Modified Hand–Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Brief Overview of the Hand–Eye Equation
1.2. Dual Quaternion Algebra and Hand–Eye Calibration
2. Methodology
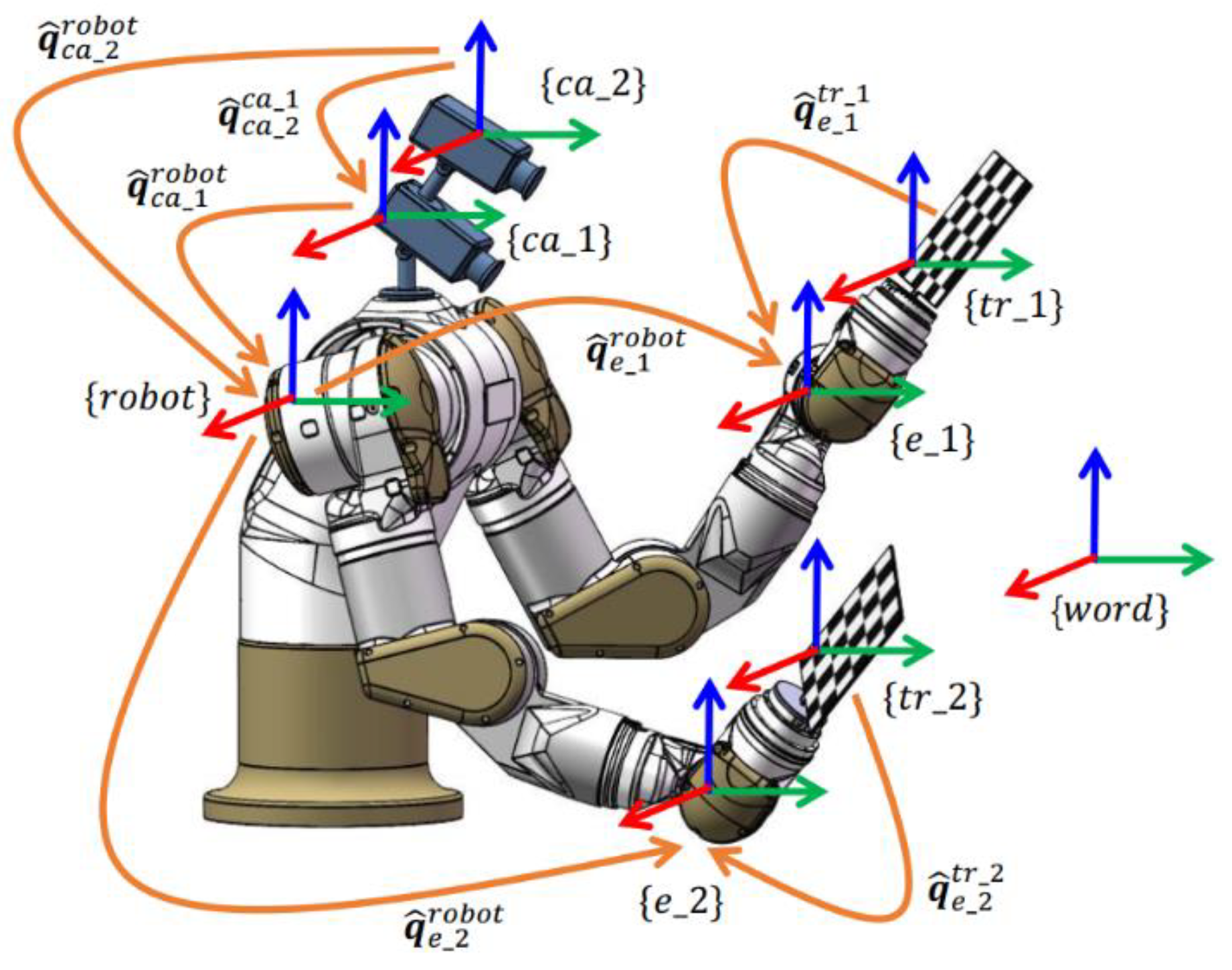
2.1. Kinematic Analysis of the Dual-Arm Hand–Eye Robot Based on Dual Quaternion
2.2. Identification Algorithm of Each Dual Part and Scalar Part of the Dual Quaternion
| Algorithm 1: Modified hand–eye calibration for the dual-arm robot system using dual quaternion |
| Input: The pictures captured by cameras; the poses data of end-effectors; the corresponding dual quaternions , . 1: Compute the real part and the dual part of based on Equations (6), (11), and (12). 2: initial the first solution in step 1; 3: while , do Form solution based on Equations (11) and (12); ; 4: Form kinematic equation of robot system based on Equations (15) and (16); end while Output: |
3. Simulation and Discussion
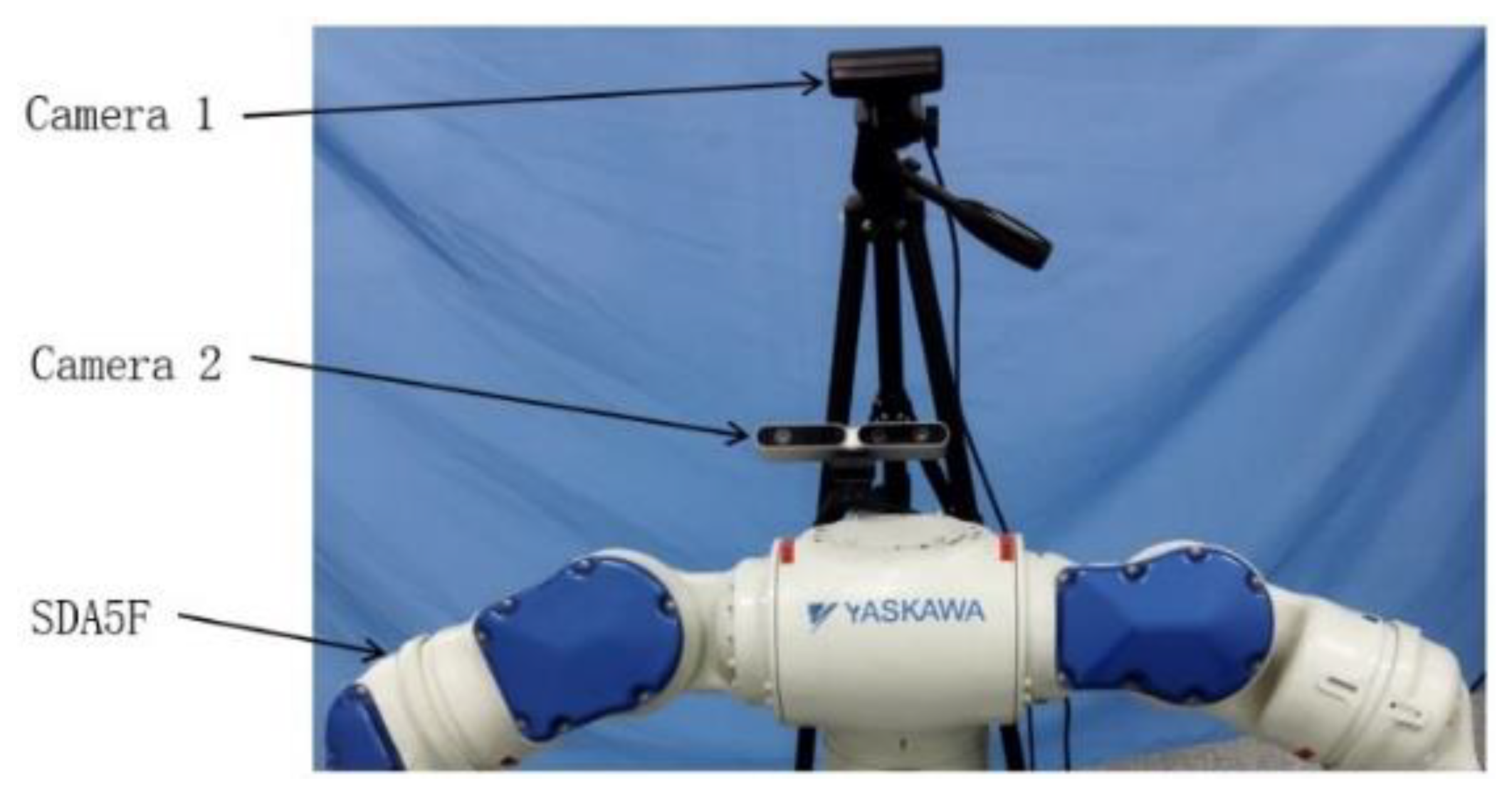
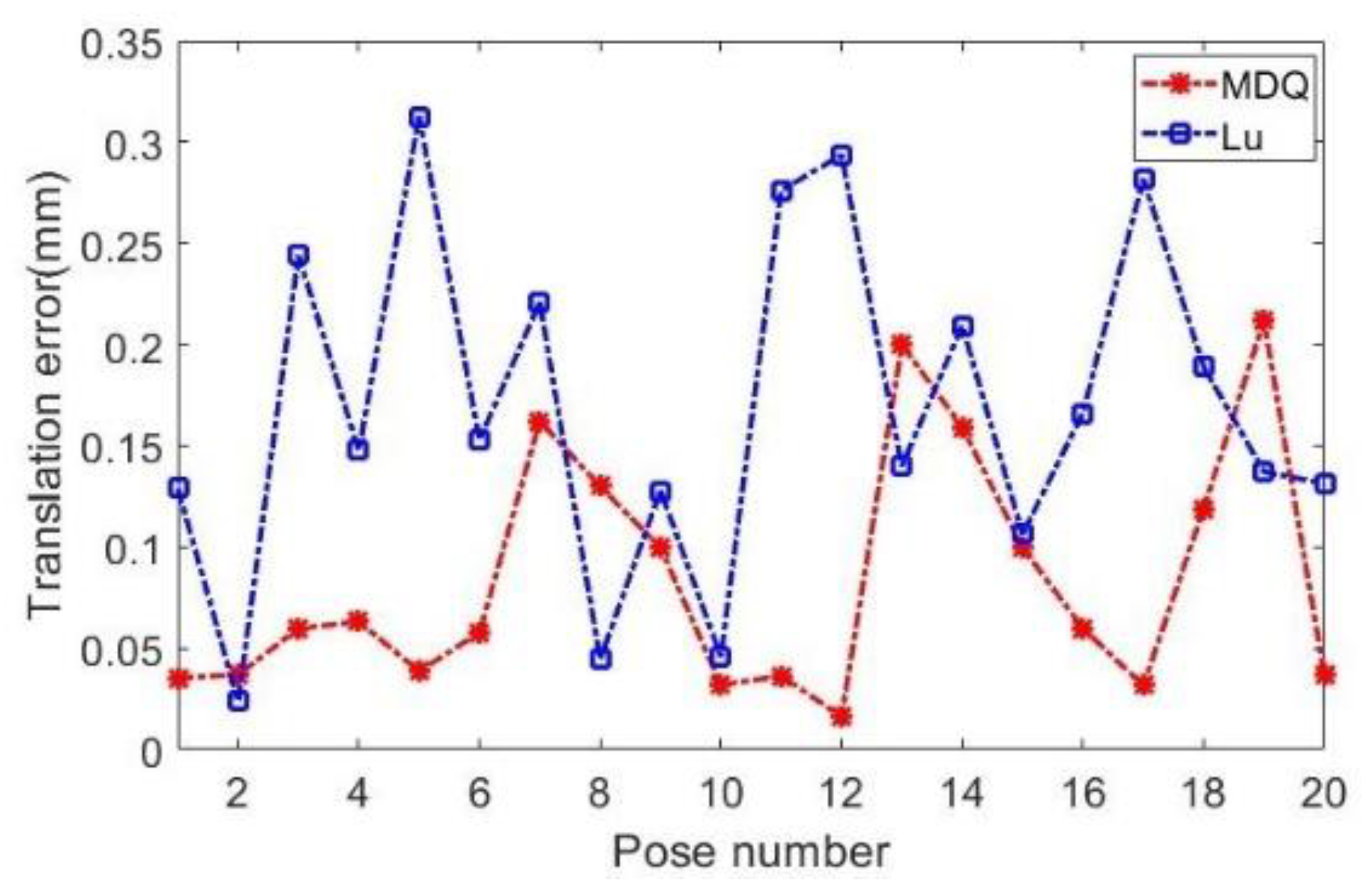
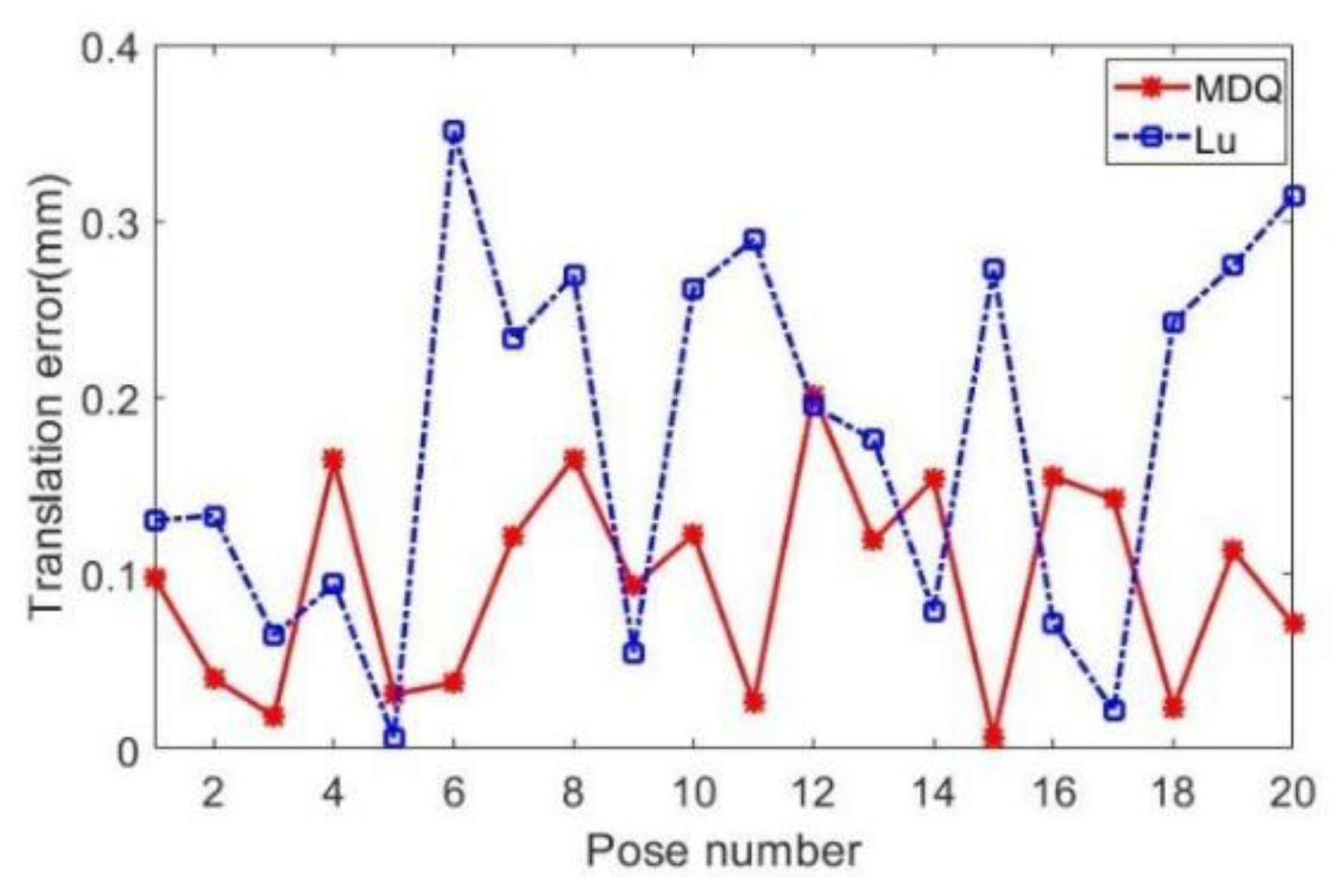
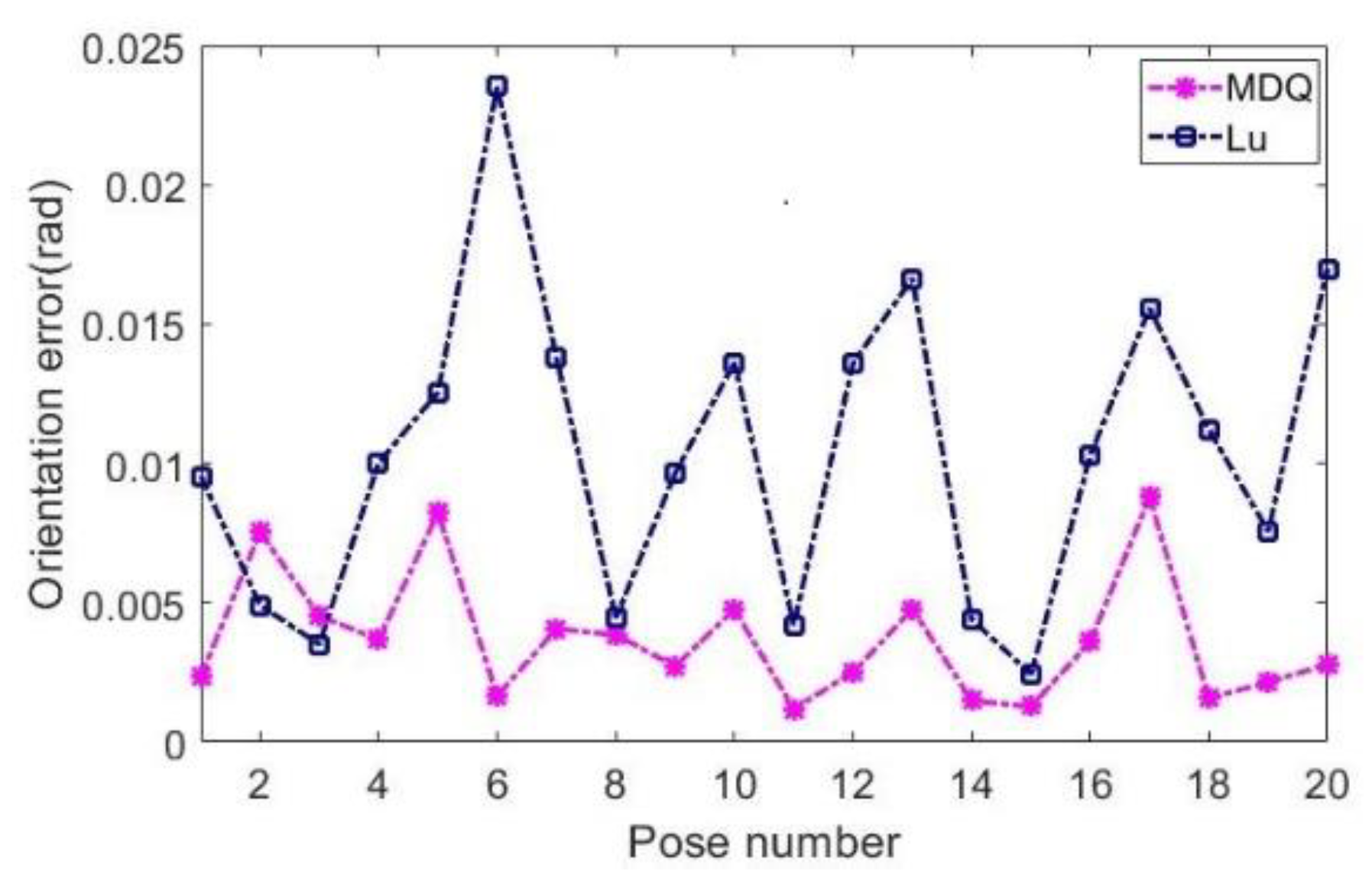
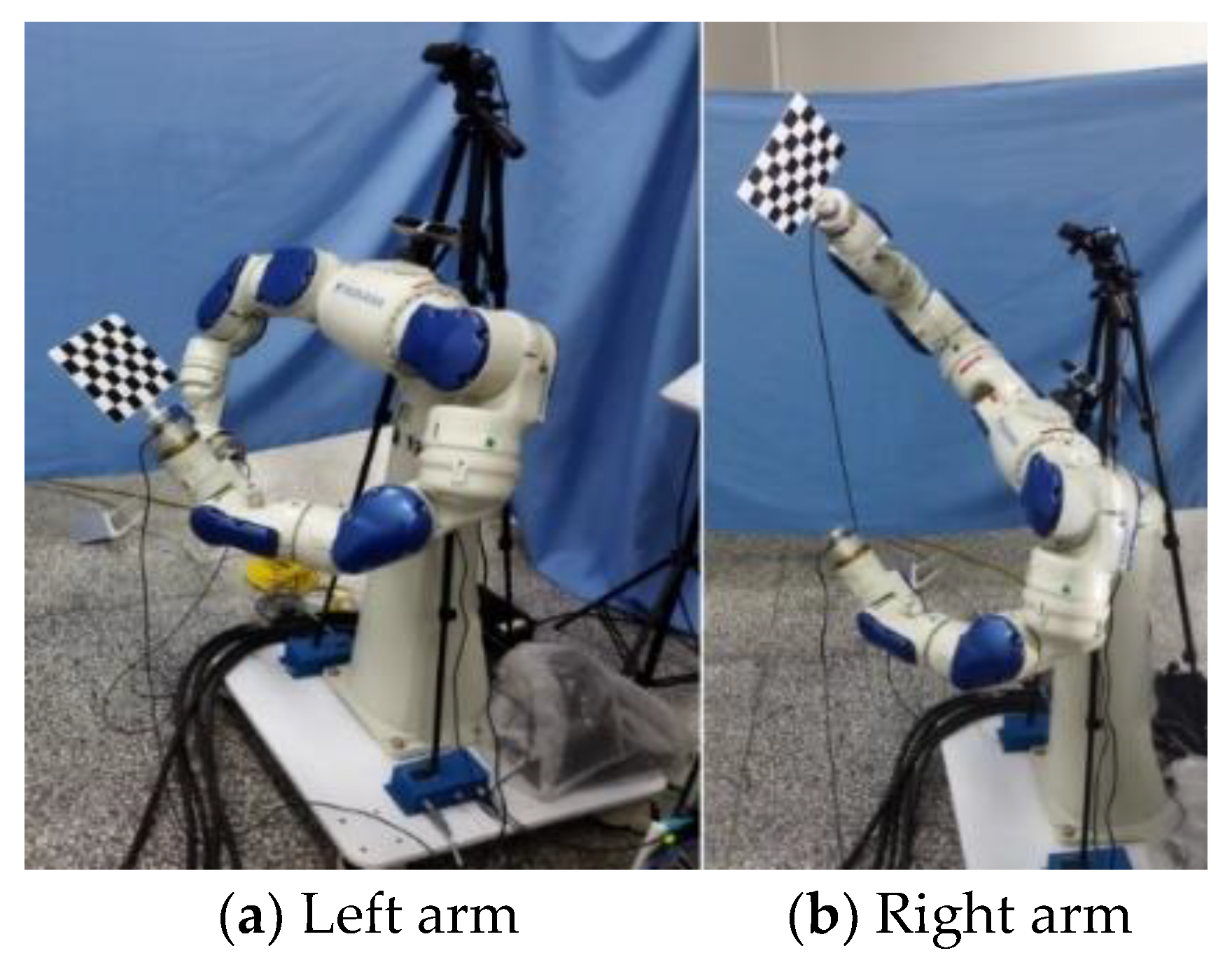
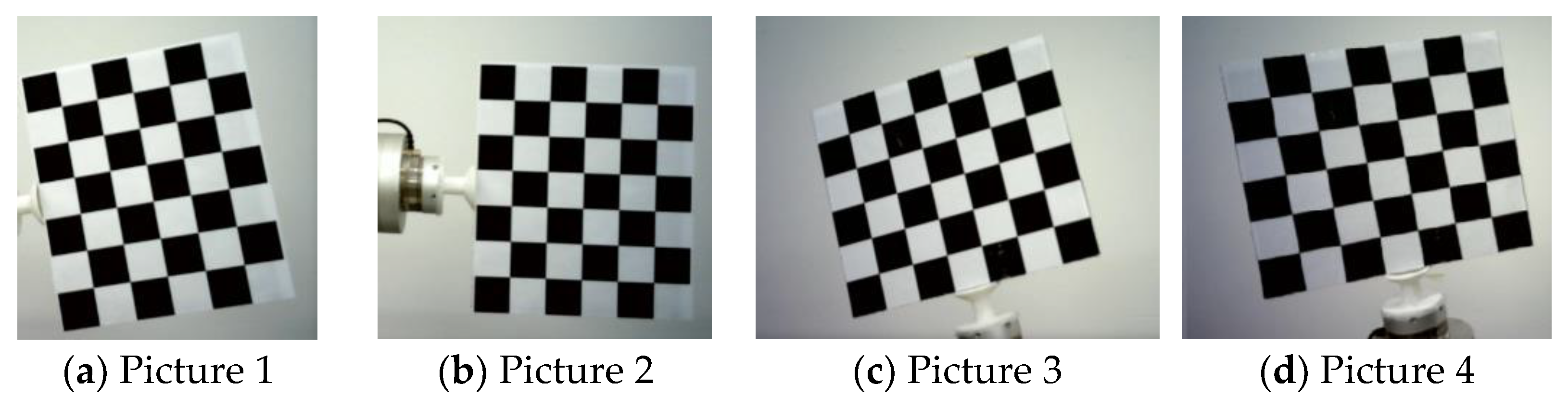
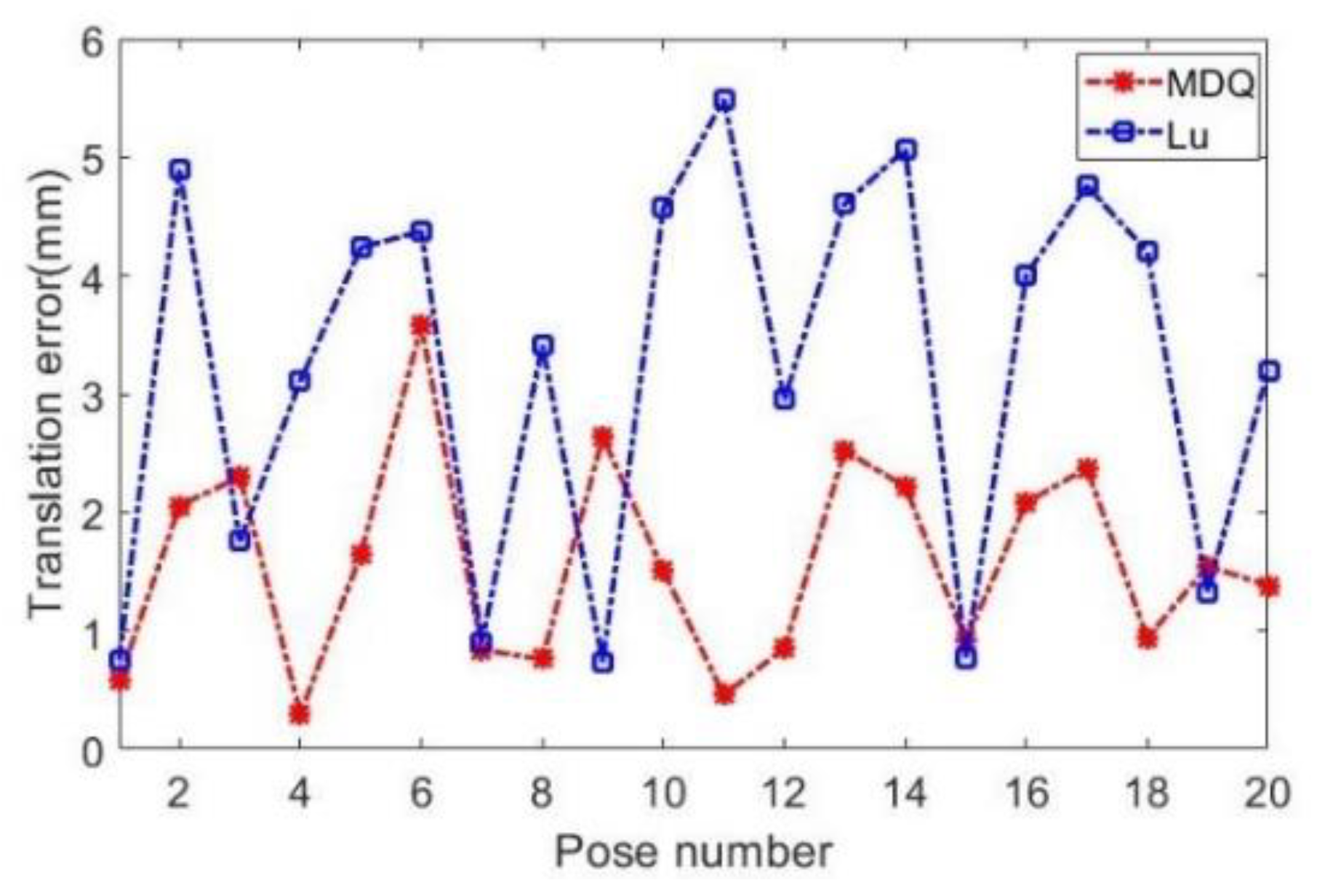
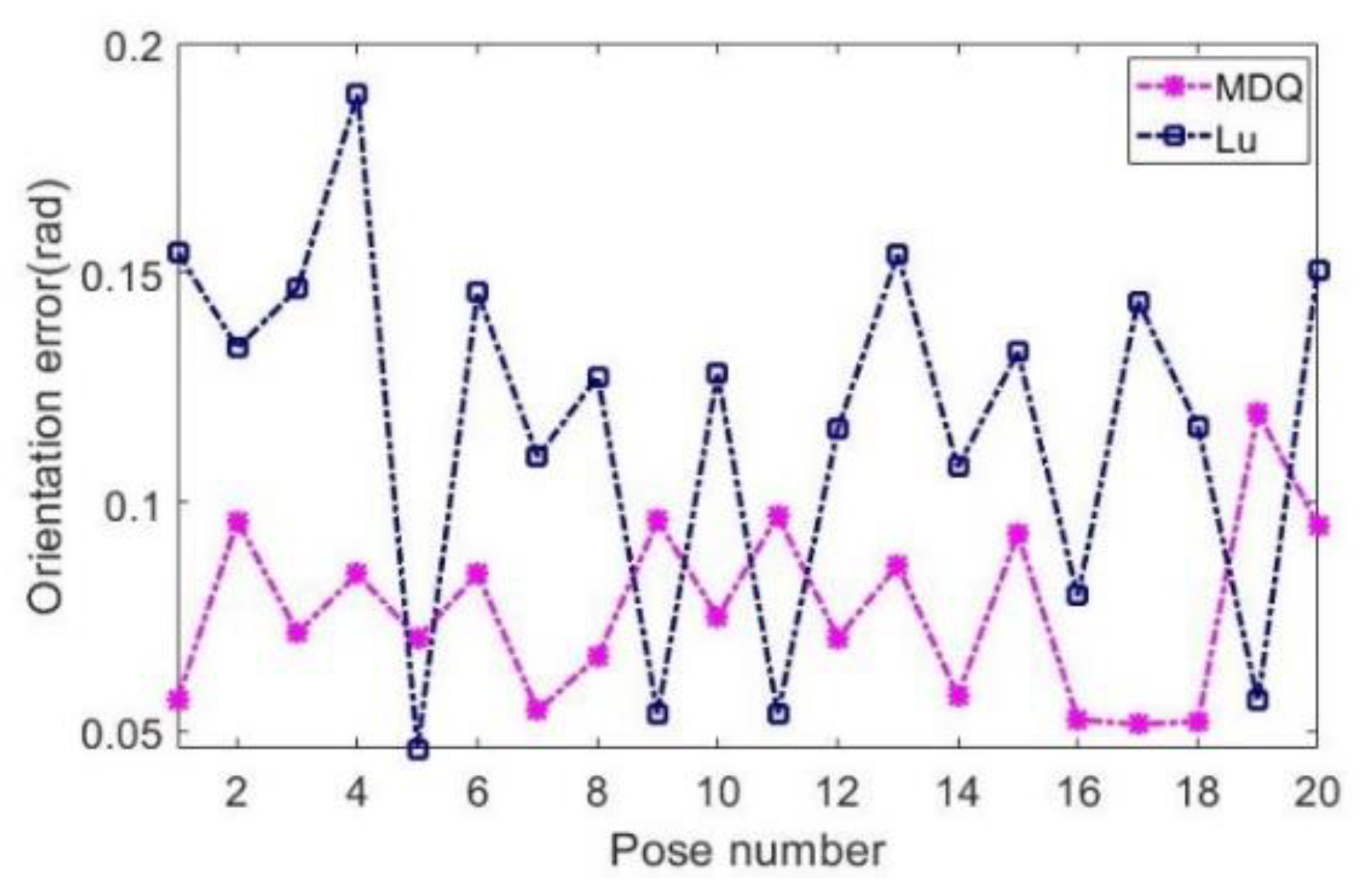
4. Experiment and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z. Estimating Motion and Structure from Correspondences of Line Segments Between Two Perspective Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Cambridge, MA, USA, 20–23 June 1995; pp. 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Olagoke, A.S.; Ibrahim, H.; Teoh, S.S. Literature Survey on Multi-Camera System and Its Application. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 172892–172922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, Q.; Wang, T.; Chirikjian, G.S. Simultaneous Hand-Eye and Robot-World Calibration by Solving the AX = YB Problem Without Correspondence. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Wang, N.L.; Qin, Y.S. A closed-form solution to eye-to-hand calibration towards visual grasping. Ind. Robot Int. J. 2014, 41, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wen, K.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, Y.; Yang, J. A simple and rapid calibration methodology for industrial robot based on geometric constraint and two-step error. Ind. Robot Int. J. 2018, 45, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Song, H. Simultaneous robot–world and hand–eye calibration based on a pair of dual equations. Measurement 2021, 181, 109623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachtrachai, K.; Vasconcelos, F.; Edwards, P.; Stoyanov, D. Learning to Calibrate—Estimating the Hand-eye Transformation Without Calibration Objects. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 7309–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z. Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration by the alternative linear programming. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 127, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, X. A Simultaneous Optimization Method of Calibration and Measurement for a Typical Hand–Eye Positioning System. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5002111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, E.; Oliveira, M.; Lau, N.; Santos, V. A General Approach to Hand–Eye Calibration Through the Optimization of Atomic Transformations. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 37, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Schmidt, A.; Knoll, A.C. Extrinsic Calibration of an Eye-In-Hand 2D LiDAR Sensor in Unstructured Environments Using ICP. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, M.; Barreto, J.P. Robust hand-eye calibration for computer aided medical endoscopy. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 5543–5549. [Google Scholar]
- Mili, S. Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the Kronecker product. J. Mech. Robot. 2013, 5, 031007. [Google Scholar]
- Maybank, S.J.; Faugeras, O.D. A theory of self-calibration of a moving camera. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1992, 8, 123–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.C.; Morgan, I.; Jayarathne, U.; Ma, B.; Peters, T.M. Hand-eye calibration using a target registration error model. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, H.; Henrion, D.; Pajdla, T. Hand-eye and robot-world calibration by global polynomial optimization. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–5 June 2014; pp. 3157–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Pachtrachai, K.; Vasconcelos, F.; Dwyer, G.; Hailes, S.; Stoyanov, D. Hand-eye calibration with a remote centre of motion. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 3121–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. A Flexible New Technique for Camera Calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Ma, S. Camera Calibration by Vanishing Point and Cross Ratio. Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 3, 1630–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Boudine, B.; Kramm, S.; El Akkad, N.; Bensrhair, A.; Saaidi, A.; Satori, K. A flexible technique based on fundamental matrix for camera self-calibration with variable intrinsic parameters from two views. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2016, 39, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Chen, X. Hand–eye calibration of arc welding robot and laser vision sensor through semidefinite programming. Ind. Robot Int. J. 2018, 45, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Basu, A. Simplified Active Calibration. Image Vis. Comput. 2019, 91, 103799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Song, H. Optimal robot-world and hand-eye calibration with rotation and translation coupling. Robotica 2022, 40, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. Optical Remote Sensor Calibration Using Micromachined Multiplexing Optical Focal Planes. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, C.; Qi, L.; Yan, H. A regularization-patching dual quaternion optimization method for solving the hand-eye calibration problem. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.07870. [Google Scholar]
- Grossmann, B.; Krüger, V. Continuous hand-eye calibration using 3D points. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 15th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Emden, Germany, 24–26 July 2017; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Huang, J.; Song, H. Robot-world and hand–eye calibration based on quaternion: A new method and an extension of classic methods, with their comparisons. Mech. Mach. Theory 2023, 179, 105127. [Google Scholar]
- Radu, H.; Dornaika, F. Hand-eye calibration. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1995, 14, 195–210. [Google Scholar]
- Park, F.C.; Martin, B.J. Robot sensor calibration: Solving AX = XB on the Euclidean group. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1994, 10, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Li, A.; Kalakrishnan, M.; Pastor, P. Learning Probabilistic Multi-Modal Actor Models for Vision-Based Robotic Grasping. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 4804–4810. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, A. Active Calibration: Alternative Strategy and Analysis. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, NY, USA, 15–17 June 1993; pp. 495–500. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, D. On the Comparison of Fuzzy Interpolations and Neural Network Fitting Functions in Modeless Robot Calibrations. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–26 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Deniz, C.; Cakir, M. A solution to the hand-eye calibration in the manner of the absolute orientation problem. Ind. Robot Int. J. 2018, 45, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, M.; Wodtko, T.; Buchholz, M.; Dietmayer, K. Online Extrinsic Calibration Based on Per-Sensor Ego-Motion Using Dual Quaternions. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorno, B.V.; Marinho, M.M. DQ Robotics: A Library for Robot Modeling and Control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2021, 28, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Pan, J.; Spyrakos-Papastavridis, E.; Chen, X.; Li, M. A Dual Quaternion-Based Approach for Coordinate Calibration of Dual Robots in Collaborative Motion. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4086–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Zou, S.; Din, S.; Qi, B. Modified Hand–Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312480
Li G, Zou S, Din S, Qi B. Modified Hand–Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(23):12480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312480
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guozhi, Shuizhong Zou, Shuxue Din, and Bin Qi. 2022. "Modified Hand–Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions" Applied Sciences 12, no. 23: 12480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312480
APA StyleLi, G., Zou, S., Din, S., & Qi, B. (2022). Modified Hand–Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions. Applied Sciences, 12(23), 12480. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312480







