Pseudo-Phoneme Label Loss for Text-Independent Speaker Verification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We compare the performance of existing primary loss methods on speaker verification. The loss function includes softmax loss, center loss, triplet loss, log-likelihood-ratio cost loss, additive margin softmax loss and additive angular margin loss.
- Based on HuBERT and DeepCluster, we propose a pseudo-phoneme label loss for TI-SV that introduces speech context information to boost speaker verification performance without an additional ASR component. We also tried different implementations of PPL loss and experimented with the VoxCeleb dataset.
- We test the performance of PPL loss on the x-vector system. Including the combination of PPL loss with different loss functions, it is proven by experiments that our proposed PPL loss can improve the system performance.
- Experimental results on the VoxCeleb database demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. We also explored the impact of different parameter settings of PPL loss on the final performance. It was verified through experiments that when using PPL loss, different parameter settings were improved compared to the baseline system, proving the effectiveness of PPL loss.
2. Related Work
2.1. Loss Function
2.1.1. Cross-Entropy Loss
2.1.2. Center Loss
2.1.3. Margin Loss
2.1.4. Triplet Loss
2.1.5. CLLR Loss
2.2. Self-Supervised and Multi-Task Learning
2.2.1. Self-Supervised Learning
2.2.2. Multi-Task Learning
3. Proposed Methods
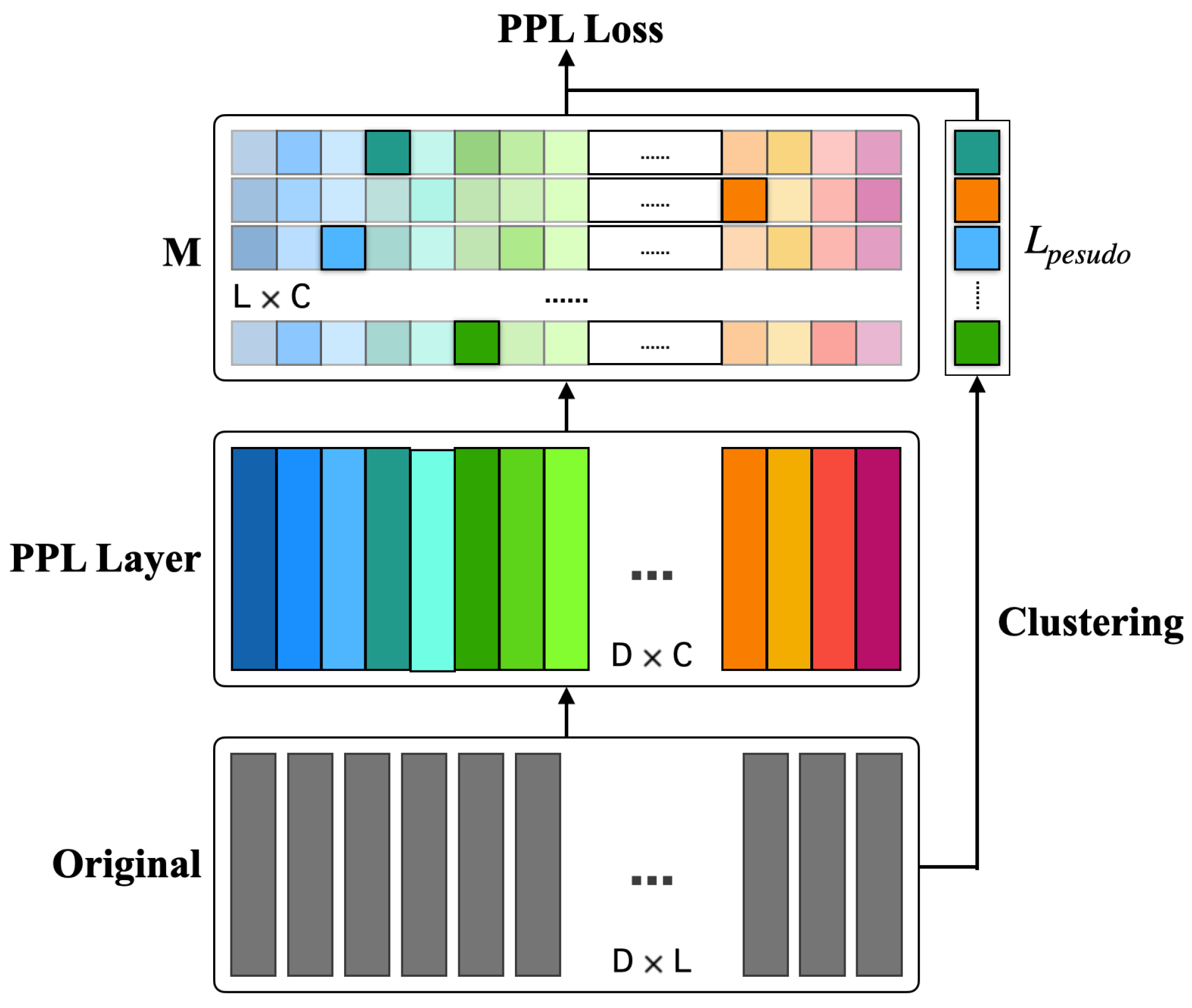
3.1. Pseudo-Phoneme Label Loss
3.2. Different Implementation Methods
- Version 1: We use the multi-task learning method to jointly train the network. On the one hand, we use the deep cluster method to generate pseudo-phoneme labels for frame-level features and then calculate the PPL loss. On the other hand, we use the speaker labels to calculate the classification loss. See more details in Section 3.1.
- Version 2: We directly calculate the PPL loss in the learnable dictionary encoding (LDE) [41,42] pooling layer, train the dictionary components and assign weights through pseudo-phoneme labels, so that the network can better map the frame-level features to the dictionary components, and obtain the phoneme-based pooling results.
- Version 3: The PPL loss is calculated at the frame4 layer. In the process of calculating the PPL loss, a method similar to attentive statistics pooling (ASP) [20] is used to calculate the weight of each frame feature through the attention mechanism, and then the obtained weight matrix is multiplied by frame5 to obtain the features based on attention and PPL loss.
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Dataset
4.2. System Setup
4.3. Implementation Details
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Experiments under Different Loss Functions
5.2. Results of Different Implementation Methods
5.3. Experiments for Add PPL Loss to TDNN
5.4. Effectiveness of Hyperparameters
5.5. Visualization
5.6. Analyses
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kinnunen, T.; Li, H. An overview of text-independent speaker recognition: From features to supervectors. Speech Commun. 2010, 52, 12–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gales, M.J. Maximum likelihood linear transformations for HMM-based speech recognition. Comput. Speech Lang. 1998, 12, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, W.; Sturim, D.; Reynolds, D. Support vector machines using GMM supervectors for speaker verification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2006, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcher, A.; Lee, K.A.; Ma, B.; Li, H. Text-dependent speaker verification: Classifiers, databases and RSR2015. Speech Commun. 2014, 60, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; He, L.; Liu, J.; Johnson, M.T. Introducing phonetic information to speaker embedding for speaker verification. EURASIP J. Audio Speech Music. Process. 2019, 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tejedor-García, C.; Cardeñoso-Payo, V.; Escudero-Mancebo, D. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) Systems Applied to Pronunciation Assessment of L2 Spanish for Japanese Speakers. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Li, T.; Liao, D.; Xia, S.; Li, S.; Hong, Q.; Li, L. The XMUSPEECH System for Accented English Automatic Speech Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Rai, A. Learning Discriminative Features for Speaker Identification and Verification. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 2237–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; He, L.; Liu, J. Large Margin Softmax Loss for Speaker Verification. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2019, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; pp. 2873–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Gao, F.; Ou, Z.; Sun, J. Angular Softmax Loss for End-to-end Speaker Verification. In Proceedings of the 2018 11th International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing (ISCSLP), Taipei City, Taiwan, 26–29 November 2018; pp. 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chagas Nunes, J.A.; Macêdo, D.; Zanchettin, C. Additive Margin SincNet for Speaker Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, H. Angular Margin Centroid Loss for Text-Independent Speaker Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2020, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 3820–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Nai, R.; Wang, D. Real Additive Margin Softmax for Speaker Verification. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 7527–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Koishida, K. End-to-End Text-Independent Speaker Verification with Triplet Loss on Short Utterances. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2017, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 1487–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novoselov, S.; Shchemelinin, V.; Shulipa, A.; Kozlov, A.; Kremnev, I. Triplet Loss Based Cosine Similarity Metric Learning for Text-independent Speaker Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 2242–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mingote, V.; Miguel, A.; Ortega, A.; Lleida, E. Log-Likelihood-Ratio Cost Function as Objective Loss for Speaker Verification Systems. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2021, Brno, Czech Republic, 30 August–3 September 2021; pp. 2361–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.; Ghahremani, P.; Povey, D.; Garcia-Romero, D.; Carmiel, Y.; Khudanpur, S. Deep neural network-based speaker embeddings for end-to-end speaker verification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), San Diego, CA, USA, 13–16 December 2016; pp. 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.; Garcia-Romero, D.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. Deep Neural Network Embeddings for Text-Independent Speaker Verification. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2017, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, D.; Garcia-Romero, D.; Sell, G.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. X-Vectors: Robust DNN Embeddings for Speaker Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5329–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, K.; Koshinaka, T.; Shinoda, K. Attentive Statistics Pooling for Deep Speaker Embedding. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 2252–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Ko, T.; Snyder, D.; Mak, B.; Povey, D. Self-Attentive Speaker Embeddings for Text-Independent Speaker Verification. In Proceedings of the Proc. Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 3573–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehak, N.; Kenny, P.J.; Dehak, R.; Dumouchel, P.; Ouellet, P. Front-End Factor Analysis for Speaker Verification. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2011, 19, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Song, Y.; McLoughlin, I.; Gao, Z.; Dai, L.R. An Effective Deep Embedding Learning Architecture for Speaker Verification. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2019, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; pp. 4040–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, L.; Wang, Q.; Papir, A.; Moreno, I.L. Generalized End-to-End Loss for Speaker Verification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 4879–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.; Mak, M.W. Wav2Spk: A Simple DNN Architecture for Learning Speaker Embeddings from Waveforms. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2020, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 3211–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Yang, J. A Deep Neural Network Model for Speaker Identification. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desplanques, B.; Thienpondt, J.; Demuynck, K. ECAPA-TDNN: Emphasized Channel Attention, Propagation and Aggregation in TDNN Based Speaker Verification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.07143. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, N.; Han, J.; Ding, G.; Sun, J. RepVGG: Making VGG-style ConvNets Great Again. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13728–13737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruder, S. An overview of multi-task learning in deep neural networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05098. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. A Discriminative Feature Learning Approach for Deep Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 499–515. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Cheng, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, H. Additive Margin Softmax for Face Verification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakubec, M.; Jarina, R.; Lieskovska, E.; Chmulik, M. On Deep Speaker Embeddings for Speaker Verification. In Proceedings of the 2021 44th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Virtual, 26–28 July 2021; pp. 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Pang, J. Improved Far-field Speaker Recognition Method Based Geometry Acoustic Simulation and SpecAugment. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Automation and Applications (ICAA), Nanjing, China, 25–27 June 2021; pp. 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Xue, N.; Zafeiriou, S. ArcFace: Additive Angular Margin Loss for Deep Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 4685–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. FaceNet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bredin, H. TristouNet: Triplet loss for speaker turn embedding. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 5430–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Koishida, K.; Hansen, J.H.L. Text-Independent Speaker Verification Based on Triplet Convolutional Neural Network Embeddings. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2018, 26, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.N.; Bolte, B.; Tsai, Y.H.H.; Lakhotia, K.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Mohamed, A. HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 3451–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, M.; Bojanowski, P.; Joulin, A.; Douze, M. Deep clustering for unsupervised learning of visual features. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 132–149. [Google Scholar]
- Mridha, M.F.; Ohi, A.Q.; Monowar, M.M.; Hamid, M.A.; Islam, M.R.; Watanobe, Y. U-Vectors: Generating Clusterable Speaker Embedding from Unlabeled Data. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Chen, J.; Li, M. Exploring the Encoding Layer and Loss Function in End-to-End Speaker and Language Recognition System. In Proceedings of the Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop (Odyssey 2018), Les Sables d’Olonne, France, 26–29 June 2018; pp. 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, W.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, M. A Novel Learnable Dictionary Encoding Layer for End-to-End Language Identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5189–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagrani, A.; Chung, J.S.; Zisserman, A. VoxCeleb: A Large-Scale Speaker Identification Dataset. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2017, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 2616–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, J.S.; Nagrani, A.; Zisserman, A. VoxCeleb2: Deep Speaker Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadjadi, O.; Greenberg, C.; Singer, E.; Mason, L.; Reynolds, D. NIST 2021 Speaker Recognition Evaluation Plan. 2021. Available online: https://www.nist.gov/publications/nist-2021-speaker-recognition-evaluation-plan (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Brown, A.; Huh, J.; Chung, J.S.; Nagrani, A.; Zisserman, A. VoxSRC 2021: The Third VoxCeleb Speaker Recognition Challenge. 2022. Available online: https://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/data/voxceleb/competition2021.html (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Snyder, D.; Chen, G.; Povey, D. Musan: A music, speech, and noise corpus. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.08484. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, T.; Peddinti, V.; Povey, D.; Seltzer, M.L.; Khudanpur, S. A study on data augmentation of reverberant speech for robust speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 5220–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povey, D.; Ghoshal, A.; Boulianne, G.; Burget, L.; Glembek, O.; Goel, N.; Hannemann, M.; Motlicek, P.; Qian, Y.; Schwarz, P.; et al. The Kaldi speech recognition toolkit. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2011 Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 11–15 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, F.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, J.; Lu, H.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Hong, Q. ASV-SUBTOOLS: Open Source Toolkit for Automatic Speaker Verification. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 6184–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, S.J.; Elder, J.H. Probabilistic linear discriminant analysis for inferences about identity. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pronunciator, M. CMU Pronouncing Dictionary. 1990. Available online: http://www.speech.cs.cmu.edu/cgi-bin/cmudict (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]




| Layer | Layer Context | Total Context | Input × Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| frame1 | {t−2,t+2} | 5 | 26 × 512 |
| frame2 | {t−2,t,t+2} | 9 | 512 × 512 |
| frame3 | {t−3,t,t+3} | 15 | 512 × 512 |
| frame4 | {t} | 15 | 512 × 512 |
| frame5 | {t} | 15 | 512 × 1500 |
| statistics pooling | {0,T} | T | 1500 × 3000 |
| segment6 | {0} | T | 3000 × 512 |
| segment7 | {0} | T | 512 × 512 |
| Loss Function | EER (%) | minDCF (0.01) |
|---|---|---|
| Softmax Loss | 3.932 | 0.4103 |
| Center Loss | 3.606 | 0.3647 |
| AM-Softmax Loss | 3.473 | 0.3469 |
| AAM-Softmax Loss | 3.754 | 0.3657 |
| Triplet Loss(end-to-end) | 3.876 | 0.3961 |
| CLLR Loss(end-to-end) | 3.282 | 0.3594 |
| Implementation Method | EER (%) | minDCF (0.01) |
|---|---|---|
| baseline(1&3) | 3.473 | 0.3469 |
| baseline(2) | 4.364 | 0.3797 |
| Version 1 | 3.321 | 0.3234 |
| Version 2 | 4.168 | 0.3887 |
| Version 3 | 3.244 | 0.3459 |
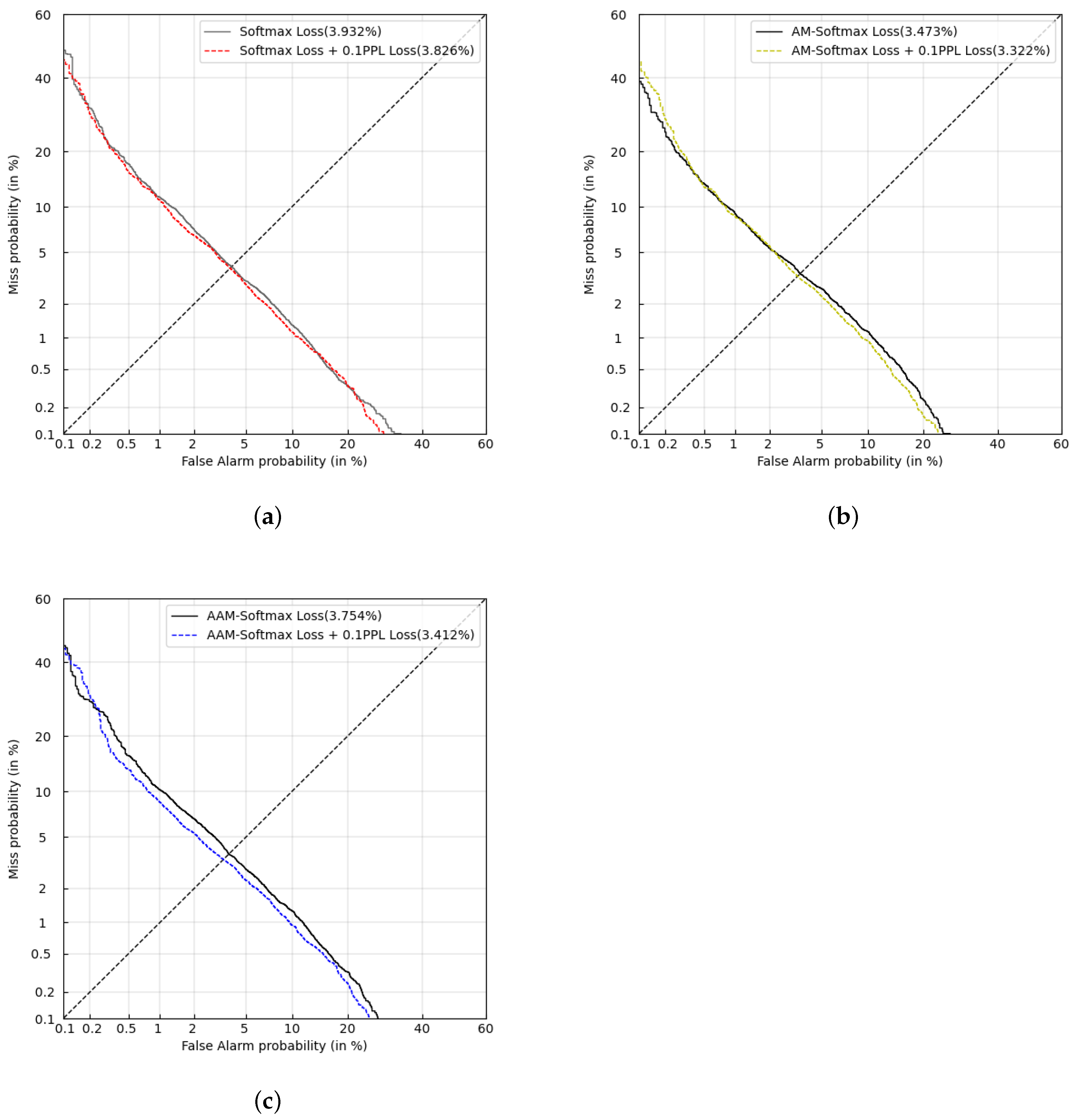
| Loss Function | EER (%) | minDCF (0.01) |
|---|---|---|
| Softmax Loss | 3.932 | 0.4103 |
| Softmax Loss + PPL Loss | 3.825 | 0.3643 |
| AM-Softmax Loss | 3.473 | 0.3469 |
| AM-Softmax Loss + PPL Loss | 3.321 | 0.3234 |
| AAM-Softmax Loss | 3.754 | 0.3657 |
| AAM-Softmax Loss + PPL Loss | 3.412 | 0.3445 |
| (C = 32) | EER (%) | minDCF (0.01) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 3.473 | 0.3469 |
| 0.05 | 3.332 | 0.3242 |
| 0.01 | 3.367 | 0.3520 |
| 0.10 | 3.321 | 0.3234 |
| 0.20 | 3.346 | 0.3285 |
| C ( = 0.1) | EER (%) | minDCF (0.01) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3.473 | 0.3469 |
| 32 | 3.321 | 0.3234 |
| 40 | 3.372 | 0.3074 |
| 48 | 3.428 | 0.3343 |
| 56 | 3.362 | 0.3344 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, M.; He, L.; Fang, Z.; Zhao, B.; Wang, K. Pseudo-Phoneme Label Loss for Text-Independent Speaker Verification. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7463. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157463
Niu M, He L, Fang Z, Zhao B, Wang K. Pseudo-Phoneme Label Loss for Text-Independent Speaker Verification. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7463. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157463
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Mengqi, Liang He, Zhihua Fang, Baowei Zhao, and Kai Wang. 2022. "Pseudo-Phoneme Label Loss for Text-Independent Speaker Verification" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7463. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157463
APA StyleNiu, M., He, L., Fang, Z., Zhao, B., & Wang, K. (2022). Pseudo-Phoneme Label Loss for Text-Independent Speaker Verification. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7463. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157463







