A Practical Multiclass Classification Network for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. The Proposed Methodology
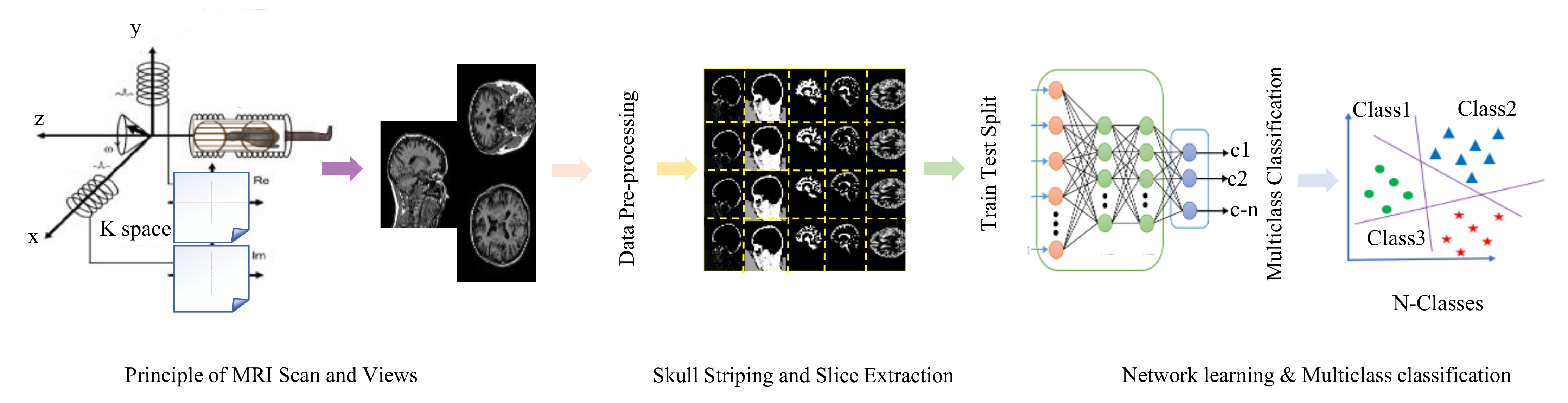
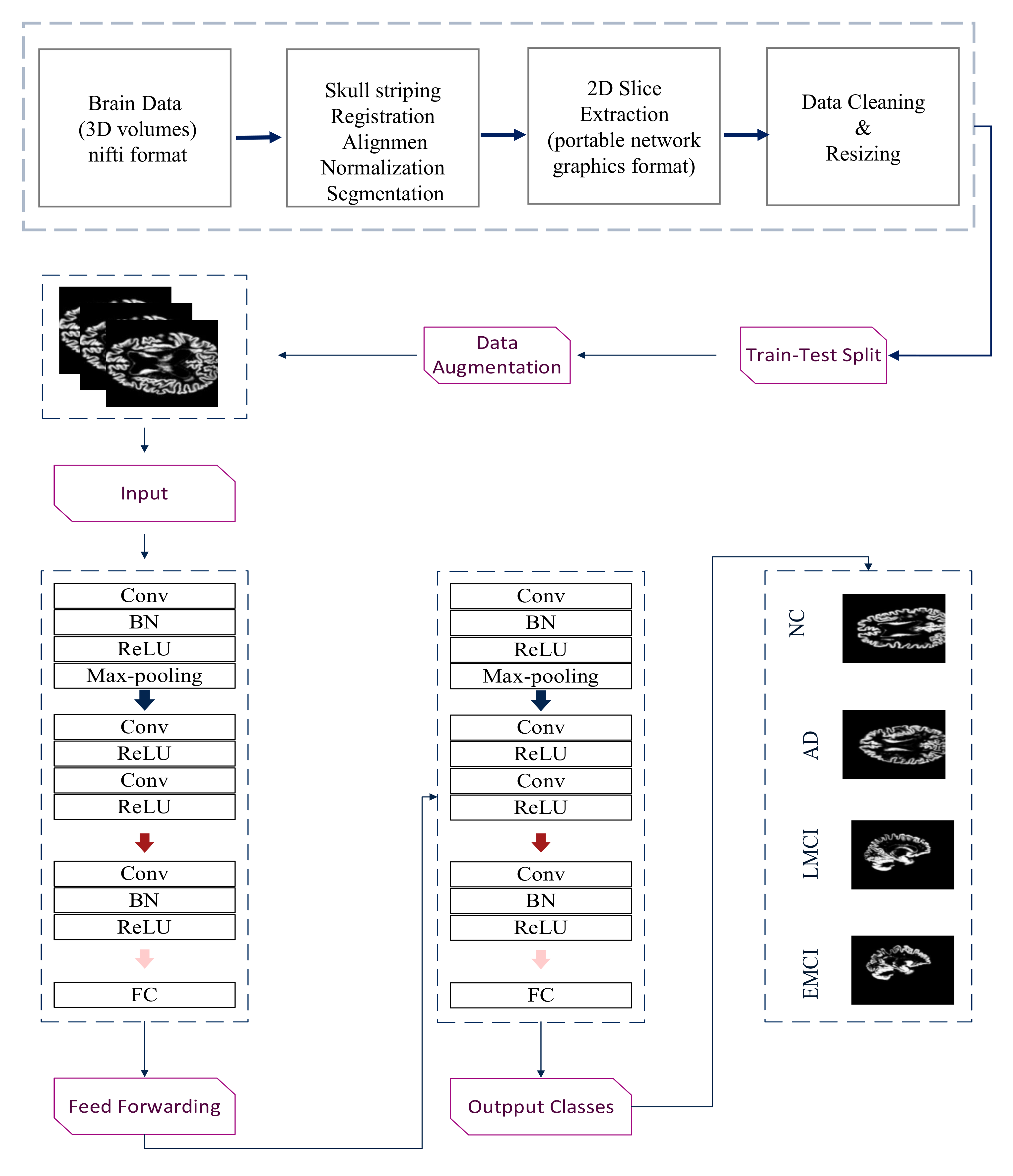
3.1. The Proposed Practical Multiclass Classification Network for Alzheimer’s Disease
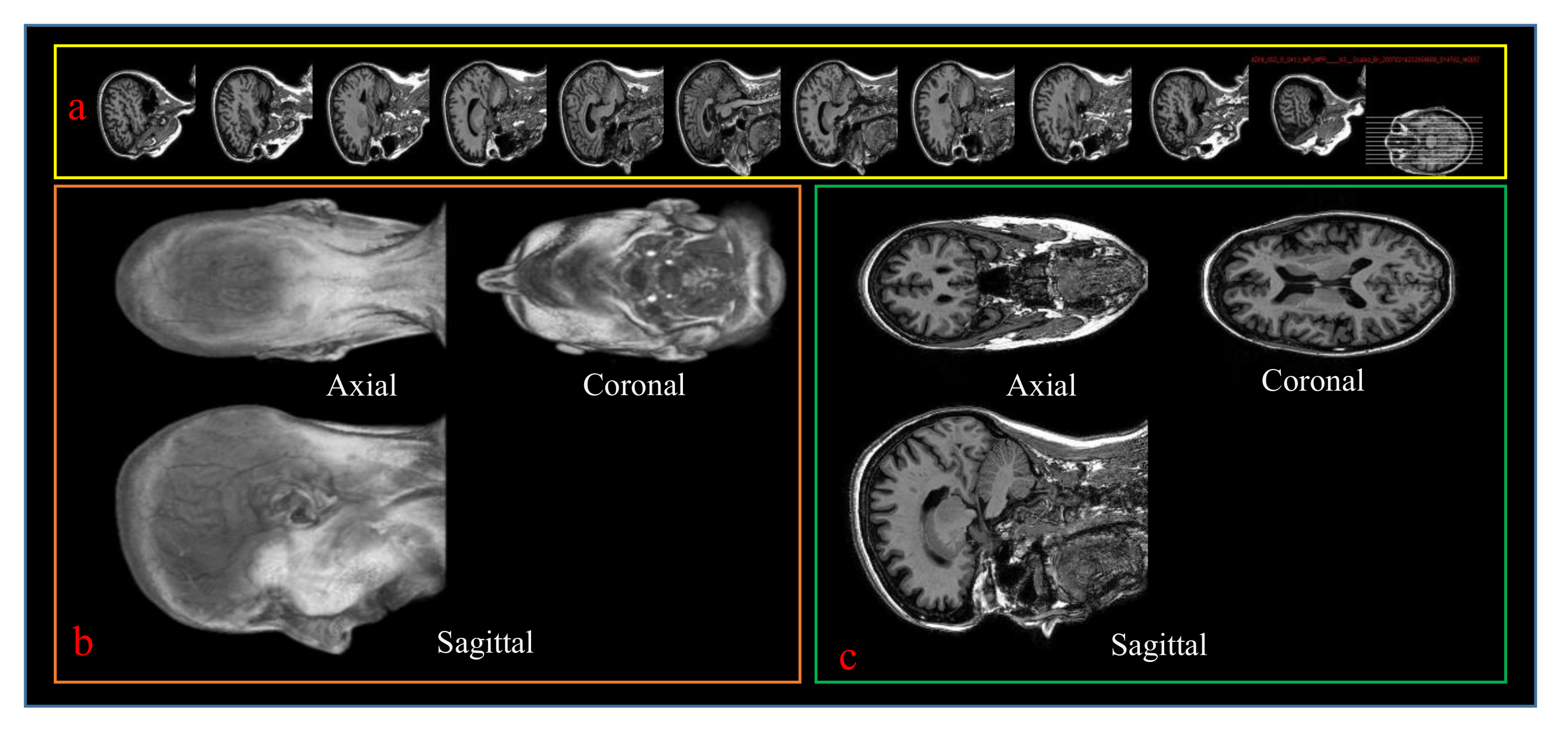
3.2. Data Pre-Processing for the Proposed Network
4. Dataset, Experiments and Discussions
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Setting
4.3. Experimental Evaluations and Discussions
4.3.1. Positive Predictive Value
4.3.2. Sensitivity
4.3.3. Specificity
4.3.4. Accuracy
4.3.5. F1 Measurement
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Citron, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Treatments in discovery and development. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 1055–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masdeu, J.C.; Zubieta, J.L.; Arbizu, J. Neuroimaging as a marker of the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 236, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Ekavali. A review on Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology and its management: An update. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajbakhsh, N.; Shin, J.Y.; Gurudu, S.R.; Hurst, R.T.; Kendall, C.B.; Gotway, M.B.; Liang, J. Convolutional Neural Networks for Medical Image Analysis: Full Training or Fine Tuning? IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demetriades, A.K. Functional neuroimaging in Alzheimer’s type dementia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 203, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, B.; Gao, A.; Feng, X.; Liang, D.; Long, X. A 3D densely connected convolution neural network with connection-wise attention mechanism for Alzheimer’s disease classification. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 78, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.; Jain, N.; Aggarwal, A.; Hemanth, D.J. Convolutional neural network based Alzheimer’s disease classification from magnetic resonance brain images. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2019, 57, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Thibeau-Sutre, E.; Diaz-Melo, M.; Samper-González, J.; Routier, A.; Bottani, S.; Dormont, D.; Durrleman, S.; Burgos, N.; Colliot, O.; et al. Convolutional neural networks for classification of Alzheimer’s disease: Overview and reproducible evaluation. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 63, 101694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Qaisar, Z.H. Divide and Conquer: Ill-Light Image Enhancement via Hybrid Deep Network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 182, 115034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.R.; Dash, R.; Majhi, B. Automated diagnosis of multi-class brain abnormalities using MRI images: A deep convolutional neural network based method. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Gray, K.; Gao, Q.; Chen, L.; Rueckert, D.; The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Multi-modal classification of Alzheimer’s disease using nonlinear graph fusion. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 63, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, H.; Shen, D.; The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Multimodal classification of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage 2011, 55, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sørensen, L.; Igel, C.; Pai, A.; Balas, I.; Anker, C.; Lillholm, M.; Nielsen, M.; The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Differential diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease using structural MRI cortical thickness, hippocampal shape, hippocampal texture, and volumetry. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 13, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petot, G.J.; Friedland, R.P. Lipids, diet and Alzheimer disease: An extended summary. J. Neurol. Sci. 2004, 226, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, T.; Nho, K.; Saykin, A.J. Deep learning in Alzheimer’s disease: Diagnostic classification and prognostic prediction using neuroimaging data. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talo, M.; Yildirim, O.; Baloglu, U.B.; Aydin, G.; Acharya, U.R. Convolutional neural networks for multi-class brain disease detection using MRI images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 78, 101673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, V.N.; Singh, V.; Chen, T.; Manmatha, R.; Comaniciu, D. Deep decision network for multi-class image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2240–2248. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, M.J.; Wimo, A.; Guerchet, M.; Ali, G.C.; Wu, Y.T.; Prina, M.A. World Alzheimer Report 2015—The Global Impact of Dementia: An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Cost and Trends; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ramzan, F.; Khan, M.U.G.; Rehmat, A.; Iqbal, S.; Saba, T.; Rehman, A.; Mehmood, Z. A deep learning approach for automated diagnosis and multi-class classification of Alzheimer’s disease stages using resting-state fMRI and residual neural networks. J. Med. Syst. 2020, 44, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.; Akram, A.; Mehmood, A. Multiview Ghost-Free Image Enhancement for In-the-Wild Images With Unknown Exposure and Geometry. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 24205–24220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shen, J.; Li, B. Deep image enhancement for ill light imaging. JOSA A 2021, 38, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Qaisar, Z.H. A ghostfree contrast enhancement method for multiview images without depth information. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2021, 78, 103175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y. A deep hybrid few shot divide and glow method for ill-light image enhancement. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 17767–17778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, M.Y.; Elzeki, O.M.; Abouelmagd, L.M.; Hassanien, A.E.; Abd Elfattah, M.; Salem, H. HANA: A healthy artificial nutrition analysis model during COVID-19 pandemic. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hasnony, I.M.; Elzeki, O.M.; Alshehri, A.; Salem, H. Multi-label active learning-based machine learning model for heart disease prediction. Sensors 2022, 22, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, S.; Maqsood, M.; Khan, U.; Mehmood, I.; Nawaz, H.; Aadil, F.; Song, O.Y.; Nam, Y. Alzheimer Disease Detection Techniques and Methods: A Review. Int. J. Interact. Multimed. Artif. Intell. 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Bao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yu, M.; Zhang, D.; Risacher, S.L.; Saykin, A.J.; Yao, X.; Shen, L.; Initiative, A.D.N.; et al. Multi-modal neuroimaging feature selection with consistent metric constraint for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 60, 101625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, A.; Maqsood, M.; Bashir, M.; Shuyuan, Y. A Deep Siamese Convolution Neural Network for Multi-Class Classification of Alzheimer Disease. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Ayhan, M.; Maida, A. Natural image bases to represent neuroimaging data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; pp. 987–994. [Google Scholar]
- Suk, H.I.; Lee, S.W.; Shen, D. Deep sparse multi-task learning for feature selection in Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 2569–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farooq, A.; Anwar, S.; Awais, M.; Rehman, S. A deep CNN based multi-class classification of Alzheimer’s disease using MRI. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Imaging Systems and Techniques (IST), Beijing, China, 18–20 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, A.; Yang, S.; Feng, Z.; Wang, M.; Ahmad, A.S.; Khan, R.; Maqsood, M.; Yaqub, M. A transfer learning approach for early diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease on MRI images. Neuroscience 2021, 460, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, H.; Mehta, R.; Singh, D.K. Alzheimer Disease Classification Using Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC), Erode, India, 8–10 April 2021; pp. 1503–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Murugan, S.; Venkatesan, C.; Sumithra, M.; Gao, X.Z.; Elakkiya, B.; Akila, M.; Manoharan, S. DEMNET: A deep learning model for early diagnosis of Alzheimer diseases and dementia from MR images. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 90319–90329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Zhang, Y. Brain MRI analysis for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using an ensemble system of deep convolutional neural networks. Brain Inform. 2018, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goceri, E. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease with Sobolev gradient-based optimization and 3D convolutional neural network. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2019, 35, e3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payan, A.; Montana, G. Predicting Alzheimer’s Disease—A Neuroimaging Study with 3D Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.02506. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.M.; Abraham, N.; Hon, M. Transfer learning with intelligent training data selection for prediction of Alzheimer’s disease. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 72726–72735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Asl, E.; Ghazal, M.; Mahmoud, A.H.; Aslantas, A.; Shalaby, A.M.; Casanova, M.F.; Barnes, G.N.; Gimel’farb, G.L.; Keynton, R.S.; El-Baz, A.S. Alzheimer’s disease diagnostics by a 3D deeply supervised adaptable convolutional network. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 584–596. [Google Scholar]
- Lundervold, A.S.; Lundervold, A. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on MRI. Z. Für Med. Phys. 2019, 29, 102–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.X.; Pan, H.; Liang, Z.P. Further analysis of interpolation effects in mutual information-based image registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2003, 22, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Florkow, M.C.; Zijlstra, F.; Kerkmeijer, L.G.; Maspero, M.; van den Berg, C.A.; van Stralen, M.; Seevinck, P.R. The impact of MRI-CT registration errors on deep learning-based synthetic CT generation. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2019: Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–21 February 2019; Volume 10949, p. 1094938. [Google Scholar]
- Jack, C.R.; Bernstein, M.A.; Fox, N.C.; Thompson, P.; Alexander, G.; Harvey, D.; Borowski, B.; Britson, P.J.; Whitwell, J.L.; Ward, C.; et al. The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI): MRI methods. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 27, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques with Java implementations. ACM Sigmod Rec. 2002, 31, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Subjects | Age | MMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 80 | 73 ± 8.5 | 26.5 ± 1.4 |
| EMCI | 75 | 74 ± 7.7 | 29.5 ± 1.2 |
| LMCI | 70 | 72 ± 7.9 | 28.5 ± 1.6 |
| AD | 75 | 75 ± 9.5 | 24.5 ± 1.9 |
| Classes | Sensitivity | Accuracy | Specificity | Precision | Overall Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 99.3 | 98.3 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.15 |
| EMCI | 99.4 | 99.6 | 99.1 | 99.2 | 99.32 |
| LMCI | 98.7 | 99.4 | 99.8 | 99.6 | 99.37 |
| AD | 99.5 | 98.3 | 99.7 | 99.5 | 99.25 |
| Average per group (Proposed Work) | 99.2 | 98.9 | 99.5 | 99.4 | 99.27 |
| Authors | Methods | Modalities | Distinction | Data | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hosseni et al. [40] | CNN-3D | MRI | NC, MCI, AD | ADNI | 94.8 |
| Ayan et al. [38] | 3D-CNN-PAD | MRI | NC, MCI, AD | ADNI | 85.3 |
| Gupta et al. [29] | NIBR-Net | MRI | NC, MCI, AD | ADNI | 78.2 |
| Suk et al. [30] | DSMAD-Net | MRI+PET | NC, MCI, AD | ADNI | 62.9 |
| Farooq et al. [31] | DLMCC-Net | MRI | AD, MCI, LMCI, NC 4-way classification | ADNI | 98.6 |
| Mehmood et al. [28] | SCNN | MRI | Stages of Dementia 4 way classification | OASIS | 99.05 |
| Atif et al. [33] | TLEDA-Net | MRI | AD, MCI, LMCI, NC 2 way classification | ADNI | 83.64 |
| Proposed Work | PMCAD-Net (This Work) | MRI | AD, MCI, LMCI, NC 4 way classification | ADNI | 99.25 |
| Authors | Methods | Modalities | Distinction | Dataset | F1 Measure | Accuracy | Sensitivity Recall | Positive PredictionPrecision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murugun et al. [35] | DEMNET | MRI | AD, MCI, LMCI, NC | Kaggle | 95.2 | 95.2 | 95 | 95.2 |
| Jian et al. [7] | CNN-AD (VGG-16) | MRI | AD, CN, MCI | ADNI | 95 | 95.13 | 96 | 96.3 |
| Acharya et al. [34] | ADTL-Net | MRI | AD, MCI, LMCI, NC | Kaggle | 94.7 | 95.7 | 92.3 | 91.9 |
| Proposed Work | PMCAD-Net (This work) | MRI | AD, MCI, LMCI, NC | ADNI | 96.34 | 99.2 | 96.3 | 96.4 |
| Groups | N | Min | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Max | Mean | Excess Kurtosis | Skewness Shape | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (Sensitivity) | 4 | 98.7 | 99 | 99.35 | 99.45 | 99.5 | 99.225 | −1.696387 | Potentially symmetrical (pval = 0.094) | 3.01436 |
| Group 2 (Accuracy) | 4 | 98.3 | 98.3 | 98.85 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 98.9 | −5.593263 | Potentially symmetrical pval = 0.944) | 0.070691 |
| Group 3 (Specificity) | 4 | 99.1 | 99.3 | 99.6 | 99.75 | 99.8 | 99.525 | 0.757656 | Potentially symmetrical (pval = 0.262) | 0.757656 |
| Group 4 (Precision) | 4 | 99.2 | 99.35 | 99.5 | 99.55 | 99.6 | 99.45 | 2.888889 | Potentially symmetrical (pval=0.129) | −1.539601 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, R.; Qaisar, Z.H.; Mehmood, A.; Ali, G.; Alkhalifah, T.; Alturise, F.; Wang, L. A Practical Multiclass Classification Network for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6507. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136507
Khan R, Qaisar ZH, Mehmood A, Ali G, Alkhalifah T, Alturise F, Wang L. A Practical Multiclass Classification Network for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(13):6507. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136507
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Rizwan, Zahid Hussain Qaisar, Atif Mehmood, Ghulam Ali, Tamim Alkhalifah, Fahad Alturise, and Lingna Wang. 2022. "A Practical Multiclass Classification Network for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease" Applied Sciences 12, no. 13: 6507. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136507
APA StyleKhan, R., Qaisar, Z. H., Mehmood, A., Ali, G., Alkhalifah, T., Alturise, F., & Wang, L. (2022). A Practical Multiclass Classification Network for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Applied Sciences, 12(13), 6507. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12136507






