Abstract
Water wall tube temperature is a major parameter in the steam generator design which has a significant role in keeping the steam generator available. Thus, knowing the tube average temperature in different operating conditions is very important to avoid the causes of tube failures. High temperatures are a major cause of various types of failures, such as overheating, hydrogen damage, thermal stress, etc. Furthermore, deposits on the inner tube wall contribute to such failure by changing the thermal resistance of the tube wall, which causes a significant increase in the tube wall’s average temperature, consequently lowering the allowable stress. Therefore, the model was created by using ANSYS FLUENT (Canonsburg, PA, USA) to determine the wall average water tube wall temperature considering the deposit layer thickness (magnetite). Furthermore, this model was verified. It was found that increasing tube thickness can increase the average tube temperature but combining it with increasing deposit thickness leads to higher temperatures. In other words, the effect of the deposit on the tube with higher thickness is higher than on the tube with lower thickness. By discussing the minimum thickness of the water wall tube, the suitable selection of the tube thickness and courses of action concerning the operating conditions that minimize the potential overheating of water tubes in the furnace section of the boiler can be determined.
1. Introduction
The increasing energy demand induces continuous development in creating new energy generation systems and enhances the existing ones, making them more robust and reliable. One such technology is steam thermal power plants, which possess a remarkable share in energy production worldwide and contribute to several applications. The boiler is an essential component in a thermal power plant to generate steam, driving the turbine to produce power or direct it to subsystems for subsequent use, such as in the desalination plant and fuel heating systems.
The tubes in water tube boilers are subjected to several types of failure [1] caused by stress rupture, waterside and fireside corrosion [2,3], fatigue [4], erosion [5] and lack of quality control. The main focus of the present work is the stress rupture, particularly in water tubes, caused by the overheating associated with being exposed to high temperatures and pressure that lead to tube failure. These conditions are induced in the short or long term. For example, the former is associated with decreasing cooling rate possibly attributed to complete or partial plugging, sudden shutdown of boiler circulating water pump, the rabid temperature increased during the start-up of the boiler evaporation of water in the liquid section, and the increase in the overall thermal resistance due to deposits accumulation inside the tube. The visual examination of the ruptured wall presents with fish mouth appearance, usually in overheating conditions [6]. Ref. [6] described that the plastic deformation in the rupture area shows deformation with elongated grains in the tube over a period during prolonged heat transfer. Refs. [7,8] further explained that the impact of the difference in temperature conditions on either side of the tube displays variation in the appearance. It has been reported that the different temperatures on either side of the wall, hot wall (fireside), and cool wall demonstrated microstructural changes, especially more toward the hotter side [7,8]. Concurring, ref. [9] stated that the fireside wall presented in the trials with partial degradation (spheroidization) of the lamellar structure mainly of iron carbide in pearlite colonies. The lamellar structure indicates the main driving force for change, excessive surface energy, which reduces the internal energy of the tube. Ref. [9] further pointed out that after the rupture of the tube, the rapid cooling causes a change in the structure and formation of bainite. However, Refs. [10,11] demonstrated that the substantial increase in the temperature lowers the yield stress of the metal. Thus, if the yield stress becomes equal to or less than the hoop stress of a metal tube at high temperature, the tube starts to deform, bulge, and thin [10,11]. Ref. [9] have studied the short-term overheating failure of a boiler water wall tube and examined the evolution of different microstructures during the failure through visual examination. They have concluded from the microstructure examination that the failure occurred due to overheating above the eutectoid temperature (lower critical temperature) of the tube material.
One solution to prevent overheating problems is enhancing the heat transfer through the tube wall to the water. Several researchers enhance the heat transfer by modifying the water tubes’ inner surface area or inserting different shapes of obstructions inside tubes to induce more flow turbulence and mixings [12]. Either way, considerable concerns exist regarding these techniques for the possible increasing accumulation rate of deposits inside tubes.
Most of the literature paid attention to enhancing the heat transfer through the tubes without considering the adverse effect of the accumulated deposits inside the tube on the thermal-mechanical consequences. Therefore, the main objectives addressed in the present work are the numerical investigation of the impact of deposit thickness inside tubes on the minimum thickness of the water tube for safe operation under different working loads and the influence the operating conditions, such as heat flux and flow rate, on the minimum thickness of the furnace water tube during the boiler lifetime.
Ansys fluent software student version 2021 R2 provides a suite to cover the entire range of physics, which enables virtual access to any field of engineering simulation, thereby permitting designing models to identify problems and functional processes. Conventional gas boilers have been shown to dissipate a high heat loss. Thus, the engineers designed a new type of boiler with thermal efficiency [13,14]. Regardless, the efficient boiler engineers continued to develop to minimize complete heat loss and designed Ansys software that analyzes the internal water distribution within the heat exchanger [14,15]. Thus, ref. [14] pointed out that the engineers aim to improve the heat exchange coefficient within the tube to permit higher water flow velocity.
Furthermore, ref. [16] added that the system predicts the fluid flow behavior of water in the heat exchanger and throughout its distribution. In addition, ref. [16] showed that the software supported the designing of the simulation model for the boiler with boundary conditions of heat transfer and heat loss in the system. Thus, using the software, several simulations were garnered over many years for a substantial improvement in the flow and heat exchanging behavior of the boiler with the updated shape of the baffle.
This study concentrates on the CFD model, which provides easy simulation of different input parameters. The CFD is categorized into three types of systems: Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) computations, large-eddy simulations (LES), and direct numerical simulations (DNS). The RANS technique applied is used mainly for resolving the mean values of each quantity that uses turbulent models for unclosed terms, whereas DNS solves the full instantaneous Navier–Stokes equations without the inclusion of turbulent motions models [17]. On the other hand, LES measures the turbulent large eddies and models the small-scale eddies that prove to be effective in establishing the mechanism required to stabilize the problem [17]. Ref. [17], integrated LES with Computational Fluid Dynamics to successfully simulate the effectiveness simulate the ultra-supercritical boiler at different operation load conditions, which concurred with the findings of [18]. Nevertheless, ref. [19] presented use of the DNS only to be feasible for calculating academic issues, such as heat flow due to the computational cost.
Refs. [20,21] studies have shown its application in terms of superheaters where the thermal efficiency of the furnace is based on the performance of the boiler.
CFD analysis is mostly employed at the designed stage, troubleshooting stage, and performance evaluation during the plant operation [22]. Ref. [22], stated that the outcome obtained from the CFD analysis had shown an effective approach to visualize the condition of the tubes and predict the further life of the tube depending upon the condition. Recently, the implementation of the PRO-E design software enabled the authors to evaluate the thermal flow at different velocities in the 3D model simulation that provided a complex identification of the transfer of heat flux along with ANSYS analysis [22]. Moreover, it enabled the engineer to adjust the high-temperature zone to prevent tube erosion and refrain from tube leakage issues [23]. Ref. [23] demonstrated crude oil substitution with oil using the CFD approach. Thus, the advanced property of the system allowed several authors to study the operating parameters responsible for erosion without halting the process [23,24,25].
This article aims to study the impact of deposit thickness on the thickness of the water tube under different working loads and determine the minimum thickness of the tube wall by comparing the maximum allowable thickness with the hoop stress to assure safe operation. The tube thickness is the first line of defense to prevent the tube failure during regular operation. So, if the tube thickness is less than the required thickness, the boiler tube will fail. In other words, the tubes with thicknesses less than the required thickness will cost a lot during the life of the boiler.
2. Methodology
2.1. Physical Model
The present work focuses on the water tube boiler. Figure 1 shows a schematic of the different components of the water tube boiler. These are lower water drums where the water is introduced after passing through the economizer and upper steam drum where the steam is extracted and directed to the superheater section. Both drums are connected via water tubes, and the present work concentrates on the furnace section where the water remains in the liquid phase, as shown in Figure 1a. The considered tube has the current dimensions shown in Figure 1b in terms of tube length (), outer pipe diameter (), tube thickness (), and deposit layer thickness (). The water tubes are made from carbon steel seamless pipe (SA210 C) and the deposit layer (Magnetite) is considered in the present work using a generic material with a variable range of thickness. Table 1 shows the material properties of the deposit. The used material properties and driving dimensions for different parts are presented in Table 1. The outer diameter of the tubes and original thicknesses are 44.45 mm and 5.588 mm, respectively. The new thickness of the water tube is set between 1 mm to 6 mm, whereas the thicknesses are based on a deposit maximum length of 0.2 mm. The present work is focused on the water tubes in the furnace section and therefore is considered a single-phase with temperature-independent material properties at the average temperature of inlet water and outlet temperature at the working pressure. Note that the pressure is based on maximum operating pressure at 210 bar, however, which is expected to result in higher stresses on the water tubes.
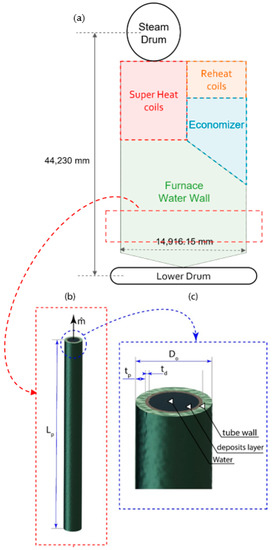
Figure 1.
Schematic of (a) boiler, (b) the simulated water tube, and (c) magnification of the tube tip with written parametric dimensions.

Table 1.
Material properties and related dimensions.
2.2. Numerical Model
2.2.1. Governing Equations
A comprehensive three-dimensional thermal model conjugate with an incompressible turbulent flow model is developed to determine the thermo-fluid characteristics of the proposed heated water considering deposit layer. The governing equations include applying conservation of energy on solid parts and conservation of mass, momentum, and energy with the turbulence model on fluid parts.
Solid Regions: Tube Wall and Deposit Layer
The conservation of energy governs the thermal characteristics and energy transfer through the solid domain, including the tube wall and deposit layer, and can be written as follows:
- Conservation of Energy:
Fluid Region
The flow inside the tube is considered to be single-phase, steady, Newtonian, incompressible, and turbulent. Therefore, the flow characteristics can be represented using the conservation of mass, momentum-based on Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) equations coupled with turbulence model, and conservation of energy as indicated by Equations (2)–(7):
- Conservation of mass and momentum:
- Turbulence Model: Realizable k-ε turbulent model
the realizable k-ε turbulent model with enhanced wall function is used following [26,27] to account for the existing fully turbulent flow while obtaining an accurate solution at a reasonable computational time. The model is based on model transport equations for the turbulence kinetic energy () and its dissipation rate (). The modeled transport equations for Realizable k-ε model for steady, incompressible, fully turbulent flow can be written as follows
and
where
where and refer to the generation of turbulence kinetic energy due to the mean velocity gradients and the generation of turbulence kinetic energy due to buoyancy, respectively. and are constants where and are the turbulent Prandtl numbers for and , respectively.
- Conservation of Energy:
2.2.2. Boundary Conditions
The applied boundary conditions are presented in Figure 2. To reduce the computational costs, the quartile of the domain (i.e., water tube) is considered, and therefore, a symmetry boundary condition is applied on the XZ plane, as indicated in Figure 2. Instead of applying constant heat flux on the outer surface of the water tube from one side and the other side being isolated, the heat transfer at the outer surface of the tube is as follows:
where h0 and hi are the enthalpy at outlet and enthalpy at inlet. is the outer surface area of the water tube, is the boiler efficiency, is the mass flow rate, and is the heat flux. The heat flux and mass flow rate are varied in the present work; the mass flow rate value is between 350, 231, and 156 kg/s and the heat flux value is between 263,703.57, 218,028.07, and 152,917.44 W/m2 to represent different loads of 50%, 75%, and 100%. Furthermore, the heat flux is constant on the surface not affected by the outer surface shape.
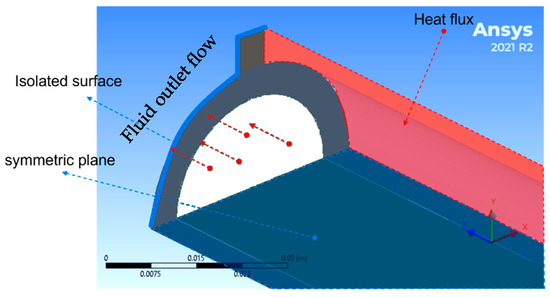
Figure 2.
Boundary conditions on the simulated domain.
Thermally coupled boundary conditions are used at the interfaces, such as the interface between the inner surface of the water tube and the outer surface of the deposit layer and the interface between the inner surface of the deposit layer with water volume circumferential surface in the case of the tube with deposit layer. Moreover, the inlet and outlet are set to mass flow rate inlet and pressure outlet boundary conditions, respectively. At the inlet, the constant mass flow rate is adopted equal to 0.368, 0.2432, and 0.1642, representing the total mass flow rate circulated between drums divided by the number of tubes. The Reynolds number for the presented cases beyond critical value and therefore turbulent flow model is considered. The inlet temperature of the water is set to and the minimum temperature recommended at the operating pressure is bar. Nevertheless, the maximum value of the range, bar, is considered in the present work, which leads to the minimum thickness attained under severe working conditions.
2.2.3. Minimum Tube Thickness Calculations (ASME)
The minimum thickness is determined using the following relation:
where P is the operating pressure inside the tube, is the outer diameter of the water tube; is the maximum allowable stress, tube thickness which is varied between 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 mm. Note that both allowable stress and yield strength of carbon steel seamless pipe (SA210 C) are temperature-dependent, as shown in Figure 3.
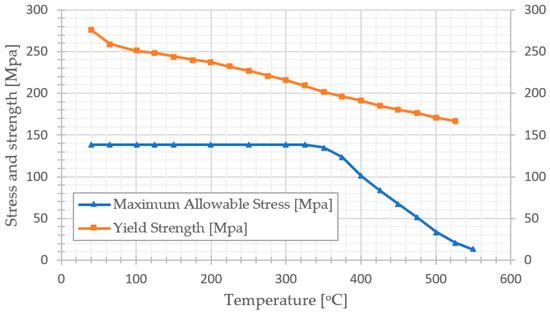
Figure 3.
The maximum allowable stress and yield strength based on ASME code section II Part D for carbon steel seamless pipe (SA210 C) edited from [28].
2.3. Numerical Solution and Model Verification
The model was created in a 3D symmetric model by ANSYS. The model had three surface areas, and the axis of symmetry was on the XZ plane, as shown in Figure 2. These areas include water, scale, and tube. The water surface area had a dimension of 500 mm in length and 33.27 mm in width. Moreover, the scale and tube areas had a dimension of 500 mm in length and 1 mm in width. In addition, the mesh has been created in water, deposit layer, and tube wall domains via ANSYS meshing. A mesh independence test and validation are performed to exclude the influence of the mesh on the simulation calculations. The boundary conditions for the simulation are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Boundary condition and geometry.
Figure 4 shows the correlation Reynolds Number and Nusselt Number Curve with multiple element numbers of 476,370, 202,400, 137,410, and 92,516 mm (see Figure 5), and the 202,400 cells have been chosen to be accurately sufficient with the correlation of Reynolds Number and Nusselt number and lower computational time.
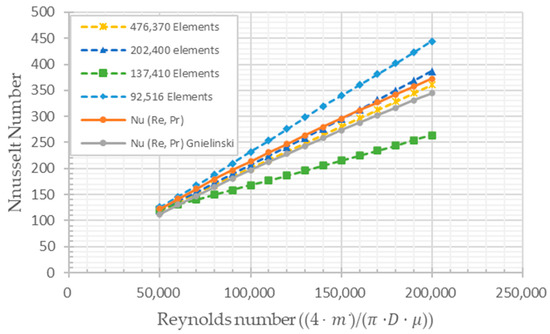
Figure 4.
Correlation Reynolds Number and Nusselt Number Curve.
Figure 5.
Mesh Dependency Test. (a) 476,370 Cells, (b) 202,400 Cells, (c) 137,410 Cells, and (d) 92,516 Cells.
The Reynolds number, convection heat transfer coefficient, and Nusselt number at a fully developed area were calculated as follows:
3. Results and Discussion
In the present section, the average water wall tube temperature was extracted at different loads, and the maximum allowable stress was calculated at the average tube temperature via linear interpolation that assures the safe operation of the water tubes in the furnace section of the boiler. Furthermore, the stress of working pressure Sworking Pressure was calculated via Equation (10). Increasing tube thickness can increase the average tube temperature but combining it with increasing deposit thickness leads to higher temperatures. In other words, the effect of the deposit on the tube with higher thickness is higher than on the tube with lower thickness. The following sections will analyze the impact of the deposits in full load, 75% of full load, and 50% of full load.
As shown in Figure 6, the high temperature concentrates on the region exposed to direct fire. So, this region is prone to overheating failure. Also, the temperature on the internal surface in this region is higher than in the opposite region. So, the Scale deposition in the area near the flame will be higher than in the other area.
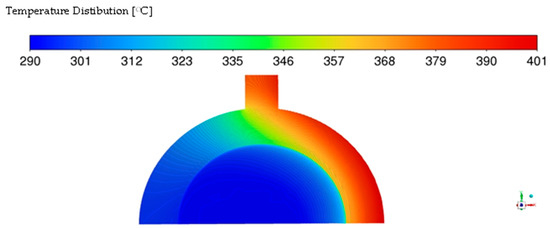
Figure 6.
Average temperature distribution of water wall tube at full load.
As shown in Figure 7, the increase in the average temperature of the water wall tube is conjugated with accumulating deposit layer of Magnetite with low thermal conductivity. For example, the average temperature reaches 400.19, 395.56, 391.49, 387.90, 384.68, and 381.77 °C at respectively, in the case of compared with 342.71, 341.48, 340.44, 339.51, 338.67, and 337.94 °C in the case of at respectively. Therefore, an increase in the tube and deposit thickness leads to a significant reduction in yield strength (Figure 3) or allowable stress based on the ASME code (Figure 3). It can be noticed that in the deposit layer with , the allowable stress divided by hoop stress Equation (9) at full load reaches 1.3, 0.72 in 6 mm and 3 mm tube thickness, respectively. See Figure 7 and Figure 8.
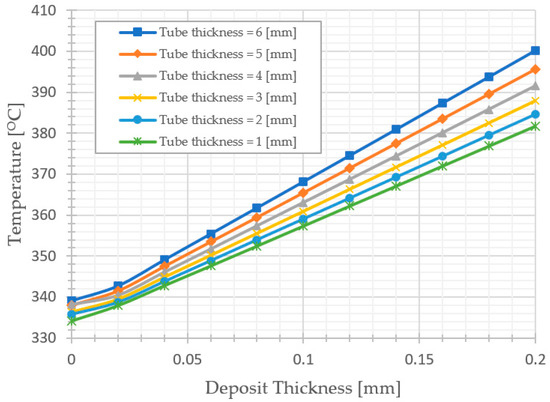
Figure 7.
Thickness variation effects of deposit layer on average water wall tube temperature at full load.
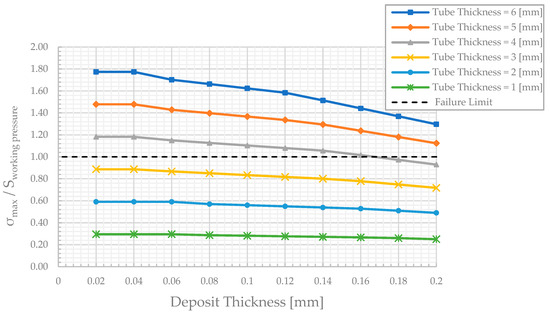
Figure 8.
The effect of the deposits’ thickness on the tube stress at full load.
Overall, the minimum value of the wall tube thickness is 4 mm, with magnetite thickness less than 0.16 mm, which is approximately equal to the maximum allowable stress in the ASME code at full load.
A similar analysis, as previously discussed, is conducted in the present section to determine the minimum tube thickness and shows the effect of magnetite deposit on the average tube temperature under 75% of full load. As shown in Figure 9, the average tube temperature was also affected by the deposits’ thickness. However, it is noted that the temperatures here are lower than what was previously discussed. Furthermore, it can be noticed that the deposit layer with k = 0.625 W/m K, the allowable stress divided by hoop stress Equation (9) at 75% of full load, reaches 1.39, 0.75 in 6 mm and 3 mm tube thickness, respectively; see Figure 10. The minimum thickness of the water wall tube is 4 mm, with magnetite thickness less than 0.18 mm.
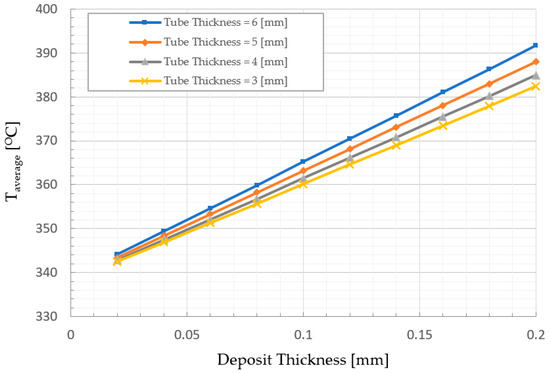
Figure 9.
Thickness variation effects of deposit layer on average water wall tube temperature at 75% of full load.
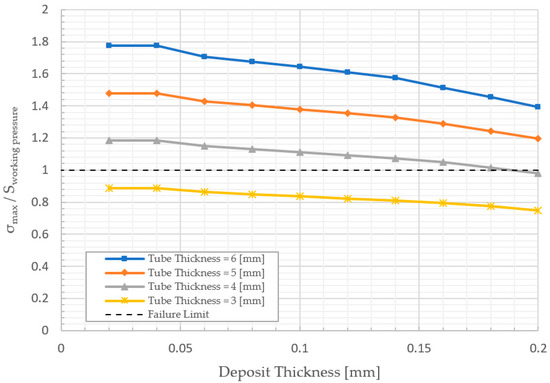
Figure 10.
The effect of the deposits’ thickness on the tube stress at 75% of full load.
In addition, the average temperature at 50% of full is discussed. As shown in Figure 11, the increase in the average temperature of the water wall tube is conjugated with accumulating deposit layer of Magnetite with low thermal conductivity. For example, the average temperature Taverage reaches 409.38, 405.25, 401.55, and 398.21 °C at tp = 6, 5, 4, and 3 mm, respectively, in the case of td = 0.4 mm, compared with 338.89, 338.92, 339.00, and 338.82 °C in the case of td = 0.02 mm at tp = 6, 5, 4, and 3 mm, respectively.
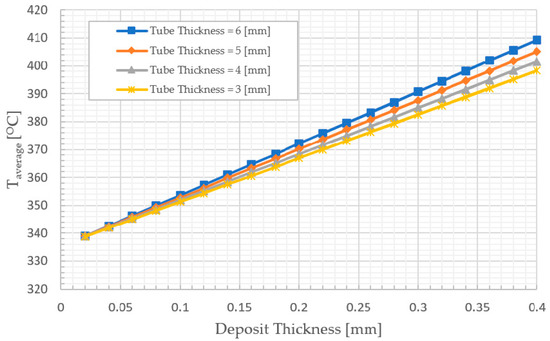
Figure 11.
Thickness variation effects of deposit layer on average water wall tube temperature at 50% of full load.
Finally, as shown in Figure 7, Figure 9 and Figure 11, the change in average temperature in the tube with higher thickness is greater than the change in the tube with lower thickness. Chemical treatment and tube replacement are recommended for the water tubes in the case of the formation of a deposit layer with thermal conductivity less than 0.625 W/m K. Table 3 shows the relation between the maximum deposit thickness and the minimum tube thickness at different load. The table data was extracted from Figure 8, Figure 10 and Figure 12, the effect of changing of load can be observed. So, another temporal action is considering the operation should be at a lower load if it isn’t feasible to conduct the chemical treatment.

Table 3.
Summary.
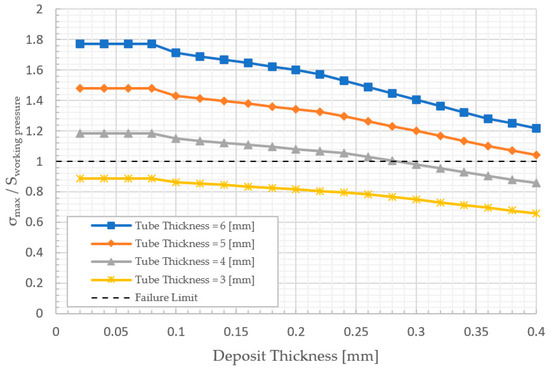
Figure 12.
The effect of the deposit thickness on the tube stress at 50% of full load.
4. Conclusions
The present work was set to numerically determine the effect of the deposit layer thickness and thermal conductivity on the minimum thickness of the tube wall that attains safe operation, considering the different working loads of 50%, 75%, and 100% at the maximum operating working pressure of 210 bar. Based on the adopted parameters, the investigation of the minimum thickness of the water tube wall has revealed that:
- The thermal conductivity of deposits affects the maximum temperature of the tubes. Consequently, the high potential for overheating, particularly at the deposit layer with thermal conductivity is 0.625 W/m2 K. The maximum crown temperature exceeds 495 °C at 100% load in the 6 mm tube thickness with deposit thickness of 0.2 mm, which is near the maximum temperature of 539 °C of SA-210 C.
- Increasing the thickness of the deposit layer leads to a linear increase in the tube wall average temperature. Consequently, it is essential to consider the consistency between the chosen wall tube thickness and the maintenance schedule considering the deposit accumulation rates and the operating conditions.
- The deposit and tube thickness are mandatory inspection requirements. Furthermore, if the deposit thickness and tube thickness exceed the previous results, chemical cleaning and tube replacement are mandatory requirements.
The present study is limited to the water tube in the furnace section. The identified effect of the deposit layer of magnetite on the tube wall temperature and the corresponding minimum thickness assists our understanding of the role of the deposit layer attributes for suitable selection of the tube thickness. Furthermore, it presents courses of action concerning the operating conditions that minimize the potential overheating of water tubes in the furnace section of the boiler.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.A. and K.I.A.; methodology, A.S.A. and K.I.A.; software, A.S.A. and K.I.A.; validation, A.S.A. and M.H.A.; formal analysis, A.S.A. and K.I.A.; investigation, A.S.A. and K.I.A.; resources, K.I.A. and M.H.A.; data curation, A.S.A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.A.; writing—review and editing, K.I.A. and M.H.A.; visualization, A.S.A., K.I.A. and M.H.A.; super-vision, K.I.A. and S.A.; project administration, K.I.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Melville, J.; Foster, G.G. A pictorial review of failures in conventional boiler plant. Press. Vessel. Pip. 1975, 3, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.A.; Espejo, E.; Martinez, J.C. Failure analysis of the wall tubes of a water-tube boiler. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 79, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, M.R.; Abdolmaleki, A.R.; Adibi, N.; Mirfendereski, S. Failure analysis of bank front boiler tubes. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2007, 14, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Roy, H.; Saha, A.; Subramanian, C. Failure Analysis of Boiler Water Wall Tube: A Case Study from Thermal Power Plant. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2022, 22, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himarosa, R.A.; Hariyanto, S.D.; Hasan, W.H.; Muflikhun, M.A. Failure analysis of platen superheater tube, water wall tube, and sealpot plate: A case study from electricity power plant in indonesia. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 135, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taler, J.; Dzierwa, P.; Jaremkiewicz, M.; Taler, D.; Kaczmarski, K.; Trojan, M.; Sobota, T. Thermal stress monitoring in thick walled pressure components of steam boilers. Energy 2019, 175, 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yan, W. Prediction of wall temperature and oxide scale thickness of ferritic–martensitic steel superheater tubes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 134, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modliński, N.; Szczepanek, K.; Nabagło, D.; Madejski, P.; Modliński, Z. Mathematical procedure for predicting tube metal temperature in the second stage reheater of the operating flexibly steam boiler. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 146, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munda, P.; Husain, M.M.; Rajinikanth, V.; Metya, A.K. Evolution of Microstructure During Short-term Overheating Failure of a Boiler Water Wall Tube Made of Carbon Steel. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2018, 18, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardy, H.; Bangun, D.A. Failure Analysis of Superheater Boiler Tube SA 213 T12. In IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering: Bandung, Indonesia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dehnavi, F.; Eslami, A.; Ashrafizadeh, F. A case study on failure of superheater tubes in an industrial power plant. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 80, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Srivastava, G.P.; Kumar, M.; Patil, A.K. A review of heat transfer and fluid flow mechanism in heat exchanger tube with inserts. Chem. Eng. Processing—Process Intensif. 2018, 123, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barma, M.C.; Saidur, R.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Allouhi, A.; Akash, B.A.; Sait, S.M. A review on boilers energy use, energy savings, and emissions reductions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakaç, S.; Liu, H.; Pramuanjaroenkij, A. Heat Exchangers: Selection, Rating, and Thermal Design, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mohite, N.T.; Benni, R.G. Optimization of Wall Thickness for Minimum Heat Losses for Induction Furnace. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2017, 10, 645–653. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Yan, J. Numerical investigation of heat transfer characteristics in utility boilers of oxy-coal combustion. Appl. Energy 2014, 130, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoshu, S.; Yuxin, W.; Minmin, Z.; Hai, Z.; Guangxi, Y.; Junfu, L. Large eddy simulation of a 660 MW utility boiler under variable load conditions. Front. Energy 2020, 15, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Xueli, G.; Zhongxiao, Z.; Haojie, F.; Jian, Z.; Degui, B. Unsteady-state heat transfer characteristics of spiral water wall tube in advanced-ultra-supercritical boilers from experiments and distributed parameter model. Energy 2019, 189, 116158. [Google Scholar]
- Paweł, M. Numerical study of a large-scale pulverized coal-fired boiler operation using CFD modeling based on the probability density function method. Applied Thermal Engineering. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 145, 352–363. [Google Scholar]
- Laubscher, R.; Rousseau, P. CFD study of pulverized coal-fired boiler evaporator and radiant superheaters at varying loads. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 160, 114057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijun, F.; Zhuojun, X.; Chen, L.; Zhixiang, W.; Shaojun, X. Constructal design for supercharged boiler superheater. Energy 2020, 191, 116484. [Google Scholar]
- Jalendar, M.; Kumar, G. Design and thermal analysis of steam boiler used in power plants. Int. J. Recent Dev. Sci. Technol. 2019, 3, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Filkoski, R.; Petrovski, I. Computational Fluid Dynamics in Function of Boilers’ Revitalisation; Academia: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vandani, A.M.K.; Bidi, M.; Ahmadi, F. Exergy analysis and evolutionary optimization of boiler blowdown heat recovery in steam power plants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 106, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stifanese, R.; Belsanti, L.; Toselli, M.; Letardi, P.; Traverso, P. Corrosion investigation of a steam turbine after power generator failure onboard a vessel: A case study. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 64, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Nie, H.; Xu, L.; Yue, J.; Huang, Y. A thermal stress analysis of fluid–structure interaction applied to boiler water wall. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 15, e2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H. Heat transfer to supercritical water in circular tubes with circumferentially non-uniform heating. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 70, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASME. Pressure Vessel Code; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).