Three-Dimensional Anatomical Analysis of Muscle–Skeletal Districts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Erosion Sites on the Wrist
2.2. Morphological Characterisation of the Spine
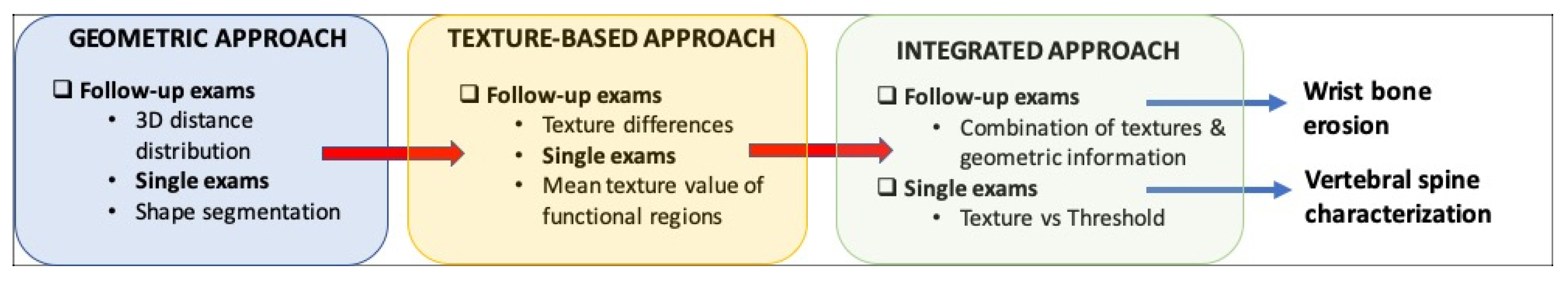
3. Geometrical and Texture-Based Features of Anatomical Districts
3.1. Geometrical Features of Single and Follow-Up Exams
3.2. Texture-Based Features of Single and Follow-Up Exams
3.3. Integrated Approach
4. Results
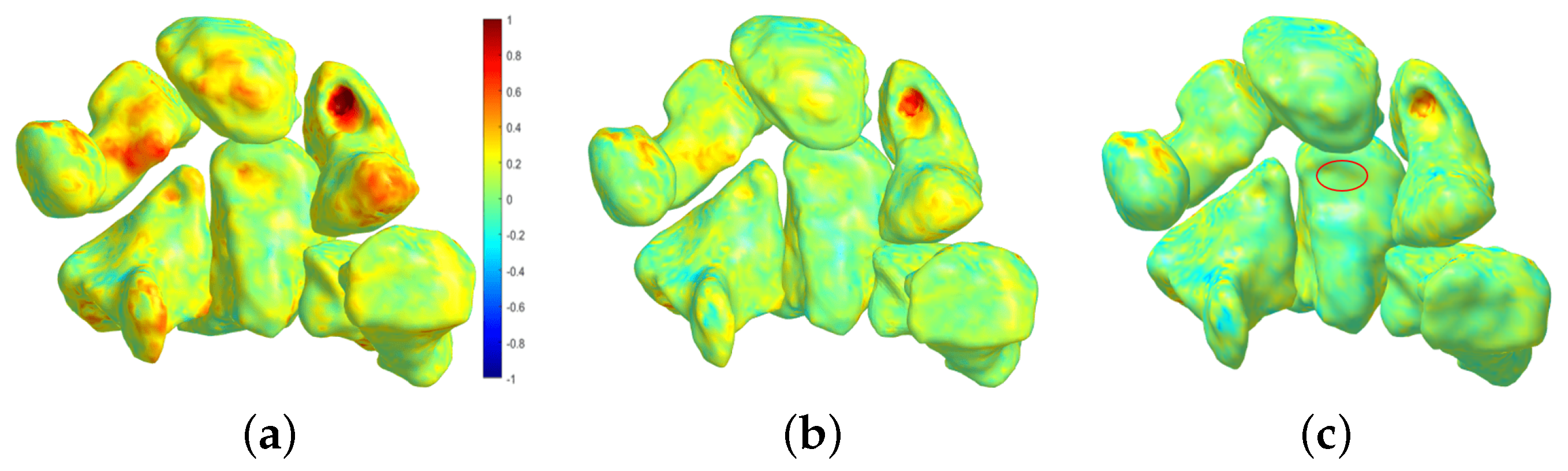
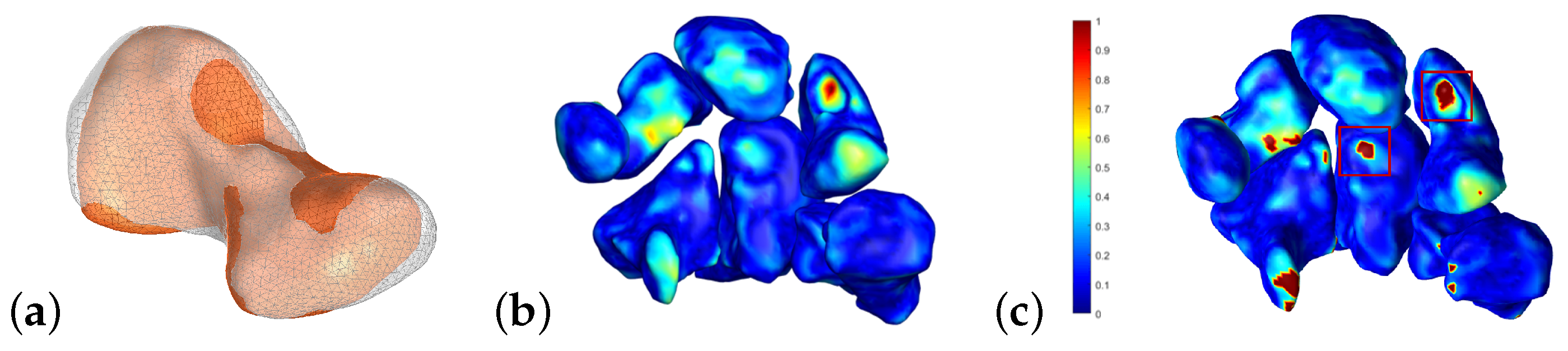
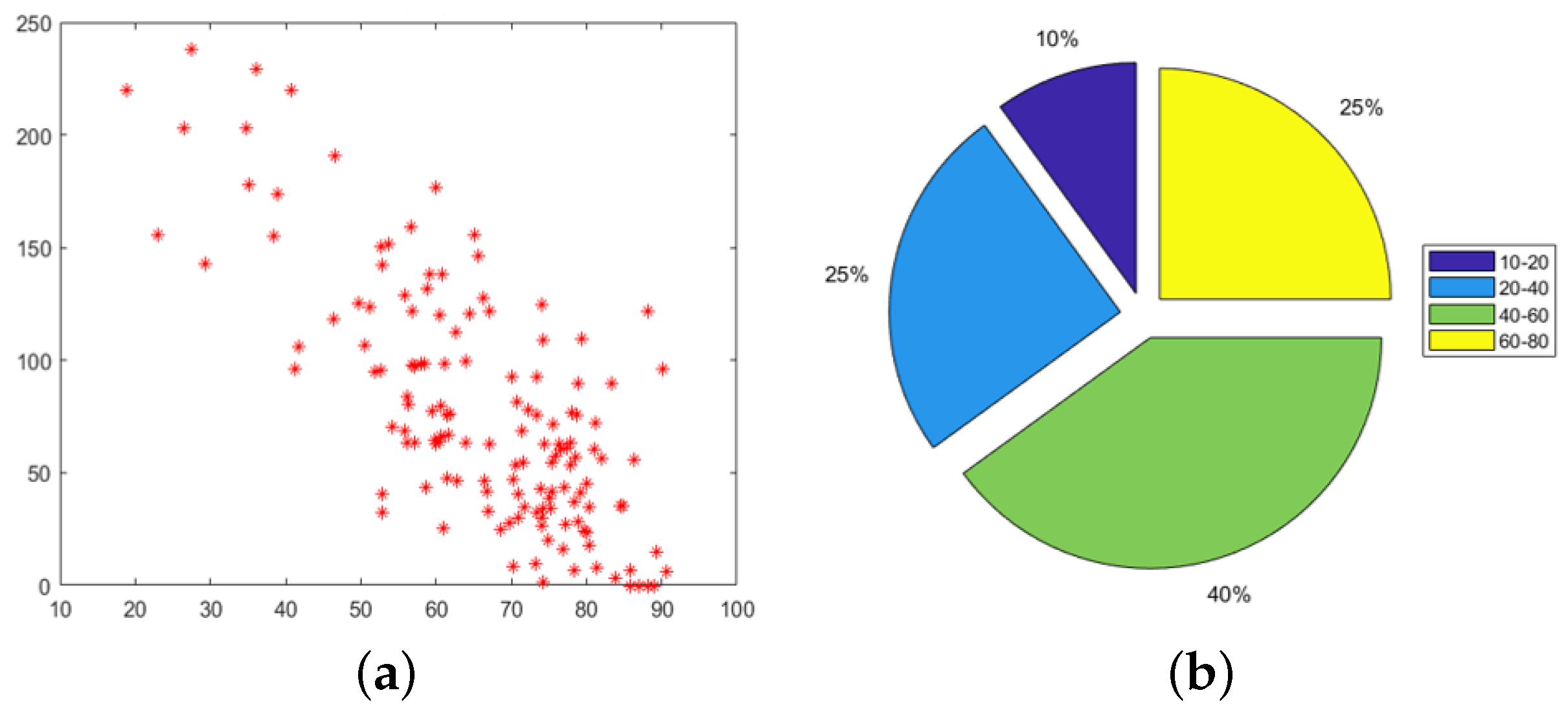
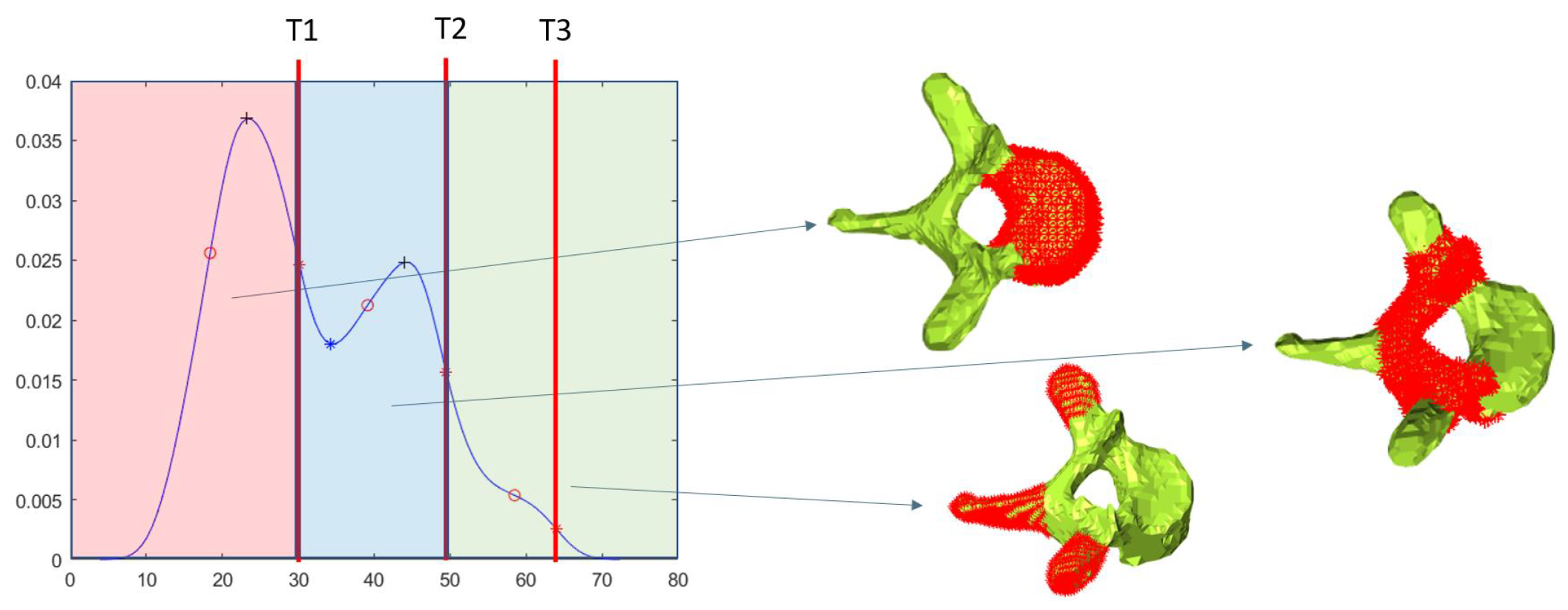
4.1. Follow-Up Evaluation: Erosion Sites’ Identification for the Wrist District
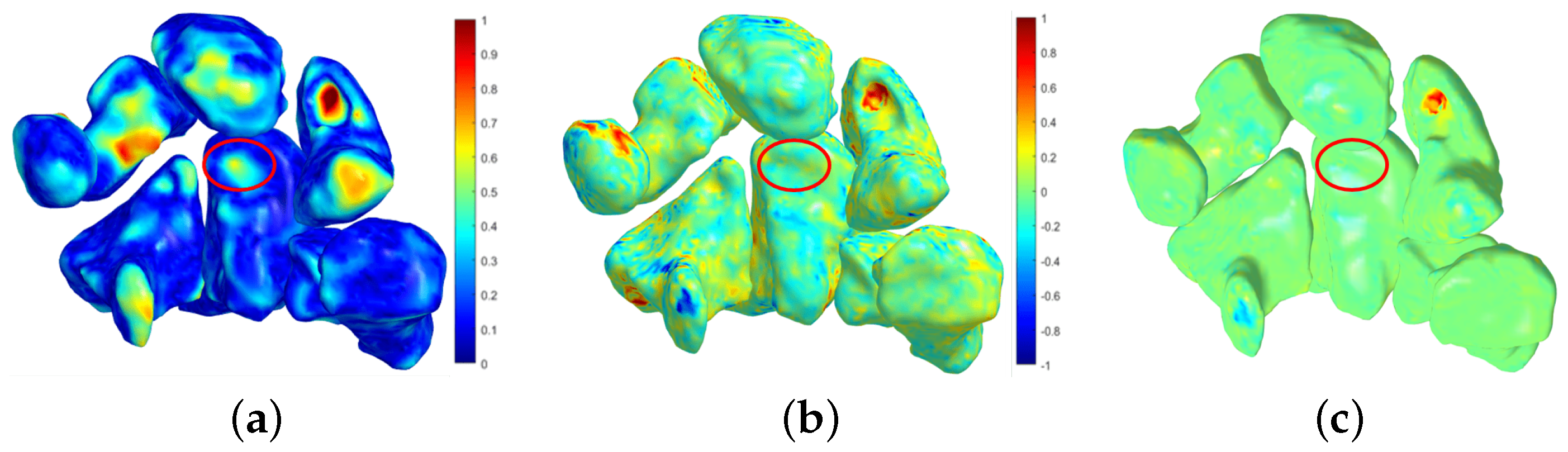
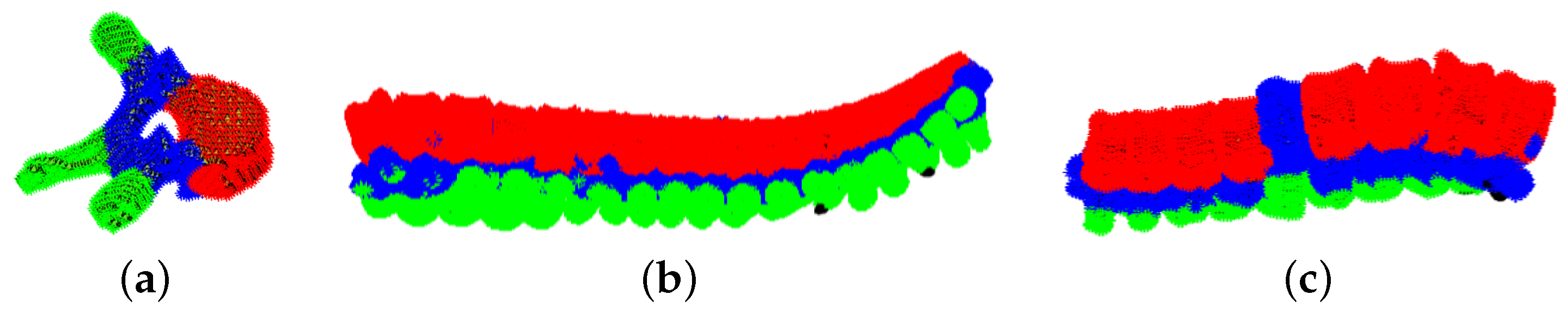
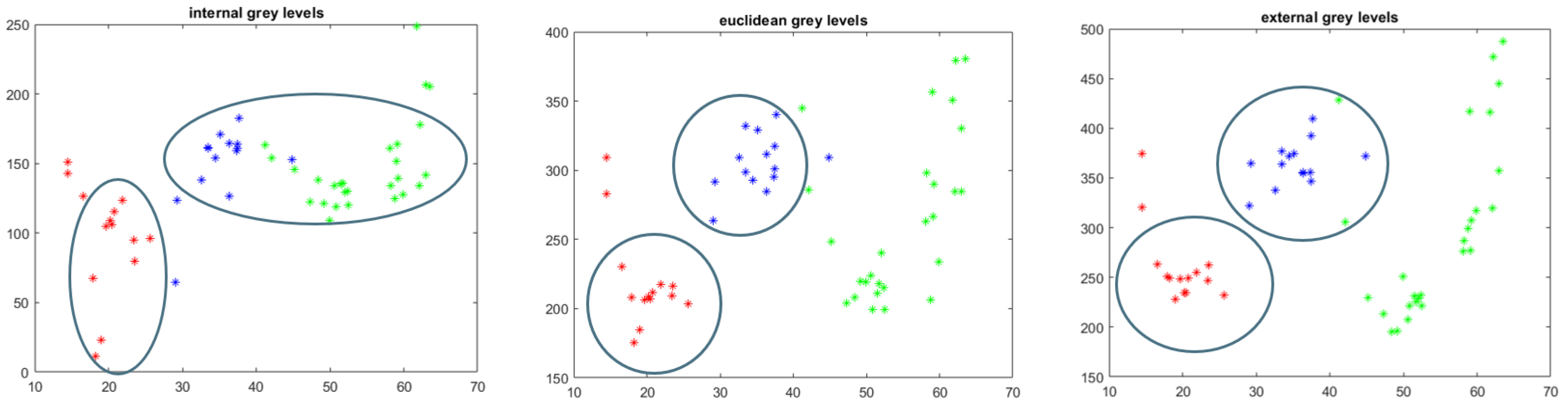
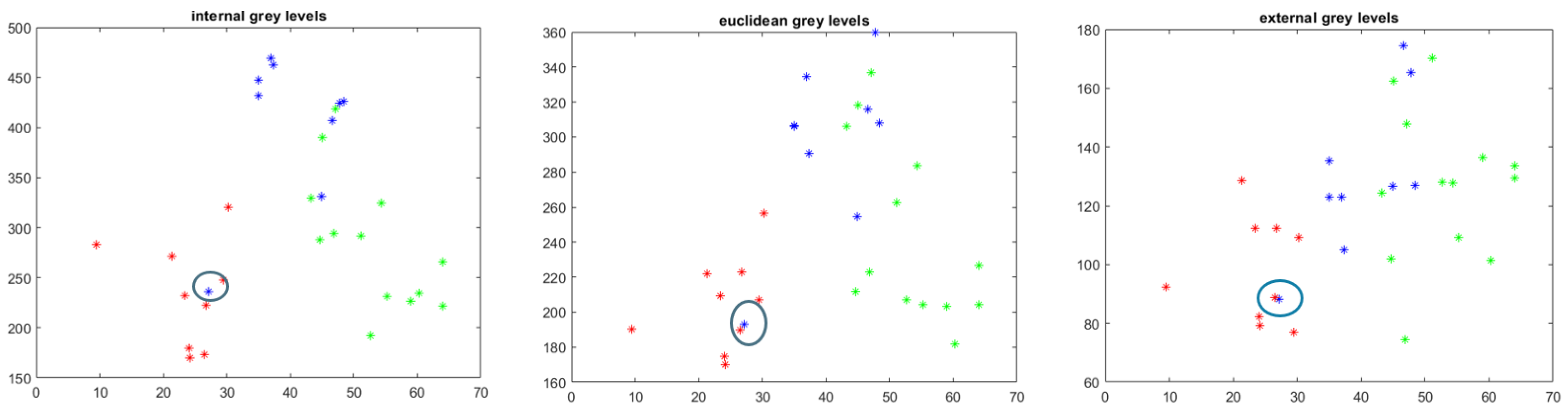
4.2. Single Exam Evaluation: Vertebral Spine Characterisation
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paccini, M.; Patané, G.; Spagnuolo, M. Combining Image and Geometry Processing Techniques for the Quantitative Analysis of Muscle-Skeletal Diseases. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, Lecce, Italy, 23–27 May 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 450–461. [Google Scholar]
- Sekuboyina, A.; Husseini, M.E.; Bayat, A.; Löffler, M.; Liebl, H.; Li, H.; Tetteh, G.; Kukačka, J.; Payer, C.; Štern, D.; et al. VerSe: A vertebrae labelling and segmentation benchmark for multi-detector CT images. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 73, 102166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomatis, V.; Cimmino, M.A.; Barbieri, F.; Troglio, G.; Parascandolo, P.; Cesario, L.; Viano, G.; Vosilla, L.; Pitikakis, M.; Schiappacasse, A.; et al. A database of segmented MRI images of the wrist and the hand in patients with rheumatic diseases. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, Genoa, Italy, 7–11 September 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, K.T. Pain in the forearm, wrist and hand. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2003, 17, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Døhn, U.M.; Ejbjerg, B.J.; Hasselquist, M.; Narvestad, E.; Møller, J.; Thomsen, H.S.; Østergaard, M. Detection of bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis wrist joints with magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography and radiography. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheel, A.; Hermann, K.A.; Ohrndorf, S.; Werner, C.; Schirmer, C.; Detert, J.; Bollow, M.; Hamm, B.; Müller, G.; Burmester, G.; et al. Prospective 7 year follow up imaging study comparing radiography, ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis finger joints. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhaus, M.; Burmester, G.; Sandrock, D.; Loreck, D.; Hess, D.; Scholz, A.; Blind, S.; Hamm, B.; Bollow, M. Prospective two year follow up study comparing novel and conventional imaging procedures in patients with arthritic finger joints. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busby, L.P.; Courtier, J.L.; Glastonbury, C.M. Bias in radiology: The how and why of misses and misinterpretations. Radiographics 2018, 38, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, C.P.; Kleyer, A.; Simon, D.; Stemmler, F.; D’Oliveira, I.; Weissenfels, A.; Museyko, O.; Friedberger, A.; Hueber, A.J.; Haschka, J.; et al. Methods for segmentation of rheumatoid arthritis bone erosions in high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT). Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 47, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornale, S.S.; Patravali, P.U.; Manza, R.R. A survey on exploration and classification of osteoarthritis using image processing techniques. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2016, 7, 334–355. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, K.K.; Holden, M.; Saeed, N.; Brooks, K.J.; Buckton, J.B.; Williams, A.A.; Campbell, S.P.; Changani, K.; Reid, D.G.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Automatic quantification of changes in bone in serial MR images of joints. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2006, 25, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Vincken, K.L.; van der Heijde, D.; De Hair, M.J.; Lafeber, F.P.; Viergever, M.A. Automatic quantification of radiographic finger joint space width of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 63, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langs, G.; Peloschek, P.; Bischof, H.; Kainberger, F. Automatic quantification of joint space narrowing and erosions in rheumatoid arthritis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2008, 28, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Hatano, K.; Tan, J.; Kim, H.; Aoki, T. Automatic identification of bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis from hand radiographs based on deep convolutional neural network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 10921–10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, J.; Reinhard, T.; Sick, B.; Dürr, O. Bone erosion scoring for rheumatoid arthritis with deep convolutional neural networks. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2019, 78, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevidanes, L.; Hajati, A.K.; Paniagua, B.; Lim, P.; Walker, D.; Palconet, G.; Nackley, A.; Styner, M.; Ludlow, J.; Zhu, H.; et al. Quantification of condylar resorption in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 2010, 110, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Gollmer, S.; Schumann, S.; Dong, X.; Feilkas, T.; Ballester, M.A.G. A 2D/3D correspondence building method for reconstruction of a patient-specific 3D bone surface model using point distribution models and calibrated X-ray images. Med. Image Anal. 2009, 13, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.C. 3D-printed patient-specific applications in orthopedics. Orthop. Res. Rev. 2016, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, F.; Tomatis, V.; Zampogna, G.; Aleo, E.; Prono, V.; Migone, S.; Parascandolo, P.; Cesario, L.; Viano, G.; Cimmino, M.A. An MRI Study of Bone Erosions Healing in the Wrist and Metacarpophalangeal Joints of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, Genoa, Italy, 7–11 September 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, I.; Catalano, C.E.; Patané, G.; Spagnuolo, M. Semantic annotation of 3D anatomical models to support diagnosis and follow-up analysis of musculoskeletal pathologies. Int. J. Comput.-Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2016, 11, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.A.; Leahy, R.M.; Badawi, R.D.; Chaudhari, A.J. Registration-based morphometry for shape analysis of the bones of the human wrist. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 35, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paccini, M.; Patané, G.; Spagnuolo, M. Analysis of 3D Segmented Anatomical Districts through Grey-Levels Mapping. Comput. Graph. 2020, 91, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauley, J.; Thompson, D.; Ensrud, K.; Scott, J.; Black, D. Risk of mortality following clinical fractures. Osteoporos. Int. 2000, 11, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, T. Spine Anatomy|Mayfield Brain & Spine. 2018. Available online: https://mayfieldclinic.com/pe-anatspine.htm (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Bibb, R.; Eggbeer, D.; Paterson, A. Medical Modelling: The Application of Advanced Design and Rapid Prototyping Techniques in Medicine; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Löffler, M.; Sollmann, N.; Mei, K.; Valentinitsch, A.; Noël, P.; Kirschke, J.; Baum, T. X-ray-based quantitative osteoporosis imaging at the spine. Osteoporos. Intern. 2020, 31, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Li, W.; Deng, C.; Du, G.; Xu, N. The use of CT Hounsfield unit values to identify the undiagnosed spinal osteoporosis in patients with lumbar degenerative diseases. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.I.; Choi, B.K.; Han, I.H.; Nam, K.H. Hounsfield units on lumbar computed tomography for predicting regional bone mineral density. Open Med. 2019, 14, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Chung, C.K.; Oh, S.H.; Park, S.B. Correlation between bone mineral density measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and Hounsfield units measured by diagnostic CT in lumbar spine. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2013, 54, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, V. Generation of a finite element model of the thoracolumbar spine. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2007, 9, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Aroeira, R.M.C.; Pertence, A.E.d.M.; Kemmoku, D.T.; Greco, M. Three-dimensional geometric model of the middle segment of the thoracic spine based on graphical images for finite element analysis. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 33, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsabili, N.; López, J.S.; Barrio, M.I.P. Simplifying the human lumbar spine (L3/L4) material in order to create an elemental structure for the future modeling. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2019, 42, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Petrella, A. Automated finite element modeling of the lumbar spine: Using a statistical shape model to generate a virtual population of models. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 2593–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, D.P.; Baum, T.; Kirschke, J.S.; Subburaj, K. Effect of the intervertebral disc on vertebral bone strength prediction: A finite-element study. Spine J. 2020, 20, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Mateos, I.; Pozo, J.M.; Pereañez, M.; Lekadir, K.; Lazary, A.; Frangi, A.F. Statistical interspace models (SIMs): Application to robust 3D spine segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1663–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štern, D.; Likar, B.; Pernuš, F.; Vrtovec, T. Parametric modelling and segmentation of vertebral bodies in 3D CT and MR spine images. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laouissat, F.; Sebaaly, A.; Gehrchen, M.; Roussouly, P. Classification of normal sagittal spine alignment: Refounding the Roussouly classification. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 2002–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.C.; Weng, C.H.; Huang, Y.J.; Fu, C.J.; Tsai, T.T.; Yeh, C.Y. Deep learning approach for automatic landmark detection and alignment analysis in whole-spine lateral radiographs. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussouly, P.; Pinheiro-Franco, J.L. Sagittal parameters of the spine: Biomechanical approach. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, T.S.; Colloca, C.J.; Harrison, D.E.; Harrison, D.D.; Janik, T.J. Influence of spine morphology on intervertebral disc loads and stresses in asymptomatic adults: Implications for the ideal spine. Spine J. 2005, 5, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lois Zlolniski, S.; Torres-Tamayo, N.; García-Martínez, D.; Blanco-Pérez, E.; Mata-Escolano, F.; Barash, A.; Nalla, S.; Martelli, S.; Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A.; Bastir, M. 3D geometric morphometric analysis of variation in the human lumbar spine. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2019, 170, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciaro, S.; Massoptier, L. Automatic vertebral morphometry assessment. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual Intern. Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 5571–5574. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, J.D.; Shaw, D.L.; Cooperman, D.R.; Eubanks, J.D.; Li, L.; Kim, D.H. Characterization of lumbar spinous process morphology: A cadaveric study of 2955 human lumbar vertebrae. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labelle, H.; Aubin, C.E.; Jackson, R.; Lenke, L.; Newton, P.; Parent, S. Seeing the spine in 3D: How will it change what we do? J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2011, 31, S37–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzalari, N.L.; Manthey, B.; Parkinson, I.H. Intervertebral disc disorganisation and its relationship to age adjusted vertebral body morphometry and vertebral bone architecture. Anat. Rec. 2001, 262, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parascandolo, P.; Cesario, L.; Vosilla, L.; Viano, G. Computer aided diagnosis: State-of-the-art and application to musculoskeletal diseases. In 3D Multiscale Physiological Human; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 277–296. [Google Scholar]
- Østergaard, M.; Edmonds, J.; McQueen, F.; Peterfy, C.; Lassere, M.; Ejbjerg, B.; Bird, P.; Emery, P.; Genant, H.; Conaghan, P. An introduction to the EULAR–OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, i3–i7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Craene, M.; du Bois d’Aische, A.; Macq, B.; Warfield, S.K. Multi-subject registration for unbiased statistical atlas construction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Saint-Malo, France, 26–29 September 2004; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Löffler, M.T.; Sekuboyina, A.; Jacob, A.; Grau, A.L.; Scharr, A.; El Husseini, M.; Kallweit, M.; Zimmer, C.; Baum, T.; Kirschke, J.S. A Vertebral Segmentation Dataset with Fracture Grading. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2020, 2, e190138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paccini, M.; Patanè, G.; Spagnuolo, M. Three-Dimensional Anatomical Analysis of Muscle–Skeletal Districts. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12048. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312048
Paccini M, Patanè G, Spagnuolo M. Three-Dimensional Anatomical Analysis of Muscle–Skeletal Districts. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(23):12048. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312048
Chicago/Turabian StylePaccini, Martina, Giuseppe Patanè, and Michela Spagnuolo. 2022. "Three-Dimensional Anatomical Analysis of Muscle–Skeletal Districts" Applied Sciences 12, no. 23: 12048. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312048
APA StylePaccini, M., Patanè, G., & Spagnuolo, M. (2022). Three-Dimensional Anatomical Analysis of Muscle–Skeletal Districts. Applied Sciences, 12(23), 12048. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312048







