Bone Modifications Induced by Rapid Maxillary Expander: A Three-Dimensional Cephalometric Pilot Study Comparing Two Different Cephalometric Software Programs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yitschaky, O.; Redlich, M.; Abed, Y.; Faerman, M.; Casap, N.; Hiller, N. Comparison of common hard tissue cephalometric measurements between computed tomography 3D reconstruction and conventional 2D cephalometric images. Angle Orthod. 2011, 81, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feragalli, B.; Rampado, O.; Abate, C.; Macrì, M.; Festa, F.; Stromei, F.; Caputi, S.; Guglielmi, G. Cone beam computed tomography for dental and maxillofacial imaging: Technique improvement and low-dose protocols. Radiol. Med. 2017, 122, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarfe, W.C.; Azevedo, B.; Toghyani, S.; Farman, A.G. Cone Beam Computed Tomographic imaging in orthodontics. Aust Dent. J. 2017, 62 (Suppl. 1), 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapila, S. Contemporary concepts on cone-beam computed tomography in orthodontics. In Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Orthodontics: Indications, Insights and Innovations; Kapila, S., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 5–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kapila, S.D.; Nervina, J.M. CBCT in orthodontics: Assessment of treatment outcomes and indications for its use. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2015, 44, 20140282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salagnac, J.M. Proposition d’un indice définissant les indications médicales d’une disjonction intermaxillaire chez un sujet en période de croissance [Proposal for a clinical diagnosis index in rapid palatal expansion (RPE) in childhood]. Orthod. Fr. 2019, 90, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneima, A.; Abdel-Fattah, E.; Hartsfield, J.; El-Bedwehi, A.; Kamel, A.; Kula, K. Effects of rapid maxillary expansion on the cranial and circummaxillary sutures. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2011, 140, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, A.J. Rapid expansion of the maxillary dental arch and nasal cavity by opening the mid palatal suture. Angle Orthod. 1961, 31, 73–89. [Google Scholar]
- Starnbach, H.; Bayne, D.; Cleall, J.; Subtelny, J.D. Facioskeletal and dental changes resulting from rapid maxillary expansion. Angle Orthod. 1966, 36, 152–164. [Google Scholar]
- Babacan, H.; Sokucu, O.; Doruk, C.; Ay, S. Rapid maxillary expansion and surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion effects on nasal volume. Angle Orthod. 2006, 76, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Christie, K.F.; Boucher, N.; Chung, C.H. Effects of bonded rapid palatal expansion on the transverse dimensions of the maxilla: A cone-beam computed tomography study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 137 (Suppl. 4), S79–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.D.S.; Jacob, H.B.; Locks, A.; Brunetto, M.; Ribeiro, G.L.U. Evaluation of the rapid and slow maxillary expansion using cone-beam computed tomography: A randomized clinical trial. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2017, 22, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. 1990 recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 60. Ann. ICRP 1991, 21, 1–201. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. The 2007 recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103. Ann. ICRP 2008, 37, 1–332. [Google Scholar]
- Durao, A.R.; Pittayapat, P.; Rockenbach, M.I.; Olszewski, R.; Ng, S.; Ferreira, A.P.; Jacobs, R. Validity of 2D lateral cephalometry in orthodontics: A systematic review. Prog. Orthod. 2013, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rischen, R.J.; Breuning, K.H.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. Records needed for orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, U.; Orhan, K.; Abe, N. Comparison of linear and angular measurements using two-dimensional conventional methods and three-dimensional cone beam CT images reconstructed from a volumetric rendering program in vivo. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2011, 40, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Ludlow, J.; Soares Cevidanes, L.H.; Mol, A. In vivo comparison of conventional and cone beam CT synthesized cephalograms. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Hwang, C.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Houschyar, K.S.; Yu, J.H.; Bae, S.Y.; Cha, J.Y. Registration of digital dental models and cone-beam computed tomography images using 3-dimensional planning software: Comparison of the accuracy according to scanning methods and software. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 157, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawchuk, D.; Alhadlaq, A.; Alkhadra, T.; Carlyle, T.D.; Kusnoto, B.; El-Bialy, T. Comparison of two three-dimensional cephalometric analysis computer software. J. Orthod. Sci. 2014, 3, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Farronato, G.; Garagiola, U.; Dominici, A.; Periti, G.; de Nardi, S.; Carletti, V.; Farronato, D. “Ten-point” 3D cephalometric analysis using low-dosage cone beam computed tomography. Prog. Orthod. 2010, 11, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhard, J.P.; Dietrich, A.D.; Jacobsen, C.; Roos, M.; Lübbers, H.T.; Obwegeser, J.A. Cephalometric and three-dimensional assessment of the posterior airway space and imaging software reliability analysis before and after orthognathic surgery. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koretsi, V.; Tingelhoff, L.; Proff, P.; Kirschneck, C. Intra-observer reliability and agreement of manual and digital orthodontic model analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2018, 40, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joda, T.; Brägger, U. Digital vs. conventional implant prosthetic workflows: A cost/time analysis. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coachman, C.; Calamita, M.A.; Coachman, F.G.; Coachman, R.G.; Sesma, N. Facially generated and cephalometric guided 3D digital design for complete mouth implant rehabilitation: A clinical report. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baan, F.; de Waard, O.; Bruggink, R.; Xi, T.; Ongkosuwito, E.M.; Maal, T.J.J. Virtual setup in orthodontics: Planning and evaluation. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2020, 24, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruder, C.; Ortolani, C.L.F.; Lima, T.A.; Artese, F.; Faltin Junior, K. Evaluation of palate area before and after rapid maxillary expansion, using cone-beam computed tomography. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2019, 24, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuzian, M.; Ju, X.; Almukhtar, A.; Ayoub, A.; Al-Muzian, L.; McDonald, J.P. Does rapid maxillary expansion affect nasopharyngeal airway? A prospective Cone Beam Computerised Tomography (CBCT) based study. Surgeon 2018, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastuca, R.; Turiaco, H.; Assandri, F.; Zecca, P.A.; Levrini, L.; Caprioglio, A. Condylar Changes in Children with Posterior Crossbite after Maxillary Expansion: Tridimensional Evaluation. Children 2021, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindaroğlu, F.; Doğan, S. Evaluation and comparison of root resorption between tooth-borne and tooth-tissue borne rapid maxillary expansion appliances: A CBCT study. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangrazio-Kulbersh, V.; Jezdimir, B.; de Deus Haughey, M.; Kulbersh, R.; Wine, P.; Kaczynski, R. CBCT assessment of alveolar buccal bone level after RME. Angle Orthod. 2013, 83, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Park, J.K.; Kim, H.; Han, S.S.; Jeong, H.G.; Park, H. Comparison of conventional lateral cephalograms with corresponding CBCT radiographs. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2012, 42, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luebbert, J.; Ghoneima, A.; Lagravère, M.O. Skeletal and dental effects of rapid maxillary expansion assessed through three-dimensional imaging: A multicenter study. Int. Orthod. 2016, 14, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sygouros, A.; Motro, M.; Ugurlu, F.; Acar, A. Surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion: Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of different surgical techniques and their effects on the maxillary dentoskeletal complex. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2014, 146, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mummolo, S.; Marchetti, E.; Albani, F.; Campanella, V.; Pugliese, F.; Di Martino, S.; Tecco, S.; Marzo, G. Comparison between rapid and slow palatal expansion: Evaluation of selected periodontal indices. Head Face Med. 2014, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugolini, A.; Doldo, T.; Ghislanzoni, L.T.; Mapelli, A.; Giorgetti, R.; Sforza, C. Rapid palatal expansion effects on mandibular transverse dimensions in unilateral posterior crossbite patients: A three-dimensional digital imaging study. Prog. Orthod. 2016, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagravère, M.O.; Major, P.W. Proposed reference point for 3-dimensional cephalometric analysis with cone-beam computerized tomography. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2005, 128, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, S.; Hu, C.; Zhang, H. Automatic classification of CT images of cerebral hemorrhage in dicom format based on BP neural network. J. Phys.Conf. Ser. 2020, 1629, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagravère, M.O.; Carey, J.; Heo, G.; Toogood, R.W.; Major, P.W. Transverse, vertical, and anteroposterior changes from bone-anchored maxillary expansion vs. traditional rapid maxillary expansion: A randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 137, 304.e1-12; discussion 304–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vlijmen, O.J.; Maal, T.; Bergé, S.J.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Katsaros, C.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. A comparison between 2D and 3D cephalometry on CBCT scans of human skulls. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratieri, C.; Alves, M., Jr.; Bolognese, A.M.; Nojima, M.C.; Nojima, L.I. Changes in skeletal and dental relationship in Class II Division I malocclusion after rapid maxillary expansion: A prospective study. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2014, 19, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.H.; Font, B. Skeletal and dental changes in the sagittal, vertical, and transverse dimensions after rapid palatal expansion. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2004, 126, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habeeb, M.; Boucher, N.; Chung, C.H. Effects of rapid palatal expansion on the sagittal and vertical dimensions of the maxilla: A study on cephalograms derived from cone-beam computed tomography. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2013, 144, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissheimer, A.; de Menezes, L.M.; Mezomo, M.; Dias, D.M.; de Lima, E.M.; Rizzatto, S.M. Immediate effects of rapid maxillary expansion with Haas-type and hyrax-type expanders: A randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2011, 140, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, N.L.; Da Silveira, A.C.; Kusnoto, B.; Viana, G. Three-dimensional assessment of morphologic changes of the maxilla: A comparison of 2 kinds of palatal expanders. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2004, 126, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Façanha, A.J.; Lara, T.S.; Garib, D.G.; da Silva Filho, O.G. Transverse effect of Haas and Hyrax appliances on the upper dental arch in patients with unilateral complete cleft lip and palate: A comparative study. Dental Press J. Orthod. 2014, 19, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerruto, C.; Ugolini, A.; Di Vece, L.; Doldo, T.; Caprioglio, A.; Silvestrini-Biavati, A. Cephalometric and dental arch changes to Haas-type rapid maxillary expander anchored to deciduous vs permanent molars: A multicenter, randomized controlled trial. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2017, 78, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugolini, A.; Cerruto, C.; Di Vece, L.; Ghislanzoni, L.H.; Sforza, C.; Doldo, T.; Silvestrini-Biavati, A.; Caprioglio, A. Dental arch response to Haas-type rapid maxillary expansion anchored to deciduous vs permanent molars: A multicentric randomized controlled trial. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimring, J.F.; Isaacson, R.J. Forces Produced by Rapid Maxillary Expansion. 3. FORCES Present during Retention. Angle Orthod. 1965, 35, 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Geran, R.G.; McNamara, J.A.; Baccetti, T.; Franchi, L.; Shapiro, L.M. A prospective long-term study on the effects of rapid maxillary expansion in the early mixed dentition. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2006, 129, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, L.; De Rosa, A.; Iaselli, F.; D’Apuzzo, F.; Grassia, V.; Cappabianca, S. Comparison between rapid and mixed maxillary expansion through an assessment of dento-skeletal effects on posteroanterior cephalometry. Prog. Orthod. 2014, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baldini, A.; Nota, A.; Santariello, C.; Assi, V.; Ballanti, F.; Cozza, P. A comparative as-sessment of changes in dental arches associated with different activation protocols of rapid maxillary expansion. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2018, 19, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baldini, A.; Nota, A.; Santariello, C.; Caruso, S.; Assi, V.; Ballanti, F.; Gatto, R.; Cozza, P. Sagittal dentoskeletal modifications associated with different activation protocols of rapid maxillary expansion. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2018, 19, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lagravère, M.O.; Ling, C.P.; Woo, J.; Harzer, W.; Major, P.W.; Carey, J.P. Transverse, vertical, and anterior-posterior changes between tooth-anchored versus Dresden bone-anchored rapid maxillary expansion 6 months post-expansion: A CBCT randomized controlled clinical trial. Int. Orthod. 2020, 18, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürler, G.; Akar, N.K.; Delilbaşı, Ç.; Kaçar, İ. Skeletal changes following surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion (SARME). Eur. Oral. Res. 2018, 52, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Dakhno, L.; Vyshemyrska, T.; Flis, P.; Burlakov, P. Comparative Transversal Evaluation of Upper Jaw following Rapid Maxillary Expansion in the Mixed Dentition Period. Cbct Analysis. Georgian Med. News. 2021, 316–317, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Bazargani, F.; Lund, H.; Magnuson, A.; Ludwig, B. Skeletal and dentoalveolar effects using tooth-borne and tooth-bone-borne RME appliances: A randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Eur. J. Orthod. 2021, 43, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribante, A.; Gallo, S.; Pascadopoli, M.; Canzi, P.; Marconi, S.; Montasser, M.A.; Bressani, D.; Gandini, P.; Sfondrini, M.F. Properties of CAD/CAM 3D Printing Dental Materials and Their Clinical Applications in Orthodontics: Where Are We Now? Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, T.M.A.D.; Barbosa, I.D.S.; Palma, K.K. Orthodontic digital workflow: Devices and clinical applications. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2021, 26, e21spe6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnagar, M.H.; Aronovich, S.; Kusnoto, B. Digital Workflow for Combined Orthodontics and Orthognathic Surgery. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
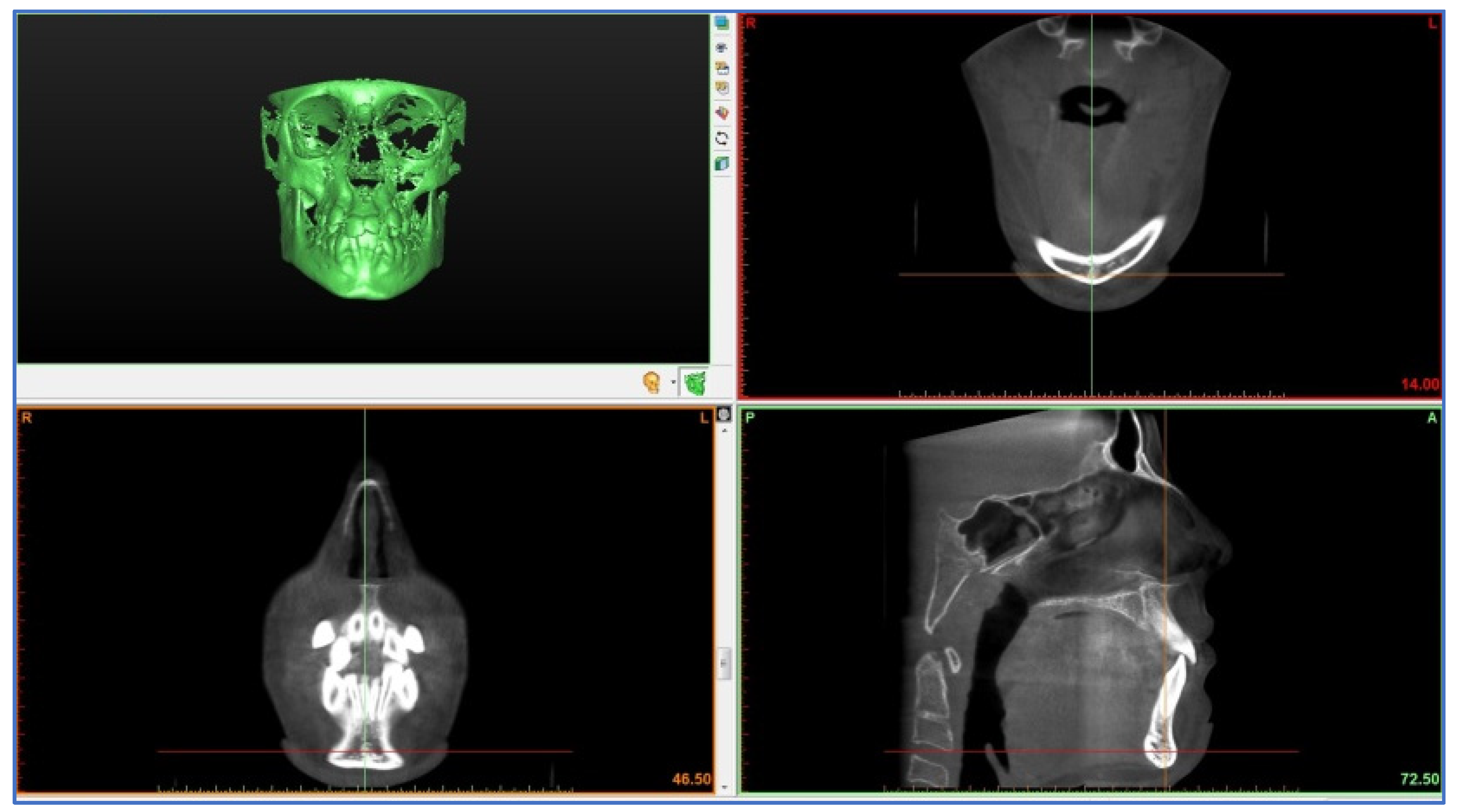
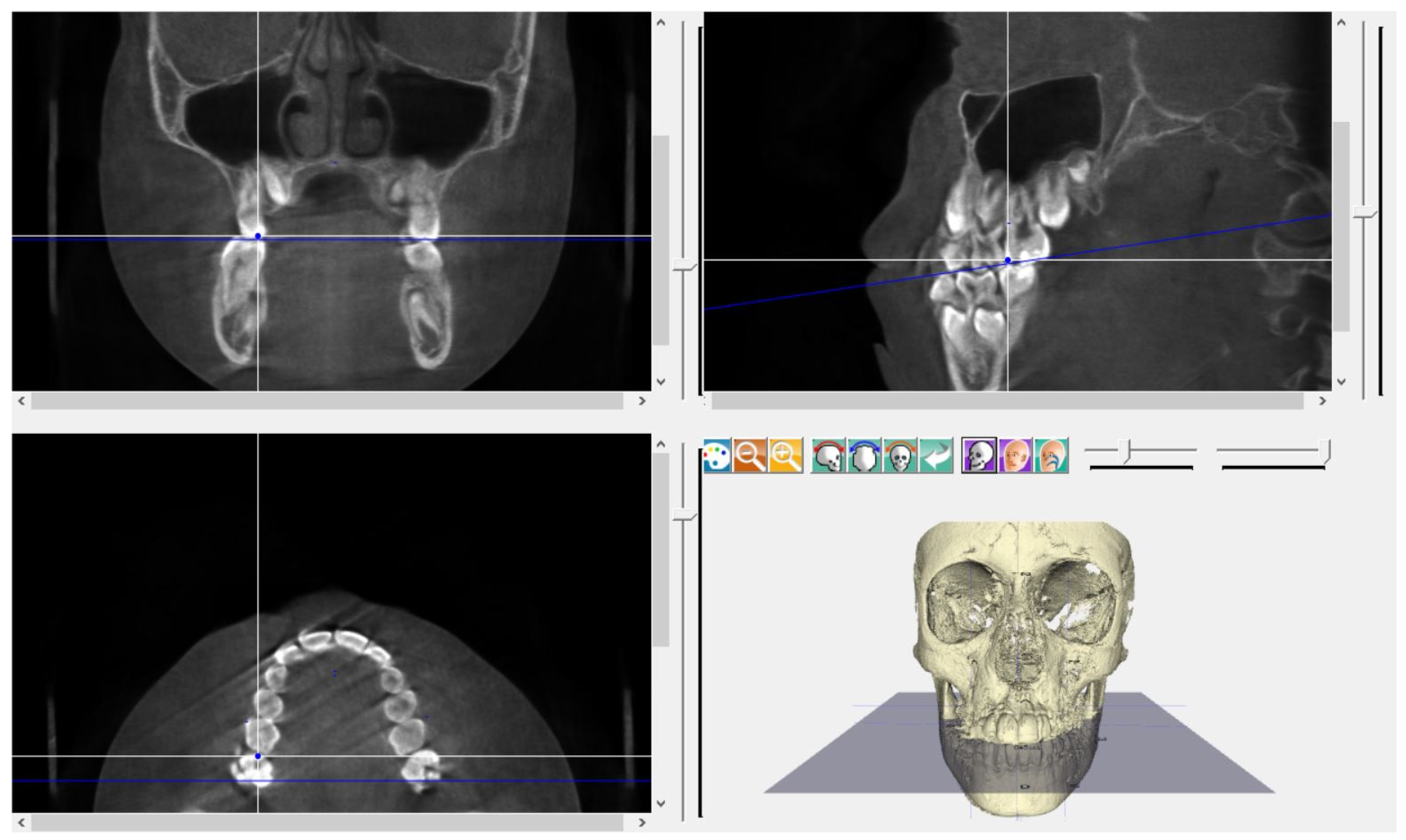
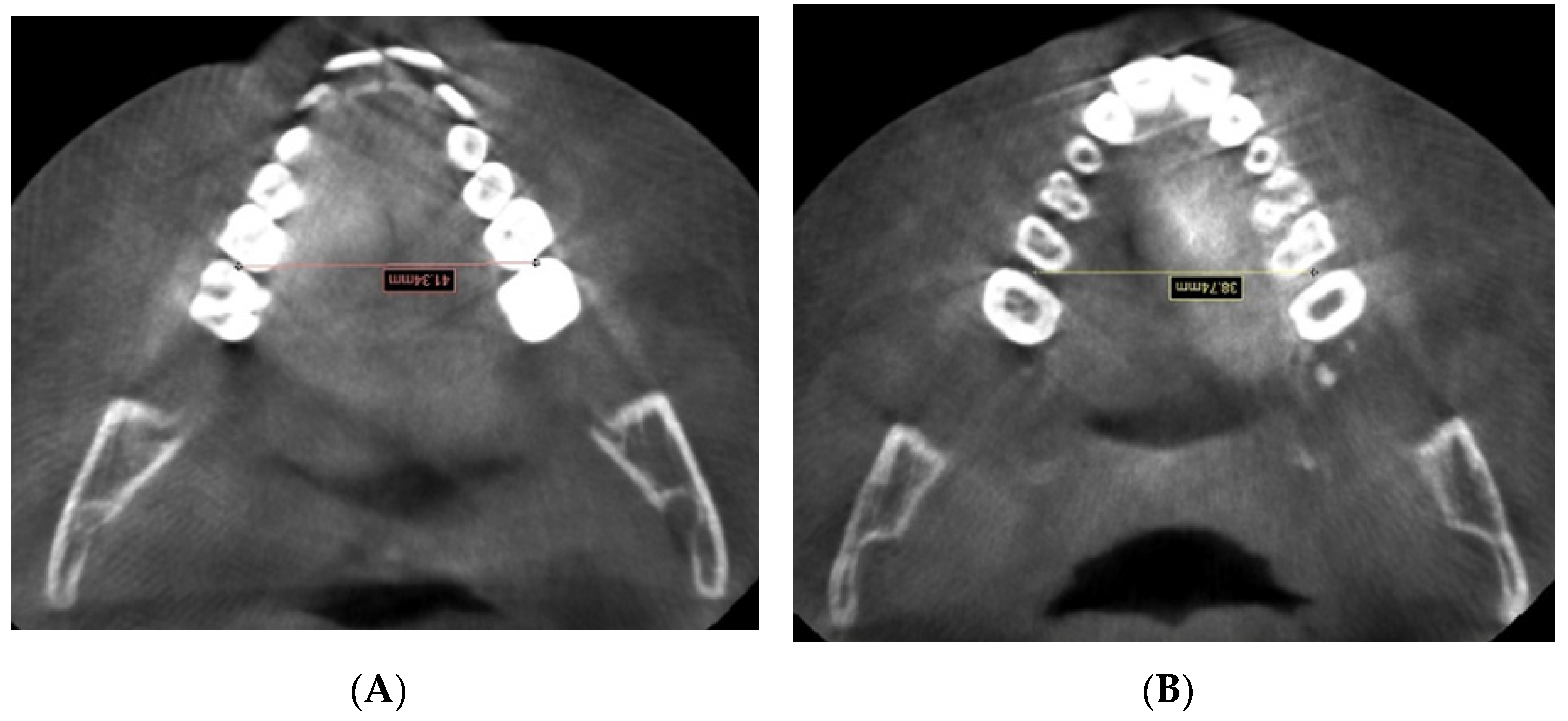
| Skeletal Landmarks | ||
|---|---|---|
| Point (Abbr.) | Acronym | Explanation |
| ANS | Anterior Nasal Spine | Anterior point on maxillary bone |
| PNS | Posterior Nasal Spine | Posterior limit of bony palate or maxilla |
| S | Sella Turcica | Midpoint of sella turcica |
| N | Nasion | Most anterior point on frontonasal suture |
| Point A | Subspinale | Most concave point on anterior maxilla |
| Point B | Supramentale | Most concave point on mandibular symphysis |
| Me | Menton | Lowest point on mandibular symphysis |
| Go | Gonion | Most posterior inferior point on angle of mandible |
| It can also be constructed by bisecting the angle formed by | ||
| intersection of mandibular plane and ramus of mandible | ||
| MGo | Mid-Gonion | Middle point between right gonion and left gonion |
| If | Infraorbital Foramen | RIf (right); LIf (left) |
| Mf | Mental Foramen | RMf (right); LMf (left) |
| S-Go | Sella–Gonion | Posterior facial height |
| N-Me | Nasion–Menton | Anterior facial height |
| N-Ans | Nasion–Anterior | Upper anterior facial height |
| Nasal Spine | ||
| Ans-Me | Anterior Nasal Spine– | Lower anterior facial height |
| Menton | ||
| N-Ans+Ans-Me | Nasion–Anterior Nasal | Total anterior facial height |
| Spine+Anterior Nasal | ||
| Spine–Menton | ||
| SNA | Angle between Sella/ | Antero-position of maxilla relative to |
| Nasion plane and | upper cranial structures | |
| Nasion/A plane | ||
| SNB | Angle between Sella/ | Antero-position of mandible relative |
| Nasion plane and | to upper cranial structures | |
| Nasion/B plane | ||
| ANB | SNA—SNB | Anteroposterior relationship of the |
| mandible to the maxilla | ||
| Dental landmarks | ||
| 6RIM-6LIM | Distance between the interproximal contact point on the | |
| mesial surface of the first right molar and the interproximal | ||
| contact point on the mesial surface of the first left molar | ||
| 6RABM-6LABM | Distance between the mesial surface of the first right molar | |
| and the mesial surface of the first left molar at the | ||
| alveolar bone level | ||
| A0B0 | Orthogonal projections on the occlusal plane of points | |
| A and B | ||
| AOcl | Anterior occlusal point: middle point of the line that links | |
| upper and lower incisal points | ||
| MAOcl | Mid-anterior occlusal point: middle point between right | |
| AOcl and left AOcl | ||
| POcl | Posterior occlusal point: middle point of the occlusal surface of first permanent molars |
| Variables | Simplant | ‡ | Deltadent | ‡ | ¥ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Exp | Post-Exp | Pre-Exp | Post-Exp | ||||
| 6RABM-6LABM | 36.18 (2.88) a | 40.85 (2.59) b | p < 0.0001 | 36.47 (2.77) a | 41.25 (2.74) b | p < 0.0001 | NS |
| 6RIM-6LIM | 37.40 (2.79) a | 41.71 (2.85) b | p < 0.0001 | 39.49 (6.58) a | 43.97 (6.71) b | p < 0.0001 | NS |
| RIf-RMf | 54.63 (4.48) a | 56.24 (4.93) a | NS | 52.83 (5.29) a | 56.54 (4.84) b | p = 0.0211 | NS |
| LIf-LMf | 54.10 (4.63) a | 57.17 (4.96) a | NS | 52.73 (5.39) a | 56.28 (4.23) b | p = 0.0039 | NS |
| N-Ans+Ans-Me | 104.42 (11.09) a | 107.00 (10.29) b | p = 0.0436 | 103.94 (10.05) a | 107.50 (9.84) b | p = 0.0078 | NS |
| N-Ans | 46.39 (5.69) a | 48.62 (5.62) b | p = 0.0126 | 46.28 (5.83) a | 48.50 (5.94) b | p = 0.0015 | NS |
| Ans-Me | 58.03 (6.75) a | 58.38 (6.14) a | NS | 57.68 (5.84) a | 59.00 (5.54) a | NS | NS |
| Sup/inf facial H | 80.09 (9.85) a | 83.27 (8.78) a | NS | 80.36 (9.55) a | 81.64 (10.48) a | NS | NS |
| S-Go | 63.90 (6.16) a | 66.62 (6.31) b | p = 0.0024 | 62.72 (5.42) a | 65.05 (6.02) b | p = 0.0279 | NS |
| N-Me | 100.58 (10.35) a | 103.47 (9.92) a | NS | 101.07 (9.45) a | 104.64 (9.50) a | NS | NS |
| S-Go/N-Me (%) | 63.82 (4.98) a | 64.64 (5.30) a | NS | 62.28 (3.58) a | 62.36 (3.72) a | NS | NS |
| SNA | 83.12 (1.88) a | 83.02 (1.83) a | NS | 83.27 (1.64) a | 82.75 (1.73) a | NS | NS |
| SNB | 78.48 (2.93) a | 78.44 (1.91) a | NS | 78.53 (2.71) a | 78.08 (1.71) a | NS | NS |
| ANB | 4.71 (2.16) a | 4.67 (1.79) a | NS | 4.72 (2.22) a | 4.73 (1.75) a | NS | NS |
| WITS | 2.27 (0.85) a | 2.83 (1.28) a | NS | 3.21 (1.49) a | 2.53 (1.35) a | NS | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sfondrini, M.F.; Pascadopoli, M.; Dicorato, S.; Todaro, C.; Nardi, M.G.; Gallo, S.; Gandini, P.; Scribante, A. Bone Modifications Induced by Rapid Maxillary Expander: A Three-Dimensional Cephalometric Pilot Study Comparing Two Different Cephalometric Software Programs. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094313
Sfondrini MF, Pascadopoli M, Dicorato S, Todaro C, Nardi MG, Gallo S, Gandini P, Scribante A. Bone Modifications Induced by Rapid Maxillary Expander: A Three-Dimensional Cephalometric Pilot Study Comparing Two Different Cephalometric Software Programs. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(9):4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094313
Chicago/Turabian StyleSfondrini, Maria Francesca, Maurizio Pascadopoli, Serena Dicorato, Claudia Todaro, Maria Gloria Nardi, Simone Gallo, Paola Gandini, and Andrea Scribante. 2022. "Bone Modifications Induced by Rapid Maxillary Expander: A Three-Dimensional Cephalometric Pilot Study Comparing Two Different Cephalometric Software Programs" Applied Sciences 12, no. 9: 4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094313
APA StyleSfondrini, M. F., Pascadopoli, M., Dicorato, S., Todaro, C., Nardi, M. G., Gallo, S., Gandini, P., & Scribante, A. (2022). Bone Modifications Induced by Rapid Maxillary Expander: A Three-Dimensional Cephalometric Pilot Study Comparing Two Different Cephalometric Software Programs. Applied Sciences, 12(9), 4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094313









