Weaknesses in ENT Battery Design
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. ENT Battery
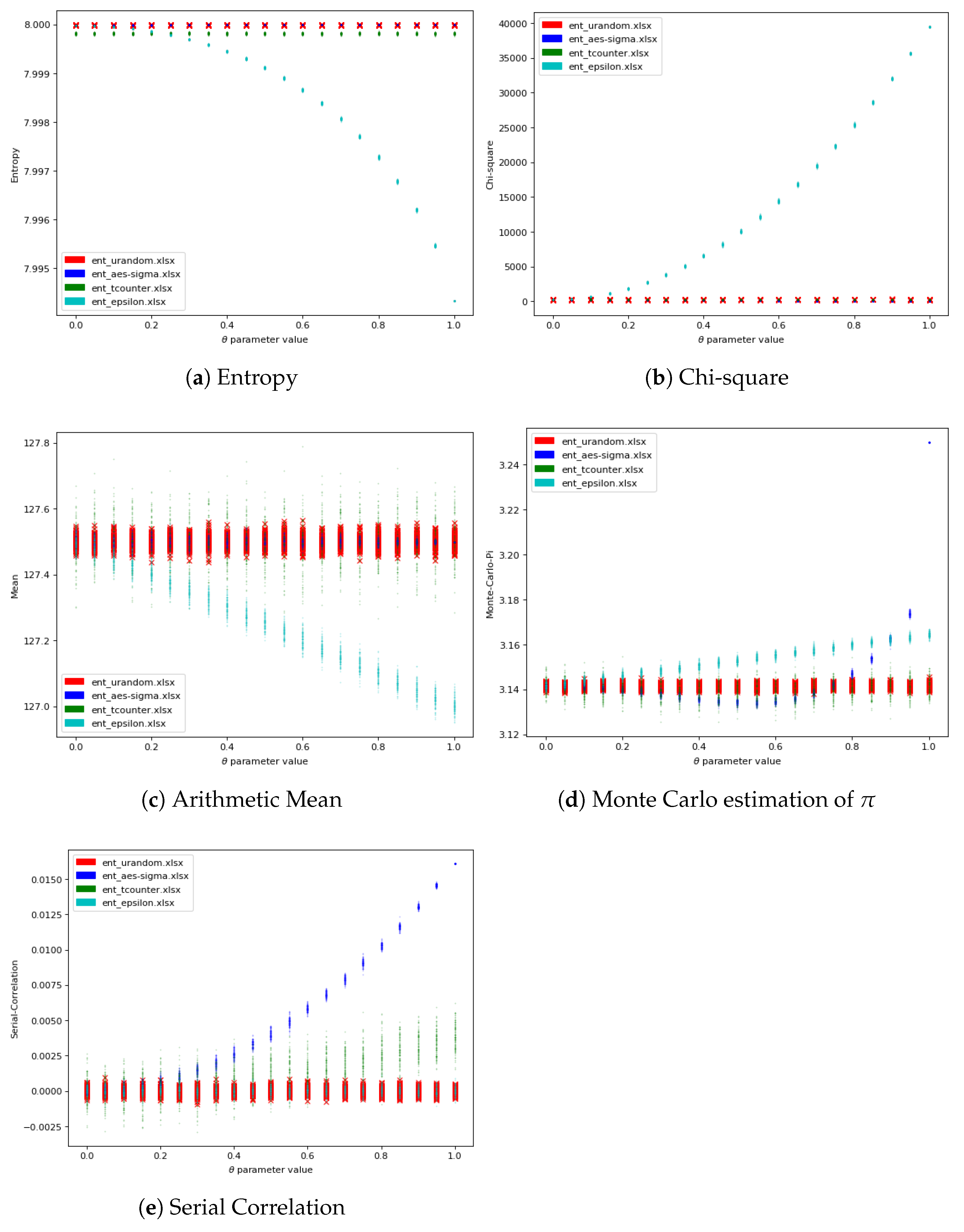
2.1. Entropy
2.2. Chi-Square
2.3. Arithmetic Mean
2.4. Monte Carlo Estimation of
2.5. Serial Correlation
3. Experimentation Design and Results
3.1. AES -Counter
3.2. -Hole
3.3. t-Counter
3.4. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Cheng, H. Pseudo-Random Number Generator Based on Logistic Chaotic System. Entropy 2019, 21, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figueroa-García, J.C.; Varón-Gaviria, C.A.; Barbosa-Fontecha, J.L. Fuzzy Random Variable Generation Using α-Cuts. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 29, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrina, G.; Peinado, A.; Ortiz, A. Gaussian Pseudorandom Number Generator Using Linear Feedback Shift Registers in Extended Fields. Mathematics 2021, 9, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergely, A.M.; Crainicu, B. A succinct survey on (Pseudo)-random number generators from a cryptographic perspective. In Proceedings of the 2017 5th International Symposium on Digital Forensic and Security (ISDFS), Tirgu Mures, Romania, 26–28 April 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; You, F.; He, S. Design of Broadband Compressed Sampling Receiver Based on Concurrent Alternate Random Sequences. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 135525–135538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, A.I.; Gómez-Pérez, D.; Pillichshammer, F. Secure pseudorandom bit generators and point sets with low star-discrepancy. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2021, 396, 113601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley-Smith, D.; Hernández-Castro, J. Certifiably Biased: An In-Depth Analysis of a Common Criteria EAL4+ Certified TRNG. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Jho, N.S.; Chung, D.; Kang, Y.; Kim, M. Rcryptect: Real-Time Detection of Cryptographic Function in the User-Space Filesystem. Comput. Secur. 2021, 112, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Jiao, L.; Zeng, K.; Wen, H.; Qin, K.Y. Physical Layer Secure MIMO Communications against Eavesdroppers with Arbitrary Number of Antennas. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhin, A.L.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.R.; Smid, M.E.; Barker, E.; Leigh, S.; Levenson, M.; Vangel, M.; Banks, D.; Heckert, A.; et al. SP 800-22 Rev. 1a. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; Technical Report; Special Publication (NIST SP); National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2010. Available online: https://tsapps.nist.gov/publication/get_pdf.cfm?pub_id=906762 (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- Marsaglia, G. The Marsaglia Random Number CDROM Including the Diehard Battery of Tests of Randomness; National Science Foundation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.G.; Eddelbuettel, D.; Bauer, D. Dieharder: A Random Number Test Suite (Version 3.31.1). 2014. Available online: https://webhome.phy.duke.edu/~rgb/General/dieharder.php (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- Gustafson, H.; Dawson, E.; Nielsen, L.; Caelli, W. A computer package for measuring the strength of encryption algorithms. Comput. Secur. 1994, 13, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J. ENT: A Pseudorandom Number Sequence Test Program. 2018. Available online: https://www.fourmilab.ch/random/ (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- Almaraz Luengo, E.; García Villalba, L.J. Recommendations on Statistical Randomness Test Batteries for Cryptographic Purposes. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.M. Entropy and Information Theory, 2nd. ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hurley-Smith, D.; Patsakis, C.; Hernández-Castro, J. On the unbearable lightness of FIPS 140-2 randomness tests. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almaraz Luengo, E.; Alaña Olivares, B.; García Villalba, L.J.; Hernández-Castro, J. Weaknesses in ENT Battery Design. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4230. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094230
Almaraz Luengo E, Alaña Olivares B, García Villalba LJ, Hernández-Castro J. Weaknesses in ENT Battery Design. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(9):4230. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094230
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmaraz Luengo, Elena, Bittor Alaña Olivares, Luis Javier García Villalba, and Julio Hernández-Castro. 2022. "Weaknesses in ENT Battery Design" Applied Sciences 12, no. 9: 4230. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094230
APA StyleAlmaraz Luengo, E., Alaña Olivares, B., García Villalba, L. J., & Hernández-Castro, J. (2022). Weaknesses in ENT Battery Design. Applied Sciences, 12(9), 4230. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094230






