The Application of Game-Based Teaching for Water Resources Science Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Science Games and Teaching
2.2. Learning Satisfaction
3. Research Methodology
4. Analysis Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amahmid, O.; El Guamri, Y.; Yazidi, M.; Razoki, B.; Rassou, K.K.; Rakibi, Y.; Knini, G.; El Ouardi, T. Water education in school curricula: Impact on children knowledge, attitudes and behaviours towards water use. Int. Res. Geogr. Environ. Educ. 2018, 28, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Gosling, S.N.; Kummu, M.; Flörke, M.; Pfister, S.; Hanasaki, N.; Wada, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; et al. Water scarcity assessments in the past, present, and future. Earth’s Futur. 2017, 5, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buytaert, W.; Zulkafli, Z.; Grainger, S.; Acosta, L.; Alemie, T.C.; Bastiaensen, J.; De Biã¨vre, B.; Bhusal, J.; Clark, J.; Dewulf, A.; et al. Citizen science in hydrology and water resources: Opportunities for knowledge generation, ecosystem service management, and sustainable development. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.-J.D.; Lee, M.; Ha, J.E.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, H.S.; Son, E.; Chung, Y.; Bong, M. Science for all: Boosting the science motivation of elementary school students with utility value intervention. Learn. Instr. 2018, 60, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.S.; Gotwals, A.W. Supporting Disciplinary Talk from the Start of School: Teaching Students to Think and Talk Like Scientists. Read. Teach. 2017, 71, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amory, A. Game object model version II: A theoretical framework for educational game development. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2006, 55, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Lai, C.S. A Study of the Effects of Science Play Instruction with Assisted Scientific Toys on the “Air” Unit Learning for Third-Grade Students. Sci. Educ. Mon. 2009, 318, 2–16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.-C.; Tsai, C.-C. Game-Based Learning in Science Education: A Review of Relevant Research. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2013, 22, 877–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, D.H.; Dixon, J.; Archer, J. Identifying underlying causes of situational interest in a science course for preservice elementary teachers. Sci. Educ. 2016, 100, 1039–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, R.; Verma, N. An Impact of Using Multimedia Presentations on Engineering Education. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 172, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prensky, M. Digital Game-Based Learning; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jääskä, E.; Aaltonen, K.; Kujala, J. Game-Based Learning in Project Sustainability Management Education. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, A.; Shah, M. Principles for Advancing Game-Based Learning in Teacher Education. J. Digit. Learn. Teach. Educ. 2020, 36, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.M.; Chang, C.-I.; Wang, S.; Beier, M.E.; Klisch, Y. Learning and motivational impacts of a multimedia science game. Comput. Educ. 2011, 57, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prebensen, N.K.; Kim, H.; Uysal, M. Cocreation as moderator between the experience value and satisfaction relationship. J. Travel Res. 2016, 55, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Su, C.-H. A Game-based learning system for improving student’s learning effectiveness in system analysis course. Procedia—Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 31, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholihah, D.F.; Bachri, B.S.; Jannah, M. Capilarization Game Foster Childrens’s Cognitive and Language Abilities. IJORER Int. J. Recent Educ. Res. 2022, 3, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlan, J.D.; Rivkin, M.S. Science Experiences for the Early Childhood Years: An Integrated Affective Approach, 8th ed.; Merrill/Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.S.; Wang, C.M. A Study of Science Play Instruction in Conjunction with Scientific Toys for 5th Graders. Res. Dev. Sci. Educ. Q. 2010, 56, 29–52. [Google Scholar]
- Siew, N.M.; Amir, N.; Chong, C.L. The perceptions of pre-service and in-service teachers regarding a project-based STEM approach to teaching science. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.B.; Ashill, N. The determinants of students’ perceived learning outcomes and satisfaction in university online education: An update. Decis. Sci. J. Innov. Educ. 2016, 14, 185–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita-Stank, P.J.; Thompson, J.A. The Effects of Motivation and Classroom Environment on the Satisfaction of Noncredit Continuing Education Student; ERIC Document Reproduction Service No.ED: 3730646; University of Hawai’i at Manoa: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lim, C.; Kim, H. Development of an instructional design model for flipped learning in higher education. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2016, 65, 427–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.-Y.; Wang, Y.-S.; Ni Lee, Y. Investigating factors affecting learning satisfaction and perceived learning in flipped classrooms: The mediating effect of interaction. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonassen, D.H.; Grabowski, B.L. Handbook of Individual Differences Learning and Instruction; Routledge: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, H.Y.; Hwang, G.J. A collaborative game-based learning approach to improving students’ learning performance in science courses. Comput. Educ. 2013, 63, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Yang, H.C. The Study on Customer’s Cognitive Value and Learning Satisfaction of Technology Education Activities. Technol. Mus. Rev. 2012, 16, 111–144. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.Z.F.; Chen, P.K. The effect of game-based learning on students’ learning performance in science learning—A case of “conveyance go”. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 103, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Leung, S.-O. Can Likert Scales be Treated as Interval Scales?—A Simulation Study. J. Soc. Serv. Res. 2017, 43, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C. Water Resources Primary School; Shu-Chuan Publishing House: Taipei, Taiwan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Taber, K.S. The Use of Cronbach’s Alpha When Developing and Reporting Research Instruments in Science Education. Res. Sci. Educ. 2018, 48, 1273–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, J.M.; Manfredo, P.A. Kolb’s learning style theory revisited. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1994, 54, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.-J.; Chang, S.-C. Effects of a peer competition-based mobile learning approach on students’ affective domain exhibition in social studies courses. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2015, 47, 1217–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kember, D.; Biggs, J.; Leung, D.Y. Examining the multidimensionality of approaches to learning through the development of a revised version of the Learning Process Questionnaire. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2004, 74, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
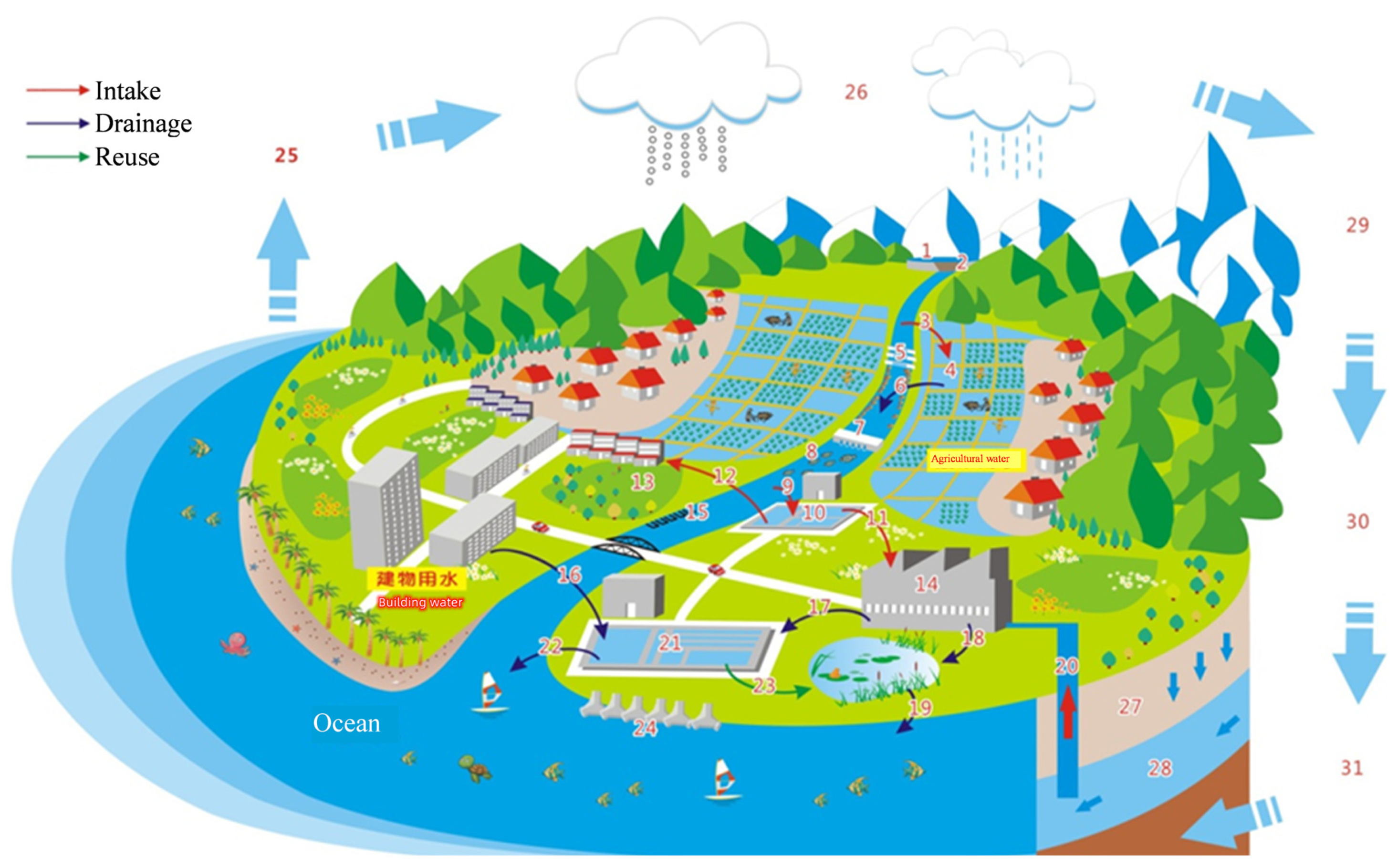
| Learning Style | Learning Interest | Learning Process | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Knowing how to operate the teaching tools gives you a sense of achievement. | 0.744 | ||
| Hands-on experience makes it easier for you to understand the contents. | 0.731 | ||
| Playing games gives you a sense of achievement. | 0.720 | ||
| Game-based teaching makes it easier for you to understand the contents. | 0.708 | ||
| Understanding what the teacher is teaching gives you a sense of achievement. | 0.675 | ||
| You like hands-on experience. | 0.610 | ||
| You like game-based teaching. | 0.548 | ||
| You understand the contents taught in class. | 0.490 | ||
| You like this activity. | 0.774 | ||
| You like the contents taught in class. | 0.697 | ||
| You will participate in the next science related activity. | 0.729 | ||
| You will recommend that friends participate in related science activities. | 0.480 | ||
| You concentrate on the lecture in class. | 0.754 | ||
| You are eager to answer questions in class. | 0.699 | ||
| You work hard with members of your group in class. | 0.703 | ||
| Eigenvalue | 6.312 | 10348 | 1.040 |
| Variance (%) | 42.083 | 8.986 | 6.936 |
| Cumulative variance (%) | 42.083 | 51.069 | 58.005 |
| KMO value: 0.897, Bartlett ball test chi-square value: 2473.592, significance: 0.000 | |||
| Factor | Variable | Number | Mean | Standard Deviation | f Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| learning style | male | 188 | 4.65 | 0.46 | −1.24 | 0.346 |
| female | 200 | 4.71 | 0.46 | |||
| learning interest | male | 188 | 4.66 | 0.45 | 1.04 | 0.159 |
| female | 200 | 4.61 | 0.56 | |||
| learning process | male | 188 | 4.38 | 0.62 | −0.34 | 0.395 |
| female | 200 | 4.39 | 0.68 |
| Learning Interest | Learning Style | Learning Process | |
|---|---|---|---|
| learning interest | --- | 0.666 (**) | 0.448 (**) |
| learning style | 0.666 (**) | --- | --- |
| learning process | 0.448 (**) | --- | --- |
| Original Regression Coefficient (B) | Standard Deviation | Standardized Regression Coefficient (Beta) | t Value | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| learning style | 0.736 | 0.042 | 0.666 | 6.007 | 0.000 |
| R = 0.666; R2 = 0.444; Adjusted R2 = 0.442; F = 308.082 | |||||
| learning process | 0.352 | 0.036 | 0.448 | 9.833 | 0.000 |
| R = 0.448; R2 = 0.200; Adjusted R2 = 0.198; F = 96.692 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.-C.; Lee, M.-T.; Lin, L.-C. The Application of Game-Based Teaching for Water Resources Science Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9920. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199920
Yang H-C, Lee M-T, Lin L-C. The Application of Game-Based Teaching for Water Resources Science Learning. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(19):9920. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199920
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Han-Chung, Meng-Tsung Lee, and Li-Chun Lin. 2022. "The Application of Game-Based Teaching for Water Resources Science Learning" Applied Sciences 12, no. 19: 9920. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199920
APA StyleYang, H.-C., Lee, M.-T., & Lin, L.-C. (2022). The Application of Game-Based Teaching for Water Resources Science Learning. Applied Sciences, 12(19), 9920. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199920






