Processing the Artificial Edge-Effects for Finite-Difference Frequency-Domain in Viscoelastic Anisotropic Formations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Foundations
2.1. Frequency Domain Elastic VTI Equation
2.2. Absorbing Boundary Condition
2.3. Numerical Implementation
3. Synthetic Examples
3.1. Comparative Analysis of the Stability of PML and M-PML
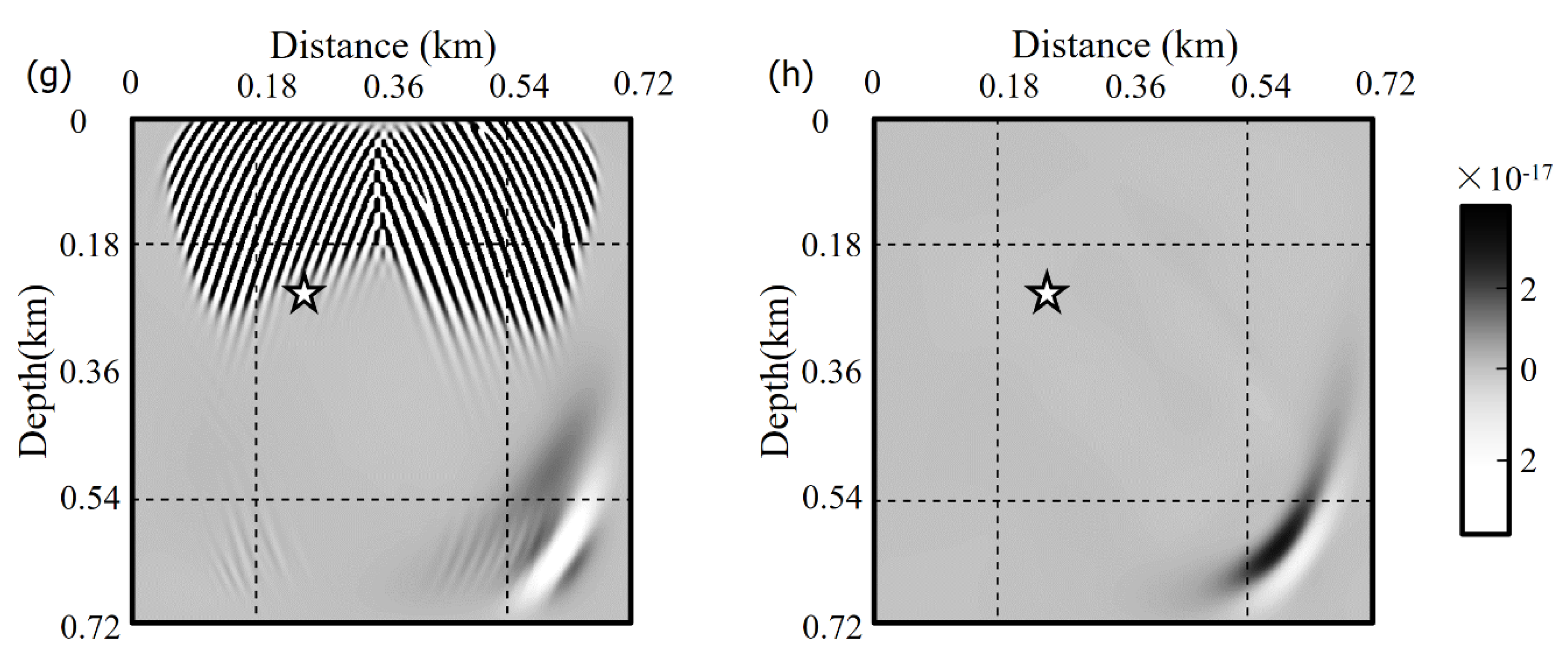
3.2. Comparative Analysis in Homogeneous Elastic Anisotropic Media
3.3. Wave Propagation in a Complex Anisotropic Medium
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hestholm, S. Acoustic VTI modeling using high-order finite differences. Geophysics 2009, 74, T67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Two-dimensional seismic wave simulation in anisotropic media by non-staggered finite difference method. Chin. J. Geophys. 2009, 52, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Z.; Sun, C.; Wu, D. Theory and modeling of constant-Q viscoelastic anisotropic media using fractional derivative. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 217, 798–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaney, A.J. Geophysical Diffraction Tomography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1984, GE-22, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, R.G.; Worthington, M.H. The application of diffraction tomography to cross-hole seismic data. Geophysics 1988, 53, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baysal, E.; Kosloff, D.; Sherwood, J. Reverse time migration. Geophysics 1983, 48, 1514–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMechan, G. Migration by extrapolation of time-dependent boundary values. Geophys. Prospect. 1983, 31, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Wang, X.; Schuster, G. Least-squares migration of multi-source data with a deblurring filter. Geophysics 2011, 76, R135–R146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantola, A. Inversion of seismic reflection data in the acoustic approximation. Geophysics 1984, 49, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, R.G.; Worthington, M.H. Acoustic wave equation inverse theory applied to multi-source cross-hole tomography Part I: Acoustic wave-equation method. Geophys. Prospect. 1990, 38, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virieux, J.; Operto, S. An overview of full-waveform inversion in exploration geophysics. Geophysics 2009, 74, WCC1–WCC26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfurt, K.J. Accuracy of finite difference and finite element modeling of scalar and elastic wave equations. Geophysics 1984, 49, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Hadj-Ali, H.; Operto, S.; Virieux, J. An efficient frequency-domain full-waveform inversion method using simultaneous encoded sources. Geophysics 2011, 76, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operto, S.; Virieux, J.; Ribodetti, A.; Anderson, J.E. Finite-difference frequency-domain modeling of viscoacoustic wave propagation in 2D tilted transversely isotropic (TTI) media. Geophysics 2009, 74, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Min, D.J.; Lee, G.H.; Lee, H.Y. 2D frequency-domain elastic full waveform inversion using finite-element method for VTI media. In SEG Technical Program. Expanded Abstracts 2011; SEG: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2011; pp. 2654–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Won, M.; Greenhalgh, S.; Liu, X. Generalizeded stiffness reduction method to remove the artificial edge-effects for seismic wave modeling in elastic anisotropic media. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 220, 1394–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhou, B.; Riahi, M.; Ai-Khaleel, M. A new generalized stiffness reduction method for 2D/2.5D frequency domain seismic wave modeling in viscoelastic anisotropic media. Geophysics 2020, 85, T315–T329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenger, J.P. A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves. J. Comput. Phys. 1994, 114, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.; Tsogka, C. Application of the perfectly matched absorbing layer model to the linear elastodynamic problem in anisotropic heterogeneous media. Geophysics 2001, 66, 294–307. [Google Scholar]
- Komatitsch, D.; Tromp, J. A perfectly matched layer absorbing boundary condition for the second-order seismic wave equation. Geophys. J. Int. 2003, 154, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Niu, F. An unsplit complex frequency-shifted perfectly matched layer for second-order acoustic wave equations. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, Y. Unsplit complex frequency-shifted PML implementation using auxiliary differential equations for seismic wave modeling. Geophysics 2010, 75, T141–T154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opertp, S.; Virieux, J.; Amestoy, P.; L’Excellent, J.; Giraud, L.; Ali, H. 3D finite-difference frequency-domain modeling of visco-acoustic wave propagation using a massively parallel direct solver: A feasibility study. Geophysics 2007, 72, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskooi, A.; Johnson, S.G. Distinguishing correct from incorrect PML proposals and a corrected unsplit PML for anisotropic dispersive media. J. Comput. Phys. 2011, 230, 2369–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Fajardo, K.C.; Papageorgiou, A.S. A non-convolutional, split-field, perfectly matched layer for wave propagation in isotropic and anisotropic elastic media: Stability analysis. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 2008, 98, 1811–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. A multi-axial perfectly matched layer (M-PML) for the long-time simulation of elastic wave propagation in the second-order equations. J. Appl. Geophys. 2014, 101, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Complex frequency-shifted multi-axial perfectly matched layer for elastic wave modeling on curvilinear grids. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 198, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, L. Weak elastic anisotropy. Geophysics 1986, 51, 1954–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toksoz, M.N.; Johnston, D.H. Seismic Wave Attenuation; SEG Geophysical Reprint Series, No. 2; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; He, J.; Liu, Q. The application of the perfectly matched layer in numerical modeling of wave propagation in poroelastic media. Geophysics 2001, 66, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, P.F.; Hron, F. Reflection and transmission coefficients for transversely isotropic media. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 1977, 67, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Medium | Density (kg/m3) | Qp | Qs | Elastic Moduli (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium 1 | 3200 | 20 | 10 | |
| Medium 2 | 8900 | 20 | 10 | |
| Medium 3 | 1000 | — | — |
| Layer Media | Vp (m/s) | Vs (m/s) | Qp | Qs | ε | δ | ρ (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer 1 | 1875 | 826 | 10 | 10 | 0.225 | 0.100 | 2000 |
| Layer 2 | 2202 | 969 | 10 | 10 | 0.015 | 0.060 | 2250 |
| Layer 3 | 2868 | 1350 | 15 | 15 | 0.970 | −0.090 | 1860 |
| Layer 4 | 3368 | 1829 | 21 | 18 | 0.110 | −0.035 | 2500 |
| Layer 5 | 3688 | 2774 | 30 | 19 | 0.081 | 0.057 | 2730 |
| Layer 6 | 3901 | 2682 | 38 | 25 | 0.137 | −0.012 | 2640 |
| Layer 7 | 4296 | 2471 | 42 | 35 | 0.081 | 0.129 | 2660 |
| Layer 8 | 4529 | 2703 | 50 | 40 | 0.034 | 0.211 | 2520 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; He, X.; Chen, H. Processing the Artificial Edge-Effects for Finite-Difference Frequency-Domain in Viscoelastic Anisotropic Formations. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094719
Yang J, He X, Chen H. Processing the Artificial Edge-Effects for Finite-Difference Frequency-Domain in Viscoelastic Anisotropic Formations. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(9):4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094719
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jixin, Xiao He, and Hao Chen. 2022. "Processing the Artificial Edge-Effects for Finite-Difference Frequency-Domain in Viscoelastic Anisotropic Formations" Applied Sciences 12, no. 9: 4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094719
APA StyleYang, J., He, X., & Chen, H. (2022). Processing the Artificial Edge-Effects for Finite-Difference Frequency-Domain in Viscoelastic Anisotropic Formations. Applied Sciences, 12(9), 4719. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094719






