Electrode Kinetics of Ion Jelly and Ion Sol-Gel Redox Materials on Screen-Printed Electrodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of IJ and ISG
2.2. Electrochemical and Conductivity Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Conductivity Characterization of Ion Jelly and Ion Sol-Gel
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of IJ and ISG
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vioux, A.; Viau, L.; Volland, S.; LE Bideau, J. Use of ionic liquids in sol-gel; ionogels and applications. C. R. Chim. 2010, 13, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bideau, J.; Viau, L.; Vioux, A. Ionogels, ionic liquid based hybrid materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 40, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, P.C.; Marr, A.C. Ionic liquid gel materials: Applications in green and sustainable chemistry. Green Chem. 2015, 18, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiago, G.A.O.; Matias, I.A.S.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S. Application of Ionic Liquids in Electrochemistry—Recent Advances. Molecules 2020, 25, 5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, L.; Tourné-Péteilh, C.; Devoisselle, J.-M.; Vioux, A. Ionogels as drug delivery system: One-step sol–gel synthesis using imidazolium ibuprofenate ionic liquid. Chem. Commun. 2009, 46, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedro, S.; Freire, C.; Silvestre, A.; Freire, M. Ionic Liquids in Drug Delivery. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-R.; Cao, J.-F.; Shu, Y.; Wang, J.-H. Research progress of ionic liquids-based gels in energy storage, sensors and antibacterial. Green Chem. Eng. 2021, 2, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.-G.; Hu, Y.-S.; Xing, H.; Dai, S. Ionic liquids and derived materials for lithium and sodium batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2020–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshminarayana, G.; Nogami, M. Inorganic–organic hybrid membranes with anhydrous proton conduction prepared from tetramethoxysilane/methyl-trimethoxysilane/trimethylphosphate and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium-bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide for H2/O2 fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-Q.; Apodaca, D.C.; Peng, W.-C.; Chen-Yang, Y.-W. Protic ionic liquid-containing silica-based ionogels for nonhumidified PEMFC applications. Ionics 2017, 24, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Watanabe, M. Protic ionic liquids: Fuel cell applications. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhao, F.; Li, J.; Xiao, F.; Fan, S.; Zeng, B. Direct electrochemistry of horseradish peroxidase in gelatin-hydrophobic ionic liquid gel films. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 7425–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, S.C.; Lourenço, N.M.T.; Fonseca, L.J.P.; Cordas, C.M. Comparative Electrochemical Behavior of Cytochrome c on Aqueous Solutions Containing Choline-Based Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 8701–8705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, J. Carbon nanotube–ionic liquid composite gel based high-performance bioanode for glucose/O2 biofuel cells. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 5060–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.; Almeida, R.M.; Moura, J.J.G.; Lourenço, N.T.; Fonseca, L.J.P.; Cordas, C.M. Sandwich-Type Enzymatic Fuel Cell Based on a New Electro-Conductive Material—Ion Jelly. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 6546–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.K.; Rawat, K.; Aswal, V.K.; Kohlbrecher, J.; Bohidar, H.B. DNA ionogel: Structure and self-assembly. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 19, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidinha, P.; Lourenço, N.M.T.; Pinheiro, C.; Brás, A.R.; Carvalho, T.; Santos-Silva, T.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Romão, M.J.; Parola, J.; Dionisio, M.; et al. Ion jelly: A tailor-made conducting material for smart electrochemical devices. Chem. Commun. 2008, 5842–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordas, C.; Lourenço, N.; Vidinha, P.; Afonso, C.; Barreiros, S.; Fonseca, L.P.; Cabral, J.M. New conducting biomaterial based on Ion Jelly® technology for development of a new generation of biosensors. New Biotechnol. 2009, 25, S138–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, N.M.T.; Österreicher, J.; Cabral, J.M.S.; Fonseca, L.P.; Vidinha, P.; Barreiros, S. Evaluation of Ion Jelly biopolymer on glucose biosensing. In Proceedings of the 1st Portuguese Biomedical Engineering Meeting, Lisbon, Portugal, 1–4 March 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, R.; Neves, L.; Simões, P.; Coelhoso, I. Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes and Ion-Jelly® Membranes with [BMIM][DCA]: Comparison of Its Performance for CO2 Separation. Membranes 2015, 5, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dos Santos, R.; Rocha, Â.; Matias, A.; Duarte, C.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Lourenço, N.; Borges, J.P.; Vidinha, P. Development of antimicrobial Ion Jelly fibers. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 24400–24405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.; Augusto, V.; Brás, A.R.; Lourenço, N.M.T.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Barreiros, S.; Correia, N.T.; Vidinha, P.; Cabrita, E.J.; Dias, C.J.; et al. Understanding the Ion Jelly Conductivity Mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 2664–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, T.; Augusto, V.; Rocha, A.; Lourenço, N.M.T.; Correia, N.T.; Barreiros, S.; Vidinha, P.; Cabrita, E.J.; Dionísio, M. Ion Jelly Conductive Properties Using Dicyanamide-Based Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 9445–9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, R.N.L.; Lourenço, N.M.T.; Gomes, P.M.V.; da Fonseca, L.J.P. Swelling behavior of gelatin-ionic liquid functional polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2013, 51, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevstrueva, D.; Murashko, K.; Vunder, V.; Aabloo, A.; Pihlajamäki, A.; Mänttäri, M.; Pyrhönen, J.; Koiranen, T.; Torop, J. Natural cellulose ionogels for soft artificial muscles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 161, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Chavero, M.M.; Domínguez, J.C.; Alonso, M.V.; Rigual, V.; Oliet, M.; Rodriguez, F. Viscoelastic properties of physical cellulosic bionogels of cholinium lysinate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, K.; Hata, K.; Katakabe, T.; Kondoh, M.; Watanabe, M. Nanocomposite Ion Gels Based on Silica Nanoparticles and an Ionic Liquid: Ionic Transport, Viscoelastic Properties, and Microstructure. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 9013–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, J. A novel room temperature ionic liquid sol–gel matrix for amperometric biosensor application. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; He, P.; Liu, H.; Li, J. Highly active horseradish peroxidase immobilized in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate room-temperature ionic liquid based sol–gel host materials. Chem. Commun. 2005, 1778–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchipunov, Y.A.; Karpenko, T.Y.; Bakunina, I.Y.; Burtseva, Y.V.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. A new precursor for the immobilization of enzymes inside sol–gel-derived hybrid silica nanocomposites containing polysaccharides. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2004, 58, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanizamani, F.; Timur, S. Ionic Liquids from Biocompatibility and Electrochemical Aspects toward Applying in Biosensing Devices. Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, S.A.M.; Bayley, P.; Forsyth, M.; MacFarlane, D. Ionogels based on ionic liquids as potential highly conductive solid state electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 91, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Fischer, A.; Hoffmann, H. Novel Ringing Silica Gels That Do Not Shrink. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, K.G. A two-component, non-aqueous route to silica gel. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1994, 2, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Néouze, M.-A.; Le Bideau, J.; Leroux, F.; Vioux, A. A route to heat resistant solid membranes with performances of liquid electrolytes. Chem. Commun. 2005, 1082–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Néouze, M.-A.; Le Bideau, J.; Gaveau, P.; Bellayer, S.; Vioux, A. Ionogels, New Materials Arising from the Confinement of Ionic Liquids within Silica-Derived Networks. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 3931–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.N.L. Design of Ionic Liquid-Based Biomaterials for Development of a New Generation of Biofuel Cells. Ph.D. Thesis, Instituto Superior Tècnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portigal, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Brazel, C.S. On the importance and mechanisms of burst release in matrix-controlled drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2001, 73, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stealey, S.; Khachani, M.; Zustiak, S.P. Adsorption and Sustained Delivery of Small Molecules from Nanosilicate Hydrogel Composites. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissig, V.; Pettinger, T.K.; Murdock, N. Nanopharmaceuticals (part 1): Products on the market. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4357–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilczewska, A.Z.; Niemirowicz, K.; Markiewicz, K.H.; Car, H. Nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 1020–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, G.J.; Singh, R.K.; Foroutan, F.; Alqaysi, M.; Han, C.-M.; Mahapatra, C.; Kim, H.-W.; Knowles, J.C. Sol–gel based materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 77, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sankoh, S.; Vagin, M.Y.; Sekretaryova, A.N.; Thavarungkul, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Mak, W.C. Colloid electrochemistry of conducting polymer: Towards potential-induced in-situ drug release. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 228, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bott, A.W.; Jackson, B.P. Study of Ferricyanide by Cyclic Voltammetry Using the CV-50W. Curr. Sep. 1996, 15, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Feeney, R. Determination of heterogeneous electron transfer rate constants at microfabricated iridium electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 1999, 1, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.E.G.; Keeley, G.P. The Redox Behaviour of Randomly Dispersed Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes both in the Absence and in the Presence of Adsorbed Glucose Oxidase. Sensors 2006, 6, 1791–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lourenço, N.M.; Österreicher, J.A.; Vidinha, P.; Barreiros, S.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Cabral, J.M.; Fonseca, L.P. Effect of gelatin–ionic liquid functional polymers on glucose oxidase and horseradish peroxidase kinetics. React. Funct. Polym. 2011, 71, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan, L. Humidity fixed points of binary saturated aqueous solutions. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. A Phys. Chem. 1977, 81A, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanello, P. Inorganic Electrochemistry: Theory, Practice and Application; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.; Vidinha, P.; Vieira, B.R.; Li, R.W.C.; Gruber, J. Ion Jelly: A novel sensing material for gas sensors and electronic noses. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 2, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazet, A.; Sokolov, S.; Sonnleitner, T.; Makino, T.; Kanakubo, M.; Buchner, R. Densities, Viscosities and Conductivities of the Imidazolium Ionic Liquids [Emim][Ac], [Emim][FAP], [Bmim][BETI], [Bmim][FSI], [Hmim][TFSI], and [Omim][TFSI]. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 2400–2411, Correction to J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 61, 699–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavagnini, I.; Antiochia, R.; Magno, F. An Extended Method for the Practical Evaluation of the Standard Rate Constant from Cyclic Voltammetric Data. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neghmouche, N.S.; Lanez, T. Calculation of Diffusion Coefficients and Layer Thickness for Oxidation the Ferrocene using Voltammetry Technique. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2013, 1, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Tan, C.; Lowe, M.A.; Abruña, H.D.; Ralph, D.C. Electrochemistry of Individual Monolayer Graphene Sheets. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 2264–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uçar, M.; Solak, A.O.; Aksu, M.; Levent, M.T. Electrochemical Investigation of 4’-Haloderivatives of N,N-Dimethyl-4-Aminoazobenzene. Turk. J. Chem. 2002, 26, 509–520. [Google Scholar]
- Lesniewski, A.; Niedziolka, J.; Palys, B.; Rizzi, C.; Gaillon, L.; Opallo, M. Electrode modified with ionic liquid covalently bonded to silicate matrix for accumulation of electroactive anions. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 2580–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedziolka-Jonsson, J.; Jonsson-Niedziolka, M.; Nogala, W.; Palys, B. Electrosynthesis of thin sol–gel films at a three-phase junction. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 3311–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.S. Theory and Application of Cyclic Voltammetry for Measurement of Electrode Reaction Kinetics. Anal. Chem. 1965, 37, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daum, P.H.; Enke, C.G. Electrochemical kinetics of the ferri-ferrocyanide couple on platinum. Anal. Chem. 1969, 41, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.C. Sol-gel Silica Nanoparticles in Medicine: A Natural Choice. Design, Synthesis and Products. Molecules 2018, 23, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sercombe, L.; Veerati, T.; Moheimani, F.; Wu, S.Y.; Sood, A.K.; Hua, S. Advances and Challenges of Liposome Assisted Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
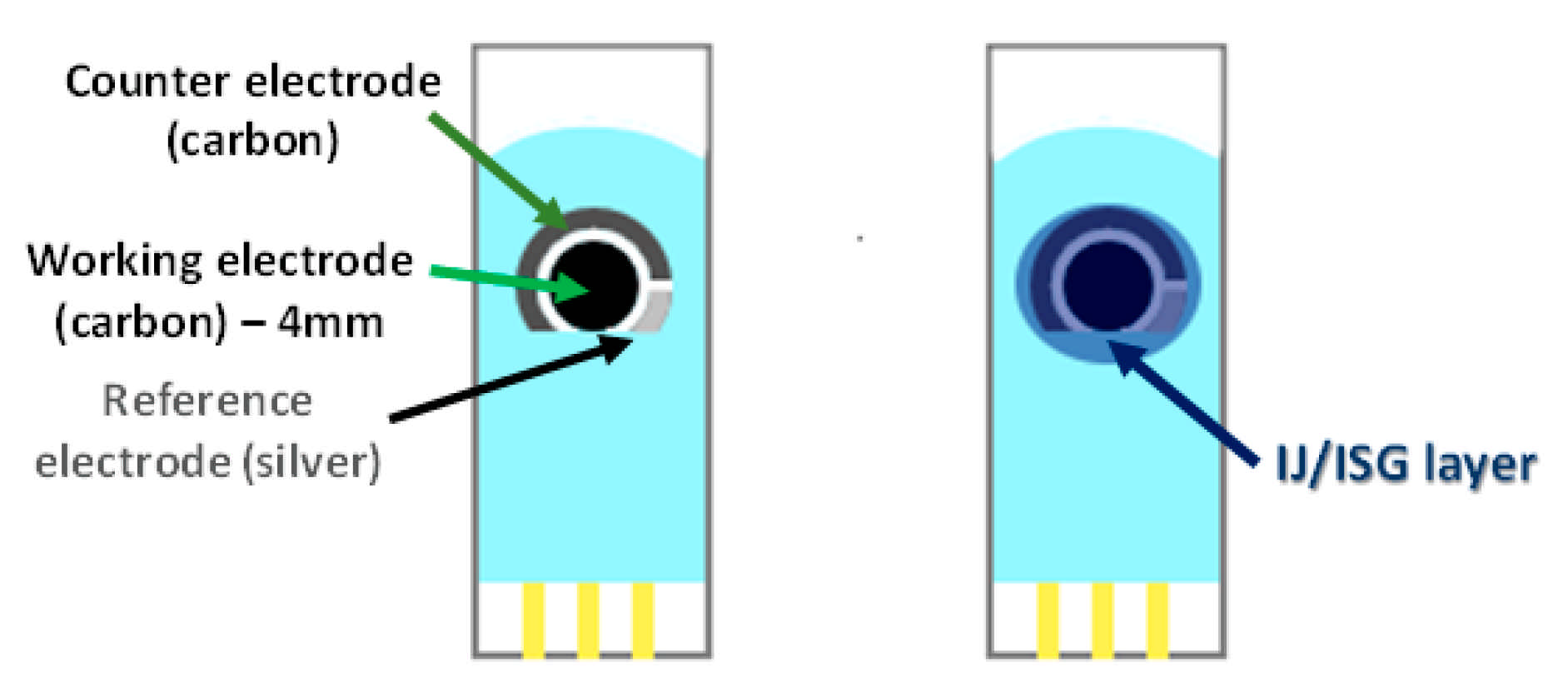

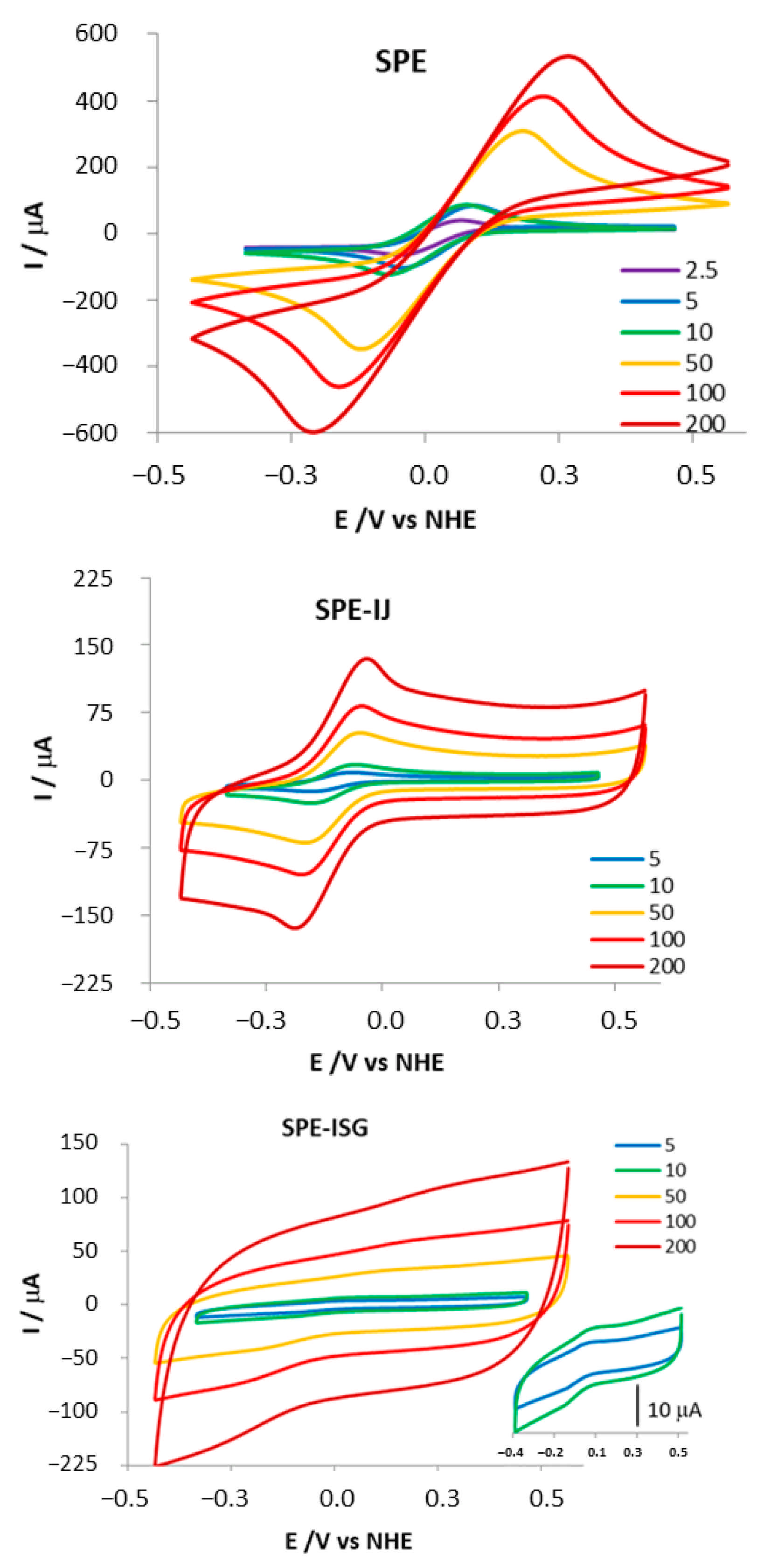

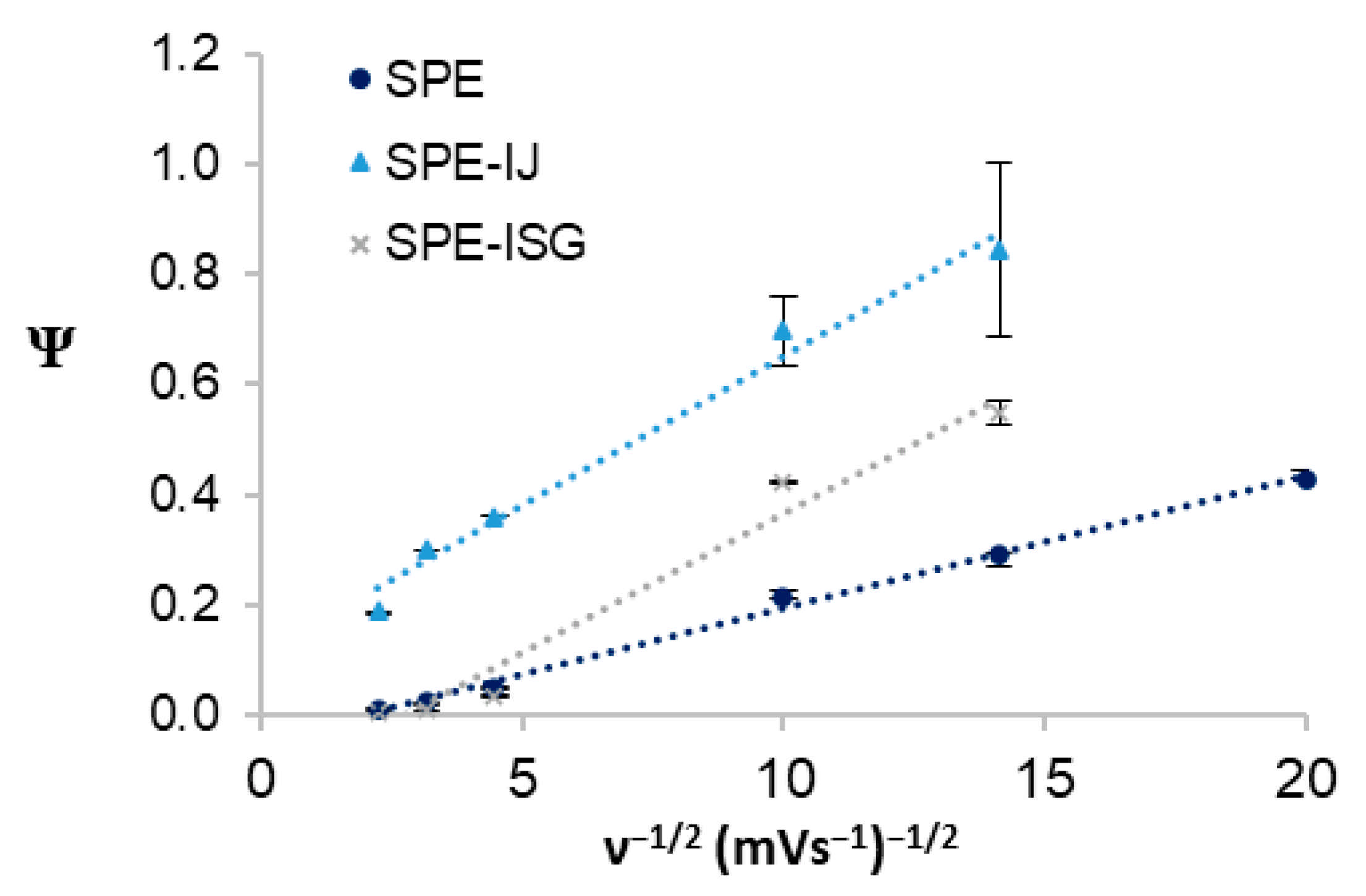
| ν (mV·s−1) | 2.5 | 5 | 10 | 50 | 100 | 200 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPE | E°’ (mV) | 145 ± 5 | 159 ± 4 | 141 ± 2 | 166 ± 1 | 165 ± 1 | 162 ± 3 |
| ∆Ep (mV) | 113 ± 2 | 130 ± 1 | 147 ± 2 | 302 ± 1 | 381 ± 2 | 477 ± 4 | |
| Ipc/Ipa | 1.05 ± 0.03 | 1.01 ± 0.01 | 1.02 ± 0.01 | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 1.03 ± 0.02 | 1.07 ± 0.05 | |
| SPE-IJ | E°’ (mV) | 24 ± 2 | 28 ± 1 | 26 ± 1 | 25 ± 1 | 23 ± 2 | |
| ∆Ep (mV) | - | 90 ± 1 | 95 ± 3 | 120 ± 1 | 129 ± 1 | 155 ± 1 | |
| Ipc/Ipa | 1.14 ± 0.02 | 1.24 ± 0.02 | 1.15 ± 0.01 | 1.16 ± 0.01 | 1.17 ± 0.02 | ||
| SPE-ISG | E°’ (mV) | 103 ± 1 | 98 ± 1 | 100 ± 2 | 113 ± 9 | 117 ± 5 | |
| ∆Ep (mV) | - | 103 ± 1 | 113 ± 2 | 256 ± 6 | 412 ± 5 | 542 ± 10 | |
| Ipc/Ipa | 0.40 ± 0.01 | 0.41 ± 0.04 | 0.95 ± 0.13 | 1.37 ± 18 | 1.15 ± 0.25 | ||
| Electrode Type | DO (cm2·s−1) | DR (cm2·s−1) | k0 (cm·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPE | (1.57 ± 0.14) × 10−5 | (1.38 ± 0.01) × 10−5 | (1.03 ± 0.03) × 10−3 |
| SPE-IJ | (3.07 ± 0.56) × 10−7 | (2.29 ± 0.62) × 10−7 | (1.54 ± 0.38) × 10−2 |
| SPE-ISG | (1.73 ± 0.35) × 10−9 | (4.79 ± 1.37) × 10−10 | (7.53 ± 0.11) × 10−6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho, R.N.L.; Cordas, C.M.; da Fonseca, L.J.P. Electrode Kinetics of Ion Jelly and Ion Sol-Gel Redox Materials on Screen-Printed Electrodes. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12042087
Carvalho RNL, Cordas CM, da Fonseca LJP. Electrode Kinetics of Ion Jelly and Ion Sol-Gel Redox Materials on Screen-Printed Electrodes. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(4):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12042087
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho, Rui N. L., Cristina M. Cordas, and Luís J. P. da Fonseca. 2022. "Electrode Kinetics of Ion Jelly and Ion Sol-Gel Redox Materials on Screen-Printed Electrodes" Applied Sciences 12, no. 4: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12042087
APA StyleCarvalho, R. N. L., Cordas, C. M., & da Fonseca, L. J. P. (2022). Electrode Kinetics of Ion Jelly and Ion Sol-Gel Redox Materials on Screen-Printed Electrodes. Applied Sciences, 12(4), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12042087







