An Explainable and Lightweight Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Quality Detection of Green Coffee Beans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fundamental Knowledge
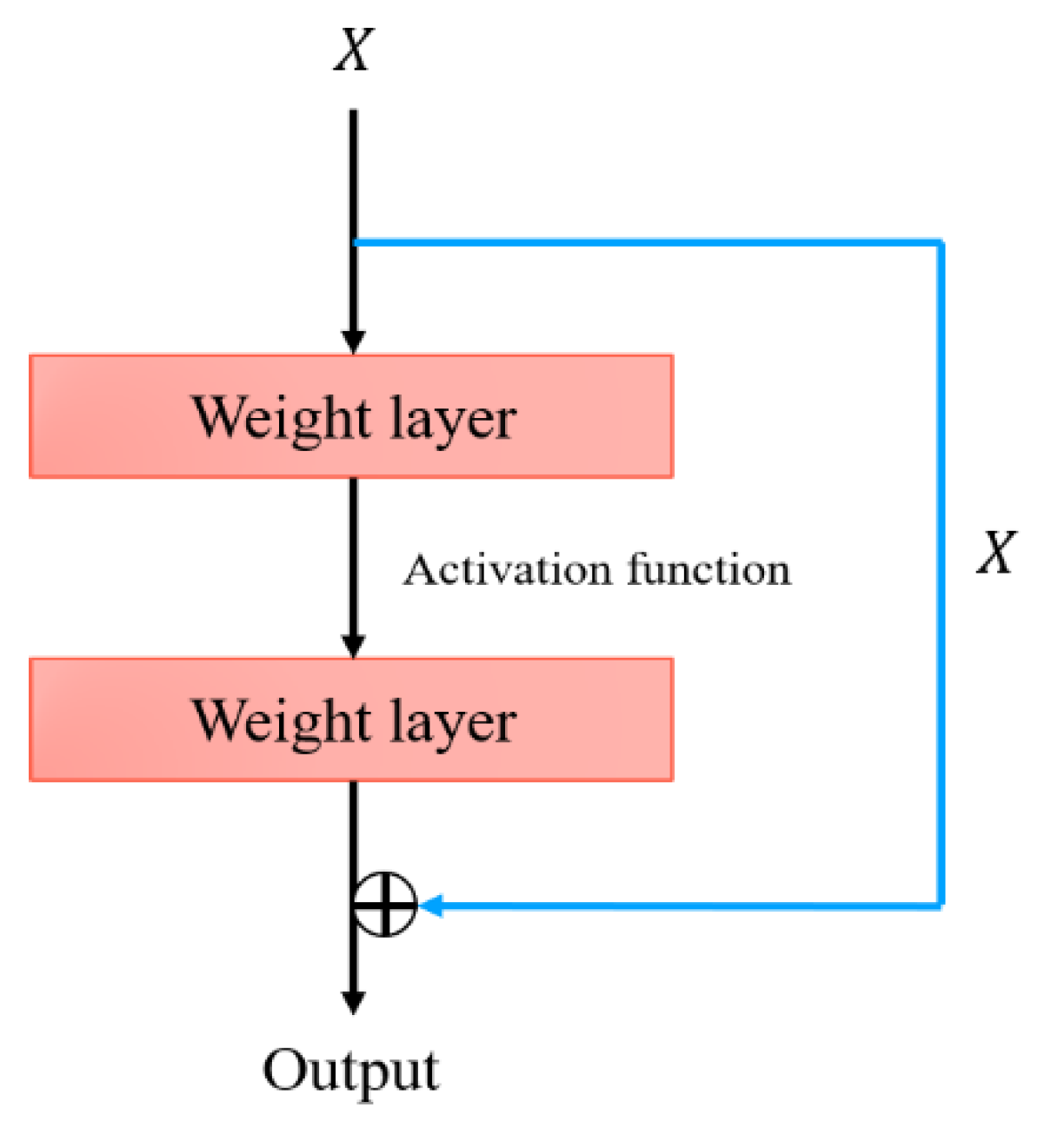
2.1. ResNet
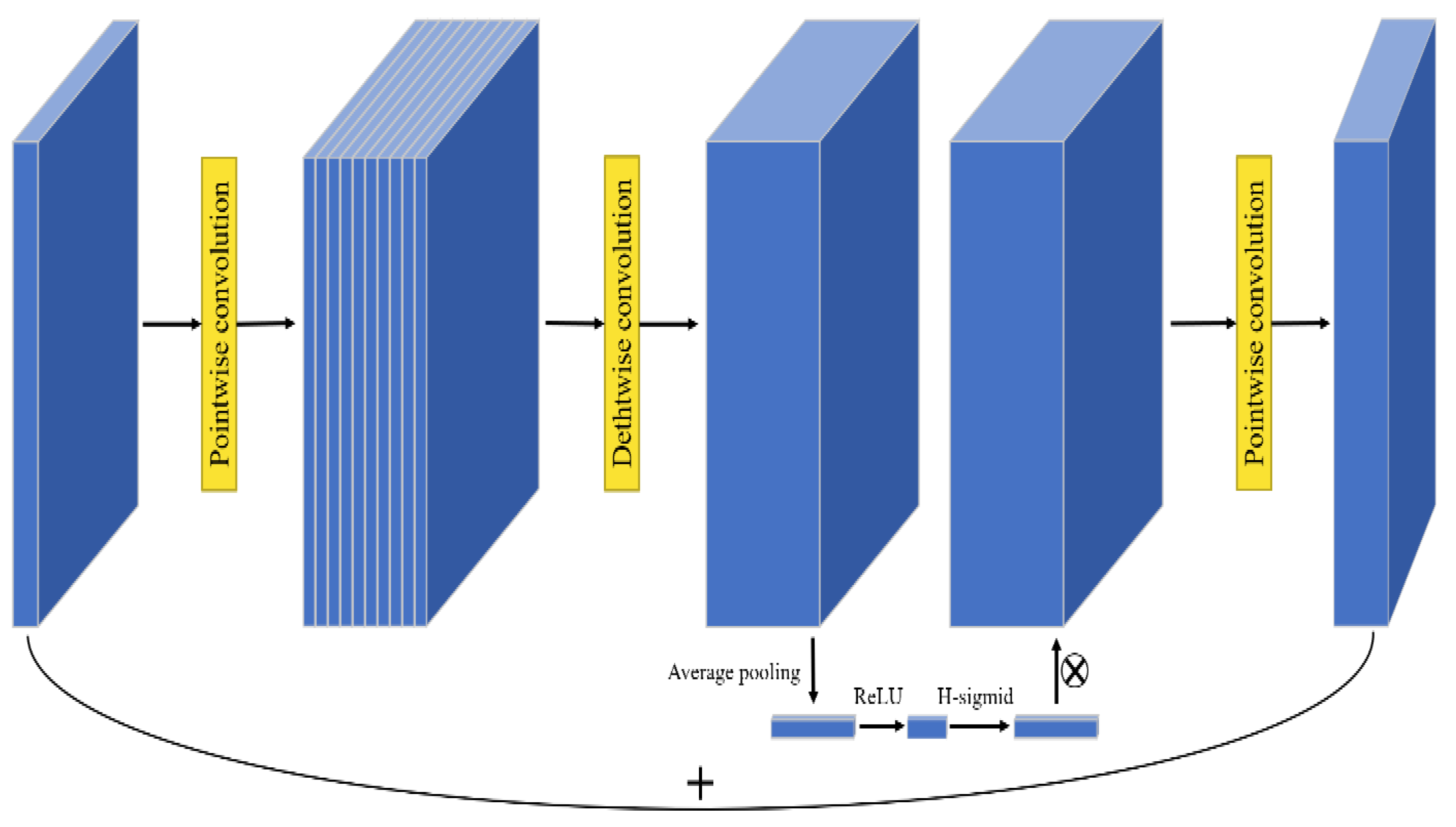
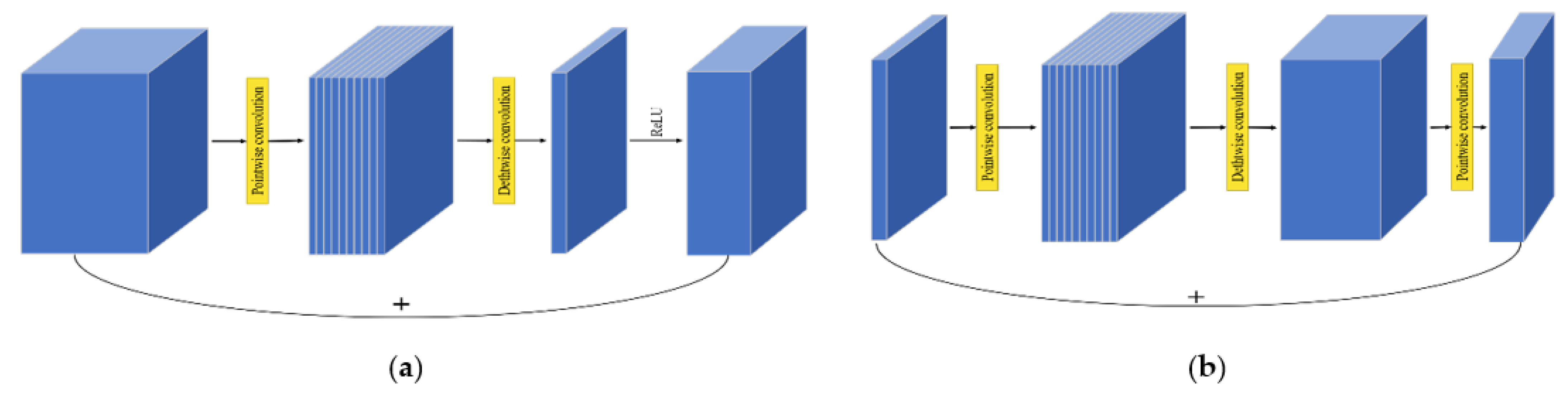
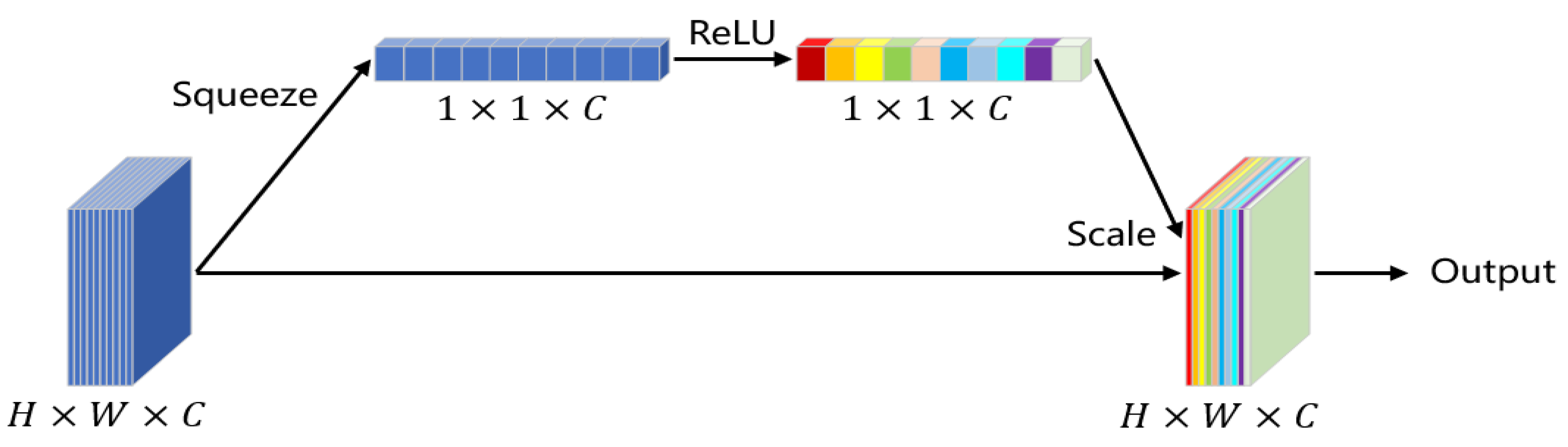
2.2. MobileNetV3
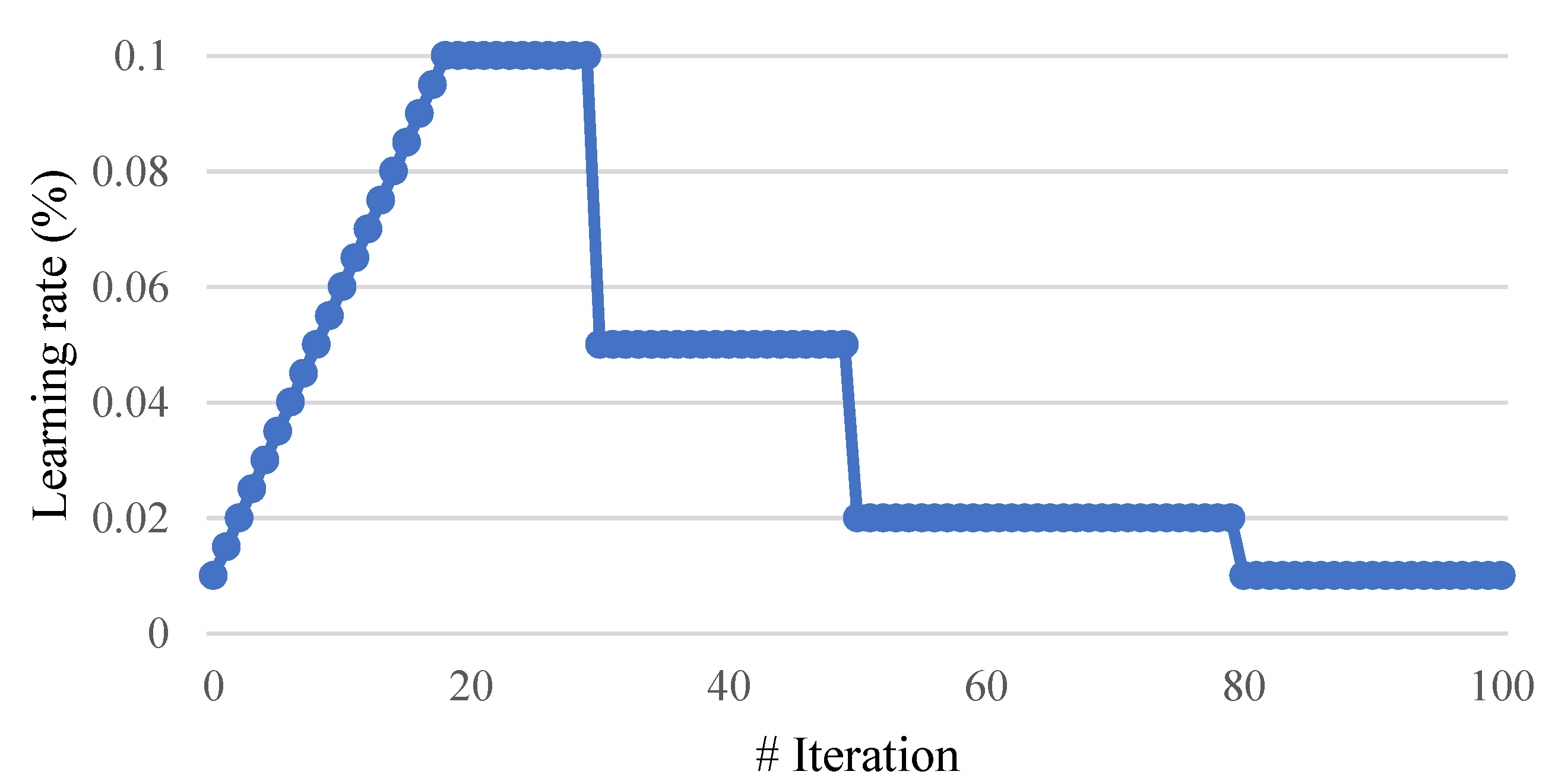
2.3. Rectified Adam (RA)
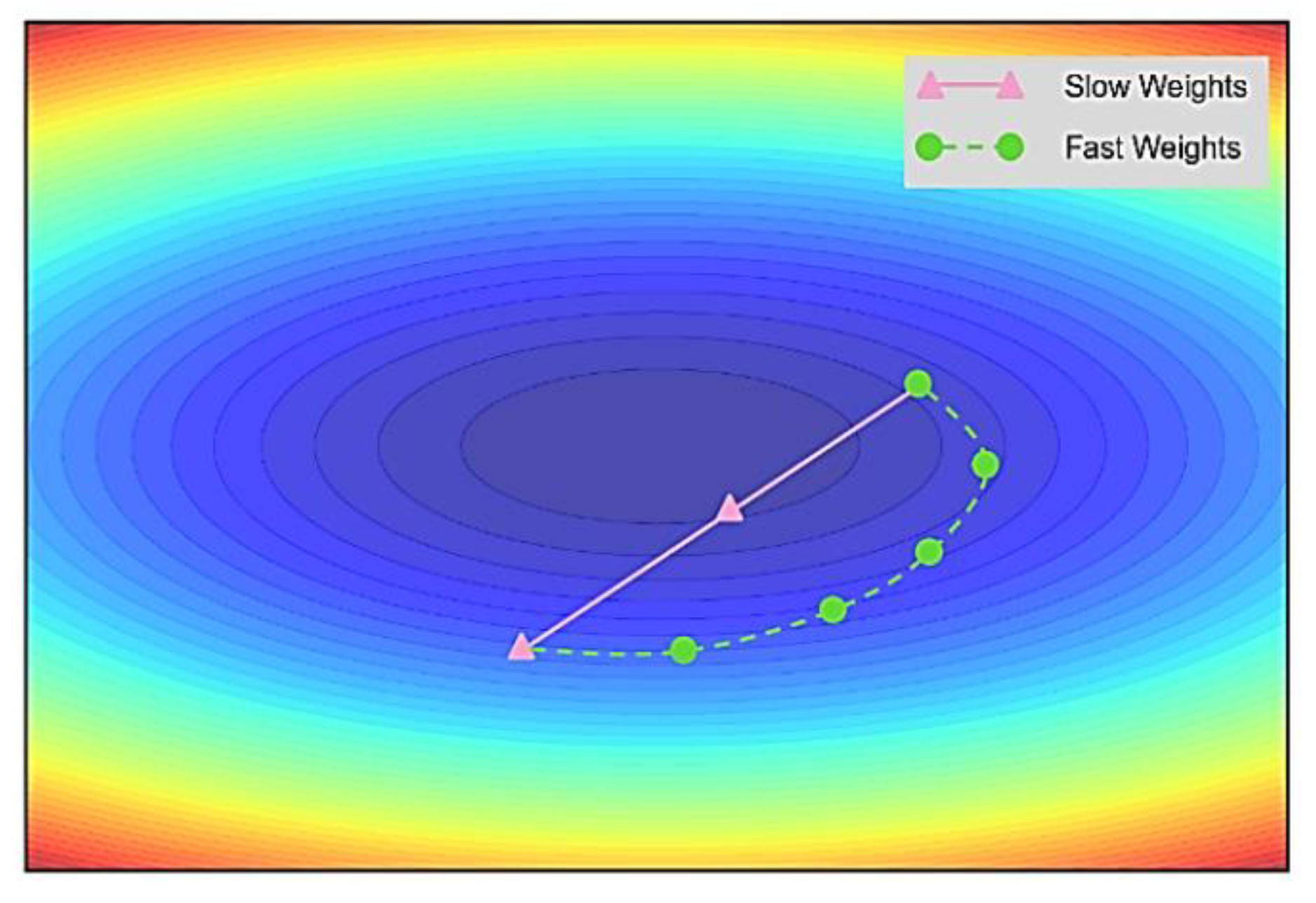
2.4. Lookahead (LA)
2.5. Gradient Centralization (GC)
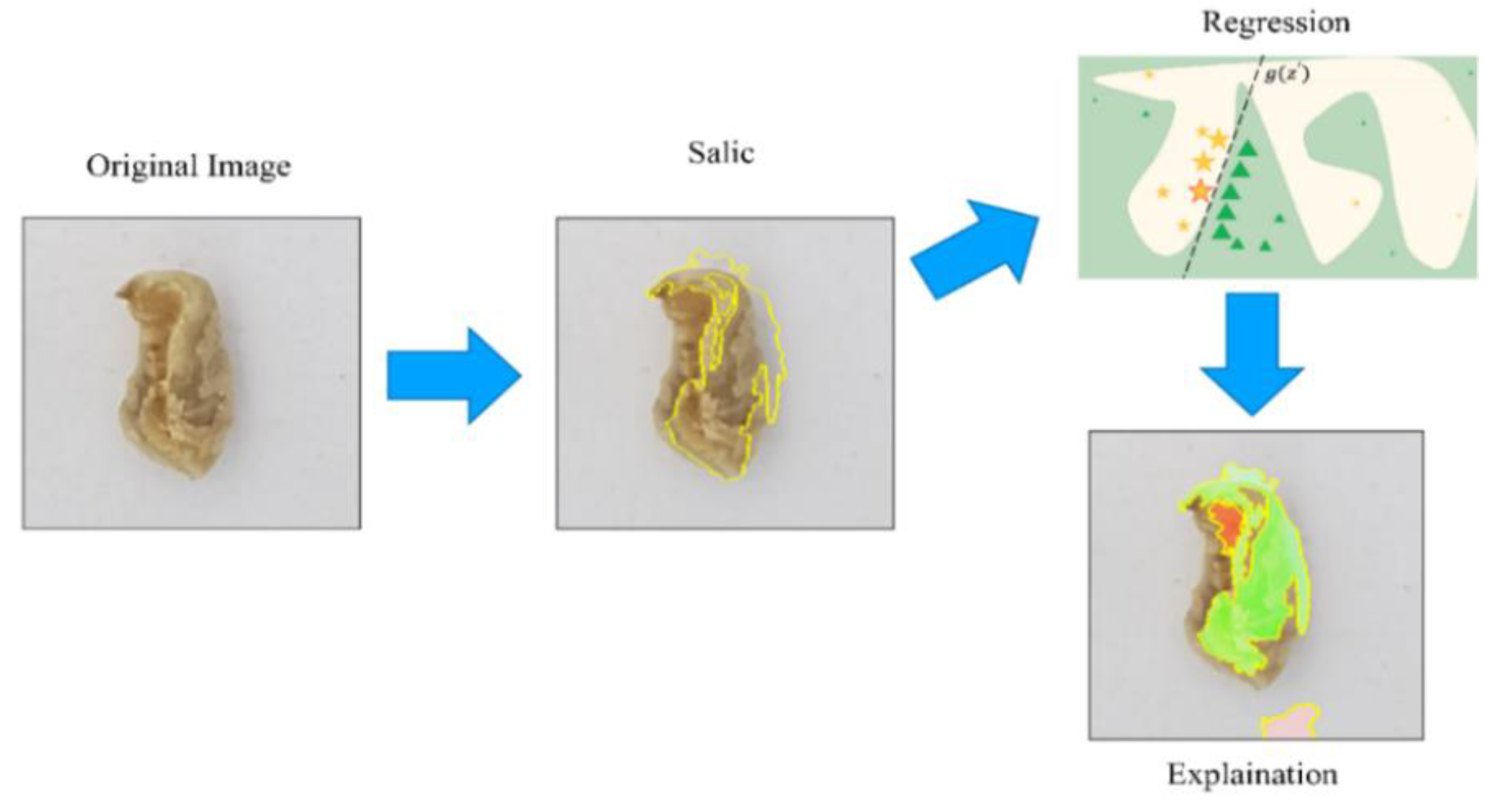
2.6. Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (LIME)
3. Proposed Methodology
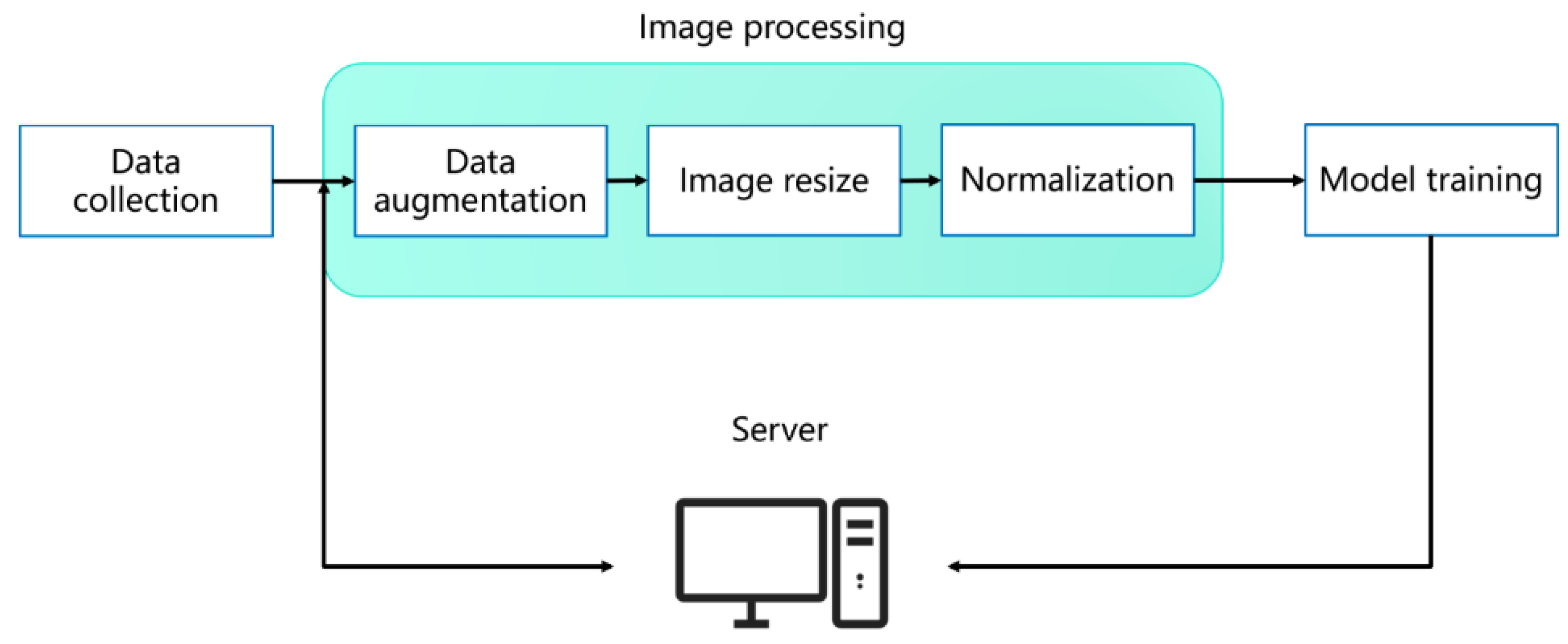
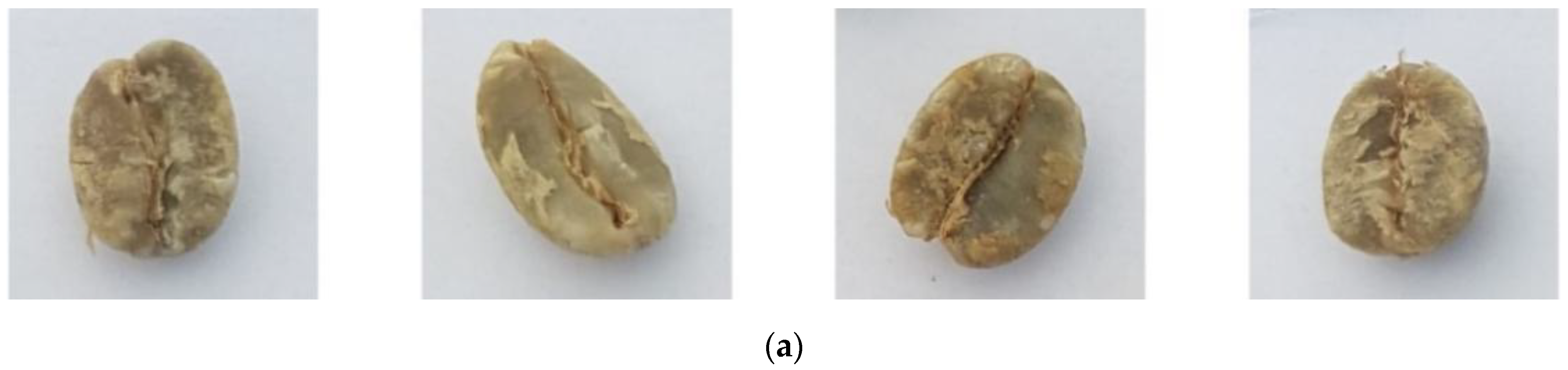
3.1. Image Preprocessing
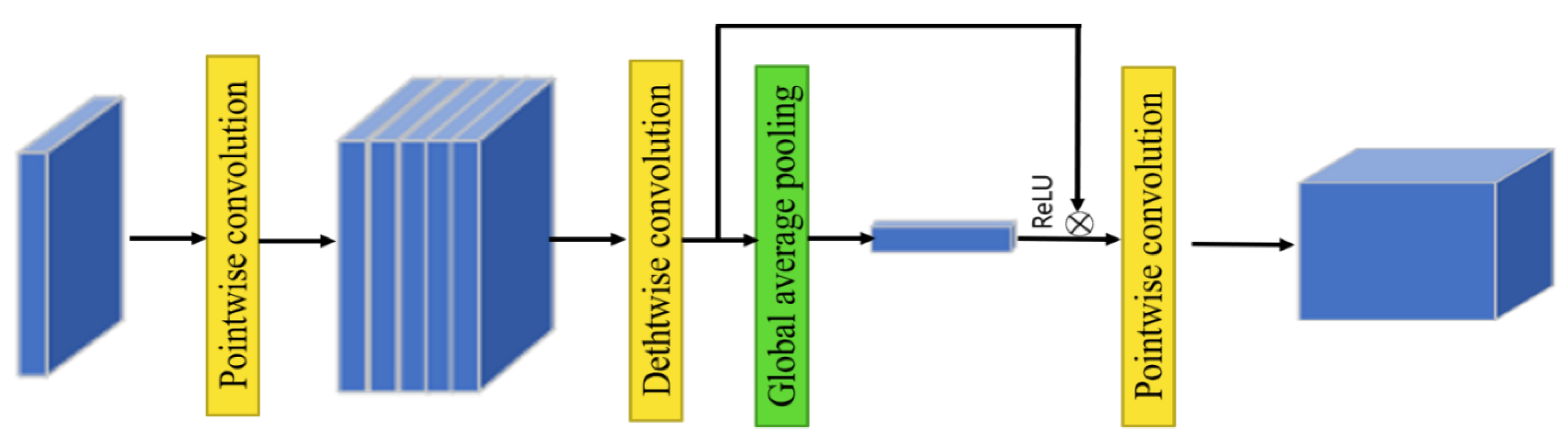
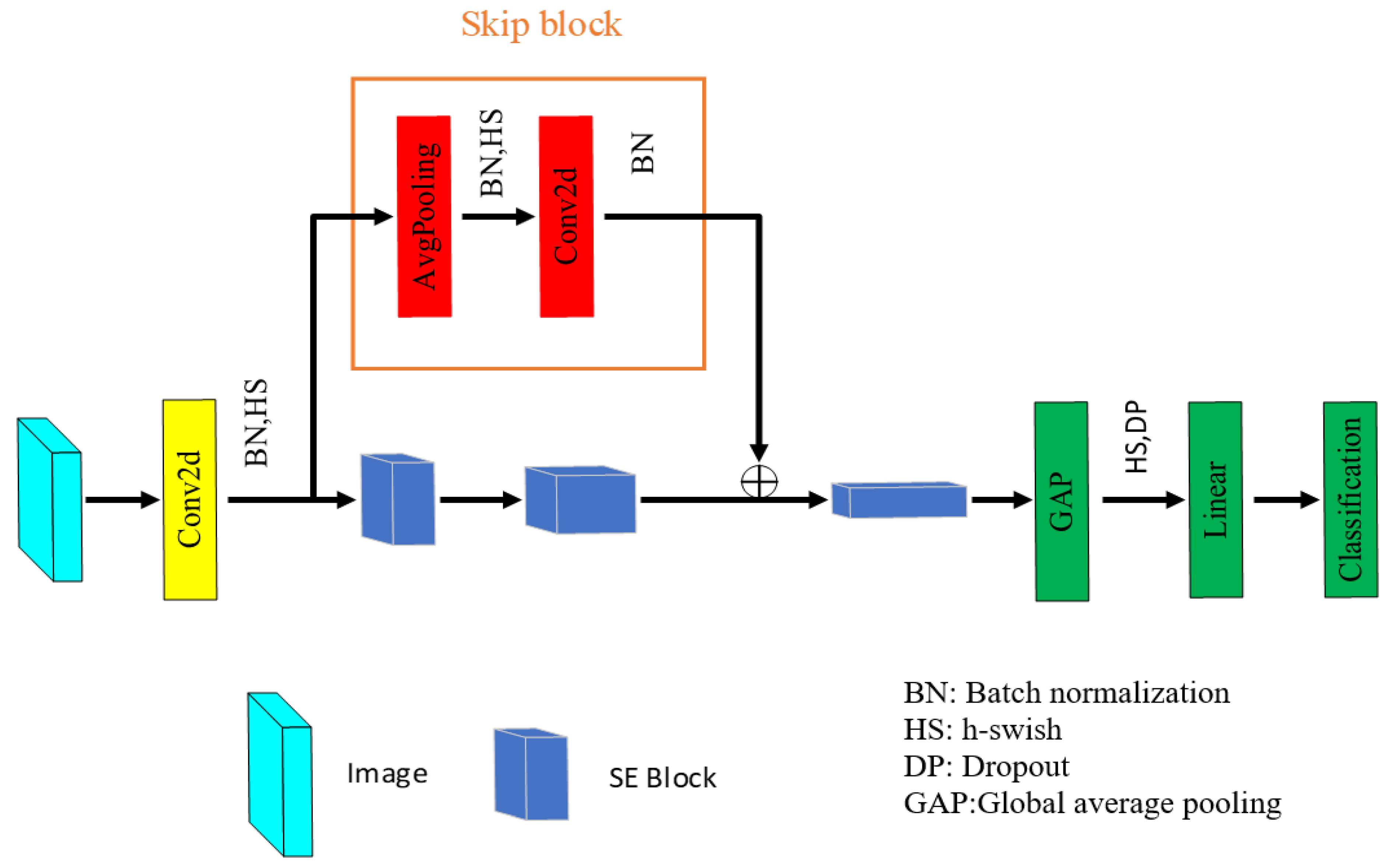
3.2. Lightweight Deep Convolutional Neural Network (LDCNN)
4. Experimental Result
4.1. The Influence of Image Normalization on Model
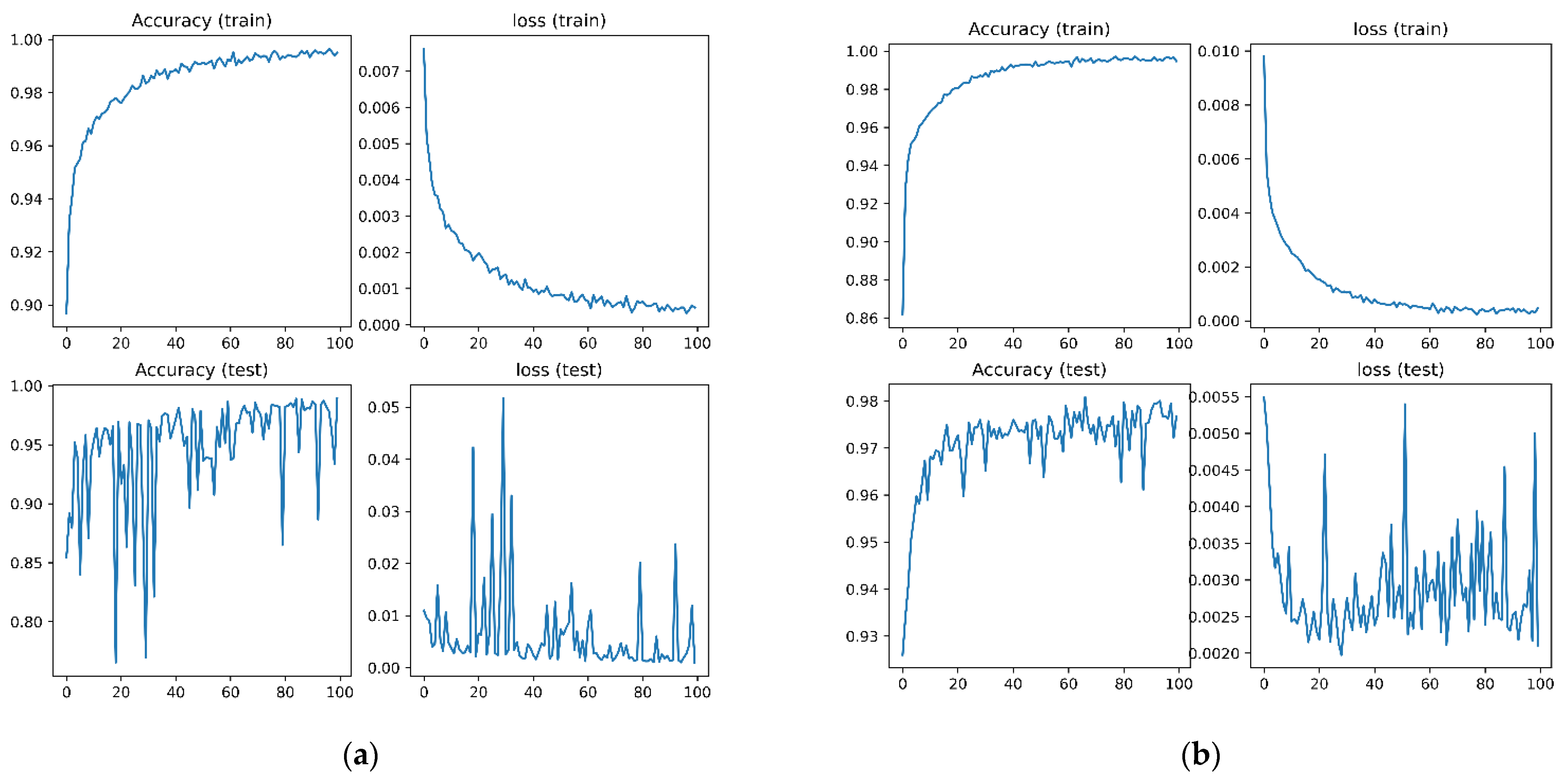
4.2. Ablation Study of Training and Optimization in the Model
4.3. Evaluation Results of Interpretable Model
4.4. Comparison of Model Efficiency & Embedded System
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inoue, M.; Yoshimi, I.; Sobue, T.; Tsugane, S. Influence of coffee drinking on subsequent risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective study in Japan. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loftfield, E.; Freedman, N.D.; Graubard, B.I.; Guertin, K.A.; Black, A.; Huang, W.-Y.; Shebl, F.M.; Mayne, S.T.; Sinha, R. Association of coffee consumption with overall and cause-specific mortality in a large US prospective cohort study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 182, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzafera, P. Chemical composition of defective coffee beans. Food Chem. 1999, 64, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chen, B.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.-C.; Tan, M.; Chu, G.; Vasudevan, V.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, H.; He, P.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Han, J. On the variance of the adaptive learning rate and beyond. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 20–30 April 2020; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, P.; Doll’ar, P.; Girshick, R.; Noordhuis, P.; Wesolowski, L.; Kyrola, A.; Tulloch, A.; Jia, Y.; He, K. Accurate, large minibatch SGD: Training ImageNet in 1 hour. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.02677. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Lucas, J.; Ba, J.; Hinton, G.E. Lookahead optimizer: K steps forward, 1 step back. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, H.; Huang, J.; Hua, X.; Zhang, L. Gradient centralization: A new optimization technique for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 635–652. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. Why should I trust you? Explaining the predictions of ant classifier. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Coffee Bean Dataset: Small Optical Sorter. Available online: https://github.com/tanius/smallopticalsorter (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- ImageNet. Available online: https://www.image-net.org/ (accessed on 11 March 2021).
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNetV2: Smaller models and faster training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online. 18–24 July 2021; pp. 10096–10106. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet V2: Practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 122–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Tseng, H.-W.; Chen, T.-C.; Hsia, C.-H. Deep convolutional neural network for coffee bean inspection. Sens. Mater. 2021, 33, 2299–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.-Y.; Jhong, S.-Y.; Hsia, C.-H. Green coffee beans classification using attention-based features and knowledge transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan, Penghu, Taiwan, 15–17 September 2021; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.R.; Sarraguça, M.C.; Rangel, A.O.S.S.; Lopes, J.A. Evaluation of green coffee beans quality using near infrared spectroscopy: A quantitative approach. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, E.M.; Leme, D.S.; Barbosa, B.H.G.; Rodarte, M.P.; Pereira, R.G.F.A. A computer vision system for coffee beans classification based on computational intelligence techniques. J. Food Eng. 2016, 171, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboleda, E.R.; Fajardo, A.C.; Medina, R.P. Classification of coffee bean species using image processing, artificial neural network and K nearest neighbors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Innovative Research and Development, Bangkok, Thailand, 11–12 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Arboleda, E.R.; Fajardo, A.C.; Medina, R.P. An image processing technique for coffee black beans identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Innovative Research and Development, Bangkok, Thailand, 11–12 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, C.; Furukawa, J.; Fukai, H.; Tamura, S. Classification of green coffee bean images based on defect types using convolutional neural network (CNN). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference of Advanced Informatics, Denpasar, Indonesia, 16–18 August 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.-F.; Chou, D.-L.; Lee, C.-A.; Wu, F.-P.; Chuang, A.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Tsai, Y.-C. Smart agriculture: Real-time classification of green coffee beans by using a convolutional neural network. IET Smart Cities 2020, 2, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, H.M.D.; Abdar, M.; Jalali, S.M.J.; Khosravi, A.; Atiya, A.; Nahavandi, S.; Srinivasan, D. SpinalNet: Deep neural network with gradual input. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.03347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post-Training Quantization. Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org/model_optimization/guide/quantization/post_training (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Huang, Q. Weight-quantized squeezenet for resource-constrained robot vacuums for indoor obstacle classification. AI 2022, 3, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blalock, D.; Gonzalez Ortiz, J.J.; Frankle, J.; Guttag, J. What is the state of neural network pruning? Proc. Mach. Learn. Syst. 2020, 2, 129–146. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Luo, L.; Xie, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, R.; Bi, L.; Lu, C. Automatic sparse connectivity learning for neural networks. IEEE Transac. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Convolutional neural network pruning with structural redundancy reduction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14913–14922. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyang, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Maaten, L.V.D.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference for Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.-H.; Jhong, S.-Y.; Hsia, C.-H. Semi-supervised learning with attention-based CNN for classification of coffee beans defect. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan, Taipei, Taiwan, 6–8 July 2022; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- de Fátima Rezende, E.; Borges, J.G.; Cirillo, M.Â.; Prado, G.; Paiva, L.C.; Batista, L.R. Ochratoxigenic fungi associated with green coffee beans (Coffea arabica L.) in conventional and organic cultivation in Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
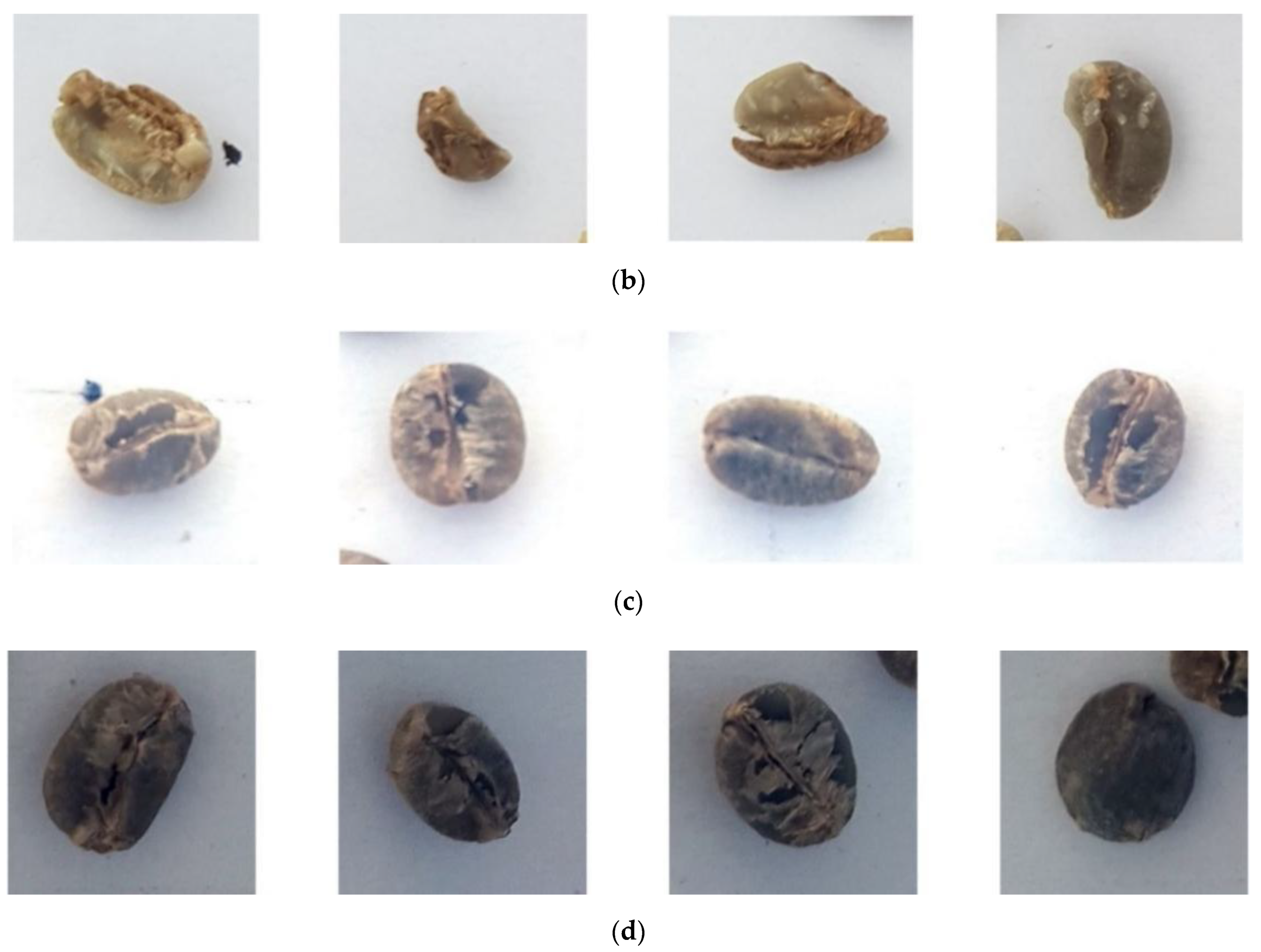






| Input Size | Operator | Exp Size | Out | Stride | HS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 224 × 224 × 3 | Conv2d, 3 × 3 | – | 16 | 2 | ✓ |
| 112 × 112 × 16 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 64 | 32 | 2 | – |
| 56 × 56 × 32 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 128 | 48 | 2 | – |
| 28 × 28 × 48 | Bneck, 3 × 3 | 128 | 48 | 1 | – |
| 28 × 28 × 48 | Pool, 28 × 28 | – | 48 | 1 | – |
| 1 × 1 × 48 | Linear | – | 1024 | – | ✓ |
| 1 × 1 × 1024 | Dropout, 0.2 | – | 1024 | – | – |
| 1 × 1 × 1024 | Linear | – | 2 | – | – |
| Normalization | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without | 89.79% | 84.86% | 94.00% | 87.78% |
| With | 96.84% | 97.06% | 96.21% | 96.50% |
| RA | LA | GC | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 96.84% | 97.06% | 96.21% | 96.50% | |||
| ✓ | 96.98% | 99.09% | 94.41% | 96.65% | ||
| ✓ | 94.24% | 93.78% | 94.22% | 93.62% | ||
| ✓ | 98.13% | 97.53% | 98.47% | 98.00% | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 98.00% | 97.79% | 97.92% | 97.85% | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 97.74% | 97.35% | 97.82% | 97.57% | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 97.81% | 98.22% | 97.07% | 97.83% | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 98.38% | 98.60% | 97.89% | 98.24% |
| Models | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Parameter | Model Size | GFLOPs | Evaluate Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SqueezeNet [14] | 95.92% | 95.25% | 96.01% | 95.58% | 1,248,424 | 4.78 MB | 0.352 | 17.57 ms |
| ResNet18 [18] | 89.66% | 89.17% | 96.07% | 91.26% | 1,1689,512 | 44.59 MB | 1.82 | 19.45 ms |
| ResNet34 [18] | 85.93% | 98.12% | 80.45% | 87.56% | 21,797,672 | 83.15 MB | 3.68 | 31.00 ms |
| ResNet50 [18] | 87.85% | 87.60% | 88.95% | 86.28% | 25,557,032 | 97.49 MB | 4.12 | 57.10 ms |
| MobileNetV3small [19] | 95.97% | 95.26% | 96.08% | 95.65% | 2,542,856 | 9.7 MB | 0.06 | 10.56 ms |
| MobileNetV3large [19] | 96.69% | 97.75% | 95.53% | 96.49% | 5,483,032 | 20.92 MB | 0.23 | 20.92 ms |
| EfficientNetV2-S [30] | 96.04% | 96.10% | 96.04% | 95.23% | 22,103,832 | 85.1 MB | 8.8 | 73.23 ms |
| ShuffleNetV2 [31] | 95.91% | 95.24% | 96.01% | 95.57% | 2,278,604 | 8.69 MB | 0.149 | 13.72 ms |
| LDCNN | 98.38% | 98.60% | 97.89% | 98.24% | 149,842 | 0.57 MB | 0.05 | 10.08 ms |
| Models | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet50 [18] | N/A | 84.00% | 84.89% | 84.21% | N/A |
| Wang et al. [9] | 91% | N/A | N/A | N/A | 256,779 |
| Yang et al. [11] | N/A | 96.48% | 97.53% | 96.54% | N/A |
| SqueezeNet [14] | 95.92% | 95.25% | 96.01% | 95.58% | 1,248,424 |
| MobileNet [32] | N/A | 76.98% | 81.31% | 77.03% | N/A |
| DenseNet121 [33] | N/A | 88.28% | 88.28% | 88.28% | N/A |
| Xception [34] | N/A | 89.70% | 89.56% | 89.60% | N/A |
| Vgg16 [35] | N/A | 93.55% | 93.52% | 93.09% | N/A |
| Chen et al. [36] | N/A | 97.38% | 97.16% | 97.21% | N/A |
| LDCNN | 98.38% | 98.60% | 97.89% | 98.24% | 156,370 |
| # Image | Evaluate Time | Average Frames per Second (FPS) |
|---|---|---|
| 3701 | 1226.57 s | 3.0174 s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsia, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lai, C.-F. An Explainable and Lightweight Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Quality Detection of Green Coffee Beans. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110966
Hsia C-H, Lee Y-H, Lai C-F. An Explainable and Lightweight Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Quality Detection of Green Coffee Beans. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(21):10966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110966
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsia, Chih-Hsien, Yi-Hsuan Lee, and Chin-Feng Lai. 2022. "An Explainable and Lightweight Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Quality Detection of Green Coffee Beans" Applied Sciences 12, no. 21: 10966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110966
APA StyleHsia, C.-H., Lee, Y.-H., & Lai, C.-F. (2022). An Explainable and Lightweight Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Quality Detection of Green Coffee Beans. Applied Sciences, 12(21), 10966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110966













