Analysis of the Development Trend of Sports Research in China and Taiwan Using Natural Language Processing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
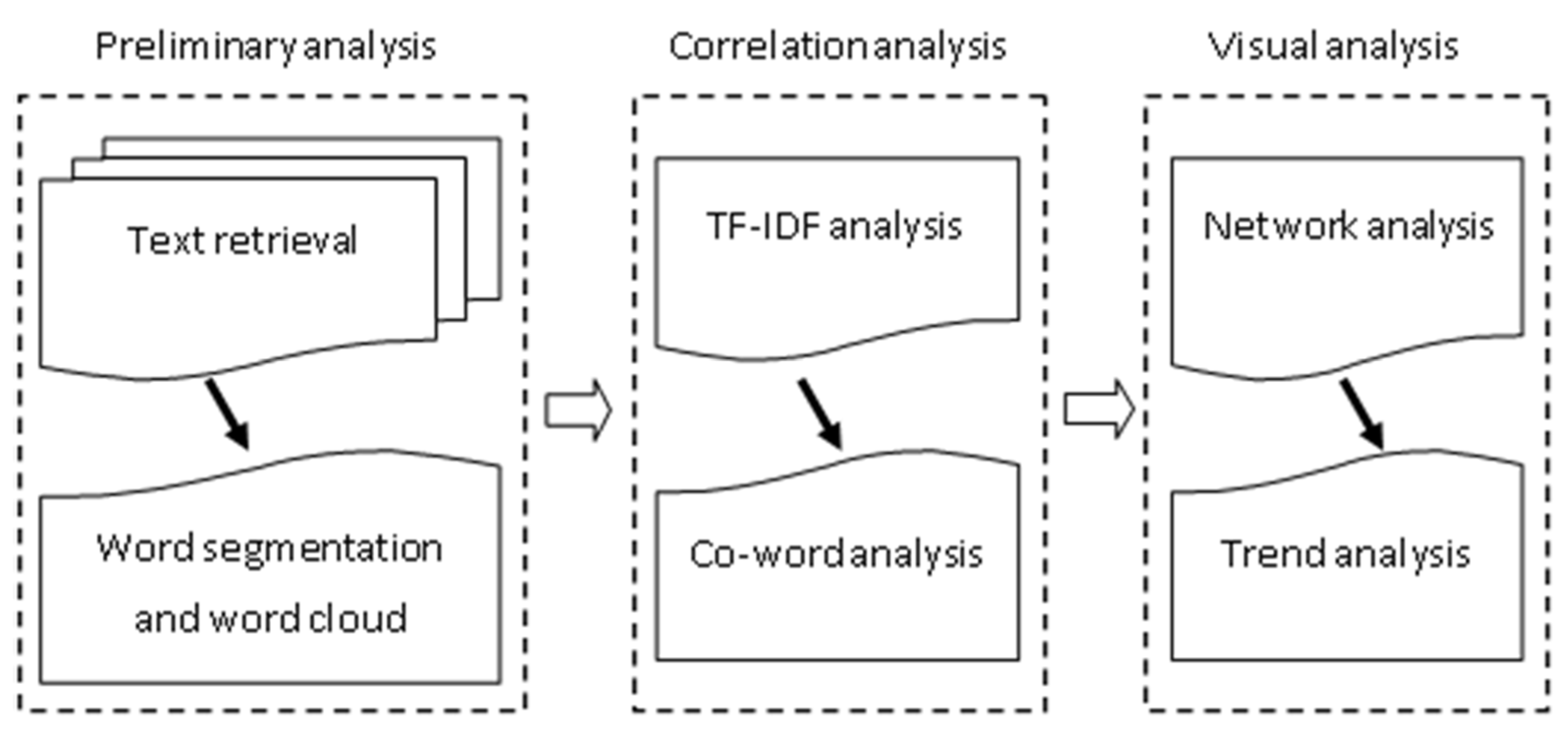
2. Methods
2.1. Text Retrieval
2.2. Word Segmentation and Word Cloud Analysis
2.3. TF-IDF Analysis
2.4. Co-Word Analysis
2.5. Network Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Analysis
3.2. Correlation Analysis
3.3. TF-IDF Analysis
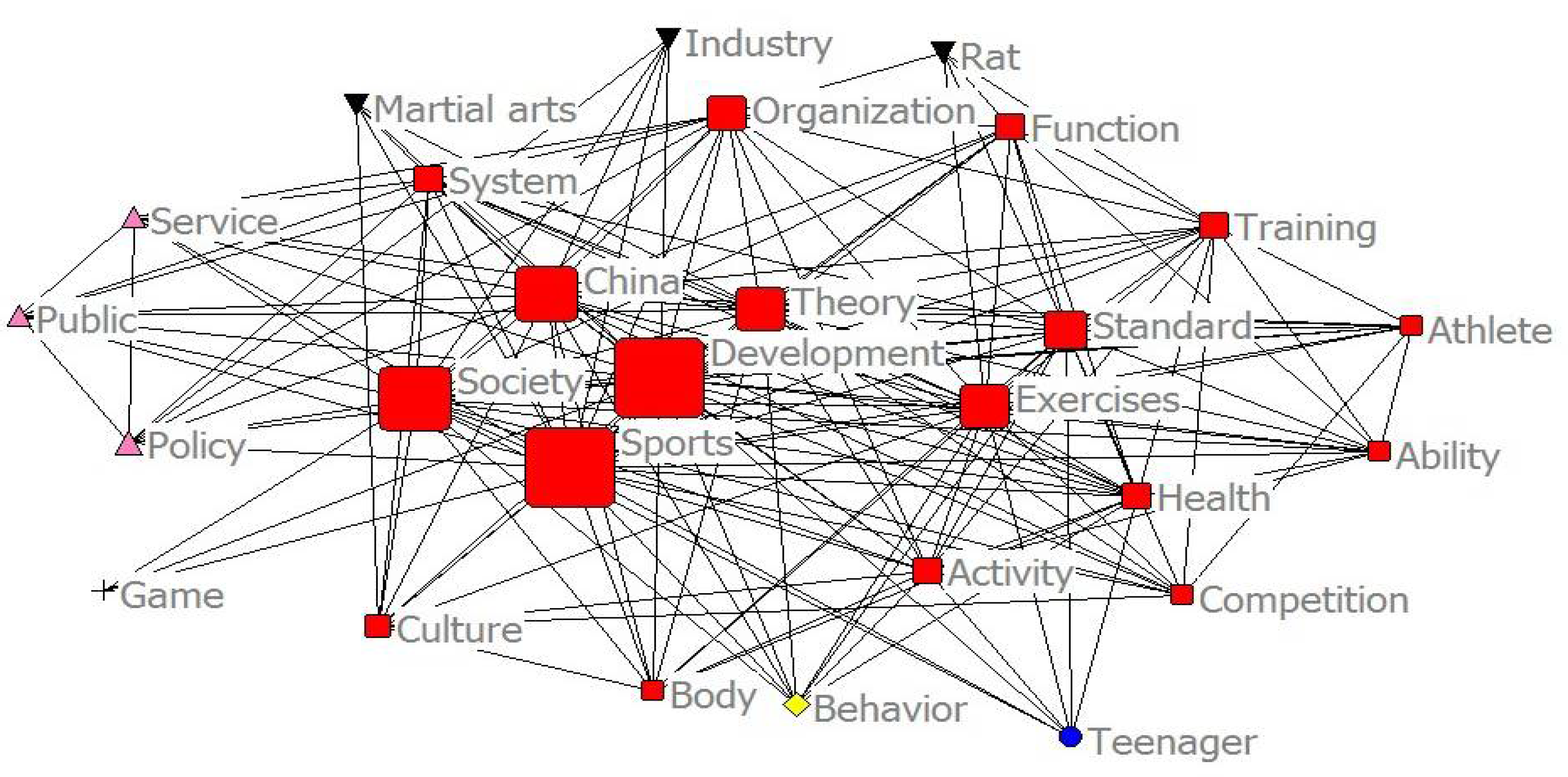
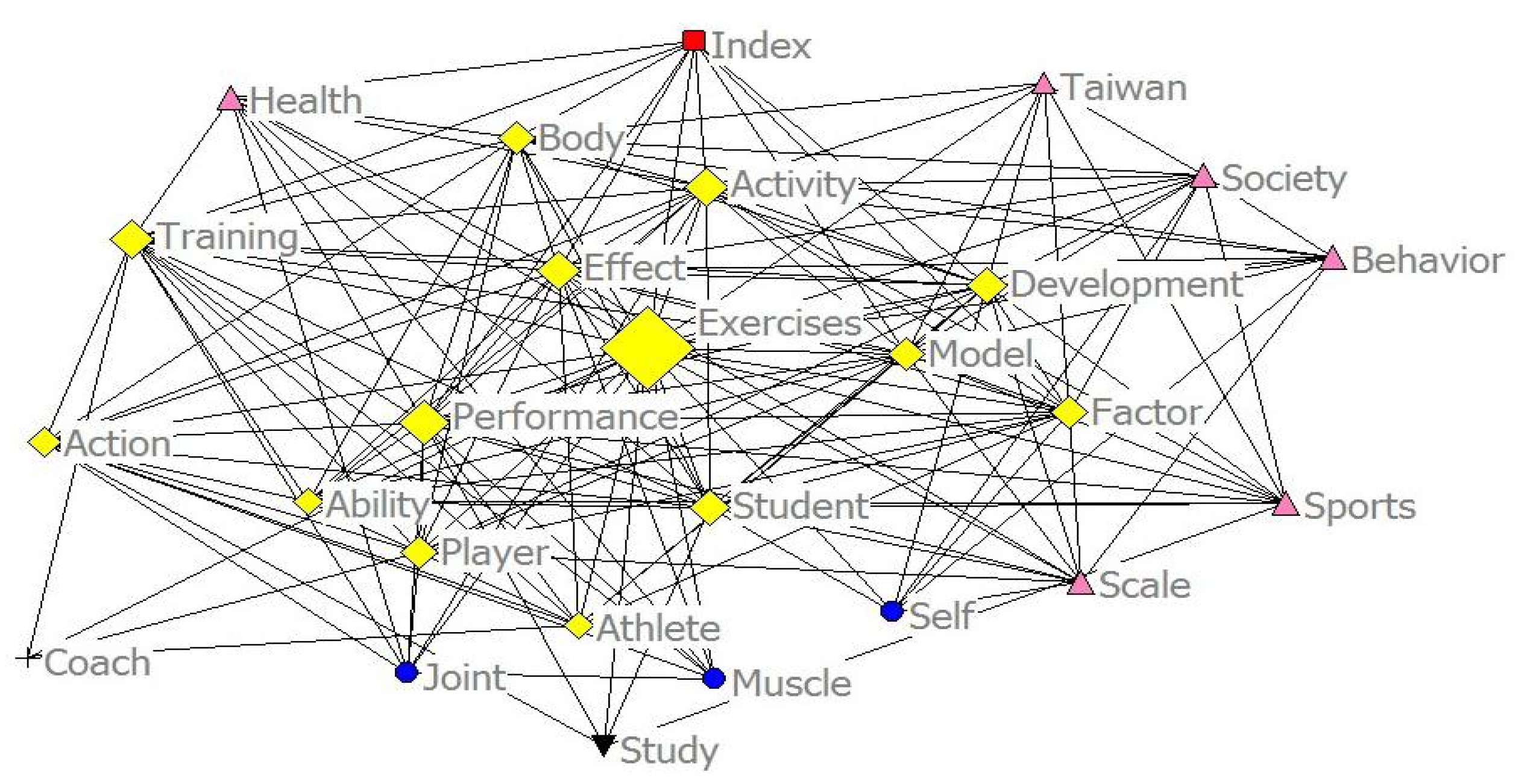
3.4. Co-Word Analysis
3.5. Visual Analysis
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- deLisle, J.; Goldstein, A.; Yang, G. The Internet, Social Media, and a Changing China; University of Pennsylvania Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, E. Taiwan and Modern China. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Asian History. Available online: https://oxfordre.com/asianhistory/view/10.1093/acrefore/9780190277727.001.0001/acrefore-9780190277727-e-155 (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Hammou, B.A.; Lahcen, A.A.; Mouline, S. Towards a real-time processing framework based on improved distributed recurrent neural network variants with fastText for social big data analytics. Inf. Process. Manag. 2019, 57, 102122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kamber, M.; Pei, J. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques, 3rd ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Waltham, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Tan, C.-W.; Huang, Q.; Liu, H. Natural language processing (NLP) in management research: A literature review. J. Manag. Anal. 2020, 7, 139–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, G.; Fan, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, H. Key word retrieval for short text via word2vec, doc2vec, and textrank. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2019, 27, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhija, V.; Ahuja, S. Rule-based text retrieval from a bibliographic database. DESIDOC J. Libr. Inf. Technol. 2018, 38, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenstein, J. Introduction to Natural Language Processing; The MIT Press: Massachusetts, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka, Y.; Lindgren, T.G.; Mintz, Y.D.; Hooper, J.; Aswani, A. Applying Natural Language Processing to Understand Motivational Profiles for Maintaining Physical Activity After a Mobile App and Accelerometer-Based Intervention: The mPED Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2018, 6, e10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Shah, D.; Shah, M. The Intertwine of Brain and Body: A Quantitative Analysis on How Big Data Influences the System of Sports. Ann. Data Sci. 2020, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y. Evaluation of Physical Education Teaching Quality in Colleges Based on the Hybrid Technology of Data Mining and Hidden Markov Model. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. (iJET) 2020, 15, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammut, C.; Webb, G.I. Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.T.; Chen, L.J.; Wu, T.Y. An investigation on the images of hakka culture tourism destinations by using natural language processing. J. Outdoor Recreat. Study 2016, 29, 81–111. [Google Scholar]
- Cecchini, F.M.; Riedl, M.; Fersini, E.; Biemann, C. A comparison of graph-based word sense induction clustering algorithms in a pseudoword evaluation framework. Comput. Humanit. 2018, 52, 733–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb-Walgren, C.J.; Pilling, B.K.; Barksdale, H.C., Jr. Does marketing need better marketing? A creative approach to understanding student perceptions of the marketing major. e-J. Bus. Educ. Scholarsh. Teach. 2017, 11, 97–117. [Google Scholar]
- Dobermann, D.; Hamilton, I.S. Publication patterns in developmental psychology: Trends and social networks. Int. J. Psychol. 2015, 52, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.-Y.; Chen, K.-J. Introduction to CKIP Chinese word segmentation system for the first international Chinese Word Segmentation Bakeoff. In Proceedings of the Second SIGHAN Workshop on Chinese Language Processing, Sapporo, Japan, 11–12 July 2003; Volume 17, pp. 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaidya, P.; Harinarayana, N.S. Social semantics and similarities from user-generated keywords to information retrieval: A case study of social tags in marine science. DESIDOC J. Libr. Inf. Technol. 2018, 38, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.; Banerjee, A.; Tong, G.; Brezovjakova, H.; Rees, S.; Byrne, M. Anatomy of an abstract: A guide to writing a scientific abstract. J. Natl. Stud. Assoc. Med. Res. 2019, 1, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donoghue, T. Planning Your Qualitative Research Thesis and Project: An Introduction to Interpretivist Research in Education and the Social Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Harzing, A.-W. Two new kids on the block: How do Crossref and Dimensions compare with Google Scholar, Microsoft Academic, Scopus and the Web of Science? Scientometrics 2019, 120, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousha, K.; Thelwall, M. Can Google Scholar and Mendeley help to assess the scholarly impacts of dissertations? J. Inf. 2019, 13, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Martín, A.; Orduna-Malea, E.; Thelwall, M.; Delgado López-Cózar, E. Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Scopus: A systematic comparison of citations in 252 subject categories. J. Informetr. 2018, 12, 1160–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zientek, L.R.; Werner, J.M.; Campuzano, M.V.; Nimon, K. The Use of Google Scholar for Research and Research Dissemination. New Horizons Adult Educ. Hum. Resour. Dev. 2018, 30, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ji, W.; Zhang, C. A Hybrid Machine Learning and Population Knowledge Mining Method to Minimize Makespan and Total Tardiness of Multi-Variety Products. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navathe, S.B.; Ramez, E. Data warehousing and data mining. In Fundamentals of Database Systems; Pearson Education: Singapore, 2000; pp. 841–872. [Google Scholar]
- Newberry, K.M.; Bailey, H.R. Does semantic knowledge influence event segmentation and recall of text? Mem. Cogn. 2019, 47, 1173–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Liou, W.-C.; Wu, J.-H. Fraud detection for financial statements of business groups. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2018, 32, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, G.; Musco, P.; Caine, S.; Howe, L. Lower limb asymmetry after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in adolescent athlete: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Athl. Train. 2020, 55, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.P.; Kushwaha, A.K. Analysis of segmentation methods for Brahmi script. DESIDOC J. Libr. Inf. Technol. 2019, 39, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.-H.Y.D.-H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Liu, X. Macro-level collaboration network analysis and visualization with Essential Science Indicators: A case of social science. Malays. J. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 25, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, A. On the quantitative representation of term specificity based on terms and documents co-occurrences. J. Inf. Processing Soc. 2000, 41, 3332–3343. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Yao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Feng, J.-J.; Wu, S.-D.; Ji, W.-X.; Yao, L.; Liu, Z.-Y. Knowledge structure and theme trends analysis on general practitioner research: A Co-word perspective. BMC Fam. Pr. 2016, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Bibliometric mapping of the computational intelligence field. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowl.-Based Syst. 2007, 15, 625–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, Y.; Benson, N.E.; Yachida, M. KeyGraph: Automatic indexing by segmenting and unifing co-occurrence graphs. Trans. Inst. Electron. Inf. Commun. Eng. 1999, 82, 391–400. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, K. How does local partners network embeddedness affect international joint venture survival in different subnational contexts? Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2017, 35, 1055–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, W.; Goodson, P.; Barry, A.E.; McLeroy, K.R.; McKyer, E.L.J.; Valente, T.W. Adolescent Social Networks and Alcohol Use: Variability by Gender and Type. Subst. Use Misuse 2016, 52, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluleka, J.R.; Onyancha, O.B. Research collaboration among library and information science schools in south africa (1991–2012): An informetrics study. Mousaion S. Afr. J. Inf. Stud. 2017, 34, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.K.; Liu, Y.Z. On the subject structure of the sports science. J. Phys. Educ. 2002, 9, 4–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Zheng, J. Development of social sports organization on the 70th anniversary of the founding of the People’s Republic of China: Course review, reality consideration and future trend. China Sport Sci. 2019, 39, 3–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shih, W.Y.; Ho, T.K. Application of the text mining method to analyze the development trends of sports research in the era of big data. Phys. Educ. J. 2020, 53, 439–452. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, S.Y. A Sociology of Sport and Sports; Lucky Book Store: Taipei, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Coakley, J. Sports in Society: Issues and Controversies; McGraw-Hill: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Amer, F.; Hockenmaier, J.; Golparvar-Fard, M. Learning and critiquing pairwise activity relationships for schedule quality control via deep learning-based natural language processing. Autom. Constr. 2021, 134, 104036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.-H.; Li, J.-Y.; Zhang, J. Evolutionary deep learning: A survey. Neurocomputing 2022, 483, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; Islam, N.; Islam, M.; Ahsan, M. A Comparative Analysis on Suicidal Ideation Detection Using NLP, Machine, and Deep Learning. Technologies 2022, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauriola, I.; Lavelli, A.; Aiolli, F. An introduction to Deep Learning in Natural Language Processing: Models, techniques, and tools. Neurocomputing 2021, 470, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, T.; Liwicki, F.; Liwicki, M. Word2Vec: Optimal hyperparameters and their impact on natural language processing downstream tasks. Open Comput. Sci. 2022, 12, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Region | Ranking | Word (Frequency) | Ranking | Word Frequency | Ranking | Word Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 1 | sports (10,388) | 6 | athlete (1638) | 11 | activity (1107) |
| 2 | exercises (4700) | 7 | culture (1533) | 12 | standard (996) | |
| 3 | China (2907) | 8 | society (1488) | 13 | industry (988) | |
| 4 | development (2736) | 9 | theory (1265) | 14 | services (983) | |
| 5 | training (2074) | 10 | martial arts (1191) | 14 | body (983) | |
| Taiwan | 1 | exercises (2792) | 6 | player (639) | 11 | behavior (394) |
| 2 | training (853) | 7 | athlete (517) | 12 | ability (381) | |
| 3 | action (737) | 8 | muscle (454) | 13 | model (372) | |
| 4 | body (673) | 9 | activity (412) | 14 | study (369) | |
| 5 | performance (658) | 10 | scale (398) | 14 | sports (369) |
| Region | Ranking | Word | TF-IDF | Ranking | Word | TF-IDF | Ranking | Word | TF-IDF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 1 | sports | 0.0044 | 10 | Rat | 0.0032 | 19 | health | 0.0024 |
| 2 | exercises | 0.0041 | 11 | public | 0.0030 | 20 | theory | 0.0024 | |
| 3 | training | 0.0039 | 12 | service | 0.0030 | 21 | behavior | 0.0023 | |
| 4 | martial arts | 0.0037 | 13 | body | 0.0030 | 22 | society | 0.0023 | |
| 5 | athlete | 0.0036 | 14 | game | 0.0029 | 23 | organization | 0.0022 | |
| 6 | culture | 0.0036 | 15 | activity | 0.0028 | 24 | standard | 0.0021 | |
| 7 | China | 0.0035 | 16 | eenager | 0.0027 | 25 | ability | 0.0021 | |
| 8 | development | 0.0034 | 17 | policy | 0.0026 | 26 | function | 0.0021 | |
| 9 | industry | 0.0033 | 18 | competition | 0.0025 | 27 | system | 0.0021 | |
| Taiwan | 1 | training | 0.0032 | 10 | behavior | 0.0021 | 19 | coach | 0.0017 |
| 2 | action | 0.0029 | 11 | scale | 0.0021 | 20 | model | 0.0017 | |
| 3 | body | 0.0027 | 12 | performance | 0.0020 | 21 | factor | 0.0016 | |
| 4 | muscle | 0.0025 | 13 | self | 0.0020 | 22 | index | 0.0016 | |
| 5 | player | 0.0025 | 14 | sports | 0.0020 | 23 | Taiwan | 0.0016 | |
| 6 | athlete | 0.0025 | 15 | society | 0.0019 | 24 | development | 0.0015 | |
| 7 | study | 0.0025 | 16 | student | 0.0018 | 25 | effect | 0.0014 | |
| 8 | sports | 0.0024 | 17 | ability | 0.0018 | 26 | health | 0.0014 | |
| 9 | joint | 0.0022 | 18 | activity | 0.0017 | 27 | - | - |
| Region | Ranking | Word | Word | Co-Occurrence | Ranking | Word | Word | Co-Occurrence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 1 | sports | development | 782 | 11 | exercises | standard | 318 |
| 2 | sports | society | 716 | 12 | sports | system | 302 | |
| 3 | development | society | 439 | 13 | exercises | development | 291 | |
| 4 | sports | theory | 427 | 14 | development | theory | 289 | |
| 5 | sports | exercises | 419 | 15 | theory | society | 245 | |
| 6 | sports | China | 415 | 16 | culture | development | 237 | |
| 7 | exercises | athlete | 394 | 17 | China | society | 233 | |
| 8 | exercises | training | 378 | 18 | sports | ctivity | 231 | |
| 9 | China | development | 327 | 19 | sports | service | 225 | |
| 10 | sports | culture | 325 | 19 | sports | organization | 225 | |
| Taiwan | 1 | exercises | performance | 193 | 11 | exercises | development | 111 |
| 2 | training | exercises | 163 | 12 | exercises | ability | 109 | |
| 3 | player | xercises | 151 | 13 | exercises | factor | 107 | |
| 4 | exercises | athlete | 137 | 14 | training | performance | 98 | |
| 5 | body | sports | 132 | 15 | exercises | ‘index | 97 | |
| 6 | exercises | effect | 123 | 16 | exercises | scale | 86 | |
| 7 | action | exercises | 121 | 16 | exercises | Taiwan | 86 | |
| 8 | exercises | activity | 120 | 18 | muscle | exercises | 85 | |
| 9 | exercises | model | 116 | 18 | exercises | society | 85 | |
| 10 | exercises | health | 112 | 20 | action | performance | 82 |
| China | A. | B. | C. | D. | E. | Taiwan | A. | B. | C. | D. | E. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. sports | 0 | 419 | 168 | 93 | 149 | A. training | 0 | 70 | 45 | 52 | 80 |
| B. exercises | 419 | 0 | 378 | 20 | 394 | B. action | 70 | 0 | 42 | 37 | 69 |
| C. training | 168 | 378 | 0 | 15 | 174 | C. body | 45 | 42 | 0 | 25 | 27 |
| D. martial arts | 93 | 20 | 15 | 0 | 1 | D. muscle | 52 | 37 | 25 | 0 | 23 |
| E. athlete | 149 | 394 | 174 | 1 | 0 | E. player | 80 | 69 | 27 | 23 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, T.-K.; Shih, W.-Y.; Kao, W.-Y.; Hsu, C.-H.; Wu, C.-Y. Analysis of the Development Trend of Sports Research in China and Taiwan Using Natural Language Processing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189006
Ho T-K, Shih W-Y, Kao W-Y, Hsu C-H, Wu C-Y. Analysis of the Development Trend of Sports Research in China and Taiwan Using Natural Language Processing. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(18):9006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189006
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Tu-Kuang, Wei-Yuan Shih, Wen-Yang Kao, Chin-Hsien Hsu, and Cheng-Ying Wu. 2022. "Analysis of the Development Trend of Sports Research in China and Taiwan Using Natural Language Processing" Applied Sciences 12, no. 18: 9006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189006
APA StyleHo, T.-K., Shih, W.-Y., Kao, W.-Y., Hsu, C.-H., & Wu, C.-Y. (2022). Analysis of the Development Trend of Sports Research in China and Taiwan Using Natural Language Processing. Applied Sciences, 12(18), 9006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189006







