Experimental Study on the Elemental Mercury Removal Performance and Regeneration Ability of CoOx–FeOx-Modified ZSM-5 Adsorbents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Sample Characterization
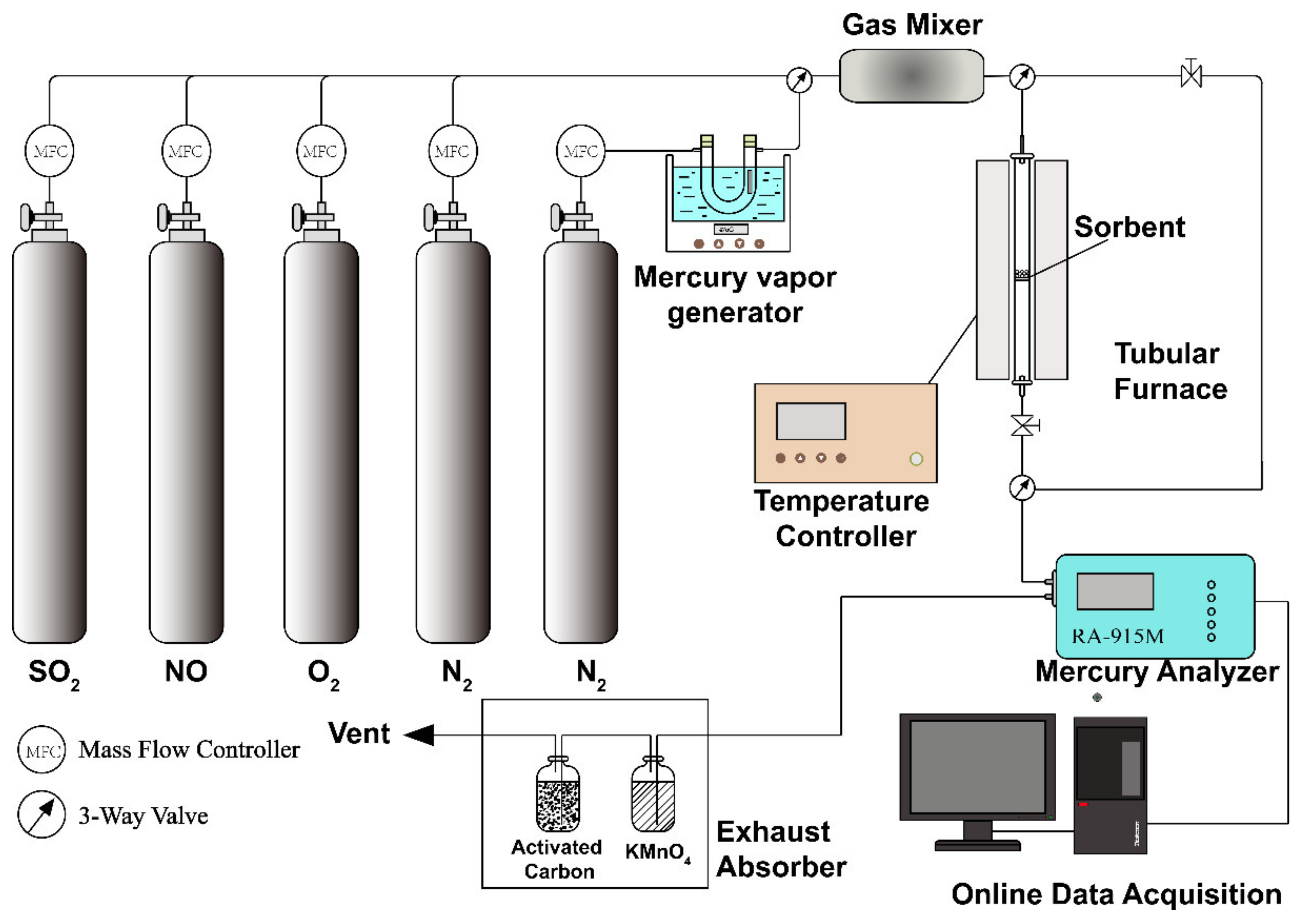
2.3. Experimental Setup and Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of a Series Samples
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of the Samples
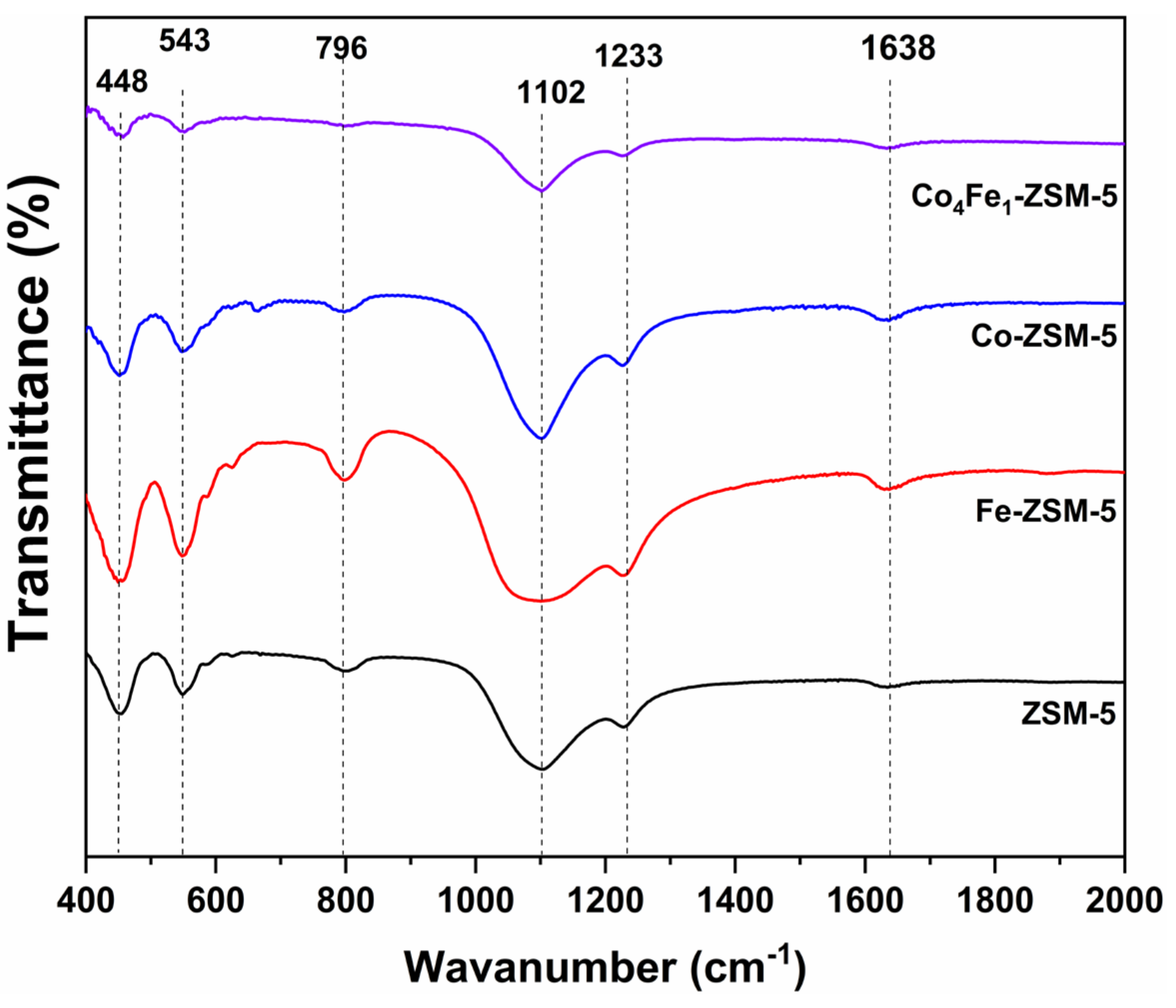
3.2.1. FTIR Analysis
3.2.2. XRD Analysis
3.2.3. BET Analysis
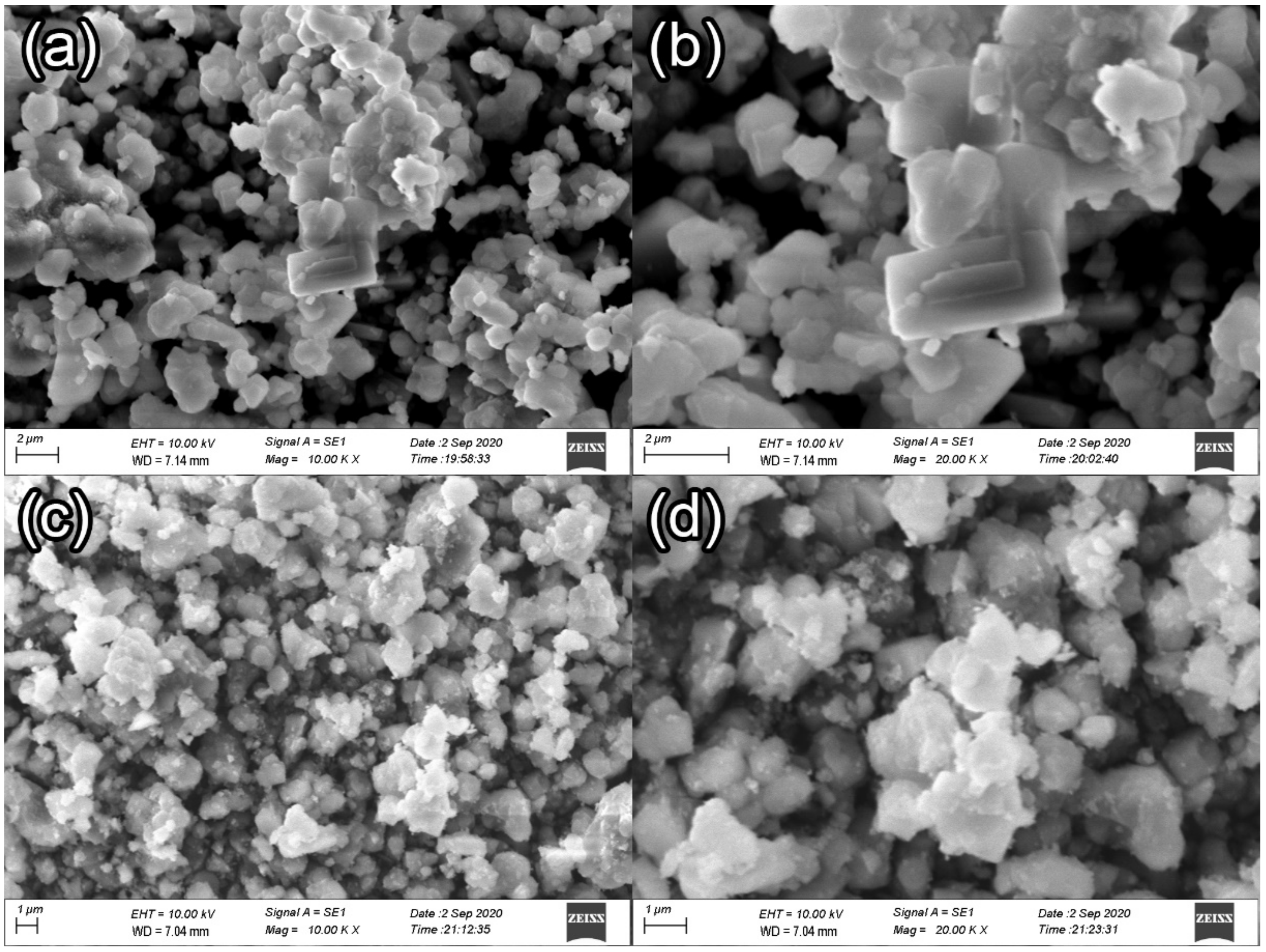
3.2.4. SEM Analysis
3.2.5. H2-TPR Analysis
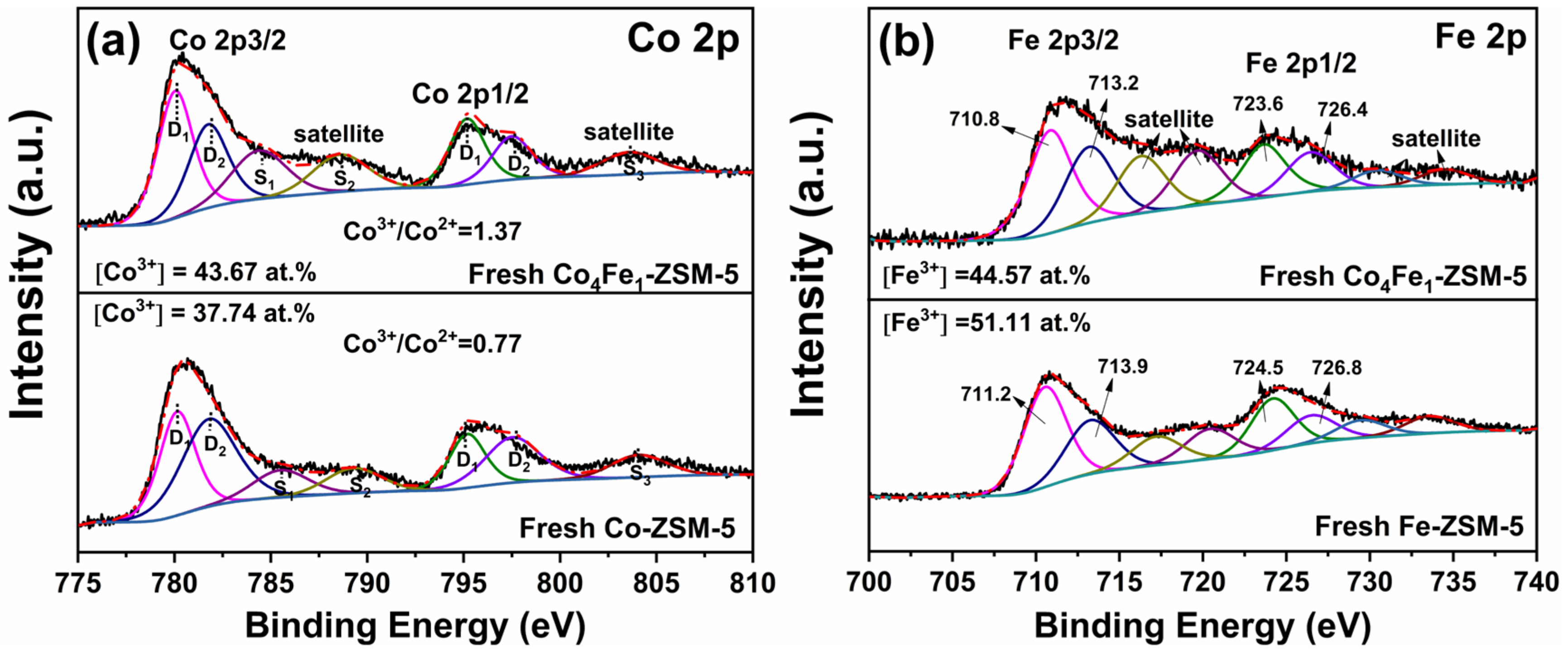
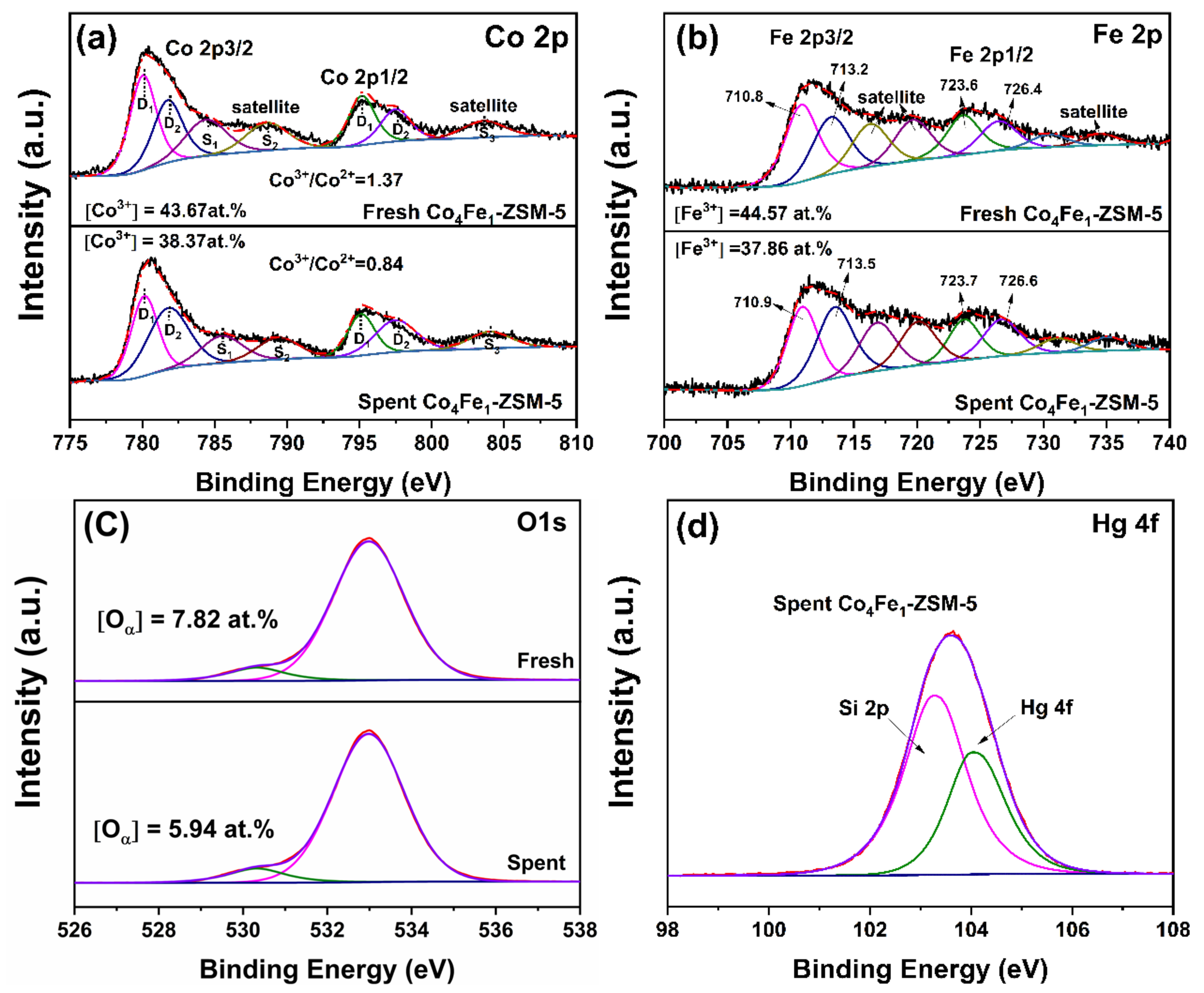
3.2.6. XPS Analysis
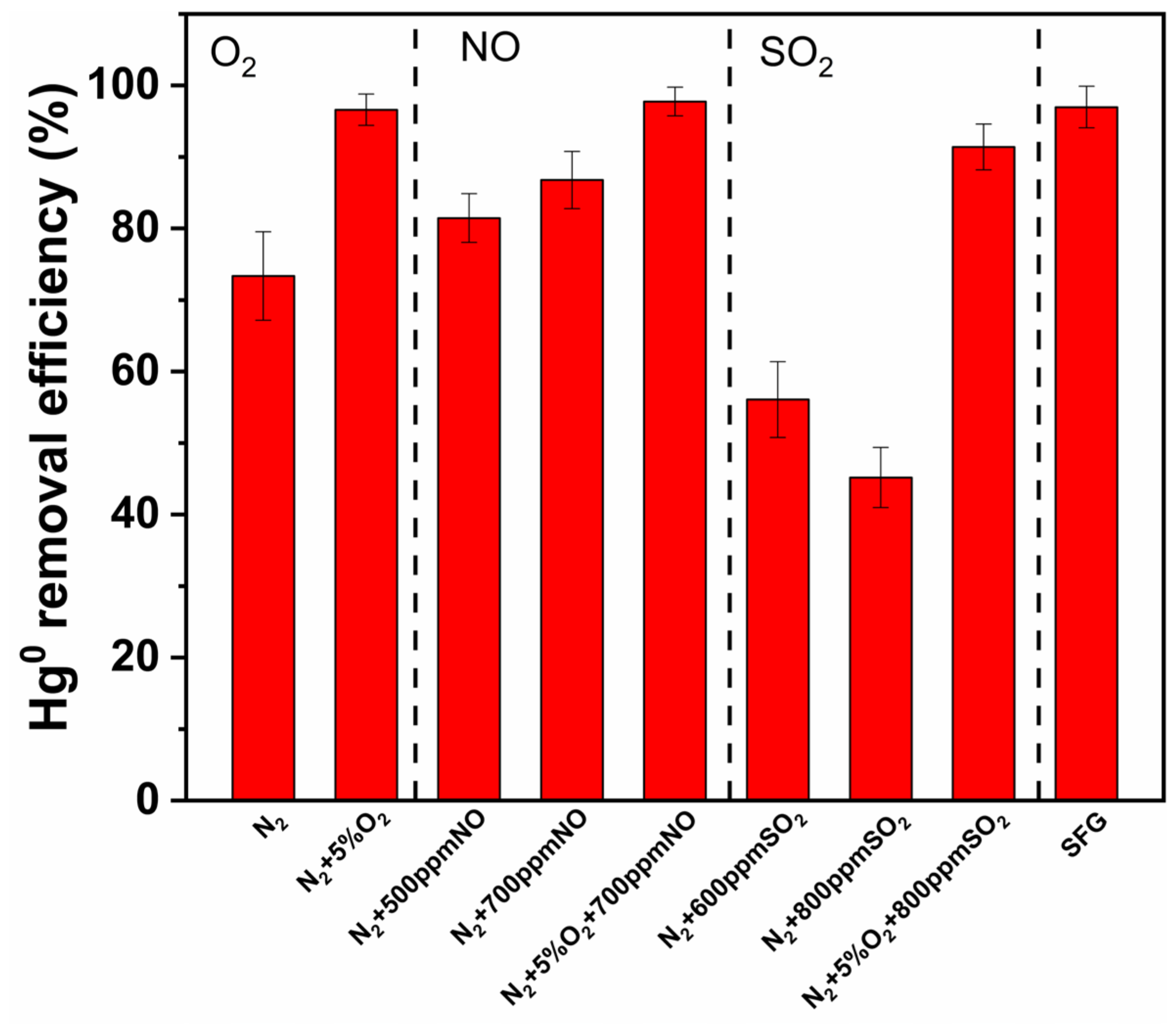
3.3. Effects of Gas Components
3.3.1. Effects of O2
3.3.2. Effects of NO
3.3.3. Effects of SO2
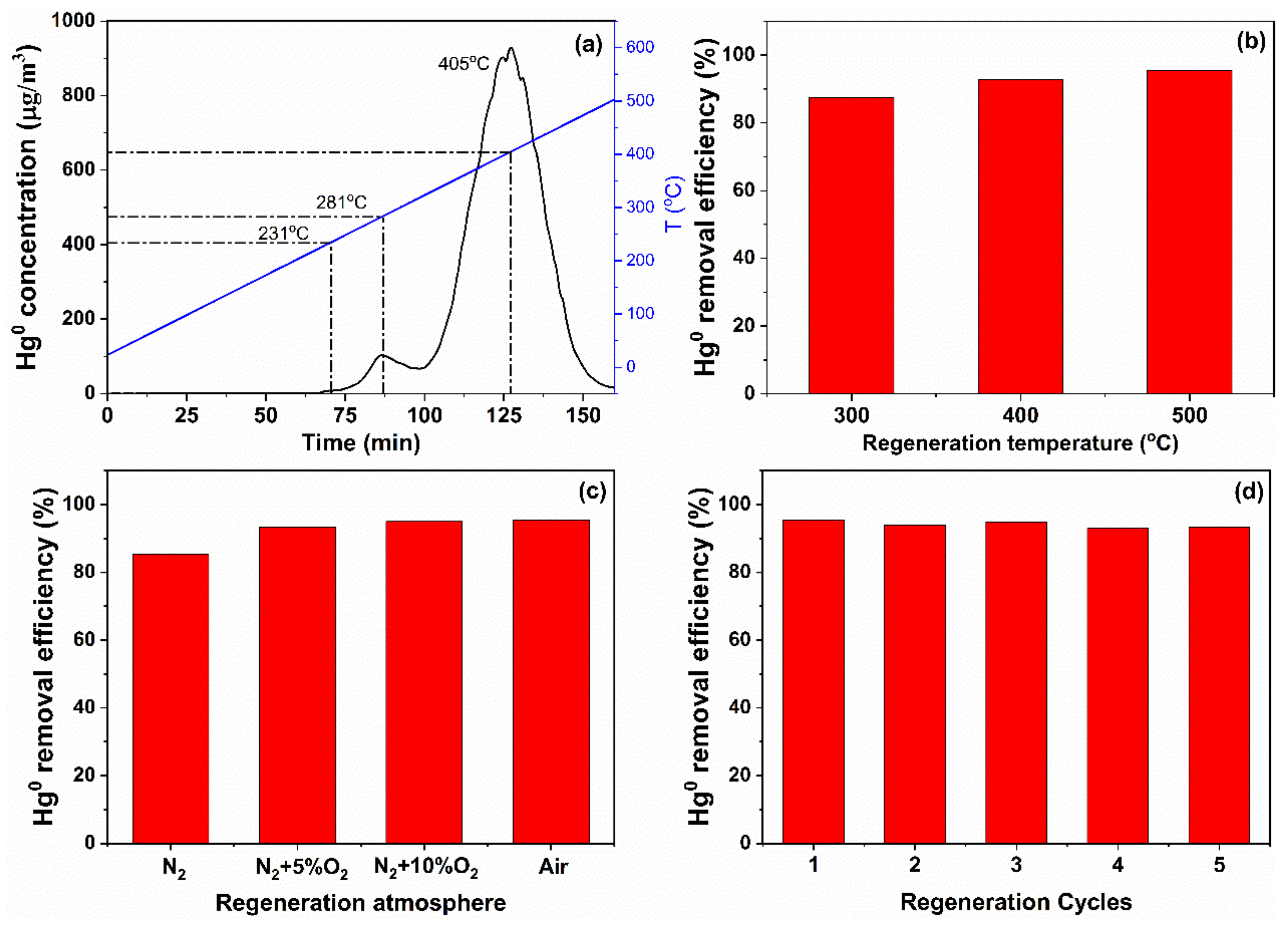
3.4. Regeneration Ability
3.5. Mercury Capture Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- Compared with other samples, Co4Fe1-ZSM-5 performed relatively better, with a roughly 96.6% Hg0 removal efficiency and a roughly 901.63 μg/g Hg0 adsorption capacity achieved at 120 °C. The interaction between CoOx and FeOx enhanced the reducibility of oxygen species, which promoted the oxidation of Hg0.
- Among various gas components, O2 and NO had a positive impact the removal of Hg0, whereas SO2 inhibited the adsorption of Hg0 to a certain extent.
- The Mars–Masson mechanism dominated the Hg0 adsorption process over Co4Fe1-ZSM-5. Co3+ and Fe3+ provided the active sites required to oxidize Hg0 into Hg0 for the subsequent deposition onto the adsorbent surface.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, W.; Hussain, A.; Liu, Y. A review on modification methods of adsorbents for elemental mercury from flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 692–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Mu, B.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Qu, Z.; Gao, L.; Li, B.; Tian, J. Ag-Fe3O4@rGO ternary magnetic adsorbent for gaseous elemental mercury removal from coal-fired flue gas. Fuel 2019, 239, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Mu, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Qu, Z.; Gao, L. Hierarchical Ag-SiO2@Fe3O4 magnetic composites for elemental mercury removal from non-ferrous metal smelting flue gas. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, G.; Gao, X.; Pang, C.H.; Kingman, S.W.; Wu, T. Hg0 Capture over CoMoS/γ-Al2O3 with MoS2 Nanosheets at Low Temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-w.; Chen, J.-y.; Zhao, K.; Niu, Q.-X.; Wang, L. Removal of vapor-phase elemental mercury from simulated syngas using semi-coke modified by Mn/Ce doping. J. Fuel. Chem. Technol. 2016, 44, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Song, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; Zhao, S.; Fan, C. Synthesis of CeO2-modified activated carbon spheres by grafting and coordinating reactions for elemental mercury removal. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 2836–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, N.; Qu, Z.; Qiao, S.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Liu, P.; Jia, J. Catalytic oxidation of elemental mercury over the modified catalyst Mn/alpha-Al2O3 at lower temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.-Y.; Norris, P.; Pan, W.-P. Use of a non-thermal plasma technique to increase the number of chlorine active sites on biochar for improved mercury removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Gaseous elemental mercury removal using VUV and heat coactivation of Oxone/H2O/O2 in a VUV-spraying reactor. Fuel 2019, 243, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Hu, T.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Tian, F.; Pan, W.; He, P.; Qi, X.; Li, F.; Xu, K. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2/graphene by tailoring oxidation degrees of graphene oxide for gaseous mercury removal. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Duan, Y.; Zhao, S.; Hu, B.; Li, N.; Yao, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, H.; Ren, S. Experimental Study on Mercury Removal and Regeneration of SO2 Modified Activated Carbon. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 58, 13190–13197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Mu, B.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, D.; Ma, C.; Xu, H.; Qu, Z.; Fang, S. Graphene enhanced Mn-Ce binary metal oxides for catalytic oxidation and adsorption of elemental mercury from coal-fired flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Adewuyi, Y.G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Removal of elemental mercury from flue gas using CuOx and CeO2 modified rice straw chars enhanced by ultrasound. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 170, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Su, S.; Xiang, J.; You, H.; Cao, F.; Sun, L.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y. Catalytic oxidation of Hg0 by MnOx–CeO2/γ-Al2O3 catalyst at low temperatures. Chemosphere 2014, 101, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, C.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, X.; Tao, S.; Lu, P.; Tan, Y.; Luo, D. Hg0 Removal from Simulated Flue Gas over CeO2/HZSM-5. Energy Fuel 2012, 26, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Dou, C.; Li, J.; Yuan, Z.; Lv, H. Experimental Study on SO2-to-SO3 Conversion Over Fe-Modified Mn/ZSM-5 Catalysts During the Catalytic Reduction of NOx. Catal. Surv. Asia 2019, 23, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; Xu, H.; Liu, D. Removal of elemental mercury from simulated flue gas by ZSM-5 modified with Mn-Fe mixed oxides. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Han, L.; Wang, J.; Bao, W.; Chang, L.; Xie, K. ZnS/AC sorbent derived from the high sulfur petroleum coke for mercury removal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 191, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z.; Huang, W.; Liao, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, H.; Yan, N.; Qu, Z. Study on the regenerable sulfur-resistant sorbent for mercury removal from nonferrous metal smelting flue gas. Fuel 2019, 241, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Han, X.; Huang, Z.; Hou, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wu, M. Superior activity of CeO2 modified V2O5/AC catalyst for mercury removal at low temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qu, Z.; Zong, C.; Huang, W.; Quan, F.; Yan, N. MnOx/Graphene for the Catalytic Oxidation and Adsorption of Elemental Mercury. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6823–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Q.; Mao, J. Removal of elemental mercury using titania sorbents loaded with cobalt ceria oxides from syngas. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 12503–12510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, H.; Han, X.; Ding, S.; Shan, Y.; Liu, Y. Preparation of magnetic Co-Fe modified porous carbon from agricultural wastes by microwave and steam activation for mercury removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tan, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; He, G. Removal of elemental mercury by Ce and Co modified MCM-41 catalyst from simulated flue gas. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Chen, N.; Deng, D.; Li, Y.; Xing, X.; Wang, Y. Meso- and macroporous coral-like Co3O4 for VOCs gas sensor. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41 Pt A, 11004–11012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oton, L.F.; Oliveira, A.C.; de Araujo, J.C.S.; Araujo, R.S.; de Sousa, F.F.; Saraiva, G.D.; Lang, R.; Otubo, L.; Carlos da Silva Duarte, G.; Campos, A. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx by CO (CO-SCR) over metal-supported nanoparticles dispersed on porous alumina. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silas, K.; Karim, A.; Choong, T.; Rashid, T.D.U. Optimization of Activated Carbon Monolith Co3O4-Based Catalyst for Simultaneous SO2/NOx Removal from Flue Gas Using Response Surface Methodology. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2019, 192, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, X.; Han, X.; Bao, J.; Zhang, N.; He, G. Co3O4-based catalysts derived from natural wood with hierarchical structure for elemental mercury oxidation. J. Energy Inst. 2021, 94, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Song, X.N.; Wang, X.X.; Wei, Y.Y.; Han, X.K.; Bao, J.J.; Zhang, N.; He, G.H. In-situ grown Co3O4 nanoparticles on wood-derived carbon with natural ordered pore structure for efficient removal of Hg0 from flue gas. J. Energy Inst. 2021, 98, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.L.; Zhong, Q.; Xing, L.L. Gas-phase elemental mercury removal from flue gas by cobalt-modified fly ash at low temperatures. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 2870–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, H. Cobalt doped ceria for abundant storage of surface active oxygen and efficient elemental mercury oxidation in coal combustion flue gas. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2018, 239, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tong, L.; Qi, H.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, T. Effect of Flue Gas Components on Hg0 Oxidation over Fe/HZSM-5 Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 54, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Mercury Removal by Magnetic Biochar Derived from Simultaneous Activation and Magnetization of Sawdust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12040–12047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Hussain, A.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.X. Removal of elemental mercury from flue gas using red mud impregnated by KBr and KI reagent. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 341, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, C.; Zeng, Q.; Du, X.; Gao, L.; Li, S.; Zhai, Y. Study on removal of elemental mercury over MoO3-CeO2/cylindrical activated coke in the presence of SO2 by Hg-temperature-programmed desorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, W.; Wu, J. CeO2–MnOx/ZSM-5 sorbents for H2S removal at high temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Liu, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, F. Enhancing the absorption of elemental mercury using hydrogen peroxide modified bamboo carbons. Fuel 2019, 235, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Yan, R.; Peng, H.; Mi, Y.; Liang, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Song, G.; Wu, P.; Liu, F. One-pot synthesis of layered mesoporous ZSM-5 plus Cu ion-exchange: Enhanced NH3-SCR performance on Cu-ZSM-5 with hierarchical pore structures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Wang, X.; Cheng, X.; Cui, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, P.; Dong, Y. Regeneration performance of activated coke for elemental mercury removal by microwave and thermal methods. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 199, 106303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, L.; Xie, Y.E.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J. Study on the removal of elemental mercury from simulated flue gas by Fe2O3-CeO2/AC at low temperature. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5099–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Tan, B.; Zhang, N.; Bao, J.; He, G. Ce-Co interaction effects on the catalytic performance of uniform mesoporous Cex-Coy catalysts in Hg0 oxidation process. Fuel 2018, 226, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Du, X.; Li, S.; Zeng, J.; Yi, Y.; Zeng, G. Simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0 from simulated flue gas over CoOx-CeO2 loaded biomass activated carbon derived from maize straw at low temperatures. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Nie, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, F.; Ma, C.; Lu, C.; Chen, Z. Phosphorus-rich network polymer supported ruthenium nanoparticles for nitroarene reduction. Mater. Lett. 2019, 240, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wei, G.; Liang, X.; Zhu, J.; Xian, H.; Su, X.; He, H.; Zhu, R. Sequestration of Gaseous Hg0 by Sphalerite with Fe Substitution: Performance, Mechanism, and Structure–Activity Relationship. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 2828–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Du, X.; Huang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Zeng, G. Superior performance and resistance to SO2 and H2O over CoOx-modified MnOx/biomass activated carbons for simultaneous Hg0 and NO removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P. Active phase, catalytic activity, and induction period of Fe/zeolite material in nonoxidative aromatization of methane. J. Catal. 2016, 338, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, G.; Xie, Y.E.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Removal of Gaseous Elemental Mercury by Cylindrical Activated Coke Loaded with CoOx-CeO2 from Simulated Coal Combustion Flue Gas. Energy Fuel 2015, 29, 6747–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Bisson, T.; Xu, Z. Magnetically responsive catalytic sorbent for removal of Hg0 and NO. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 160, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Li, P.; Yang, J.; Lee, P.-H.; Shih, K. Promotional effect of CuO loading on the catalytic activity and SO2 resistance of MnOx/TiO2 catalyst for simultaneous NO reduction and Hg0 oxidation. Fuel 2018, 227, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Shi, S.; Chen, H.; Shan, Y.; Liu, Y. Mercury removal from flue gas by magnetic iron-copper oxide modified porous char derived from biomass materials. Fuel 2019, 256, 115977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, G.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cui, W. Cost-effective sulfurized sorbents derived from one-step pyrolysis of wood and scrap tire for elemental mercury removal from flue gas. Fuel 2021, 285, 119221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Cao, X.E.; Xu, M. Seawater-assisted synthesis of MnCe/zeolite-13X for removing elemental mercury from coal-fired flue gas. Fuel 2020, 262, 116605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Bing, L.; He, Y.; YANG, D.-w.; HU, H.-q. Removal of elemental mercury (Hg0) from simulated flue gas over MnOx-TiO2 sorbents. J. Fuel. Chem. Technol. 2020, 48, 513–524. [Google Scholar]
- Presto, A.A.; Granite, E.J. Noble Metal Catalysts for Mercury Oxidation in Utility Flue Gas GOLD, PALLADIUM AND PLATINUM FORMULATIONS. Platin. Met. Rev. 2008, 52, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Z. AMn2O4 (A=Cu, Ni and Zn) sorbents coupling high adsorption and regeneration performance for elemental mercury removal from syngas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


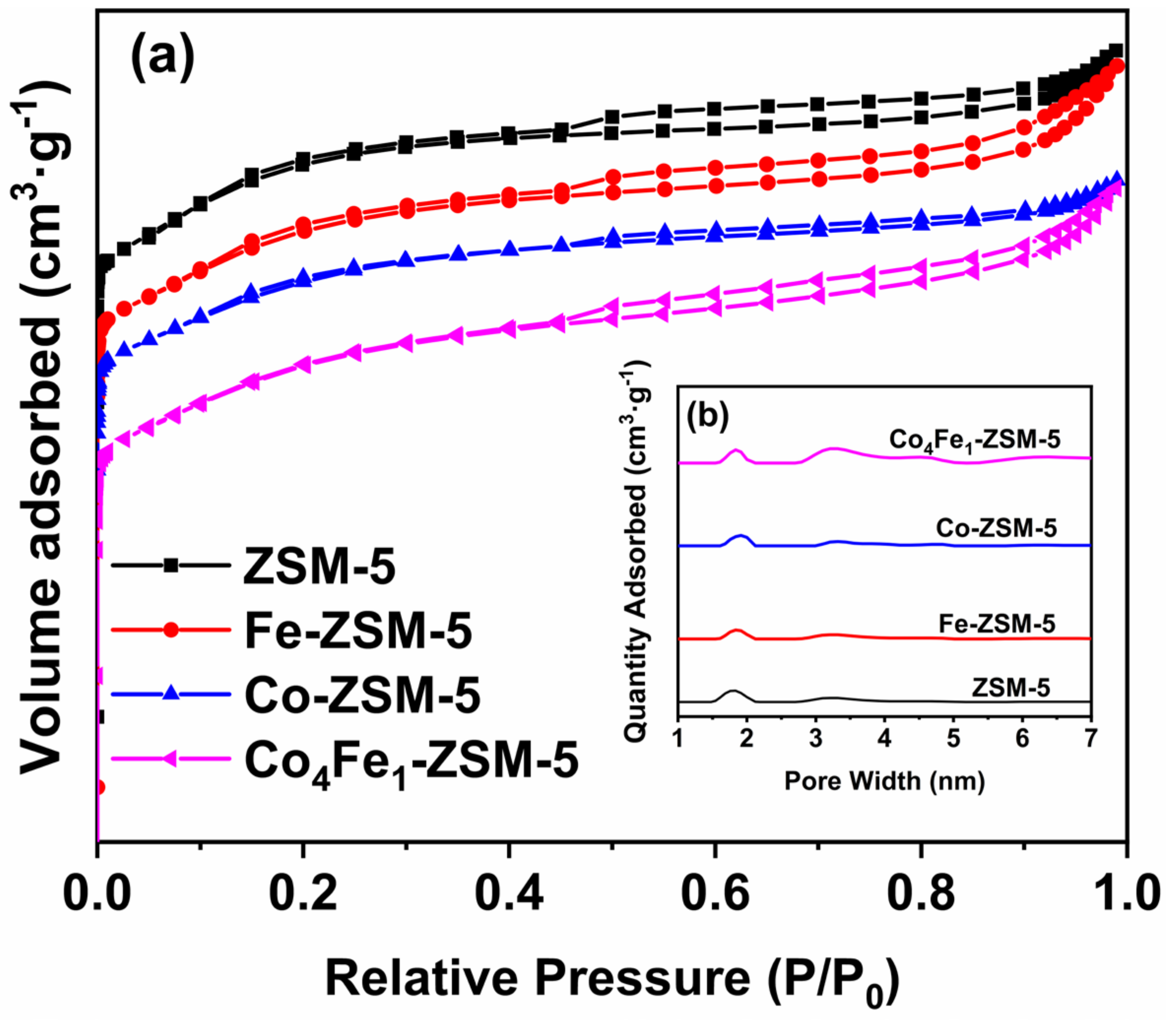


| Samples | Surface Area/(m2/g) | Micropore Surface Area/(m2/g) | External Surface Area/(m2/g) | Total Pore Volume/(cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSM-5 | 356 | 289 | 67 | 0.18 |
| Co-ZSM-5 | 336 | 260 | 76 | 0.16 |
| Fe-ZSM-5 | 343 | 269 | 74 | 0.19 |
| Co4Fe1-ZSM-5 | 351 | 264 | 87 | 0.18 |
| Samples | Concentration of the Oxygen | Co3+/Co2+ | Fe3+/Fe2+ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oα | Oβ | |||
| Fresh Co-ZSM-5 | - | - | 0.77 | - |
| Fresh Fe-ZSM-5 | - | - | - | 1.62 |
| Fresh Co4Fe1-ZSM-5 | 7.8% | 92.2% | 1.37 | 1.29 |
| Spent Co4Fe1-ZSM-5 | 5.9% | 94.1% | 0.84 | 0.93 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, W.; Ye, D.; Wang, H. Experimental Study on the Elemental Mercury Removal Performance and Regeneration Ability of CoOx–FeOx-Modified ZSM-5 Adsorbents. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083769
Ma W, Ye D, Wang H. Experimental Study on the Elemental Mercury Removal Performance and Regeneration Ability of CoOx–FeOx-Modified ZSM-5 Adsorbents. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(8):3769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083769
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Wei, Dong Ye, and Haining Wang. 2022. "Experimental Study on the Elemental Mercury Removal Performance and Regeneration Ability of CoOx–FeOx-Modified ZSM-5 Adsorbents" Applied Sciences 12, no. 8: 3769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083769
APA StyleMa, W., Ye, D., & Wang, H. (2022). Experimental Study on the Elemental Mercury Removal Performance and Regeneration Ability of CoOx–FeOx-Modified ZSM-5 Adsorbents. Applied Sciences, 12(8), 3769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083769





