Occurrence and Degradation of Free and Conjugated Estrogens in a River Receiving Feedlot Animal Discharge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
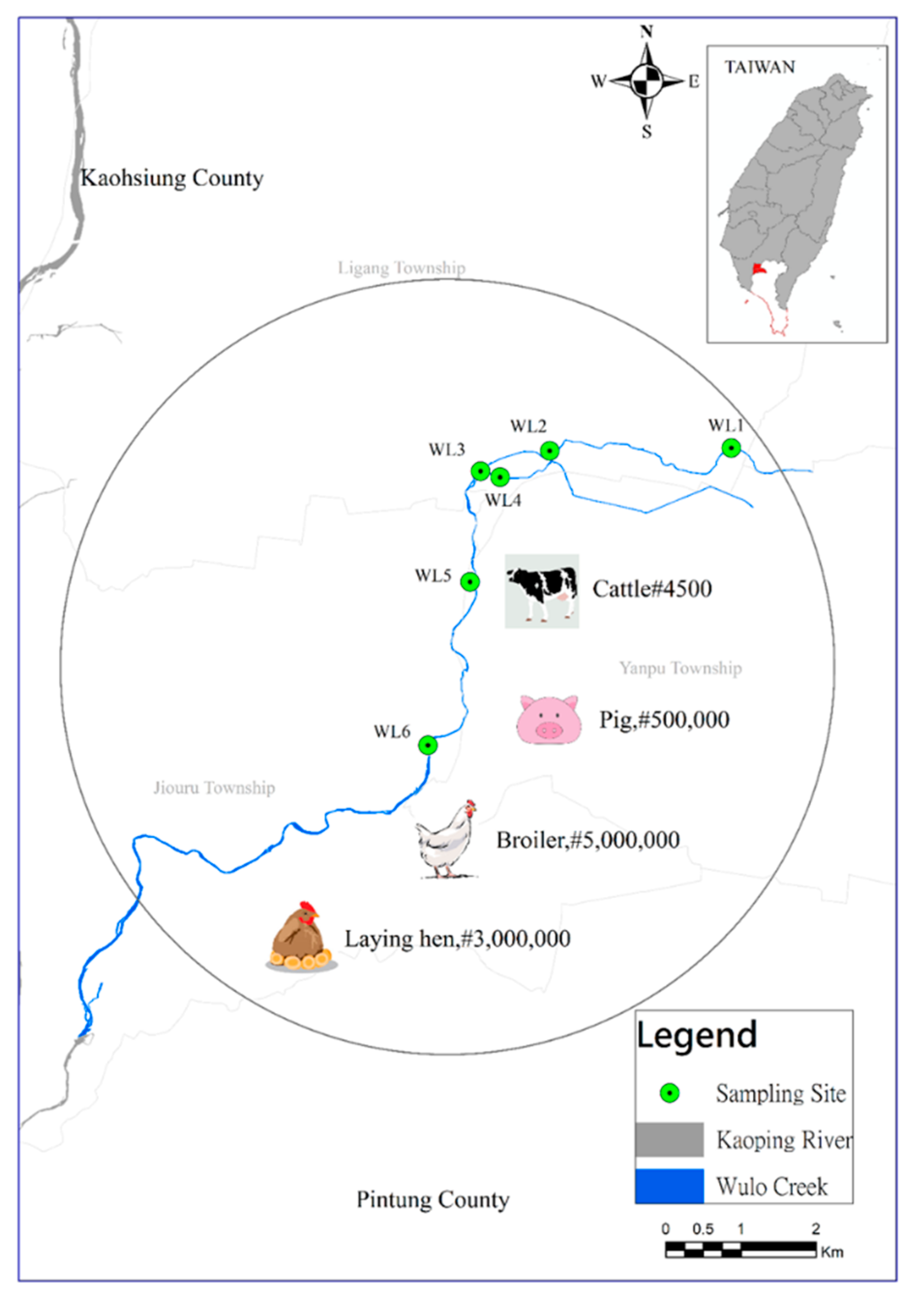
2.1. Sampling Method and Location
2.2. Water Quality Parameter
2.3. Pretreatment of the Estrogen-Containing Water Samples
2.4. LC/MS/MS Analysis Conditions
2.4.1. Instrumental Analysis
2.4.2. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.4.3. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality
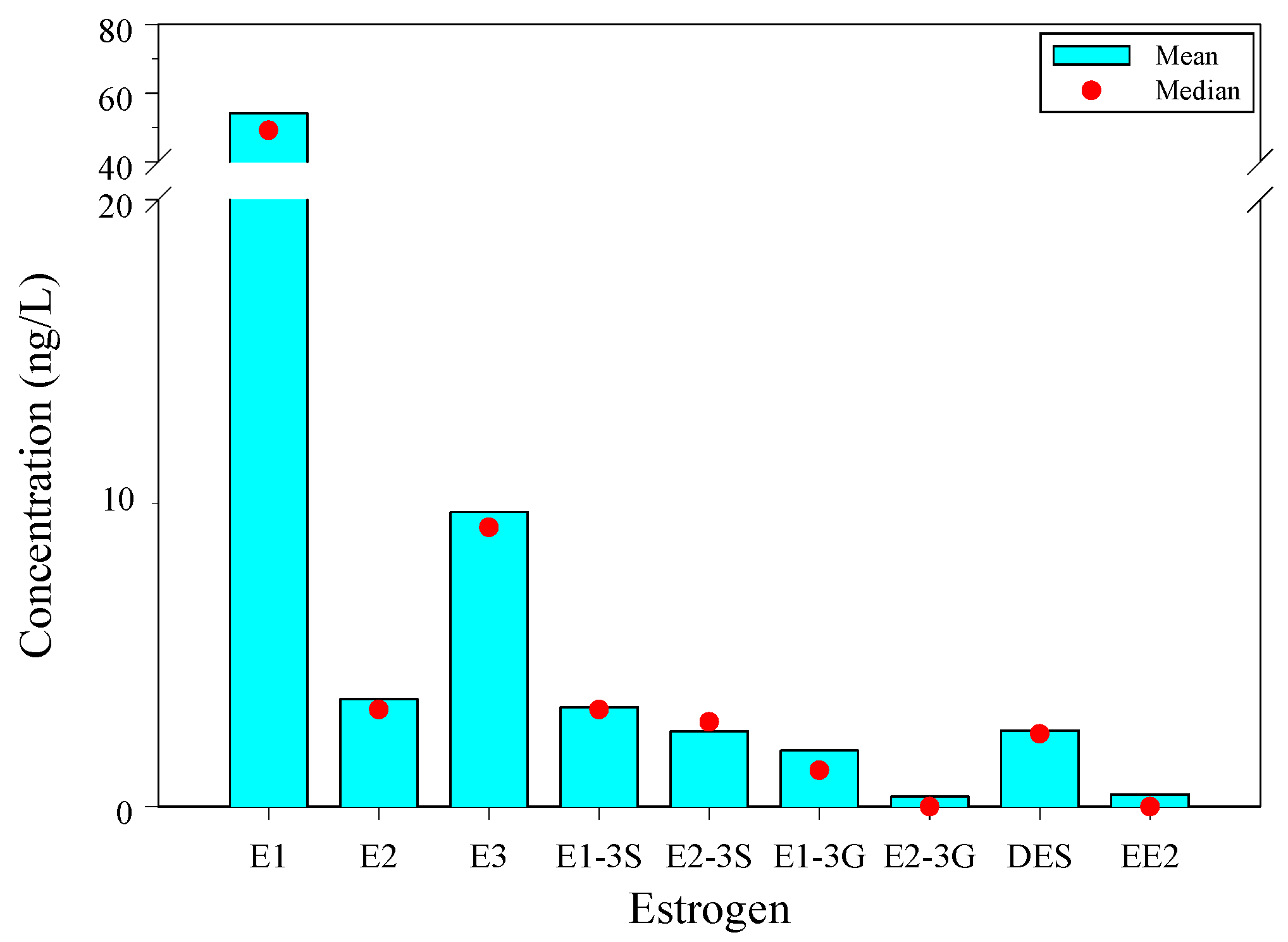
3.2. Estrogen Concentrations in Water Samples
3.2.1. Concentration of Free Estrogen
3.2.2. Concentration of Conjugated Estrogens
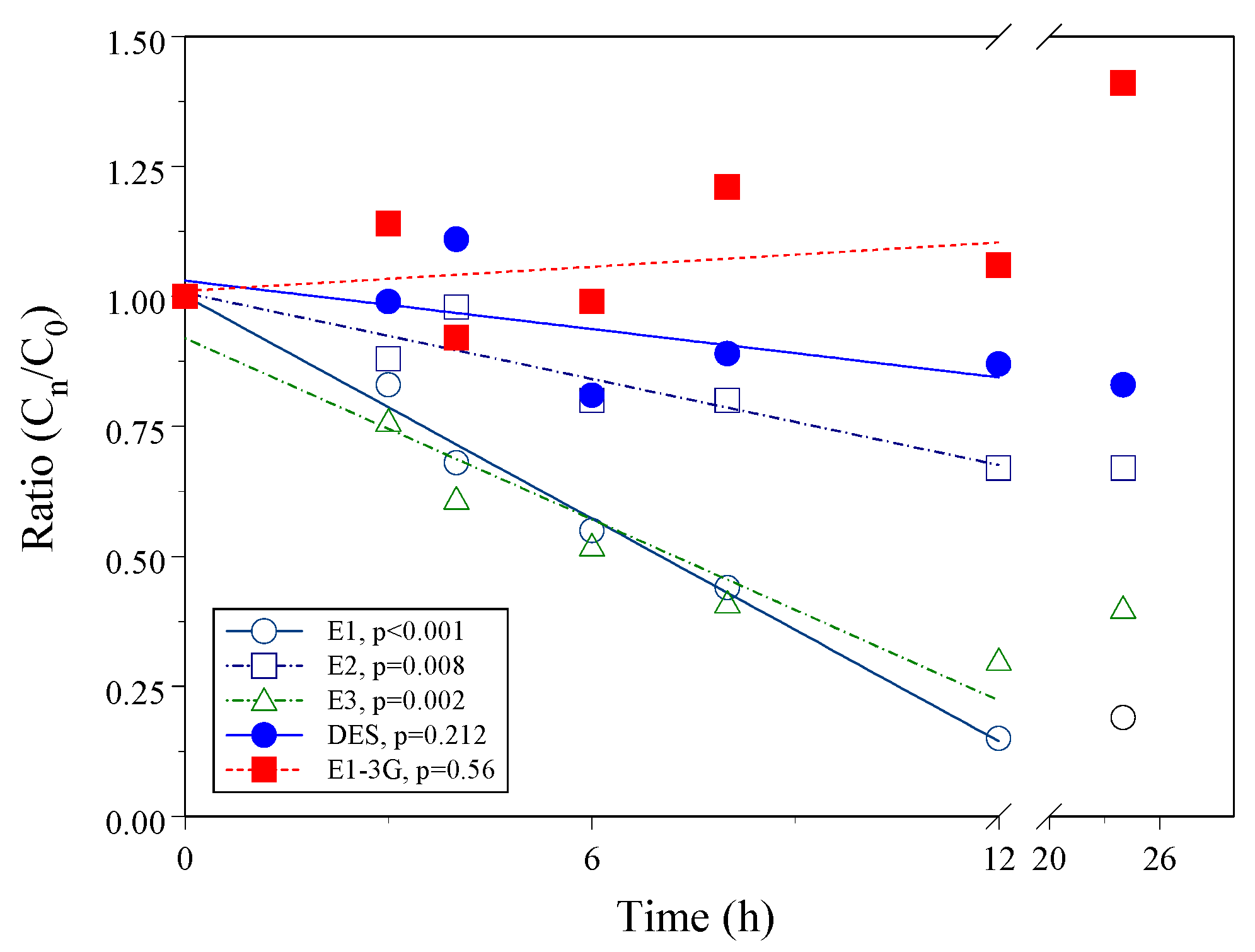
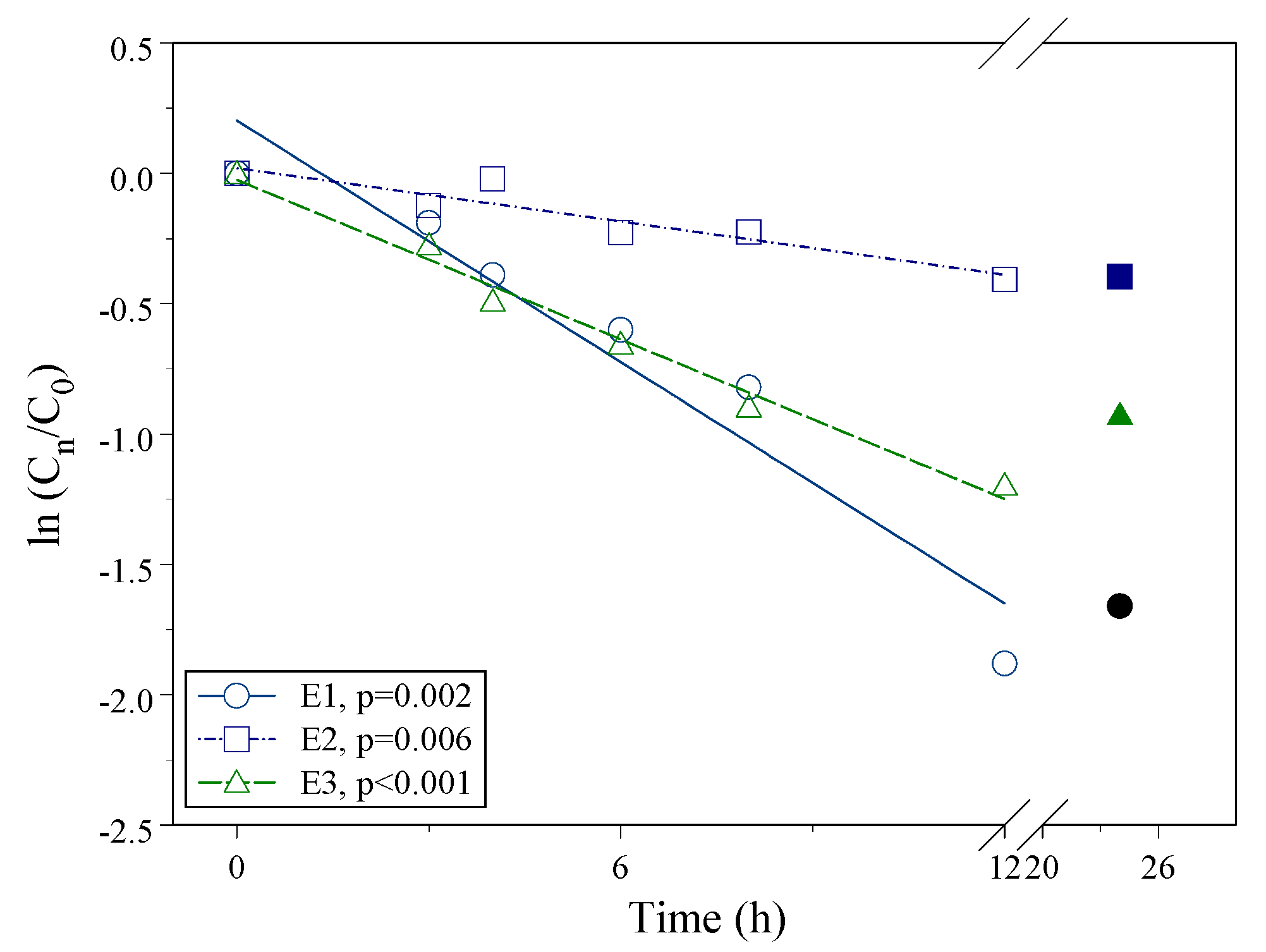
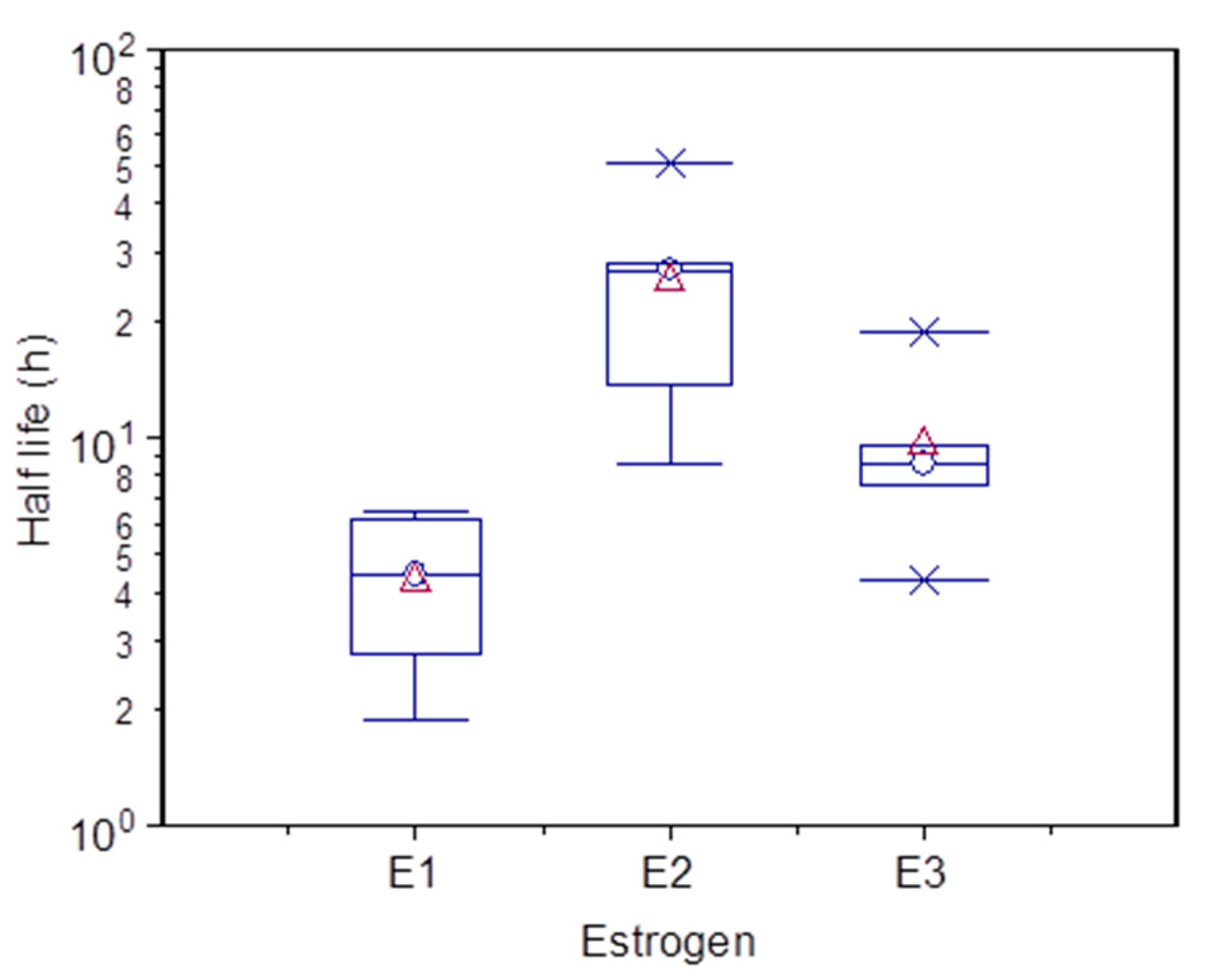
3.3. Degradation of Estrogen in the Water Sample
4. Discussion
4.1. Estrogen Concentrations
4.2. Degradation of DES and E1-3G
4.3. Degradation of Free Estrogen
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bilal, M.; Barceló, D.; Iqbal, H.M. Occurrence, environmental fate, ecological issues, and redefining of endocrine disruptive estrogens in water resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, D.J.; Mastrocco, F.; Anderson, P.D.; Länge, R.; Sumpter, J.P. Predicted-no-effect concentrations for the steroid estrogens estrone, 17β-estradiol, estriol, and 17α-ethinylestradiol. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.-K.; Markert, N.; Leser, K.; Kämpfer, D.; Crawford, S.E.; Schäffer, A.; Segner, H.; Hollert, H. Assessing endocrine disruption in freshwater fish species from a “hotspot” for estrogenic activity in sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Du, B.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, M. Occurrence, sorption, and transformation of free and conjugated natural steroid estrogens in the environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 9443–9468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, F.; Chen, C.; Yang, X.; Li, Y. Bacterial community composition and function succession under aerobic and anaerobic conditions impacts the biodegradation of 17β-estradiol and its environmental risk. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, C.D.; Metcalfe, T.L.; Kiparissis, Y.; Koenig, B.G.; Khan, C.; Hughes, R.J.; Croley, T.R.; March, R.E.; Potter, T. Estrogenic potency of chemicals detected in sewage treatment plant effluents as determined by in vivo assays with Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuster, M.; de Alda, M.J.L.; Barceló, D. Analysis and distribution of estrogens and progestogens in sewage sludge, soils and sediments. Trends Anal. Chem. 2004, 23, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.-G.; Kookana, R.S.; Ru, Y.-J. Occurrence and fate of hormone steroids in the environment. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, J. Degradation of 17β-estradiol and its conjugates: Effects of initial concentration and MLSS concentration. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.L.; Casey, F.X.; Hakk, H.; Smith, D.J.; Padmanabhan, G. Fate and transformation of an estrogen conjugate and its metabolites in agricultural soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11047–11053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xue, C.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Isolation and identification of 17β-estradiol degrading bacteria and its degradation pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, F.X.; Hakk, H.; DeSutter, T.M. Free and conjugated estrogens detections in drainage tiles and wells beneath fields receiving swine manure slurry. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’ascenzo, G.; Di Corcia, A.; Gentili, A.; Mancini, R.; Mastropasqua, R.; Nazzari, M.; Samperi, R. Fate of natural estrogen conjugates in municipal sewage transport and treatment facilities. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 302, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harraka, G.T.; Magnuson, J.T.; Du, B.; Wong, C.S.; Maruya, K.; Schlenk, D. Evaluating the estrogenicity of an effluent-dominated river in California, USA: Comparisons of in vitro and in vivo bioassays. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panter, G.H.; Thompson, R.S.; Beresford, N.; Sumpter, J.P. Transformation of a non-oestrogenic steroid metabolite to an oestrogenically active substance by minimal bacterial activity. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 3579–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherr, F.F.; Sarmah, A.K.; Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C. Modeling degradation and metabolite formation kinetics of estrone-3-sulfate in agricultural soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8388–8394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Hua, X. Fate of estrogens in a pilot-scale step-feed anoxic/oxic wastewater treatment system controlling by nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12981–12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbrow, C.; Routledge, E.; Brighty, G.; Sumpter, J.; Waldock, M. Identification of estrogenic chemicals in STW effluent. 1. Chemical fractionation and in vitro biological screening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Yu, R.M.K.; Andrew-Priestley, M.; Smith, N.; Rahman, M.M.; Tran, T.K.A.; O’Connor, W.A.; MacFarlane, G.R. Secondary treatment phase of tertiary wastewater treatment works significantly reduces estrogenic load. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Yang, F.; Liao, T.; Hui, Y.; Xu, Y. Seasonal variations of estrogenic compounds and their estrogenicities in influent and effluent from a municipal sewage treatment plant in China. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Johnson, A.C.; Nakada, N.; Yamashita, N.; Tanaka, H. De-conjugation behavior of conjugated estrogens in the raw sewage, activated sludge and river water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holbrook, R.D.; Novak, J.T.; Grizzard, T.J.; Love, N.G. Estrogen receptor agonist fate during wastewater and biosolids treatment processes: A mass balance analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4533–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, G.; Shu, H.; Cui, X.; Luo, Z.; Chang, C.; Zeng, A.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Q. Facile covalent preparation of carbon nanotubes/amine-functionalized Fe3O4 nanocomposites for selective extraction of estradiol in pharmaceutical industry wastewater. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1638, 461889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-S.; Chen, T.-C.; Yeh, K.-J.C.; Chao, H.-R.; Liaw, E.-T.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-C.; Hsieh, L.-T.; Yeh, Y.-L. High estrogen concentrations in receiving river discharge from a concentrated livestock feedlot. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3223–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Q.; Xing, C.; Cai, Y.-Y.; Yan, X.-T.; Ying, G.-G. How much do human and livestock actually contribute to steroids emission and surface water pollution from past to the future: A global research. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.-K.; Leser, K.; Kämpfer, D.; Riegraf, C.; Crawford, S.E.; Smith, K.; Vermeirssen, E.L.; Buchinger, S.; Hollert, H. Bioavailability of estrogenic compounds from sediment in the context of flood events evaluated by passive sampling. Water Res. 2019, 161, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevacqua, C.E.; Rice, C.P.; Torrents, A.; Ramirez, M. Steroid hormones in biosolids and poultry litter: A comparison of potential environmental inputs. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2120–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, J.B.; Tremblay, L.A.; Northcott, G.L. Steroid estrogens, conjugated estrogens and estrogenic activity in farm dairy shed effluents. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, S.R.; White, M.V.; Hudson, F.M.; Fine, D.D. Analysis of lagoon samples from different concentrated animal feeding operations for estrogens and estrogen conjugates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, T.; Shiraishi, H.; Yasuda, M.; Shinoda, A.; Suzuki, H.; Morita, M. Determination of estrogens and their conjugates in water using solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 984, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Williams, R.; Matthiessen, P. The potential steroid hormone contribution of farm animals to freshwaters, the United Kingdom as a case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 362, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, G.; Bagheri, A.R.; Bhatt, P.; Bilal, M. Occurrence, potential ecological risks, and degradation of endocrine disrupter, nonylphenol, from the aqueous environment. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jürgens, M.D.; Holthaus, K.I.; Johnson, A.C.; Smith, J.J.; Hetheridge, M.; Williams, R.J. The potential for estradiol and ethinylestradiol degradation in English rivers. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Yates, S.R. Degradation and metabolite formation of 17ß-estradiol-3-glucuronide and 17ß-estradiol-3-sulphate in river water and sediment. Water Res. 2018, 139, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Yates, S.R. Degradation and metabolite formation of estrogen conjugates in an agricultural soil. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.-p.; Chai, B.-w.; Wei, Q.; Hayat, W.; Dang, Z.; Liu, Z.-H. 17α-ethynylestradiol and its two main conjugates in seven municipal wastewater treatment plants: Analytical method, their occurrence, removal and risk evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zou, Y.; Li, X.; Machesky, M.L. Fate of estrogen conjugate 17α-estradiol-3-sulfate in dairy wastewater: Comparison of aerobic and anaerobic degradation and metabolite formation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 258, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanselman, T.A.; Graetz, D.A.; Wilkie, A.C. Manure-borne estrogens as potential environmental contaminants: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5471–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.K.; Xie, B.; Thompson, M.L.; Sung, S.; Ong, S.-K.; Van Leeuwen, J. Fate, transport, and biodegradation of natural estrogens in the environment and engineered systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6537–6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-C.; Yeh, K.-J.C.; Kuo, W.-C.; Chao, H.-R.; Sheu, S.-C. Estrogen degradation and sorption onto colloids in a constructed wetland with different hydraulic retention times. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 277, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.-S.; Yeh, K.-J.C.; Chen, T.-C. Investigation of free and conjugated estrogen fate and emission coefficients in three duck farms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Nakada, N.; Yasojima, M.; Yamashita, N.; Johnson, A.C.; Tanaka, H. Rapid determination of free and conjugated estrogen in different water matrices by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackwell, B.R.; Johnson, B.J.; Buser, M.D.; Cobb, G.P.; Smith, P.N. Transformation kinetics of trenbolone acetate metabolites and estrogens in urine and feces of implanted steers. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherr, F.F.; Sarmah, A.K.; Di, H.J.; Cameron, K.C. Degradation and metabolite formation of 17β-estradiol-3-sulphate in New Zealand pasture soils. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Xu, Y.-F.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Tao, H.-C. Removal of estrogens in municipal wastewater treatment plants: A Chinese perspective. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 165, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, R.; Blassengale, A.A.; Wang, Q. Degradation of estrogenic hormones in a silt loam soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9152–9158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Grimes, K.L.; Colosi, L.M.; Lung, W.-S. Attenuation, transport, and management of estrogens: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, M.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Francis, D.; Yang, Y. Environmental impact of estrogens on human, animal and plant life: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.K.; Inamdar, S.P.; Tso, J.; Aga, D.S. Concentrations of free and conjugated estrogens at different landscape positions in an agricultural watershed receiving poultry litter. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 2821–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziej, E.P.; Sedlak, D.L. Rangeland grazing as a source of steroid hormones to surface waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3514–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shappell, N.W.; Billey, L.O.; Forbes, D.; Matheny, T.A.; Poach, M.E.; Reddy, G.B.; Hunt, P.G. Estrogenic activity and steroid hormones in swine wastewater through a lagoon constructed-wetland system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Wan, Y.-P.; Liu, Z.-H.; Wang, H.; Dang, Z.; Liu, Y. Twelve natural estrogens in urines of swine and cattle: Concentration profiles and importance of eight less-studied. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deich, C.; Frazão, H.C.; Appelt, J.-S.; Li, W.; Pohlmann, T.; Waniek, J.J. Occurrence and distribution of estrogenic substances in the northern South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, C.N.; Ra, J.S.; Cho, J.; Kim, S.D.; Choi, H.K.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, K.W.; Inam, E.; Kim, S.D. Estrogenic chemicals and estrogenicity in river waters of South Korea and seven Asian countries. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Lin, C.-Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, W.; Pan, H.-Y.; Sun, Z.; Sweetman, A.; Zhang, Q.; He, M.-C. Estrogens in municipal wastewater and receiving waters in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China: Occurrence and risk assessment of mixtures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Tu, Y.; Li, H.; Qiu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z. Endocrine-disrupting compounds in the Xiangjiang River of China: Spatio-temporal distribution, source apportionment, and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, G. Endocrine disrupting chemicals in wild freshwater fishes: Species, tissues, sizes and human health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Nakada, N.; Yasojima, M.; Yamashita, N.; Johnson, A.C.; Tanaka, H. The arrival and discharge of conjugated estrogens from a range of different sewage treatment plants in the UK. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Nakada, N.; Yamashita, N.; Johnson, A.C.; Tanaka, H. How seasonality affects the flow of estrogens and their conjugates in one of Japan’s most populous catchments. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premnath, N.; Mohanrasu, K.; Rao, R.G.R.; Dinesh, G.; Prakash, G.S.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Jeyakanthan, J.; Govarthanan, M.; Kumar, P.; Arun, A. Effect of C/N substrates for enhanced extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production and Poly Cyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) degradation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Ji, R. Effects of veterinary antibiotics on the fate and persistence of 17β-estradiol in swine manure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Shapiro, C.; Kranz, W.; Mader, T.; Shelton, D.; Snow, D.D.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.L.; Tarkalson, D.; Van Donk, S.; Zhang, T.C. Current knowledge on the environmental fate, potential impact, and management of growth-promoting steroids used in the US beef cattle industry. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 68, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolafe, O.; Mrozik, W.; Dolfing, J.; Acharya, K.; Vassalle, L.; Mota, C.R.; Davenport, R. Fate of four different classes of chemicals under aerobic and anaerobic conditions in biological wastewater treatment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Yates, S.R.; Bradford, S.A. Analysis of steroid hormones in a typical dairy waste disposal system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aris, A.Z.; Shamsuddin, A.S.; Praveena, S.M. Occurrence of 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE2) in the environment and effect on exposed biota: A review. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| T | pH | EC | DO | NH3-N | SS | TS | DOC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | μS/cm | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | ||
| Mean | 27.9 | 7.3 | 698 | 2.3 | 7.3 | 106 | 815 | 9.3 |
| SD | 3.3 | 0.3 | 248 | 1.3 | 5.3 | 68 | 473 | 5.9 |
| Max | 33.5 | 8.3 | 1719 | 7.6 | 24.8 | 343 | 2867 | 22.6 |
| Min | 20.0 | 6.8 | 14 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 25 | 441 | 2.3 |
| Median | 29.0 | 7.3 | 725 | 2.1 | 5.8 | 86 | 660 | 7.8 |
| Compounds | Concentration Range (ng/L) | Detection Rate (%) | p-Value * | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | 2.0–145.6 | 100 | 0.169 | 0.200 |
| E2 | ND–13.2 | 84 | 0.003 | <0.001 |
| E3 | ND–34.0 | 95 | 0.083 | 0.200 |
| DES | ND–10.0 | 63 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| EE2 | ND–4.4 | 15 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| E1-3S | ND–13.2 | 76 | 0.455 | 0.131 |
| E2-3S | ND–10.4 | 71 | 0.053 | 0.098 |
| E1-3G | ND–10.0 | 56 | 0.001 | 0.005 |
| E2-3G | ND–3.6 | 15 | 0.005 | <0.001 |
| DES | E1 | E2 | E3 | E1-3G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | C0–C24 | C0–C24 | C0–C24 | C0–C24 | C0–C24 |
| WL1 | 2.8–2.4 | 20.4–4.0 | 3.6–2.4 | 4.0–2.0 | 2.0–2.8 |
| WL2 | 3.6–2.0 | 67.6–5.6 | 4.4–2.4 | 7.2–2.8 | 3.2–3.6 |
| WL3 | 6.2–3.2 | 145.6–3.2 | 6.4–3.6 | 13.6–2.0 | 2.0–4.0 |
| WL4 | 2.4–2.4 | 41.2–9.6 | 2.8–2.0 | 7.2–2.8 | 2.8–3.6 |
| WL5 | 2.0–2.4 | 19.6–4.0 | 2.8–2.0 | 3.6–2.0 | 2.8–4.0 |
| WL6 | 2.8–2.4 | 14.0–5.6 | 2.4–2.0 | 2.0–2.0 | 2.0–2.4 |
| Parameters | DES | E1-3G | E1 | E2 | E3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | −0.016 | 0.0078 | −0.0714 | −0.0276 | −0.058 |
| Intercept | 1.030 | 1.011 | 1.009 | 1.007 | 0.9093 |
| r | 0.60 | 0.31 | 0.996 | 0.927 | 0.963 |
| p-value | 0.212 | 0.56 | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.002 |
| F1 | 2.20 | 0.41 | 473.06 | 24.47 | 8.34 |
| F2 | 1.10 | 0.67 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 1.64 |
| Parameters | E1 | E2 | E3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | −0.154 | −0.034 | −0.102 |
| Intercept | 0.203 | 0.0197 | −0.025 |
| r | 0.964 | 0.937 | 0.99 |
| p-value (R) | 0.002 | 0.006 | <0.001 |
| F1 | 52.15 | 29.10 | 9.52 |
| F2 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.67 |
| E1 | E2 | E3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | k (h−1) | R2 | p | k (h−1) | R2 | p | k (h−1) | R2 | p |
| WL1 | 0.112 | 0.55 | 0.093 | 0.026 | 0.42 | 0.168 | 0.081 | 0.63 | 0.108 |
| WL2 | 0.251 | 0.96 | <0.001 | 0.051 | 0.56 | 0.087 | 0.092 | 0.77 | 0.051 |
| WL3 | 0.371 | 0.97 | <0.001 | 0.081 | 0.86 | 0.007 | 0.162 | 0.88 | 0.006 |
| WL4 | 0.107 | 0.45 | 0.142 | 0.014 | 0.13 | 0.486 | 0.072 | 0.76 | 0.023 |
| WL5 | 0.183 | 0.98 | <0.001 | 0.026 | 0.75 | 0.026 | 0.037 | 0.46 | 0.140 |
| WL6 | 0.138 | 0.71 | 0.035 | 0.025 | 0.27 | 0.286 | NA | NA | NA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, H.-S.; Yeh, K.-J.C.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Chen, T.-C. Occurrence and Degradation of Free and Conjugated Estrogens in a River Receiving Feedlot Animal Discharge. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122311961
Hung H-S, Yeh K-JC, Hsieh C-Y, Chen T-C. Occurrence and Degradation of Free and Conjugated Estrogens in a River Receiving Feedlot Animal Discharge. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(23):11961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122311961
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Hao-Shen, Kuei-Jyum C. Yeh, Chi-Ying Hsieh, and Ting-Chien Chen. 2022. "Occurrence and Degradation of Free and Conjugated Estrogens in a River Receiving Feedlot Animal Discharge" Applied Sciences 12, no. 23: 11961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122311961
APA StyleHung, H.-S., Yeh, K.-J. C., Hsieh, C.-Y., & Chen, T.-C. (2022). Occurrence and Degradation of Free and Conjugated Estrogens in a River Receiving Feedlot Animal Discharge. Applied Sciences, 12(23), 11961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122311961









