A Visual Saliency-Based Neural Network Architecture for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. KADID-10K Dataset
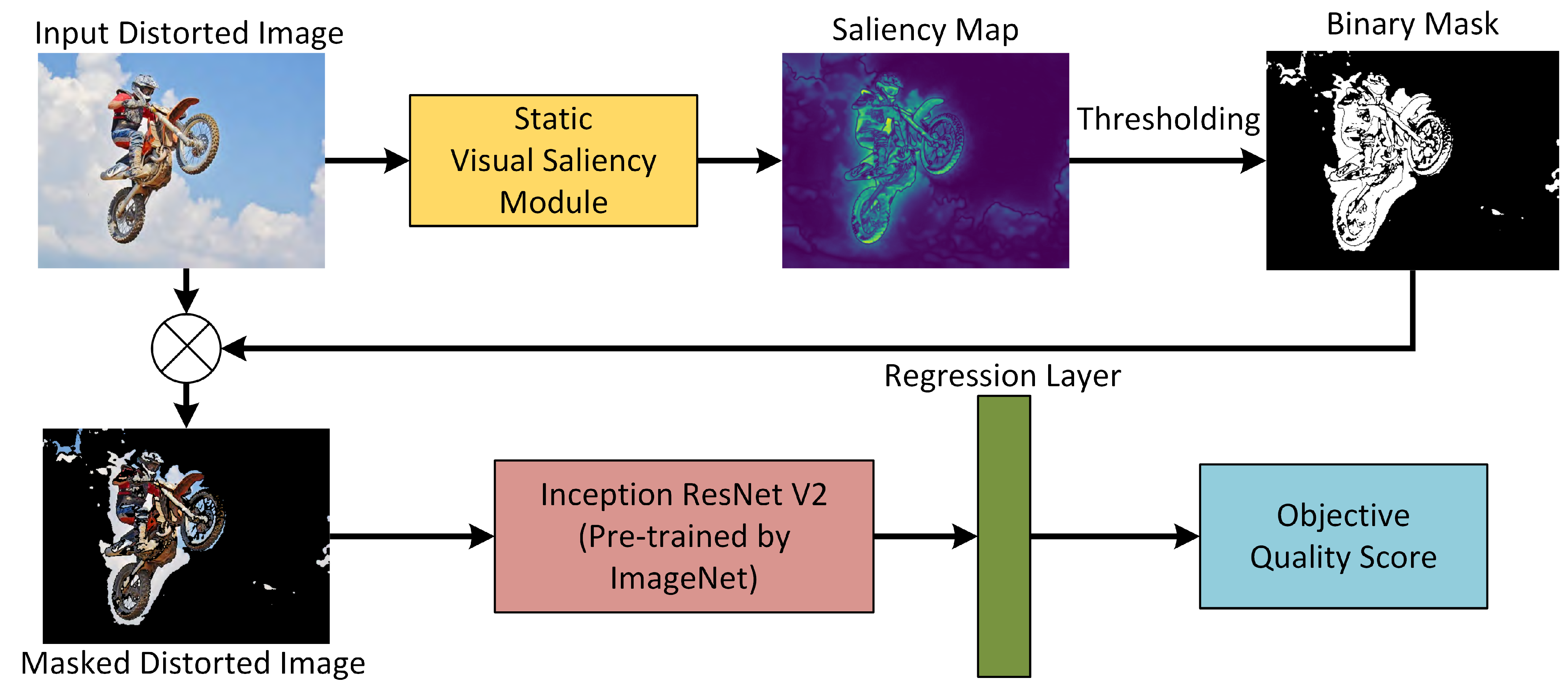
3. Proposed Framework
3.1. Static Visual Saliency Module
3.2. Inception-ResNet-V2
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Figure of Merits
4.3. Performance Comparison
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, L.; Chen, X.; Pan, Z.; Fan, K.; Li, F.; Lei, J. No-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment based on global and local content characteristics. Neurocomputing 2021, 424, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovik, A.C. Automatic prediction of perceptual image and video quality. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 2008–2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, M.; Agarwal, D.; Bansal, A. Image transmission through wireless channel: A review. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 1st International Conference on Power Electronics, Intelligent Control and Energy Systems (ICPEICES), Delhi, India, 4–6 July 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Dong, C.; Qiao, Y. Modulating image restoration with continual levels via adaptive feature modification layers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11056–11064. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Li, W.; Ning, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Cheng, C. Blind image quality assessment based on the multiscale and dual-domains features fusion. In Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; p. e6177. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, D. No-Reference Image Quality Assessment with Convolutional Neural Networks and Decision Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md, S.K.; Appina, B.; Channappayya, S.S. Full-reference stereo image quality assessment using natural stereo scene statistics. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Ngan, K.N. Reorganized DCT-based image representation for reduced reference stereoscopic image quality assessment. Neurocomputing 2016, 215, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, C.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, L. No-reference stereoscopic image quality evaluator with segmented monocular features and perceptual binocular features. Neurocomputing 2020, 405, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizami, I.F.; Majid, M.; Anwar, S.M. Natural scene statistics model independent no-reference image quality assessment using patch based discrete cosine transform. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 26285–26304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizami, I.F.; Majid, M.; Anwar, S.M.; Nasim, A.; Khurshid, K. No-reference image quality assessment using bag-of-features with feature selection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 7811–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Tayara, H.; Zou, Q.; Chong, K.T. i6mA-Caps: A CapsuleNet-based framework for identifying DNA N6-methyladenine sites. Bioinformatics 2022, 8, 3885–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Akhtar, S.; Zakwan, M.; Mahmood, M.H. Novel architecture with selected feature vector for effective classification of mitotic and non-mitotic cells in breast cancer histology images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 71, 103212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Cho, S.; Kim, J.; Chong, K.T. Brainseg-net: Brain tumor mr image segmentation via enhanced encoder–decoder network. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, M.U.; Tayara, H.; Chong, K.T. DCNN-4mC: Densely connected neural network based N4-methylcytosine site prediction in multiple species. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 6009–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, M.U.; Cho, S.; Kim, J.H.; Chong, K.T. Bu-net: Brain tumor segmentation using modified u-net architecture. Electronics 2020, 9, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ur Rehman, M.; Nizami, I.F.; Majid, M. DeepRPN-BIQA: Deep architectures with region proposal network for natural-scene and screen-content blind image quality assessment. Displays 2022, 71, 102101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizami, I.F.; Waqar, A.; Majid, M. Impact of visual saliency on multi-distorted blind image quality assessment using deep neural architecture. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 25283–25300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Ye, P.; Li, Y.; Doermann, D. Convolutional neural networks for no-reference image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1733–1740. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S. Fully deep blind image quality predictor. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2016, 11, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Yan, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ge, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Blindly assess image quality in the wild guided by a self-adaptive hyper network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3667–3676. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Hosu, V.; Saupe, D. KADID-10k: A large-scale artificially distorted IQA database. In Proceedings of the 2019 Eleventh International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), Berlin, Germany, 5–7 June 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Cosman, P.C. MMMNet: An end-to-end multi-task deep convolution neural network with multi-scale and multi-hierarchy fusion for blind image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 4798–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jiang, Q.; Lin, W.; Wang, Y. SGDNet: An end-to-end saliency-guided deep neural network for no-reference image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1383–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, Y.; Li, H. VSI: A visual saliency-induced index for perceptual image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 4270–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Xu, M.; Gao, G.; Kankanhalli, M.; Tian, Q.; Yan, S. Static saliency vs. dynamic saliency: A comparative study. In Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Barcelona, Spain, 21–25 October 2013; pp. 987–996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Bai, R.; Wei, H. Saliency Detection with Features From Compressed HEVC. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 62528–62537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montabone, S.; Soto, A. Human detection using a mobile platform and novel features derived from a visual saliency mechanism. Image Vis. Comput. 2010, 28, 391–402. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, M. Content-aware rate control scheme for HEVC based on static and dynamic saliency detection. Neurocomputing 2020, 411, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Moorthy, A.K.; Bovik, A.C. No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 4695–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthy, A.K.; Bovik, A.C. A two-step framework for constructing blind image quality indices. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2010, 17, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Kumar, J.; Kang, L.; Doermann, D. Unsupervised feature learning framework for no-reference image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 1098–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Liu, B.; Huang, H.; Bovik, A.C. No-reference image quality assessment based on spatial and spectral entropies. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2014, 29, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, A.K.; Bovik, A.C. Blind image quality assessment: From natural scene statistics to perceptual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 3350–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.A.; Bovik, A.C.; Charrier, C. Blind image quality assessment: A natural scene statistics approach in the DCT domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 3339–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ye, P.; Li, Q.; Du, H.; Liu, Y.; Doermann, D. Blind image quality assessment based on high order statistics aggregation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 4444–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosse, S.; Maniry, D.; Wiegand, T.; Samek, W. A deep neural network for image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 3773–3777. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar]


| Technique | SROCC | PLCC | KROCC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRISQUE [30] | 0.519 | 0.554 | 0.368 | |
| BIQI [31] | 0.431 | 0.460 | 0.229 | |
| CORNIA [32] | 0.541 | 0.580 | 0.384 | |
| SSEQ [33] | 0.424 | 0.463 | 0.295 | |
| DIVINE [34] | 0.489 | 0.532 | 0.341 | |
| BLINDS-II [35] | 0.527 | 0.559 | 0.375 | |
| HOSA [36] | 0.609 | 0.653 | 0.438 | |
| CNN [19] | 0.603 | 0.619 | - | |
| BosICIP [37] | 0.630 | 0.628 | - | |
| LPIPS [38] | 0.721 | 0.713 | - | |
| InceptionResNetV2 [22] | 0.731 | 0.734 | 0.546 | |
| Proposed Framework | 0.834 | 0.867 | 0.680 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, J. A Visual Saliency-Based Neural Network Architecture for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199567
Ryu J. A Visual Saliency-Based Neural Network Architecture for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(19):9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199567
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Jihyoung. 2022. "A Visual Saliency-Based Neural Network Architecture for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment" Applied Sciences 12, no. 19: 9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199567
APA StyleRyu, J. (2022). A Visual Saliency-Based Neural Network Architecture for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment. Applied Sciences, 12(19), 9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199567











