Abstract
In high-brightness excimer systems, the direct amplification of short pulses allows temporal filters to be integral parts of the ultraviolet (UV) amplifier chain, where the only origin of the noise is the amplified spontaneous emission (ASE), generated by the amplifier(s) following the filter. The ASE, however, develops faster than the short main pulse; in this paper, the dynamic short- and long-pulse amplification properties of KrF, XeCl and XeF excimers are studied, with special emphasis on the temporal contrast. It was found that, beyond the saturation of amplification, the relaxation of the B state in KrF, together with the contribution of the absorption of the transiently populated X state in XeCl and XeF, are the main limitations for both the extraction efficiency and the contrast. For all excimers, the stimulated transition rates and the dependence of the achievable contrast on the level of saturation were derived. Local quantities were introduced to characterize the deterioration of the contrast for a unit gain length of KrF amplifiers. A KrF power amplifier of limited gain (G ≈ 3), following the newly introduced nonlinear Fourier filter, is capable of reaching contrast levels beyond the previously reported 1011–1012.
1. Introduction
1.1. Comparison of Solid-State and Excimer Systems
Ultrashort laser pulses have the unique potential to concentrate the energy of the electromagnetic field in both time and space. The best concentration, which is limited by the uncertainty principle and diffraction, can only be carried out if the pulse has optimum quality. For this reason, the pulse quality and its improvement is one of the most important features of present laser systems. Short-pulse ultraviolet (UV) laser systems are efficient tools to produce high-intensity fields, even for moderate power levels [1]. At a higher power level, however, maintaining the beam quality becomes complicated; moreover, the amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) rapidly increases as a consequence of the frequency scaling of the Einstein coefficients. This scaling also means a drastic decrease of the lifetime of the spontaneous emission in the ultraviolet (typically down to nanoseconds for excimers). The long (>microsecond) energy storage time of the lasing materials in the infrared is one of the reasons why, nowadays, the most powerful laser systems are operating in that spectral range. In the last decades, remarkable progress in the generation of intense electromagnetic fields was driven by the chirped pulse amplification (CPA) technique [2] using solid-state (e.g., Ti:sapphire) lasers. The peak power of these laser systems already surpasses the petawatt level and the focused intensities are up to the 1022–1023 W/cm2 range [3,4,5,6,7,8].
In the UV part of the spectrum—due to the frequency scaling of the spontaneous emission and the short pumping time—the gradual evolution of the temporal, spatial, and spectral qualities of the pulse, as a result of many roundtrips in the laser cavity, are generally not allowed. The straightforward way is to use a dual-wavelength system, where the generation of the high spatial and temporal quality pulse is carried out at longer wavelengths. After frequency conversion (usually frequency doubling or tripling) the short-pulse is amplified in UV gain modules [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16], as shown in Figure 1. This approach provides a great ability to precisely control the pulse parameters and, therefore, the characteristics of the system output. Moreover, the frequency converter, as a nonlinear optical device, can efficiently decouple the temporal noise of the long wavelength front end, and using a novel technique (called as active spatial filtering [17]), both the directional and spectral properties of the main pulse can efficiently be controlled [17,18]. The basic idea behind this method is that the frequency converter is positioned at the Fourier plane of the beam. It is the most intense zeroth order that is efficiently converted with the simultaneous removal of the high-order spatial frequencies from the beam. In this way, both the temporal and the spatial properties of the main pulse are reset in the “middle” of the system, prior to the amplification in the excimer amplifier chain.
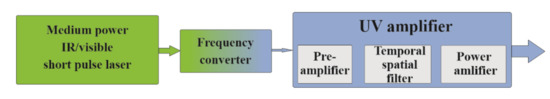
Figure 1.
Hybrid strategy involving the use of a UV seed-beam produced with a femtosecond IR or visible source that subsequently undergoes amplification in excimer amplifier modules (based on [9]).
Excimer denotes a molecule that exists only in the excited state [19]. A typical potential diagram of such a molecule for KrF is shown in Figure 2, offering an ideal four-level system for efficient amplification of long pulses, even in case of amplifying media of short storage times.
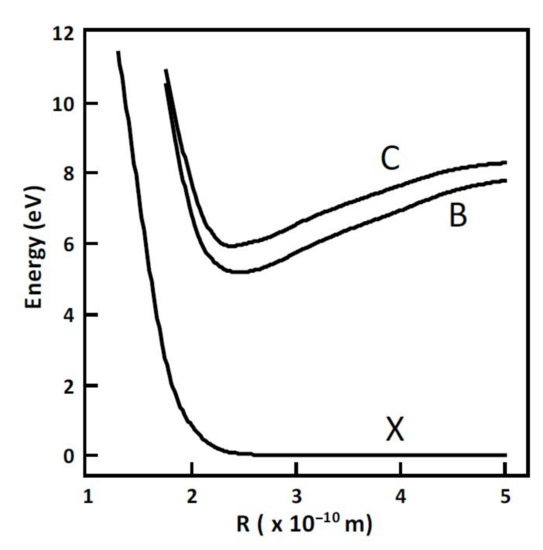
Figure 2.
Typical potential diagram of an excimer (KrF) molecule (based on [19]).
KrF excimer is a high gain medium and best suited for short-pulse amplification in the UV [1]. It has a relatively narrow spectral bandwidth (∆λ/λ ≈ 1/300) and low saturation energy density () compared to solid-state media [1]. This allows the use of direct amplification of the short-pulse. Moreover, the low density gaseous medium provides minimum phase front distortions [1,20].
As a consequence of the shorter wavelength—in case of proper phase front control—short-pulse KrF excimer laser systems can reach >1019 W/cm2 focused intensity (or >1020 W/cm−2 sterad-1 brightness) despite the moderate level of output power [14,20]. Although CPA systems have reached much higher peak power (up to 10 PW) in the recent decades [21], UV systems have the advantage of high focusability. Up to now, most large-scale CPA systems have mainly been characterized by their maximum peak-power, while short-pulse excimer systems were compared to other systems by their high focused intensities (or brightness).
1.2. Contrast Issues
Recently, a great amount of experiments have confirmed that the key element in performing high-intensity laser–matter interactions is the temporal and spatial contrast of the pulses [22,23,24]. These experiments showed that prepulses and ASE of 107–108 W/cm2 intensity can considerably change laser–matter interactions [25,26]. Considering that the focused intensity of the present laser systems surpass 1022 W/cm2, and ambitious plans are targeting 1025 W/cm2, the necessary intensity contrast is in the 1012–1017 regime. Several techniques have been successfully applied for the improvement of the temporal contrast of intense laser pulses. The most straightforward methods are the plasma mirror technique [27,28] or frequency conversion [29,30] at the output of the laser system, or the use of the cross-polarized wave generation (XPW) technique in a double-CPA arrangement [8,31,32,33]. These techniques usually provide the 1010 and 1012 temporal contrast on the ns scale. However, an inherent shortcoming of the CPA-based systems is that the coherent pedestal (on the intensity scale from 10−5 to 10−10) in the ps temporal vicinity of the main pulse—caused by the imperfect compensation of the spectral phase during compression and/or re-scattering on the compressor elements—still remains [4,6,7,8,23,31,32,33]. It means that, by the use of the pulse cleaning techniques (e.g., XPW), where further amplification and the subsequent use of CPA are needed, one has to face additional inherent deterioration of the temporal contrast. This is one of the reasons why, after compression of the amplified pulses, additional temporal filters are often used to suppress the background. This necessitates the use of energy scalable pulse cleaning methods, such as frequency conversion, plasma mirror technique, or the recently introduced nonlinear Fourier filtering (NFF) [34]. In such cases, however, high-throughput operations have absolutely been required since no additional amplification could compensate for the energy loss.
In contrast to solid-state systems, short-pulse UV laser systems use direct amplification; therefore, the only source of the temporal background is the ASE, which is uniformly distributed over its duration in the 10 ns range. As mentioned earlier, the short wavelength (consequently the short storage time) and the special gain dynamics of the KrF medium (see later) cause rapidly growing ASE. These features have set the temporal contrast to ~1010 already for several times the 10 mJ output energy at 248 nm. When a higher output power/intensity range is approached, contrast improvement techniques are needed to be applied in (or preferably after) the amplifier chain. The former considerations can be recognized in Figure 1, where the UV amplifier chain is split into two parts (called pre- and power amplifier) by the spatial/temporal filter.
1.3. Energy Scalable Pulse Cleaning Techniques
1.3.1. Plasma Mirror
The plasma mirror technique [27] was proven to be an efficient method to remove prepulses. The low intensity part of the beam, arriving before the main pulse, is transmitted through an antireflection-coated transparent target. Above the ionization threshold, an overdense plasma is generated, reflecting the laser beam, leading to improved temporal contrast. Since reflectivities up to 80% are reached [35], plasma mirrors, even in a double arrangement, are often used [36]. Recently, reflectivity of up to 97% was reached by [37], using a prepulse some picoseconds before the main pulse of the PHELIX laser [38]. Plasma mirrors are used mainly for infrared laser systems, as the deeper penetration depth of a UV beam results in a lower reflectivity. Recently, the plasma mirror effect was also demonstrated for a short-pulse KrF laser [39,40]. In an improved experiment, reflectivity up to 70% was obtained for the 248 nm pulse [41].
The plasma mirror technique, however, has shortcomings, that the contrast improvement in a single stage is moderate (roughly two orders of magnitude), moreover, a fresh target area is needed for each shot.
1.3.2. Nonlinear Fourier-Filter
To exceed the shortcomings associated with the use of plasma mirrors, an alternative method, called nonlinear Fourier-filtering (NFF), has been proposed for temporal filtering of short UV pulses [34]. In this arrangement, the separation of the intense main pulse from the noise is based on a nonlinear interaction in the Fourier-plane and on the resulting directional modulation of the beam. The experimental realization (see the right half of Figure 3) uses a confocal telescope and a pair of conjugate filters, where the middle and outer parts of the beam are filtered out at the input and output of the system, respectively. The low intensity ASE is not (or negligibly) modulated and the output diaphragm blocks the remaining part of the beam. However, for the intense main pulse, the self-generated plasma introduces selective nonlinear phase-modulation of the different diffraction orders of the beam, which leads to modified directional properties, and as a result, significant throughput appears. In this way, the noise becomes spatially separable from the main pulse. An important feature of this arrangement is that the temporal filtering is accompanied by efficient spatial filtering.
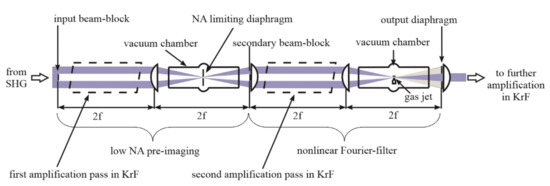
Figure 3.
Schematic of the nonlinear Fourier-filter completed by a low NA pre-imaging and by possible positions of the amplifiers (based on [42]).
The first demonstration of this filtering technique in [34] showed 103 temporal contrast improvement and >40% energy throughput with a stable performance. Later investigations showed that the moderate value of contrast improvement was limited by the spatial contrast of “conventional” imaging of the input annular aperture containing (high) spatial frequency components that cannot be processed by the imaging system of NFF [42]. The most preferable solution was to introduce an imaging of low numerical aperture (NA) prior to Fourier-filtering (called pre-imaging) to exclude the higher spatial frequencies in the intermediate picture created by this pre-image system, as shown in the left half of Figure 3.
Calculations show remarkable improvement; the spatial contrast of imaging was increased to the theoretical 1010 level. A contrast improvement of >107 and >105 was experimentally demonstrated in the visible, and in the UV [42], providing significantly higher contrast improvement than the former techniques. Further advantages of this arrangement are that the amplification could be carried out simultaneously during the imaging (see Figure 3), and the pre-imaging part acts as a spatial filter at the same time, reducing the ASE coupling between the amplifiers.
The nonlinear Fourier-filter uses subsequent imaging systems and ionization of noble gases; therefore, it is expected to be energy scalable, and an excellent candidate for filtering short-pulses in a wide wavelength range. The special gain dynamics of excimer amplifiers—studied in detail later—necessitates the use of the filtering technique as close to the end of the amplifier chain as possible. Since the extension of this technique towards larger energies and larger cross-sections is technically challenging (and rather complicated), integration of this method had been realized in subsequent steps into a high-brightness KrF laser system.
1.3.3. Former Experimental Results concerning the Use of NFF
As the first step toward improving the temporal contrast of UV systems, the nonlinear Fourier-filter was integrated into our short-pulse hybrid KrF excimer laser system after the first and second passes of amplification [43]. This part of the experimental arrangement is illustrated in Figure 3. The input pulse at 248 nm was generated by frequency doubling of subpicosecond dye laser pulses [12], where the frequency converter uses the so-called active spatial filtering phenomena [17], providing temporally and spatially clean UV pulses of several times of 10 µJ energy for the first amplification pass in KrF. This is also part of the low NA pre-imaging, which images the input annular beam block to the plane of a secondary beam block, which acts as an input for the following NFF. Here, the second amplification pass is part of the image system of NFF, whose output is amplified in a subsequent four passes to ~100 mJ (not indicated in Figure 3). The final power amplification stage is used in a two-beam interferometric multiplexing arrangement [44,45], extracting a higher portion of the energy stored in the amplifier. With this arrangement, more than 2 orders of magnitude higher intensity contrast (>1011) is achieved for the same output energy as in former cases [43]. It is important to note that the ASE at the output of the system is measured to be generated exclusively by the amplifier chain following the temporal filter [43].
Due to the direct amplification scheme in excimer amplifiers, the use of amplifier(s) following the pulse cleaning element seems possible, since deterioration of the temporal contrast in the following amplifier(s) is only originated by the development of ASE connected to the gain-length product of these amplifiers. From the point of view of contrast, this additional amplification is only tolerable as long as the amplification for the main pulse is comparable to that of the ASE. This, however, is not fulfilled in the above mentioned arrangement, because a rapid increase of the ASE compared to the short signal-pulse was experimentally observed in the relatively “long” amplifier chain following the temporal filter [43]. This necessitates the use of a temporal filter of high contrast improvement and high throughput as close to the end of the amplifier chain as possible. On the other hand, the origin of the moderate amplification of short pulses (compared to that of ASE) in excimers needs further investigations.
1.4. Effect of Saturated Amplification in KrF, in the Presence of Nonsaturable Absorption
It is known from former studies [15,46] that, from the point of view of energy extraction, KrF is a superior amplifying medium for short-pulse amplification compared to other excimers. Even this medium equal amplification for a short signal pulse and the (long) ASE in KrF cannot be realized for two reasons. One reason is associated with the fact that KrF is an amplifying medium, exhibiting saturable amplification with considerable nonsaturable absorption [1,47,48]. Amplification in such a medium can be described by the
coupled differential equations [47,48], where I is intensity of the short-pulse, is stimulated emission cross-section, is the population density of the upper lasing level (accessible by a short pulse), α is the absorption coefficient, and v is the velocity of light in the active medium.
Without the Iα quantity, these equations are the well-known Frantz–Nodvik equations [49], which describe the amplifications of short pulses in an ideal four-level system, whose analytical solution is
Here, , where is the small-signal gain coefficient for a (weak) short pulse, L is the length of the medium, and are the normalized output and input energy densities, defined by the
equations, where and are the energy densities of the output and incoming pulses, respectively, and is the saturation energy density (see later).
Solving (1) and (2), the amplification properties of KrF can be derived. For such a medium, both the extraction efficiency (η) and the contrast coefficient (c)—the ratio of the effective gain coefficients for an “energetic” and a weak signal—deteriorate rapidly with increasing energy density when approaching saturation. This feature can be followed in Figure 4, taken from [1,48], where the local efficiency [48]
and the c contrast coefficient [48]
are shown as functions of the normalized energy density ().
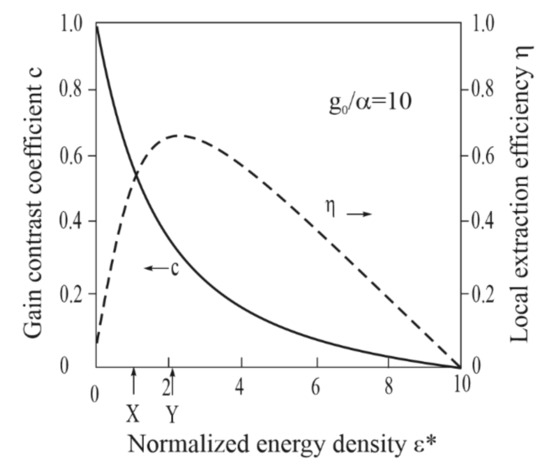
Figure 4.
Local extraction efficiency η (dashed line) and contrast coefficient c (solid line) as functions of the normalized energy density in a KrF amplifier. The optimum operations, with regard to both efficiency and contrast for a preamplifier and a power amplifier, are marked by the arrows X and Y, respectively (based on [48]).
The “effective gain coefficient” [48] is defined as
The optimum operation with regard to both efficiency and contrast for a preamplifier is marked by the arrow X. Here, the contrast coefficient is below 0.6. On the other hand, a power amplifier primarily must be optimized for efficiency. This condition is marked by the arrow Y in the Figure 4, where the contrast coefficient falls to below 0.4.
Our experiments, connected to the integration of NFF into our KrF excimer system, revealed that the experimentally obtained extraction efficiency () for a saturated (short and linearly polarized) signal pulse, and the ratio of gain coefficients for the same signal pulse, and a long ASE () is even smaller in KrF than that obtained as a result of the former consideration (for η and c) [43]. The reason for this disagreement is connected to the incomplete evaluation of the temporal feature of the gain (of the gain dynamics) of excimers in former publications.
In the present paper, the dynamic amplification properties of KrF, XeCl, and XeF excimers—for both long and short pulses—are studied with special emphasis on the temporal contrast of the short signal pulse referred to the long ASE.
1.5. Picosecond Gain Dynamics of Excimers
The additional (formerly not considered) issue leading to reduced gain and intensity contrast for the signal pulse is connected to the gain dynamics of KrF, XeCl, and XeF, which was studied earlier, extensively, from the point of view of energy extraction only [15,46,50]. In Figure 5a–c, the logarithm of the gain is shown versus the delay between a saturating and a probe pulse for KrF, XeCl, and XeF. In Figure 5a, the gain of KrF is followed over the first 300 ps after passage of the saturating pulse. After the initial drop, the gain recovers with a τ = 57 ps time, constant to 25% of its initial value.
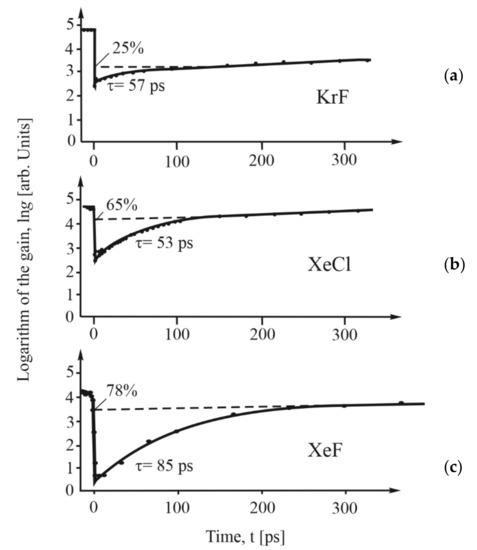
Figure 5.
Logarithm of the gain in KrF (a), in XeCl (b) and in XeF (c), versus the delay between the saturating and the probe pulse, followed over a 300 ps time window (based on [15,46]).
For comparison, the result of the same measurements for XeCl and XeF shows that, with XeCl, there is also a gain recovery with a similar time constant (τ = 53 ps), but with a much larger amplitude (65%). Compared to the previous two cases for XeF, the gain recovers with larger time constant (τ = 85 ps) and with an even larger amplitude (85%).
When these measurements were repeated with pump and probe beams of parallel and orthogonal polarization, the difference of the gain in the first picosecond is revealed to be a molecular reorientation effect [46]. From these results, a molecular reorientation time of T/4 = 1.1 ps and 0.7 ps is obtained for XeCl and KrF, respectively.
In all cases, the recovery of the gain is the evidence of leftover optical energy in the active medium; meaning that some part of the energy of the excited molecules is not accessible by subpicosecond pulses, only by pulses of sufficiently longer durations than the corresponding recovery time. The observed gain recovery was attributed to rotational relaxation in the B state and to C → B relaxation, with possible contribution of the incomplete relaxation (therefore, transient population) of the X state. The latter assumption was expected to be valid, mainly for XeCl and XeF, where the slightly bound X state can be populated by the short and intense saturating pulse; thus, its reabsorption also contributes to the limited energy extraction. Since the density of accessible molecules in the B state is coupled to the logarithm of the small-signal gain, the gain coefficients for short () and long pulses () are expected to be different. This, however, leads to more pronounced amplification of the long temporal noise than that of the short signal pulse. This phenomenon was already studied in [51], where, for the estimation of the ratio (K) of the small-signal gain coefficients for short and long pulses (), a simple equation was used, based on the measurement of the short pulse gain (Gshort) and the ASE energy (EASE). Unfortunately, this method resulted in an inaccurate and unexpectedly high value for K, i.e., K = 0.9 ± 0.3. The reported high value of K (nearly 1) predicts a similar gain for both the short signal pulse and for the ASE, which, however, is in contrast to our experimental observations. On the other hand, if amplification for long and short pulses—even in the small-signal regime—is different (K ≠ 1), the former considerations for extraction efficiency (η) and for contrast coefficient (c) must be corrected with the K value to get the overall efficiency () and overall contrast coefficient (), which already takes into account the limited access to the stored energy on the upper level by the short pulse as
The main objective of this paper is to deduct the correct value of K from the known experimental data of gain dynamics measurements, and to differentiate between the relative contributions of the relaxation processes (both in the excited and ground states) to the short-pulse amplification properties of KrF, XeCl, and XeF excimers.
From this information, the corresponding stimulated transition rates and the dependence of the overall contrast coefficients on the energy density can be deduced for all excimers.
The practical consequence of these finding is that the deterioration of the contrast for a unit gain-length of an excimer amplifier can be determined, which also determines the maximum allowable gain-length product of the excimer amplifier chain following the temporal filter, with regard to optimum contrast.
2. Amplification Properties of Excimers for Long and Intense Short Pulses
2.1. Contrast Issues for Short-Pulse Amplification in Excimers
Before going into detail about the correct evaluation of the gain dynamics measurements, which also needs to consider the eventual population of the X state by the saturating pulse, we do believe that the best way is to determine the K value in the small-signal regime. The K value is only dependent on the ratio of the accessible molecules in the B state by a weak short pulse; therefore, one has to compare the small-signal gain of the excimers for short and long pulses. From the input–output curves measured for both excimers in [15,46], small-signal gains of 6500, 450 and 3300 were obtained for short-pulse amplification in KrF, XeCl and XeF, respectively. These correspond to gain-length products of 8.7, 6.1, and 8.1 in the KrF, XeCl and XeF case. If it is compared to the usual gain-length product of ASE-depleted excimer gain modules, whose value is typically around 11 for all cases, as seen in Figure 1 of [52], different K values are obtained for the KrF, XeCl and XeF with KKrF = 0.76, KXeCl = 0.53, and KXeF = 0.74.
In the small-signal regime—since no (or not significant) change of the population of the B state occurs; therefore, no relaxation from the C state is expected—the primary origin of the limited access to the stored energy of the B state by a polarized weak short pulse (in comparison with that by the ASE) is the molecular reorientation effect. While the unpolarized ASE has “access” to all molecules in the B state, the (weak) polarized short signal pulse only has limited access, depending on its pulse duration and the molecular reorientation time. For our 0.3–0.5 ps pulse durations, the different K values (KKrF = 0.76 and KXeCl = 0.53) are in good qualitative agreement with the different measured reorientation times (T/4KrF ≈ 0.7 ps, T/4XeCl ≈ 1.1 ps; [46]).
Using these values, interpretation of the gain dynamic curves for intense saturating pulses, including determination of the contribution of C → B relaxation to the population of the B state, and/or of the population/relaxation of the X state [19] to the gain recovery, becomes possible. For such calculation in the KrF case, we assume zero population in the repulsive X state, and an initial population density () accessible by a long pulse in the upper states (whose portion defined by K is accessible by a short pulse). This is reduced to by the saturating pulse (followed by a gain recovery). Assuming that in both the initial and final (relaxed) conditions, the same part of the population is accessible by a short pulse (the K factor is the same),
Note that is defined by the relative amplitude of the recovery (by the amplitude of the recovery referred to that of the initial drop). According to Figure 5,
are obtained. In the KrF case, assuming no population in the X state during the process, the remaining population is the inaccessible part of the initial population, as
This gives KKrF = 0.75, practically the same value as obtained from the small-signal gain measurements. It confirms the assumption that the X state has no influence on the energy extraction; the part of the initial population on the B state is extracted by the saturating pulse.
Since rotational relaxation takes place on the ps time scale, the recovery of the population of the B state (of amplitude, on the τ ≈ 57 ps timescale) can only be attributed to the C → B relaxation. We should note that the coincidence of the and the quantities is just accidental. In the small-signal regime, where no significant change of the population of the B state takes places, it is the rotational relaxation that plays a primary role, while in the strong signal case, a deeper “directional hole” is burned into the B state population, which lowers the impact of the rotational relaxation, but at the same time, a considerable C → B relaxation is initiated. In between the two measured cases (at intermediate values of of the signal pulse), the effective extraction efficiency together with the left-in energy can slightly change. Considering the limited amplitude of this change, its effect was disregarded in our considerations; a constant ratio of the left-in energy in the excited states was used independently of the normalized energy density of the signal pulse.
Regarding XeCl and XeF, the same way of calculations leads to a contradiction; it results in a left-in energy, which is significantly different from that obtained from the small-signal gain measurements. In those cases—connected to the slightly bound feature of the X state—only partial extraction of the “accessible” population of the B state can be assumed due to the significant population of the X state, whose balance value—in case of strong saturation—is determined by the ratio of the stimulated transition rates of the B and X states, by the emission () and absorption cross-sections (). In this way, the remaining population () is the sum of the inaccessible initial population and a fraction of the “accessible” initial population, as
where
In the XeCl case, substituting KXeCl = 0.53 (obtained from the gain measurements) to this equation, β = 0.66 is obtained. This gives
From the measurement data obtained by Zhao et al. [15] for XeF, a similar calculation results in KXeF ≈ 0.74, a value that is comparably high to that in KrF; however, the energy extraction is limited by the (rapidly populated) bound X state, which only takes a fraction, and leaves as high as a fraction of the population in the B state, resulting in a ratio of
From the gain dynamics of the three excimers, a conclusion, to some extent similar to that of [46], can be drawn: it is only KrF that behaves as a real, four-level system, offering good energy extraction; therefore, it is preferable for the generation of high contrast, short pulses. In KrF, beyond the saturation of amplification, the only limitation for energy extraction and temporal contrast is imposed by the partial access to the excited molecules in the B state. However, regarding XeCl and XeF, not only the partial access in the B state, but also absorption in the transiently populated X state limits the efficiency and contrast. Their relative contributions are different; in XeCl the former effect, in XeF the latter one are found dominant, as will be shown later.
Then, the final ratio of gain coefficients for intense, short pulses and weak, long pulses, called as overall contrast coefficient (), is the product of K and , as defined by Equation (9). The former considerations suggest that even in KrF—as the best choice among short-pulse excimer amplifiers where —one must face a certain decrease of the gain coefficient for short, intense pulses. This is caused not only by the saturation of the gain in the presence of nonsaturable absorption, but also by the limited access to the population on the B state by the short pulse (for different reasons in the small-signal and saturated regimes, as explained before).
A similar correction of the local extraction efficiency (η) curves with the same value of K is necessary to get the overall local efficiency (), as defined by Equation (8). The dependence of and on the normalized energy density are shown in Figure 6 for two values of ; namely for 10 and 15. Actually, the and quantities, defined by Equations (5) and (6), respectively, are obtained by solving numerically the Equations (1) and (2) coupled differential equations for different initial gain coefficients; for different values (for more details, see Section 1.4). It is seen that both curves are dependent on ; better contrasts and extraction efficiencies can be realized in case of larger values. Since the initial gas mixture and the pumping conditions influence both and α, both must be optimized for the best ratio. Absorption is mainly caused by the fluorine content of the gas mixture; therefore, the unpumped volume must be minimized, moreover, by optimized pumping, the highest possible gain coefficient must be produced with the lowest possible fluor partial pressure.
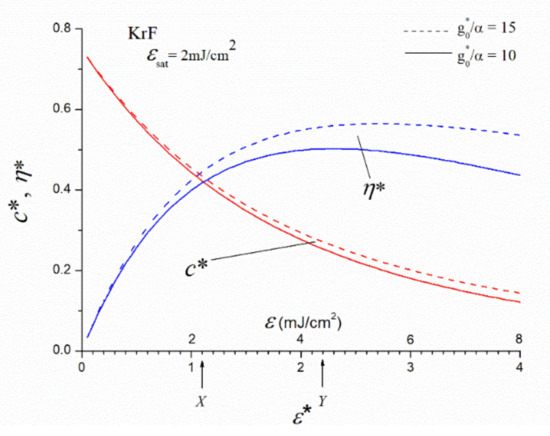
Figure 6.
Overall gain contrast coefficient and overall extraction efficiency ( ) as a function of the normalized energy density ( ) in a KrF amplifier. The solid and dashed curves belong to , respectively.
As seen in Figure 6, the overall contrast coefficient (), depending slightly on the ratio, is
at X and Y values of the normalized energy density.
Since the optimum energy density, defined by the arrows X and Y for pre- and power amplifiers, is generally adjusted for the output-end of the amplifier, in both cases, the “integrated” value of is somewhat larger for amplifiers of finite product (where the “input-end” of the amplifier tends to increase the integrated value). For this reason, in our following considerations,
values are used for the evaluation of the performance of KrF preamplifiers and power amplifiers, respectively.
Then, a similar consideration can also be done for the other two excimers; for XeCl and XeF. In both cases, measuring K and calculating the energy density dependence of and of the active media, thus “separating” the effect of the B and X states to the gain, makes it possible to define whether transient ground-state absorption (with a given absorption cross-section) occurs at all, and whether its contribution dominates over the eventual initial (nonsaturable) absorption of the active medium. In our calculations performed both for XeCl and XeF, the initial nonsaturable absorption of the medium (α) could be neglected for two reasons: at the longer wavelength of these excimers, this kind of absorption was found to be much smaller than in the KrF case (), moreover, its effect occurs in a relatively high energy density range, which is hardly accessible due to the “early-emerging” saturation of short-pulse amplification, where the effect of the transient ground-state absorption dominates (deteriorates) both the overall efficiency and contrast coefficient.
It means that, in both the XeCl and XeF cases, instead of solving Equations (1) and (2), one must solve the somewhat different
coupled differential equations (see for example [53]), which account for transient ground-state absorption, but assume no initial nonsaturable absorption.
In these equations, and are the population densities in the upper and lower lasing states, and are the corresponding cross-sections. With regard to the short pulse duration and the slightly bound ground states of XeCl and XeF, within the duration of the pulse, no relaxation from the ground state is assumed:
Introducing the and the quantities, the differential equations can be simplified to
and
(similarly to [53]). Introducing , one arrives to the well-known Frantz–Nodvik equations [49], whose solution is the same as Equation (3), but instead of , one has to consider as the “weighted” differential population, moreover the saturation energy density is lowered from to .
It means that from the value of , obtained by fitting the Frantz-Nodvik curves to the measured input-output characteristics [15,46], one can define not only (such as in the KrF case), but both and , by knowing their ratios from the gain dynamics measurements, as for XeCl and for XeF (see Equations (15) and (16)). From this approach, the values listed in Table 1 are obtained.

Table 1.
Emission and absorption cross-sections for KrF, XeCl, and XeF excimers associated with the B → X laser transitions (* has no contribution; therefore, cannot be measured on this time scale).
Comparing our value of for KrF and for XeCl with that found in the literature ( for KrF in [19], and for XeCl in [54]), the deviations can be explained by the completely different pulse durations used for the measurements in the present and the cited two former publications. We expect the present data to be more accurate, since our values for the emission cross-section are directly derived from the experimentally obtained saturation energy density measured/defined by pulses of relevant (short) pulse duration.
Note, that one can hardly obtain data for (X → B) with other methods, since the X state can only be populated for a short time through the B state. In such a case, however, transient absorption can contribute to saturation of amplification; from the former considerations, the overall local efficiency () and the overall local contrast coefficient () can be calculated as a function of the normalized local energy density (for a given small volume of the excimer amplifier) in a similar way as in the KrF case (using Equations (5)–(7)). Here, the and curves are obtained by solving the (21) and (22) coupled differential equations—in a way described by Equations (24) and (25)—assuming no relaxation from the ground state during the amplification process (23). The results are shown both for XeCl and XeF in Figure 7a,b, respectively.
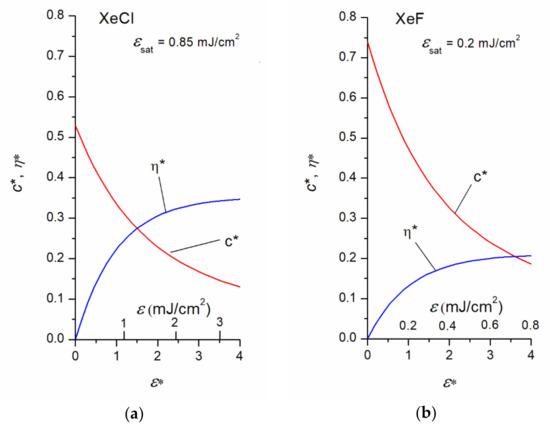
Figure 7.
Overall gain contrast coefficient and overall extraction efficiency ( ) as a function of the normalized energy density ( ) in a XeCl amplifier (a) and in a XeF amplifier (b).
By comparing the corresponding curves, the superior performance of KrF as a short-pulse amplifier is clearly visible; while the curves are more or less comparable (only the initial value is somewhat worse in the XeCl case), the overall energy extraction efficiency () is definitely worse in the XeCl and even in the XeF case. While the maximum efficiency is around 50–55% for KrF, it is 30% for XeCl and only 20% for XeF. The differences of operations among KrF, XeCl, and XeF—as short pulse amplifiers—are made even more pronounced by the fact that the same value of the normalized energy density for the three excimers corresponds to significantly different energy densities, because of the different saturation energy densities of the three excimers; and .
2.2. Practical Consequences of the Gain Dynamics for Short-Pulse KrF Amplifiers
Going back to the case of the most practical KrF, the relatively low value of suggests a considerably higher gain for the weak ASE than for the intense subpicosecond signal pulse. It means that the temporal filter of the laser system must be used as close to the end of the amplifier chain as possible, or preferably after the amplifier chain. In solid-state systems, even a minor amplification following the temporal filter necessitates the use of CPA (i.e., a subsequent use of a stretcher, an amplifier and a compressor). That is why in solid-state systems the only possible position of an effective temporal filter (usually plasma mirror) is after the CPA amplifier chain. In such cases, a high-throughput operation is absolutely required since no additional amplification can compensate for the energy loss. In contrast to solid-state systems, short-pulse UV laser systems use direct amplification; therefore, the use of a power amplifier following the pulse cleaning element seems possible, since deterioration of the temporal contrast in a power amplifier is moderate compared to that of the CPA scheme. For these reasons, amplification in KrF of a limited product following the temporal filter is feasible, without significant deterioration of the contrast. For the calculation of the maximum value of short-pulse amplification, we have to refer to Equation (18) as and .
Assuming a KrF amplifier, which typically allows the development of ASE in a solid angle Ω = 104 as seen in Figure 1 of [52], one can set a limit of , where ASE remains in the low intensity, slowly rising region. This, however, also limits the effective gain length product (for saturated short-pulse amplification) to gpowerL ~ 1.2, allowing a power amplification of somewhat more than Gpower ~ 3 for short pulses. This can compensate for the typical energy loss of both plasma mirrors [41] and NFF [34] at this wavelength.
The most important features of a temporal filter are the throughput and the contrast enhancement. In a similar manner, a KrF amplifier can best be characterized by its short-pulse amplification (G) and by the associated deterioration of the contrast (D). From the former considerations, even “local” values (normalized to the unit length) can be defined. For the most important power amplifier case:
It is seen from the equations that a KrF power amplifier of a given gain coefficient deteriorates the contrast with a twice larger “coefficient”.
A similar calculation for a KrF preamplifier, using Equation (17), as , yields , i.e., a KrF preamplifier deteriorates the contrast with the same coefficient as it amplifies the short-pulse.
For the above detailed reasons, in excimer amplifier systems, additional amplification following the temporal filter is possible, but its gain must be minimized. A good compromise is to set the gain to be somewhat more than necessary to compensate for the loss of the filter. In this case, the deterioration of the contrast caused by the ASE generated by this “following” amplifier has minor contribution to the final temporal contrast. Considering the high contrast improvement and high throughput of NFF, such a combination of the filter and the final amplifier offers a much higher final temporal contrast (in excess of 1012) than reported before.
For the experimental realization of this, however, the energy scalability of NFF must be demonstrated, necessitating further experimental work.
3. Conclusions
In excimer systems, the direct amplification scheme allows possible use of temporal filters, not only after, but even before the final amplifier(s). In the preferred latter case, however, the larger gain for the noise compared to the short signal pulse rapidly deteriorates the contrast. In this paper, we point out that this is not only the result of the saturation of amplification, but also of the dynamic amplification properties of excimers; of the limited reorientation/relaxation times of the upper B state in KrF, together with the contribution of transient absorption of the lower X state in XeCl and XeF. For all excimers, both the emission and absorption transition rates are determined, moreover, the dependence of the overall extraction efficiency and contrast coefficient are calculated on the energy density of the signal pulse to be amplified. Based on these results, the applicable maximum short pulse gain-length product of the KrF power amplifier following the temporal filter is found to be limited to gpowerL ~ 1.2, allowing somewhat more gain (Gpower ≈ 3) than necessary for the compensation of the typical energy loss of the filter.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, resources, writing—original draft preparation, visualization, supervision, funding acquisition, S.S.; validation S.S. and I.B.F.; formal analysis, G.A.; investigation, S.S. and R.D.; writing—review and editing, S.S., R.D. and I.B.F.; project administration, R.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the European Social Fund EFOP-3.6.2-16-2017-00005 “Ultrafast physical processes in atoms, molecules, nanostructures and biological systems”, by the Ministry of Innovation and Technology, Hungary, grant NKFIH-1279-2/2020, and by the National Research, Development and Innovation (NKFIH) K138339 project. This work received funding from the European Union’s Horizon2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement number 871124, Laserlab-Europe.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Zs. Tóth for the critical reading of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Szatmári, S.; Marowsky, G.; Simon, P. Femtosecond excimer lasers and their applications. In Landolt–Börnstein—Group VIII Advanced Materials and Technologies; Herziger, G., Weber, H., Poprawe, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 1B1, pp. 215–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, D.; Mourou, G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses. Opt. Com. 1985, 56, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanovsky, V.; Chvykov, V.; Kalinchenko, G.; Rousseau, P.; Planchon, T.; Matsuoka, T.; Maksimchuk, A.; Nees, J.; Cheriaux, G.; Mourou, G.; et al. Ultra-high intensity- 300-TW laser at 0.1 Hz repetition rate. Opt. Exp. 2008, 16, 2109–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Teng, H.; Wei, Z. High-contrast 1.16 PW Ti: Sapphire laser system combined with a doubled Chirped-pulse amplification scheme and a femtosecond optical-parametric amplifier. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 3194–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M.; Bang, W.; Dyer, G.; Wang, X.; Gaul, E.; Borger, T.; Ringuette, M.; Spinks, M.; Quevedo, H.; Bernstein, A.; et al. The Texas Petawatt Laser and Current Experiments. In AIP Conference, Proceedings of the Advanced Accelerator Concepts. 15th Advanced Accelerator Concepts Workshop, Austin, TX, USA, 10–15 June 2012; Zgadzaj, R., Gaul, E., Downer, C.M., Eds.; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2012; Volume 1507, pp. 874–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, F.; João, C.P.; Fils, J.; Gottschall, T.; Hein, J.; Körner, J.; Limpert, J.; Roth, M.; Stöhlker, T.; Bagnoud, V. Temporal contrast control at the PHELIX petawatt laser facility by means of tunable sub-picosecond optical parametric amplification. Appl. Phys. B 2014, 116, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, T.M.; Lee, J. Femtosecond petawatt laser. Ann. Phys. 2014, 526, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Liang, X.; Yu, L.; Xu, Y.; Xu, L.; Ma, L.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y.; Leng, Y.; Li, R.; et al. High-contrast 2.0 Petawatt Ti:sapphire laser system. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 29231–29239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borisov, B.A.; McCorkindale, C.J.; Poopalasingam, S.; Longworth, J.W.; Simon, P.; Szatmári, S.; Rhodes, C.K. Rewriting the rules governing high intensity interactions of light with matter. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 046401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glownia, J.H.; Misewich, J.; Sorokin, P.P. Ultrafast ultraviolet pump-probe apparatus. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1986, B3, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, A.P.; Luk, T.S.; McIntyre, I.A.; Johann, U.; McPherson, A.; Boyer, K.; Rhodes, C.K. Subpicosecond KrF* excimer-laser source. Opt. Lett. 1986, 11, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, S.; Schäfer, F.P. Simplified laser system for the generation of 60 fs pulses at 248 nm. Opt. Com. 1988, 68, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, B.; Szatmári, S.; Rácz, B.; Schäfer, F.P. Bandwidth limited amplification of 220 fs pulses in XeCl: Theoretical and experimental study of temporal and spectral behavior. Opt. Com. 1987, 62, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Békési, J.; Szatmári, S.; Simon, P.; Marowsky, G. Table-top KrF amplifier delivering 270 fs output pulses with over 9 W average power at 300 Hz. Appl. Phys. B 2002, 75, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Szatmári, S.; Schäfer, F.P. Gain dynamics of XeF ans subpicosecond pulse generation at 351 nm. Appl. Phys. B 1988, 47, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseev, S.V.; Aristov, A.I.; Grudtsyn, Y.V.; Ivanov, N.G.; Koval’chuk, B.M.; Losev, V.F.; Mamaev, S.B.; Mesyats, G.A.; Mikheev, L.D.; Panchenko, Y.N.; et al. Visible-range hybrid femtosecond systems based on a XeF (C–A) amplifier: State of the art and prospects. Quantum Electron. 2013, 43, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, S.; Bakonyi, Z.; Simon, P. Active spatial filtering of laser beams. Opt. Comm. 1997, 134, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P.; Nagy, T.; Szatmári, S. Nonlinear spectral filtering of femtosecond pulses. Opt. Comm. 1998, 145, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.K. Excimer lasers. In Topics in Applied Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Szatmari, S.; Almási, G.; Feuerhake, M.; Simon, P. Production of intensities of ~1019 W/cm2 by a table-top KrF laser. Appl. Phys. B 1996, 63, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danson, C.N.; Haefner, C.; Bromage, J.; Butcher, T.; Chanteloup, J.-C.F.; Chowdhury, E.A.; Galvanauskas, A.; Gizzi, L.A.; Hein, J.; Hillier, D.I.; et al. Petawatt and exawatt class lasers worldwide. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccotti, T.; Lévy, A.; Popescu, H.; Réau, F.; D’Oliveira, P.; Monot, P.; Geindre, J.P.; Lefebvre, E.; Martin, P. Proton Acceleration with High-Intensity Ultrahigh-Contrast Laser Pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 185002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flacco, A.; Sylla, F.; Veltcheva, M.; Carrié, M.; Nuter, R.; Lefebvre, E.; Batani, D.; Malka, V. Dependence on pulse duration and foil thickness in high-contrast-laser proton acceleration. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 036405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, J.S.; Robinson, A.P.L.; Booth, N.; Carroll, D.C.; Dance, R.J.; Gray, R.J.; MacLellan, D.A.; McKenna, P.; Murphy, C.D.; Rusby, D.; et al. High efficiency proton beam generation through target thickness control in femtosecond laser-plasma interactions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 214101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wharton, K.B.; Boley, C.D.; Komashko, A.M.; Rubenchik, A.M.; Zweiback, J.; Crane, J.; Hays, G.; Cowan, T.E.; Ditmitre, T. Effects of nonionizing prepulses in high-intensity laser-solid interactions. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 025401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Földes, I.B.; Bakos, J.S.; Gál, K.; Juhász, Z.; Kedves, M.A.; Kocsis, G.; Szatmári, S.; Veres, G. Properties of high harmonics generated by ultrashort UV laser pulses on solid surfaces. Laser Phys. 2000, 10, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Kapteyn, H.; Murnane, M.; Szoke, A.; Falcone, R. Prepulse energy suppression for high-energy ultrashort pulses using self-induced plasma shuttering. Opt. Lett. 1991, 16, 490–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaury, C.; Quéré, F.; Geinder, J.-P.; Levy, A.; Ceccotti, T.; Monot, P.; Bougeard, M.; Réau, F.; D’Oliveira, P.; Audebert, P.; et al. Plasma mirrors for ultrahigh-intensity optics. Nat. Phys. 2007, 3, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkevičius, A.; Tommasini, R.; Tsakiris, G.D.; Witte, K.J.; Gaižauskas, E.; Teubner, U. Frequency doubling of multi-terawatt femtosecond pulses. Appl. Phys. B 2004, 79, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, D.; Danson, C.; Duffield, S.; Egan, D.; Elsmere, S.; Girling, M.; Harvey, E.; Hopps, N.; Norman, M.; Parker, S.; et al. Ultrahigh contrast from a frequency-doubled chirped-pulse-amplification beamline. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 4258–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, A.; Jullien, A.; Rousseau, J.-P.; Liu, Y.; Houard, A.; Ramirez, P.; Papadopoulos, D.; Pellegrina, A.; Georges, P.; Druon, F.; et al. Energy-scalable temporal cleaning device for femtosecond laser pulses based on cross-polarized wave generation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 043106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Leng, Y.; Guo, X.; Zou, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, R.; et al. Pulse temporal quality improvement in a petawatt Ti: Sapphire laser based on cross-polarized wave generation. Opt. Commun. 2014, 313, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikov, M.P.; Risse, E.; Schonnagel, H.; Sandner, W. Double chirped-pulse-amplification laser: A way to clean pulses temporally. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 923–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatmári, S.; Dajka, R.; Barna, A.; Gilicze, B.; Földes, I.B. Improvement of the temporal and spatial contrast of high-brightness laser beams. Laser Phys. Lett. 2016, 13, 075301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziener, C.; Foster, P.S.; Divall, E.J.; Hooker, C.J.; Hutchinson, M.H.R.; Langley, A.J.; Neely, D. Specular reflectivity of plasma mirrors as a function of intensity, pulse duration, and angle of incidence. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, T.; Geindre, J.P.; Audebert, P.; Marjoribanks, R.S.; Rousseau, J.P.; Burgy, F.; Douillet, D.; Lefrou, T.; Ta Phuoc, K.; Chamberet, J.P. Towards ultrahigh-contrast ultraintense laser pulses-complete characterization of a double plasma-mirror pulse cleaner. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 083109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G.G.; Bagnoud, V.; Brabetz, C.; Clark, R.J.; Green, J.S.; Heathcote, R.I.; Powell, H.W.; Zielbauer, B.; Arber, T.D.; McKenna, P.; et al. Optimization of plasma mirror reflectivity and optical quality using double laser pulses. New J. Phys. 2015, 17, 033027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagnoud, V.; Wagner, F. Ultrahigh temporal contrast performance of the PHELIX petawatt facility. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Földes, I.B.; Barna, A.; Csáti, D.; Szűcs, F.L.; Szatmári, S. Plasma mirror effect with a short-pulse KrF laser. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 244, 032004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Földes, I.B.; Csáti, D.; Szűcs, F.L.; Szatmári, S. Plasma mirror and temperature evolution for short pulse KrF lasers. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2010, 165, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilicze, B.; Barna, A.; Kovács, Z.; Szatmári, S.; Földes, I.B. Plasma mirrors for short pulse KrF lasers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 083101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilicze, B.; Dajka, R.; Földes, I.B.; Szatmári, S. Improvement of the temporal and spatial contrast of the nonlinear Fourier-filter. Opt. Exp. 2017, 25, 20791–20797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilicze, B.; Homik, Z.; Szatmári, S. High-contrast, high-brightness ultraviolet laser system. Opt. Exp. 2019, 12, 17377–17386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatmári, S.; Simon, P. Interferometric multiplexing scheme for excimer amplifiers. Opt. Commun. 1993, 98, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Békési, J.; Marowsky, G.; Szatmári, S.; Simon, P. A 100 mJ table-top short pulse amplifier for 248 nm using interferometric multiplexing. Z. Phys. Chem. 2001, 215, 1543–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, S.; Schäfer, F.P. Comparative study of the gain dynamics of XeCl and KrF with subpicosecond resolution. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1987, 4, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilleman, M.M.; Jacob, J.H. Short pulse amplification in the presence of absorption. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1987, 50, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almási, G.; Szatmári, S.; Simon, P. Optimized operation of short-pulse KrF amplifiers by off-axis amplification. Opt. Commun. 1992, 88, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, L.M.; Nodvik, J.S. Theory of pulse propagation in a laser amplifier. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.J.; Gibson, R.B.; Roberts, J.P. Picosecond gain dynamics in KrF amplifiers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1987, 52, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnle, G.; Teubner, U.; Szatmári, S. Amplified spontaneous emission in short-pulse excimer amplifiers. Appl. Phys. B 1990, 51, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani Moghadam, G.; Farahbod, A.H. General formula for calculation of amplified spontaneous emission intensity. Opt. Quant. Electron 2016, 48, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milonni, W.P.; Eberly, H.J. Amplification of short pulses. In Laser Physics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Chapter 6; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Hokazono, H.; Midorikawa, K.; Obara, M.; Fujioka, T. Theoretical analysis of a self-sustained discharge pumped XeCl. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 56, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).