Prediction of Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Displacements Using Gaussian Process Regression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Finite Element Analysis
1.2. Simplified Analytical Models
1.2.1. Sliding Block Model
1.2.2. Minimum Potential Energy Model
1.2.3. Shear Strength Loss and Strain Re-Hardening Model
1.2.4. Viscous Models
1.3. Empirical Models and Soft Computing Techniques
- Seismic parameters—seismic source distance (R, km) and earthquake magnitude, (M).
- Topographic characteristics (in percent)—gradient of ground surface (S) and free face ratio.
- Geotechnical parameters (in percent)—average mean particle size within T15 (D5015, mm) and averaged fines contents in T15 (F15)
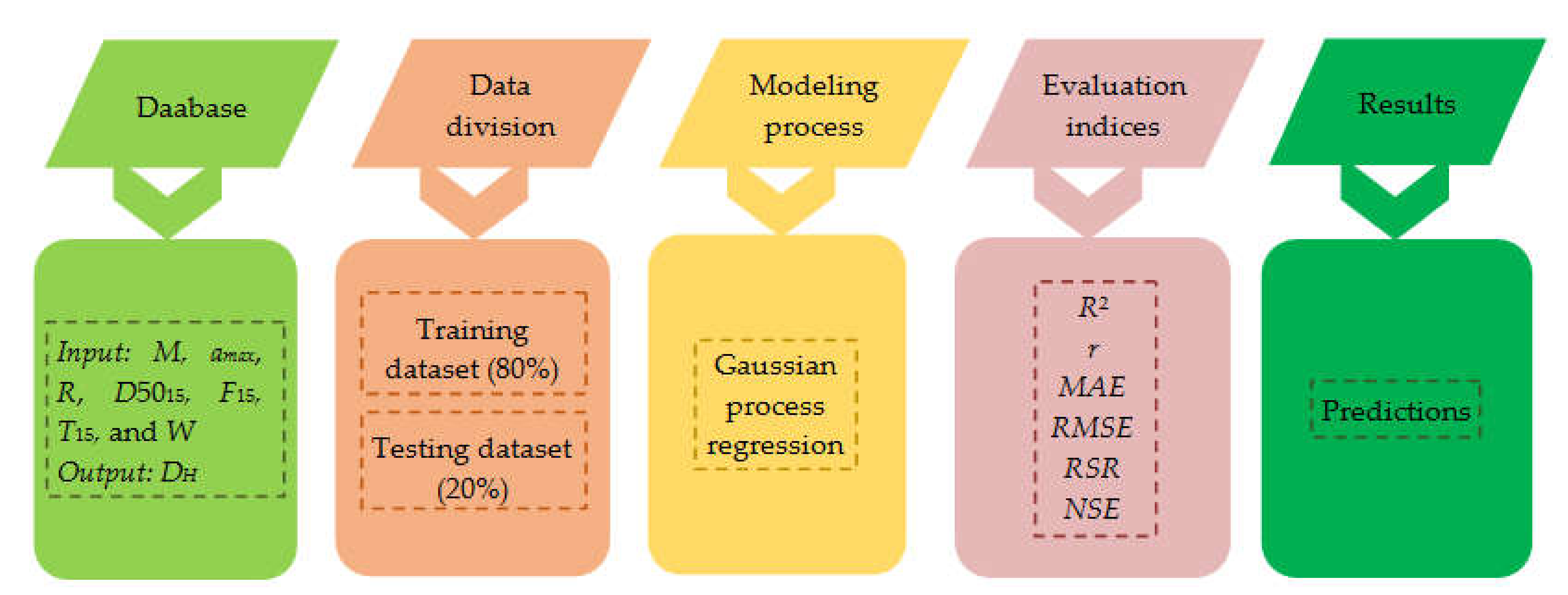
2. Gaussian Process Regression
3. Case-History Database
4. Correlation Analysis
5. Construction and Evaluation of Prediction Model
6. Result and Discussion
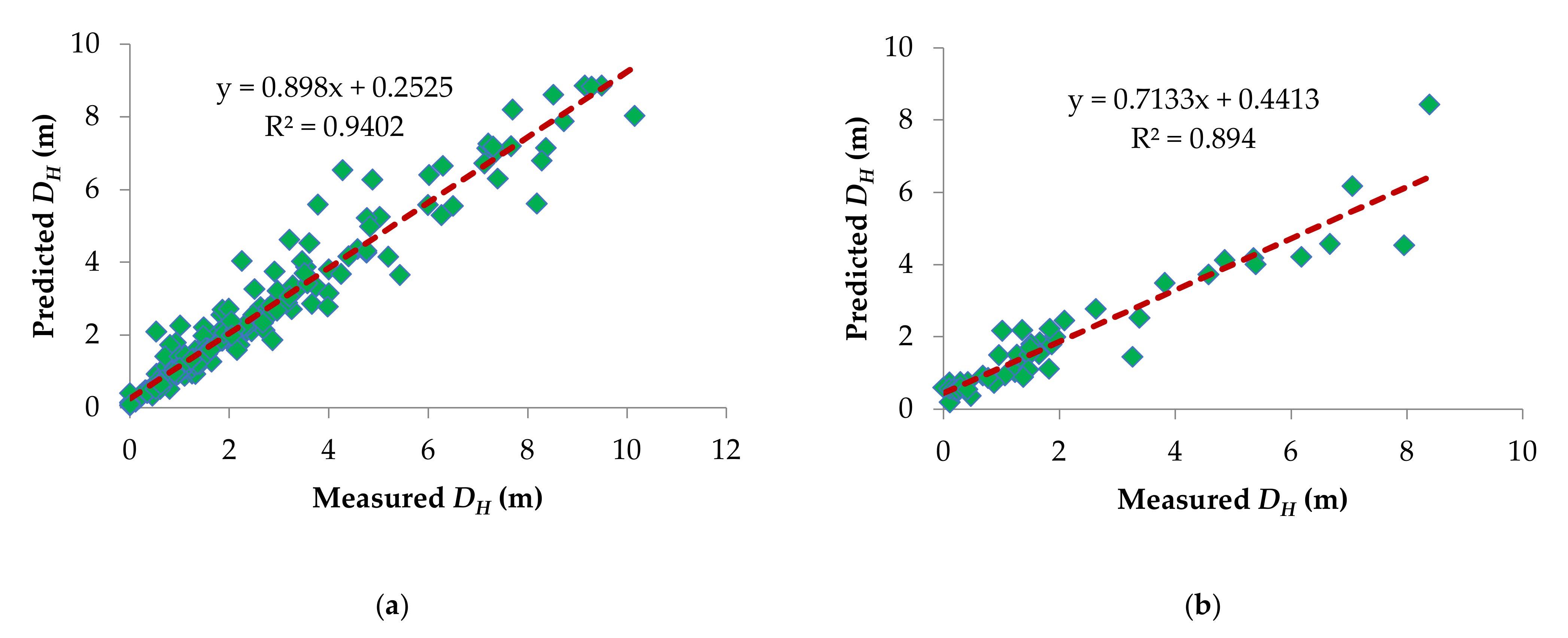
6.1. Performance of GPR Model
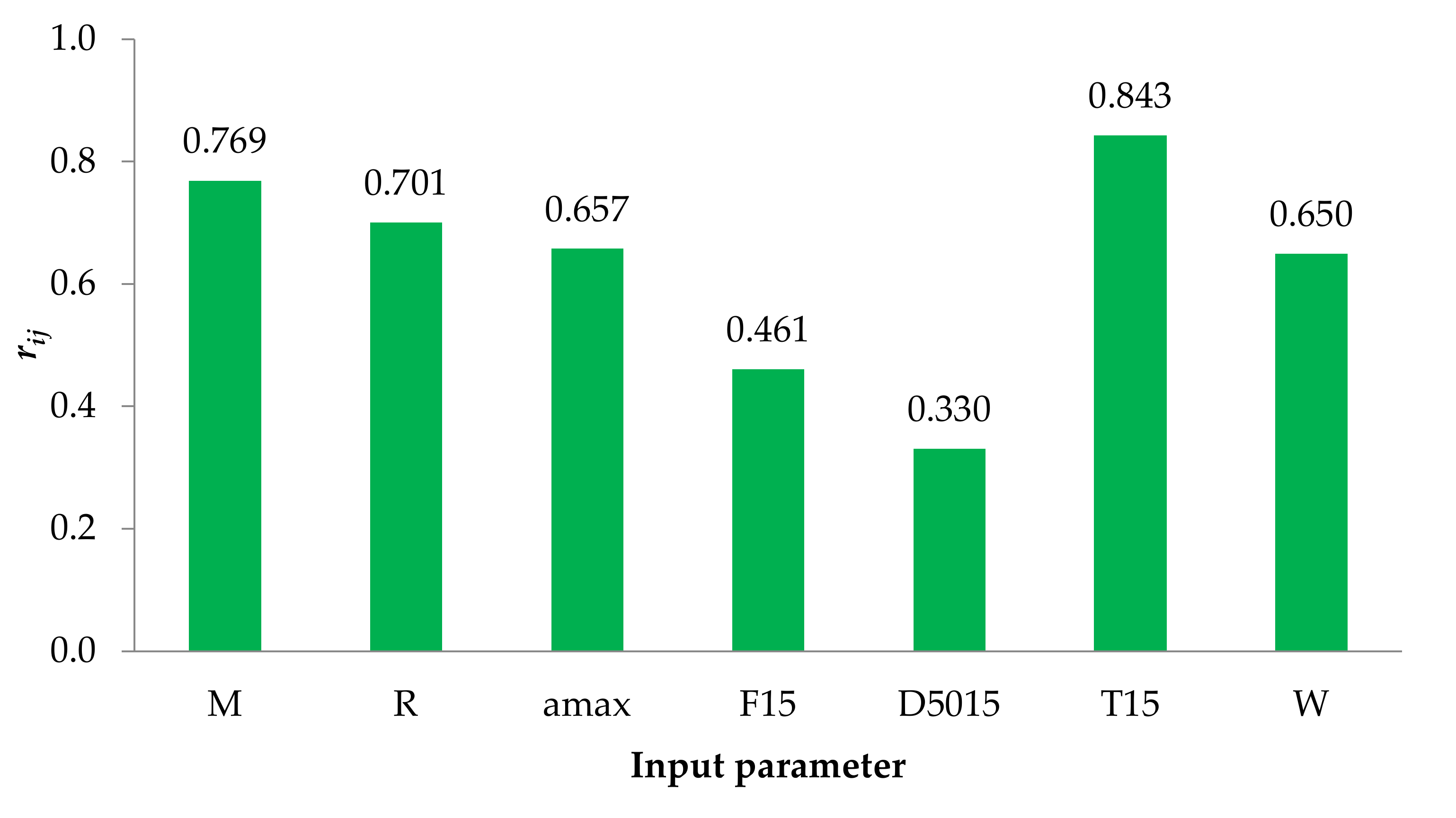
6.2. Sensitivity Analysis
7. Conclusions
- With respect to the values of GPR with R2 = 0.9402, r = 0.9697, MAE = 0.3403, RMSE = 0.5597, RSR = 0.248 and NSE = 0.938 in training phase whereas for testing phase it performed equally well with R2 = 0.894, r = 0.9455, MAE = 0.5443, RMSE = 0.8438, RSR = 0.387 and NSE = 0.851, In comparison to the EPR, ANN, and MLR models in literature, the GPR model was found to be more accurate and stable than the other models.
- The results of sensitivity analysis show that the degree of importance of different input parameters on lateral displacement is as T15 > M > R > amax> W > F15 > D5015.
- The developed Pearson VII kernel function-based GPR model makes predictions accurate and outperforms the others for this dataset and may be applied to a range of geotechnical engineering situations involving uncertainties.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Earthquake | M | R (km) | amax (g) | F15 (%) | D5015 (mm) | T15 (m) | W (%) | DH (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1906, San Francisco | 7.9 | 27 | 0.24 | 23 | 0.25 | 7.2 | 22.02 | 1.84 |
| 1906, San Francisco | 7.9 | 24 | 0.26 | 30 | 0.16 | 1.5 | 17.76 | 0.92 |
| 1964, Alaska | 9.2 | 60 | 0.3 | 21 | 1.35 | 3.4 | 24.59 | 1.86 |
| 1964, Alaska | 9.2 | 100 | 0.2 | 13 | 1 | 10.4 | 7.03 | 1.38 |
| 1964, Alaska | 9.2 | 60 | 0.3 | 23 | 1.47 | 3.8 | 16.07 | 1.58 |
| 1964, Alaska | 9.2 | 60 | 0.3 | 66 | 0.07 | 3.1 | 48.98 | 1.92 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.35 | 12.7 | 3.06 | 1.01 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 4 | 0.34 | 13.6 | 3.15 | 5.2 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 24 | 0.19 | 8.6 | 5.36 | 0.82 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 3.43 | 1.1 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 32 | 0.1 | 2.4 | 2.03 | 0.54 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 26 | 0.16 | 2.5 | 20.61 | 0.91 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 22.37 | 0.88 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 10 | 0.25 | 11.3 | 29.7 | 5.03 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.29 | 7.5 | 7.32 | 3.75 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 24 | 0.19 | 8.6 | 8.78 | 0.93 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 12 | 0.27 | 12.2 | 5.01 | 2.36 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 24 | 0.19 | 8.6 | 24.02 | 3.07 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 9 | 0.26 | 11.3 | 19.62 | 10.16 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 12 | 0.26 | 12.3 | 5.76 | 1.49 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 31 | 0.12 | 2.4 | 3.26 | 1.25 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 10 | 0.39 | 9 | 3.27 | 2.48 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 32 | 0.11 | 2.4 | 2.09 | 1.32 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 14 | 0.36 | 7.1 | 19.62 | 3.34 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 4 | 0.57 | 8.6 | 2.82 | 1.23 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.26 | 11.9 | 5.93 | 2.97 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.32 | 15.6 | 4.94 | 7.36 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 16 | 0.22 | 9.6 | 3.06 | 2.41 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 24 | 0.19 | 8.6 | 18.49 | 1.78 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.27 | 12 | 4.83 | 1.84 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.32 | 12.4 | 4.82 | 3.66 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 12 | 0.26 | 12.4 | 5.01 | 1.75 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 31 | 0.12 | 2.4 | 3.35 | 0.69 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 7 | 0.35 | 9.8 | 4.5 | 0.53 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.32 | 15.6 | 7.86 | 8.37 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.32 | 13.9 | 5.77 | 4.58 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 12 | 0.26 | 12 | 9.18 | 4.4 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 12 | 0.24 | 11.8 | 5.54 | 4 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 12 | 0.26 | 12.2 | 5.36 | 2.38 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.44 | 10.1 | 2.42 | 1.25 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.28 | 12.1 | 3.68 | 2.09 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 3.39 | 0.86 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 14 | 0.25 | 12.6 | 13.73 | 6.27 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.4 | 7.9 | 3.59 | 1.46 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.32 | 15.6 | 17.75 | 9.15 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 4.26 | 0.72 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.29 | 14.3 | 6.51 | 3.61 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 8 | 0.23 | 6.8 | 1.85 | 0.91 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 24 | 0.19 | 8.6 | 5.29 | 1.64 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.36 | 13.6 | 8.52 | 4.77 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.5 | 10.9 | 4.77 | 0.81 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.35 | 12.7 | 9.12 | 6 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 15 | 0.25 | 9.6 | 2.68 | 1.89 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 24 | 0.19 | 8.6 | 8.19 | 2.2 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 3 | 0.35 | 13.3 | 4.05 | 4.76 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.26 | 12 | 6.53 | 2.51 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.32 | 15.6 | 17.75 | 9.49 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.24 | 11.6 | 11.06 | 8.19 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.29 | 13.6 | 2.76 | 1.01 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 7 | 0.34 | 10.5 | 6.03 | 5.43 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.45 | 10.5 | 5.84 | 1.86 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.32 | 15.5 | 9.98 | 6.02 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.39 | 9.2 | 4.87 | 1.86 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 12 | 0.24 | 11.9 | 5.06 | 3.98 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.32 | 15.6 | 17.05 | 9.29 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 15 | 0.32 | 11.3 | 2.86 | 1.41 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 16 | 0.31 | 11 | 3.06 | 1.3 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 18 | 0.21 | 6.7 | 4.45 | 0.9 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 15 | 0.32 | 7 | 7.72 | 1.92 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.28 | 12.1 | 2.88 | 1.56 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.38 | 11.6 | 3.22 | 2.71 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.32 | 15.6 | 5.25 | 7.19 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 16 | 0.3 | 10.8 | 3.68 | 0.71 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.38 | 7.2 | 20.55 | 3.28 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 9 | 0.4 | 13 | 2.05 | 1.11 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.25 | 12.5 | 16.07 | 7.4 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.37 | 12.7 | 7.05 | 3.54 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 2.68 | 0.82 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 9 | 0.39 | 9.3 | 3.72 | 1.96 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.39 | 7.3 | 2.76 | 1.23 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 24 | 0.19 | 8.6 | 12.86 | 2.74 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 12 | 0.25 | 12.1 | 16.72 | 4.88 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.27 | 12.1 | 3.38 | 1.83 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.32 | 15.6 | 5.77 | 7.21 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 2 | 0.33 | 10.4 | 8.89 | 4.76 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.25 | 12.4 | 35 | 7.67 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 7 | 0.32 | 9.4 | 2.99 | 1.31 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 4 | 0.34 | 13.5 | 3.36 | 3.46 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.26 | 11.6 | 11.32 | 3.78 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 3 | 0.44 | 11.3 | 3.82 | 1.52 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.29 | 13 | 3.1 | 0.56 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 28 | 0.14 | 2.5 | 4.79 | 0.88 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.32 | 15.6 | 19.62 | 7.7 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 3 | 0.44 | 11.3 | 4.87 | 1.9 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 9 | 0.37 | 10 | 16.4 | 6.5 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 7 | 0.35 | 9.8 | 3.9 | 2.87 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 12 | 0.25 | 12.2 | 12.47 | 4.83 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.34 | 13.8 | 12.01 | 8.73 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 24 | 0.19 | 8.6 | 25.93 | 3.57 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 14 | 0.25 | 12.6 | 11.32 | 3.51 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 17 | 0.24 | 6.8 | 4.26 | 1.37 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.25 | 11.6 | 17.05 | 8.29 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.31 | 14.1 | 16.4 | 8.52 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 24 | 0.19 | 8.6 | 5.76 | 1.27 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 15 | 0.25 | 9.5 | 3.04 | 2.68 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.27 | 11.8 | 2.27 | 1.56 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.25 | 12.4 | 12.47 | 3.21 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 24 | 0.19 | 8.6 | 7.14 | 2.15 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 24 | 0.19 | 8.6 | 5.15 | 1.06 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 7 | 0.43 | 10.4 | 15.25 | 2.25 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.35 | 16.7 | 11.06 | 2.91 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 8 | 0.15 | 3.7 | 1.64 | 0.62 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.32 | 15.6 | 7.72 | 7.31 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.25 | 12.5 | 55.68 | 7.13 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.31 | 15.2 | 12.44 | 6.3 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.35 | 11.9 | 2.86 | 1.11 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.25 | 11.6 | 19.37 | 4.28 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 10 | 0.28 | 12.1 | 3.09 | 1.66 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.36 | 9.6 | 3.72 | 3.26 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.25 | 12.3 | 16.07 | 7.06 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 2 | 0.33 | 10.4 | 13.65 | 5.35 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.26 | 12.6 | 6.23 | 1.87 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 3 | 0.44 | 11.3 | 3.27 | 0.96 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 7 | 0.33 | 10.6 | 12.01 | 7.95 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 3 | 0.44 | 11.3 | 5.12 | 1.36 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 30 | 0.13 | 2.4 | 4.18 | 0.68 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 4 | 0.34 | 13.6 | 2.99 | 4.85 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 28 | 0.14 | 2.5 | 20.61 | 1.06 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.28 | 12.1 | 3.86 | 1.93 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 2 | 0.33 | 10.4 | 7.58 | 4.57 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.28 | 12.2 | 2.9 | 1.65 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 8 | 0.34 | 11.4 | 3.1 | 2.09 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.45 | 10 | 2.86 | 1.82 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 12 | 0.24 | 11.9 | 4.45 | 3.38 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.35 | 12.7 | 2.79 | 1.01 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 13 | 0.29 | 12.9 | 3.04 | 0.42 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.31 | 14.1 | 17.75 | 8.39 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.24 | 12.1 | 2.11 | 1.27 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 7 | 0.28 | 8.1 | 17.05 | 6.18 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 5.96 | 0.77 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 2.29 | 1.38 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 5 | 0.31 | 14.1 | 4.55 | 6.67 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.27 | 12 | 3.98 | 1.83 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 6 | 0.29 | 7.9 | 17.05 | 5.39 |
| 1964, Niigata | 7.5 | 21 | 0.32 | 11 | 0.27 | 12.1 | 2.97 | 1.49 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 5.3 | 19.96 | 2.93 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 5.6 | 4.7 | 0.47 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 6.5 | 5.08 | 0.52 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 4.6 | 20.3 | 3.16 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 3.6 | 20.34 | 3.18 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 3 | 17.07 | 1.81 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 2.3 | 13.59 | 2.14 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 1.6 | 20.41 | 2.45 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 4.8 | 19.61 | 2.78 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 2.7 | 15.43 | 2.02 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 2 | 13.59 | 1.46 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 4 | 18.87 | 3.26 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 2.7 | 20.47 | 3.16 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 5.9 | 4.89 | 0.54 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 4.5 | 19.26 | 1.99 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 1 | 20.27 | 1 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 3.1 | 18.26 | 2.04 |
| 1971, San Fernando | 6.4 | 0.5 | 0.68 | 47 | 0.08 | 5.2 | 19.96 | 2.63 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 20 | 0.12 | 3 | 8.57 | 2.63 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 32 | 0.09 | 1.5 | 6.25 | 0.37 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 23 | 0.11 | 2 | 7.89 | 2.04 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 17 | 0.12 | 3.6 | 3.08 | 0.92 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 15 | 0.12 | 3.8 | 6.56 | 2.02 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.6 | 6 | 0.36 | 70 | 0.04 | 0.2 | 4.26 | 0.01 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.6 | 6 | 0.36 | 54 | 0.12 | 1.8 | 10.66 | 0.01 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 17 | 0.12 | 3.7 | 9.6 | 4 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 22 | 0.11 | 2.6 | 3.68 | 0.31 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 23 | 0.11 | 2.4 | 6.35 | 1.41 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 23 | 0.11 | 2 | 6.15 | 1.1 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 22 | 0.11 | 2.7 | 6.45 | 1.53 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 23 | 0.11 | 2.9 | 7.02 | 1.43 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 25 | 0.1 | 2.5 | 6.78 | 0.72 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 15 | 0.12 | 4 | 6.56 | 1.48 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 17 | 0.12 | 3.7 | 6.78 | 2.3 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 21 | 0.11 | 1.6 | 4.8 | 0.67 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 25 | 0.1 | 2.5 | 9.84 | 2.63 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 22 | 0.11 | 1.8 | 6.67 | 1.13 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 30 | 0.09 | 1.8 | 8.05 | 1.03 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 22 | 0.11 | 2.7 | 8.05 | 2.12 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 25 | 0.11 | 2.2 | 3.68 | 0.47 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 16 | 0.12 | 3.8 | 9.37 | 4.25 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 22 | 0.11 | 3 | 10.08 | 3.21 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 16 | 0.12 | 3.7 | 3.72 | 1.23 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 18 | 0.12 | 3.4 | 9.16 | 3.82 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 19 | 0.12 | 3.3 | 6.15 | 1.51 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 21 | 0.11 | 1.4 | 4.69 | 0.87 |
| 1979, Imperial Valley | 6.5 | 2 | 0.49 | 25 | 0.11 | 2.2 | 3.52 | 0.47 |
| 1987, Superstition Hills | 6.6 | 23 | 0.15 | 27 | 0.09 | 3.5 | 17.91 | 0.19 |
| 1987, Superstition Hills | 6.6 | 23 | 0.15 | 22 | 0.09 | 3.3 | 41.38 | 0.21 |
| 1987, Superstition Hills | 6.6 | 23 | 0.15 | 43 | 0.07 | 1.7 | 17.52 | 0.11 |
| 1987, Superstition Hills | 6.6 | 23 | 0.15 | 44 | 0.07 | 3.6 | 7.5 | 0.01 |
| 1987, Superstition Hills | 6.6 | 23 | 0.15 | 38 | 0.08 | 2.7 | 13.11 | 0.11 |
| 1987, Superstition Hills | 6.6 | 23 | 0.15 | 25 | 0.09 | 3.4 | 41.38 | 0.24 |
| 1989, Loma Prieta | 7 | 27.2 | 0.2 | 1 | 0.6 | 3.4 | 29.73 | 0.26 |
| 1989, Loma Prieta | 7 | 27.2 | 0.2 | 2 | 0.8 | 2.7 | 33.54 | 0.29 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 7.5 | 0.35 | 12.6 | 0.47 | 14.2 | 13.95 | 1.18 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 6 | 0.38 | 13.4 | 0.94 | 12.5 | 9.25 | 1.01 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 8 | 0.34 | 14.6 | 1.98 | 16 | 6.67 | 0.45 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 8 | 0.34 | 14.6 | 1.98 | 16 | 16.82 | 0.93 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 7.5 | 0.35 | 12.6 | 0.47 | 14.2 | 10.4 | 0.89 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 5.5 | 0.39 | 10 | 1.36 | 15 | 14.56 | 1.34 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 5.5 | 0.39 | 10 | 1.36 | 15 | 30.21 | 2.83 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 6.5 | 0.37 | 10 | 1.88 | 12.5 | 5.16 | 0.34 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 5.5 | 0.39 | 10 | 1.36 | 15 | 56.8 | 2.48 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 8 | 0.34 | 14.6 | 1.98 | 16 | 18 | 0.97 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 8 | 0.34 | 14.6 | 1.98 | 16 | 20.69 | 0.9 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 7.5 | 0.35 | 12.6 | 0.47 | 14.2 | 18.56 | 1.33 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 8 | 0.34 | 14.6 | 1.98 | 16 | 14.63 | 0.66 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 6.5 | 0.37 | 10 | 1.88 | 12.5 | 9.84 | 1.03 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 5.5 | 0.39 | 10 | 1.36 | 15 | 14.34 | 1.31 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 6.5 | 0.37 | 10 | 1.88 | 12.5 | 14.63 | 1.47 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 6 | 0.38 | 13.4 | 0.94 | 12.5 | 15 | 1.48 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 5.5 | 0.39 | 10 | 1.36 | 15 | 9.79 | 1.47 |
| 1995, Hyogo-Ken Nanbu | 6.8 | 8 | 0.34 | 14.6 | 1.98 | 16 | 8.45 | 0.41 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 20.8 | 0.11 | 0.5 | 7.4 | 0 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 20.8 | 0.11 | 0.8 | 13.7 | 0.45 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 20.8 | 0.11 | 0.8 | 18.4 | 0.55 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 20.8 | 0.11 | 0.8 | 25.2 | 0.8 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 20.8 | 0.11 | 0.8 | 37.3 | 1.05 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 20.8 | 0.11 | 0.8 | 49.9 | 2.05 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 13 | 0.18 | 0.75 | 21.2 | 0.49 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 20.8 | 0.11 | 1.1 | 11.9 | 0 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 20.8 | 0.11 | 1.1 | 26.3 | 0 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 30 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 12.2 | 0.4 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 30 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 14.3 | 0.65 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 30 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 24.6 | 1 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 30 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 57.7 | 1.24 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 31.4 | 0.1 | 1 | 8 | 0.35 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 31.4 | 0.1 | 1 | 10.5 | 0.61 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 31.4 | 0.1 | 1 | 19 | 0.96 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 31.4 | 0.1 | 1 | 31.3 | 2.96 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 48.5 | 0.1 | 1.8 | 9.6 | 0.35 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 48.5 | 0.1 | 1.8 | 11.7 | 0.52 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 48.5 | 0.1 | 1.8 | 13.3 | 0.62 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 48.5 | 0.1 | 1.8 | 23.7 | 1.62 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 13 | 0.18 | 0.5 | 5.7 | 0 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 13 | 0.18 | 0.75 | 6.6 | 0.1 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 13 | 0.18 | 0.75 | 7.9 | 0.17 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 13 | 0.18 | 0.75 | 9 | 0.23 |
| 1999, Chi-Chi | 7.6 | 5 | 0.67 | 13 | 0.18 | 0.75 | 15 | 0.29 |
| 1999, Kocaeli | 7.4 | 0.5 | 0.57 | 11 | 7.7 | 1.2 | 8 | 0.9 |
| 1999, Kocaeli | 7.4 | 0.5 | 0.57 | 31 | 0.55 | 1.7 | 6 | 0.1 |
References
- Huang, W.; Zou, M.; Qian, J.; Zhou, Z. Consistent damage model and performance-based assessment of structural members of different materials. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 109, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gong, J.X. Probability Identification of Seismic Failure Modes of Reinforced Concrete Columns based on Experimental Observations. J. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 22, 1881–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fang, D.; Zhao, L. Reflection on earthquake damage of buildings in 2015 Nepal earthquake and seismic measures for post-earthquake reconstruction. Structures 2021, 30, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, M.; Faramarzi, A.; Javadi, A.A. An evolutionary based approach for assessment of earthquake-induced soil liquefaction and lateral displacement. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2011, 24, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, W.; Ledbetter, R.; Wu, G. Liquefaction in silty soils: Design and analysis. 1994; pp. 51–76. In Ground Failures under Seismic Conditions; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA; p. 51.
- Liao, T.; McGillivray, A.; Mayne, P.; Zavala, G.; Elhakim, A. Seismic Ground Deformation Modeling Final Report for MAE HD-7a (Year 1); Geosystems Engineering/School of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Arulanandan, K.; Li, X.S.; Sivathasan, K. (Siva) Numerical Simulation of Liquefaction-Induced Deformations. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2000, 126, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newmark, N.M. Effects of earthquakes on dams and embankments. Geotechnique 1965, 15, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Towhata, I.; Sasaki, Y.; Tokida, K.I.; Matsumoto, H.; Tamari, Y.; Yamada, K. Prediction of Permanent Displacement of Liquefied Ground by Means of Minimum Energy Principle. Soils Found. 1992, 32, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokusho, T.; Fujita, K. Site Investigations for Involvement of Water Films in Lateral Flow in Liquefied Ground. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2002, 128, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M. Study on liquefaction induced permanent ground displacements. Report of Association for the Development of Earthquake Prediction 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youd, T.L.; Hansen, C.M.; Bartlett, S.F. Revised Multilinear Regression Equations for Prediction of Lateral Spread Displacement. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2002, 128, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Rahman, M.S. A neural network model for liquefaction-induced horizontal ground displacement. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 1999, 18, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Towhata, I.; Yasuda, S.; Isoyama, R. Study on permanent ground displacement induced by seismic liquefaction. Comput. Geotech. 1987, 4, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orense, R.; Towhata, I. Prediction of liquefaction—induced permanent ground displacements: A three—dimensional approach. Tech. Rep. NCEER 1992, 1, 335–349. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, W.H.; Morgenstern, N.R.; Robertson, P.K. Progressive failure of lower San Fernando dam. J. Geotech. Eng. 1993, 119, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.H.; Morgenstern, N.R.; Robertson, P.K. Postearthquake Deformation Analysis of Wildlife Site. J. Geotech. Eng. 1994, 120, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegian, M.K.; Marciano, E.A.; Ghahraman, V.G. Earthquake-induced permanent deformations: Probabilistic approach. J. Geotech. Eng. 1991, 117, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baziar, M.H.; Dobry, R.; Elgamal, A.-W.M. Engineering Evaluation of Permanent Ground Deformations Due to Seismically Induced Liquefaction. Tech. Rep. NCEER-92-0007. 1992; 306. [Google Scholar]
- Tokida, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Azuma, T.; Towhata, I. Simplified Procedure to Estimate Lateral Ground Flow by Soil Liquefaction. WIT Trans. Built Environ. 1993, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bardet, J.; Mace, N.; Tobita, T. Liquefaction-Induced Ground Deformation and Failure, a Report to PEER/PG&E. Task 4A-Phase 1; Civil Engineering Department, University of Southern California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hadush, S.; Yashima, A.; Uzuoka, R.; Moriguchi, S.; Sawada, K. Liquefaction induced lateral spread analysis using the CIP method. Comput. Geotech. 2001, 28, 549–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydan, Ö. The stress state of the earth and the earth’s crust due to the gravitational pull. In Proceedings of the 35th US Rock Mechanics Symposium, Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 4–7 June 1995; pp. 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, M.; Sato, H.; Kawakami, T. A consideration of the mechanism for liquefaction-related large ground displacement. In Proceedings of the Fifth US-Japan Workshop on Earthquake Resistant Design of Lifeline Facilities and Countermeasures Against Soil Liquefaction, Technical Report NCEER-94-0026, Snowbird, UT, USA, 29 September–1 October 1994; pp. 217–232. [Google Scholar]
- Youd, T.L.; Perkins, D.M. Mapping of liquefaction severity index. J. Geotech. Eng. 1987, 113, 1374–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, S.F.; Youd, T.L. Empirical prediction of lateral spread displacement. In Proceedings of the Fourth Japan-U.S. Workshop on Earthquake Resistant Design of Lifeline Facilities and Countermeasures for Soil Liquefaction, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27–29 May 1992; pp. 351–365. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, S.F.; Leslie Youd, T. Empirical prediction of liquefaction-induced lateral spread. J. Geotech. Eng. 1995, 121, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jounrnal, A.; Jafarian, Y.; Nasri, E. Evaluation of uncertainties in the existing empirical models and probabilistic prediction of liquefaction-induced lateral. AJSR-Civil Environ. Eng. 2016, 48, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kanibir, A. Investigation of the Lateral Spreading at Sapanca and Suggestion of Empirical Relationships for Predicting Lateral Spreading; Department of Geological Engineering, Hacettepe University: Ankara, Turkey, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bawwab, W. Al Probabilistic assessment of liquefaction-induced lateral ground deformations. P.h.D. Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey, November 2005.
- Javadi, A.A.; Rezania, M.; Nezhad, M.M. Evaluation of liquefaction induced lateral displacements using genetic programming. Comput. Geotech. 2006, 33, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baziar, M.; Saeedi Azizkandi, A. Evaluation of lateral spreading utilizing artificial neural network and genetic programming. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Trans. B Geotech. Eng. 2013, 11, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Baziar, M.H.; Ghorbani, A. Evaluation of lateral spreading using artificial neural networks. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2005, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javdanian, H. Field data-based modeling of lateral ground surface deformations due to earthquake-induced liquefaction. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2019, 134, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.K.; Rasmussen, C.E. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 2, p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, D.B.; Stewart, J.P.; Youd, T.L.; Chu, B.L. Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Spreading in Near-Fault Regions during the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan Earthquake. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2006, 132, 1549–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, K.O.; Youd, T.L.; Seed, R.B.; Bray, J.D.; Stewart, J.P.; Durgunoglu, H.T.; Lettis, W.; Yilmaz, M.T. Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Spreading at Izmit Bay During the Kocaeli (Izmit)-Turkey Earthquake. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 1300–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadigh, K.; Chang, C.Y.; Egan, J.A.; Makdisi, F.; Youngs, R.R. Attenuation Relationships for Shallow Crustal Earthquakes Based on California Strong Motion Data. Seismol. Res. Lett. 1997, 68, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vuren, T. Modeling of transport demand—Analyzing, calculating, and forecasting transport demand. Transp. Rev. 2020, 40, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gong, J.; Gao, S.; Wang, D.; Cui, T.; Li, Y.; Wei, B. Susceptibility assessment of earthquake-induced landslides using Bayesian network: A case study in Beichuan, China. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 42, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üstün, B.; Melssen, W.J.; Buydens, L.M.C. Facilitating the application of Support Vector Regression by using a universal Pearson VII function based kernel. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2006, 81, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, H.B.; Nguyen, T.A.; Pham, B.T. Estimation of Soil Cohesion Using Machine Learning Method: A Random Forest Approach. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8873993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, F.; Wróblewski, P.; Al-Mansob, R.A.; Olczak, P.; Kamiński, P.; Safdar, M.; Rai, P.; Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, F.; et al. Prediction of Ultimate Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundations on Cohesionless Soils: A Gaussian Process Regression Approach. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Kamiński, P.; Olczak, P.; Alam, M.; Iqbal, M.; Ahmad, F.; Sasui, S.; Khan, B.; Ahmad, M.; Kamiński, P.; et al. Development of Prediction Models for Shear Strength of Rockfill Material Using Machine Learning Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Hu, J.-L.; Ahmad, F.; Tang, X.-W.; Amjad, M.; Iqbal, M.; Asim, M.; Farooq, A.; Ahmad, M.; Hu, J.-L.; et al. Supervised Learning Methods for Modeling Concrete Compressive Strength Prediction at High Temperature. Materials 2021, 14, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hasanipanah, M.; Nikafshan Rad, H.; Jahed Armaghani, D.; Tahir, M.M. A new design of evolutionary hybrid optimization of SVR model in predicting the blast-induced ground vibration. Eng. Comput. 2021, 37, 1455–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method and Technique | Model | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical model | Regression Analysis | Hamada et al. [11] | |
| Youd and Perkins [25] | |||
| Bardet et al. [21] | |||
| Youd et al. [12] | |||
| Jafarian and Nasri [28] | |||
| Soft computing methods | ANN | Wang and Rahman [13] | |
| Baziar and Ghorbani [33] | |||
| GP | Javadi et al. [31] | ||
| ANFIS | Javdanian [34] | ||
| Dataset | Statistical Parameters | Seismic Parameter | Geotechnical Parameter | Topographic Parameter | Output | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | amax | R | D5015 | F15 | T15 | W | DH | ||
| - | g | km | mm | % | m | % | m | ||
| Training | Minimum | 6.4 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 1 | 0.2 | 1.64 | 0 |
| Average | 7.26 | 0.41 | 15.10 | 0.36 | 18.83 | 7.80 | 11.69 | 2.45 | |
| Maximum | 9.2 | 0.68 | 100 | 7.7 | 70 | 16.7 | 57.7 | 10.16 | |
| Standard deviation | 0.51 | 0.15 | 11.61 | 0.65 | 13.71 | 5.16 | 9.96 | 2.26 | |
| Testing | Minimum | 6.4 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.07 | 2 | 0.5 | 2.11 | 0 |
| Average | 7.3 | 0.38 | 16.10 | 0.39 | 13.96 | 7.98 | 10.04 | 2.17 | |
| Maximum | 9.2 | 0.68 | 60 | 1.98 | 66 | 16 | 48.98 | 8.39 | |
| Standard deviation | 0.49 | 0.13 | 10.61 | 0.42 | 12.14 | 5.20 | 9.78 | 2.21 | |
| Parameters | M | amax | R | D5015 | F15 | T15 | W | DH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 1.000 | |||||||
| amax | −0.341 | 1.000 | ||||||
| R | 0.761 | −0.722 | 1.000 | |||||
| D5015 | 0.033 | −0.112 | 0.013 | 1.000 | ||||
| F15 | −0.370 | 0.560 | −0.371 | −0.230 | 1.000 | |||
| T15 | 0.208 | −0.573 | 0.360 | 0.237 | −0.591 | 1.000 | ||
| W | 0.003 | 0.178 | −0.046 | 0.025 | 0.245 | −0.145 | 1.000 | |
| DH | 0.179 | −0.250 | 0.230 | −0.078 | −0.354 | 0.518 | 0.146 | 1.000 |
| Performance | RSR | NSE |
|---|---|---|
| Very Good | ||
| Good | ||
| Adequate | ||
| Inadequate |
| Model | Indicators | R2 | r | MAE (m) | RMSE (m) | RSR | NSE | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPR | Training model | 0.9402 | 0.9697 | 0.3403 | 0.5597 | 0.248 | 0.938 | Present study |
| Testing model | 0.894 | 0.9455 | 0.544 | 0.8438 | 0.387 | 0.851 | ||
| EPR | Training model | 0.913 | - | 0.537 | 1.003 | - | - | [4] |
| Testing model | 0.883 | - | 0.291 | 1.158 | - | - | ||
| ANN | Training model | 0.875 | - | 0.702 | 1.074 | - | - | |
| Testing model | 0.872 | 0.82 | 1.21 | - | - | |||
| MLR | Training model | 0.868 | - | 0.81 | 1.24 | - | - | |
| Testing model | 0.875 | - | 0.43 | 1.196 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, M.; Amjad, M.; Al-Mansob, R.A.; Kamiński, P.; Olczak, P.; Khan, B.J.; Alguno, A.C. Prediction of Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Displacements Using Gaussian Process Regression. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041977
Ahmad M, Amjad M, Al-Mansob RA, Kamiński P, Olczak P, Khan BJ, Alguno AC. Prediction of Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Displacements Using Gaussian Process Regression. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(4):1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041977
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Mahmood, Maaz Amjad, Ramez A. Al-Mansob, Paweł Kamiński, Piotr Olczak, Beenish Jehan Khan, and Arnold C. Alguno. 2022. "Prediction of Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Displacements Using Gaussian Process Regression" Applied Sciences 12, no. 4: 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041977
APA StyleAhmad, M., Amjad, M., Al-Mansob, R. A., Kamiński, P., Olczak, P., Khan, B. J., & Alguno, A. C. (2022). Prediction of Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Displacements Using Gaussian Process Regression. Applied Sciences, 12(4), 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041977








