Abstract
In recent years, there has been an impressive development of nanotechnology. This has resulted in the increasing release of nanomaterials (NM) into the environment, thereby causing the risk of an uncontrolled impact on living organisms, including plants. More studies indicated the biotoxic effect of NM on plants, including crops. The interaction of nanoparticles (NP) with food crops is extremely important as they are a link to the food chain. The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of negatively charged gold nanoparticles (-) AuNP (at two concentrations; 25 µg/mL or 50 µg/mL) on barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) root development. Morphological, histological and ultrastructural analyses (with the use of stereomicroscope, bright filed microscope and transmission electron microscope) revealed that regardless of the concentration, (-) AuNP did not enter into the plant body. However, the dose of (-) AuNP proved to be important for the plant’s response because different morphological, histological and ultrastructural changes were observed in the treated roots. The NP treatment caused: red root colouration, a local increase in the root diameter and a decreased formation of the root hair cells (on morphological level), damage to the rhizodermal cells, vacuolisation of the cortical cells, a detachment of the cell files between the cortical cells, atypical divisions of the cells, disorder of the meristem organisation (on the histological level), the appearance of periplasmic space, numerous vesicles and multivesicular bodies, electron-dense spots in cytoplasm, alterations in the structure of the mitochondria, breakdown of the tonoplast and the plasmalemma (on the ultrastructural level).
1. Introduction
The rapid development of nanotechnology is related to the use of nanomaterials (NM) in a growing number of applications [1,2,3]. Recently, there has been an increase in the use of NM in agriculture, where it can provide new strategies to improve plant production for human consumption and animal feed as well as to promote a reduction in pesticide usage [4,5]. Nanoparticles (NP) are currently used as nanofertilisers, nanopesticides, nanosensors and exposure to wastewater and soil remediation additives [6]. However, more research has indicated that an accumulation of NP in the aquatic, terrestrial and atmospheric environments could induce adverse effects on plant development [7,8,9,10,11]. Moreover, the accumulation of NP in plants could allow them to enter the food chain, thereby potentially affecting human health. Hence, it is extremely important to examine the impact of NP on crops. Therefore, the focus of our research was to study the effect of NP on barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) as it is one of the most important food crops in the world.
Information on the impact of manufactured nanomaterials on food crops is increasing. This knowledge is important in connection with increasing production and use of manufactured nanomaterials, including nanopesticides. The toxic effects of CuO NP on cultivated crop plants by inhibiting seed germination, decreasing shoot and root lengths, reducing photosynthesis and the respiration rate and morphological as well enzymatic changes were also proven (for a review, see [12]). The effect of NP on crops also includes a decrease in the germination rate, a reduction in the biomass and the length of roots and shoots, an alteration in the process of photosynthesis and the transpiration rate and an increase in the chromatin condensation and lipid peroxidation [12]. The influence of AgNP on wheat plants revealed severe phytotoxicity and a decrease in the content of micronutrients such as Fe, Cu and Zn [13]. A significant part of the publication describes the effect of NP on the growth and physiological parameters of crop plants [14,15,16]. Despite numerous studies in this field, there is still no complete picture of the impact of NP on crops. Thus, on the one hand, nanofertilisers and nanopesticides are necessary to obtain the right yields, but on the other hand, the effects of NP may be detrimental to plant growth.
Nanofertilisers provide nutritional management benefits due to their strong potential for increasing the efficacy of nutrient utilisation. When used alone or in combination, the nutrients are bound to nano-sized adsorbents that release nutrients very slowly compared to conventional fertilisers [17]. Metal NP that can be used as fertilisers or plant growth stimulants were described, among others, silver (Ag), zinc oxide (ZnO), iron (Fe), titanium (Ti), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu) and also gold (Au) nanoparticles [4]. This enables nanoparticles, including AuNP, to be present in the soil and therefore has an impact on the interaction with plants, especially cultivated plants. AuNP have become the subject of our interest because they have the potential to stimulate plant growth, and they can also be accumulated or have a toxic effect on plants. Moreover, AuNP also have many other commercial applications [18,19,20,21,22] that inevitably cause them to be increasingly released and accumulated in the environment, including soil, water, air, etc. This makes the need to study the interaction of the AuNP with plants.
Arabidopsis thaliana seeds and seedlings that were exposed to 80 μg/mL AuNP increased their germination capacity and seed yield, thus accelerating plant growth. Moreover, enhanced flowering and an increase in the length of the pods in the treated plants were also observed [23]. AuNP at a concentration of 0.013% (w/w) in the soil increased the shoot length ratio to the root length of Lactuca sativa but did not disturb the community of soil microorganisms or the germination of seeds [24]. A foliar spray of AuNP on Brassica juncea indicated that at a concentration of 10 ppm, germination and growth were accelerated, and the chlorophyll content, seed oil content, seed yield and the number of pods per plant was increased. However, higher doses (50–100 ppm) caused oxidative stress in plants [25]. This indicates that AuNP can positively affect the development and yield of plants. However, it is important to remember that the interaction of NP with plants depends on their physico-chemical properties (such as their shape, size, coating properties), their concentration as well as the plant species. Experiments on four plant species (Raphanus raphanistrum subsp. sativusr, Cucurbita pepo, Oryza sativa, Lolium perenne) that was treated with AuNP at different surface charges indicated that positively charged AuNP had a greater ability to enter the plant roots while negatively charged AuNP were most efficiently transferred from the roots to plant shoots. Moreover, the radish (Raphanus raphanistrum subsp. Sativusr) and ryegrass (Lolium perenne) roots accumulated higher amounts of AuNP than the rice (Oryza sativa) and pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo) roots [26]. Another study showed that AuNP did not penetrate into the roots of Arabidopsis; however, it had an influence on root development and ultra-structure that was dependent on the NP surface charge [27]. Similarly, it was demonstrated that positively charged AuNP influenced the development of Hordeum vulgare roots without penetrating into the plant body. A high concentration of AuNP (50 μg/mL) caused changes in the rhizodermis differentiation and formation of the hairless phenotype [27]. Sabo-Attwood et al. [28] showed that AuNP might penetrate and translocate within the plant body in a size-dependent manner as 3.5 nm of AuNP entered into the roots of Nicotiana xinthi and moved into the vasculature, while 18 nm of AuNP were retained on the root surface. Moreover, after 14 days of exposure to 3.5 nm of AuNP, leaf necrosis was observed, which indicates their toxicity.
The presented data showed that many parameters affect the interaction of NP with plants, and our knowledge in this area is still insufficient. There is no doubt that the rapid development of nanotechnology requires just as much research into their potential toxicity, especially in relation to crops. Knowledge about the response of plants to NP at the morphological, histological and ultrastructural levels enables the effect of NP on plant growth and development to be predicted and thus to effectively minimise the toxicity of the NP that are a component of nanofertilisers and nanopesticides that are used to increase yields. Information on the influence of NP on root morphology and histology showed that root anatomy could be changed in terms of cellular alterations in the apical meristem, zone of elongation and metaxylem differentiation, e.g., [29,30], however, it should be added that this information is scarce. Our previous research showed the effects of neutral [27] and positively charged (+) AuNP on barley roots [27]. Therefore, we undertook research on the effects of negatively charged AuNP on morphology, histology and ultrastructure of Hordeum vulgare roots to obtain a complete picture of the influence of AuNP with different surface charges on barley root development. The results presented in this paper indicate that regardless of the concentration, NP did not penetrate to the roots but that the plant’s response was manifested by various morphological, histological and ultrastructural changes in the treated roots.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterisation of Gold Nanoparticles
Gold nanoparticles in the form of 5 ± 0.6 nm spheres were purchased from nanoComposix Europe, the Czech Republic. The AuNP were citrate coated, which conferred a negative surface charge to the NP. The solution of the gold nanoparticles had an intense red tint.
2.2. Plant Material
Hordeum vulgare L. cultivar Karat was used as the model crop plant for the research. Caryopses were provided from the collection of Iwona Szarejko’s team at the Institute of Biology, Biotechnology and Environmental Protection, Faculty of Natural Sciences, the University of Silesia in Katowice, Poland.
2.3. Culture and Treatment
Barley caryopses were immersed in a 20% (v/v) sodium hypochlorite solution for 20 min for surface sterilisation. After washing three times with distilled water for five minutes, seeds were left in distilled water for 24 h (at room temperature, RT) for imbibition. Caryopses were placed in Petri dishes filled with filter paper moistened with distilled water. Petri dishes were closed with Parafilm (Parafilm®M, Bionovo, Legnica, Poland) to prevent evaporation and incubated at RT in the dark (48 h). Subsequently, the caryopsis with emerging radicle (the first day of the culture) was cultivated in glass tubes sealed with Parafilm under hydroponic conditions: the control plants were grown in a 1/16-strength Hoagland’s solution (prepared on distilled water), while the experimental plants were grown in a solution of 5 nm of negatively charged AuNP at two different concentrations: 25 µg/mL or 50 µg/mL (nanoparticles were dissolved in Hoagland’s solution). The colour of the AuNP solutions had a red tint (the intensity of the solution’s colour correspond to AuNP concentration) and did not change during the culture indicating that the tested NP were stable. The plants were grown for seven days in a growth chamber under 16 h photoperiod conditions, 20 °C and 180 μE m−2 s−1 of light. Barley roots were analysed in the research. The specimens were viewed under a light microscope.
The experiment was repeated three times, and the photo documentation is representative of all the replicates.
2.4. Light Microscopy
In order to analyse the morphology of the roots, an SMZ 1500 stereomicroscope (Nikon) equipped with a Nikon Digital DS-Fi digital camera was used.
Sample preparation for the histological analysis was conducted according to the method for ultrastructural studies (described below). Sections were stained with a 0.05% (w/v) water solution of Toluidine blue 0 (TBO; Sigma) for 10 min. Five minutes of staining with Lugol’s iodine solution (Sigma-Aldrich) was used to detect the amyloplasts. The stained sections were rinsed in water and mounted in Euparal (mounting media; Carl Roth). The observations and photography were performed using an Olympus BX60 bright field equipped with a CCD matrix digital camera.
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
The control and the treated roots were fixed according to the procedures that were described earlier [31]. Briefly, the samples were fixed in a solution of 2.5% (v/v) glutaraldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich) and 2.5% (w/v) paraformaldehyde (Polysciences, Warrington, PA, USA) in a 0.05 M cacodylate buffer (CB; Sigma; pH 7.2), rinsed in CB, postfixed in 1% osmium tetraoxide (OsO4; Serva) in CB, washed in CB, dehydrated in a graded ethanol series and embedded in Epon resin (Polysciences, Warrington, PA, USA). The ultrathin sections (70 nm) were obtained using a Leica EM UC6 ultramicrotome and were collected on carbon-coated copper grids (200 mesh, Electron Microscopy Science, Hatfield, PA, USA). Subsequently, the grids were contrasted with uranyl acetate (Polysciences, Warrington, PA, USA) followed by lead citrate agent (Sigma). The samples were analysed using a Jeol JEM-3010 (300 kV) High-Resolution Electron Microscope (HR-TEM) equipped with an EDS (Energy Dispersive Spectrometry) spectrometer and a Gatan 2 k × 2 k OriusTM 833 SC200D CCD camera. TEM has specific limitations, especially for the determination of NP in section. Thus, the EDS was used to determine the diffraction pattern of electron-dense spots presented in the cells. HR-TEM allows the determination of the characteristic morphology and structure of the tested NP, and this assay was used in the presented analyses [32].
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Changes after Treatment with (-) AuNP
Barley roots that were treated with gold nanoparticles at different concentrations exhibited a different morphology than the control roots (Figure 1A–O). The morphology of the control barley roots was described earlier [31] and was briefly characterised by the presence of four root zones: a lateral root zone (Figure 1B), differentiation (with the presence of root hair cells, Figure 1C), elongation and meristematic zones (Figure 1D). These four zones were also observed in the treated roots (Figure 1E–O). The first visible change in the roots that were growing in the presence of (-) AuNP, regardless of the concentration, was the appearance of a red colour on the surface of the organs (the colour intensity corresponded to the AuNP concentration, Figure 1E–O). The colouration of the roots was not regular (Figure 1E–O) and was only observed up to the level of the immersion of the roots in the (-) AuNP solution (Figure 1F). A local increase in the root diameter was observed in the roots that were growing in a solution with (-) AuNP at both concentrations (Figure 1G,N). These thickenings were present in the differentiation zone (DZ). In the treated roots, regardless of the concentration, a reddish suspension appeared around the root cap and border cells (Figure 1J,O). In the roots that were treated with a higher concentration, there was a decreased formation of the root hair cells (Figure 1L,N).
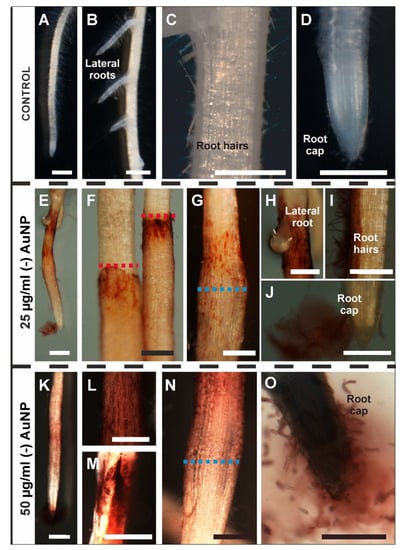
Figure 1.
Morphology of the barley roots that were growing in the control conditions (A–D), 25 µg/mL (-) AuNP (E–J) or 50 µg/mL (-) AuNP (K–O). The red dotted lines indicate the boundary level of the (-) AuNP solution in which the roots were growing; blue dotted lines indicate the local radial thickening of the roots. Scale bars: (A,E,K) = 1 mm; (B–D,F–J,L–O) = 0.5 mm.
3.2. Histological Changes after Treatment with (-) AuNP
An investigation of the histological changes under the influence of (-) AuNP (two concentrations: 25 µg/mL or 50 µg/mL compared to the control roots was conducted in the root apex (RA; Figure 2A–N) and DZ (Figure 3A–L). The RA is composed of the distal meristem (lateral root cap and columella), proximal meristem (according to [33]) and a central organising centre, which is known as the quiescent centre (Figure 2A–C). In the meristematic zone, the rhizodermis, cortex and the central cylinder can be distinguished (Figure 2A,B). The root cap cells consist of the columella cells, peripheral cells and border cells (Figure 2C).
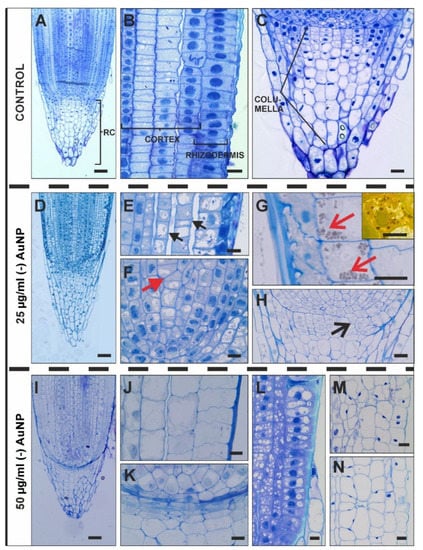
Figure 2.
Longitudinal section through the barley RA (root apex) from the control roots (A–C), the roots growing in the 25 µg/mL (-) AuNP (D–H) or 50 µg/mL (-) AuNP (I–N) conditions. Black arrows—large intercellular spaces between the cortical cells (E); red arrow—atypical division of the central metaxylem vessel in the distal meristem (F); red open arrows—the amyloplast in the outer cortical cells (G); black open arrow—rearrangement of the proximal meristem organisation (H). TBO staining (apart from the G inset—Lugol’s staining that indicates the presence of amyloplasts in the cortical cell). Scale bars: (A,D,I) = 50 µm; (B,C,H,L,M,N) = 20 µm; (E,F,G,G Inset,J,K) = 10 µm.
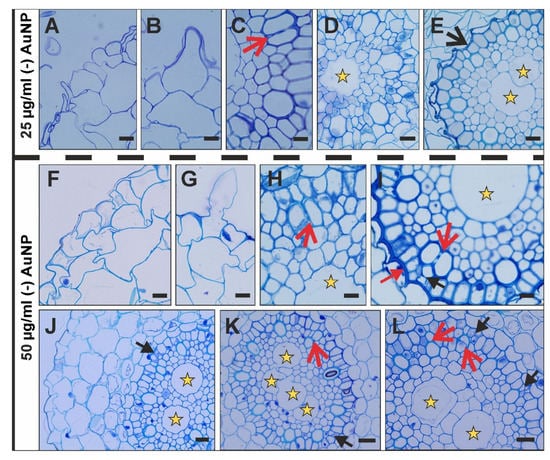
Figure 3.
Cross-sections through the DZ (differentiation zone) of the roots growing in 25 µg/mL (-) AuNP (D–H) or 50 µg/mL (-) AuNP (I–L). Red open arrows—multiplicated metaxylem vessels; black open arrow—collapse of the endodermis; black arrow—atypical divisions of the pericycle cells; red arrow—ticked inner periclinal wall of the endodermis; yellow asterisks—central metaxylem. TBO staining. Scale bars: (A–I) = 10 µm; (E–G) = 20 µm.
In the roots that were treated with the lower concentration of (-) AuNP (25 µg/mL), disturbances were detected in the rhizodermis. The rhizodermal cells were squashed, had an unregular shape and were smaller compared to the control and had a very dense cytoplasm (Figure 2E). In the cortical cells, increased vacuolisation was another visible alteration at the lower concentration of (-) AuNP (Figure 2E,G). A detachment of the cell files, especially between the cortical cells, was also observed (Figure 2E). In some cases, there was a visible accumulation of amyloplasts in the outer cortical cells (Figure 2G, G inset). Another disorder in the root histology that was caused by the lower concentration of (-) AuNP was the atypical divisions of the cells as was visible in the central metaxylem (Figure 2F) and in the disrupted pattern of the meristem organisation (Figure 2H). At the higher concentration of (-) AuNP, there was a disrupted morphology in distal meristem and columella mother cells (Figure 2K). Moreover, increased vacuolisation of rhizodermal and cortical cells was observed (Figure 2J,L). In some cases, there were prominent alterations in the arrangement of the cortical cells (Figure 2M,N).
The histology of the control roots of Hordeum vulgare from the DZ was previously presented and described in detail [31]. In brief, it consists of a one-layer rhizodermis (composed with hair and non-hair cells), four-layer cortical cells and a central cylinder (characteristic eight outer metaxylem vessels and one central metaxylem vessel). After (-) AuNP treatment, the morphology of the rhizodermal cells was disrupted as the cells were more or less irregular (Figure 3A,F,J). Hair cells were detected at both concentrations (Figure 3B,G); however, at the higher concentration, there was a decrease in the formation of these cells (Figure 3F,J). Other changes after the (-) AuNP treatment (both concentrations) concerned the division of the outer metaxylem vessels (Figure 3C,H,I,K,L) and multiplication of the central metaxylem (Figure 3E,J–L). At the higher concentration of (-) AuNP, there were two or more central metaxylem vessels; however, at the lower dose of (-) AuNP, disturbances in the metaxylem division resulted in the formation of two vessels (compare Figure 3D,E). Alterations were also detected in the endodermis at the lower concentration of (-) AuNP, in which there was a collapse of these cells. At the higher dose of (-) AuNP, there was a thickening of the inner periclinal wall of the endodermis (this might be related to the earlier maturation of the endodermal cells, Figure 3I). Moreover, in the roots that were growing in the higher concentration of (-) AuNP, there were atypical divisions of the pericycle (Figure 3I–L).
3.3. Ultrastructural Changes after Treatment with (-) AuNP
At first, the root cap cells and rhizodermis came into contact with the AuNP. Observations at the cellular level showed some changes between the control and treated roots in these root parts. Therefore, we decided to investigate whether there were any differences in the ultrastructure of the columella root cap cells (Figure 4A–Q) and the rhizodermis (Figure 5A–L). Firstly, it was determined whether the (-) AuNP had penetrated into the root cells. Regardless of the concentration, (-) AuNP did not cross through the cell wall of the peripheral root cap cells (Figure 4F,L) or the outer periclinal wall of the rhizodermal cells (Figure 5E,I). In both cases, the (-) AuNP were retained on the cell wall surface, especially in the fibrous material structures that are characteristic of the outer cell wall of the peripheral root cap cells (Figure 4A) and the rhizodermis (Figure 5A).
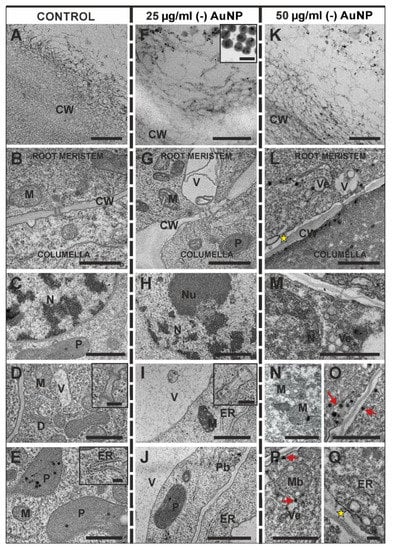
Figure 4.
Ultrastructure of the root cap outer cell wall of the control (A), those that were treated with 25 µg/mL (-) AuNP (F) or 50 µg/mL (-) AuNP (K) roots. The outer cell wall had a fibrous character and was a barrier to the entry of (-) AuNP into the root cells regardless of the concentration (F,K). The ultrastructure of the columella root cap cells from control (A–E), the barley roots that were treated with 25 µg/mL (-) AuNP (F–J) or 50 µg/mL (-) AuNP (K–Q). Red arrows indicate electron-dense spots inside the cytoplasm; yellow asterisks indicate the periplasmic space; CW—cell wall; ER—endoplasmic reticulum; M—mitochondrion; Mb—multivesicular body; N—nucleus; NU—nucleolus; P—plastid; Pb—paramural body; V—vacuole; Ve—vesicles. Scale bars: (A,F,K,Q; D,E,I Insets) = 200 nm; (F Inset) = 10 nm; (B–E,G–J,L–P) = 1 µm.
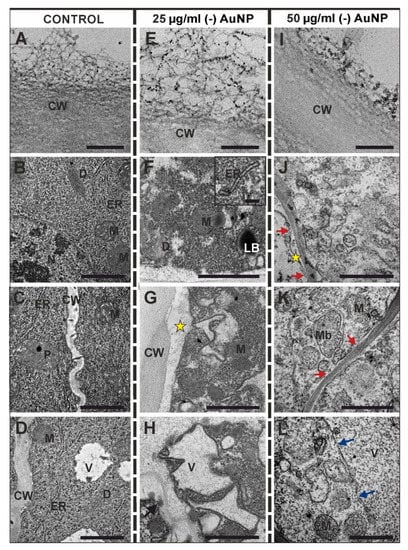
Figure 5.
The ultrastructure of the rhizodermal cells from the control (A–E), the barley roots that were treated with 25 µg/mL (-) AuNP (E–H) or 50 µg/mL (-) AuNP (I–L). The outer periclinal rhizodermal cell wall of the control (A), the barley roots that were treated with 25 µg/mL (-) AuNP (E) or 50 µg/mL (-) AuNP (I). The electron-dense dots in the control root are the result of overlapping fibrils running in different directions (A). In the treated roots, the AuNP were retained in the fibrous of the cell wall (E,I). Black arrow indicates electron-dense spots in the cell wall; red arrows indicate a cell membrane rupture; blue arrows indicate a tonoplast rupture; yellow asterisks indicate the periplasmic space; CW—cell wall; D—dictyosome; ER—endoplasmic reticulum; LB—lipid body; M—mitochondrion; Mb—multivesicular body; N—nucleus; NU—nucleolus; P—plastid; Pb—paramural body; V—vacuole; Ve—vesicles. Scale bars: (A,E,I; F Inset) = 200 nm; (B–D,F–H,J–L) = 1 µm.
The ultrastructure of the columella cells was investigated along the first three layers in the root cap. In the control, each cell contained a cytoplasm with numerous ribosomes, a rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER), dictyosomes, mitochondria, plastids and a large spherical nucleus with electron-dense heterochromatin and electron-lucent euchromatin, which is specific for the interphase nuclei (Figure 4B–E and inset on E). The cell wall, which is a junction of the proximal meristem and distal columella cells of the distal meristem, was not altered in the roots that were treated with the low concertation of (-) AuNP compared to the control and was characterised by the presence of plasmodesmata (Figure 4B,G; insets D,I). However, at the high concentration of (-) AuNP, there was a periplasmic space between the cell wall and the plasmalemma of the cells from the proximal meristem (Figure 4L). There were no changes in the plastid, nucleus or ER ultrastructure of the columella cells in the roots that were treated with the lower dose of (-) AuNP (Figure 4G–J). However, alterations were observed in the structure of the mitochondria, which had a dense matrix and dilated cristae (Figure 4B,D,G,I,N). Moreover, at the lower concentration of (-) AuNP, there was an increased vacuolisation (Figure 4J,K). At the higher concentration of (-) AuNP, a very dense cytoplasm was observed in the columella cells (Figure 4L,M). In these cells, the nucleus structure was changed compared to the control (Figure 4M). Moreover, numerous vesicles and multivesicular bodies (Figure 4M,P), as well as a periplasmic space with vesicles, were also visible (Figure 4Q). Furthermore, in these cells, electron-dense spots were visible in the cytoplasm compartments and in the vicinity of the cell membrane (Figure 4O,P). There were plasmodesmata in all of the analysed variants (Figure 4D, inset I).
In the control roots, the ultrastructure of the rhizodermal cells from meristematic zone was characterised by a dense cytoplasm and organelles such as mitochondria, dictyosomes, ER, plastids, small vacuoles and a large round-shaped nucleus (Figure 5B–D). At the lower (-) AuNP concentration, the rhizodermal cytoplasm was very electron dense; however, electron-lucent regions were also observed (Figure 5J). In these cells, irregular-shaped vacuoles and membranous structures developed (Figure 5H,J), and lipid bodies were also observed. (Figure 5F). A wide periplasmic space was also detected (Figure 5D). At the lower (-) AuNP dose, electron-dense spots were observed in the cell wall (Figure 5H). The rhizodermal cells from the roots that were treated with the higher (-) AuNP concentration had a less dense cytoplasm compared to the control (Figure 5J–L). In these cells, there was a breakdown of the membranes (Figure 5J–L). The vacuoles were large and filled with granular electron-dense spots, and there was an interrupted continuity of the tonoplast (Figure 5L). Moreover, the continuity of the plasmalemma was also disrupted (Figure 5J,K). In these cells, the multivesicular bodies (Figure 5K) and vesicles of different sizes were present (Figure 5J–L). Additionally, some mitochondria had degenerated in their structure (Figure 5K,L).
4. Discussion
In this paper, we described a detailed morphological, histological and ultrastructural analysis of barley roots that were treated with (-) AuNP. The obtained results showed that although (-) AuNP did not penetrate into the roots, it caused them to be altered. To the best of our knowledge, such thorough research has not yet been conducted on barley, which is an important crop plant. The studies indicate that (-) AuNP: 1/ affect the hair cell differentiation, which can influence the micronutrient uptake and decrease plant growth; 2/ disrupt the apical root meristem, which may lead to root length growth and histological disorders; and 3/ cause the death of the rhizodermal cells in which case the roots are not protected against pathogens.
4.1. Morphological Malformations of the Roots
Analyses were performed on the seminal roots, and the main visible difference in their morphology was a decrease in the formation of root hairs after treatment with the higher concentration of (-) AuNP, which confirms our earlier results [31]. A similar reaction to NP was described for Lolium multiflorum, which did not develop root hairs when exposed to silver NP (AgNP) [34], and in Arabidopsis that was exposed to AgNP and titanium dioxide NP (TiO2 NP) [35,36]. Seedlings of Fagopyrum esculentum that were exposed to zinc oxide NP (ZnO NP) and copper oxide NP (CuO NP) responded with a decreased number of root hair cells [37]. In NP-exposed Arabidopsis plants, the transcriptional analysis revealed the repression of the genes that are directly involved in root hair development [35]. The opposite reaction was described for wheat (Triticum L.) roots that were exposed to CuO NP, in which there was an increase in the formation of the root hair cells [38]. In tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants treated with cerium oxide NPs, there was also no inhibition of the formation of root hair cells [39].
However, it should be remembered that the above-mentioned examples are only small fragments of our current knowledge. It is difficult to make generalisations about the effect of NP on plant organisms at this time. When undertaking research on this topic, one should always remember the enormous differences in this interaction depending on the factors mentioned above.
This also indicates that further research is needed to understand how crops react to NP. It was postulated that the reduction in plant growth after NP treatment is connected with phosphate starvation. Such a reaction was documented for Arabidopsis seedlings that were treated with TiO2 NP and AgNP [35] and Nicotiana tabacum roots that were treated with aluminum oxide NP (Al2O3 NP) [40]. Studies with tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) also indicated that NP might influence the availability of copper for plants [40]. The above examples show that the reduction in plant growth of NP-treated crops might result from the lack of the basic elements that are necessary for the proper functioning of the biochemical processes. In the case of crops, preventing such effects is extremely important.
4.2. Histological Changes
Abnormalities in the histology of plant roots that were treated with NP were described for many plant species, including crops [41]. In Gossypium hirsutum, ZnO NP caused anatomical alterations in the roots, such as the vacuolisation of the cortical cells [42]. The treatment of Asparagus officinalis with the ZnO NP resulted in an increased size of its cells and the number of cell files in specific root tissues [41]. In Capsicum annuum roots, selenium NP (nSe) resulted in the development of secondary tissues and fibres, a restriction in the differentiation of vascular tissues or the repression of the vascular tissues after a higher dose of nSe [43]. Studies on maize (Zea mays L.) and cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) that were treated with Ag NP and ZnO NP exhibited cellular alternation in the root apical meristem and elongation zone as well as a diverse metaxylem development compared to the control roots [29]. In the roots of Lolium perenne that was treated with ZnO NP, collapsed cortical cells and the destroyed continuity of the rhizodermis and root cap were described [44]. A similar reaction to NP was described for Brassica juncea [45] and Brassica napus [46]. In the roots of Hordeum sativum that was treated with CuO NP, abnormalities in the root histology were also detected, and it was shown that the rhizodermis had undergone a disruption and that the cortical cells had collapsed [47]. The presented examples indicate that histological changes are an important aspect of the plant-NP interaction (for a review, see [14]). This knowledge is essential for investigating the impact of NP on the growth and development of crops, especially in terms of their nanotoxicity. A previous study showed that positively charged AuNPs modified the root morphology, inhibited the differentiation of rhizodermal cells into hair cells and caused qualitative changes in the components of the cell walls [27]. The results presented in this paper are the first (to the best of our knowledge) showing the influence of negatively charged AuNP on the histology of barley roots, although our research has shown that AuNP do not enter the root cells.
4.3. Ultrastructural Distortion
An ultrastructural analysis of barley roots that were treated with (-) AuNP showed that the peripheral cells of the root cap cells produced a thicker network layer on the wall surface compared to the control roots. This layer was composed, among others, of pectins, which was confirmed by many studies [48,49,50]. The retention of NP in this layer is because the root surface is negatively charged, and therefore the (-) AuNP were repelled and were located only within this external network of pectin. In the mucilage layer, several functional groups (-OH and -CO) were detected that might be involved in the interaction with negatively charged ions [51].
From the studies presented here, it appears that the cell ultrastructure was also influenced by NP, which was evidenced by the increased area of the periplasmic space, a distortion of the organelles, including the breakdown of the tonoplast and the presence of electron-dense spots within the cytoplasm. Studies on Vicia faba roots that were treated with TiO2 NP showed that such treatment resulted in the presence of an electron-dense cytoplasm and numerous not well recognisable organelles and weakly electron-lucent bodies of about 0.3–0.5 mm diameter [52]. In the roots of Hordeum sativum, there were also changes in the ultrastructure of the root cells [53]. In Pisum sativum, the roots that were treated with TiO2 NP, there were cell ultrastructure changes such as plasmolysis, mitochondria with swollen cristae and crystals as well as a cytoplasm with the features of degeneration [54]. Alterations in the root cell ultrastructure were also detected in Oryza sativa plants that were treated with ZnO NP [55]. In these plants, besides the ruptured cell wall and changed ultrastructure of organelles, an increased level of starch was detected. Disruption of the root cell ultrastructure was also described for tobacco plants that were treated with iron oxide NP (Fe3O4 NP) [56]. Changes in the ultrastructure of the root cells of Brassica napus after treatment with ZnO NP were described, and when the observed differences were compared to the control plants, they concerned the degree of cytoplasm density, the appearance of the periplasmic space and changes in the ultrastructure of the plastids and mitochondria [57]. In the case of barley that was treated with Cu NP, it was shown that NP accumulated in the intercellular spaces and altered the histology of the roots [12]. The presented research also showed that at the ultrastructural level, NP significantly affected the root cells. The detected changes for barley roots that were treated with (-) AuNP were similar to those that were described for other crop plants. The ultrastructural changes affected the proper functioning of the cells, especially disturbances in the structure of the mitochondria and plastids and the disruption of the continuity of the tonoplast, which indicated that cells might decay under the influence of NP.
5. Conclusions
The obtained results provide important information about the reaction of barley roots to AuNP. Our study is the first to investigate changes in Hordeum vulgare roots under the impact of (-) AuNP on the morphological, histological and ultrastructural levels, and it depended on the concentration. In the case of barley roots, although NPs do not enter the cells, they cause anatomical changes that may affect barley physiology. It is worth mentioning that the reaction was concentration dependent. At the current stage of the research, it is not possible to state whether the observed changes have a long-term effect, so it cannot be determined whether the influence of the analysed AuNP is positive or negative on growth. It is definitely negative in the context of morphological, histological and ultrastructural changes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.-H. and E.K.; methodology, A.M.-H.; photo documentation A.M.-H. and M.Z.; formal analysis, A.M.-H. and W.G.; investigation, A.M.-H.; data curation, A.M.-H. and E.K.; designing the figures, A.M.-H.; writing the manuscript A.M.-H. and E.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported financially by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Poland as part of the statutory activities of the Institute of Biology, Biotechnology and Environmental Protection, Faculty of Natural Sciences, the University of Silesia in Katowice.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudramurthy, G.R.; Swamy, M.K. Potential applications of engineered nanoparticles in medicine and biology: An update. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 23, 1185–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Xie, H. Nanoparticles in Daily Life: Applications, Toxicity and Regulations. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxol. Oncol. 2018, 37, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestovsky, Y.S.; Martinez-Antonio, A. The Use of Nanoparticles and Nanoformulations in Agriculture. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 8699–8730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, S.; Yadav, A.; Debnath, N.; Das, S. Application of Core/Shell Nanoparticles in Smart Farming: A Paradigm Shift for Making the Agriculture Sector More Sustainable. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 3267–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.; Farooq, M.; Wakeel, A.; Nawaz, A.; Cheema, S.A.; Rehman, H.U.; Ashraf, I.; Sanaullah, M. Nanotechnology in agriculture: Current status, challenges and future opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, U.; Jun, H.; Waldman, B.; Roh, J.; Kim, Y.; Yi, J.; Lee, E.J. Functional analyses of nanoparticle toxicity: A comparative study of the effects of TiO2 and Ag on tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 93, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakrashi, S.; Jain, N.; Dalai, S.; Jayakumar, J.; Chandrasekaran, P.T. In Vivo Genotoxicity Assessment of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles by Allium cepa Root Tip Assay at High Exposure Concentrations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Levard, C.; Judy, J.D.; Unrine, J.M.; Durenkamp, M.; Martin, B.; Jefferson, B.; Lowry, G.V. Fate of Zinc Oxide and Silver Nanoparticles in a Pilot Wastewater Treatment Plant and in Processed Biosolids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Garg, R.; Kumari, A. A Review on Biogenic Synthesis, Applications and Toxicity Aspects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 1325–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.T.; Zeb, A.R.; Lian, J.P.; Wu, J.N.; Xiong, H.X.; Tang, J.C.; Zheng, S.N. Interactions of metal-based nanoparticles (MBNPs) and metal-oxide nanoparticles (MONPs) with crop plants: A critical review of research progress and prospects. Environ. Rev. 2020, 28, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Suskova, S.; Mandzhieva, S.; Tsitsuashvili, V.; Chapligin, V.; Fedorenko, A. Effects of Copper Nanoparticles (CuO NPs) on Crop Plants: A Mini Review. Bionanoscience 2018, 8, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Chen, Z. Impacts of Silver Nanoparticles on Plants: A Focus on the Phytotoxicity and Underlying Mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Xianyu, Y. When nano meets plants: A review on the interplay between nanoparticles and plants. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Singh, U.; Adisa, I.O.; Bindraban, P.S.; Elmer, W.H.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; White, J.C. Effects of Manganese Nanoparticle Exposure on Nutrient Acquisition in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Agronomy 2018, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zulfiqar, F.; Navarro, M.; Ashraf, M.; Akram, N.A.; Munne-Bosch, S. Nanofertilizer use for sustainable agriculture: Advantages and limitations. Plant Sci. 2019, 289, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, N. Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2256–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.T. Using gold nanoparticles for catalysis. Nano Today 2007, 2, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.B.; Gao, T.; Hong, H.; Sun, J.T. Applications of gold nanoparticles in cancer nanotechnology. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2008, 1, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeh, Y.C.; Creran, B.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles: Preparation, properties, and applications in bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafleur, J.P.; Senkbeil, S.; Jensen, T.G.; Kutter, J.P. Gold nanoparticle-based optical microfluidic sensors for analysis of environmental pollutants. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 4651–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Guleria, P.; Kumar, V.; Yadav, S.K. Gold nanoparticle exposure induces growth and yield enhancement in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, V.; Belozerova, I. Influence of Metal Nanoparticles on the Soil Microbial Community and Germination of Lettuce Seeds. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 197, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, S.; Nayan, R.; Khanna, P.K.; Zaidi, M.G.H. Gold-nanoparticle induced enhancement in growth and seed yield of Brassica juncea. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 66, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.J.; Wang, H.H.; Yan, B.; Zheng, H.; Jiang, Y.; Miranda, O.R.; Rotello, V.M.; Xing, B.S.; Vachet, R.W. Effect of Surface Charge on the Uptake and Distribution of Gold Nanoparticles in Four Plant Species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12391–12398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milewska-Hendel, A.; Zubko, M.; Stroz, D.; Kurczynska, E.U. Effect of Nanoparticles Surface Charge on the Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Roots Development and Their Movement into the Root Cells and Protoplasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milewska-Hendel, A.; Witek, W.; Rypien, A.; Zubko, M.; Baranski, R.; Stroz, D.; Kurczynska, E.U. The development of a hairless phenotype in barley roots treated with gold nanoparticles is accompanied by changes in the symplasmic communication. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabo-Attwood, T.; Unrine, J.M.; Stone, J.W.; Murphy, C.J.; Ghoshroy, S.; Blom, D.; Bertsch, P.M.; Newman, L.A. Uptake, distribution and toxicity of gold nanoparticles in tobacco (Nicotiana xanthi) seedlings. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, L.R.; Dubey, B. Evaluation of developmental responses of two crop plants exposed to silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 452, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen, A. Plant Response to Engineered Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milewska-Hendel, A.; Zubko, M.; Karcz, J.; Stroz, D.; Kurczynska, E. Fate of neutral-charged gold nanoparticles in the roots of the Hordeum vulgare L. cultivar Karat. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurczyńska, E.; Godel-Jędrychowska, K.; Sala, K.; Milewska-Hendel, A. Nanoparticles—Plant Interaction: What We Know, Where We Are? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszewska-Zalewska, A.J.; Wolny, E.A.; Smialek, L.; Hasterok, R. Tissue-Specific Epigenetic Modifications in Root Apical Meristem Cells of Hordeum vulgare. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.Y.; Cheng, Y.W.; Espinasse, B.; Colman, B.P.; Auffan, M.; Wiesner, M.; Rose, J.; Liu, J.; Bernhardt, E.S. More than the Ions: The Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on Lolium multiflorum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2360–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Sanchez, S.; Bernales, I.; Cristobal, S. Early response to nanoparticles in the Arabidopsis transcriptome compromises plant defence and root-hair development through salicylic acid signalling. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ke, M.J.; Qu, Q.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Lu, T.; Pan, X.L.; Qian, H.F. Phytotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles and silver ions to Arabidopsis thaliana as revealed by analysis of molecular responses and of metabolic pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chung, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, I. The Genotoxic Effect of ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles on Early Growth of Buckwheat, Fagopyrum esculentum. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.; Wright, M.; Wagner, H.; Valiente, J.; Britt, D.; Anderson, A. Cu from dissolution of CuO nanoparticles signals changes in root morphology. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 110, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Ebbs, S.E.; Chenc, Y.; Ma, X. Trans-generational impact of cerium oxide nanoparticles on tomato plants. Metallomics 2013, 5, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burklew, C.E.; Ashlock, J.; Winfrey, W.B.; Zhang, B.H. Effects of Aluminum Oxide Nanoparticles on the Growth, Development, and microRNA Expression of Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34783. [Google Scholar]
- Desoukey, S.F.; Taha, Z.; El-Shabrawi, H.M.; Sabh, A.Z. Impact of zinc oxide nanoparticles on Asparagus officinalis plant. Plant Arch. 2020, 20, 9323–9338. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam, P.; Priyanka, N.; Manikandan, K.; Ganeshbabu, I.; Indiraarulselvi, P.; Geetha, N.; Muralikrishna, K.; Bhattacharya, R.C.; Tiwari, M.; Sharma, N.; et al. Enhanced plant growth promoting role of phycomolecules coated zinc oxide nanoparticles with P supplementation in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 110, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotoodehnia-Korani, S.; Iranbakhsh, A.; Ebadi, M.; Majd, A.; Ardebili, Z.O. Selenium nanoparticles induced variations in growth, morphology, anatomy, biochemistry, gene expression, and epigenetic DNA methylation in Capsicum annuum; an in vitro study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.H.; Xing, B.S. Root uptake and phytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5580–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, B.B.M.; Diehl, S.V.; Han, F.X.; Monts, D.L.; Su, Y. Anatomical changes due to uptake and accumulation of Zn and Cd in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2005, 54, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhi, S.M.M.; Lahouti, M.; Ganjeali, A.; Entezari, M.H. Comparative Effects of ZnO Nanoparticles, ZnO Bulk Particles, and Zn2+ on Brassica napus After Long-Term Exposure: Changes in Growth, Biochemical Compounds, Antioxidant Enzyme Activities, and Zn Bioaccumulation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Fedorenko, A.; Mandzhieva, S.; Sushkova, S.; Lysenko, V.; Duplii, N.; Azarov, A.; Chokheli, V. Destructive Effect of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles on Ultrastructure of Chloroplast, Plastoglobules and Starch Grains in Spring Barley (Hordeum sativum). Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2019, 21, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, K.; Kunieda, T.; Tamura, K.; Hatano, K.; Hara-Nishimura, I.; Shimada, T. Identification of Periplasmic Root-Cap Mucilage in Developing Columella Cells of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Iyer-Pascuzzi, A.S. Shedding the Last Layer: Mechanisms of Root Cap Cell Release. Plants 2020, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.S.; Mittra, B.; Sharma, S.; Das, T.K.; Babu, C.R. Detection of root mucilage using an anti-fucose antibody. Ann. Bot. 2002, 89, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, D.I.; Pichler, T.; Yeh, D.H.; Alcantar, N.A. Removing Heavy Metals in Water: The Interaction of Cactus Mucilage and Arsenate (As (V)). Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4553–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiglione, M.R.; Giorgetti, L.; Bellani, L.; Muccifora, S.; Bottega, S.; Spano, C. Root responses to different types of TiO2 nanoparticles and bulk counterpart in plant model system Vicia faba L. Exp. Bot. 2016, 130, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorenko, A.G.; Minkina, T.M.; Chernikova, N.P.; Fedorenko, G.M.; Mandzhieva, S.S.; Rajput, V.D.; Burachevskaya, M.V.; Chaplygin, V.A.; Bauer, T.V.; Sushkova, S.N.; et al. The toxic effect of CuO of different dispersion degrees on the structure and ultrastructure of spring barley cells (Hordeum sativum distichum). Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 1673–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muccifora, S.; Castillo-Michel, H.; Barbieri, F.; Bellani, L.; Castiglione, M.R.; Spano, C.; del Real, A.E.P.; Giorgetti, L.; Tassi, E.L. Synchrotron Radiation Spectroscopy and Transmission Electron Microscopy Techniques to Evaluate TiO2 NPs Incorporation, Speciation, and Impact on Root Cells Ultrastructure of Pisum sativum L. Plants. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheteiwy, M.S.; Dong, Q.; An, J.Y.; Song, W.J.; Guan, Y.J.; He, F.; Huang, Y.T.; Hu, J. Regulation of ZnO nanoparticles-induced physiological and molecular changes by seed priming with humic acid in Oryza sativa seedlings. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 83, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, R.; Alkhatib, B.; Abdo, N.; AL-Eitan, L.; Creamer, R. Physio-biochemical and ultrastructural impact of (Fe3O4) nanoparticles on tobacco. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kouhi, S.M.M.; Lahouti, M.; Ganjeali, A.; Entezari, M.H. Long-term exposure of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) to ZnO nanoparticles: Anatomical and ultrastructural responses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10733–10743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).