Piezomagnetic Anomalies Associated with the 2021 MW 7.3 Maduo (China) Earthquake
Abstract
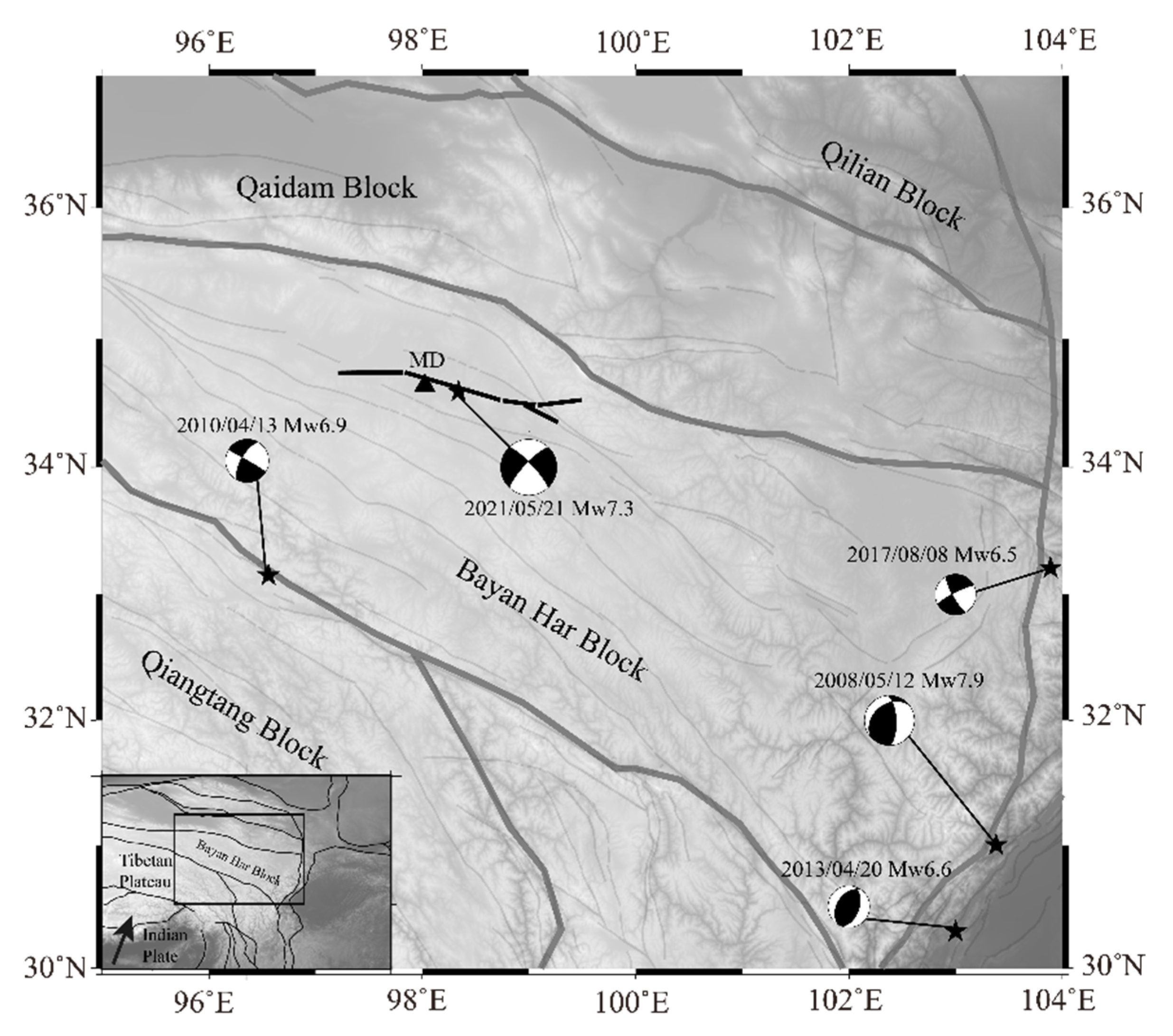
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
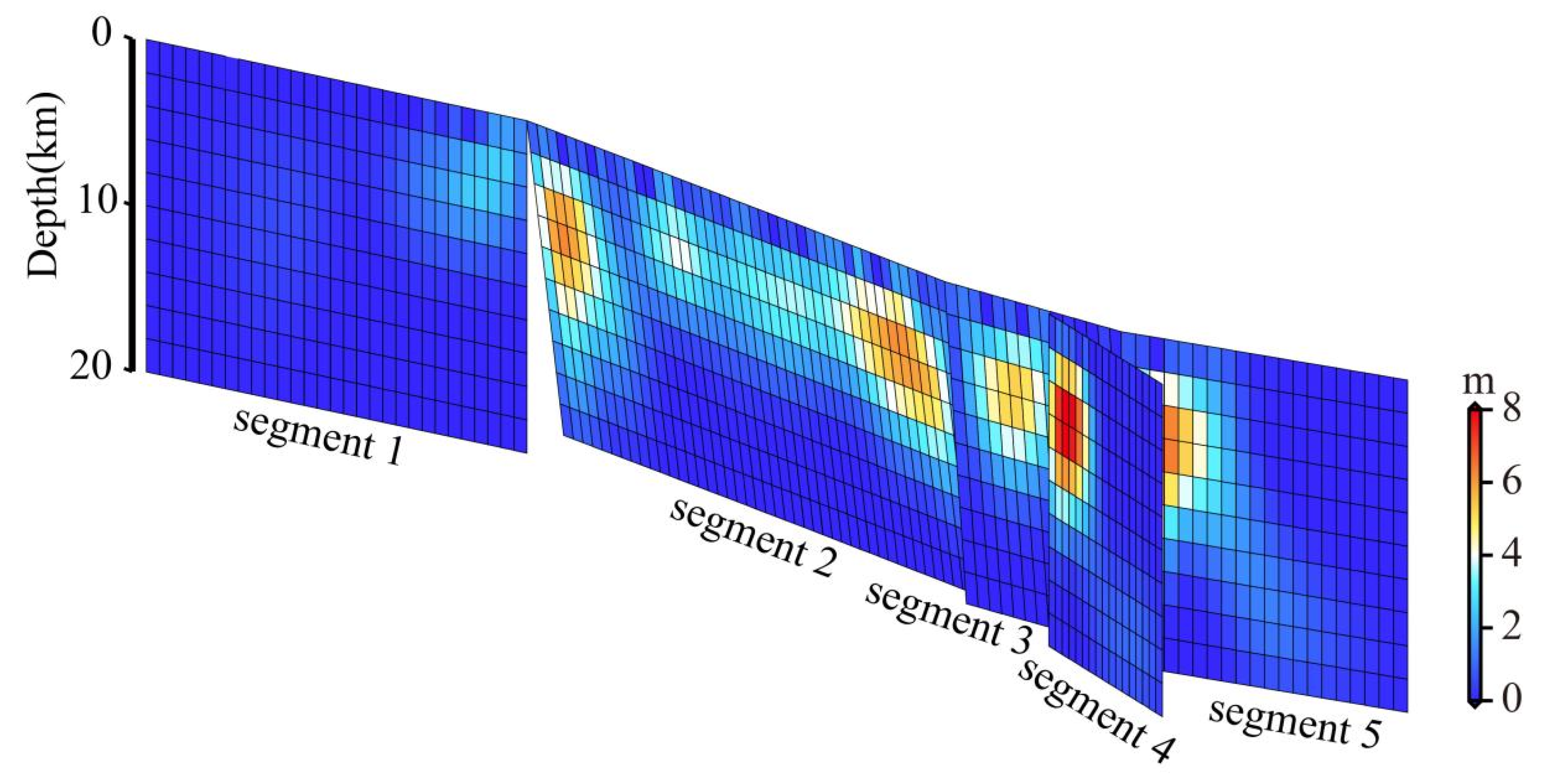
2.1. Coseismic Slip Model
2.2. Layer Elastic Model
2.3. Piezomagnetic Model
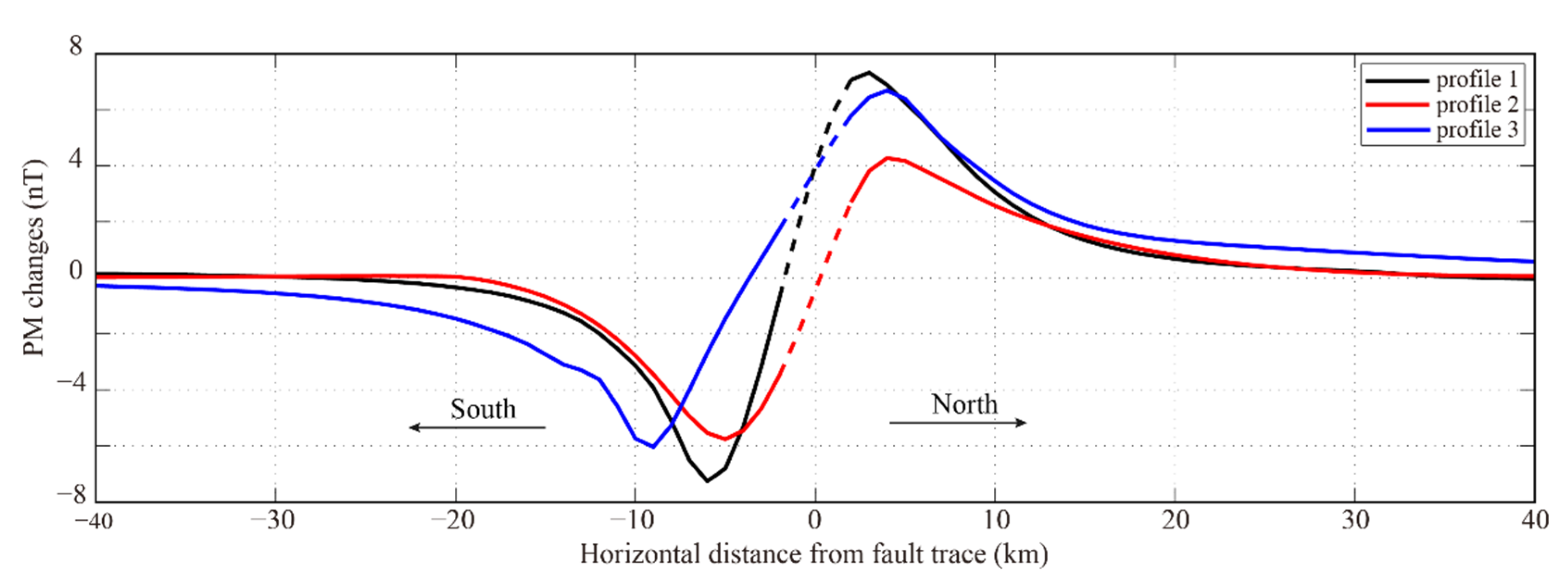
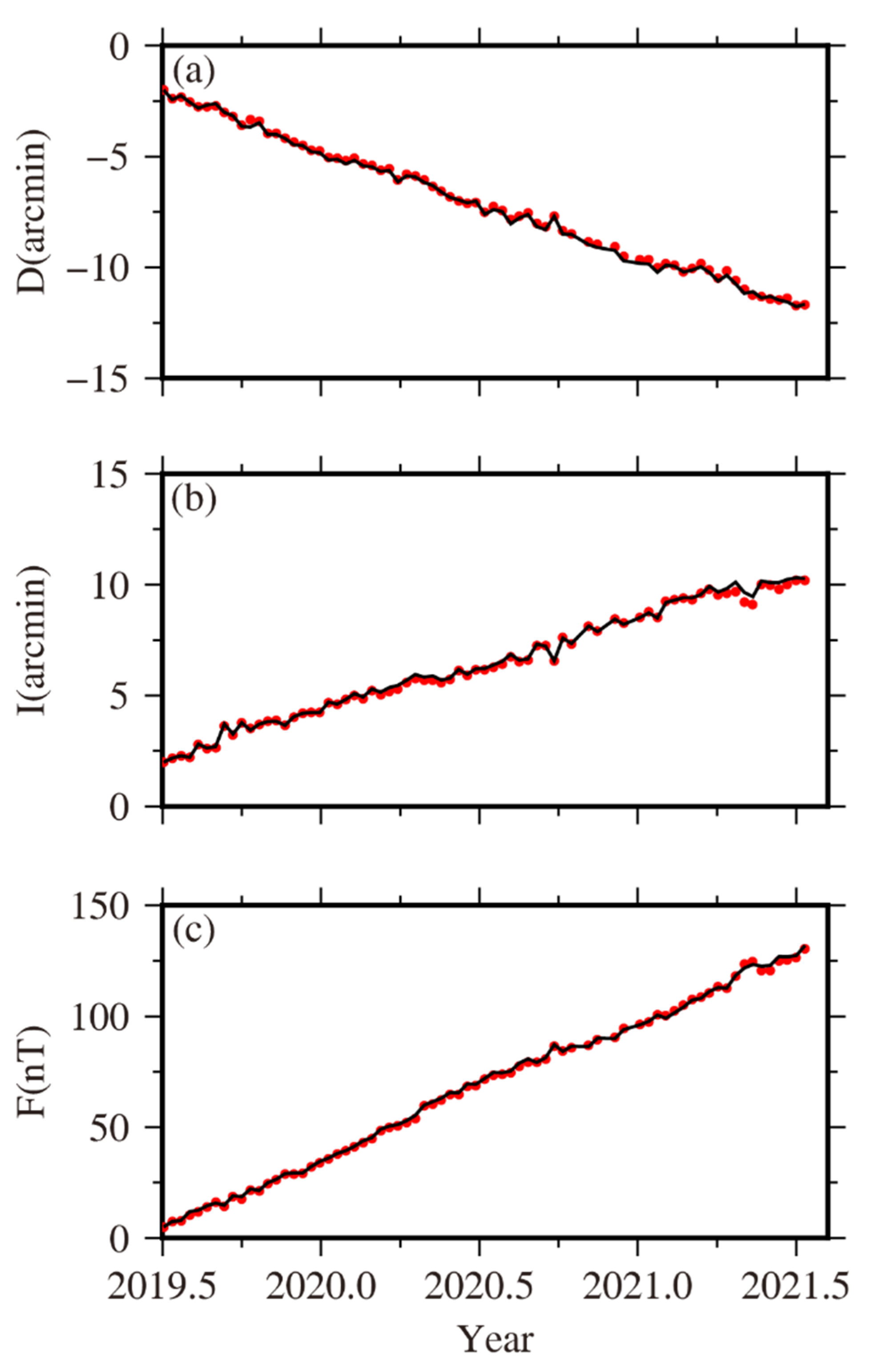
3. Results
4. Discussion
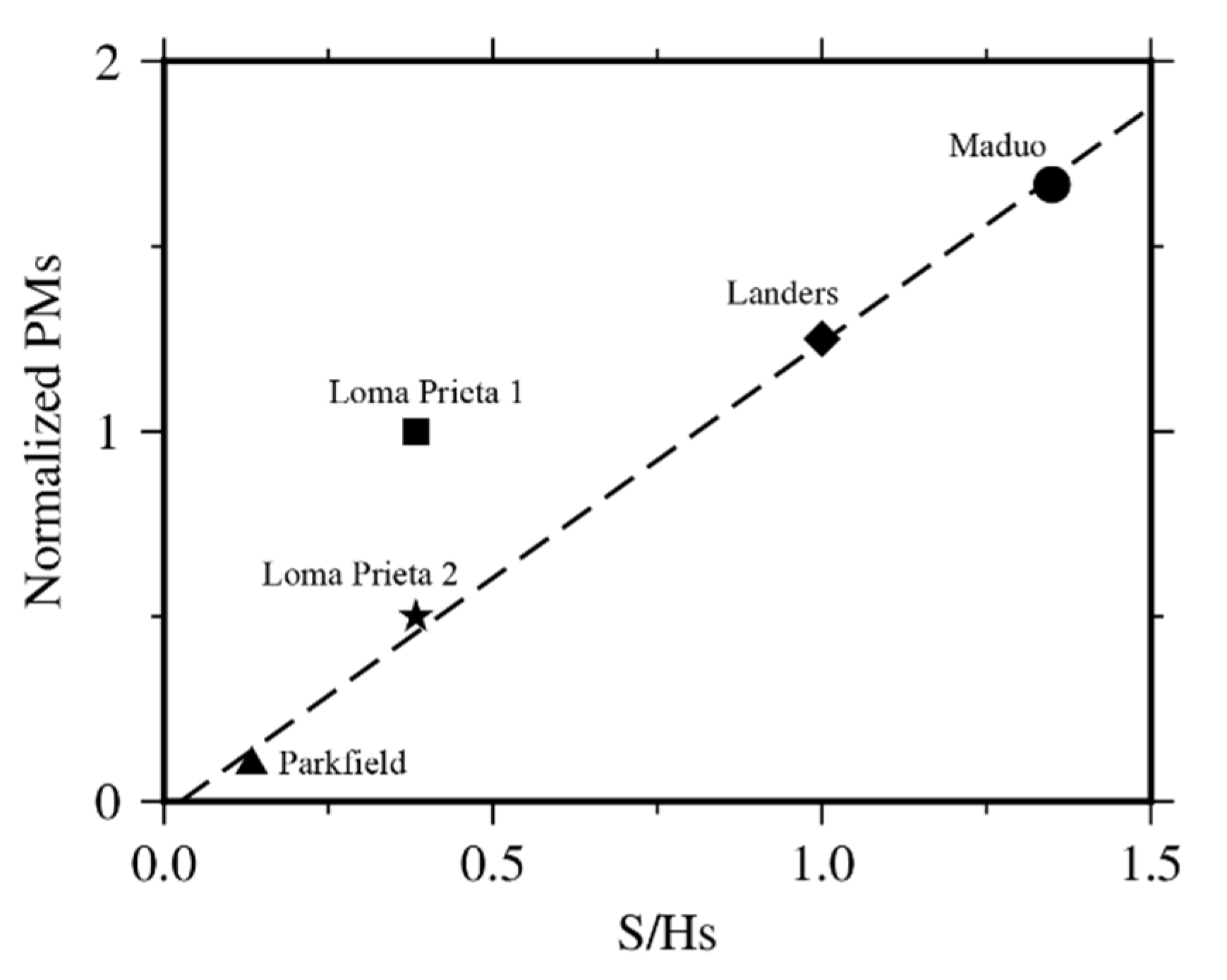
4.1. Validation of Piezomagnetic Model
4.2. Possible Values of Initial Magnetization and Stress Sensitivity
4.3. Potential Usefulness of Observations along Fault
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stacey, F.D. Seismo-magnetic effect and the possibility of forecasting earthquakes. Nature 1963, 200, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, F.D. The Seismomagnetic Effect. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1964, 58, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.J.S.; Mueller, R.J. Seismomagnetic observation during the 8 July 1986 magnitude 5.9 North Palm Springs earthquake. Science 1987, 237, 1201–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser-Smith, A.C.; Bernardi, A.; McGill, P.R.; Ladd, M.E.; Helliwell, R.A.; Villard, O.G. Low-frequency magnetic field measurements near the epicenter of the Ms 7.1 Loma Prieta earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Kawate, R.; Molchanov, O.A.; Yumoto, K. Results of ultra-low-frequency magnetic field measurements during the Guam earthquake of 8 August 1993. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.J.S.; Sasai, Y.; Egbert, G.D.; Mueller, R.J. Seismomagnetic effects from the long-awaited 28 September 2004 M 6.0 Parkfield earthquake. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2006, 96, S206–S220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, K.; Takeuchi, N.; Utsugi, M.; Yumoto, K.; Sasai, Y. Direct magnetic signals from earthquake rupturing: Iwate-Miyagi earthquake of M 7.2, Japan. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 305, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Han, P.; Huang, Q.; Hattori, K.; Febriani, F.; Yamaguchi, H. Anomalous behaviors of geomagnetic diurnal variations prior to the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku earthquake (Mw9.0). J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 77, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Hattori, K.; Hirokawa, M.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, C.; Febriani, F.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yoshino, C.; Liu, J.; Yoshida, S. Statistical analysis of ULF seismomagnetic phenomena at Kakioka, Japan, during 2001–2010. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 4998–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Chong, J.; Klemperer, S.L.; Han, B.; Jiang, F.; Wen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhan, Y.; Tang, J.; et al. Coseismic electric and magnetic signals observed during 2017 Jiuzhaigou Mw6.5 earthquake and explained by electrokinetics and magnetometer rotation. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 223, 1130–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lin, J.Y.; Gao, Y.; Lin, C.H.; Han, P.; Chen, C.R.; Lin, L.C.; Huang, R.; Liu, J.Y. Magnetic Pulsations Triggered by Microseismic Ground Motion. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth. 2021, 126, e2020JB021416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K. Calculation of the piezomagnetic field arising from uniform regional stress in inhomogeneously magnetized crust (II): Limitation in general cases. Earth Planets Space 2021, 63, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Utada, H.; Shimizu, H.; Ogawa, T.; Maeda, T.; Furumura, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamazaki, N.; Yoshitake, Y.; Nagamachi, S. Geomagnetic field changes in response to the 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake and Tsunami. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 311, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Harris, J.M.; Wen, J.; Huang, Y.; Twardzik, C.; Chen, X.; Hu, H. Modeling of the coseismic electromagnetic fields observed during the 2004 Mw 6.0 Parkfield earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlis, N.V.; Skordas, E.S.; Varotsos, P.A. Order parameter fluctuations of seismicity in natural time before and after mainshocks. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 2010, 91, 59001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotsos, P.A.; Sarlis, N.V.; Skordas, E.S. Study of the temporal correlations in the magnitude time series before major earthquakes in Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 9192–9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlis, N.V.; Skordas, E.S.; Varotsos, P.A.; Nagao, T.; Kamogawa, M.; Uyeda, S. Spatiotemporal variations of seismicity before major earthquakes in the Japanese area and their relation with the epicentral locations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 986–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, F.D.; Johnston, M.J.S. Theory of the piezomagnetic effect in titanomagnetite-bearing rocks. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1972, 97, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.J.; Johnston, M.J.S. Seismomagnetic effect generated by the October, 1989, ML, 7.1 Loma Prieta, California, Earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1990, 17, 1231–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.J.S.; Mueller, R.J.; Sasai, Y. Magnetic Field Observations in the Near-Field the 28 June 1992 Mw 7.3 Landers, California, Earthquake. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1994, 84, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, Y.; Sugisaki, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Utsugi, M.; Oshima, H. Tectonomagnetic study in the eastern part of Hokkaido, NE Japan: Discrepancy between observed and calculated results. Earth Planets Space 2004, 56, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, Y. A surface integral representation of the tectonomagnetic field based on the linear piezomagnetic effect. Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. 1983, 58, 763–785. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, M.J.S. Local Magnetic Fields, Uplift, Gravity, and Dilational Strain Changes in Southern California. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 1986, 38, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikitake, T. Magnetic and electric signals precursory to earthquake an analysis of Japanese data. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 1987, 39, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K. Improved models of the piezomagnetic field for the 2011 Mw 9.0 Tohoku-oki earthquake. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 363, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamazaki, K. Temporal variations in magnetic signals generated by the piezomagnetic effect for dislocation sources in a uniform medium. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 206, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Peltzer, G.; Le Dain, A.Y.; Armijo, R.; Cobbold, P. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: New insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology 1982, 10, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Cheng, S.; Ma, J.; Du, P. Seismic activities and earthquake potential in the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 2025–2042. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Zhang, H. Analysis of coseismic variations in magnetic field of the Lushan Ms7.0 earthquake in 2013. Seismol. Geol. 2020, 42, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, R.J.; Johnston, M.J.S. Review of magnetic field monitoring near active faults and volcanic calderas in California: 1974–1995. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1998, 105, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Liang, M.; Sun, X.; Huang, F.; Zhao, L.; Gong, Y.; Han, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H. Deep structure and seismogenic pattern of the 2021.5.22 Madoi (Qinghai) MS7.4 earthquake. Chin. J. Geophys. 2021, 64, 2232–2252. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Qu, C.; Chen, H.; Shan, X.; Song, X.; Gong, W. Tectonic and Geometric Control on Fault Kinematics of the 2021 Mw7.3 Maduo (China) Earthquake Inferred From Interseismic, Coseismic, and Postseismic InSAR Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, Y. Application of the Elasticity Theory of Dislocations to Tectonomagnetic Modelling. Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. 1980, 55, 387–447. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Lorenzo-Martín, F.; Roth, F. PSGRN/PSCMP—A new code for calculating co- and post-seismic deformation, geoid and gravity changes based on the viscoelastic-gravitational dislocation theory. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Shan, B.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, R. Stress transfer and its implication for earthquake hazard on the Kunlun Fault, Tibet. Tectonophysics 2010, 482, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, A.; Oshiman, N. Piezomagnetic field associated with a numerical solution of the Mogi model in a non-uniform elastic medium. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 159, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Gao, G.M.; Bai, C.H.; Shao, D.; Feng, L.L. Characteristics of the crustal magnetic anomaly and regional tectonics in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the adjacent areas. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Utsugi, M.; Nishida, Y.; Sasai, Y. Piezomagnetic potentials due to an inclined rectangular fault in a semi-infinite medium. Geophys. J. Int. 2000, 140, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Ren, Z. Equinoctial asymmetry in solar quiet field along the 120° E meridian chain. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Yuan, J.; Yang, F.; Jia, L.; Wang, C. Localized geomagnetic field anomalies in an underground gas storage. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2018, 283, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Fialko, Y. Coseismic and Early Postseismic Deformation Due to the 2021 M7.4 Maduo (China) Earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, Y.; Xu, X.; Tapponnier, P.; Van der Woerd, J.; Lasserre, C.; King, G. High-resolution satellite imagery mapping for the surface rupture and slip distribution of the Mw ∼7.8, 14 November 2001 Kokoxili earthquake, Kunlun fault, northern Tibet, China. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2005, 95, 1970–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Layers | Depth/km | VP/km·s−1 | VS/km·s−1 | Density/kg·m−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | 4.8 | 2.82 | 2600 |
| 2 | 10 | 5.9 | 3.47 | 2700 |
| 3 | 20 | 6.1 | 3.59 | 2850 |
| 4 | 48 | 6.5 | 3.82 | 3000 |
| 5 | 68 | 7.0 | 4.12 | 3100 |
| 6 | 100 | 8.1 | 4.76 | 3320 |
| Event | Maximum PMs (nT) | Magnetization (A/m) | Stress Sensitivity (10−3 MPa−1) | S (m) | Hs (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maduo | ~10 | 3 | 2 | 8.1 | 6 |
| Landers | ~5 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| Loma Prieta | ~1.5 | 1.5 | 1 or 2 | 2.3 | 6 |
| Parkfield | ~0.4 | 2 | 2 | 0.4 | 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, C.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Chu, F. Piezomagnetic Anomalies Associated with the 2021 MW 7.3 Maduo (China) Earthquake. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031017
Song C, Zhang P, Wang C, Chu F. Piezomagnetic Anomalies Associated with the 2021 MW 7.3 Maduo (China) Earthquake. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(3):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031017
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Chengke, Pengtao Zhang, Can Wang, and Fei Chu. 2022. "Piezomagnetic Anomalies Associated with the 2021 MW 7.3 Maduo (China) Earthquake" Applied Sciences 12, no. 3: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031017
APA StyleSong, C., Zhang, P., Wang, C., & Chu, F. (2022). Piezomagnetic Anomalies Associated with the 2021 MW 7.3 Maduo (China) Earthquake. Applied Sciences, 12(3), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031017






