A Denoising Method for Seismic Data Based on SVD and Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
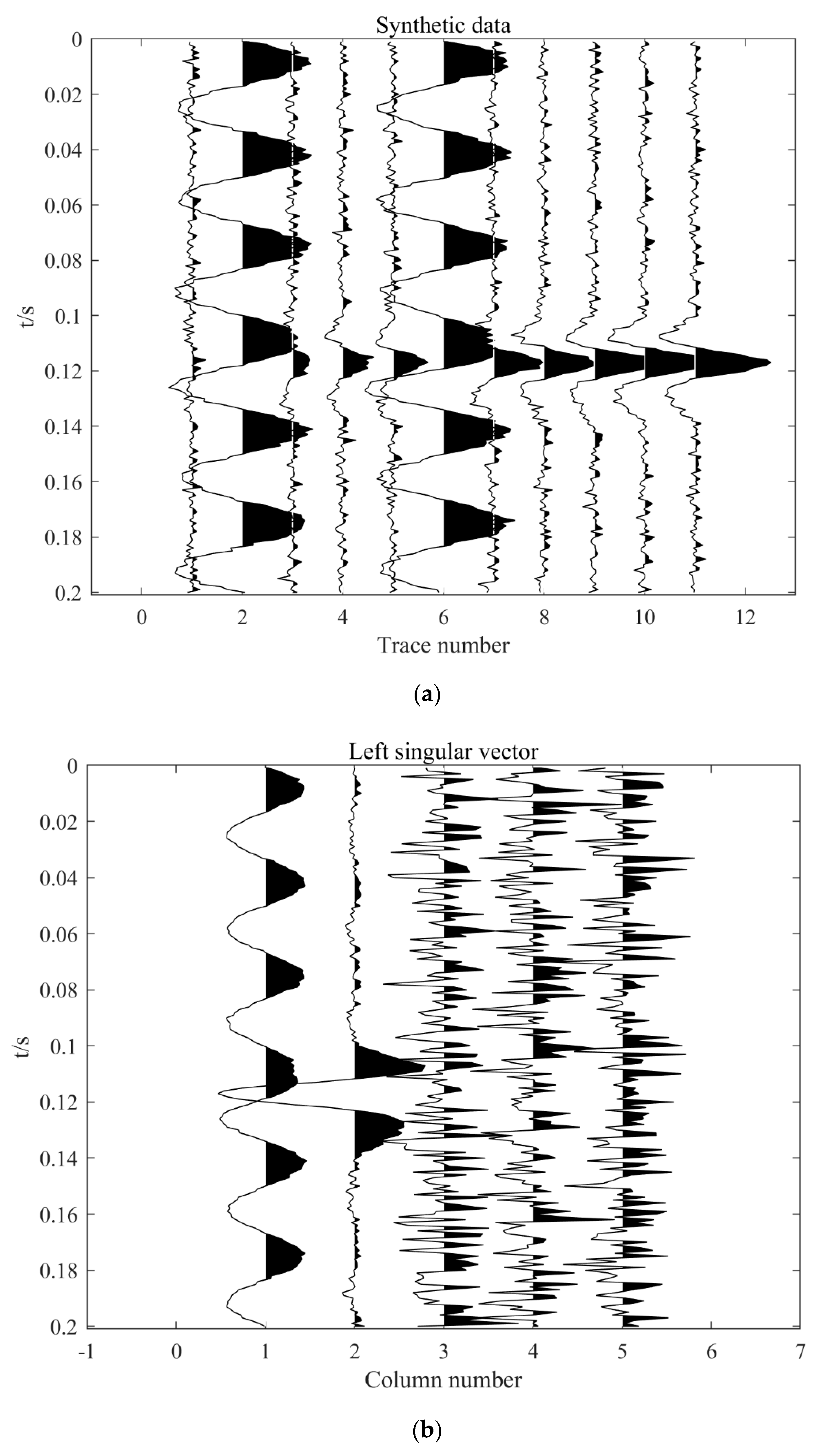
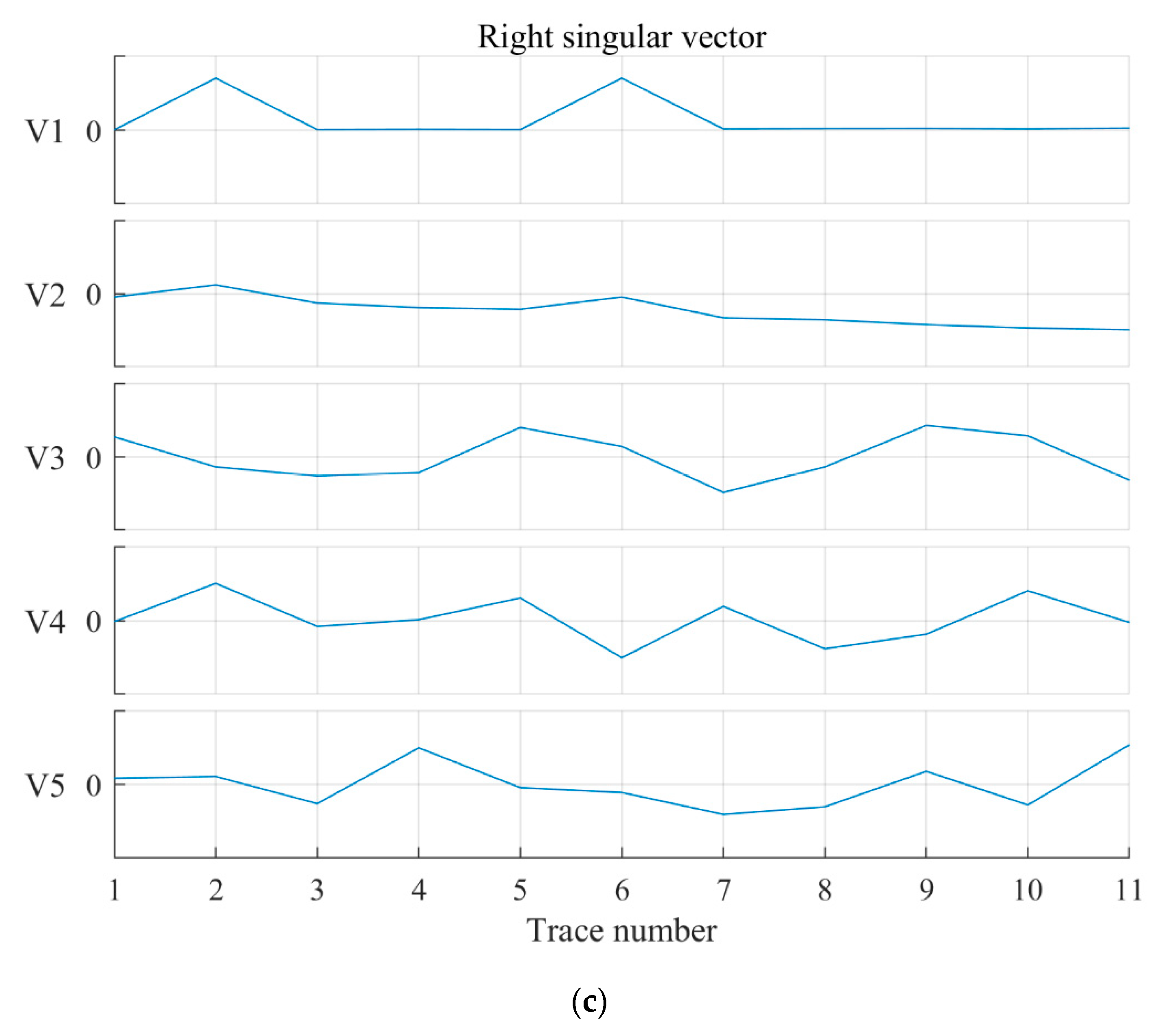
2.1. Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
2.2. Denoising Method Based on SVD and Deep Learning
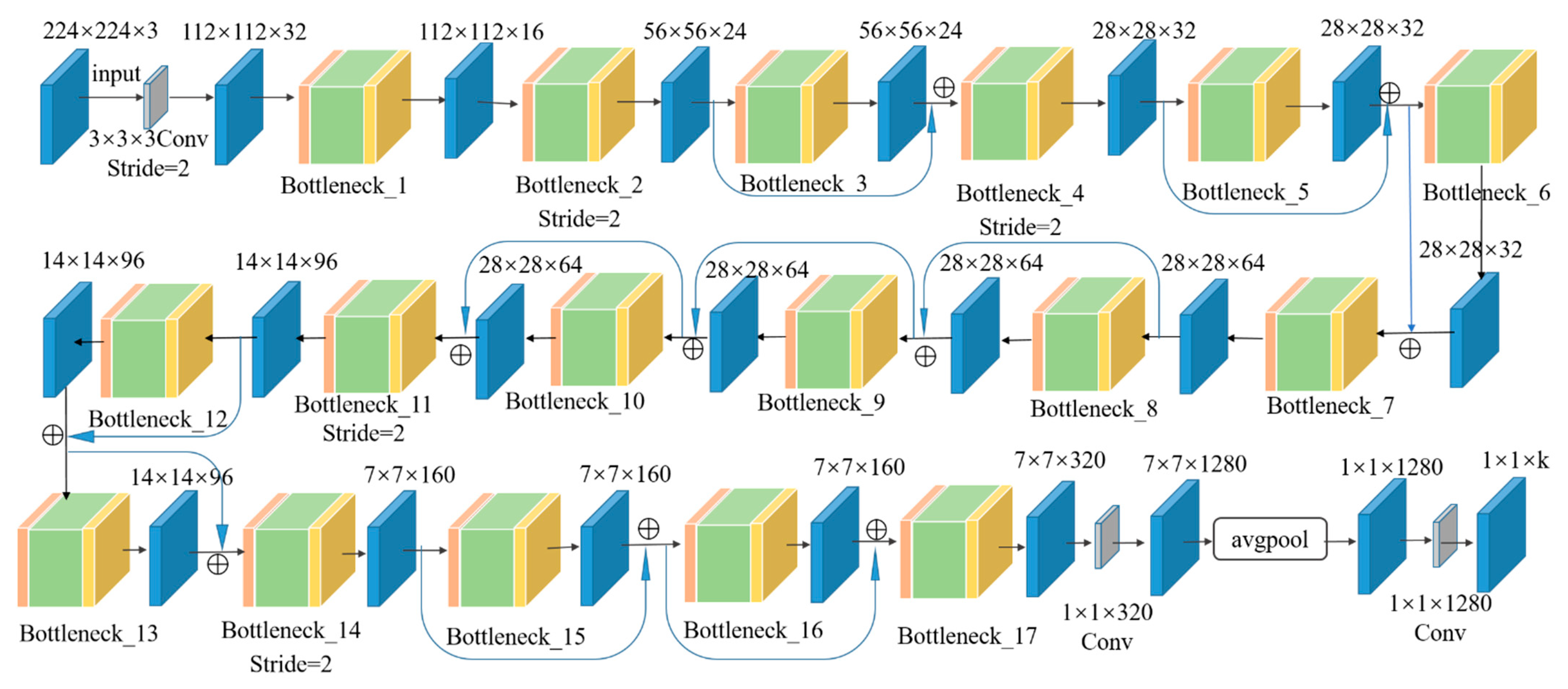
2.2.1. Selection of Deep Learning Networks
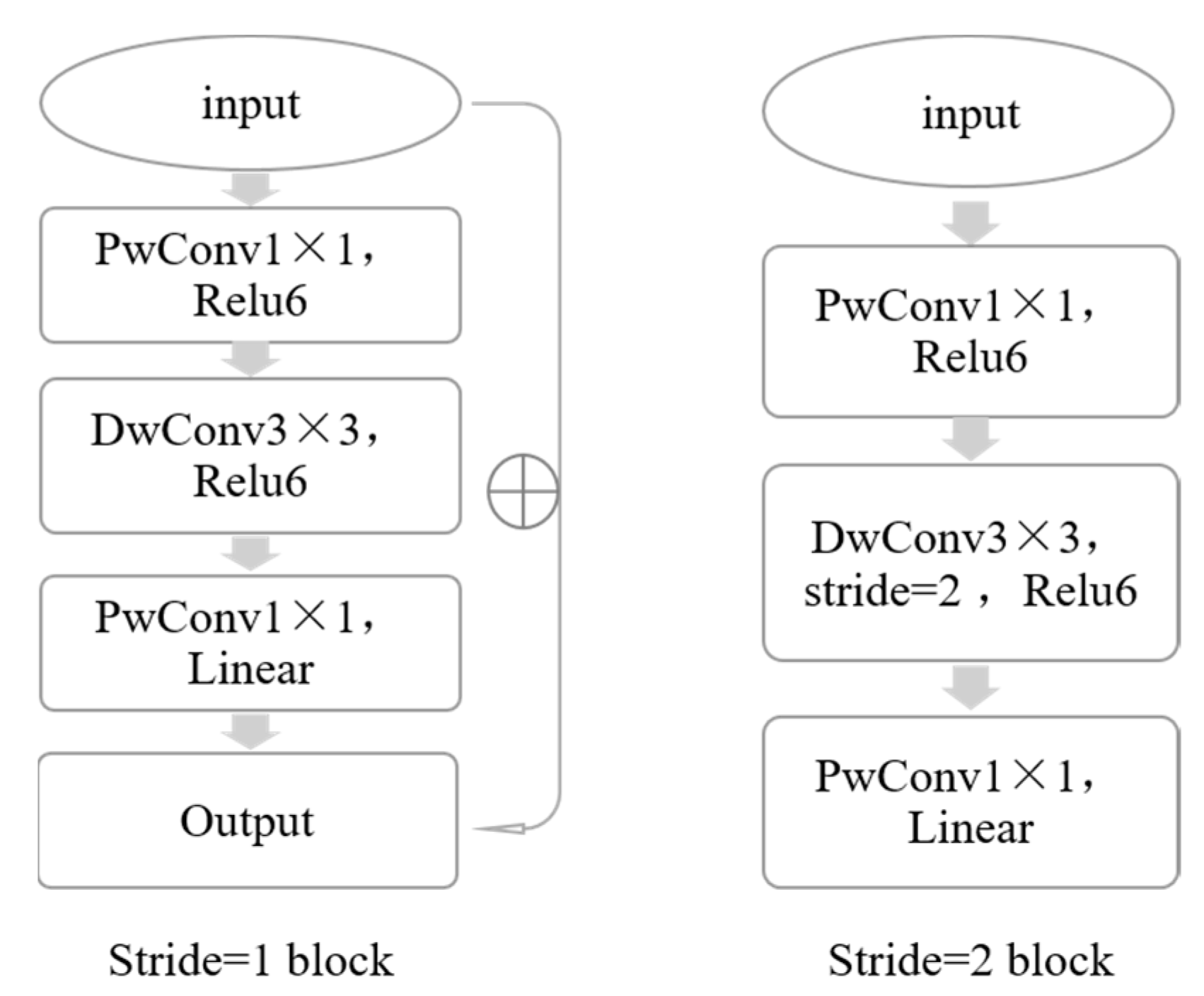
2.2.2. Deeply Separable Convolution in MobileNetV2 Networks
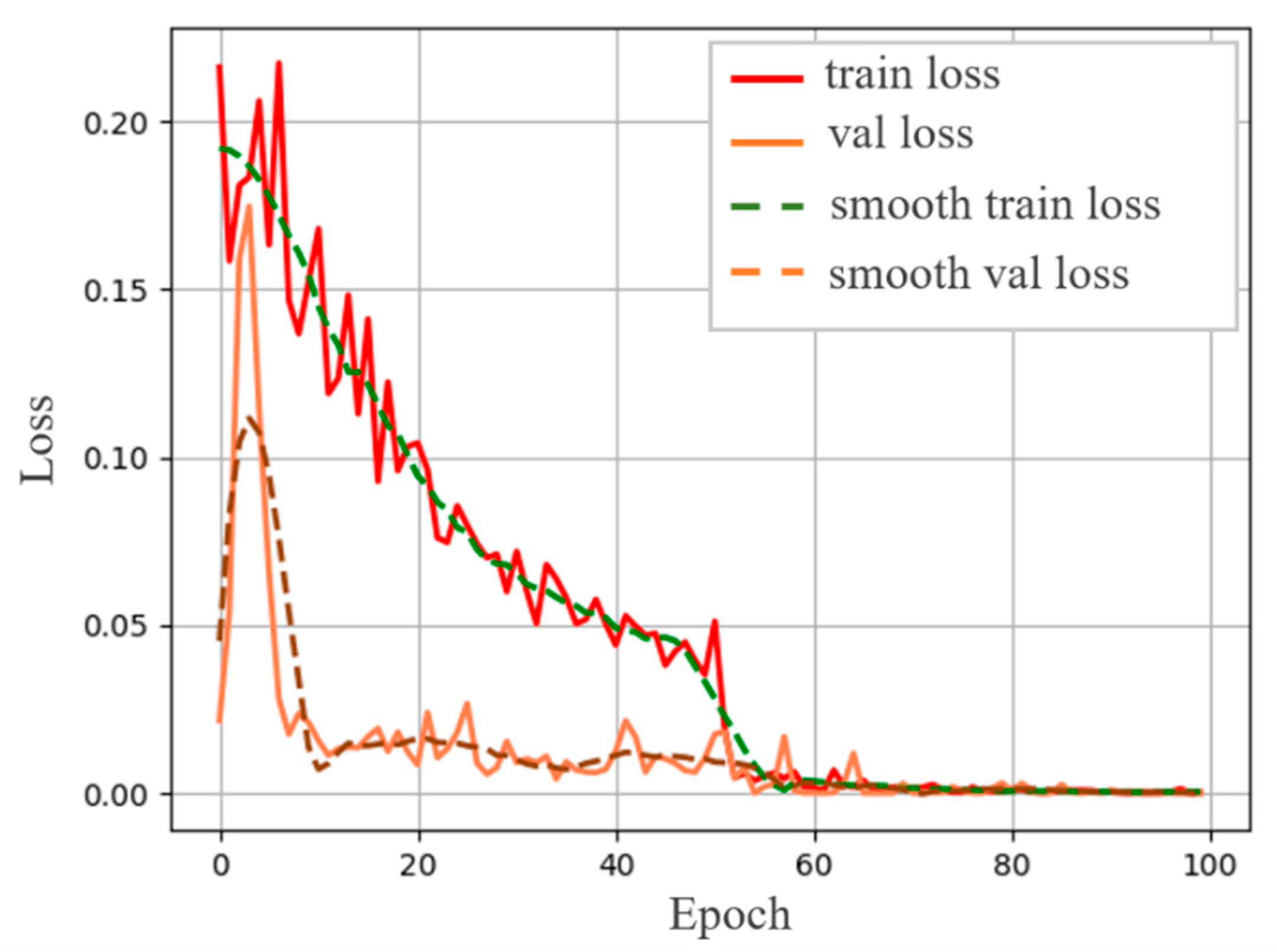
2.2.3. MobileNetV2 Network Training
2.2.4. Algorithm Program Steps
| Algorithm 1 Pseudocode of Seismic Denoising Algorithm |
| Input:: seismic data have m traces, n samples, window parameters were set to a traces, b samples, (a is an odd number and b is an even number), rank of matrix K = 4; |
| Output: denoised seismic data; |
| 1: = ; |
| 2: for () + 1 < i m − a/2 + 1, i + a do |
| 3: for (b-1)/2 + 1 < j n − (b − 1)/2, j + 1 do |
| 4: Set window = a * b (a < m, b < n), obtain ; |
| 5: Compute SVD function USV = svd(d), obtain : left singular matrix,: singular value matrix,: right singular matrix; |
| 6: for 0 < k K do |
| 7: Transform the kth RSV into 224*224 pictures; |
| 8: Using a trained MobileNetV2 network to predict the kth RSV; |
| 9: if V[:,k] = “effective” then |
| 10: S[k,k] = S[k,k]; |
| 11: A five-point smoothing is applied to the kth RSV; |
| 12: else V[:,k] = noise” |
| 13: S[k,k] = 0; |
| 14: end if |
| 15: end for |
| 16: =; |
| 17: Extract the reconstruction matrix w[] and insert it into the M[] matrix data; |
| 18: end for |
| 19: end for |
| 20: Return . |
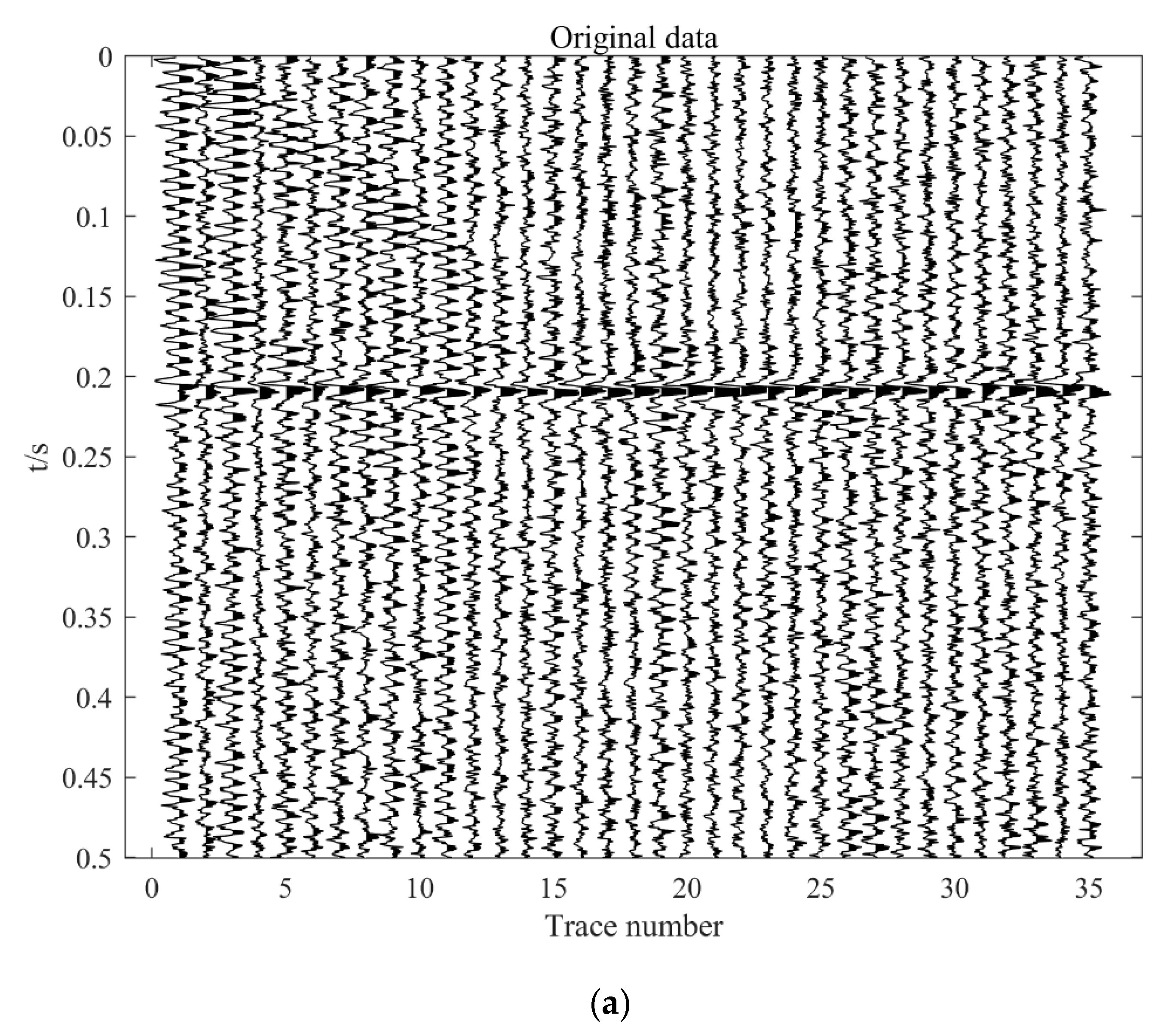
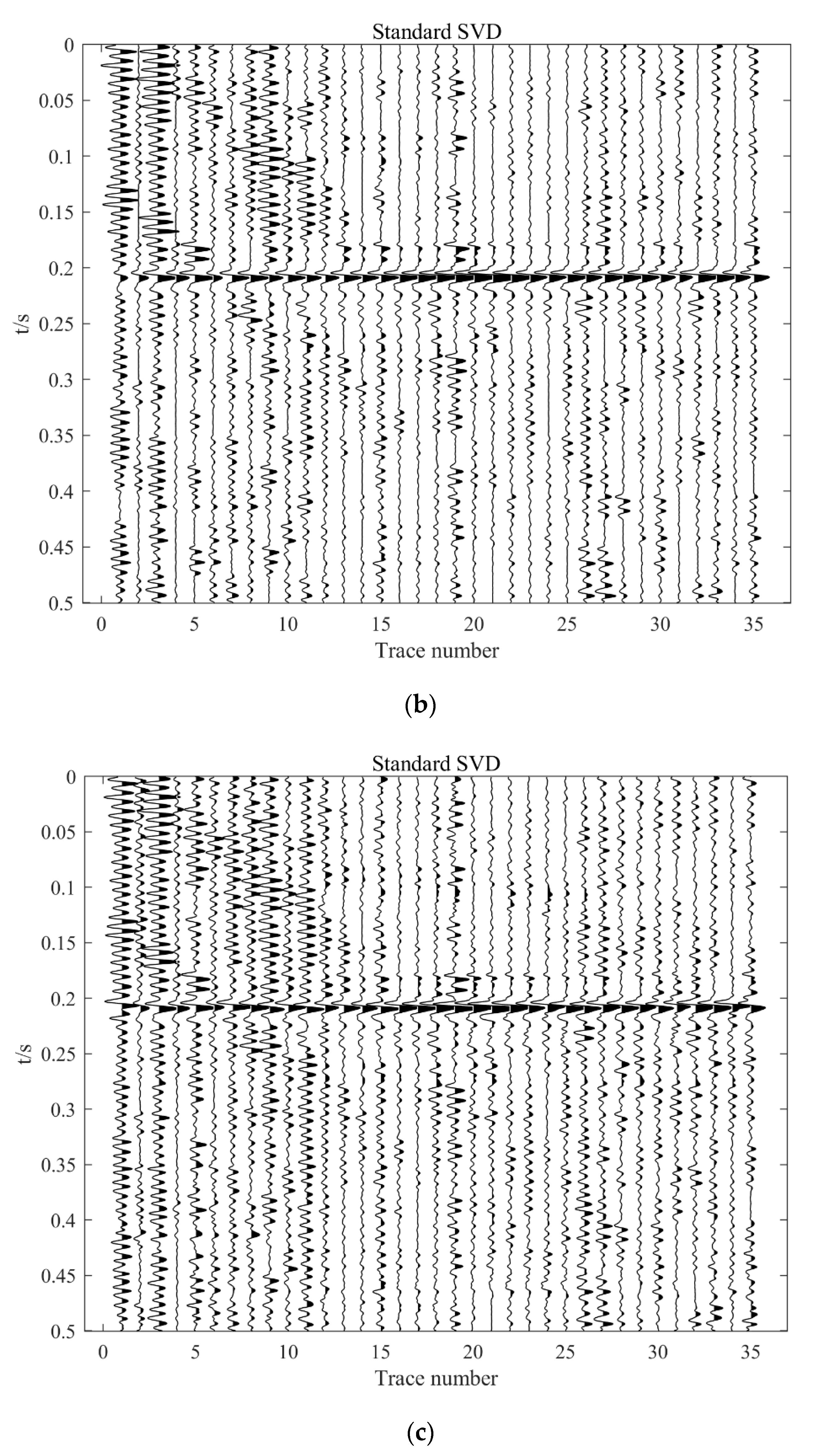
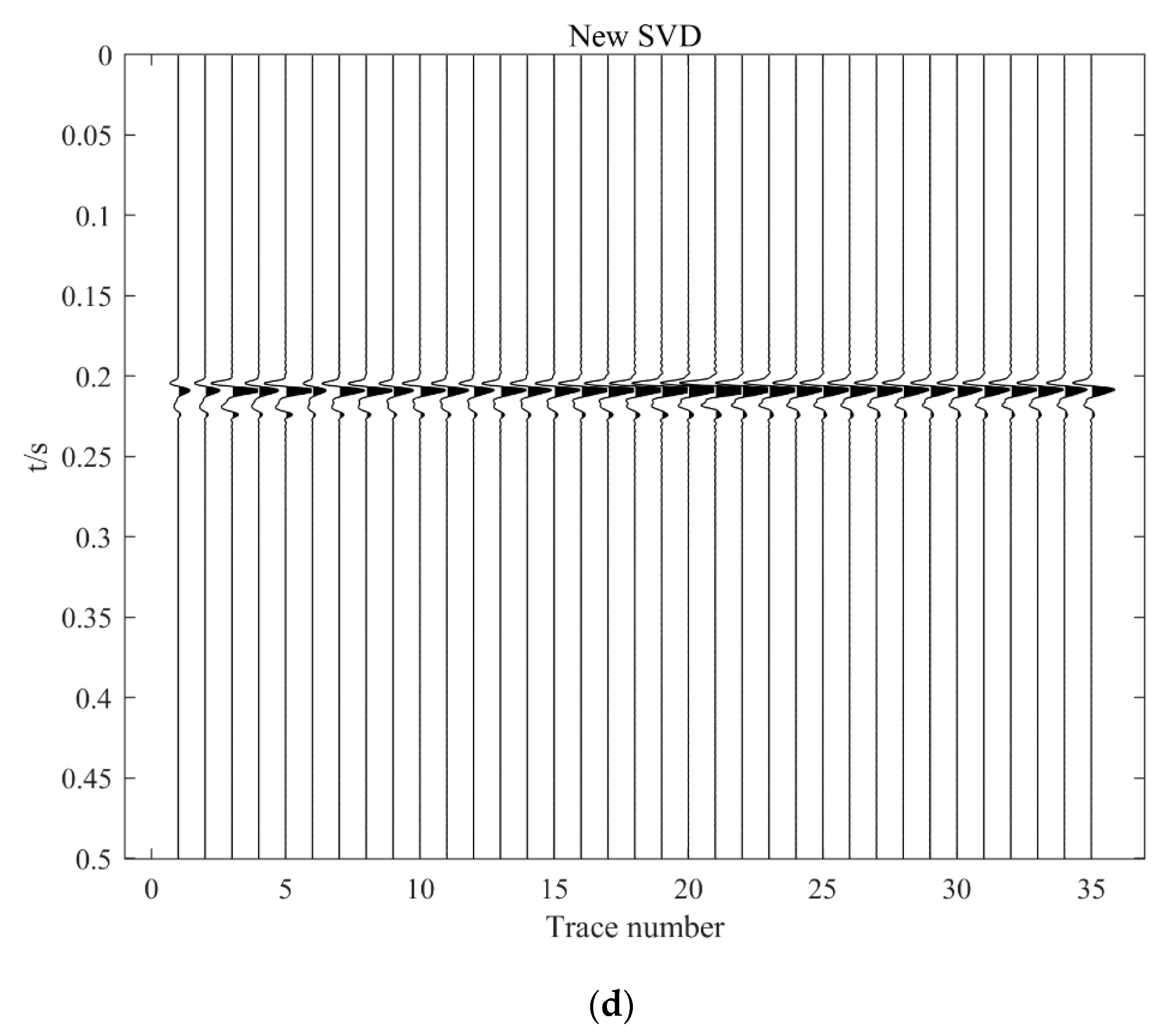
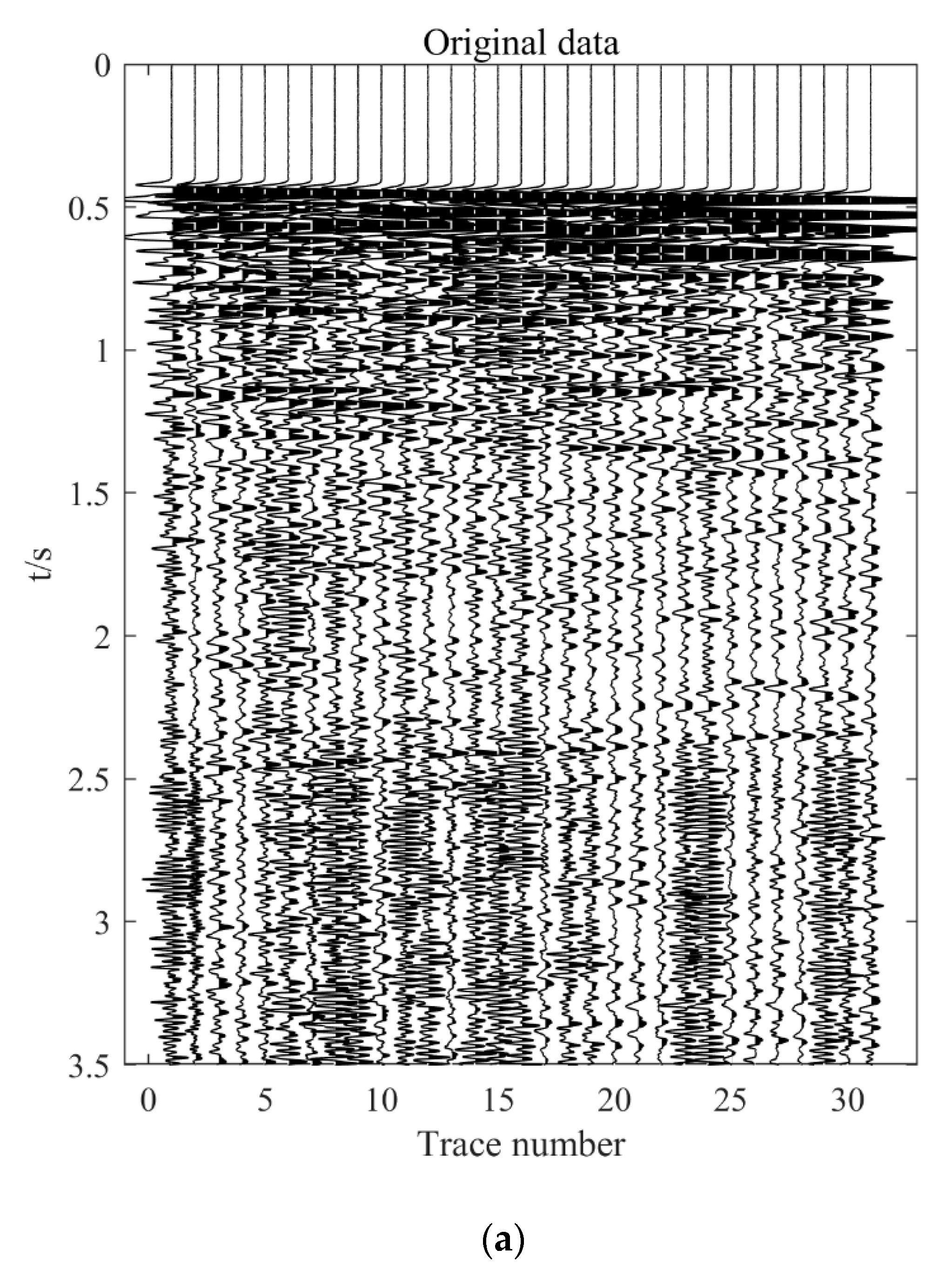
3. Results
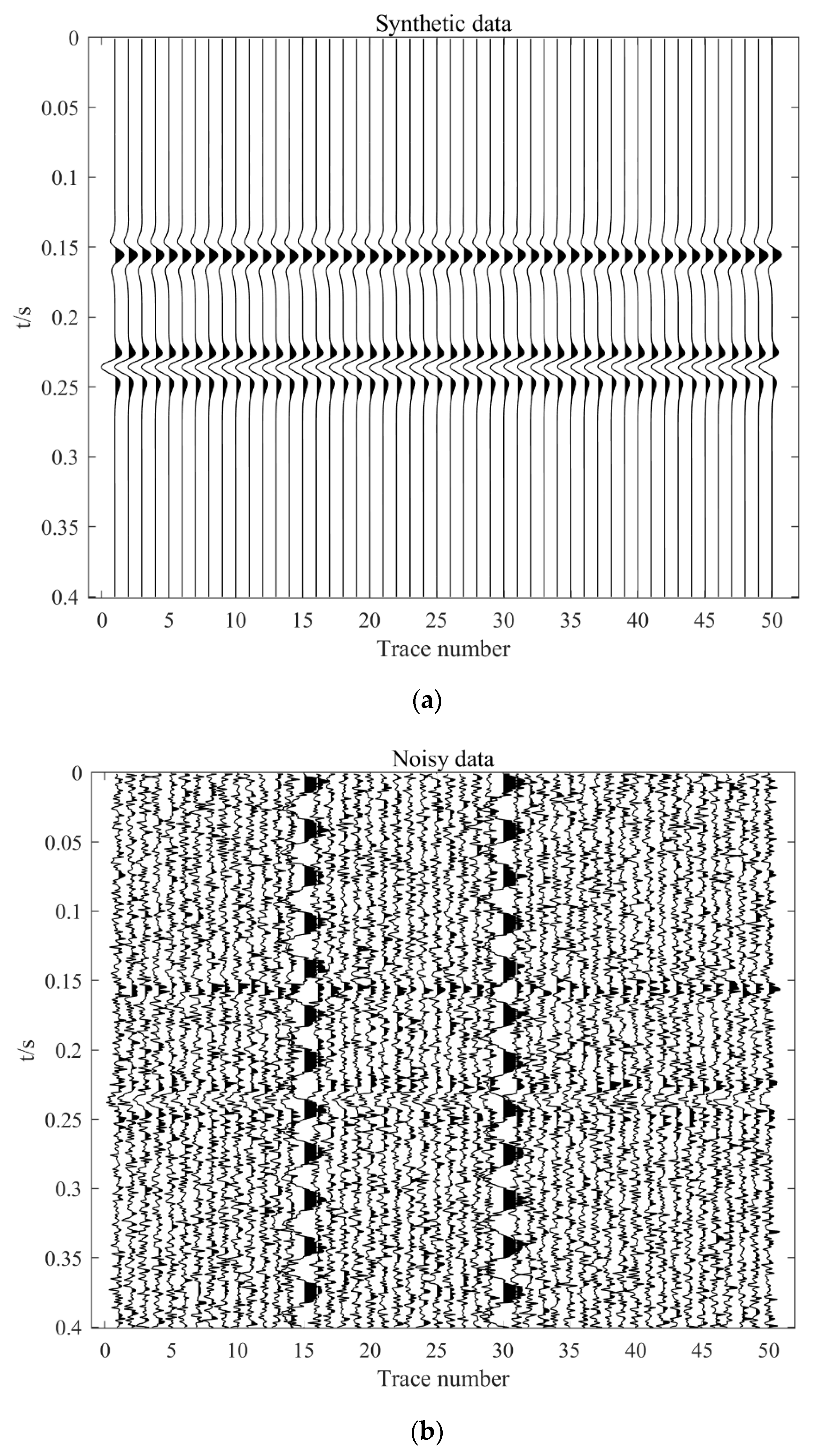
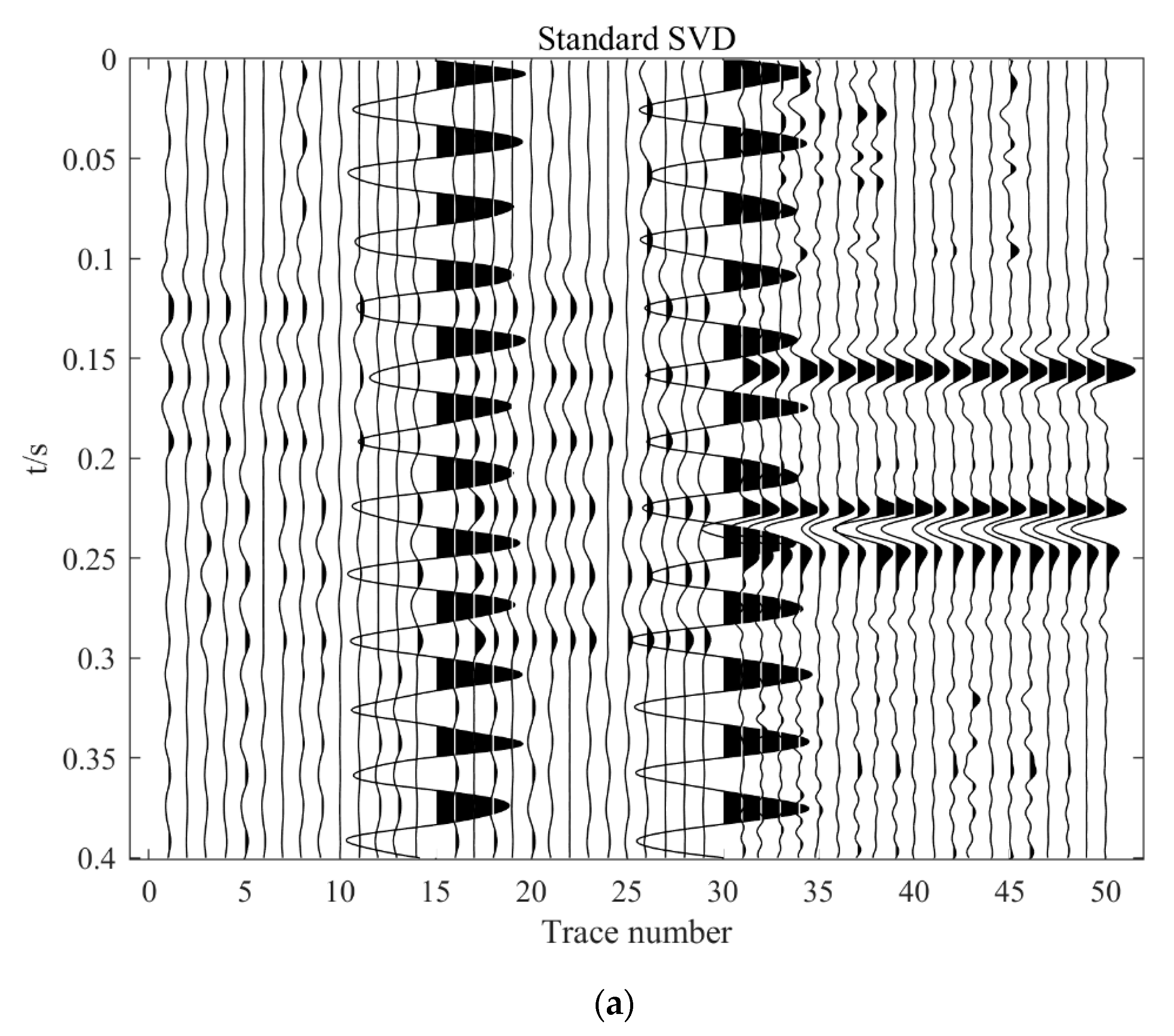
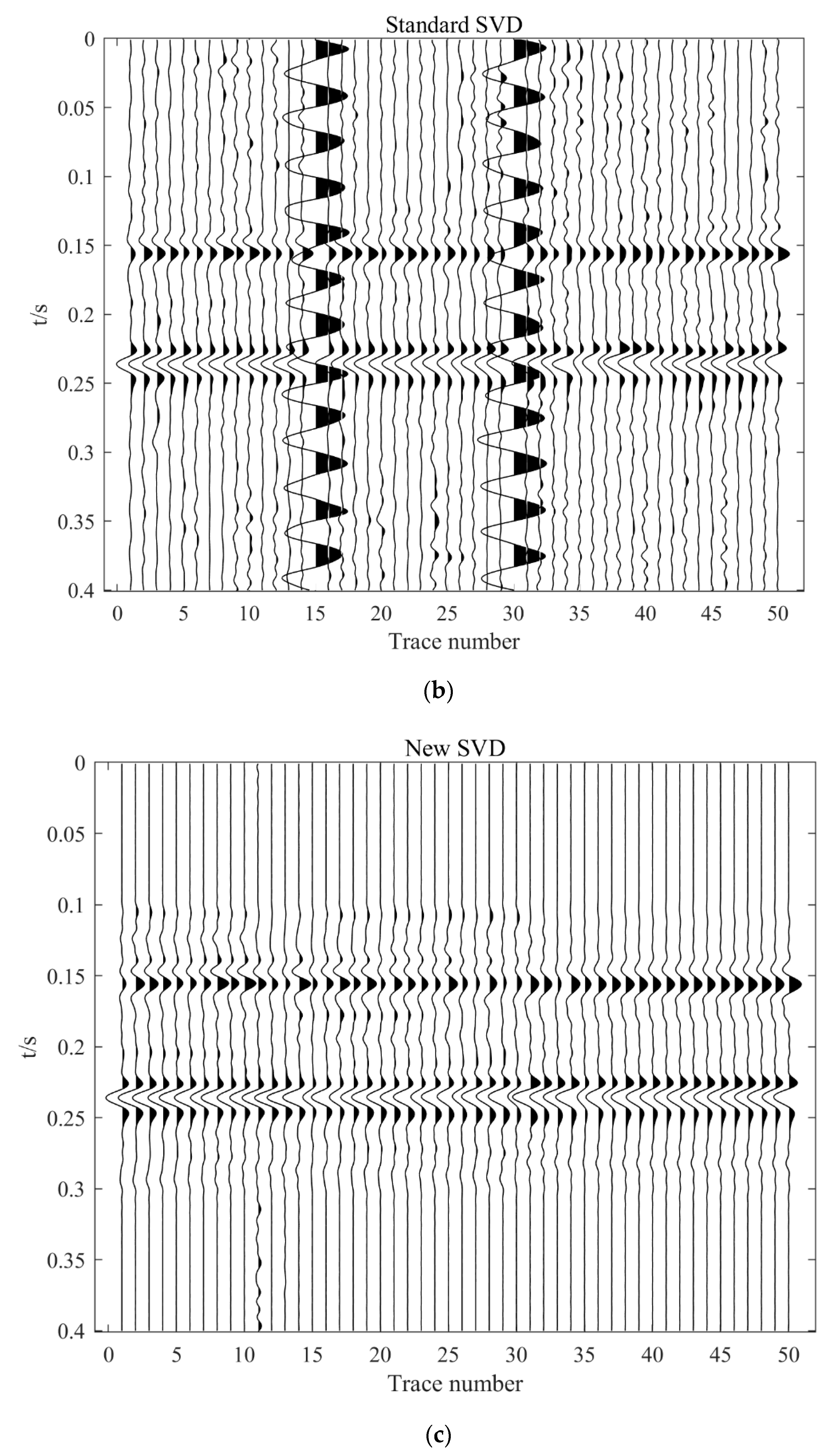
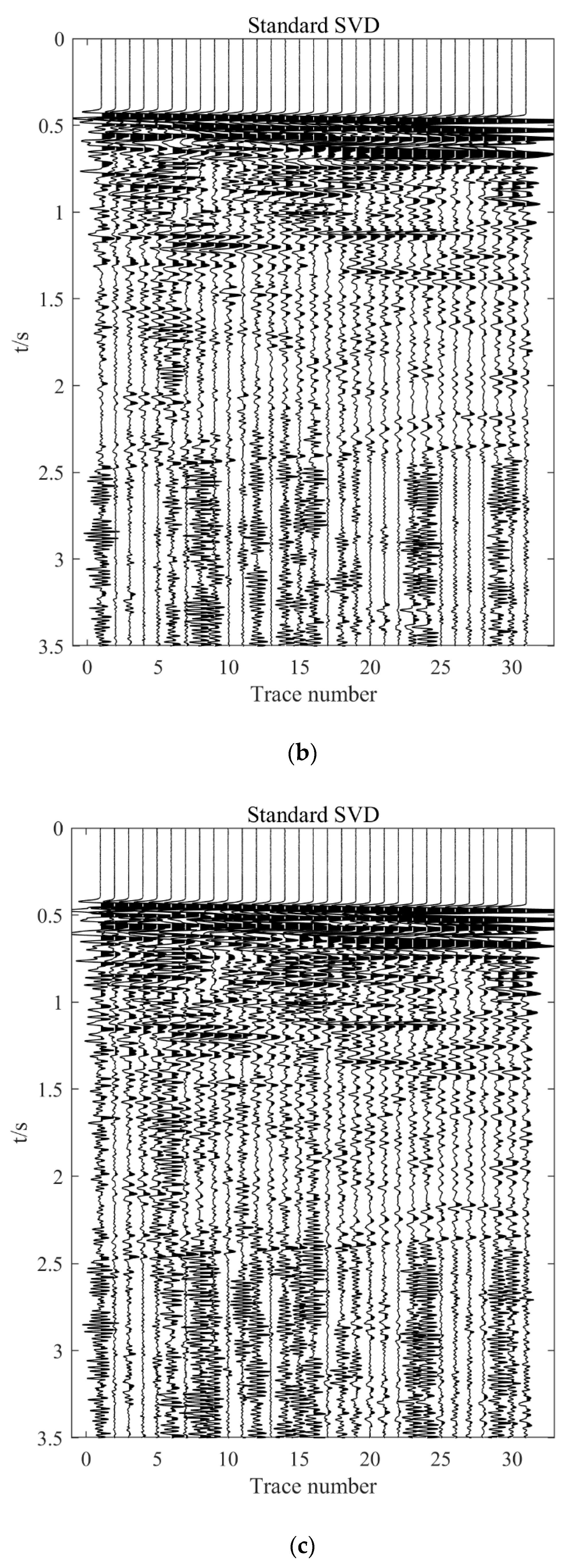
3.1. Synthetic Data
3.2. Field Data
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Lin, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. A Branch Construction-Based CNN Denoiser for Desert Seismic Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Z. Random-Noise Suppression in Seismic Data: What Can Deep Learning Do? In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2018; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2018; pp. 2016–2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Duan, Z. Seismic Signal Denoising Using f-x Variational Mode Decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Du, J.; Wu, K. Random noise attenuation using f-x regularized nonstationary autoregression. Geophysics 2012, 77, V61–V69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cai, J.; Hong, L.; Zheng, J. Research on Deep Convolutional Neural Network Time-Frequency Domain Seismic Signal Denoising Combined with Residual Dense Blocks. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, B. Streaming orthogonal prediction filter in the t-x domain for random noise attenuation. Geophysics 2018, 83, F41–F48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuehua, C.; Zhenhua, H.E. Improved S-Transform and Its Application in Seismic Signal Processing. J. Data Acquis. Process. 2005, 20, 449–453. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.J.; Gao, J.Y.; Hu, H.; Zhou, M.J. Wavelet transform based on GCV criterion and CUDA technology for ground roll attenuation. Prog. Geophys. 2018, 33, 760–768. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, S.; Luo, Y.; Kelamis, P.G. Simultaneous sources separation via multidirectional vector-median filtering. Geophysics 2012, 77, V123–V131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y. Vertical Seismic Profile Wavefield Separation Using Median Filtering Constrained by the Linear Radon Transform. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, P. Research on Seismic Signal Classification and Recognition Based on EEMD and CNN. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronics and Communication Engineering (ICECE), Xi’An, China, 14–16 December 2020; pp. 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Robust singular value decomposition filtering for low signal-to-noise ratio seismic data. Geophysics 2021, 86, V233–V244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekara, M.; van der Baan, M. Local singular value decomposition for signal enhancement of seismic data. Geophysics 2007, 72, V59–V65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Sacchi, M.D. Robust reduced-rank filtering for erratic seismic noise attenuation. Geophysics 2015, 80, V1–V11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brankovic, M.; Gildin, E.; Gibson, R.L.; Everett, M.E. A Machine Learning-Based Seismic Data Compression and Interpretation Using a Novel Shifted-Matrix Decomposition Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Li, Y. Denoising Deep Learning Network Based on Singular Spectrum Analysis—DAS Seismic Data Denoising with Multichannel SVDDCNN. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Mi, B.; Dai, T.; Liu, Y.; Ning, L. Spurious signals attenuation using SVD-based Wiener filter for near-surface ambient noise surface wave imaging. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 183, 104220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.; Ma, H. A Patch Based Denoising Method Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Seismic Image. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 156883–156894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liang, L.; Shi, Y.; Fomel, S. FaultSeg3D: Using synthetic data sets to train an end-to-end convolutional neural network for 3D seismic fault segmentation. Geophysics 2019, 84, IM35–IM45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ren, H.; Zhang, M. A Convolutional Autoencoder Method for Simultaneous Seismic Data Reconstruction and Denoising. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, X.; Fomel, S. SaltSeg: Automatic 3D salt segmentation using a deep convolutional neural network. Interpretation 2019, 7, SE113–SE122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Liu, F.; Cai, R.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ning, M.; Shen, S. Research on Seismic Signal Analysis Based on Machine Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]



| Model | Batch Size | Run Time (h) | ImageNet Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| restnet50 | 8 | 8.77 | 99.91 |
| MobileNetV2 | 16 | 3.25 | 99.94 |
| Input | Network Layer | Expansion Multiplier | Output Channels | Number Repetitions | Stride |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| conv2d | - | 32 | 1 | 2 | |
| bottleneck | 6 | 16 | 1 | 1 | |
| bottleneck | 6 | 24 | 2 | 2 | |
| bottleneck | 6 | 32 | 3 | 2 | |
| bottleneck | 6 | 64 | 4 | 2 | |
| bottleneck | 6 | 96 | 3 | 1 | |
| bottleneck | 6 | 160 | 3 | 2 | |
| bottleneck | 6 | 320 | 1 | 1 | |
| conv2d 1 1 | - | 1280 | 1 | 1 | |
| avgpool 7 7 | - | - | 1 | - | |
| conv2d 1 1 | - | k | - |
| Method | Seismic Data with Noise | Conventional SVD,K = 1 | Conventional SVD,K = 2 | Improved SVD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR (dB) | −10.2592 | −6.8822 | −6.5176 | 8.1007 |
| Method | Original Data | Conventional SVD, K = 1 | Conventional SVD, K = 2 | Improved SVD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR (dB) | 11.3336 | 18.5297 | 16.8173 | 65.7588 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, G.; Wang, C. A Denoising Method for Seismic Data Based on SVD and Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12840. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412840
Ji G, Wang C. A Denoising Method for Seismic Data Based on SVD and Deep Learning. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):12840. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412840
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Guoli, and Chao Wang. 2022. "A Denoising Method for Seismic Data Based on SVD and Deep Learning" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 12840. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412840
APA StyleJi, G., & Wang, C. (2022). A Denoising Method for Seismic Data Based on SVD and Deep Learning. Applied Sciences, 12(24), 12840. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412840





