JARUA: Joint Embedding of Attributes and Relations for User Alignment across Social Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel embedding-based UA model to incorporate attributes and network structure into a unified optimization framework which is robust to user attributes missing or sparse networks.
- A multi-granularity attribute representation method is developed to effectively process multi-type user attributes.
- An iterative training algorithm with filtering mechanics, which utilizes numerous unlabeled data to bootstrap the model performances.
- Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of JARUA over a series of comparison methods.
2. Related Work
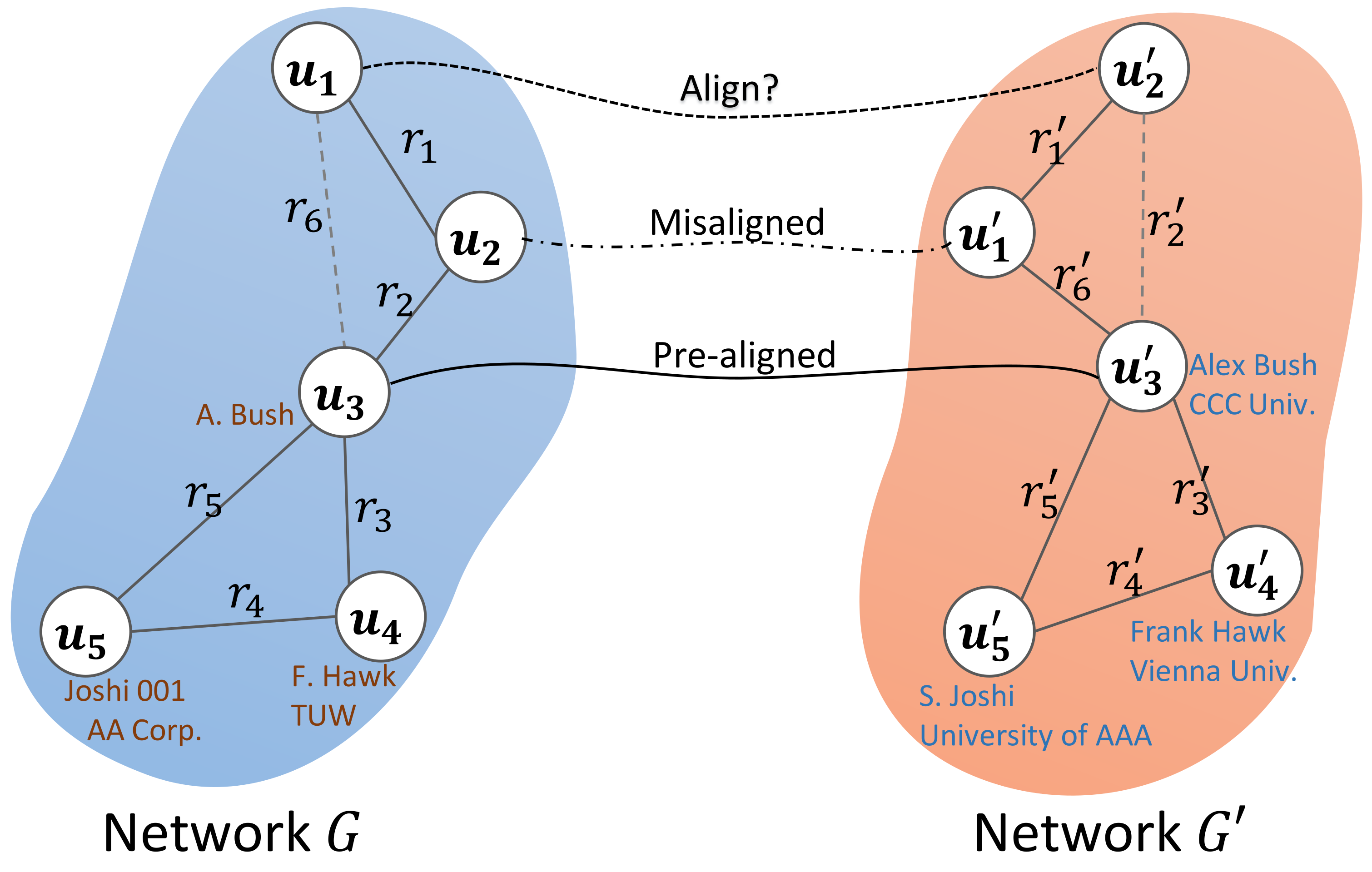
3. Problem Formulation
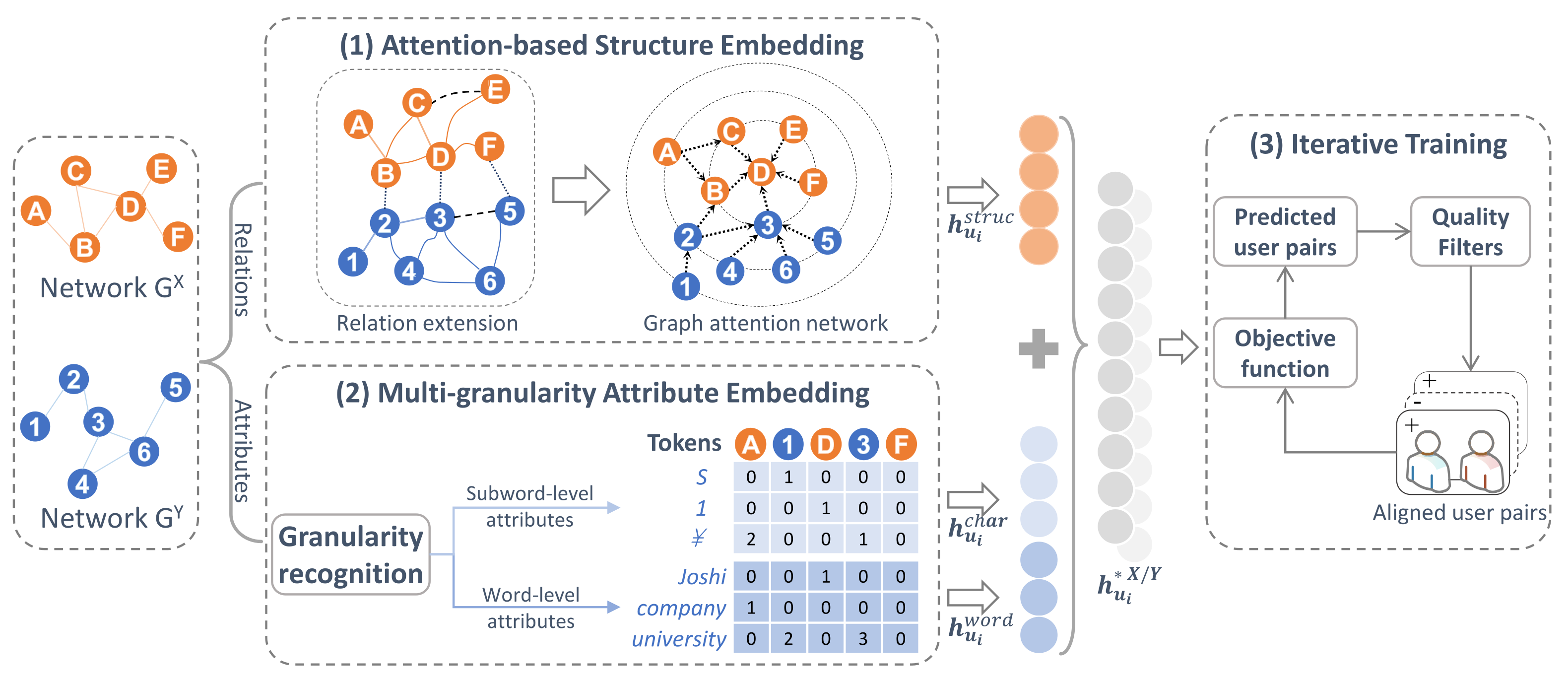
4. Methodology
4.1. Overview
4.2. Multi-Granularity Attribute Embedding
4.2.1. Attribute Granularity Recognition
4.2.2. Subword-Level Attribute Embedding
4.2.3. Word-Level Attribute Embedding
4.3. Attention-Based Structure Embedding
4.3.1. Relation Extension
4.3.2. Graph Attention Network
4.4. User Alignment
4.5. Iterative Training
- (1)
- Train the model with a set of initially labeled data, i.e., pre-linked user pairs.
- (2)
- Predict the new auto-labeled data iteratively and add them to the next iteration until no new one can be populated.
| Algorithm 1: Iterative procedure of JARUA. |
 |
5. Experiments
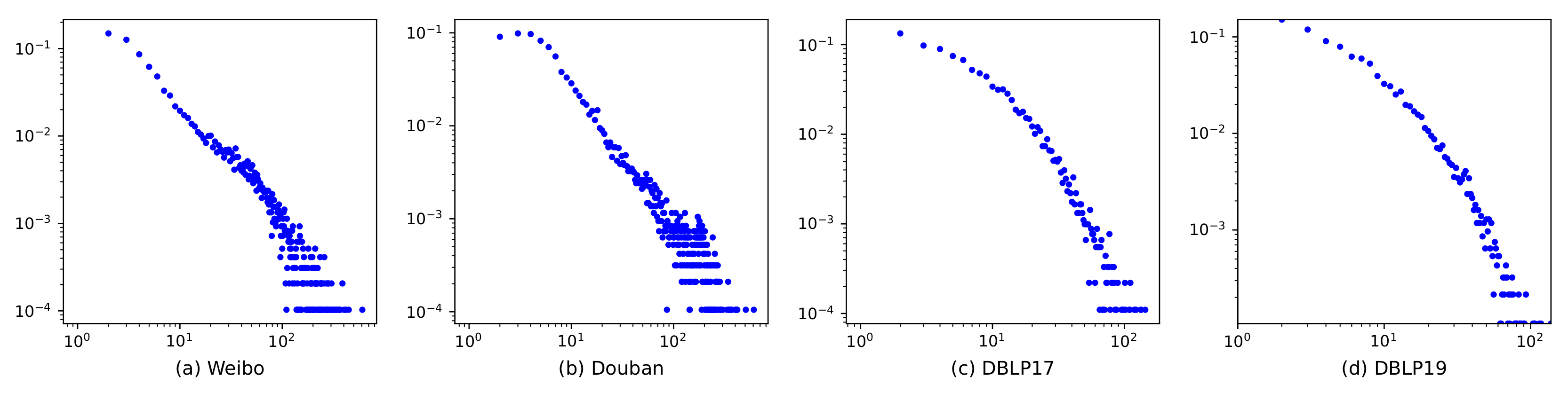
5.1. Data Sets
5.2. Experimental Settings
5.2.1. Comparison Methods
- IONE [38]: A semi-supervised method based on network structures, in which users’ relations are represented as input/output context vectors.
- REGAL [13]: An unsupervised network alignment method that incorporates both network structures and attributes. In this experiment, TF-IDF is utilized to represent node attributes.
- ABNE [25]: A graph attention-based UA model, which exploits the network structure by modeling the contribution probabilities in users’ relationships.
- TADW [50]: An attributed network embedding model. In our experiment, an MLP is employed to map source embeddings to target space for the UA task.
- CENALP [52]: An embedding model that jointly performs link prediction and network alignment using the skip-gram framework. The weight parameter c is fine-tuned from 0.1 to 0.9 with a step size 0.1 for optimal results.
- Grad-Align [53]: A semi-supervised model that gradually predicts aligned node pairs by node consistency and prior information. The gradual matching function is set to a base-2 exponential function.
- Grad-Align+ [54]: An extension of Grad-Align that use attribute augmentation for UA.
- JARUA-a, which ignores the components of structure embedding. Attributes are adopted as the only features to perform the UA task.
- JARUA-s, which takes only network structural features for user alignment, ignoring attribute features.
- JARUA-v, which directly combines the attribute embedding component and structure embedding component to align users without iterative training.
- JARUA-t, which replaces the multi-granularity attribute embedding module of JARUA with TF-IDF vectors to represent user attributes.
- (1)
- Structure based: IONE, ABNE, PALE, and JARUA-s.
- (2)
- Attribute based: JARUA-a.
- (3)
- Combination of structure and attributes: REGAL, TADW, CENALP, Grad-Align, Grad-Align+, JARUA-v, JARUA-t, and JARUA.
5.2.2. Evaluation Metric
5.2.3. Implementation Details
5.3. Experimental Results
5.3.1. Comparative Performances
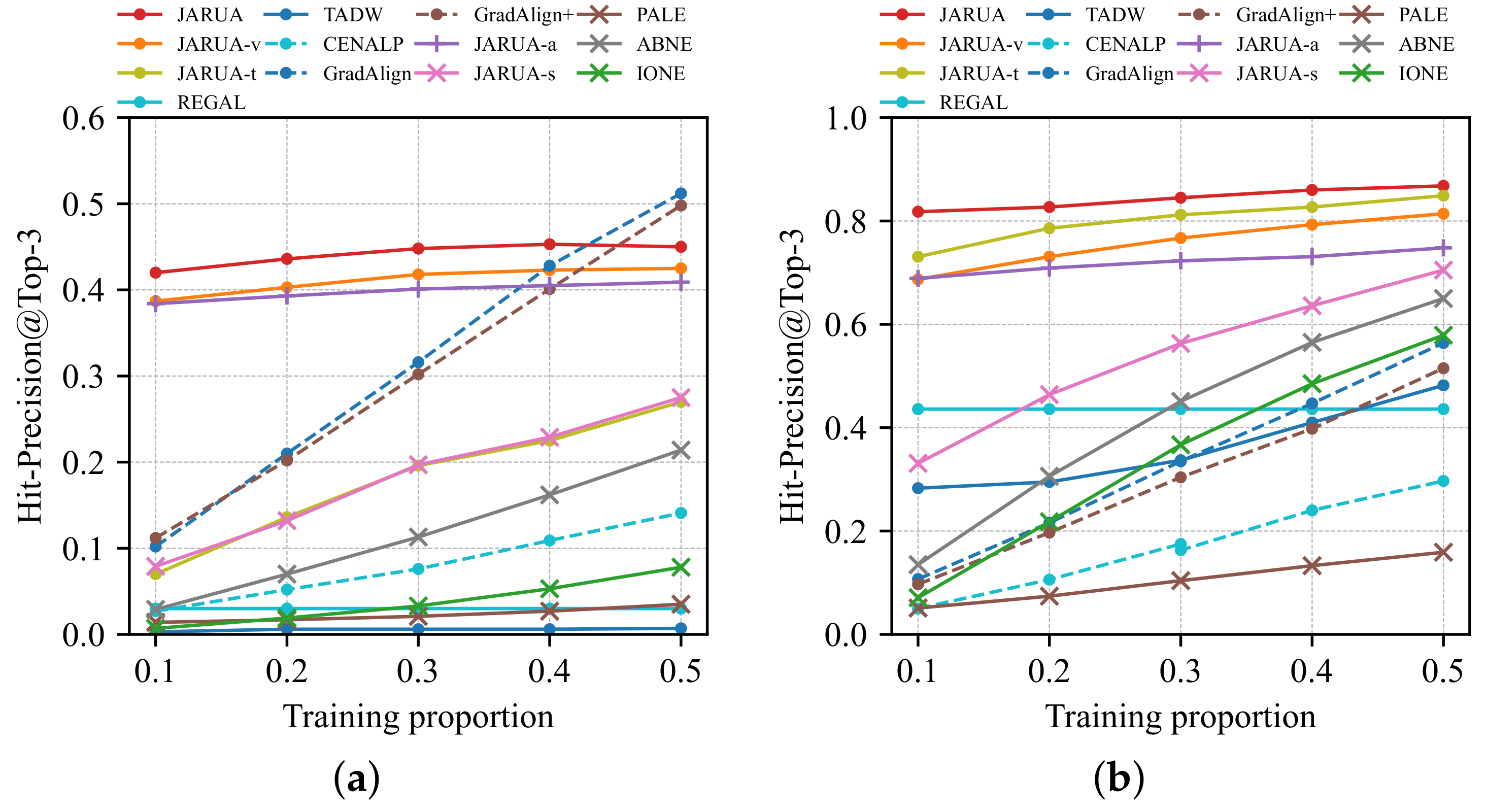
5.3.2. The Effect of Training Proportions
5.3.3. The Contribution of Model Components
5.3.4. Parameter Analysis
5.3.5. Discussions
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shu, K.; Wang, S.; Tang, J.; Zafarani, R.; Liu, H. User Identity Linkage across Online Social Networks: A Review. Sigkdd Explor. Newsl. 2017, 18, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Hua, X.S. Social Friend Recommendation Based on Multiple Network Correlation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2016, 18, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, P.S.; Zhou, Z.H. Meta-path based multi-network collective link prediction. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, NY, USA, 24–27 August 2014; pp. 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafarani, R.; Liu, H. Users joining multiple sites: Distributions and patterns. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1–4 June 2014; pp. 635–638. [Google Scholar]
- Zafarani, R.; Liu, H. Users joining multiple sites: Friendship and popularity variations across sites. Inf. Fusion 2016, 28, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Song, G.; Chen, H.; Li, C.; Jin, F.; Zhang, Y. MEgo2Vec: Embedding matched ego networks for user alignment across social networks. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Torino, Italy, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, X. MAUIL: Multi-level attribute embedding for semi-supervised user identity linkage. Inf. Sci. 2022, 593, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Totti, L.; Meira, W., Jr.; Kumaraguru, P.; Almeida, V. Studying User Footprints in Different Online Social Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining, Istanbul, Turkey, 26–29 August 2012; pp. 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquisti, A.; Gross, R.; Stutzman, F. Face Recognition and Privacy in the Age of Augmented Reality. J. Priv. Confid. 2014, 6, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Jin, D. DPlink: User identity linkage via deep neural network from heterogeneous mobility data. In Proceedings of the World Wide Web Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kong, X.; Yu, P.S. Transferring Heterogeneous Links across Location-Based Social Networks. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM international Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, New York, NY, USA, 24–28 February 2014; pp. 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaolin, C.; Xuemeng, S.; Siwei, C.; Tian, G.; Zhiyong, C.; Liqiang, N. User Identity Linkage Across Social Media via Attentive Time-Aware User Modeling. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 3957–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, M.; Safavi, T.; Shen, H.; Koutra, D. REGAL: Representation Learning-based Graph Alignment. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Torino, Italy, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, Z. Social network alignment: A bi-layer graph attention neural networks based method. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 16310–16333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Cao, Y.; Guo, M.; Nie, Z. CoLink: An unsupervised framework for user identity linkage. In Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 5714–5721. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, J.; Yang, Z.; Pei, J.; Yu, P.S. COSNET: Connecting Heterogeneous Social Networks with Local and Global Consistency. In Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 10–13 August 2015; pp. 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikovi, P.; Casanova, A.; Lio, P.; Cucurull, G.; Romero, A.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zafaranl, R.; Liu, H. Connecting Corresponding Identities across Communitie. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; pp. 354–357. [Google Scholar]
- Vosecky, J.; Hong, D.; Shen, V.Y. User identification across multiple social networks. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Networked Digital Technologies, Ostrava, Czech Republic, 28–31 July 2009; pp. 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, P.S. Inferring anchor links across multiple heterogeneous social networks. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27 October–1 November 2013; pp. 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iofciu, T.; Fankhauser, P.; Abel, F.; Bischoff, K. Identifying Users Across Social Tagging Systems. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, Barcelona, Spain, 17–21 July 2011; pp. 522–525. [Google Scholar]
- Man, T.; Shen, H.; Liu, S.; Jin, X.; Cheng, X. Predict anchor links across social networks via an embedding approach. In Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 9–15 July 2016; pp. 1823–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, X.; Zhu, F.; Lim, E.P.; Xiao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.H. User identity linkage by latent user space modelling. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Zhu, F. Structured Learning from Heterogeneous Behavior for Social Identity Linkage. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2015, 27, 2005–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Fu, S.; Zhong, F.J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, P. ABNE: An Attention-Based Network Embedding for User Alignment Across Social Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 23595–23605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Duo, F.; Lin, W.; Yang, J. Siamese Neural Networks for User Identity Linkage Through Web Browsing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 31, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Su, Z.; Yang, J.; Gao, C. Exploiting similarities of user friendship networks across social networks for user identification. Inf. Sci. 2020, 506, 78–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wang, G.; Xia, S.; Liu, L. Deep multi-granularity graph embedding for user identity linkage across social networks. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 193, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Cao, Y.A.; Li, Q.; Shang, Y.M.; Li, Y.X.; Liu, Y.B.; Xu, G.D. RLINK: Deep reinforcement learning for user identity linkage. World Wide Web 2021, 24, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, F.; Song, X.; Song, Y.I.; Lin, C.Y.; Hon, H.W. What’s in a name? An unsupervised approach to link users across communities. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Rome, Italy, 4–8 February 2013; pp. 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, S.; Yu, P.S.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y. Distribution distance minimization for unsupervised user identity linkage. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Torino, Italy, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoste-Julien, S.; Palla, K.; Davies, A.; Kasneci, G.; Graepel, T.; Ghahramani, Z. SiGMa: Simple greedy matching for aligning large knowledge bases. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Chicago, IL, USA, 11–14 August 2013; pp. 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.P.; Jia, Y.; Li, S.D.; Zhu, X.; Li, A.P.; Zhou, B. Identifying users across social networks based on dynamic core interests. Neurocomputing 2016, 210, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riederer, C.; Kim, Y.; Chaintreau, A.; Korula, N.; Lattanzi, S. Linking Users Across Domains with Location Data: Theory and Validation. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on World Wide Web, Montréal, QC, Canada, 11–15 May 2016; pp. 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, X.; Du, X.; Zhao, J. Structure Based User Identification across Social Networks. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2018, 30, 1178–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Wen, Z.J.; Zhong, T.; Trajcevski, G.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.Y. Unsupervised User Identity Linkage via Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM 2020), Taipei, Taiwan, 7–11 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ji, W.; Gao, X.; Deng, Y.; Dong, W.; Li, D. Matching user accounts with spatio-temporal awareness across social networks. Inf. Sci. 2021, 570, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cheung, W.K.; Li, X.; Liao, L. Aligning users across social networks using network embedding. In Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 9–15 July 2016; pp. 1774–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.; Guan, Z.; Cai, D.; Qin, X.; Bu, J.; Chen, C. Mapping users across networks by manifold alignment on hypergraph. In Proceedings of the 28th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Québec, QC, Canada, 27–31 July 2014; pp. 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Liang, X.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y. Cross-Platform Identification of Anonymous Identical Users in Multiple Social Media Networks. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2016, 28, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Tan, S.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, B.; Gong, M.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Q. Learning to Map Social Network Users by Unified Manifold Alignment on Hypergraph. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 5834–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, P.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Adversarial Learning for Weakly-Supervised Social Network Alignment. In Proceedings of the 33nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Liang, Y.; Yu, P.S.; Li, Z.; Wang, W. Partially shared adversarial learning for semi-supervised multi-platform user identity linkage. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Beijing, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, X.; Cheung, W.K.; Liao, L.J. Structural Representation Learning for User Alignment Across Social Networks. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 32, 1824–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Chen, Y.J.; Fu, J.M. MFRep: Joint user and employer alignment across heterogeneous social networks. Neurocomputing 2020, 414, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tata, S.; Patel, J. Estimating the Selectivity of tf-idf based Cosine Similarity Predicates. SIGMOD Rec. 2007, 36, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halko, N.; Martinsson, P.G.; Tropp, J.A. Finding Structure with Randomness: Probabilistic Algorithms for Constructing Approximate Matrix Decompositions. SIAM Rev. 2009, 53, 217–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, H.; Lan, M.; Wu, Y. MRAEA: An Efficient and Robust Entity Alignment Approach for Cross-lingual Knowledge Graph. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Houston, TX, USA, 3–7 February 2020; pp. 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J.L. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Sun, M.; Chang, E.Y. Network Representation Learning with Rich Text Information. In Proceedings of the 24th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 25–31 July 2015; pp. 2111–2117. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Qu, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M.; Yan, J.; Mei, Q. LINE: Large-scale Information Network Embedding. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web, Florence, Italy, 18–22 May 2015; pp. 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, R.; Zha, H. Cross-Network Skip-Gram Embedding for Joint Network Alignment and Link Prediction. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 34, 1080–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.D.; Tran, C.; Shin, W.Y.; Cao, X. Grad-Align: Gradual Network Alignment via Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, virtually, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 13027–13028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.D.; Tran, C.; Shin, W.Y.; Cao, X. Grad-Align+: Empowering Gradual Network Alignment Using Attribute Augmentation. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–21 October 2022; CIKM 2022. pp. 4374–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Texts | Basic Tokens | |
|---|---|---|
| ♣Joshi♣ | ♣, Joshi, ♣ | 0.33 |
| Joshi0001 | Joshi, 0001 | 0.50 |
| University of Florida | University, of, Florida | 1.00 |
| A hierarchical three way interconnect architecture for hexagonal processors | A, hierarchical, three, way, interconnect, architecture, for, hexagonal, processors | 1.00 |
| Dataset | Network | #Users | #Relations | Min. Degree | Ave. Degree | Max. Degree | Ave. Coeff. | #Aligned Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social networks | 9714 | 117,218 | 2 | 12.1 | 607 | 0.112 | 1397 | |
| Douban | 9526 | 120,245 | 2 | 12.6 | 608 | 0.101 | ||
| Coauthor networks | DBLP17 | 9086 | 51,700 | 2 | 5.7 | 144 | 0.280 | 2832 |
| DBLP19 | 9325 | 47,775 | 2 | 5.1 | 138 | 0.322 |
| Method | Weibo-Douban | DBLP17-DBLP19 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k = 1 | k = 3 | k = 5 | k = 1 | k = 3 | k = 5 | |
| IONE | 0.022 | 0.033 | 0.042 | 0.282 | 0.367 | 0.418 |
| PALE | 0.012 | 0.021 | 0.029 | 0.062 | 0.104 | 0.136 |
| ABNE | 0.089 | 0.113 | 0.128 | 0.362 | 0.451 | 0.502 |
| REGAL | 0.016 | 0.030 | 0.041 | 0.411 | 0.436 | 0.452 |
| TADW | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.241 | 0.337 | 0.398 |
| CENALP | 0.076 | 0.076 | 0.076 | 0.175 | 0.175 | 0.176 |
| Grad-Align | 0.300 | 0.316 | 0.329 | 0.306 | 0.335 | 0.353 |
| Grad-Align+ | 0.299 | 0.302 | 0.305 | 0.288 | 0.304 | 0.316 |
| JARUA-s | 0.156 | 0.197 | 0.220 | 0.467 | 0.563 | 0.615 |
| JARUA-a | 0.368 | 0.401 | 0.419 | 0.696 | 0.723 | 0.738 |
| JARUA-v | 0.383 | 0.418 | 0.436 | 0.740 | 0.767 | 0.782 |
| JARUA-t | 0.159 | 0.196 | 0.221 | 0.785 | 0.812 | 0.829 |
| JARUA | 0.416 | 0.448 | 0.464 | 0.821 | 0.845 | 0.858 |
| Parameters | Weibo-Douban | DBLP17-DBLP19 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k = 1 | k = 3 | k = 5 | k = 1 | k = 3 | k = 5 | |
| 0.385 | 0.418 | 0.436 | 0.743 | 0.770 | 0.785 | |
| 0.383 | 0.418 | 0.436 | 0.740 | 0.767 | 0.782 | |
| 0.385 | 0.417 | 0.435 | 0.739 | 0.767 | 0.782 | |
| 0.384 | 0.415 | 0.433 | 0.740 | 0.769 | 0.783 | |
| Range | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| 0.387 | 0.419 | 0.437 | 0.732 | 0.762 | 0.777 | |
| 0.389 | 0.419 | 0.436 | 0.743 | 0.770 | 0.784 | |
| 0.383 | 0.418 | 0.436 | 0.740 | 0.767 | 0.782 | |
| 0.382 | 0.414 | 0.432 | 0.741 | 0.767 | 0.782 | |
| Range | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.011 | 0.008 | 0.008 |
| 0.382 | 0.412 | 0.429 | 0.712 | 0.740 | 0.756 | |
| 0.381 | 0.415 | 0.433 | 0.727 | 0.755 | 0.771 | |
| 0.383 | 0.418 | 0.436 | 0.740 | 0.767 | 0.782 | |
| 0.387 | 0.419 | 0.438 | 0.750 | 0.777 | 0.791 | |
| Range | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.038 | 0.037 | 0.036 |
| 0.384 | 0.414 | 0.431 | 0.734 | 0.770 | 0.789 | |
| 0.383 | 0.418 | 0.436 | 0.740 | 0.767 | 0.782 | |
| 0.375 | 0.411 | 0.430 | 0.731 | 0.757 | 0.770 | |
| 0.369 | 0.400 | 0.417 | 0.719 | 0.742 | 0.755 | |
| Range | 0.015 | 0.018 | 0.019 | 0.021 | 0.027 | 0.034 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Chen, B.; Chen, X. JARUA: Joint Embedding of Attributes and Relations for User Alignment across Social Networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412709
Yang M, Chen B, Chen X. JARUA: Joint Embedding of Attributes and Relations for User Alignment across Social Networks. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):12709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412709
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Min, Baiyang Chen, and Xiaoliang Chen. 2022. "JARUA: Joint Embedding of Attributes and Relations for User Alignment across Social Networks" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 12709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412709
APA StyleYang, M., Chen, B., & Chen, X. (2022). JARUA: Joint Embedding of Attributes and Relations for User Alignment across Social Networks. Applied Sciences, 12(24), 12709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412709









