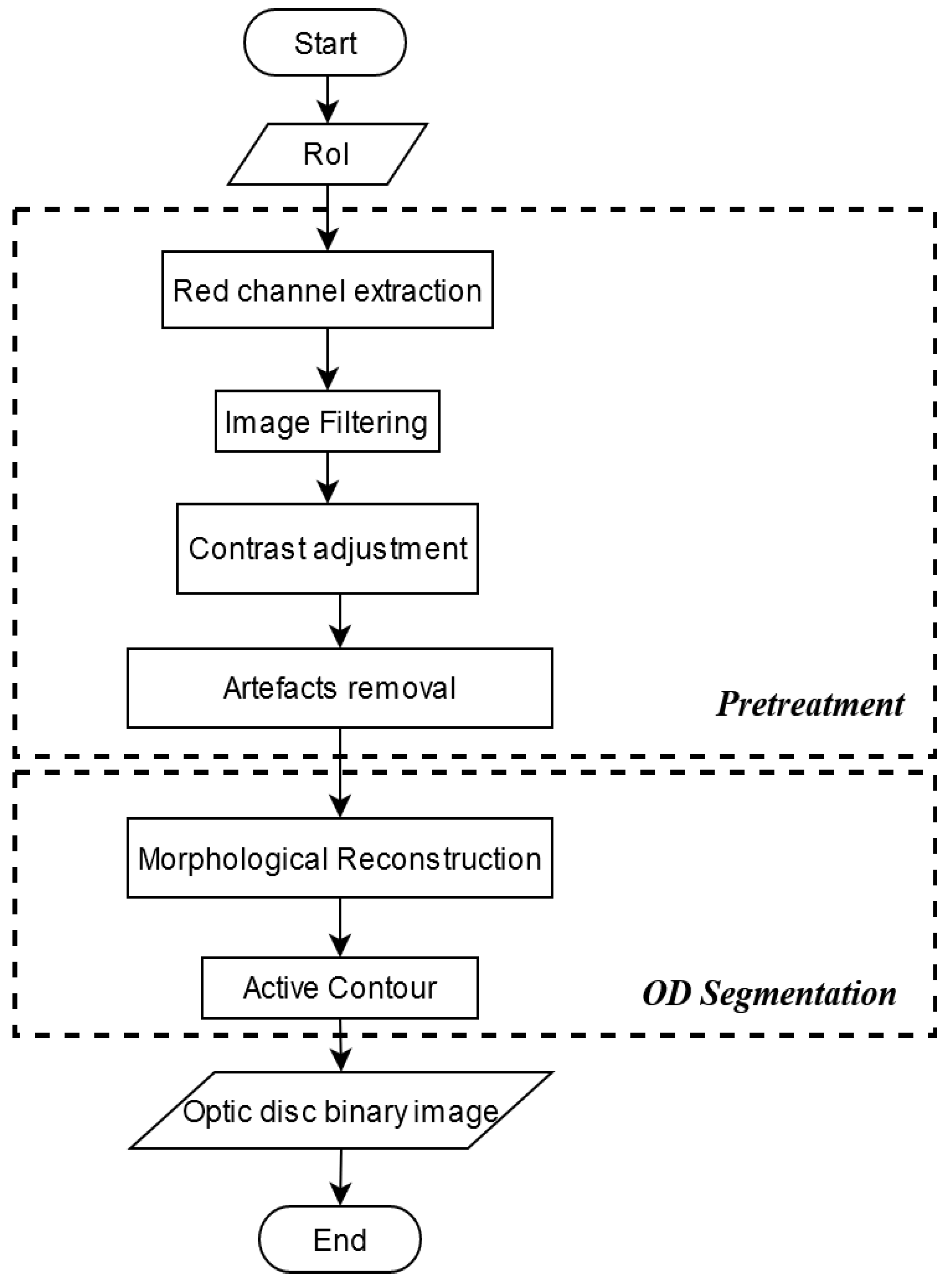
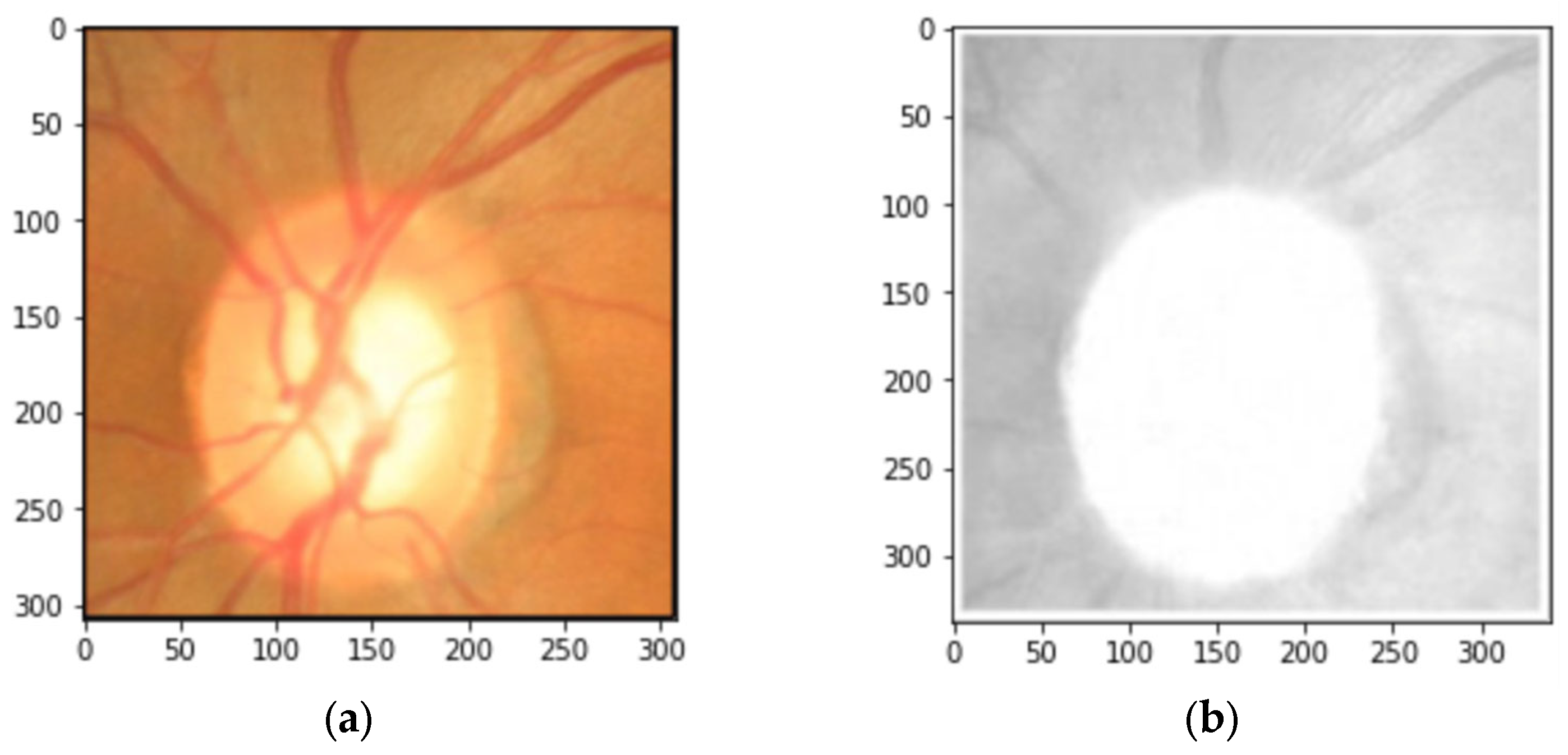
2.2. Data Preprocessing
| Algorithm 1. The search for the highest pixel value from every column of the image. |
| 1: input: given I |
| 2: given queue |
| 3: for n = 1 to Total_Column do |
| 4: val = maximum value of |
| 5: Idx = index of val |
| 6: If val ≥ 100 then |
| 7: store Idx to queue |
| 8: end if |
| 9: end for |
| Algorithm 2. The sample selection process. |
| 1: input: import queue |
| 2: initialize qvalue size to queue size |
| 3: set all qvalue elements to zero |
| 4: get Area from queue |
| 5: for n = 1 to Total_queue |
| 6: Mean = mean value of |
| 7: SD = standard deviation value of |
| 8: k = 0.1 × Mean |
| 9: If SD < k then → conditional statement to satisfy the first requirement |
| 10: store Mean to qvalue[n] |
| 11: end if |
| 12: end for |
| 13: search the maximum value of qvalue |
| 14: get the index of the maximum value |
| 15: return queue[index] |
| 16: get Idx |
2.3. Data Augmentation
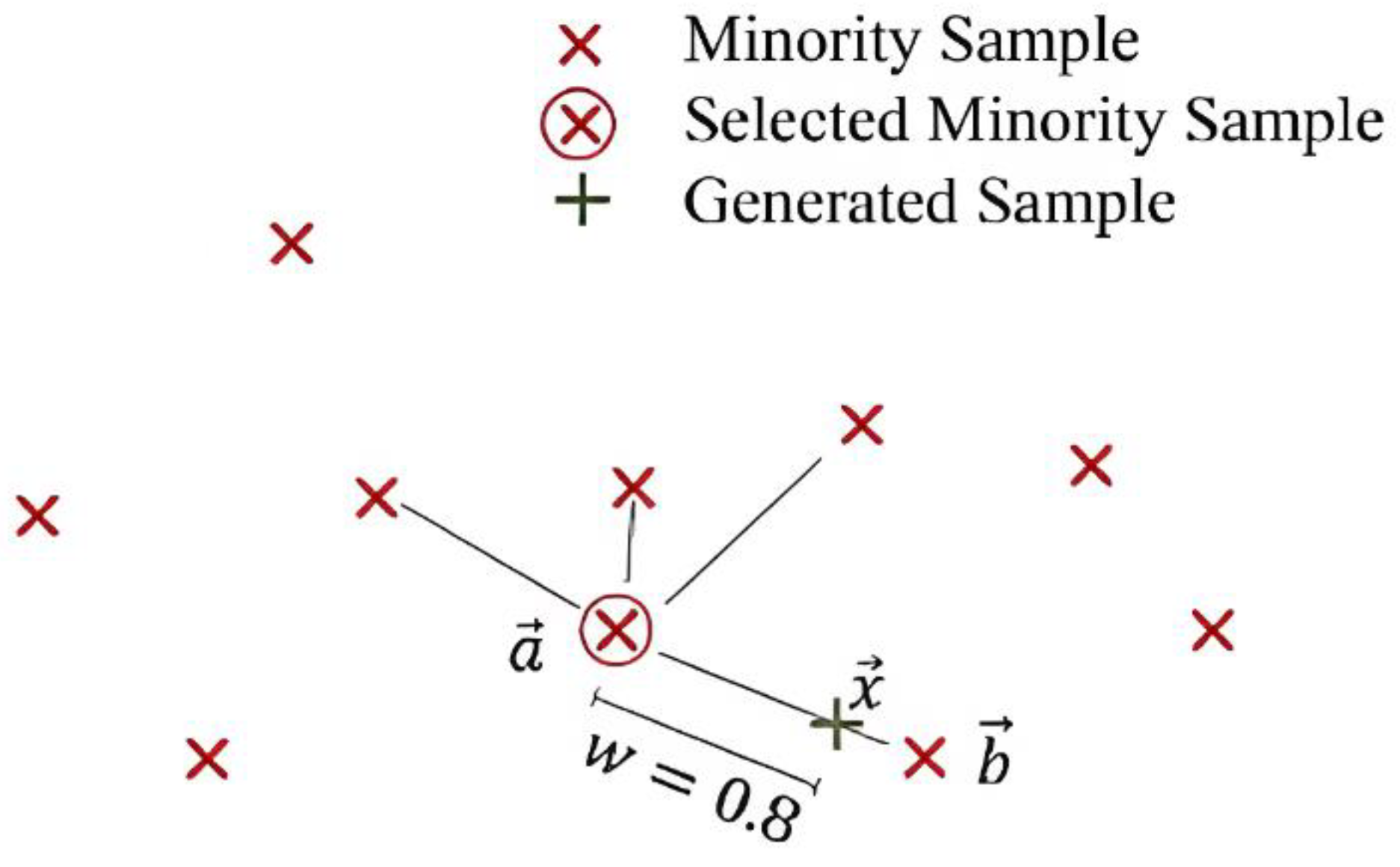
- Select a random minority observation .
- Select instance amidst its k nearest minority-class neighbors.
- Create a new sample by applying (8) as a randomly interpolating formula of two samples with defining a random weight (see Figure 11).
2.4. Glaucoma Classification
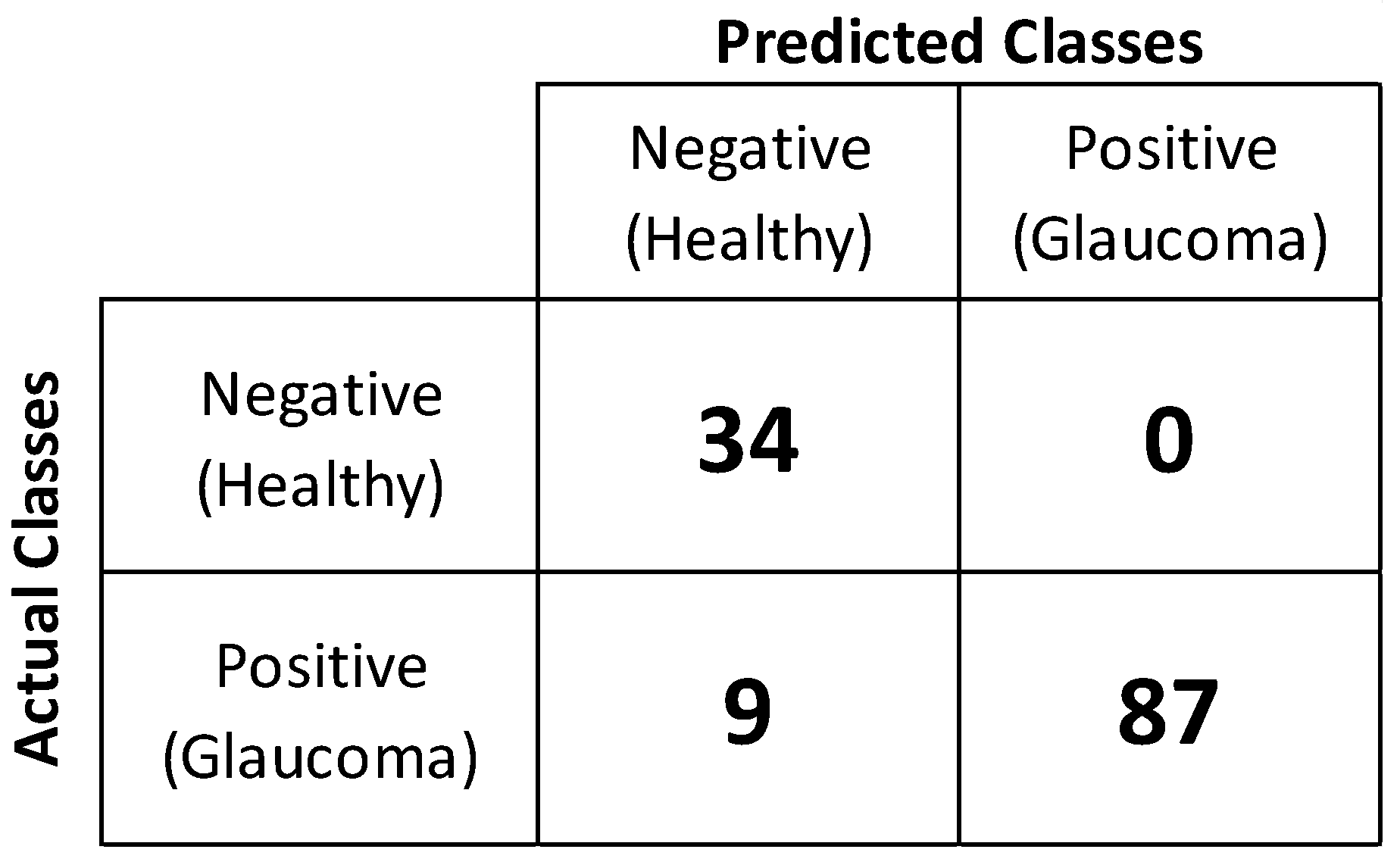
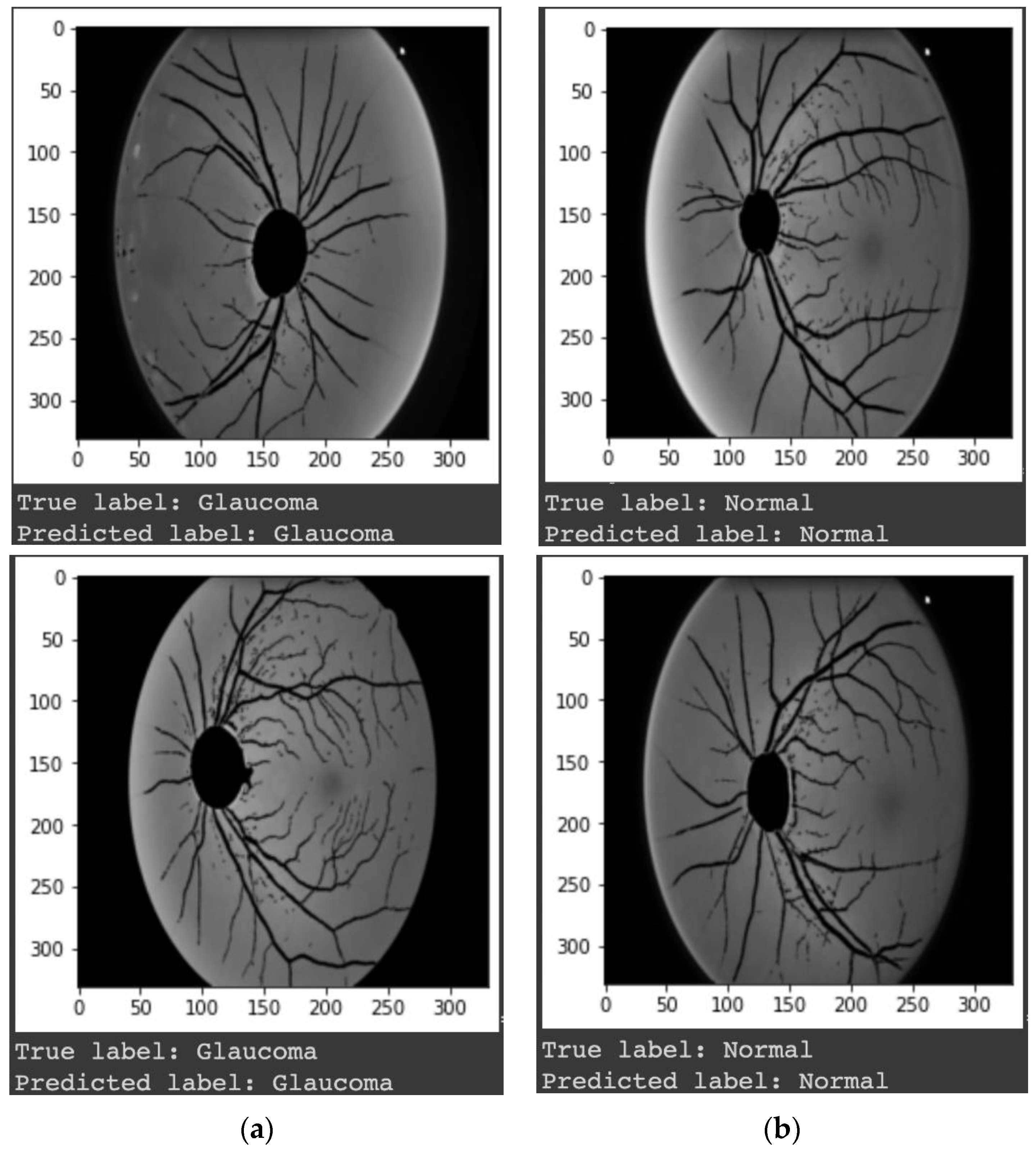
3. Results
4. Discussions
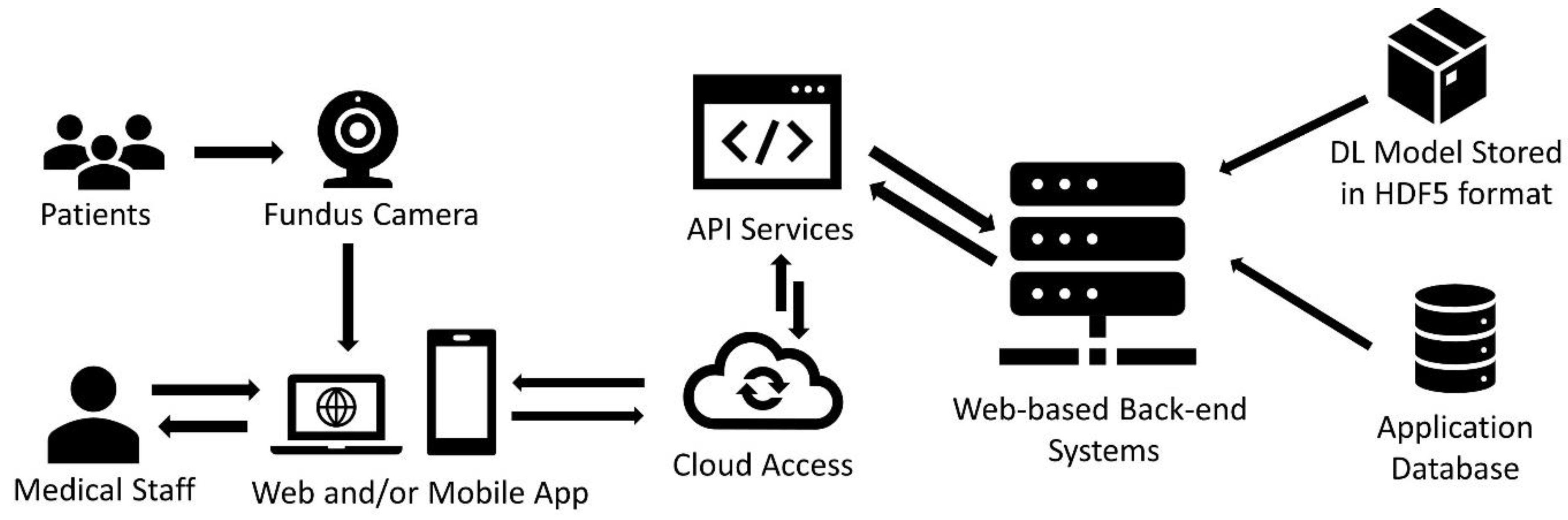
5. Practical Application
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| CDR | Cup-to-disc ratio |
| DDLS | Disc damage likelihood scale |
| OD | Optic disc |
| OC | Optic cup |
| RNFL | Retinal nerve fiber layer |
| ONH | Optic nerve head |
| RGB | Red green blue |
| CAD | Computer-aided diagnosis |
| DL | Deep learning |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| RoI | Region of interest |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| CDF | Cumulative distribution function |
| CLAHE | Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization |
| SMOTE | Synthetic minority over-sampling technique |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| HDF5 | Hierarchical data format version 5 |
| API | Application programming interface |
References
- Diaz-Pinto, A.; Colomer, A.; Naranjo, V.; Morales, S.; Xu, Y.; Frangi, A.F. Retinal Image Synthesis and Semi-Supervised Learning for Glaucoma Assessment. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2211–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella Mary, M.C.V.; Rajsingh, E.B.; Naik, G.R. Retinal Fundus Image Analysis for Diagnosis of Glaucoma: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 4327–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Xiao, D.; Frost, S.; Kanagasingam, Y. Robust Optic Disc and Cup Segmentation with Deep Learning for Glaucoma Detection. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 74, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claro, M.; Veras, R.; Santana, A.; Araújo, F.; Silva, R.; Almeida, J.; Leite, D. An Hybrid Feature Space from Texture Information and Transfer Learning for Glaucoma Classification. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 64, 102597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mvoulana, A.; Kachouri, R.; Akil, M. Fully Automated Method for Glaucoma Screening Using Robust Optic Nerve Head Detection and Unsupervised Segmentation Based Cup-to-Disc Ratio Computation in Retinal Fundus Images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 77, 101643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odstrčilík, J.; Kolář, R.; Harabiš, V.; Gazárek, J. Jan Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Analysis via Markov Random Fields Texture Modelling. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th European Signal Processing Conference, Aalborg, Denmark, 23–27 August 2010; pp. 1650–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.-H.; Lee, K.Y.; Chong, J.I.T.; Lam, A.K.C.; Lai, J.S.M.; Lam, D.C.C. Comparison of Ocular Biomechanical Machine Learning Classifiers for Glaucoma Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Madrid, Spain, 3–6 December 2018; IEEE: Madrid, Spain, 2018; pp. 2539–2543. [Google Scholar]
- Thangaraj, V.; Natarajan, V. Glaucoma Diagnosis Using Support Vector Machine. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 15–16 June 2017; pp. 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Shalini, S.; Srinivasan, N. WITHDRAWN: Retinal Image Classification by Glaucoma Based on ANFIS Classifier. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, S2214785320407746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, A.; Yohannan, J.; Boland, M.V. Assessing Glaucoma Progression Using Machine Learning Trained on Longitudinal Visual Field and Clinical Data. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Shen, J.; Chang, R.; Moloney, M.; Torres, M.; Burkemper, B.; Jiang, X.; Rodger, D.; Varma, R.; Richter, G.M. Machine Learning Models for Diagnosing Glaucoma from Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Maps. Ophthalmol. Glaucoma 2019, 2, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Juneja, M. Classification of Glaucoma Using Hybrid Features with Machine Learning Approaches. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 62, 102137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Huang, N.-F.; Hussain, I.; Bibi, F.; Sajjad, U.; Sultan, M.; Alsubaie, A.S.; Mahmoud, K.H. On the Classification of a Greenhouse Environment for a Rose Crop Based on AI-Based Surrogate Models. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Sergin, N.D.; Brenneman, W.A.; Lange, S.J.; Ba, S. Deep Multistage Multi-Task Learning for Quality Prediction of Multistage Manufacturing Systems. J. Qual. Technol. 2021, 53, 526–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Azkune, G. Predicting Human Behaviour with Recurrent Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, U.; Fujita, H.; Bhandary, S.V.; Gudigar, A.; Tan, J.H.; Acharya, U.R. Deep Convolution Neural Network for Accurate Diagnosis of Glaucoma Using Digital Fundus Images. Inf. Sci. 2018, 441, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinícius dos Santos Ferreira, M.; Oseas de Carvalho Filho, A.; Dalília de Sousa, A.; Corrêa Silva, A.; Gattass, M. Convolutional Neural Network and Texture Descriptor-Based Automatic Detection and Diagnosis of Glaucoma. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 110, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bander, B.; Al-Nuaimy, W.; Al-Taee, M.A.; Zheng, Y. Automated Glaucoma Diagnosis Using Deep Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 14th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD), Marrakech, Morocco, 28–31 March 2017; pp. 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzifard, M.; Nemati, A.; GholamHosseini, H.; Klette, R.; Nouri-Mahdavi, K.; Yousefi, S. Automated Glaucoma Diagnosis Using Deep and Transfer Learning: Proposal of a System for Clinical Testing. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Image and Vision Computing New Zealand (IVCNZ), Auckland, New Zealand, 19–21 November 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Phasuk, S.; Poopresert, P.; Yaemsuk, A.; Suvannachart, P.; Itthipanichpong, R.; Chansangpetch, S.; Manassakorn, A.; Tantisevi, V.; Rojanapongpun, P.; Tantibundhit, C. Automated Glaucoma Screening from Retinal Fundus Image Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 904–907. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, M.; Ordieres-Meré, J. Comparison of Data Preprocessing Approaches for Applying Deep Learning to Human Activity Recognition in the Context of Industry 4.0. Sensors 2018, 18, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tam, R.M.; Al-Hejri, A.M.; Narangale, S.M.; Samee, N.A.; Mahmoud, N.F.; Al-masni, M.A.; Al-antari, M.A. A Hybrid Workflow of Residual Convolutional Transformer Encoder for Breast Cancer Classification Using Digital X-Ray Mammograms. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, O.; Nozaki, K.; Matsumura, M.; Yanaka, W.; Miura, H.; Fueki, K. Texture-Based Neural Network Model for Biometric Dental Applications. JPM 2022, 12, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RNFL Analysis in the Diagnosis of Glaucoma. Available online: https://glaucomatoday.com/articles/2016-may-june/rnfl-analysis-in-the-diagnosis-of-glaucoma (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Zhang, Z.; Yin, F.S.; Liu, J.; Wong, W.K.; Tan, N.M.; Lee, B.H.; Cheng, J.; Wong, T.Y. ORIGA-light: An Online Retinal Fundus Image Database for Glaucoma Analysis and Research. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 3065–3068. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Gu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Pu, J.; Chen, H. Automated Segmentation of the Optic Disc from Fundus Images Using an Asymmetric Deep Learning Network. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 112, 107810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hong, J.; Lu, X.; Jia, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H. Joint Optic Disc and Cup Segmentation Using Semi-Supervised Conditional GANs. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 115, 103485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, J.; Yi, C.; Huang, H.; Wu, Q. Deep Level Set Learning for Optic Disc and Cup Segmentation. Neurocomputing 2021, 464, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hong, X.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zou, B. A Spatial-Aware Joint Optic Disc and Cup Segmentation Method. Neurocomputing 2019, 359, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulsani, A.; Kumar, P.; Pathan, S. Automated Segmentation of Optic Disc and Optic Cup for Glaucoma Assessment Using Improved UNET++ Architecture. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, W.; You, T.; Liu, J. Optic Disc Segmentation from Retinal Fundus Images via Deep Object Detection Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 17–21 July 2018; pp. 5954–5957. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.; Cheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Wong, D.W.K.; Liu, J.; Cao, X. Joint Optic Disc and Cup Segmentation Based on Multi-Label Deep Network and Polar Transformation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, D.; Xu, P.; Wan, C.; Cheng, J.; Liu, J. Automatic Localization of Optic Disc Based on Deep Learning in Fundus Images. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Singapore, 4–6 August 2017; pp. 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Zou, B.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Y. A Deep Gradient Boosting Network for Optic Disc and Cup Segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 971–975. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.-L.; Chou, C.-A.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-K. Retinal Fundus Image Segmentation Based on Channel-Attention Guided Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence (PRAI), Chengdu, China, 19–21 August 2022; pp. 1055–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.; Lyu, J.; Huang, Y.; Tang, X. Probability Distribution Guided Optic Disc and Cup Segmentation from Fundus Images. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 1976–1979. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, L.K.; Khanna, M.; Thawkar, S.; Singh, R. Collaboration of Features Optimization Techniques for the Effective Diagnosis of Glaucoma in Retinal Fundus Images. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2022, 173, 103283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, K.; Ananthamoorthy, N.P. Correlation-Based Feature Selection Using Bio-Inspired Algorithms and Optimized KELM Classifier for Glaucoma Diagnosis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 128, 109432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, K.; Ramya, K.; Gayathri Devi, K. Improved Swarm Optimization of Deep Features for Glaucoma Classification Using SEGSO and VGGNet. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 77, 103845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Liu, J. Combining Multiple Deep Features for Glaucoma Classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, USA, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 985–989. [Google Scholar]
- Elakkiya, B.; Saraniya, O. A Comparative Analysis of Pretrained and Transfer-Learning Model for Automatic Diagnosis of Glaucoma. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Conference on Advanced Computing (ICoAC), Chennai, India, 18–20 December 2019; pp. 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, R.; Alipour, K.; Bowd, C.; Christopher, M.; Brye, N.; Proudfoot, J.A.; Goldbaum, M.H.; Belghith, A.; Girkin, C.A.; Fazio, M.A.; et al. Detecting Glaucoma from Fundus Photographs Using Deep Learning without Convolutions: Transformer for Improved Generalization. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2022, 3, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.S.; Singh, V. Glaucoma Detection Using Mask Region-Based Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), Coimbatore, India, 2–4 December 2021; pp. 1642–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, Z.; Guo, L.; Bian, G.-B. Glaucoma Detection: Joint Segmentation and Classification Framework via Deep Ensemble Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM), Shenzhen, China, 18–21 December 2020; pp. 678–685. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, A.; Vyas, A.; Parashar, L.; Singh, U. A Glaucoma Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 2–4 July 2020; pp. 815–820. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Muswi, W.A.K.; Al-Saadi, E.H. Extraction of The Neural Edge and Its Properties for The Retina Infected with Glaucoma. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Advance of Sustainable Engineering and Its Application (ICASEA), Wasit, Iraq, 27–28 October 2021; pp. 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Guo, F.; Li, S. Direct Cup-to-Disc Ratio Estimation for Glaucoma Screening via Semi-Supervised Learning. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deperlioglu, O.; Kose, U.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A.; Giampaolo, F.; Fortino, G. Explainable Framework for Glaucoma Diagnosis by Image Processing and Convolutional Neural Network Synergy: Analysis with Doctor Evaluation. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 129, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Zou, B.; Zhao, R.; Chen, Y.; He, Z.; Zhou, M. Clinical Interpretable Deep Learning Model for Glaucoma Diagnosis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.F.; Vese, L.A. Active Contours without Edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, A.M. Realization of the Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) for Real-Time Image Enhancement. J. VLSI Signal Process. -Syst. Signal Image Video Technol. 2004, 38, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V. Data Mining for Imbalanced Datasets: An Overview. In Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook; Maimon, O., Rokach, L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 853–867. ISBN 978-0-38724-435-8. [Google Scholar]
- Douzas, G.; Bacao, F.; Last, F. Improving Imbalanced Learning through a Heuristic Oversampling Method Based on K-Means and SMOTE. Inf. Sci. 2018, 465, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. Assoc. Adv. Artif. Intell. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Zoph, B.; Vasudevan, V.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Learning Transferable Architectures for Scalable Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8697–8710. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Sreng, S.; Maneerat, N.; Hamamoto, K.; Win, K.Y. Deep Learning for Optic Disc Segmentation and Glaucoma Diagnosis on Retinal Images. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, M.N.; Malik, M.I.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Dengel, A.; Shafait, F.; Neumeier, W.; Ahmed, S. Correction to: Two-Stage Framework for Optic Disc Localization and Glaucoma Classification in Retinal Fundus Images Using Deep Learning. BMC Med. Inf. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Kee Wong, D.W.; Wong, T.Y.; Liu, J. Glaucoma Detection Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 715–718. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Yan, S.; Wong, D.W.K.; Wong, T.Y.; Liu, J. Automatic Feature Learning for Glaucoma Detection Based on Deep Learning. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 669–677. ISBN 978-3-31924-573-7. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, S.; Wong, D.W.K.; Liu, J.; Xu, D. Efficient Reconstruction-Based Optic Cup Localization for Glaucoma Screening. In Advanced Information Systems Engineering; Salinesi, C., Norrie, M.C., Pastor, Ó., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2013; Volume 7908, pp. 445–452. ISBN 978-3-64238-708-1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Cheng, J.; Wong, D.W.K.; Liu, J. Integrating Holistic and Local Deep Features for Glaucoma Classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 1328–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Al-antari, M.A.; Al-masni, M.A.; Choi, M.-T.; Han, S.-M.; Kim, T.-S. A Fully Integrated Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for Digital X-Ray Mammograms via Deep Learning Detection, Segmentation, and Classification. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2018, 117, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfian, G.; Syafrudin, M.; Fahrurrozi, I.; Fitriyani, N.L.; Atmaji, F.T.D.; Widodo, T.; Bahiyah, N.; Benes, F.; Rhee, J. Predicting Breast Cancer from Risk Factors Using SVM and Extra-Trees-Based Feature Selection Method. Computers 2022, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipschitz, J.; Miller, C.J.; Hogan, T.P.; Burdick, K.E.; Lippin-Foster, R.; Simon, S.R.; Burgess, J. Adoption of Mobile Apps for Depression and Anxiety: Cross-Sectional Survey Study on Patient Interest and Barriers to Engagement. JMIR Ment. Health 2019, 6, e11334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, N.; Huang, P.; Lee, J.; Keane, P.A.; Chuan, T.S.; Richhariya, A.; Teoh, S.; Lim, T.H.; Agrawal, R. Fundus Photography in the 21st Century—A Review of Recent Technological Advances and Their Implications for Worldwide Healthcare. Telemed. E-Health 2016, 22, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardes, R.; Serranho, P.; Lobo, C. Digital Ocular Fundus Imaging: A Review. Ophthalmologica 2011, 226, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- File:Retinal camera.jpg-Wikimedia Commons. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Retinal_camera.jpg (accessed on 1 December 2022).




| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Case of dataset | Glaucoma |
| Type of data | RGB image |
| Dimension of data | 3072 by 2048 pixel |
| Availability | Online access in [19] |
| Number of classes | 2 classes (normal and glaucomatous) |
| Ground truth information | CDR value, segmentation ground truth of OD and OC, classification ground truth (normal and glaucomatous classes) |
| Number of data in each class | 168 glaucomatous images and 482 healthy images |
| Scope of Research | Researcher |
|---|---|
| Optic disc and optic cup localization and segmentation | [26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36] |
| Classification of glaucoma disease | [20,37,38,39,40,41] |
| Glaucoma detection | [42,43,44,45,46] |
| CDR estimation | [47] |
| Explainable or interpretable AI for glaucoma detection | [48,49] |
| Network [Ref.] | Depth | Size (MB) | Parameters | Input Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlexNet [55] | 8 | 227 | 58,266,306 | 227 × 227 |
| GoogleNet [56] | 22 | 27 | 1,252,072 | 224 × 224 |
| Inception V3 [57] | 48 | 89 | 23,855,837 | 299 × 299 |
| XceptionNet [58] | 71 | 85 | 20,865,578 | 299 × 299 |
| ResNet-50 [59] | 107 | 98 | 23,591,810 | 224 × 224 |
| InceptionResNet [60] | 164 | 209 | 26,530,290 | 299 × 299 |
| MobileNet [61] | 53 | 13 | 4,256,893 | 224 × 224 |
| NasNet [62] | * | 360 | 5,329,777 | 331 × 331 |
| DenseNet [63] | 201 | 77 | 7,039,554 | 224 × 224 |
| Network [Ref.] | Input Size | Accuracy (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sreng et al. (2020) [64] | Our Proposed Model (2022) | |||
| Pre-Trained Model | CNN+SVM | |||
| AlexNet [55] | 227 × 227 | 68.42 | 76.41 | 92.61 |
| GoogleNet [56] | 224 × 224 | 71.79 | 74.87 | 87.95 |
| Inception V3 [57] | 299 × 299 | 75.38 | 78.97 | 75.57 |
| XceptionNet [58] | 299 × 299 | 77.44 | 75.9 | 71.76 |
| ResNet-50 [59] | 224 × 224 | 75.9 | 75.38 | 84.93 |
| InceptionResNet [60] | 299 × 299 | 80 | 78.46 | 74.05 |
| MobileNet [61] | 224 × 224 | 80.51 | 74.36 | 75.57 |
| NasNet [62] | 331 × 331 | 73.85 | 74.87 | 78.63 |
| DenseNet [63] | 224 × 224 | 77.44 | 78.46 | 92.88 |
| Reference | Accuracy (%) | AUC (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| [64] | 88.86 | 83.59 | Experiment 1: using CNN pre-trained model |
| [64] | 85.26 | 80 | Experiment 2: using CNN+SVM |
| [65] | - | 86.8 | Experiment 1: using a random training technique |
| [65] | - | 87.4 | Experiment 2: using cross-validation |
| [66] | - | 83.1 | - |
| [67] | - | 83.8 | - |
| [68] | - | 83.8 | - |
| [69] | - | 82.3 | - |
| [32] | - | 85.1 | - |
| [40] | - | 84.83 | - |
| [41] | 91.2 | - | - |
| Our proposed method (2022) | 92.88 | 89.34 | Using DenseNet |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prananda, A.R.; Frannita, E.L.; Hutami, A.H.T.; Maarif, M.R.; Fitriyani, N.L.; Syafrudin, M. Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Analysis Using Deep Learning to Improve Glaucoma Detection in Eye Disease Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010037
Prananda AR, Frannita EL, Hutami AHT, Maarif MR, Fitriyani NL, Syafrudin M. Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Analysis Using Deep Learning to Improve Glaucoma Detection in Eye Disease Assessment. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010037
Chicago/Turabian StylePrananda, Alifia Revan, Eka Legya Frannita, Augustine Herini Tita Hutami, Muhammad Rifqi Maarif, Norma Latif Fitriyani, and Muhammad Syafrudin. 2023. "Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Analysis Using Deep Learning to Improve Glaucoma Detection in Eye Disease Assessment" Applied Sciences 13, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010037
APA StylePrananda, A. R., Frannita, E. L., Hutami, A. H. T., Maarif, M. R., Fitriyani, N. L., & Syafrudin, M. (2023). Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Analysis Using Deep Learning to Improve Glaucoma Detection in Eye Disease Assessment. Applied Sciences, 13(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010037







