Ecofriendly, Simple, Fast and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for Determination of Erdafitinib, a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Plasma and Its Application to Metabolic Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instrumentations and Analytical Conditions
2.3. Standard Solutions, Calibration Standards and Quality Control (QC) Samples
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. Method Validation
2.5.1. Selectivity
2.5.2. Accuracy and Precision
2.5.3. Matrix Effect and Recovery
2.5.4. Linearity
2.5.5. Stability
2.6. In Vitro Metabolic Stability of ERDA
2.7. Assessment of the Method Greenness
3. Results
3.1. Sample Preparation
3.2. Method Validation
3.2.1. Specificity
3.2.2. Linearity and Lower Limit of Quantification (LLOQ)
3.2.3. Precision and Accuracy
3.2.4. Recovery and Matrix Effect
3.2.5. Stability
3.3. In Vitro Metabolic Stability of ERDA
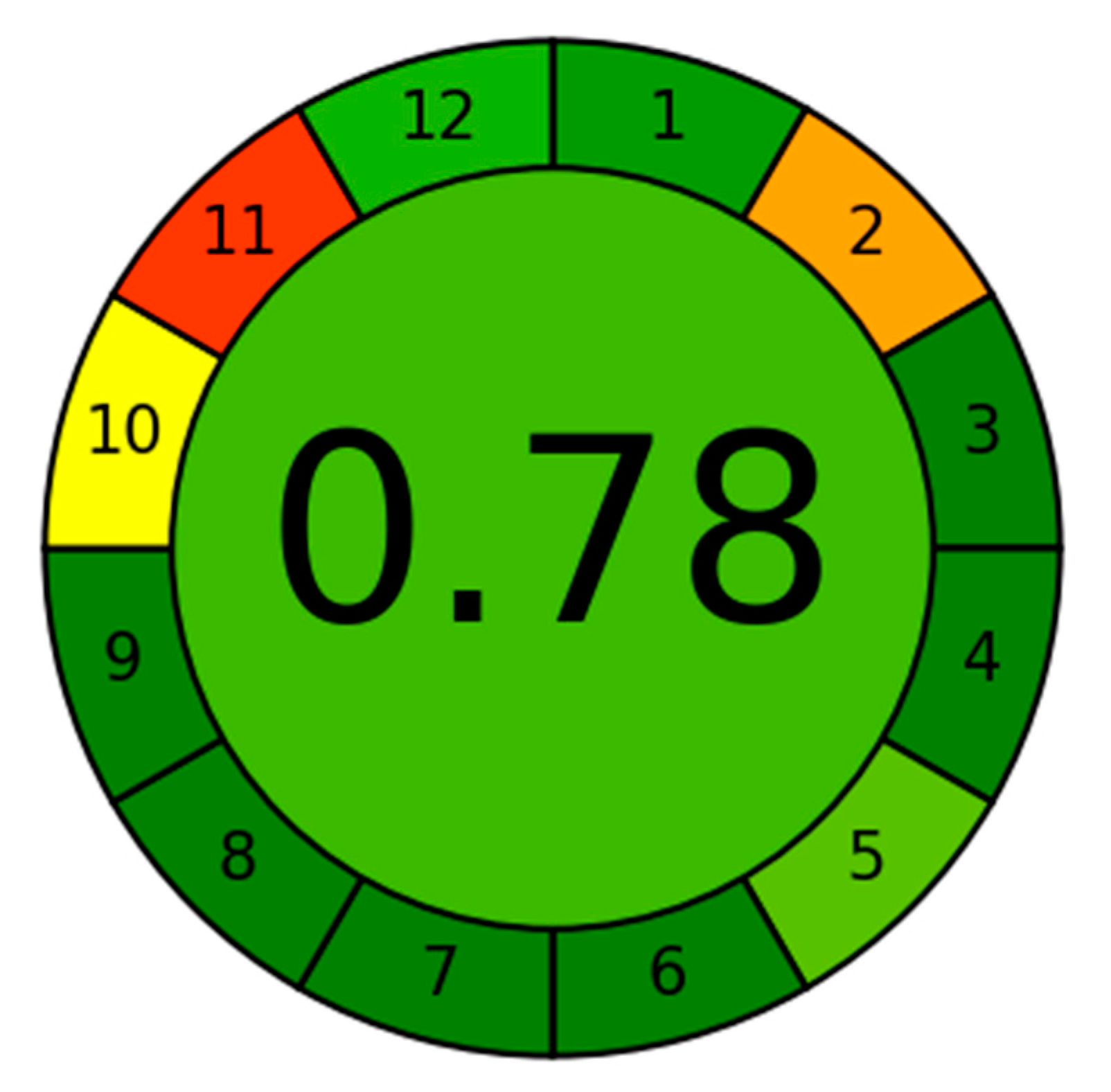
3.4. Greenness of the Method
3.5. Comparison with the Previously Published Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Kong, C. High expression of polo-like kinase 1 is associated with the metastasis and recurrence in urothelial carcinoma of bladder. Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, K.S. Erdafitinib to treat urothelial carcinoma. Drugs Today 2019, 55, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Quisp, E.C.; Javed, Z.; Iqbal, M.J.; Sadia, H.; Raza, S.; Irshad, A.; Salehi, B.; Reiner, Ž.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Resveratrol curcumin, paclitaxel and miRNAs mediated regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: Go four better to treat bladder cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahleda, R.; Italiano, A.; Hierro, C.; Mita, A.; Cervantes, A.; Chan, N.; Awad, M.; Calvo, E.; Moreno, V.; Govindan, R.; et al. Multicenter Phase I Study of Erdafitinib (JNJ-42756493), Oral Pan-Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced or Refractory Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4888–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauseef, J.T.; Villamar, D.M.; Lebenthal, J.; Vlachostergios, P.J.; Tagawa, S.T. An evaluation of the efficacy and safety of erdafitinib for the treatment of bladder cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 21, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. The role of fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of cancers including those of the urinary bladder. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 151, 104567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, H.; Kitagawa, C.; Kogure, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Fujikawa, K.; Sagawa, T.; Iwasa, S.; Takahashi, N.; Fukao, T.; Tchinou, C.; et al. Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of the fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor AZD4547 in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumours: A Phase I study. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palakurthi, S.; Kuraguchi, M.; Zacharek, S.J.; Zudaire, E.; Huang, W.; Bonal, D.M.; Liu, J.; Dhaneshwar, A.; DePeaux, K.; Gowaski, M.R.; et al. The Combined Effect of FGFR Inhibition and PD-1 Blockade Promotes Tumor-Intrinsic Induction of Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1457–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, T.; Takahashi, S.; Iwasawa, R.; Noguchi, H.; Aoki, M.; Doi, T. Safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamics of erdafitinib, a pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced or refractory solid tumors. Investig. N. Drugs 2018, 36, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, J.; Bahleda, R.; Dienstmann, R.; Infante, J.R.; Mita, A.; Italiano, A.; Calvo, E.; Moreno, V.; Adamo, B.; Gazzah, A.; et al. Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of JNJ-42756493, an Oral Pan-Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggesi, I.; Li, L.Y.; Jiao, J.; Hellemans, P.; Rasschaert, F.; de Zwart, L.; Snoeys, J.; De Meulder, M.; Mamidi, R.; Ouellet, D. Effect of Fluconazole and Itraconazole on the Pharmacokinetics of Erdafitinib in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Open-Label, Drug-Drug Interaction Study. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 45, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, L.H.; Fan, L.L.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W.Q.; Wang, X.J.; Qiu, X.J. The Effect of Posaconazole and Isavuconazole on the Pharmacokinetics of Erdafitinib in Beagle Dogs by UPLC-MS/MS. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazeri, K.; Bellmunt, J. Erdafitinib for the treatment of metastatic bladder cancer. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claiborne, R.T.; Tsan, G.L. Case Report: Erdafitinib-induced Central Serous Chorioretinopathy. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2022, 99, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauters, G.; Paques, M.; Borderie, V.; Bouheraoua, N. Reversible corneal stromal thinning, acute-onset white cataract and angle-closure glaucoma due to erdafitinib, a fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor: Report of three cases. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2021, 44, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, V. Grade 3 Hepatotoxicity following Fulvestrant, Palbociclib, and Erdafitinib Therapy in a Patient with ER-Positive/PR-Negative/HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Case Report. Case Rep. Oncol. 2020, 13, 304–308. [Google Scholar]
- Roubal, K.; Myint, Z.W.; Kolesar, J.M. Erdafitinib: A novel therapy for FGFR-mutated urothelial cancer. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2020, 77, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elawady, T.; Khedr, A.; El-Enany, N.; Belal, F. HPLC-UV determination of erdafitinib in mouse plasma and its application to pharmacokinetic studies. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1171, 122629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Zhou, C.Y.; Su, Y.D.; Gou, K.F.; Geng, X.N.; Qiu, X.J. The Pharmacokinetic Effect of Itraconazole and Voriconazole on Ripretinib in Beagle Dogs by UPLC-MS/MS Technique. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 4865–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elawady, T.; Khedrb, A.; El-Enanya, N.; Belal, F. LC-MS/MS determination of erdafitinib in human plasma after SPE: Investigation of the method greenness. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry; Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2018.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation; European Medicines Agency (EMA): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012.
- Manzo, A.; Montanino, A.; Costanzo, R.; Sandomenico, C.; Palumbo, G.; Schettino, C.; Daniele, G.; Morabito, A.; Perrone, F.; Piccirillo, M.C. Chapter 33—EGFR mutations: Best results from second- and third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors. In Oncogenomics; Dammacco, F., Silvestris, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 477–486. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, L.H.; Gron, L.U.; Young, J.L. Green Analytical Methodologies. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2695–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (EPCRA). 2004. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/epcra#:~:text=Emergency%20Planning%20and%20Community%20Right%2Dto%2DKnow%20Act%20(EPCRA) (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.M.; Konieczka, P.; Namieśnik, J. Analytical Eco-Scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. TRAC 2012, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aken, K.; Strekowski, L.; Patiny, L. EcoScale, a semi-quantitative tool to select an organic preparation based on economical and ecological parameters. Beilstein. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE-Analytical GREEnness metric approach and software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakelidou, E.; Virgiliou, C.; Valianou, L.; Gika, H.G.; Raikos, N.; Theodoridis, G. Sample Preparation Strategies for the Effective Quantitation of Hydrophilic Metabolites in Serum by Multi-Targeted HILIC-MS/MS. Metabolites 2017, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
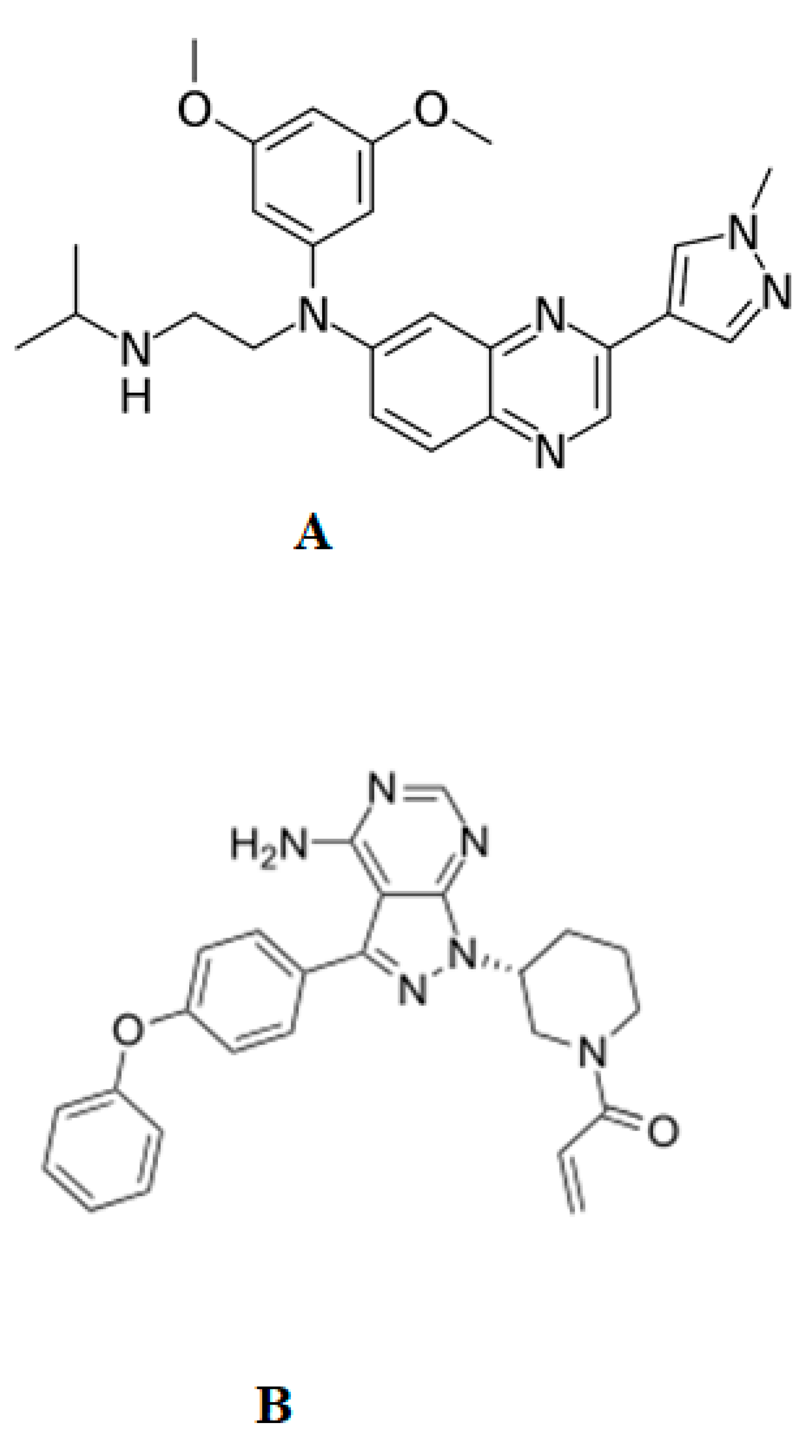
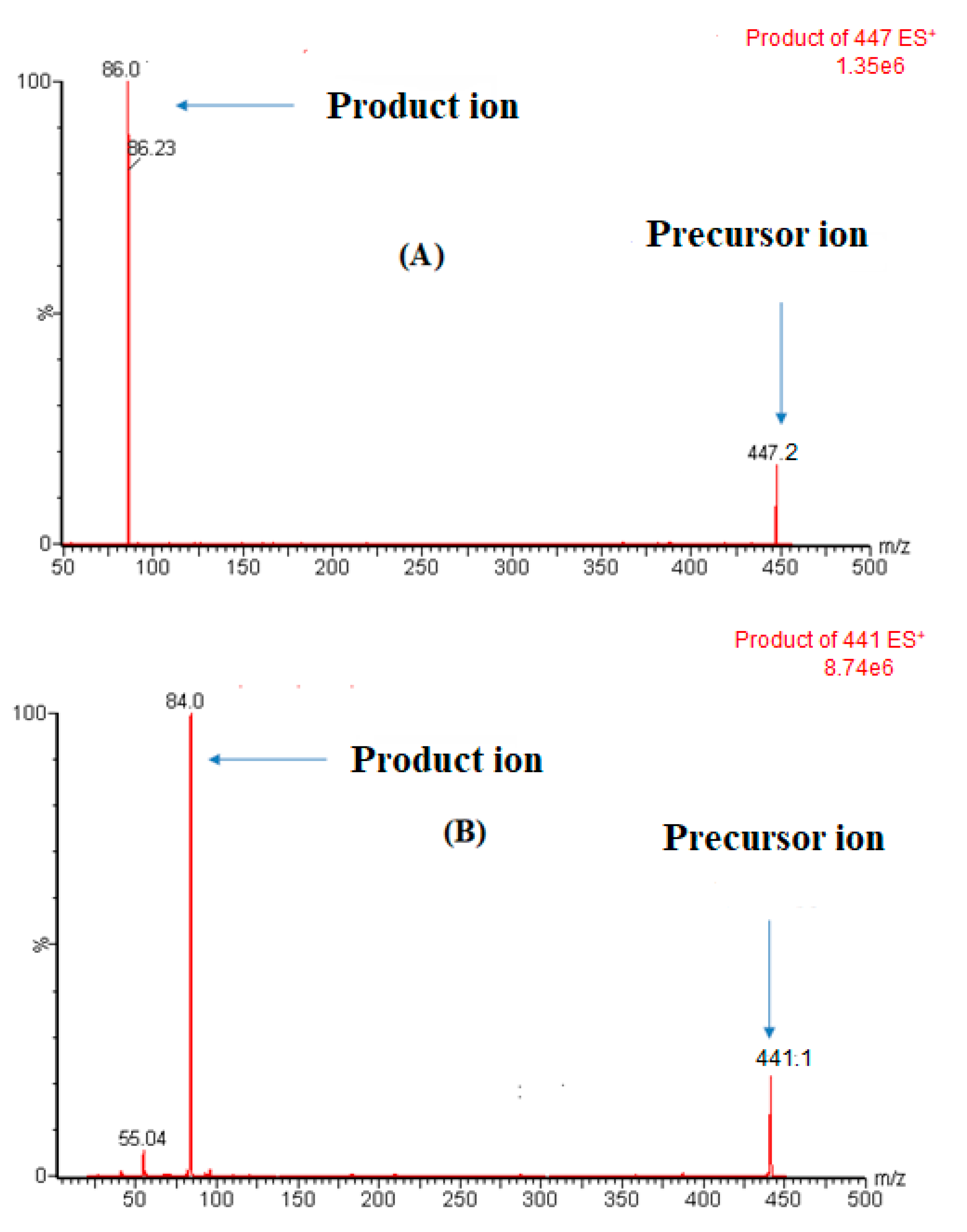
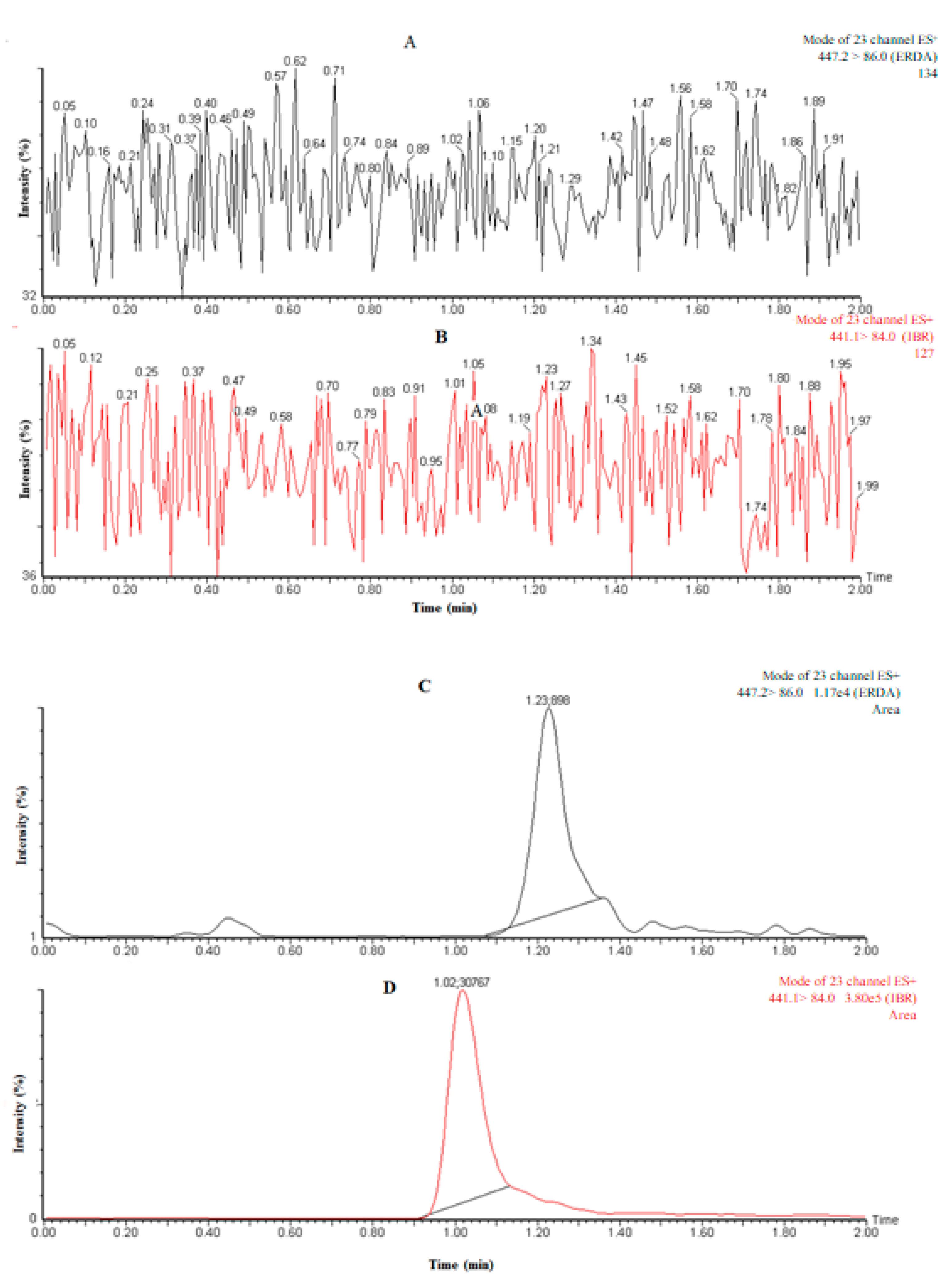

| Parameters | ERDA | IS |
|---|---|---|
| I. Compound Parameters | ||
| Precursor ion (m/z) | 447.2 | 441.1 |
| Product ion (m/z) | 86.0 | 84.0 |
| Dwell time (s) | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Cone Voltage (V) | 38 | 50 |
| Collision energy (eV) | 30 | 40 |
| II. Instrument Parameters | ||
| Collision gas flow rate (mL/min) | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Nitrogen flow rate (L/h) | 600 | 600 |
| Nominal Conc. (ng/mL) | Inter-Day | Intra-Day | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Conc. (Mean ± SD) | Precision (CV %) | Accuracy (%) | Actual Conc. (Mean ± SD) | Precision (CV %) | Accuracy (%) | |
| 0.5 | 0.41 ± 0.04 | 9.76 | 82.00 | 0.41 ±0.046 | 11.22 | 82.00 |
| 1.5 | 1.32 ± 0.18 | 13.50 | 88.00 | 1.30 ± 0.11 | 8.46 | 86.66 |
| 150 | 130.75 ±15.62 | 11.95 | 87.16 | 130.23 ± 6.87 | 5.28 | 86.82 |
| 750 | 644.15 ±37.10 | 5.76 | 85.88 | 643.21 ± 77.17 | 11.99 | 85.76 |
| Compound | Nominal Conc. (ng/mL) | Extraction Recovery | Matrix Effects | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (%) | RSD (%) | Mean (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| ERDA | 1.5 | 86.34 | 6.56 | 91.6 | 7.81 |
| 150 | 86.93 | 10.39 | 90.03 | 5.16 | |
| 750 | 85.06 | 2.90 | 89.89 | 4.69 | |
| IS | 100 | 86.25 | 6.50 | 89.49 | 5.61 |
| Stability | Nominal Con. (ng/mL) | Measured Con. (ng/mL) | Precision (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short-term | 15 | 13.09 ± 1.56 | 11.92 | 87.27 |
| 750 | 621.15 ± 59.82 | 9.63 | 82.82 | |
| Long-term | 15 | 12.76 ± 1.57 | 12.30 | 85.07 |
| 750 | 648.58 ± 35.38 | 5.45 | 86.48 | |
| Thaw and freeze | 15 | 12.91 ± 0.92 | 7.13 | 86.07 |
| 750 | 639.32 ± 61.90 | 9.68 | 85.24 | |
| Auto-sampler (24 h) | 15 | 12.93 ± 0.83 | 6.41 | 86.20 |
| 750 | 671.88 ± 54.78 | 8.15 | 89.58 |
| Analytical Method | Linearity Range | MRM Transition | LLOQ (ng/mL) | Sample Volume µL | Sample Preparation | Separation Retention Time (min) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC-UV | 50–2000 | ____ | 50 | 100.0 | Sep-pack column | 7.7 | [18] |
| UPLC-MS/MS | 1.0–500 | 447.0 → 361.9 | 1.0 | 100.0 | LLE (Ethyl acetate +Na OH) | 0.92 | [12] |
| LC-MS/MS | 3.0–800 | 447.10 → 362.0 | 3.0 | 150.0 | SPE | 2.6 | [20] |
| UPLC-MS/MS | 0.5–1000 | 447.0 → 86.0 | 0.5 | 100 | PPT +LLE | 1.2 | Current method |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, E.A.; Iqbal, M.; Mostafa, G.A.; Alhazani, M.R.; Asiri, Y.A. Ecofriendly, Simple, Fast and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for Determination of Erdafitinib, a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Plasma and Its Application to Metabolic Stability. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178625
Ali EA, Iqbal M, Mostafa GA, Alhazani MR, Asiri YA. Ecofriendly, Simple, Fast and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for Determination of Erdafitinib, a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Plasma and Its Application to Metabolic Stability. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(17):8625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178625
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Essam A., Muzaffar Iqbal, Gamal A. Mostafa, Mohamed R. Alhazani, and Yousif A. Asiri. 2022. "Ecofriendly, Simple, Fast and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for Determination of Erdafitinib, a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Plasma and Its Application to Metabolic Stability" Applied Sciences 12, no. 17: 8625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178625
APA StyleAli, E. A., Iqbal, M., Mostafa, G. A., Alhazani, M. R., & Asiri, Y. A. (2022). Ecofriendly, Simple, Fast and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for Determination of Erdafitinib, a Novel Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Plasma and Its Application to Metabolic Stability. Applied Sciences, 12(17), 8625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178625







