Evaluation and Optimization of Biomedical Image-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network Model for COVID-19 Status Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
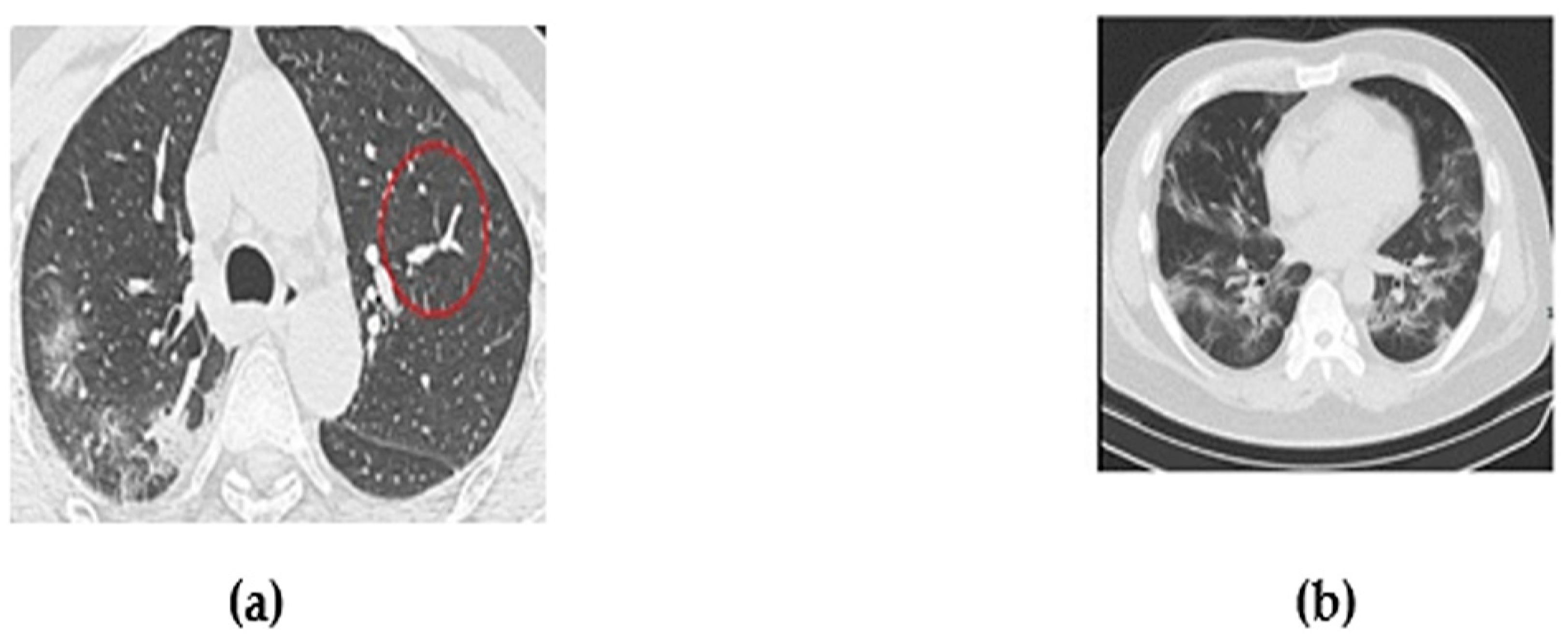
3. Dataset Description
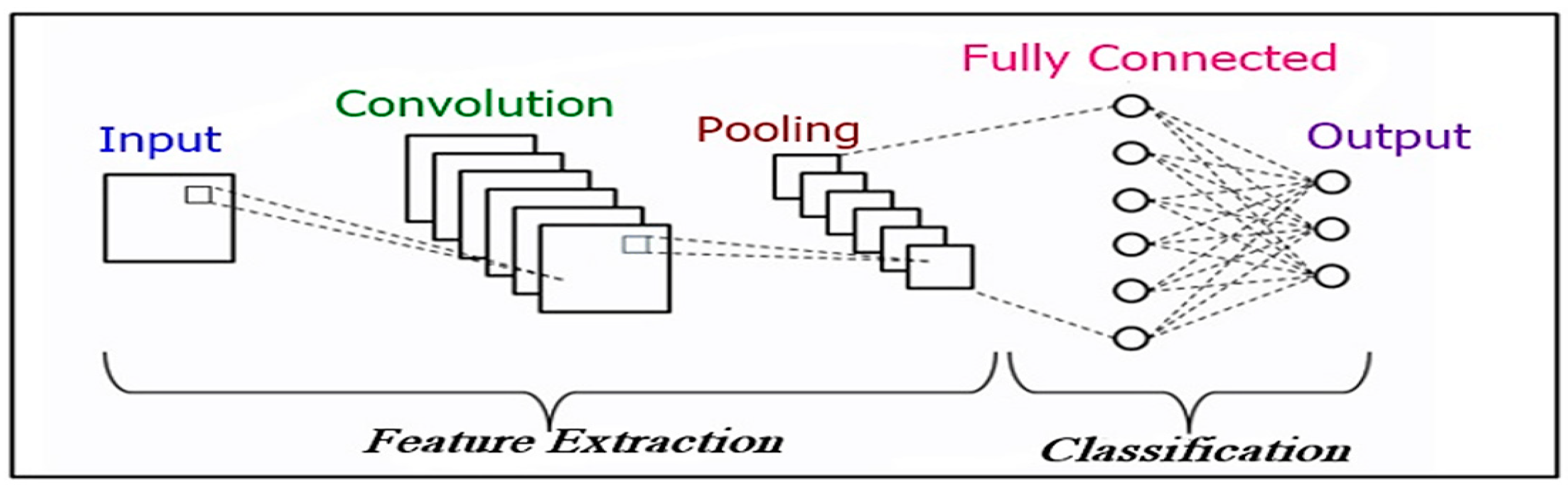
4. Architecture of CNN Model
- A.
- Convolutional Layer;
- B.
- Pooling Layer;
- C.
- Fully Connected Layer (FC layer).
- A.
- Convolutional Layer: The first layer in the CNN architecture is the convolutional layer. It consists of a set of convolutional kernels (i.e., filters) where each neuron performs as the kernel. Here, the mathematical operation of convolution is accomplished between the input image and a filter of a specific size M × M. Convolution operation of a feature matrix can be expressed as follows:
- B.
- Pooling Layer: Generally, a pooling layer comes after a convolutional layer. The primary goal of this layer is to reduce the size of the feature map generated by convolution to decrease the computational costs. It is executed by reducing the connections between layers and separately operating on each feature map.
- C.
- Fully Connected Layer (FC Layer): This layer contains weights and biases associated with the neurons and is utilized to connect the neurons between two separate layers. These layers are normally located prior to the output layer in a CNN Architecture.
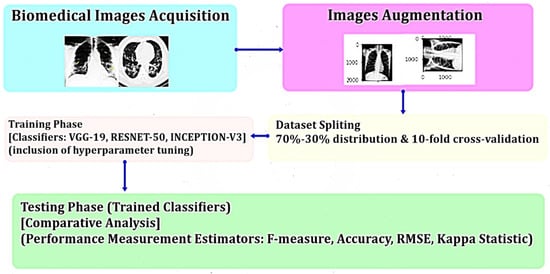
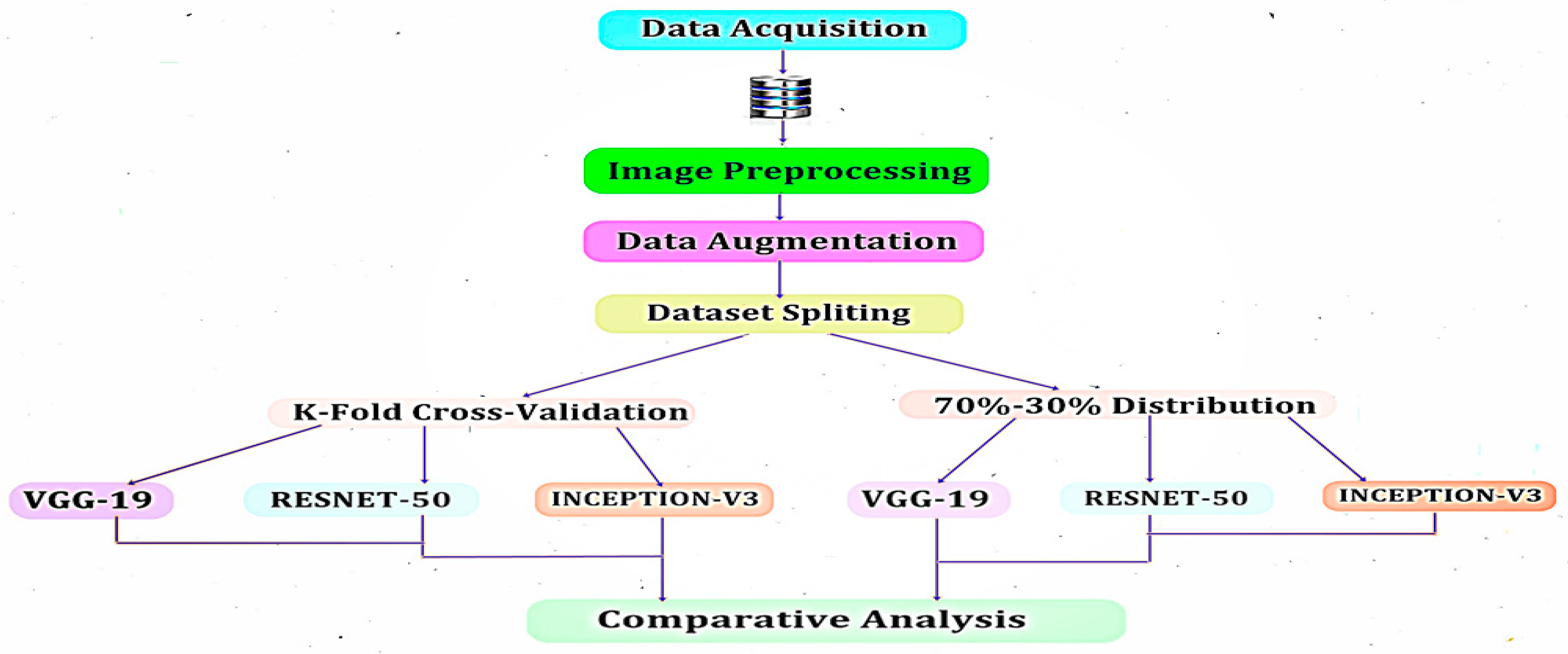
5. Materials and Methods
6. Results and Discussion
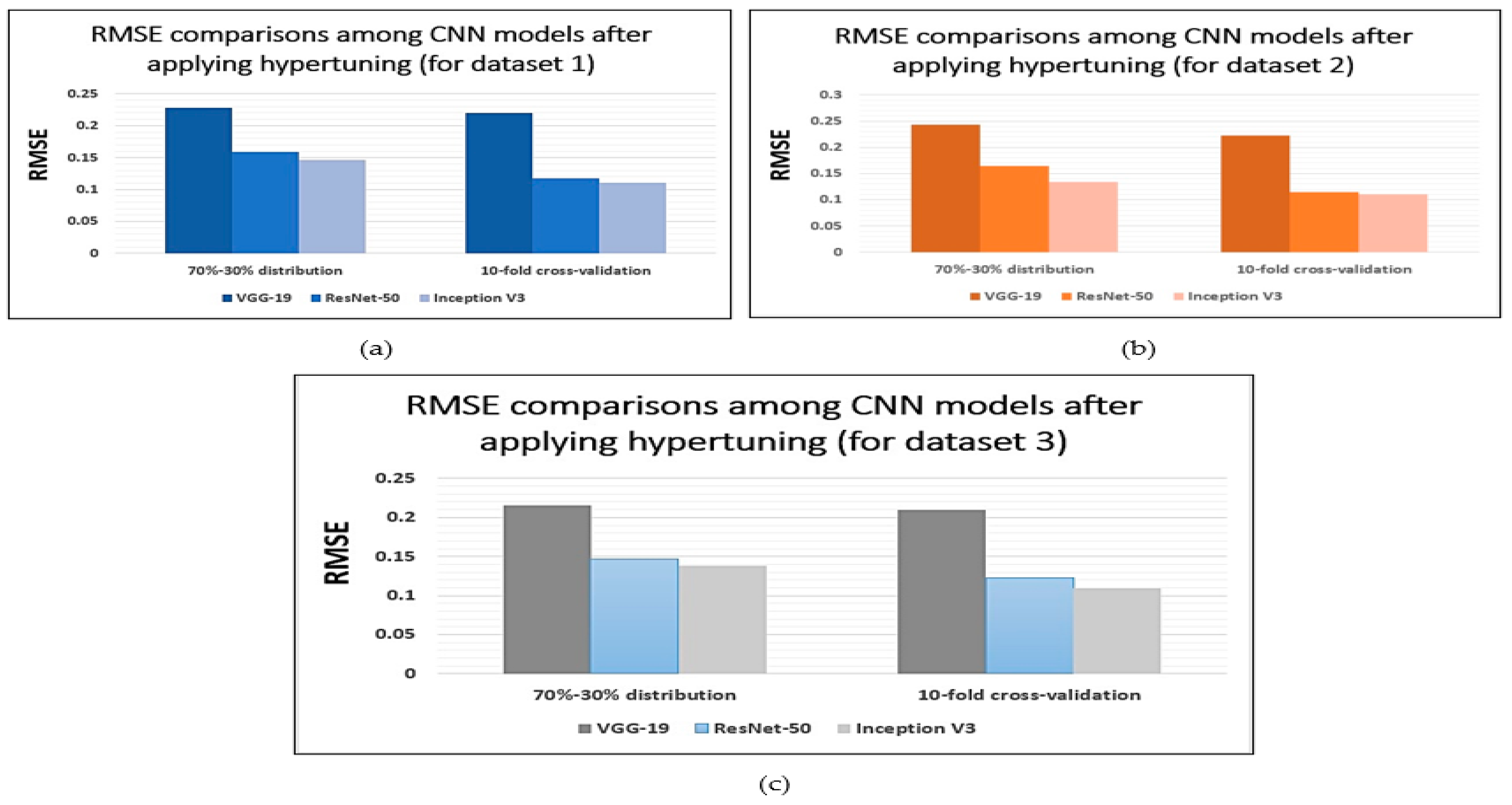
6.1. Root-Mean-Square Error (RMSE)
6.2. Kappa Statistic
6.3. Confusion Matrix
- ■
- True-Positive (TP) indicates the number of ‘positive’ examples classified as ‘positive.’
- ■
- False-Positive (FP) implies the number of ‘negative’ examples classified as ‘positive.’
- ■
- False-Negative (FN) denotes the number of ‘positive’ examples classified as ‘negative.’
- ■
- True-Negative (TN) means the number of ‘negative’ examples classified as ‘negative.’
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, Y.; Zhao, K.; Shi, Z.L.; Zhou, P. Bat Coronaviruses in China. Viruses 2019, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Huang, Y.; Lau, S.K.; Yuen, K.Y. Coronavirus Genomics and Bioinformatics Analysis. Viruses 2010, 2, 1804–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Definition of Coronavirus by Merriam-Webster. Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Available online: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/coronavirus (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Yazdanpanah, F.; Hamblin, M.R.; Rezaei, N. The immune system and COVID-19: Friend or foe? Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Seo, K.W.; Song, K.H. Clinical evaluation of a rapid diagnostic test kit for detection of canine coronavirus. Korean J. Vet. Res. 2018, 58, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 60, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciregan, D.; Meier, U.; Schmidhuber, J. Multi-column deep neural networks for image classification. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 3642–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Denmark, 2014; pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Sermanet, P.; Eigen, D.; Zhang, X.; Mathieu, M.; Fergus, R.; LeCun, Y. OverFeat: Integrated Recognition. Localization Detection using Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y. Using Deep Learning for Image-Based Different Degrees of Ginkgo Leaf Disease Classification. Information 2020, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, S.; Seth, S.; Bhadra, T.; Zhao, Z. A linear regression and deep learning approach for detecting reliable genetic alterations in cancer using dna methylation and gene expression data. Genes 2020, 11, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Balabantaray, B.K.; Bora, K.; Mallik, S.; Kasugai, K.; Zhao, Z. An ensemble-based deep convolutional neural network for computer-aided polyps identification from colonoscopy. Front. Genet. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Yan, F.; Simon, L.M.; Dai, Y.; Jia, P.; Zhao, Z. deCS: A tool for systematic cell type annotations of single-cell RNA sequencing data among human tissues. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Hu, R.; Dai, Y.; Manuel, A.M.; Zhao, Z.; Jia, P. Predicting regulatory variants using a dense epigenomic mapped CNN model elucidated the molecular basis of trait-tissue associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.; Hu, R.; Pei, G.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Deep generative neural network for accurate drug response imputation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Integration of millions of transcriptomes using batch-aware triplet neural networks. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Mondal, S.; Ghosh, B. A comparative study of breast cancer detection based on SVM and MLP BPN classifier. In Proceedings of the 2014 First International Conference on Automation, Control, Energy and Systems (ACES), Adisaptagram, India, 1–2 February 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Lin, M.; Ying, L.; Pang, P.; Ji, W. Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: Comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology 2020, 296, E115–E117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madaan, V.; Roy, A.; Gupta, C.; Agrawal, P.; Sharma, A.; Bologa, C.; Prodan, R. XCOVNet: Chest X-ray image classification for COVID-19 early detection using convolutional neural networks. New Gener. Comput. 2021, 39, 583–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, T.; Mallik, S.; Sohel, A.; Zhao, Z. Unsupervised Feature Selection Using an Integrated Strategy of Hierarchical Clustering with Singular Value Decomposition: An Integrative Biomarker Discovery Method with Application to Acute Myeloid Leukemia. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2022, 19, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Biswas, D.; Biswas, S.; Sarkar, D.C.; Sarkar, P.P. Soil classification from large imagery databases using a neuro-fuzzy classifier. Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2016, 39, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinnuwesi, B.A.; Fashoto, S.G.; Mbunge, E.; Odumabo, A.; Metfula, A.S.; Mashwama, P.; Uzoka, F.M.; Owolabi, O.; AutOkpeku, M.; Amusa, O.O. Application of intelligence-based computational techniques for classification and early differential diagnosis of COVID-19 disease. Data Sci. Manag. 2021, 4, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, F.; Makridakis, S. Forecasting the novel coronavirus COVID-19. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. COVID-net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zissermanm, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Lundervold, A.S.; Lundervold, A. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on MRI. Z. Für Med. Phys. 2019, 29, 102–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jia, P.; Zhao, Z. DeepVISP: Deep learning for virus site integration prediction and motif discovery. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.H.; Jia, J.; Dai, Y.; Simons, L.M.; Zhao, Z. Investigating cellular trajectories in the severity of COVID-19 and their transcriptional programs using machine learning approaches. Genes 2021, 12, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mallik, S.; Qin, G. Feature Selection, Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms on Multi-Modal Omics Data. In Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Computational Biology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Cho, N.; Yoon, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J. Transfer Learning of a Deep Learning Model for Exploring Tourists’ Urban Image Using Geotagged Photos. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, C.-C. Content-Based Image Copy Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network. Electronics 2020, 9, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M. Ground truth labeling and samples selection for hyperspectral image classification. Optik 2021, 230, 166267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musleh, A.A.W.A.; Maghari, A.Y. COVID-19 detection in X-ray images using CNN algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Promising Electronic Technologies (ICPET), Jerusalem, Palestine, 16–17 December 2020; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, E.-H.; Amer, H.; Jiang, Y. Compression Helps Deep Learning in Image Classification. Entropy 2021, 23, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Lau, R.Y.K.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Huang, X. Synergistic 2D/3D Convolutional Neural Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistie, T.T. COVID-19 outbreak data analysis and prediction modeling using data mining technique. Int. J. Comput. (IJC) 2020, 38, 37–60. [Google Scholar]
- Cortés-Martínez, K.V.; Estrada-Esquivel, H.; Martínez-Rebollar, A.; Hernández-Pérez, Y.; Ortiz-Hernández, J. The State of the Art of Data Mining Algorithms for Predicting the COVID-19 Pandemic. Axioms 2022, 11, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahouz, F.; Golabpour, A. Predicting the incidence of COVID-19 using data mining. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmapriya, V.; Kaliyappan, M. Fuzzy fractional mathematical model of COVID-19 epidemic. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, Preprint, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaloofi, H.; Hussain, J.; Azhar, Z.; Ahmad, H.F. Performance evaluation of machine learning approaches for COVID-19 forecasting by infectious disease modeling. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference of Women in Data Science at Taif University (WiDSTaif). Taif, Saudi Arabia, 30–31 March 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Brunese, L.; Mercaldo, F.; Reginelli, A.; Santone, A. Explainable deep learning for pulmonary disease and coronavirus COVID-19 detection from X-rays. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haritha, D.; Praneeth, C.; Krishna, M. COVID Prediction from X-ray images. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS), Patna, India, 14–16 October 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bodapati, S.; Bandarupally, H.; Trupthi, M. COVID-19 time series forecasting of daily cases, deaths caused and recovered cases using long short term memory networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Conference on Computing Communication and Automation (ICCCA), Greater Noida, India, 30–31 October 2020; pp. 525–530. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, V.; Keniya, R.; Shridharani, A.; Punjabi, M.; Shah, J.; Mehendale, N. Diagnosis of COVID-19 using CT scan images and deep learning techniques. Emerg. Radiol. 2021, 28, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, A.; Keles, M.B.; Keles, A. COV19-CNNet and COV19-ResNet: Diagnostic inference Engines for early detection of COVID-19. Cogn. Comput. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Tang, Z.; Wang, S.; Hui, H.; Gong, L.; Lu, Y.; Xue, Z.; Liao, H.; Chen, F.; Yang, F.; et al. The role of imaging in the detection and management of COVID-19: A review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Mpesiana, T.A. COVID-19: Automatic detection from x-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Abdelsamea, M.M.; Gaber, M.M. Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, A.M.; Şengür, A. Deep learning approaches for COVID-19 detection based on chest X-ray images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 164, 114054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, M.S.; Ebied, H.M.; Shedeed, H.A.; Tolba, M.F. COVID-19 X-rays model detection using convolution neural network. In The International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Denmark, 2021; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, G.; Mittal, D.; Thakur, D.; Mittal, M.K. A deep learning approach to detect COVID-19 coronavirus with X-ray images. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 1391–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, M.; Iftikhar, M.A.; Yasin, S.; Draz, U.; Ali, T.; Hussain, S.; Bukhari, S.; Alwadie, A.S.; Rahman, S.; Glowacz, A.; et al. Role of hybrid deep neural networks (HDNNs), computed tomography, and chest X-rays for the detection of COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Biswas, S.; Sarkar, D.; Sarkar, P.P. A novel Neuro-fuzzy classification technique for data mining. Egypt. Inform. J. 2014, 15, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouawad, P.; Dubnov, T.; Dubnov, S. Robust detection of COVID-19 in cough sounds. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehbodniya, A.; Lazar, A.J.P.; Webber, J.; Sharma, D.K.; Jayagopalan, S.; Singh, P.; Rajan, R.; Pandya, S.; Sengan, S. Fetal health classification from cardiotocographic data using machine learning. Expert Syst. 2022, 39, e12899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M. What the F-measure doesn’t measure: Features, Flaws, Fallacies and Fixes. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.06410. [Google Scholar]
- Hripcsak, G.; Rothschild, A.S. Agreement, the f-measure, and reliability in information retrieval. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2005, 12, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xu, C.; Luo, Y.; Xu, C.; Wen, Y.; Tao, D. Cost-sensitive feature selection by optimizing F-measures. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 27, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadakinamani, R.G.; Reyana, A.; Kautish, S.; Vibith, A.S.; Gupta, Y.; Abdelwahab, S.F.; Mohamed, A.W. Clinical Data Analysis for Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease Using Machine Learning Techniques. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2973324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.N.; Ahmad, W.; Khan, K.; Ahmad, A.; Nazar, S.; Alabdullah, A.A. Use of Artificial Intelligence for Predicting Parameters of Sustainable Concrete and Raw Ingredient Effects and Interactions. Materials 2022, 15, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toisoul, A.; Kossaifi, J.; Bulat, A.; Tzimiropoulos, G.; Pantic, M. Estimation of continuous valence and arousal levels from faces in naturalistic conditions. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Explaining the unsuitability of the kappa coefficient in the assessment and comparison of the accuracy of thematic maps obtained by image classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolayan, A.H.; Ojokoh, B.A.; Adetunmbi, A.O. Performance analysis of fuzzy analytic hierarchy process multi-criteria decision support models for contractor selection. Sci. Afr. 2020, 9, e00471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranjčić, N.; Medak, D.; Župan, R.; Rezo, M. Support vector machine accuracy assessment for extracting green urban areas in towns. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID Chest X-ray Dataset. Available online: https://github.com/ieee8023/COVID-chestxray-dataset (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- COVID Chest X-ray Dataset. Available online: https://github.com/agchung (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- COVID Chest X-ray Dataset. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia (accessed on 19 September 2021).
- El-Shafai, W.; El-Samie, F.A. Extensive COVID-19 X-ray and CT chest images dataset. Mendeley Data 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.S.; Collopy, F. Error measures for generalizing about forecasting methods: Empirical comparisons. Int. J. Forecast. 1992, 8, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carletta, J. Assessing agreement on classification tasks: The kappa statistic. arXiv 1996, arXiv:cmp-lg/9602004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S.V. Selecting and interpreting measures of thematic classification accuracy. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, H.; Gupta, P.K.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Morales-Menendez, R.; Bhardwaj, P.; Singh, V. A deep learning and grad-CAM based color visualization approach for fast detection of COVID-19 cases using chest X-ray and CT-Scan images. Chaos. Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Shah, J.L.; Bhat, M.M. CoroNet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest x-ray images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed, A.; Goyal, M.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A.; Al-Turjman, F.; Pinheiro, P.R. Covidgan: Data augmentation using auxiliary classifier gan for improved COVID-19 detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 91916–91923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narin, A.; Kaya, C.; Pamuk, Z. Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) using X-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2021, 24, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, V.; Narasimhan, H.; Chakraborty, C.; Pham, T.D. Deep learning-based meta-classifier approach for COVID-19 classification using CT scan and chest X-ray images. Multimed. Syst. 2022, 28, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


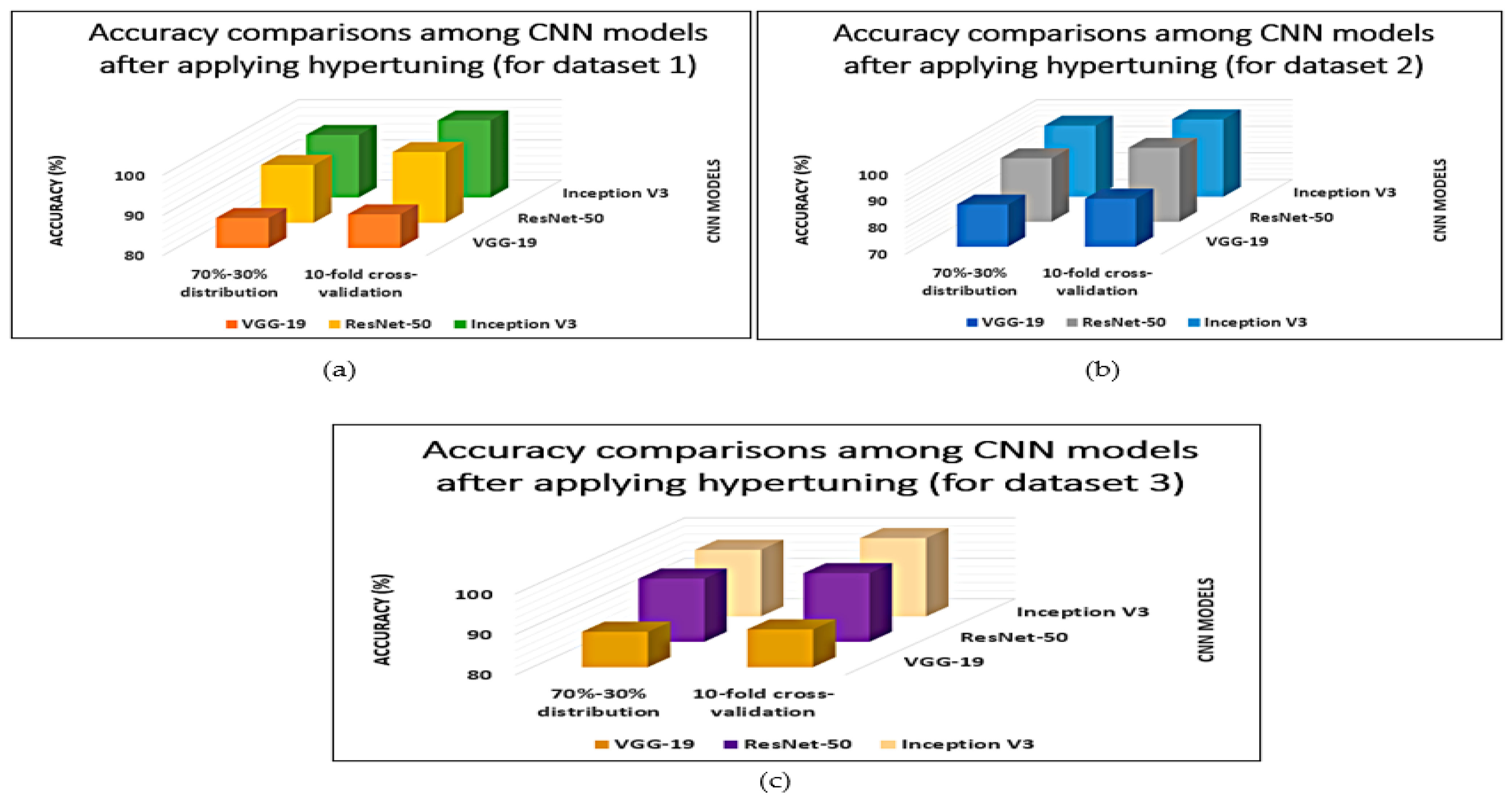



| CNN Model | 70%–30% Distribution | 10-Fold Cross-Validation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) (sd) | RMSE (sd) | Weighted Kappa (sd) | Accuracy (%) (sd) | RMSE (sd) | Weighted Kappa (sd) | |
| VGG-19 | 87.45 ( | 0.2285 ( | 0.8610 ( | 88.35 ( | 0.2195 ( | 0.8700 ( |
| ResNet-50 | 94.38 ( | 0.1592 ( | 0.9303 ( | 97.61 ( | 0.1169 ( | 0.9726 ( |
| Inception-V3 | 95.62 ( | 0.1468 ( | 0.9427 ( | 99.23 ( | 0.1107 ( | 0.9788 ( |
| CNN Model | 70%–30% Distribution | 10-Fold Cross-Validation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) (sd) | RMSE (sd) | Weighted Kappa (sd) | Accuracy (%) (sd) | RMSE (sd) | Weighted Kappa (sd) | |
| VGG-19 | 85.91 ( | 0.2439 ( | 0.8456 ( | 88.12 ( | 0.2218 ( | 0.8677 ( |
| ResNet-50 | 93.92 ( | 0.1638 ( | 0.9257 ( | 97.89 ( | 0.1141 ( | 0.9754 ( |
| Inception-V3 | 96.84 ( | 0.1346 ( | 0.9549 ( | 99.21 ( | 0.1109 ( | 0.9786 ( |
| CNN Model | 70%–30% Distribution | 10-Fold Cross-Validation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) (sd) | RMSE (sd) | Weighted Kappa (sd) | Accuracy (%) (sd) | RMSE (sd) | Weighted Kappa (sd) | |
| VGG-19 | 88.76 ( | 0.2154 ( | 0.8741 ( | 89.34 ( | 0.2096 ( | 0.8799 ( |
| ResNet-50 | 95.64 ( | 0.1466 ( | 0.9429 ( | 96.98 ( | 0.1232 ( | 0.9663 ( |
| Inception-V3 | 96.48 ( | 0.1382 ( | 0.9513 ( | 99.36 ( | 0.1094 ( | 0.9801 ( |
| Confusion Matrix | Predicted Class | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | ||
| Actual Class | positive | TP | FP |
| negative | FN | TN | |
| CNN Model | 70%–30% Distribution | 10-Fold Cross-Validation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP-Rate/Recall (%) (sd) | FP-Rate (%) (sd) | Precision (%) (sd) | F-Measure (%) (sd) | TP-Rate/Recall (%) (sd) | FP-Rate (%) (sd) | Precision (%) (sd) | F-Measure (%) (sd) | |
| VGG-19 | 87.10 ( | 12.55 ( | 87.06 ( | 87.08 ( | 88.00 ( | 11.65 ( | 87.96 ( | 87.98 ( |
| ResNet-50 | 94.03 ( | 5.62 ( | 93.99 ( | 94.01 ( | 97.26 ( | 1.39 ( | 97.22 ( | 97.24 ( |
| Inception-V3 | 95.27 ( | 4.38 ( | 95.23 ( | 95.25 ( | 98.88 ( | 0.77 ( | 98.84 ( | 98.86 ( |
| CNN Model | 70%–30% Distribution | 10-Fold Cross-Validation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP-Rate/Recall (%) (sd) | FP-Rate (%) (sd) | Precision (%) (sd) | F-Measure (%) (sd) | TP-Rate/Recall (%) (sd) | FP-Rate (%) (sd) | Precision (%) (sd) | F-Measure (%) (sd) | |
| VGG-19 | 85.56 ( | 14.09 ( | 85.52 ( | 85.54 ( | 87.77 ( | 11.88 | 87.73 ( | 87.75 ( |
| ResNet-50 | 93.57 ( | 6.08 ( | 93.53 ( | 93.55 | 97.54 | 1.11 | 97.50 ( | 97.52 ( |
| Inceptn-V3 | 96.49 ( | 3.16 ( | 96.45 ( | 96.47 ( | 98.86 ( | 0.79 ( | 98.82 ( | 98.84 ( |
| CNN Model | 70%–30% Distribution | 10-Fold Cross-Validation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP-Rate/Recall (%) (sd) | FP-Rate (%) (sd) | Precision (%) (sd) | F-Measure (%) (sd) | TP-Rate/Recall (%) (sd) | FP-Rate (%) (sd) | Precision (%) (sd) | F-Measure (%) (sd) | |
| VGG-19 | 88.41 ( | 11.24 ( | 88.37 ( | 88.39 ( | 88.99 ( | 10.66 ( | 88.95 ( | 88.97 ( |
| ResNet-50 | 95.29 ( | 4.36 ( | 95.25 ( | 95.27 ( | 96.63 ( | 2.02 ( | 96.59 ( | 96.61 ( |
| Inception-V3 | 96.13 ( | 3.52 ( | 96.09 ( | 96.11 ( | 99.21 ( | 0.64 ( | 99.17 ( | 99.19 ( |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghosh, S.; Banerjee, S.; Das, S.; Hazra, A.; Mallik, S.; Zhao, Z.; Mukherji, A. Evaluation and Optimization of Biomedical Image-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network Model for COVID-19 Status Classification. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10787. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110787
Ghosh S, Banerjee S, Das S, Hazra A, Mallik S, Zhao Z, Mukherji A. Evaluation and Optimization of Biomedical Image-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network Model for COVID-19 Status Classification. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(21):10787. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110787
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhosh, Soumadip, Suharta Banerjee, Supantha Das, Arnab Hazra, Saurav Mallik, Zhongming Zhao, and Ayan Mukherji. 2022. "Evaluation and Optimization of Biomedical Image-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network Model for COVID-19 Status Classification" Applied Sciences 12, no. 21: 10787. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110787
APA StyleGhosh, S., Banerjee, S., Das, S., Hazra, A., Mallik, S., Zhao, Z., & Mukherji, A. (2022). Evaluation and Optimization of Biomedical Image-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network Model for COVID-19 Status Classification. Applied Sciences, 12(21), 10787. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110787