A Photoplethysmogram Dataset for Emotional Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
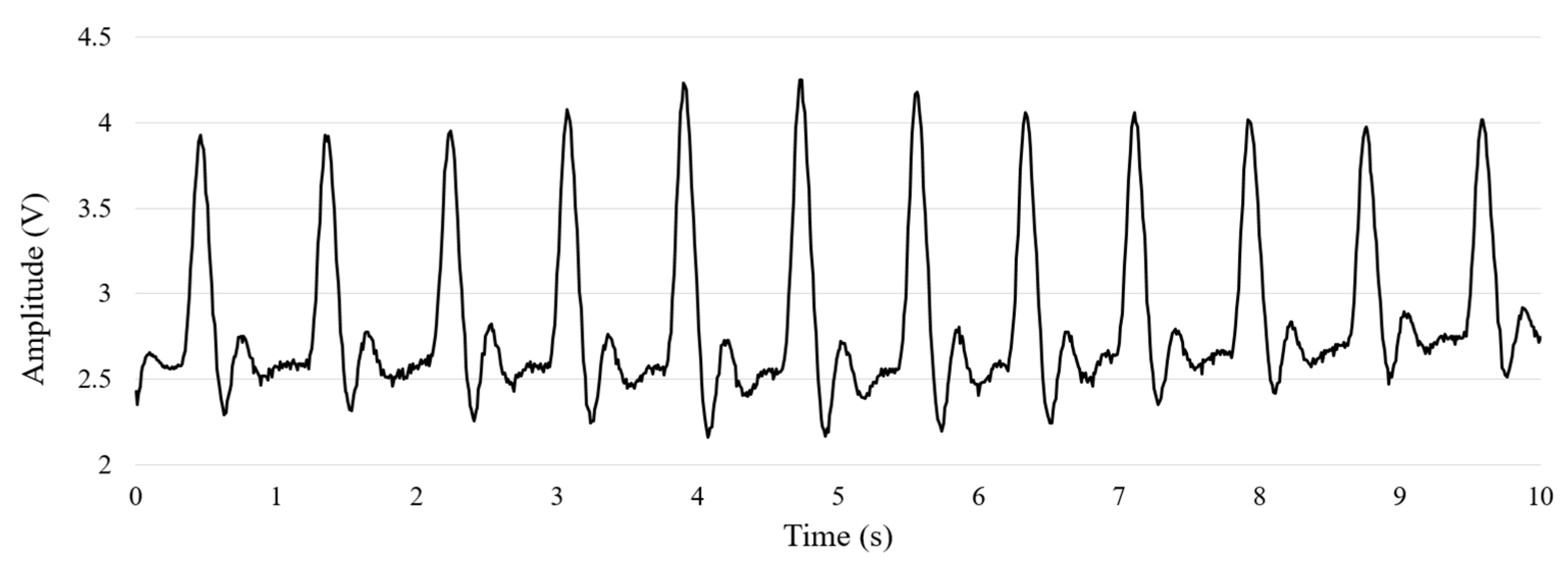
2.1. Dataset Acquisition
2.2. Frequency and Time Domain Analysis
2.3. Automatic Classification of Emotions
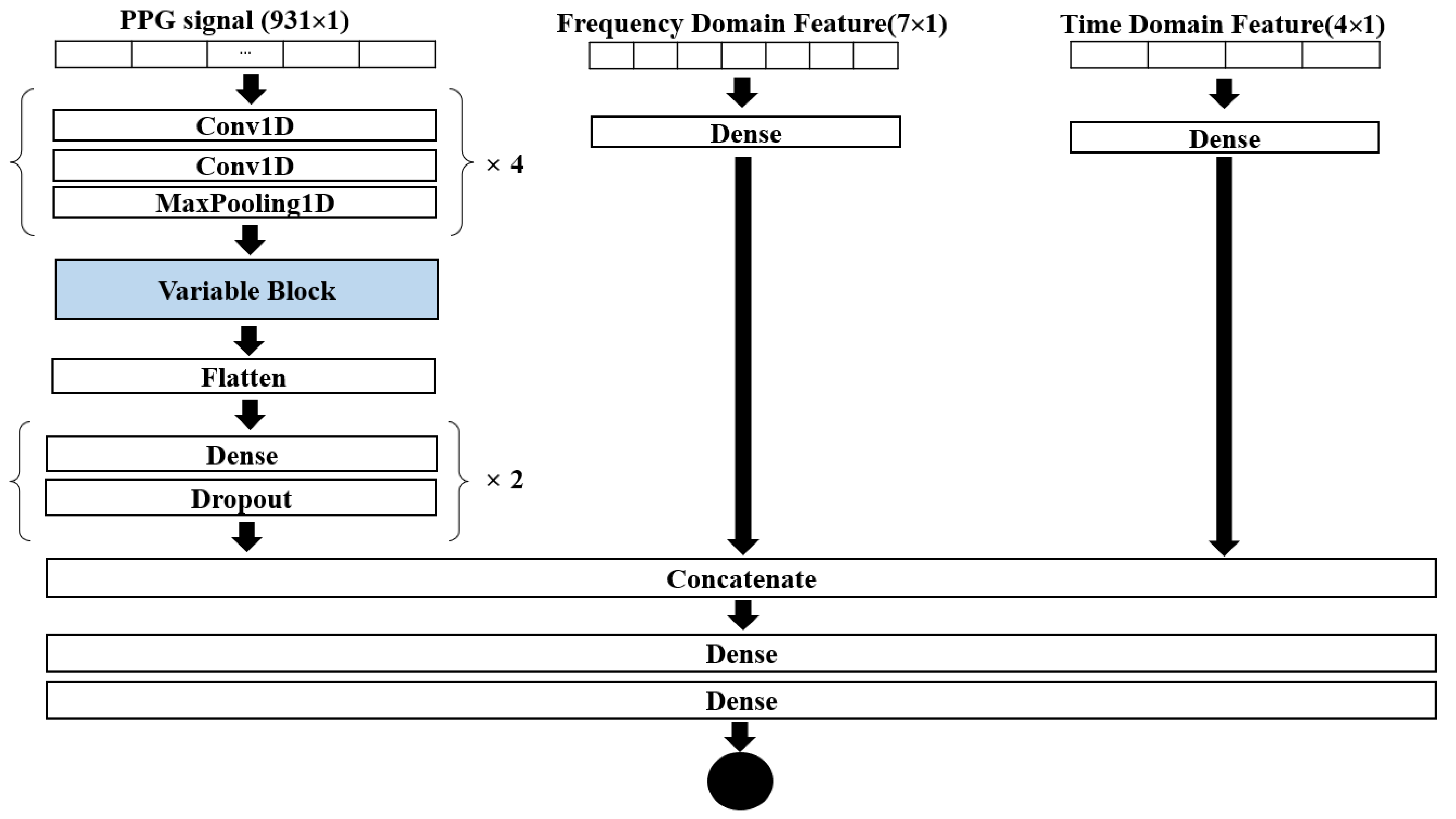
2.4. Deep Network Architecture
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis with Heartbeats per Minute
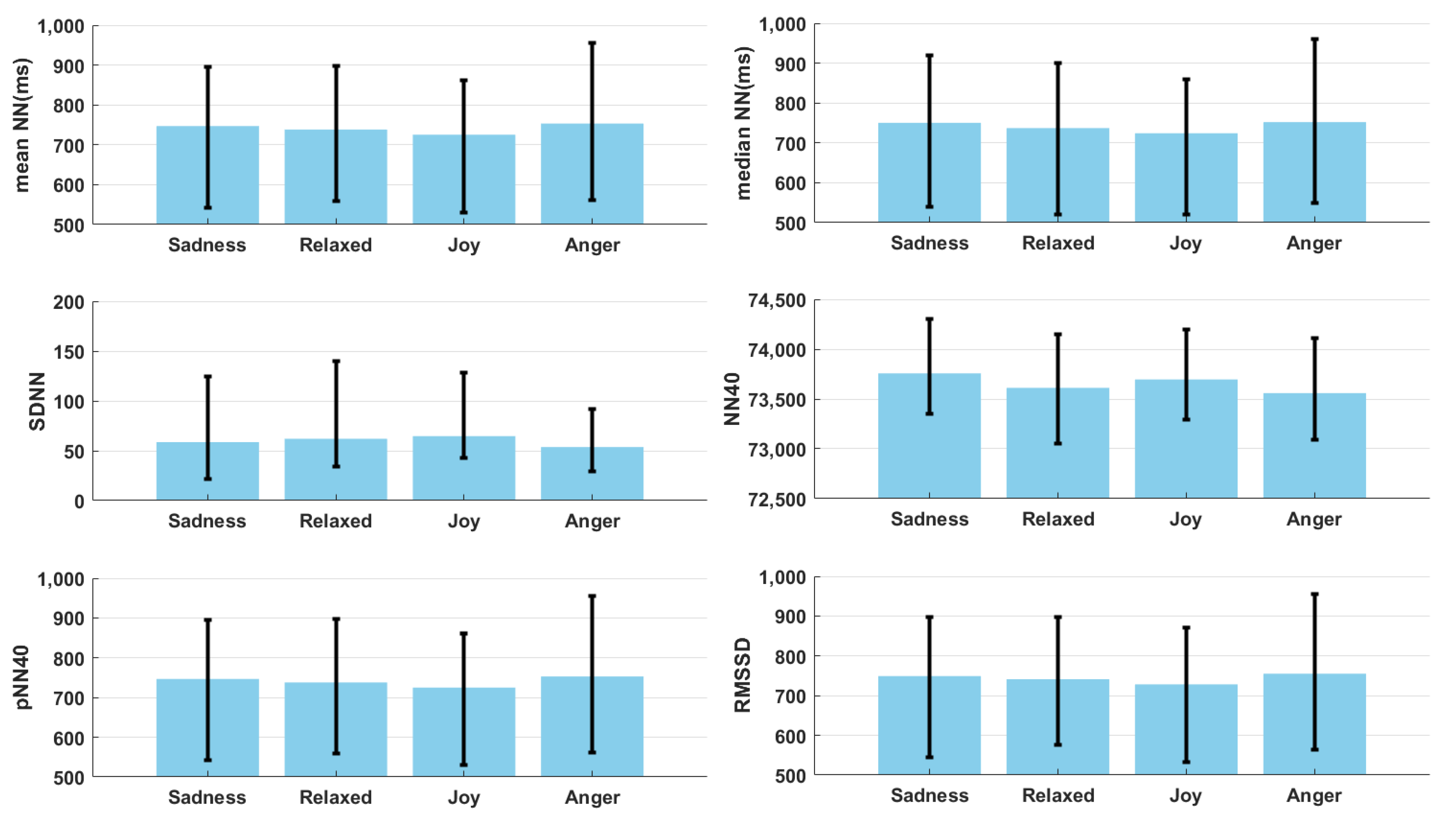
3.2. Statistics of Frequency and Time Domain Features
3.3. Responses of Participants
3.4. Emotional Classification Results
3.5. Comparison to Conventional PPG Dataset
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hwang, D.H.; Hwang, Y.H.; Yoon, H.H. The Effects of Verbal and Nonverbal Communication of Service Providers on the Customers’ Emotional Responses and Customer Satisfaction: Moderating Effects of Restaurant Type. Culin. Sci. Hosp. Res. 2018, 24, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, C.; Urban, B. Emotion in Human-Computer Interaction. In Expanding the Frontiers of Visual Analytics and Visualization; Earnshaw, J.D.R., Kasik, D., Vince, J., Wong, P., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2012; pp. 239–262. [Google Scholar]
- Beale, R.; Peter, C. The Role of Affect and Emotion in HCI. In Affect and Emotion in Human-Computer Interaction; Beale, R., Peter, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 4868, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.S.; Pan, Y.H. A Study on Human-Robot’s Emotional Communication through the Movement of the Eye of a Social Robot. Korean Des. Forum 2019, 24, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Takanishi, A.; Sato, K.; Segawa, K.; Takanobu, H.; Miwa, H. An Anthropomorphic Head-Eye Robot Expressing Emotions. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; pp. 2243–2249. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, S.S.; Reddy, N.P.; Hariharan, S. Facial Expression (Mood) Recognition from Facial Images Using Committee Neural Networks. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2009, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gannouni, S.; Aledaily, A.; Belwafi, K.; Aboalsamh, H. Emotion Detection Using Electroencephalography Signals and a Zero-time Windowing-based Epoch Estimation and Relevant Electrode Identification. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.J.; Lee, H.W.; Cha, S.M.; Seo, R.J.; Kim, J.G. An Implementation of Data Monitoring and Wireless Emergency Alarm System Which Utilize the ECG Sensors. In Proceedings of the Symposium of the Korean Institute of communications and Information Sciences, Pyeong Chang, Korea, 1–3 July 2015; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Davoudi, A.; Malhotra, K.R.; Shickel, B.; Siegel, S.; Williams, S.; Ruppert, M.; Bihorac, E.; Ozrazgat-Baslanti, T.; Tighe, P.J.; Bihorac, A.; et al. Intelligent ICU for Autonomous Patient Monitoring Using Pervasive Sensing and Deep Learning. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.-H.; Lai, C.-I.; Boorady, L. ECG Monitoring via Apparel for Female Firefighter’s Safety. In Proceedings of the International Textile and Apparel Association Annual Conference, London, UK, 30 July–1 August 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, W.; Dou, S.C. Systematic Analysis of a Military Wearable Device Based on a Multi-Level Fusion Framework: Research Directions. Sensors 2019, 19, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasnul, M.A.; Aziz, N.A.A.; Alelyani, S.; Mohana, M.; Aziz, A.A. Electrocardiogram-Based Emotion Recognition Systems and Their Applications in Healthcare—A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, P.; Reiss, A.; Duerichen, R.; van Laerhoven, K. Introducing WeSAD, a Multimodal Dataset for Wearable Stress and Affect Detection. In Proceedings of the ICMI 2018—International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Boulder, CO, USA, 16–20 October 2018; pp. 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markova, V.; Ganchev, T.; Kalinkov, K. CLAS: A Database for Cognitive Load, Affect and Stress Recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Innovations and Applications, BIA 2019, Varna, Bulgaria, 8–9 November 2019; pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Castellini, C.; van den Broek, E.L.; Albu-Schaeffer, A.; Schwenker, F. A Dataset of Continuous Affect Annotations and Physiological Signals for Emotion Analysis. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, C.Y.; Cha, N.; Kang, S.; Kim, A.; Khandoker, A.H.; Hadjileontiadis, L.; Oh, A.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, U. K-EmoCon, a Multimodal Sensor Dataset for Continuous Emotion Recognition in Naturalistic Conversations. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Correa, J.A.; Abadi, M.K.; Sebe, N.; Patras, I. AMIGOS: A Dataset for Affect, Personality and Mood Research on Individuals and Groups. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2021, 12, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, R.; Wache, J.; Abadi, M.K.; Vieriu, R.L.; Winkler, S.; Sebe, N. Ascertain: Emotion and Personality Recognition Using Commercial Sensors. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 9, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M.K.; Subramanian, R.; Kia, S.M.; Avesani, P.; Patras, I.; Sebe, N. DECAF: MEG-Based Multimodal Database for Decoding Affective Physiological Responses. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2015, 6, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsigiannis, S.; Ramzan, N. DREAMER: A Database for Emotion Recognition Through EEG and ECG Signals from Wireless Low-Cost Off-the-Shelf Devices. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Healey, J.A.; Picard, R.W. Detecting Stress during Real-World Driving Tasks Using Physiological Sensors. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2005, 6, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, Z.; Chen, X.; He, Z.; Tong, K.; Fang, Z.; Wang, X. Emotion Recognition Based on Photoplethysmogram and Electroencephalogram. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 42nd Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 23–27 July 2018; pp. 402–407. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-P.; Wang, C.-H.; Jung, T.-P.; Wu, T.-L.; Jeng, S.-K.; Duann, J.-R.; Chen, J.-H. EEG-Based Emotion Recognition in Music Listening. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Suhaimi, N.S.; Mountstephens, J.; Teo, J. EEG-Based Emotion Recognition: A State-of-the-Art Review of Current Trends and Opportunities. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020, 2020, 8875426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmatkar, N.V.; Babu, V.B. Human Emotion Classification from Brain EEG Signal Using Multimodal Approach of Classifier. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Information Technology, Hanoi, Vietnam, 26–28 February 2018; pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: Https://Pulsesensor.Com/Products/Pulse-Sensor-Amped (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- Park, J.; Li, C.; Kwon, H. Heart Rate Detection of Photoplethysmography Using a Smartphone Camera. In Proceedings of the Symposium of the Korean Institute of communications and Information Sciences, Seoul, Korea, 12–15 December 2013; pp. 617–618. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-S. Study on Heart Rate Variability and PSD Analysis of PPG Data for Emotion Recognition. J. Digit. Contents Soc. 2018, 19, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Lim, M.T.; Kang, T.K. Emotion Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Network with Selected Statistical Photoplethysmogram Features. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelstra, S.; Muehl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.-S.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. DEAP: A Database for Emotion Analysis Using Physiological Signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, W.-J.; Lee, B.-C.; Jeong, K.-S.; Lee, Y.-J. Minimum Measurement Time Affecting the Reliability of the Heart Rate Variability Analysis. Korean J. Health Promot. 2017, 17, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Chang, W.-D. Recognition of Emotional States Using Single Channel PPG Signals. In Proceedings of the 36th International Technical Conference on Circuits/Systems, Computers and Communications, Jeju, Korea, 28–30 June 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.S.; Cho, Y.R.; Lee, Y.K.; Pae, D.S.; Lim, M.T.; Kang, T.K. PPG and EMG Based Emotion Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, Prague, Czech Republic, 29–31 July 2019; pp. 595–600. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Pae, D.S.; Lim, M.T.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, T.K. Fast Emotion Recognition Based on Single Pulse PPG Signal with Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
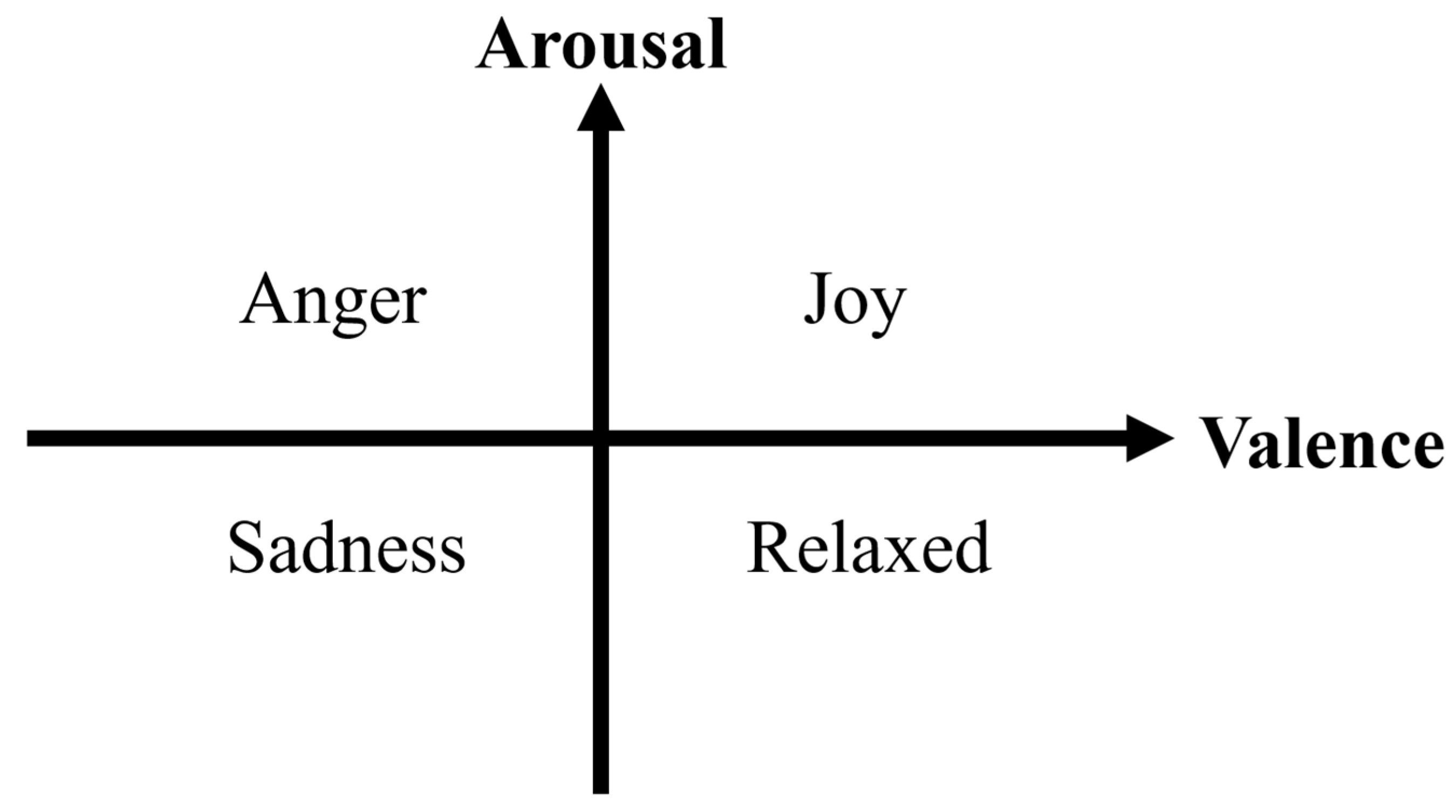
- Russell, J.A. A Circumplex Model of Affect. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1980, 39, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.; Etemad, A. Self-Supervised ECG Representation Learning for Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Shin, D.; Shin, D. Development of Emotion Recognition Interface Using Complex EEG/ECG Bio-Signal for Interactive Contents. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 11449–11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Kim, S.; Yoo, C.D. Edge-Labeling Graph Neural Network for Few-Shot Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
| Participant # | Sex | Age (Years) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male | 26 |
| 2 | Female | 30 |
| 3 | Male | 26 |
| 4 | Male | 26 |
| 5 | Male | 25 |
| 6 | Male | 25 |
| 7 | Male | 23 |
| 8 | Female | 23 |
| 9 | Male | 23 |
| 10 | Male | 28 |
| 11 | Female | 20 |
| 12 | Male | 26 |
| 13 | Female | 24 |
| 14 | Female | 27 |
| 15 | Male | 25 |
| 16 | Male | 31 |
| 17 | Male | 23 |
| 18 | Male | 23 |
| Emotion | Title and Web-Address | Genre | View |
|---|---|---|---|
| Joy | Driving lessons from a gangster https://youtu.be/wK4K9icjEO4 | Comedy | 14 M |
| The tenth of every month https://youtu.be/6gSSI1Ldfqk | Comedy | 4 M | |
| Sadness | Families sharing the saddest last moments together https://youtu.be/5zD-slYVWgI | Documentary | 1.2 M |
| Dad couldn’t keep his promise to meet his son the next day https://youtu.be/DWXO8kPKp2g | Documentary | 157 K | |
| Anger | Nursery school teacher assaults 4-year-old child https://youtu.be/xw6mOLW8Gnc | News | 1.6 M |
| The landlord who took a mortgage on the day of the tenant moving in. https://youtu.be/_oCC5omof04 | News | 6.6 M | |
| Relaxed | Chopin Nocturne Op. 9 No. 2 https://youtu.be/9E6b3swbnWg | Orchestra | 607 K |
| Bach—Air on The G String https://youtu.be/noYRi8bi0aY | Orchestra | 7.1 M | |
| Short Meditation Music —3 Minute Relaxation, Calming https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cI4ryatVkKw | Meditation Music with Images | 2.4 M |
| Name | Feature |
|---|---|
| total_power | Total power |
| [Freq.Name] a * | Integrated area of power in frequency band |
| [Freq.Name] h * | Highest power in frequency band |
| [Freq.Name] p * | [Freq.Name] h/total_power |
| LFn * | LFa/(LFa + HFa) |
| HFn * | HFa/(LFa + HFa) |
| LFHF | LFa/HFa |
| Arousal | Valence | |
|---|---|---|
| Sadness | 0 | 0 |
| Relaxed | 0 | 1 |
| Joy | 1 | 1 |
| Anger | 1 | 0 |
| Variable Block | Description * |
|---|---|
| B1 | None |
| B2 | LSTM (32) |
| B3 | LSTM (64) |
| B4 | Bi-LSTM (32) |
| B5 | Bi-LSTM (64) |
| B6 | GRU (32) |
| B7 | GRU (64) |
| B8 | Bi-GRU (32) |
| B9 | Bi-GRU (64) |
| B10 | LSTM (32), Dropout (0.2), LSTM (16) |
| B11 | LSTM (64), Dropout (0.2), LSTM (32) |
| B12 | Bi-LSTM (32), Dropout (0.2), Bi-LSTM (16) |
| B13 | Bi-LSTM (64), Dropout (0.2), Bi-LSTM (32) |
| B14 | GRU (32), Dropout (0.2), GRU (16) |
| B15 | GRU (64), Dropout (0.2), GRU (32) |
| B16 | Bi-GRU (32), Dropout (0.2), Bi-GRU (16) |
| B17 | Bi-GRU (64), Dropout (0.2), Bi-GRU (32) |
| Sadness | Relaxed | Joy | Anger |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80.65 ± 10.39 | 81.41 ± 10.17 | 82.89 ± 10.20 | 79.75 ± 10.04 |
| Features | Mean ± Standard Deviation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sadness | Relaxed | Joy | Anger | |
| VLFa | 1385.86 ± 780.99 | 1186.71 ± 513.08 | 1395.76 ± 679.54 | 1323.02 ± 715.64 |
| LFa | 2385.51 ± 969.51 | 2371.84 ± 991.23 | 2432.99 ± 957.81 | 2377.73 ± 838.47 |
| HFa | 729.1 ± 569.73 | 646.23 ± 446.17 | 661.47 ± 492.83 | 620.16 ± 407.63 |
| TOTALa | 4811.42 ± 2381.5 | 4472.3 ± 1986.65 | 4770.6 ± 2154.6 | 4567.09 ± 1968.38 |
| VLFh | 113.49 ± 69.15 | 100.73 ± 51.9 | 101.93 ± 64.02 | 99.44 ± 50.07 |
| LFh | 52.15 ± 19.65 | 56.9 ± 22.75 | 51.76 ± 22.67 | 52.09 ± 18.19 |
| HFh | 5.51 ± 4.24 | 5.35 ± 4.24 | 5.08 ± 4.31 | 4.91 ± 3.28 |
| VLFp | 0.29 ± 0.06 | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 0.3 ± 0.05 | 0.28 ± 0.05 |
| LFp | 0.52 ± 0.07 | 0.54 ± 0.07 | 0.52 ± 0.06 | 0.54 ± 0.07 |
| HFp | 0.13 ± 0.06 | 0.13 ± 0.05 | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 0.12 ± 0.04 |
| LFn | 0.8 ± 0.08 | 0.81 ± 0.08 | 0.81 ± 0.08 | 0.81 ± 0.07 |
| HFn | 0.2 ± 0.08 | 0.19 ± 0.08 | 0.19 ± 0.08 | 0.19 ± 0.07 |
| LFHF | 5.23 ± 3.15 | 5.44 ± 3.88 | 5.27 ± 2.75 | 5.23 ± 2.68 |
| Participant IDs | Sadness | Relaxed | Joy | Anger | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D * | A ** | V ** | D * | A ** | V ** | D * | A ** | V ** | D * | A ** | V ** | |
| 1 | 6 | - | - | 8 | - | - | 9 | - | - | 8 | - | - |
| 2 | 5 | - | - | 7 | - | - | 9 | - | - | 7 | - | - |
| 3 | 7 | - | - | 10 | - | - | 9 | - | - | 7 | - | - |
| 4 | 8 | - | - | 8 | - | - | 9 | - | - | 10 | - | - |
| 5 | 9 | - | - | 6 | - | - | 8 | - | - | 10 | - | - |
| 6 | 9 | - | - | 8 | - | - | 6 | - | - | 7 | - | - |
| 7 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| 8 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 3 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 3 |
| 10 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 4 |
| 11 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 3 |
| 12 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 2 |
| 13 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 9 | 2 |
| 14 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 4 | 7 | 3 |
| 15 | 8 | 8 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 2 |
| 16 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 4 |
| 17 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 9 | 3 |
| 18 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 3 |
| Avg. | 7.22 | 3.83 | 3.00 | 6.61 | 2.58 | 6.33 | 7.00 | 6.67 | 7.17 | 7.61 | 7.42 | 3.00 |
| Std. | 2.13 | 1.90 | 1.60 | 1.91 | 1.00 | 1.61 | 1.75 | 1.72 | 1.27 | 1.79 | 1.88 | 0.74 |
| Ref. | Year | Database | Signal Source | Method | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [32] | 2021 | DEAP | PPG | CNNs with statistical features | 71.50 |
| [29] | 2020 | DEAP | PPG | CNNs with statistical features | 76.2 |
| [22] | 2021 | DEAP | PPG | Logistic regression | 64.84 |
| [14] | 2019 | CLAS | PPG + GSR * | SVM * | 71.6 |
| Variable Block | Accuracies (%) for Each Iteration | Mean ± Std. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| B1 | 66.38 | 58.26 | 75.65 | 63.48 | 61.74 | 65.1 ± 5.89 |
| B2 | 81.9 | 81.74 | 64.35 | 70.43 | 77.39 | 75.16 ± 6.83 |
| B3 | 51.72 | 55.65 | 65.22 | 70.43 | 59.13 | 60.43 ± 6.68 |
| B4 | 62.93 | 60.87 | 65.22 | 70.43 | 47.83 | 61.46 ± 7.52 |
| B5 | 60.34 | 62.61 | 87.83 | 72.17 | 77.39 | 72.07 ± 10.04 |
| B6 | 69.83 | 61.74 | 73.04 | 72.17 | 73.91 | 70.14 ± 4.41 |
| B7 | 75 | 62.61 | 61.74 | 60 | 88.7 | 69.61 ± 10.92 |
| B8 | 62.07 | 74.78 | 75.65 | 53.04 | 52.17 | 63.54 ± 10.15 |
| B9 | 63.79 | 64.35 | 82.61 | 54.78 | 68.7 | 66.85 ± 9.09 |
| B10 | 62.93 | 71.3 | 48.7 | 68.7 | 66.96 | 63.72 ± 7.99 |
| B11 | 64.66 | 73.04 | 59.13 | 65.22 | 64.35 | 65.28 ± 4.46 |
| B12 | 62.07 | 81.74 | 71.3 | 73.04 | 49.57 | 67.54 ± 10.94 |
| B13 | 68.97 | 84.35 | 63.48 | 60.87 | 73.04 | 70.14 ± 8.27 |
| B14 | 71.55 | 60 | 69.57 | 73.04 | 70.43 | 68.92 ± 4.61 |
| B15 | 65.52 | 64.35 | 75.65 | 74.78 | 62.61 | 68.58 ± 5.5 |
| B16 | 52.59 | 69.57 | 51.3 | 73.04 | 66.96 | 62.69 ± 8.99 |
| B17 | 64.66 | 42.61 | 66.09 | 73.91 | 86.09 | 66.67 ± 14.23 |
| Ref. | Year | Database | Signal Source | Method | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [32] | 2021 | DEAP | PPG | CNNs with statistical features | 72.40 |
| [29] | 2020 | DEAP | PPG | CNNs with statistical features | 75.3 |
| [22] | 2021 | DEAP | PPG | Adaboost | 64.84 |
| [14] | 2019 | CLAS | PPG + GSR | SVM | 71.7 |
| Variable Block | Accuracies (%) for Each Iteration | Mean ± Std. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| B1 | 66.38 | 54.78 | 59.13 | 85.22 | 68.7 | 66.84 ± 10.45 |
| B2 | 83.62 | 91.3 | 65.22 | 64.35 | 85.22 | 77.94 ± 11.05 |
| B3 | 72.41 | 73.91 | 74.78 | 88.7 | 70.43 | 76.05 ± 6.5 |
| B4 | 58.62 | 73.91 | 64.35 | 89.57 | 71.3 | 71.55 ± 10.48 |
| B5 | 87.93 | 82.61 | 76.52 | 77.39 | 59.13 | 76.72 ± 9.7 |
| B6 | 84.48 | 69.57 | 80 | 50.43 | 64.35 | 69.77 ± 12.04 |
| B7 | 67.24 | 85.22 | 59.13 | 53.91 | 62.61 | 65.62 ± 10.72 |
| B8 | 85.34 | 57.39 | 68.7 | 60.87 | 85.22 | 71.5 ± 11.83 |
| B9 | 71.55 | 64.35 | 66.09 | 73.91 | 71.3 | 69.44 ± 3.61 |
| B10 | 58.62 | 73.04 | 67.83 | 80.87 | 78.26 | 71.72 ± 7.94 |
| B11 | 56.9 | 84.35 | 78.26 | 71.3 | 80 | 74.16 ± 9.6 |
| B12 | 87.93 | 75.65 | 80.87 | 57.39 | 82.61 | 76.89 ± 10.51 |
| B13 | 69.83 | 79.13 | 79.13 | 71.3 | 53.91 | 70.66 ± 9.22 |
| B14 | 80.17 | 79.13 | 77.39 | 64.35 | 85.22 | 77.25 ± 6.96 |
| B15 | 81.9 | 80 | 73.91 | 87.83 | 66.96 | 78.12 ± 7.13 |
| B16 | 79.31 | 57.39 | 69.57 | 52.17 | 78.26 | 67.34 ± 10.92 |
| B17 | 63.79 | 84.35 | 56.52 | 73.91 | 84.35 | 72.58 ± 11.08 |
| Ref. | Year | Name | Signal Source | Number of Subjects | Type of Stimuli | Emotions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [30] | 2012 | DEAP | EEG, EMG, EOG, GSR, PPG | 40 | Music video | Arousal, valence, liking, dominance |
| [13] | 2018 | WESAD | ECG, EMG, GSR, PPG, RSP | 15 | Music video, assessment | Neutral, stress, amusement |
| [14] | 2019 | CLAS | ECG, EDA **, PPG, GSR | 62 | Music video, picture | Arousal, valence, liking, dominance, control |
| [15] | 2019 | CASE | ECG, EMG, GSR, PPG, RSP | 30 | Movie clip | Four categories (amusing, boring, relaxing, and scary) |
| [16] | 2020 | K-EmoCon | ACC *, ECG, EDA **, EEG (1 channel), PPG | 32 | Debate | Arousal, valence, and 18 other categories |
| Proposed | 2022 | PPGE * | PPG | 18 | Narrative video | Four categories (joy, sadness, anger, and relaxed) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.-J.; Habibilloh, E.; Jang, Y.-S.; An, T.; Jo, D.; Park, S.; Chang, W.-D. A Photoplethysmogram Dataset for Emotional Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6544. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136544
Jin Y-J, Habibilloh E, Jang Y-S, An T, Jo D, Park S, Chang W-D. A Photoplethysmogram Dataset for Emotional Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(13):6544. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136544
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Ye-Ji, Erkinov Habibilloh, Ye-Seul Jang, Taejun An, Donghyun Jo, Saron Park, and Won-Du Chang. 2022. "A Photoplethysmogram Dataset for Emotional Analysis" Applied Sciences 12, no. 13: 6544. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136544
APA StyleJin, Y.-J., Habibilloh, E., Jang, Y.-S., An, T., Jo, D., Park, S., & Chang, W.-D. (2022). A Photoplethysmogram Dataset for Emotional Analysis. Applied Sciences, 12(13), 6544. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136544








