Abstract
Incorporating hand gesture recognition in human–robot interaction has the potential to provide a natural way of communication, thus contributing to a more fluid collaboration toward optimizing the efficiency of the application at hand and overcoming possible challenges. A very promising field of interest is agriculture, owing to its complex and dynamic environments. The aim of this study was twofold: (a) to develop a real-time skeleton-based recognition system for five hand gestures using a depth camera and machine learning, and (b) to enable a real-time human–robot interaction framework and test it in different scenarios. For this purpose, six machine learning classifiers were tested, while the Robot Operating System (ROS) software was utilized for “translating” the gestures into five commands to be executed by the robot. Furthermore, the developed system was successfully tested in outdoor experimental sessions that included either one or two persons. In the last case, the robot, based on the recognized gesture, could distinguish which of the two workers required help, follow the “locked” person, stop, return to a target location, or “unlock” them. For the sake of safety, the robot navigated with a preset socially accepted speed while keeping a safe distance in all interactions.
1. Introduction
Toward rendering agricultural practices more targeted, efficient, profitable, and safe, robotic systems seem to be a game changer, contributing also to meet the challenges of lack of qualified labor [1,2]. To achieve the aforementioned goals, agri-robotic applications are taking advantage of the remarkable technological advancement of information and communications technology (ICT), including artificial intelligence, sensors, and computer vision [3,4]. Robotic solutions have found fertile ground in a number of agricultural applications, such as harvesting, spraying, disease detection, and weeding [5,6]. Usually, robots can carry out programmed actions driven by restricted, task-specific, and noninteractive commands [7]. These prearranged actions can work sufficiently for structured environments, such as industrial stable settings. However, agriculture involves dynamic ill-defined ecosystems, which are vulnerable to heterogeneity and unforeseeable situations, as well as involve sensitive live produce [8]. As a means of addressing these challenges, the collaboration of humans and robots constitutes a promising solution through combining the cognitive human capabilities with the repeatable accuracy and strength of robots. The so-called human–robot interaction (HRI) in the agricultural sector is anticipated to provide (a) more flexibility in system reconfiguration, (b) workspace minimization, (c) optimization of both service quality and production, and (d) rapid capital depreciation [9,10,11].
HRI can be briefly defined as “the process that conveys the human operators’ intention and interprets the task descriptions into a sequence of robot motions complying with the robot capabilities and the working requirements” [12]. The interaction of humans with computers, in general, which relies on conventional devices such as keyboards, computer mice, and remote controls, tends not to serve any more. This is mainly due to the lack of flexibility and neutrality [13,14]. In the direction of optimizing the emerging synergistic ecosystems, more natural ways of communication are needed such as vocal interaction and body language. The former approach is particularly restricted by noisy environments and the different ways in which someone may pronounce the same command [15]. In contrast, nonverbal communication is regarded as more reliable. Body language is a concise term for summarizing body poses, facial emotions, and hand gestures. The most efficient means of natural expression that everyone is familiar with is the hand gesture interaction. A wide range of applications have taken place in HRI systems, including virtual mouse control [16], gaming technology for enhancing motor skills [17], sign language recognition [18], and human–vehicle interaction [19].
The main approaches of hand gesture recognition include the acquirement of data from either gloves equipped with sensors [20,21] or vision sensors [15,22]. Moreover, surface electromyography sensors have been proposed, which record the electric potential of muscles produced during their contractions [23,24]. Summarizing the main drawbacks of the above methodologies, (a) gloves tend to limit the natural movements and may provoke adverse skin reactions in people having sensitive skins, while the variable sizes among users can cause discomfort, as stressed in [13], (b) vision sensors face difficulties in case of complex backgrounds, multiple people, and changes of illumination [15], and (c) surface electromyography usually creates massive and noisy datasets [23], which can influence the intrinsic features of classification problems [25].
Focusing on vision sensors, different algorithms and methodologies have been developed for the purpose of detecting different hand features, such as skin color [26], motion [27], skeleton [28], and depth [29], as well as their combinations. The main problem that the skin color approach involves is that the background can present elements which may match the color of the skin; therefore, different techniques have been suggested to meet this challenge [30,31]. Concerning motion-based recognition, dynamic backgrounds or possible occlusion in front of the tracked hand can cause some issues [27,32].
In order to meet the above challenges, depth cameras are utilized that can additionally acquire higher-resolution depth measurements, unlike RGB (red–green–blue) cameras that show only a projection. Consequently, more detailed information can be provided, since every pixel of the image consists of both color and distance values [33]. In combination with depth measurements, and in the direction of improving complex feature detection, skeleton features of the hand can be exploited. In essence, skeleton-based recognition makes use of geometric points and statistic features, including space between the joints, along with joint location, orientation, curvature, and angle [13]. A representative study is that of De Smedt et al. [34], who classified hand gestures with the support vector machine (SVM) algorithm using a skeletal and depth dataset. Furthermore, Chen et al. [35], using data from a Kinect sensor for acquisition and segmentation and the skeleton-based methodology, implemented an SVM algorithm and also a hidden Markov model (HMM) for classifying hand gestures. Xi et al. [36] suggested a recursive connected component algorithm and a three-dimensional (3D) geodesic distance of the hand skeleton pixels for real-time hand gesture tracking. Lastly, deep neural networks (DNNs) were used by Tang et al. [37], Mujahid et al. [38], Agrawal et al. [39], Niloy et al. [40], and Devineau et al. [41] to learn features from hand gesture images. More information about hand gesture recognition based on machine learning (ML) and computer vision can be seen in recent review studies such as [13,42,43,44,45].
As far as the incorporation of hand gesture recognition in agricultural human–robot collaborative systems is concerned, the literature is still scarce. A part of the study presented by Vasconez et al. [46,47] investigated this nonverbal means of communication in conjunction with a faster region-based convolutional neural network (R-CNN) intended for improving the process of avocado harvesting in a simulated workspace. In particular, in [46], a robot could detect the workers and judge if they required assistance in one of the following ways; detection of hand gestures, flag detection, and human activity recognition. Moreover, Zhang et al. [48] studied a virtual assembly system regarding a harvester that was able to recognize dynamic hand gestures relying on a CNN/LSTM (long short-term memory) network.
Taking into account the great potential of using hand gesture recognition for enhancing the efficiency of agricultural collaborative systems [9,10,49], as well as for achieving fluid and safe interaction [50], the scope of the present study was to create a robust innovative paradigm. More specifically, it was aimed at developing an integrated automated communication framework between an unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) and the worker via hand gesture recognition such that the former “collaborator” assists humans when they require its help. Moreover, it focused on testing this synergistic ecosystem in different scenarios in an orchard. This study is an extension of the papers recently published on HRI that included a worker and a UGV for optimizing crop harvesting [51,52,53]. In particular, this application is based on the synchronization of the actions of the UGV and workers, with the UGV following the workers while harvesting and undertaking the transport of crates from the harvesting site to a cargo vehicle. In [51], the height of the robot deposit height was evaluated in the framework of occupational health prolepsis, while, in [52,53], wearable sensors were used for the identification of human activity signatures. We now add real-time hand gesture recognition to this syllabus for the sake of optimizing natural communication and safety by combining depth videos and skeleton-based recognition. It is the first time, at least to authors’ knowledge, that such a system is verified in an orchard and not in a simulated environment [46,47,48], proving that it is able to face the aforementioned challenges related to vision sensors and outdoor settings.
The remainder of the present paper is structured as follows: Section 2 is divided into two main subsections. The first one describes the developed framework for achieving automatic hand gesture recognition along with the data acquisition process and information about the ML approach. The second subsection elaborates on the methodology regarding the “translation” of the automated hand gesture recognition into practical commands to be executed by a UGV in different outdoor instances. Subsequently, the results are presented in Section 3 regarding the performance of the examined ML algorithms for capturing the hand gestures (Section 3.1), as well as the efficiency of the proposed system in different situations (Section 3.2). Lastly, in Section 4, concluding remarks are drawn in tandem with a discussion in a broader context along with future research directions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hand Gesture Recognition
2.1.1. Data Acquisition
The data acquisition process is an essential element in order to properly train an ML algorithm. In the present study, the data acquisition was performed using a ZED 2 depth camera (Stereolabs Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA) placed at a fixed height of 88 cm on a UGV (Thorvald, SAGA Robotics SA, Oslo, Norway). Five participants were involved in the present acquisition of data on both sunny and cloudy days at different sites of an orchard with Pistacia vera trees in the region of Thessaly, in central Greece. Additionally, the distance between the participant and the camera was changed in favor of increasing variability. Concerning the speed of the tracking, it was set equal to 60 fps, while the focus was on the left hand. The predefined hand gestures, which are depicted in Figure 1a–e, are commonly known as “fist”, “okay”, “victory”, “flat”, and “rock”.

Figure 1.
Images of the investigated hand gestures: (a) “fist”, (b) “okay”, (c) “victory”, (d) “flat”, and (e) “rock”.
For the purpose of identifying the position of hands, the MediaPipe framework was implemented [54], similarly to recent studies such as [55,56,57]. MediaPipe is an open-source framework created by Google that offers various ML solutions for object detection and tracking. An algorithm was developed using Python that implements this framework for gesture recognition, by using the holistic solution including the hand detection (for the left hand) and excluding the face detection. As described in [58], a model regarding the palm detection works on the entire image and returns an oriented bounding frame of the hand. A model of hand landmarks then works on the cropped picture and returns 3D keypoints via a regression process. Each of the identified landmarks has distinct relative x, y coordinates to the picture frame. Consequently, the requirement for data augmentation, including translation and rotation, is remarkably reduced, while the previous frame can be used in case the model cannot identify the hand so as to re-localize it. Moreover, the MediaPipe model “learns” a consistent hand pose representation and turns out to be robust even to self-occlusions and partially visible hands. Lastly, the developed algorithm computes the Euclidian distance between all the identified landmarks along with shoulder and elbow angles. The aforementioned angles refer to the body side that corresponds to the tracked hand. In Figure 2, the aforementioned landmarks are depicted pertaining to the examined hand gestures, with the images taken in the laboratory for the sake of better distinguishing the landmarks.
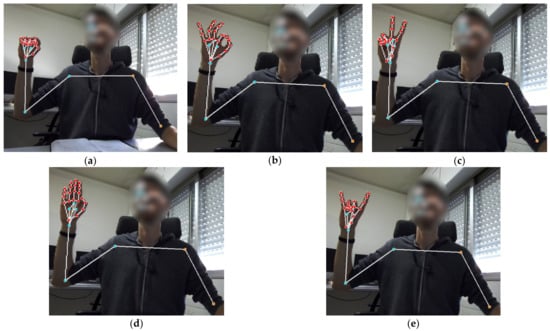
Figure 2.
Tracked hand landmarks denoted by dots for the gestures: (a) “fist”, (b) “ok”, (c) “victory”, (d) “flat”, and (e) “rock”.
The dataset, which was used for training, consisted of 4819 rows created from images taken from the RGB-D camera in the orchard. Each row of the dataset represents the generated landmarks from the MediaPipe hand algorithm for each video frame. On the other hand, each column (except the last three) indicates the Euclidian distance between two landmarks to the given frame. The last three columns represent the shoulder angle, the elbow angle, and the class, respectively. As mentioned above, the calculation of the Euclidian distance and angles was carried out by the developed algorithm, while the classification of the hand gesture was performed manually for each case.
In general, when using an ML algorithm, it is of central importance to train it by utilizing a dataset with about the same number of samples for each class. In this analysis, since the participants carried out the five preset hand gestures in the same time period, the classes resulted in approximately the same number of instances and, consequently, in balanced classes, as depicted in Figure 3.
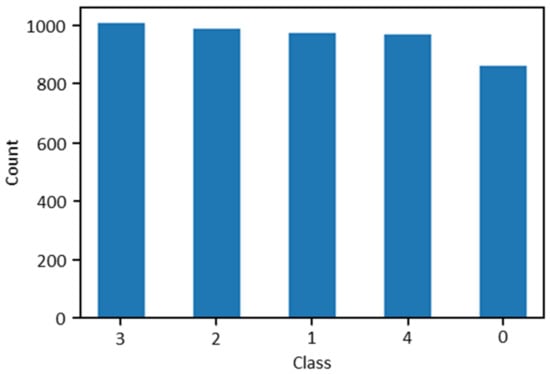
Figure 3.
Bar chart showing counts of each class; labels 0–4 correspond to “fist” (0), “flat” (1), “okay” (2), “rock” (3), and “victory” (4) hand gestures.
2.1.2. Data Preprocessing
Due to the type of the aggregated data, only two preprocessing actions were required. The first was the oversampling procedure using the SMOTE algorithm [59] for the Scikit-learn library [60]. It regards a Python module incorporating a variety of ML algorithms for both supervised and unsupervised problems. The second preprocessing action dealt with data normalization in which a min–max scaler was used in the same library.
2.1.3. Machine Learning Algorithms Tested for Classification Predictive Modeling
Classification commonly refers to problems aiming at recognition and grouping of objects and data into preset categories. The algorithms, which are used as classifiers in ML, make use of input training data in order to predict the probability that the data fall into one of the predetermined classes. There are a plethora of classification algorithms available in the literature [61,62,63]. In the present analysis, the following algorithms were used:
- Logistic regression (LR): Applied to estimate discrete values from a set of independent variables for predicting the likelihood of an event through fitting data to a logit function;
- Linear discriminant analysis (LDA): A technique whose objective is to project the features of a higher-dimensional space onto a lower one with the intention of avoiding dimensional costs;
- K-nearest neighbor (KNN): A pattern recognition algorithm, which utilizes training datasets so as to find out the closest relatives in future samples;
- Classification and regression trees (CART): A tree-based model relying on a set of “if-else” conditions;
- Naïve Bayes: A probabilistic classifier, which assumes that the existence of a specific feature in a class is independent of the existence of any other feature;
- Support vector machine (SVM): A methodology in which raw data are plotted as points in an n-dimensional space (n represents the number of features). Subsequently, each feature’s value is tied to a specific coordinate so as to enable data classification.
2.2. Real-Time Human–Robot Interaction Based on Hand Gesture Recognition
In this subsection, the methodology pipeline regarding the implementation of the automated hand gesture recognition is described as a means of achieving robust HRI in different cases. In brief, a UGV can detect the worker requiring assistance and lock onto them (“fist” gesture). Once the person has been locked onto, they are the only authorized worker who can collaborate with the UGV by using one of the other four commands/gestures, thus minimizing potential safety concerns [6]. Subsequently, on the basis of the detected hand gesture, the UGV can (a) unlock the selected worker (“okay” gesture), (b) follow the authorized worker considering a safe distance (“victory” gesture), (c) stop the current action (“flat” gesture), or (d) return to a predetermined target location (“rock” gesture). This location can be a cargo vehicle similarly to [46] or any other site of the field according to the application at hand. The five available gestures that correspond to a single class and a unique action to be executed by the UGV are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of the examined hand gestures along with the corresponding classes and actions to be executed by the UGV.
The implemented UGV was equipped, apart from the RGB-D camera needed for gesture recognition, with several sensors to facilitate the present agricultural application. In particular, a 3D laser scanner (Velodyne Lidar Inc., San Jose, CA, USA) was used in order to scan the surrounding environment and generate a two-dimensional map, and an RTK GPS (S850 GNSS Receiver, Stonex Inc., Concord, NH, USA) and inertial measurement units (RSX-UM7 IMU, RedShift Labs, Studfield, Victoria, Australia) were used for providing information about velocity, positioning of the UGV (with latitude and longitude coordinates), and time toward optimal robot localization, navigation, and obstacle avoidance. To cope with the current requirements in computational power, all the visual oriented operations were orchestrated by a Jetson TX2 Module [64] with CUDA support. In Figure 4, the UGV platform used in the present study is depicted equipped with the necessary sensors.
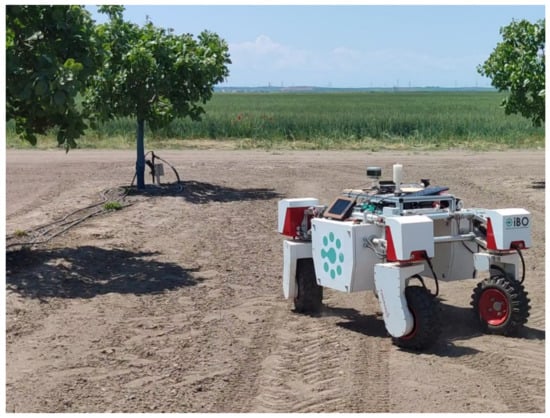

Figure 4.
The robotic system used in the present analysis equipped with the required sensors.
The selection of the above sensors was made on the basis of the capability for Robot Operating System (ROS) integration [65], which is an open-source framework related to robotic applications and constitutes an emerging framework in various fields, including agriculture [66,67]. When reconfiguring a robot, the implemented software should be modular and capable of being adapted to new configurations without requiring recompilation of the robot’s code. Toward that direction, ROS was selected to be the software of the present study. All processes running on UGV are registered to the same master ROS, constituting nodes within the same network [68]. The ROS framework was also used to navigate the UGV in the orchard. The accurate position was provided by the onboard RTK-GNSS system. In Figure 5, the operation flow of the developed system is presented. In brief, as an input, video frames from the depth camera are used. The image data are then transferred from an ROS topic to an ROS node that extracts the RGB channels from the frame along with the depth values from each frame. As a next step, the MediaPipe algorithm node incorporates the RGB channels for extracting all the essential landmarks to feed into the developed ML algorithm for gesture recognition. In addition, in conjunction with the previous step, the RGB image data are imported via a topic to a node associated with human detection. To that end, the pretrained YOLO v3 model was used with the COCO dataset [69]. Το communicate with the rest of the system, an ROS node was developed that requires as an input topic the RGB image of the depth camera. The output of this node is a topic with a custom message that consists of the relative coordinates of the bounding box of the identified person and the distance between the UGV and the collaborating person.
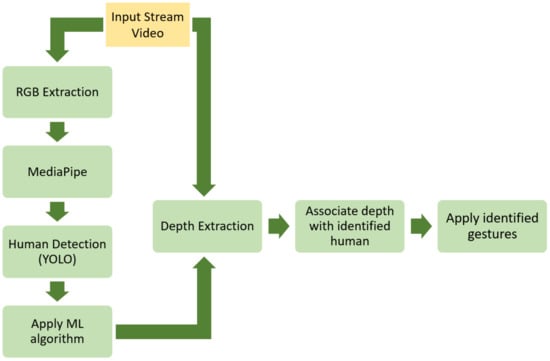
Figure 5.
Operation flow of the developed system.
In the gesture recognition node, similarly to human recognition, the input topic consists of the RGB image. The gesture recognition node implements the MediaPipe algorithm and predicts the hand gestures. The output topic constitutes, in practice, the probability of the identified gesture. Once a gesture is detected and published, the HRI node relates it with the identified person and publishes an ROS time frame (tf) between the robot and the person using a distinct ROS node.
The tf publisher/subscriber is a tool provided by the ROS framework that keeps the relationship among coordinate frames in a tree structure, allowing the user to transform vectors, points, and so on. The tree structure enables dynamic changes to this structure requiring no additional information, apart from the directed graph edge. In case an edge is published to a node referencing a separate parent node, the tree is going to resolve to the new parent node. The main purpose of this tool is to create a local coordinate system from the robot and its surrounding environment. In most cases, the “0, 0” point of each local coordination system is either the first registered point of the operational environment during the mapping procedure or the center of the robot. In more complex entities (for example, the UGVs), the entity consists of multiple tf publishers (one for each district part). For the scope of this study, the human entities consist of one tf publisher. Further details about the tf library can be found in [70].
The main scope of the HRI node is to control the UGV behavior. On the basis of the identified hand gesture (class), summarized in Table 1, the algorithm performs the following steps:
- Waits until the identified person performs a gesture. When the gesture is registered, the tf publisher is initialized (class 0). For each identified human, a unique identifier (ID) is assigned. When one of the identified persons performs the lock gesture, the HRI node is activated. Finally, the person who performed the lock gesture has the remit to control the UGV and collaborate with it. In order for a person with a different ID to be able to control the UGV, the “unlock” command must be detected;
- “Unlocks” the person and removes the tf publisher (class 1);
- Enables a tf following sequence and obstacle avoidance. The UGV moves autonomously in the field while keeping a predefined safe distance. This must be greater than or equal to 0.9 m, similarly to [46], in order to be within the so-called social acceptable zone (class 2);
- Disables the tf following sequence, but does not “unlock” the person (class 3);
- Navigates the UGV to a specific predefined location (class 4).
In order for the UGV to successfully keep a safe distance and velocity from the identified people and possible obstacles, the open-source package “ROS Navigation Stack” [71,72] was used similarly to previous studies [67,73]. An ROS node creates a tf publisher from the robot for the identified obstacles and locked person and, according to the tfs values, a velocity controller keeps a safe distance. This package prerequires that the UGV runs ROS, has a tf transform tree, and publishes sensor data by utilizing the right ROS message types [71].
3. Results
This section elaborates on the results obtained from the six ML algorithms utilized for detecting the five different hand gestures. In addition, preliminary results are summarized for testing step by step the efficiency of this nonverbal communication in real field conditions for three different scenarios.
3.1. Comparison of the Machine Learning Algorithms Performance for Classification of the Hand Gestures
Confusion matrices constitute a useful and popular measure for evaluating and visualizing the performance of ML algorithms while solving both binary and multiclass classification problems by comparing the actual values against those predicted by the ML model. In particular, a confusion matrix can be an N × N matrix, where N stands for the number of classes. In the present analysis, N was equal to the examined hand gestures, i.e., five, as depicted in Figure 6, while the correspondence of the number of classes with the hand gesture is presented in Table 1. The confusion matrices derived using the six ML algorithms, namely LR, LDA, KNN, CART, NB, and SVM, are presented in Figure 6a–f, respectively. The diagonal cells show the number of hand gestures that were correctly classified, whereas the off-diagonal cells show the number of misclassified gestures. Higher diagonal values in Figure 6 indicate a better performance of the corresponding algorithm. Overall, the most problematic hand gestures were the “rock” (label 3) and “victory” (label 4), especially for LR, LDA, CART, and SVM algorithms.
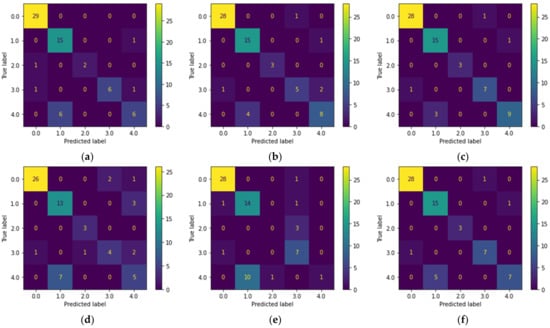
Figure 6.
Confusion matrices showing the performance of (a) LR, (b) LDA, (c) KNN, (d) CART, (e) NB, and (f) SVM algorithms. Labels 0–4 correspond to “fist” (0), “flat” (1), “okay” (2), “rock” (3), and “victory” (4) hand gestures.
The classification report depicted in Table 2 summarizes the individual performance metrics for each ML algorithm. In simple terms, these metrics indicate the proportion of, (a) true results among the entire number of examined cases (accuracy), (b) the predicted values that turned out to be truly positive (precision), and (c) actual positives that turned out to be correctly predicted (recall). Lastly, the F1-score combines the precision and recall by considering their harmonic mean. As can be deduced from Table 2, KNN, LDA, and SVM seemingly outperformed the other investigated algorithms, while the NB algorithm gave the worst results.

Table 2.
Classification report for the performance of the six investigated machine learning algorithms.
Lastly, Figure 7 depicts the box plots pertaining to the accuracy of the investigated classifiers as a means of offering a visual summary of the data regarding the identification of the mid-point of the data (the orange line), as well as the skewness and dispersion of the dataset. As an example, if the median is closer to the bottom or to the top of the box, the distribution tends to be skewed. In contrast, if the median is in the middle of the box, and the length of the whiskers is approximately the same on both sides, the distribution is symmetric. Lastly, the interquartile range (IQR), i.e., the range of the box, includes 50% of the values; thus, a longer box indicates more dispersed data.
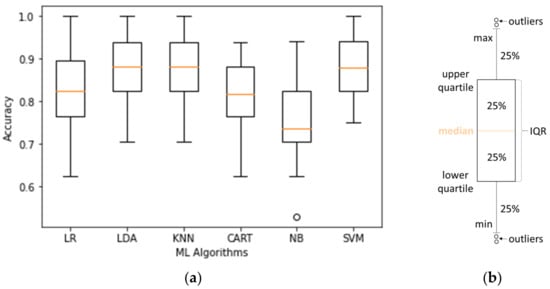
Figure 7.
(a) Box plot distribution of the accuracy of the examined machine learning algorithms; (b) illustration of the main set of data in a typical box plot.
Concerning the present analysis, the NB classifier appeared to be positively skewed, while outliers were also observed (plotted as circles beyond the whiskers) for this case. Focusing on the KNN, LDA, and SVM, which demonstrated the best performance, the obtained accuracy values had about the same median and were not symmetrical, spreading out more on the upper side. Moreover, KNN and LDA had approximately the same range of data, larger as compared to the corresponding range of SVM. Lastly, the dispersion of accuracy values was the same for the aforementioned three algorithms, as can be deduced from their IQR values.
3.2. Demonstration of the Proposed System in Differrent Scenarios
For safety purposes, a step-by-step approach was performed. We initially tested the efficacy of the proposed framework in a case where only one person existed in the same working environment with the UGV. The latter was still in a specific farm location waiting to lock its “collaborator”, in case the “fist” gesture was detected. Taking into account the above results concerning the performance of the investigated ML algorithms in predicting the five hand gestures, only the KNN algorithm was used for brevity. The UGV was able to respond to all the commands given via the hand gestures (Table 1), recorded by the RGB-D camera and recognized by the proposed framework. The fact that the UGV aborted its current task whenever the “flat” gesture was recognized is very important considering that a possible failure to comply with this command can provoke harmful consequences [10]. Lastly, a maximum speed of 0.2 m/s and a maximum safe distance of 0.9 m [46], which were programmed in the developed model, were necessary prerequisites in all occasions.
In the next experimental set, a second person was added in the working region to investigate how the proposed framework could cope with this challenge. It can be concluded that, again, the robot was able to accurately “lock” onto the selected participant in spite of the presence of the second person while also obeying the other four commands. During this scenario, although the UGV could obey only the authorized person, it was able to recognize the second person and avoid them similarly to the other existing obstacles of the orchard. Figure 8 illustrates the case where the UGV was in the “following” mode for the locked person in the case of a single person (Figure 8a) or when both persons were in the field of view of the RGB-D camera (Figure 8b). Figure 8 was generated by RVIZ [74], which is a 3D visualization tool for the ROS software.
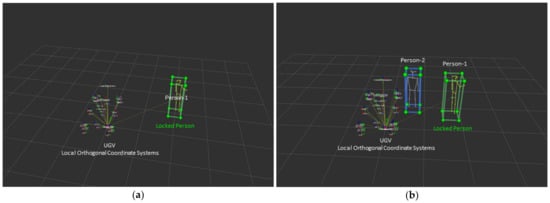
Figure 8.
Visualization of the real-time field experiments in ROS RVIZ environment showing the local orthogonal coordinate system of some parts of the UGV, as well as the “following” mode, in case of (a) a single person and (b) a second person appearing in the field of view of the RGB-D camera.
Lastly, the proposed synergistic HRI system was tested in a more complex scenario. In this case study, two persons were present in the same working space with the UGV. The first person asked to be locked onto by the UGV (“fist” gesture) (Figure 9a), and then requested to be followed (“victory” gesture) (Figure 9b) before performing a stop command (“flat” gesture) (Figure 9c). Afterward, the locked person asked to be unlocked (“okay” gesture) (Figure 9d). A second person in the field of view of the RGB-D camera asked to be locked onto (Figure 9e). By locking onto the second person, the UGV followed the participant (Figure 9f), and was then ordered to go to the target site of the farm (Figure 9g), where it arrived after navigating a few meters (Figure 9h) following the set of gestures presented in Table 1. Some indicative images taken from the pilot study are shown in Figure 9a–h, while a video is also provided in the Supplementary Materials (Video S1).


Figure 9.
Snapshots from experimental demonstration session in an orchard depicting (a) the locking onto of the first person by the UGV, as well as the UGV (b) following the locked participant, (c) stopping, and (d) unlocking this participant. Next, the UGV (e) locked onto the second participant, (f) followed him, (g) was ordered to go to the target location, and (h) reached this location.
4. Discussion and Main Conclusions
In the present study, a very crucial aspect of HRI was investigated to meet the needs of enabling natural communication. In this context, we proposed a nonverbal interaction via real-time hand gesture recognition captured by a depth camera. This combination has the potential to overcome common problems associated with illumination changes and complex backgrounds, providing reliable results [13]. In the direction of additionally facing the challenges of dynamic agricultural environments, a skeleton-based recognition methodology was designed on the basis of ML. The accuracy of six ML algorithms (LR, LDA, KNN, CART, NB, and SVM) was tested in this study on five certain hand gestures representing different actions that the UGV, equipped with an RGB-D camera and other sensors, could carry out on the basis of the detected commands. Among the examined classifiers, KNN, LDA, and SVM demonstrated the best performance.
Firstly, the UGV must detect the assigned hand gesture to “lock” onto the person with whom it is going to collaborate in a relatively crowded environment. To that end, a distinct hand gesture is used, which represents the first class of the ML implementation. Once the person is located, the UGV can perform four other actions in order to assist them, namely, following its collaborator by keeping the preset safe distance and speed, returning to the destination site, which may be the cargo vehicle zone similarly to [46] or any other site depending on the application, or stopping its current task at any time, once the corresponding hand gesture is detected.
In summary, the present integrated hand gesture recognition framework incorporated and combined several kinds of ICT. In particular, the data acquisition was performed using a ZED 2 depth camera (Stereolabs Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA) mounted on a UGV (Thorvald, SAGA Robotics SA, Oslo, Norway). The open-source MediaPipe framework [56] was used for object detection and tracking in conjunction with an algorithm developed for the present study. For the preprocessing of the data, the SMOTE algorithm [57] was implemented. Furthermore, the UGV used in this study was equipped with a variety of sensors including (i) the depth camera mentioned above, (ii) a 3D laser scanner (Velodyne Lidar Inc., San Jose, CA, USA), (iii) an RTK GPS (S850 GNSS Receiver, Stonex Inc., Concord, NH, USA), and (iv) IMUs (UM7 IMU, RedShift Labs, Studfield, Victoria, Australia). To combine these technologies, an algorithm was developed within the ROS framework using Python, whose operational flow is described in Figure 5. Moreover, different tf publishers were developed within the tf ROS package [70], while the ROS navigation stack package [72] was used for safe navigation. To meet the increased requirements necessary for the detection ML model, a Jetson TX2 Module [64] with CUDA support was embedded in the robotic platform.
Overall, the challenge of properly classifying the five hand gestures was successfully fulfilled, while the preliminary results on real conditions are encouraging enough. In fact, three different scenarios took place considering either one or two persons. In all cases, the KNN classifier was used for the sake of brevity. It was demonstrated that a fluid HRI in agriculture can be successful in sharing the same working space with the robot being navigated within a predetermined safe range of speed and distance.
Obviously, toward establishing a viable solution, each aspect of HRI design (e.g., human factors, interaction roles, user interface, automation level, and information sharing [10]) should be tackled separately, so as to identify and address possible issues. We tried to add human comfort, naturalness, and the sense of trust to the picture, which are considered very important in HRI and have received limited attention in agriculture so far. Comfort and trust can contribute, to a great extent, to the feeling of perceived safety, which is among the key issues that should be guaranteed in synergistic ecosystems [6,75,76]. In other words, users must perceive robots as safe to interact with. On the other hand, naturalness refers to the social navigation of the robot though adjusting its speed and distance from the workers.
To conclude, the present study investigated the possibility of using nonverbal communication based on hand gesture detection in real conditions in agriculture. Obviously, this framework can also be implemented in other sectors depending on the specific application at hand. Possible future work includes the expansion of the present system to incorporate more hand gestures for the purpose of other practical applications. Toward that direction, recognition models that can identify a sequence of gestures could also be useful. In addition, it would be interesting to examine the potential of combing hand gesture recognition with human activity recognition [52,53] in order to propose a more fluid HRI and test the framework in more complex applications. More experimental tests should be carried out in different agricultural environments to identify possible motion problems of the UGV, which may lead to the application of cellular neural networks [77] to address them, similar to previous studies [78]. Lastly, future research could involve workers using their own pace in real conditions and investigation of not only the efficiency of the system, but also their opinion in order to provide a viable and socially accepted solution [6].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://drive.google.com/file/d/1qHJXW5NFognF3mOVRxV1y09juVIHb4yz/view. Video S1. Video recording from an experimental demonstration session for testing the efficacy of the proposed synergistic framework.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.M., L.B. and D.B.; methodology, V.M. and D.K. (Dimitrios Katikaridis); software, V.M. and D.K. (Dimitrios Katikaridis); validation, V.M. and A.A.; visualization, V.M. and L.B.; writing—original draft preparation, V.M. and L.B.; writing—review and editing, V.M., D.K. (Dimitrios Katikaridis), L.B., P.B., A.A., D.K. (Dimitrios Kateris), S.P. and D.B.; supervision, D.B.; project administration, D.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethical Committee under the identification code 1660 on 3 June 2020.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Acknowledgments
This research was partly supported by the Project “Human–Robot Synergetic Logistics for High-Value Crops” (project acronym: SYNERGIE), funded by the General Secretariat for Research and Technology (GSRT) under reference no. 2386.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Oliveira, L.F.P.; Moreira, A.P.; Silva, M.F. Advances in Agriculture Robotics: A State-of-the-Art Review and Challenges Ahead. Robotics 2021, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechar, A. Agricultural Robotics for Precision Agriculture Tasks: Concepts and Principles. In Innovation in Agricultural Robotics for Precision Agriculture: A Roadmap for Integrating Robots in Precision Agriculture; Bechar, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 17–30. ISBN 9783030770365. [Google Scholar]
- Lampridi, M.; Benos, L.; Aidonis, D.; Kateris, D.; Tagarakis, A.C.; Platis, I.; Achillas, C.; Bochtis, D. The Cutting Edge on Advances in ICT Systems in Agriculture. Eng. Proc. 2021, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Shao, X.-F.; Wu, C.-H.; Qiao, P. A systematic literature review on applications of information and communication technologies and blockchain technologies for precision agriculture development. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysiadis, V.; Tsolakis, N.; Katikaridis, D.; Sørensen, C.G.; Pearson, S.; Bochtis, D. Mobile Robotics in Agricultural Operations: A Narrative Review on Planning Aspects. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benos, L.; Sørensen, C.G.; Bochtis, D. Field Deployment of Robotic Systems for Agriculture in Light of Key Safety, Labor, Ethics and Legislation Issues. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2022, 3, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinoudi, V.; Sørensen, C.G.; Pearson, S.; Bochtis, D. Robotics and labour in agriculture. A context consideration. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 184, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechar, A.; Vigneault, C. Agricultural robots for field operations. Part 2: Operations and systems. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 153, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconez, J.P.; Kantor, G.A.; Auat Cheein, F.A. Human–robot interaction in agriculture: A survey and current challenges. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 179, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benos, L.; Bechar, A.; Bochtis, D. Safety and ergonomics in human-robot interactive agricultural operations. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 200, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, E.; Minto, R.; Zampieri, E.G.G.; Faccio, M.; Rosati, G. Human–Robot Collaboration in Manufacturing Applications: A Review. Robotics 2019, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.C.; Ong, S.K.; Nee, A.Y.C. A novel augmented reality-based interface for robot path planning. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2014, 8, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudah, M.; Al-Naji, A.; Chahl, J. Hand Gesture Recognition Based on Computer Vision: A Review of Techniques. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Campbell, N.; Jokinen, K.; Wilcock, G. Investigating the use of Non-verbal Cues in Human-Robot Interaction with a Nao robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd International Conference on Cognitive Infocommunications (CogInfoCom), Kosice, Slovakia, 2–5 December 2012; pp. 679–683. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.-S.; Ho, N.-H.; Yang, H.-J.; Baek, E.-T.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, G. Real-Time Hand Gesture Spotting and Recognition Using RGB-D Camera and 3D Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varun, K.S.; Puneeth, I.; Jacob, T.P. Virtual Mouse Implementation using Open CV. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 23–25 April 2019; pp. 435–438. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.; Zhu, G.; Wu, Y.-T.; Liu, E.; Hu, X. A case study of gesture-based games in enhancing the fine motor skills and recognition of children with autism. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2018, 26, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastgoo, R.; Kiani, K.; Escalera, S. Hand sign language recognition using multi-view hand skeleton. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 150, 113336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, J.; Kocherovsky, M.; Paul, N.; Pleune, M.; Chung, C.-J. Autonomous Human-Vehicle Leader-Follower Control Using Deep-Learning-Driven Gesture Recognition. Vehicles 2022, 4, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Tham, C.-K.; Heng, C.-H.; Thean, A.V.-Y. A Wireless Multi-Channel Capacitive Sensor System for Efficient Glove-Based Gesture Recognition with AI at the Edge. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 1624–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, W. Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition Based on Signals from Specialized Data Glove and Deep Learning Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 2509014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, J. A multi-scale descriptor for real time RGB-D hand gesture recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 144, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Yánez, A.; Benalcázar, M.E.; Mena-Maldonado, E. Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition Using Surface Electromyography and Machine Learning: A Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanoi, Y.; Togo, S.; Jiang, Y.; Yokoi, H. Learning Data Correction for Myoelectric Hand Based on “Survival of the Fittest”. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2021, 2021, 9875814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Liu, T.; Han, X.; Yi, H. Application Research on Optimization Algorithm of sEMG Gesture Recognition Based on Light CNN + LSTM Model. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2021, 2021, 9794610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.J.; Rehg, J.M. Statistical Color Models with Application to Skin Detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2002, 46, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, C.-M.; Zhu, H.-M.; Feng, W. Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition using Motion Tracking. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2011, 4, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, A.; Giachetti, A.; Soso, S.; Pintani, D.; D’Eusanio, A.; Pini, S.; Borghi, G.; Simoni, A.; Vezzani, R.; Cucchiara, R.; et al. SHREC 2021: Skeleton-based hand gesture recognition in the wild. Comput. Graph. 2021, 99, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Hand gesture recognition using Kinect. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Science and Automation Engineering, Beijing, China, 22–24 June 2012; pp. 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Stergiopoulou, E.; Sgouropoulos, K.; Nikolaou, N.; Papamarkos, N.; Mitianoudis, N. Real time hand detection in a complex background. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2014, 35, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakumanu, P.; Makrogiannis, S.; Bourbakis, N. A survey of skin-color modeling and detection methods. Pattern Recognit. 2007, 40, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.; Pajuelo, J.A.; Martínez, J.M. Real-time Motion-based Hand Gestures Recognition from Time-of-Flight Video. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2017, 86, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fu, L.; Gao, F.; Wu, J.; Li, R.; Karkee, M.; Zhang, Q. Application of consumer RGB-D cameras for fruit detection and localization in field: A critical review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 177, 105687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smedt, Q.; Wannous, H.; Vandeborre, J.-P.; Guerry, J.; Saux, B.L.; Filliat, D. 3D hand gesture recognition using a depth and skeletal dataset: SHREC’17 track. In Proceedings of the Workshop on 3D Object Retrieval, Lyon, France, 23–24 April 2017; pp. 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, B.; Chen, Y.-L.; Liang, G.; Wu, X. A real-time dynamic hand gesture recognition system using kinect sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Zhuhai, China, 6–9 December 2015; pp. 2026–2030. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, C.; Chen, J.; Zhao, C.; Pei, Q.; Liu, L. Real-time Hand Tracking Using Kinect. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Tokyo, Japan, 25–27 February 2018; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, A.; Lu, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, H. A Real-Time Hand Posture Recognition System Using Deep Neural Networks. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2015, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujahid, A.; Awan, M.J.; Yasin, A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Abdulkareem, K.H. Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition Based on Deep Learning YOLOv3 Model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Ainapure, R.; Agrawal, S.; Bhosale, S.; Desai, S. Models for Hand Gesture Recognition using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Conference on Computing Communication and Automation (ICCCA), Greater Noida, India, 30–31 October 2020; pp. 589–594. [Google Scholar]
- Niloy, E.; Meghna, J.; Shahriar, M. Hand Gesture-Based Character Recognition Using OpenCV and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Automation, Control and Mechatronics for Industry 4.0 (ACMI), Rajshahi, Bangladesh, 8–9 July 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Devineau, G.; Moutarde, F.; Xi, W.; Yang, J. Deep Learning for Hand Gesture Recognition on Skeletal Data. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zengeler, N.; Kopinski, T.; Handmann, U. Hand Gesture Recognition in Automotive Human-Machine Interaction Using Depth Cameras. Sensors 2019, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Li, W.; Ogunbona, P.; Wan, J.; Escalera, S. RGB-D-based human motion recognition with deep learning: A survey. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2018, 171, 118–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L. Gesture recognition for human-robot collaboration: A review. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2018, 68, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benos, L.; Tagarakis, A.C.; Dolias, G.; Berruto, R.; Kateris, D.; Bochtis, D. Machine Learning in Agriculture: A Comprehensive Updated Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconez, J.P.; Guevara, L.; Cheein, F.A. Social robot navigation based on HRI non-verbal communication: A case study on avocado harvesting. In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Limassol, Cyprus, 8–12 April 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019. Volume F147772. pp. 957–960. [Google Scholar]
- Hurtado, J.P.V. Human-Robot Interaction Strategies in Agriculture; Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María: Valparaíso, Chile, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Lin, J.; He, J.; Rong, X.; Li, C.; Zeng, Z. Agricultural Machinery Virtual Assembly System Using Dynamic Gesture Recognitive Interaction Based on a CNN and LSTM Network. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5256940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolakis, N.; Bechtsis, D.; Bochtis, D. AgROS: A Robot Operating System Based Emulation Tool for Agricultural Robotics. Agronomy 2019, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benos, L.; Tsaopoulos, D.; Bochtis, D. A Review on Ergonomics in Agriculture. Part II: Mechanized Operations. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benos, L.; Kokkotis, C.; Tsatalas, T.; Karampina, E.; Tsaopoulos, D.; Bochtis, D. Biomechanical Effects on Lower Extremities in Human-Robot Collaborative Agricultural Tasks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagarakis, A.C.; Benos, L.; Aivazidou, E.; Anagnostis, A.; Kateris, D.; Bochtis, D. Wearable Sensors for Identifying Activity Signatures in Human-Robot Collaborative Agricultural Environments. Eng. Proc. 2021, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostis, A.; Benos, L.; Tsaopoulos, D.; Tagarakis, A.; Tsolakis, N.; Bochtis, D. Human activity recognition through recurrent neural networks for human-robot interaction in agriculture. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugaresi, C.; Tang, J.; Nash, H.; McClanahan, C.; Uboweja, E.; Hays, M.; Zhang, F.; Chang, C.-L.; Yong, M.G.; Lee, J.; et al. MediaPipe: A Framework for Building Perception Pipelines. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.08172. [Google Scholar]
- Veluri, R.K.; Sree, S.R.; Vanathi, A.; Aparna, G.; Vaidya, S.P. Hand Gesture Mapping Using MediaPipe Algorithm. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Communication, Computing and Electronics Systems, Coimbatore, India, 28–29 October 2021; Bindhu, V., Tavares, J.M.R.S., Du, K.-L., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2022; pp. 597–614. [Google Scholar]
- Damindarov, R.; Fam, C.A.; Boby, R.A.; Fahim, M.; Klimchik, A.; Matsumaru, T. A depth camera-based system to enable touch-less interaction using hand gestures. In Proceedings of the International Conference “Nonlinearity, Information and Robotics” (NIR), Innopolis, Russia, 26–29 August 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Boruah, B.J.; Talukdar, A.K.; Sarma, K.K. Development of a Learning-aid tool using Hand Gesture Based Human Computer Interaction System. In Proceedings of the Advanced Communication Technologies and Signal Processing (ACTS), Rourkela, India, 15–17 December 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- MediaPipe. MediaPipe Hands. Available online: https://google.github.io/mediapipe/solutions/hands.html (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- Chawla, N.; Bowyer, K.; Hall, L.; Kegelmeyer, W. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, P.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, S.S.; Nayak, S.K.; Mishra, D. A review on machine learning algorithms. In Proceedings of the Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, Virtual Event, 14–16 June 2021; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 153, pp. 495–507. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Thakur, N.; Sharma, A. A review of supervised machine learning algorithms. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 16–18 March 2016; pp. 1310–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.C.; Hajra, M.; Ghosh, M. Supervised Classification Algorithms in Machine Learning: A Survey and Review. In Emerging Technology in Modelling and Graphics; Mandal, J.K., Bhattacharya, D., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2020; pp. 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- NVIDIA Jetson: The AI platform for autonomous machines. Available online: https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/autonomous-machines/embedded-systems/ (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- ROS-Robot Operating System. Available online: https://www.ros.org/ (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Hinas, A.; Ragel, R.; Roberts, J.; Gonzalez, F. A Framework for Multiple Ground Target Finding and Inspection Using a Multirotor UAS. Sensors 2020, 20, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagarakis, A.C.; Filippou, E.; Kalaitzidis, D.; Benos, L.; Busato, P.; Bochtis, D. Proposing UGV and UAV Systems for 3D Mapping of Orchard Environments. Sensors 2022, 22, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimstad, L.; From, P.J. The Thorvald II Agricultural Robotic System. Robotics 2017, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2014), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Foote, T. tf: The transform library. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Technologies for Practical Robot Applications (TePRA), Woburn, MA, USA, 22–23 April 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Navigation: Package Summary. Available online: https://www.opera.com/client/upgraded (accessed on 28 June 2022).
- Zheng, K. ROS Navigation Tuning Guide. In Robot Operating System (ROS); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 197–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kateris, D.; Kalaitzidis, D.; Moysiadis, V.; Tagarakis, A.C.; Bochtis, D. Weed Mapping in Vineyards Using RGB-D Perception. Eng. Proc. 2021, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershberger, D.; Gossow, D.; Faust, J.; William, W. RVIZ Package Summary. Available online: http://wiki.ros.org/rviz (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Akalin, N.; Kristoffersson, A.; Loutfi, A. Do you feel safe with your robot? Factors influencing perceived safety in human-robot interaction based on subjective and objective measures. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2022, 158, 102744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinoudi, V.; Lampridi, M.; Kateris, D.; Pearson, S.; Sørensen, C.G.; Bochtis, D. The Future of Agricultural Jobs in View of Robotization. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, P.; Baglio, S.; Fortuna, L.; Manganaro, G. Cellular Neural Networks: A Survey. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1995, 28, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, P.; Fortuna, L.; Frasca, M.; Patane, L. A CNN-based chip for robot locomotion control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2005, 52, 1862–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).